Abstract
Microswimmers are key for unveiling new physical phenomena underlying their propulsion, especially when driven inside complex fluids. Liquid crystals are anisotropic complex fluids that feature long-range orientational order. The propulsion of non-charged dielectric particles can be accomplished in these systems by breaking the particles’ fore-aft symmetry thanks to anisotropies in the conductivity and dielectric permittivity parameters of the liquid crystal. Under the application of an AC electric field, asymmetric osmotic flows are generated to propel non-spherical particles, whose direction of motion depends on the orientational order of the liquid crystal molecules around the inclusions. This means that, by controlling the LC orientation, one will be able to steer driven colloidal inclusions. In this experimental work, we show that a homogeneous magnetic field that is able to control the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules also allows us to determine the direction of motion of driven particles without significant changes in the propulsion mechanism. Additionally, we show that a radial configuration of the magnetic field lines can be used to generate topological defects in the liquid crystal orientational field that attract colloidal particles, leading to their clustering as rotating mills. The generated clusters were tested to study the collective motion of particles, suggesting the presence of particle–particle interactions.
1. Introduction
Microswimmers are entities that can transform some kind of stimulus into motion inside a liquid [1,2,3,4]. According to the mechanism underlying their propulsion, they can be divided into two large groups. Particles within the first group, called active particles, are capable of transforming the energy present in their environment into motion. Biological swimmers are included in this group, as they can transform the energy stored in ATP molecules into propulsion [5,6]. Particles within the second group, called driven particles, are actuated by an external energy source, generating phoretic phenomena leading to different propulsion mechanisms. Colloids steered by rotating magnetic fields [7,8], the application of an electric signal [9], temperature gradients [10], or even light [11,12] are examples of this microswimmer class. In all cases, microswimmers have drawn the attention of the scientific community both for fundamental aspects and also due to their applicability in different fields. For instance, microswimmers could be used as transport units for drug delivery [3,4], to develop new waste treatment strategies [13], or to serve as models that imitate the dynamics of biological systems [5,14]. Although most research focuses on the motion of microswimmers in simple Newtonian fluids [2], cellular environments and, in general, biological fluids feature complex rheological behavior, and, thus, are non-Newtonian fluids, where propulsion mechanisms can be significantly different [1].
A particular case of non-Newtonian fluids is liquid crystals (LCs), anisotropic fluids that feature long-range orientational order of their constituents or mesogens [15,16]. This orientational order is characterized by a non-polar vector, known as director (), which describes the mean orientation in space of the mesogens. This orientation can be distorted by the application of external stimuli, such as an electromagnetic field. This feature is precisely what enables mechanisms for steering active or driven particles in LCs.
One particle propulsion mechanism endowed by the LC medium is liquid crystal-enabled electrophoresis (LCEEP) [17,18], which allows for the local propulsion of non-charged dielectric colloids embedded within the complex fluid as a result of the distortions in the alignment of mesogens caused by the solid inclusion combined with LC anisotropy. This distortion depends on the surface properties of the colloids and on their size. When a low-frequency AC electric field is applied, spatial charge separation induced by the deformation of the LC-colloid boundary, combined with the anisotropy in LC conductivity and dielectric permittivity, leads to colloid propulsion. This arises from the appearance of osmotic flows around the particle as a result of ion motion when the field is on. Consequently, the electric field has two functions in the propulsion mechanism: the generation of spatial separation and ion motion. Contrary to the usual electrophoresis in an isotropic fluid, LCEEP is a non-linear propulsion mechanism, as the velocity of the particles features a quadratic dependence on the field. Moreover, being able to propel colloids without the use of a DC electric field avoids electrode polarization or unwanted electrochemical reactions [19]. Provoking the net motion of colloidal particles by LCEEP requires breaking the fore-aft symmetry of the osmotic flows around the particle. To attain this, one must tune the shape or the surface anchoring properties of the inclusions to provoke an asymmetrical spatial deformation of the director field around them, leading to the generation of asymmetrical osmotic flows that drive the particle generally along the local LC director [19].
More complex mechanisms based on LCEEP can be found in the literature. For example, Li et al. [20] describe the director-induced liquid crystal-enabled electrophoresis (DI-LCEEP) phenomenon, a colloid steering mechanism based on dressing the particle with a solitonic wave called a directron. This wave is the agent breaking the fore-aft symmetry of the particle, enabling the propulsion of colloids even if they are completely symmetrical relative to the deformation of the director field.
In view of simple LCEEP, a direct way to control the heading of particle motion lies in the control of . The latter can be set using different methods, from the simplest, consisting in unidirectionally buffing the plates of the cell enclosing the LC, to more sophisticated ones [21]. For example, coating surfaces with an azo dye and shining them with polarized UV light [22] will set the alignment direction of , typically in the direction perpendicular to light polarization. Additional processes based on LC doping [23,24] or surface patterning [22,25,26] can be found in the literature. The majority of these techniques, however, do not allow an easy reconfiguration of , particularly while experiments are running, thus precluding real-time colloid steering. Thanks to the LC magnetic anisotropy, we demonstrate, here, a directionality control mechanism based on the propulsion of colloidal inclusions by LCEEP in the presence of a reconfigurable in-plane magnetic field generated by an ensemble of permanent magnets that will determine the direction of . Using mesogens with positive anisotropy of the magnetic susceptibility results in their alignment with the magnetic field. This method enables a facile reorientation of while particles are being propelled and, at the same time, provides in situ and in-time control of where particles are being driven.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Liquid Crystal Cells
Liquid crystal cells were constructed from two ITO-glasses ( mm pieces with sq purchased from Neyco, Vanves, France). Glasses were thoroughly cleaned with pure water and surfactant (Decon®90 purchased from Decon Laboratories Limited, East Sussex, UK) before their surface was activated with oxygen plasma (180 s at P = 90% using a ZEPTO plasma generator purchased from Diener, Berlin, Germany). A strip of the ITO layer was removed from each glass plate using Zn powder and concentrated hydrochloric acid to prevent electrical contact between the two ITO surfaces through the metallic spacers (see below). Surfaces were subsequently coated with a hydrophobic polyimide resin (3% Sunever 0526 polyimide varnish obtained from Nissan, Yokohama, Japan) for homeotropic anchoring, i.e., oriented perpendicular to the glass plate. The resin was applied with spin-coating (30 s at 500 rpm and 3 min at 2000 rpm using a SPIN 150i/200i Infinite spin-coater purchased from SPS-Polos, Putten, The Netherlands).
The glasses were first heated at 80 °C for 5 min to promote solvent evaporation and then cured at 180 °C for 1 h to promote bonding of the polyimide to the glass surface. Tungsten wires of diameter m, purchased from GoodFellow, Huntingdon, UK) were used as spacers to assemble the cell, generating a cell thickness equal to . The electrical connection of the cell to the devices used to apply signals was ensured through copper wires and silver paint. All parts, including the wires, were fixed with photocurable glue (NOA81 purchased from Norland, Cranbury, NJ, USA).
2.2. Particles–Liquid Crystal Mixture
The cells were filled with the nematic mixture MLC-7029 (with to allow transition into a degenerate planar state, and to allow alignment with a magnetic field; the mesogen was purchased from Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) in which m pear-shaped polystyrene particles were dispersed (purchased from Magsphere Inc., Pasadena, CA, USA). An aqueous suspension of microparticles was prepared by first redispersing 10 L of concentrated commercial polystyrene particle suspension (10% (w/v)) in 1 mL of absolute ethanol (purchased from PanReac, Barcelona, Spain). Then, after strong agitation, the particles were centrifuged until sedimentation. The supernatant was removed, and the particles were redispersed in a water–ethanol mixture with a smaller proportion of ethanol. This procedure was repeated, from sedimentation to redispersion, 5 times until the full dispersion of the PS particles in pure water was reached, reducing, at each step, the fraction of ethanol by a factor of 20% in the water–ethanol mixture. Gradual substitution of ethanol for water, instead of a one-time substitution, ensures the removal of suspension stabilizers, which might alter LC anchoring conditions.The final concentration of particles dispersed in water after this procedure was approximately 0.1% (w/v). Afterwards, 10 L of particle suspension was transferred onto the surface of a clean glass slide and the solvent was allowed to evaporate at 45 °C. The dry particles were then redispersed in 10 L of the LC, and the resultant dispersion was introduced by capillarity inside the cell. The overall process yields a suspension in which the surfaces of the polystyrene particles induce planar anchoring to the LC mesogens. Particles do not attach to the glass surface because of the anchoring mismatch between the planar alignment on the particles and the homeotropic alignment on the glass plates.
2.3. Particle Propulsion and Control
2.3.1. Unidirectional Control of Particles
The particles are propelled by the action of a low-frequency AC electric field provided by an electric signal generator (AFG-21012 purchased from Iso-tech, Merseyside, UK). The square wave signal is amplified 20-fold using an electric signal amplifier (PZD700 purchased from Trek, Waterloo, WI, USA). Directionality control is provided by the application of a homogeneous external magnetic field created by a k = 1 Halbach array of neodymium ceramic cubic magnets (25 mm side) built as described by Guillamat et al. [27,28]. A 400 mT in-plane magnetic field is applied at the center of this structure. See Figure 1 for a schematic representation of the experimental set-up.
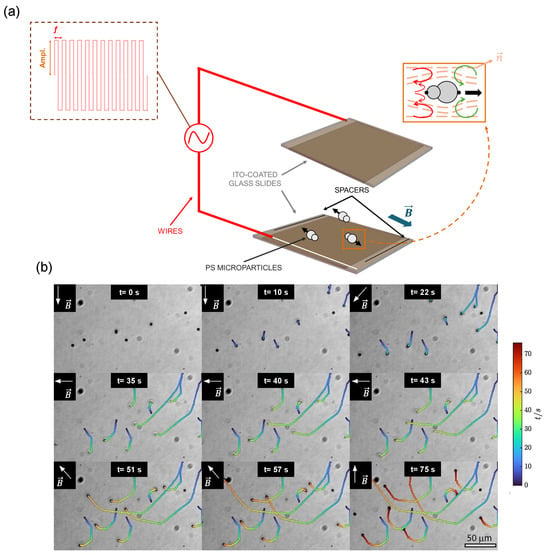
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic representation of a liquid crystal cell with dispersed pear-shaped PS microparticles propelled by a low-frequency AC electric field. Particle steering is accomplished by the application of an in-plane magnetic field, , represented by the blue arrow in the scheme. In the orange box, there is a simplified representation of the electroosmotic flows surrounding a particle when the electric field is on. The line segments correspond to the orientation of the LC director field. (b) Motion control of PS particles by the action of a fixed in-plane magnetic field of 400 mT whose direction is changed in steps. In this case, particles are propelled by the action of a low-frequency AC field (E = 0.58 V/m, f = 15 Hz). See also Supplementary Movie S1.
2.3.2. Generation of Particle Clusters
Particle clusters are generated by the application of a radial magnetic field provided by a ring-shaped Nd ceramic magnet (RX068, purchased from KJMagnetics, Pipersville, PA, USA). The magnet is located over the cell surface at a distance of approximately 2 mm by using two 1 mm thick glass slides as spacers. The radial component of the toroidal magnetic field promotes the appearance of a single umbilical defect with topological charge in the midplane of the LC cell when a voltage over the Fréedericksz threshold is applied [29]. Subsequent particle propulsion is performed as described in Section 2.3.1.
2.4. Observation, Image Acquisition, and Data Analysis
The study of the motion of the particles is performed using optical microscopy. When indicated, polarized optical microscopy (Eclipse 50iPol purchased from Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) has been used. Further analysis of the director field orientation has been performed using a fast adaptive polarized optical microscope whose description can be found in Martínez-Prat et al. [30].
For experiments in which unidirectional control of particles is present, image acquisition was performed by using a CMOS camera (PL-A741 purchased from PixeLink, Rochester, NY, USA). For the cases in which the formation of clusters has been performed, a CMOS camera is used (Marlin F131B purchased from Allied Vision Technologies, Stadtroda, Germany). The image treatment was performed using ImageJ software (version 1.54f). Single-particle tracking has been performed using the software extension TrackMate (version 7.14.0). Cluster analysis has been performed through PIV-Lab provided by MatLab (version R2024a). Image data handling and processing for velocity analysis have been performed with custom-made MatLab scripts.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Magnetic Field Control of Individual Particles
When an electric field above the Fredericks threshold is applied between the glass plates, orients parallel to them, i.e., perpendicular to the applied electric field, due to the negative dielectric anisotropy, , of the used LC mixture. This leads to a degeneracy in the in-plane orientation of (all in-plane directions are energetically equivalent), which is broken in the presence of a strong enough in-plane magnetic field but one that is below the magnetic Fredericks threshold. Since MLC-7029 has a positive value for the anisotropy in the magnetic susceptibility, , the magnetic field inside the Halbach array results in a homogeneous LC alignment parallel to the magnetic field lines inside the cell. Furthermore, since homeotropic anchoring does not induce strong azimuthal (in-plane) anchoring forces on the LC molecules [31,32], the in-plane orientation of can be tuned in situ by gradually rotating the magnetic field.
This control permits selecting the direction of particle motion inside the LC cell, as particles will move parallel to [33]. This capability is demonstrated in Figure 1b. As time goes on and particles are propelled inside the cell by a low-frequency AC electric field, they change their direction when we modify the direction of the external fixed magnetic field. One thing to be noted is that, on average, an equal number of particles will move along and along . Indeed, during the homeotropic to planar transition following application of the electric field, each particle dipole will have the same probability to turn towards and and, thus, to propel either way.
Furthermore, notice that, while most particles move along the local LC director, shape or surface irregularities result in a dispersion in their direction of motion [34].
We have verified that the presence of the magnetic field does not significantly alter particle speeds with respect to the off-field values, as we observe in Figure 2, suggesting that the osmotic flows-based propulsion mechanism remains unmodified. In fact, we observe that the trend in the velocity variation of the particles as a function of the applied electric field amplitude or frequency is consistent with what was already observed in previous studies in the absence of magnetic field alignment [17,18,33,35]. Indeed, a quadratic dependence on the amplitude (E) is observed, and the variation in the velocity magnitude with the AC frequency (f) has the same functional dependence found earlier [33]. Note that the quadratic velocity increase with E has the same functional dependence until turbulent flows are triggered by electrohydrodynamic instabilities above a threshold field amplitude.
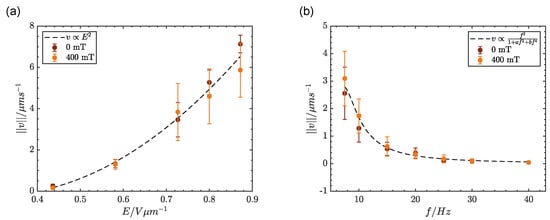
Figure 2.
Particles’ speed as a function of (a) the amplitude of the electric signal (f = 15 Hz) or (b) its frequency (E = 0.52 V/m), with or without the presence of a fixed external magnetic field.
3.2. Collective Control of Particles
3.2.1. Particle Assembly Using a Magnetic Field
LC systems can feature localized discontinuities of the director vector that are referred to as defects. They are points in space with an associated high elastic energy accumulation [15]. Since is organized in particular ways by defects, we can take advantage of these structures to configure particle trajectories and, in particular, to collect them in assemblies. For example, radial director configurations with a central defect have been previously prepared using a photosensitive surface coating of the ITO-glass plates [34,36,37,38]. Other researchers have used electric fields to select defect location [39], have employed laser beams combined with photoconductive surfaces [40], or have imposed spatial restrictions through surface patterning to tune how defects are created [41].
In our case, we create a single umbilical defect [42] with a topological charge (one full turn of around the defect) by placing a ring magnet with a toroidal magnetic field [29] over the cell surface at a distance (h) of 2 mm (Figure 3a–d). At this distance, the magnetic field has a significant radial component parallel to the LC layer, with a magnitude of 115 mT measured along the axis of the ring magnet with a HGM09s tesla-meter purchased from Goudsmit Magnetics, Netherlands. When an AC electric field of amplitude above the Fredericks threshold ( for LC MLC-7029) is applied between the glass plates, starts changing from the homeotropic alignment imposed by the surface treatment to an in-plane alignment. Similarly to what we explained above for the case of a homogeneous magnetic field, in the present case, the in-plane radial component of the toroidal magnetic field breaks the symmetry during the homeotropic to planar transition, leading to the formation of a defect from which a radial orientational field spanning more than 1 mm2 emanates. Notice that, in Figure 3b–d, does not have a pure radial alignment (pure splay distortion) but, instead, it has a significant rotational component, leading to a spiral pattern when observed between crossed polarizers. This is a consequence of the fact that, for the used mesogen, bend or rotational distortions are less energetically demanding than splay distortions [18,36]. Moreover, contrary to other techniques, the generated +1 defect is not pinned to the surfaces of the cell, resulting in its spontaneous drifting and allowing the motility of the resulting director field pattern [29].
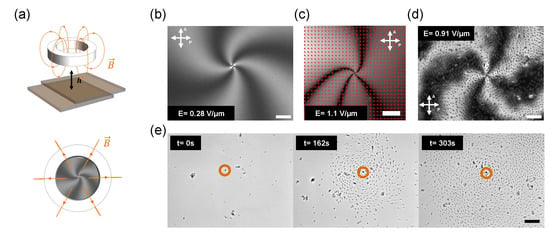
Figure 3.
(a) Top: scheme representing the disposition of the ring magnet over the liquid crystal cell. Bottom: image representation of +1 defect appearing at the center of the LC cell of the ring magnet (top view). For all the experiments, h = 2 mm. (b–d) +1 defect generated by the ring magnet under cross polarizers with (d) or without (b,c) particles. In the case of (c), the red rods indicate the local direction of . All images correspond to different experimental realizations. (e) Formation of a particle mill by the presence of a +1 defect (depicted by an orange circle) and the pseudo-radial director field. Particles accumulate around the defect following clockwise trajectories when an AC electric field is applied (E = 0.91 V/m, f = 25 Hz). Rulers are 50 m long. See also Supplementary Movie S2.
When particles within the area of influence of such a defect are propelled under the action of a low-frequency AC electric field, they move following the local pseudo-radial director field lines. Since particles were initially oriented perpendicularly to the plates, following the original homeotropic LC configuration, transition into planar alignment results in an equal number of particles oriented parallel and anti-parallel to the director field lines. While the former swim towards the central defect, the latter drift away from the field of view or never enter it. Particles that converge towards the defect form a growing compact assembly without aggregating. Indeed, it is known [37] that the same osmotic flows that result in particle propulsion provide a long-range interparticle repulsion of hydrodynamic origin. An additional long-range interparticle repulsion originates from their induced electric dipoles that are parallel to the electric field and, thus, perpendicular to the LC layer. While LC elasticity promotes particle aggregation, this attraction is a much shorter range and is dominated by the repulsion mechanisms [37]. Because of the spiral director field lines, once the centripetal particle motion is arrested and the radial component of the swimming force is compensated by the repulsion of inner neighboring particles, the azimuthal velocity component remains and particles adopt a circular trajectory centered at the defect. Collectively, particles assemble, forming a rotating mill around the defect (Figure 3e), whose dynamics we have analyzed.
In Figure 4a,b, we observe that, within the rotating mill, the tangential velocity (v) depends on the distance relative to the center. At the outer parts of the mill, the velocity reaches a plateau that increases with the strength of the electric field, an aspect that has already been described in Section 3.1 and in the literature [18,33]. Therefore, in this region, the rotating mill is an assembly composed of particles following circular trajectories with a constant and homogeneous tangential velocity. However, towards the center of the assembly, a roughly linear decrease in the speed is seen until particles become arrested. This decay in the speed is associated with the fact that particle density increases towards the center until jamming the collective rotation. When we look at the vorticity distribution (Figure 4c), we observe the expected trend described in the literature [34], namely, vorticity values reaching a maximum in areas close to the central singularity and decreasing away from the central defect. This is consistent with a structure formed by shells of particles rotating at the same speed, with the radial dependence just described. Using the expression for the vorticity, , for a velocity field with tangential velocities with radial dependence [43]
we obtain the vorticity profiles directly from the speed profile data (Figure 4d). In the central region of the mill, speed grows roughly linearly with r. As a result, fluctuates around a constant value. Towards the outer region of the mill, where the speed achieves a constant value, decays as . When the velocity values are normalized with those far from the center of the mill, speed profiles for different values of E overlap, within error bars, onto a single curve. A similar overlap is obtained when the vorticity profiles are calculated from these normalized speed profiles. The conclusion is that rotating mills obtained with different electric fields do not change their internal structure, but only alter their rotation speed according to the dependence shown in Figure 2.
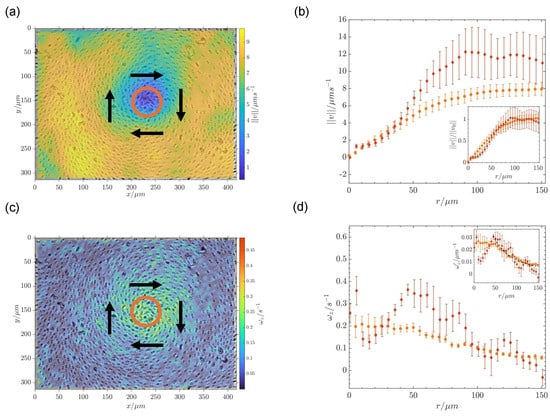
Figure 4.
(a) Speed distribution for particles surrounding a +1 defect under an electric field with parameters E = 0.91 V/m and f = 25 Hz. (b) Speed variation as a function of the radial position within the mill for (∘) E = 0.91 V/m and (⋄) E = 1.12 V/m (f = 25 Hz). In the inset, the speed has been normalized with the average speed of sparse particles. (c) Vorticity () distribution for the same rotating mill shown in panel (a). In both panels, the orange circumference indicates the region within which the defect wanders randomly during the experiment. Black arrows show the direction of rotation of the mill. (d) Vorticity variation as a function of the radial position within the mill obtained through application of Equation (1) to the speed data in panel (b). The inset includes the same calculation for the normalized speed data in the inset of panel (b). The black dashed line indicates the decay of with the inverse of r.
3.2.2. Magnetic Control of Particle Swarms
The ability to assemble large numbers of driven colloids around a designated point can also be used as an initial step to control the motion of particle swarms. This was earlier demonstrated by Hernàndez-Navarro et al. [36] using a reconfigurable photosensitive anchoring layer, and we can also do it here in an easy manner using a combination of magnetic fields. For this purpose, first, we condense a particle cluster using the ring magnet and an AC electric field, as described above. Next, we switch off the AC field and displace the ring magnet to a different location. Finally, we switch on the AC field again to provoke the propulsion of the particles. As we can observe in Figure 5, particles move as a swarm towards the location of the new +1 umbilical defect created at the new location of the ring magnet.
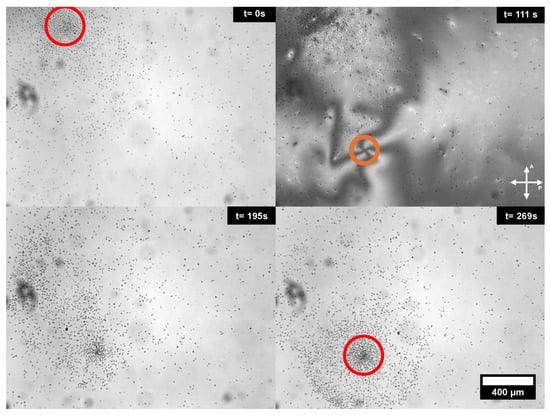

Figure 5.
Collective transport of particle clusters inside the liquid crystal cell by displacing +1 defects generated with a ring magnet. Red circles indicate the location of the center of the original particle cluster at a given time, whereas the orange circle points out the location of the newly generated +1 umbilical defect. Particles propel upon application of an AC electric field (E = 1.17 V/m, f = 25 Hz). The magnetic field acquires a value of 115 mT at the cell mid-plane. See also Supplementary Movie S3.
This control strategy for swarm translocation has a limitation due to the fact that it is a point-by-point motion: It requires switching on and off the electric field while moving the ring magnet to the desired position. An alternative strategy allows us to tune directionality while the electric signal is on and the particles are in motion. This approach is based on controlling the swarm by the unidirectional steering of the colloids using the homogeneous magnetic field created with the Halbach magnet array. We begin by assembling a particle cluster around a single +1 umbilical defect using a ring magnet, as described in Section 3.2.1. Afterwards, the ring magnet is removed and the AC field switched off. The LC cell is then placed inside the cavity of the Halbach array. Upon application of the AC field, driven particles are steered along the fixed unidirectional magnetic field, as explained in Section 3.1. This can be observed in Figure 6a, where a swarm of particles is steered into one direction when the low-frequency AC electric field is turned on. As seen in Figure 6b,c, particles propel mainly towards the same direction: parallel to , the horizontal direction in these images. However, particles could be oriented leftwards or rightwards; thus, we have a distribution of velocities with the two horizontal headings, as seen in Figure 6b. Interestingly, the vast majority of particles move to the right. In contrast, drift along the vertical direction is random, with a zero average. As explained in Section 3.1, surface or shape anomalies in the colloidal particles are likely to be responsible for such a drift. These results are further clarified with the velocity vector angle plot in Figure 6c, where most of the vectors point towards the right. These results suggest the presence of interparticle interactions that result in a coherent motion of particles within a cluster, likely due to a combination of long-range hydrodynamic and short-range elastic interactions. Understanding these effects will be the object of future studies.
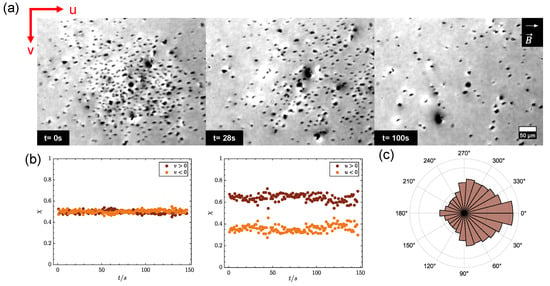
Figure 6.
Dissolution of a cluster when an electric field is applied to provoke the motion of particles through LCEEP (E = 0.86 V/m, f = 25 Hz). See also Supplementary Movie S4. In-plane directionality has been set through the use of a fixed external magnetic field (B = 400 mT) along the horizontal direction. (a) Selection of progressive frames showing the cluster’s dissolution. (b) Number fraction of particles with positive and negative vertical (v) and horizontal (u) velocity components. (c) Distribution of velocity vector angles. The value of 0° is assigned to the direction determined by the u-axis in panel (a), which is parallel to .
While motion along the vertical axis seems randomly distributed, consistent with the horizontal steering direction provided by the magnetic field, its presence leads to the progressive dissolution of the swarm. Therefore, this collective steering with a homogeneous magnetic field is not as robust as the one allowed with the ring magnet, with which swarms preserve their integrity during transport. However, it has the added flexibility of relying on a homogeneous field that can be easily oriented at will. Improving the homogeneity of particle shape and surface chemistry might improve some of the shortcomings of this technique.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we have unveiled a general steering mechanism for colloidal particles driven by liquid crystal-enabled electrophoresis based on the application of a strong enough in-plane magnetic field. When using a LC cell with homeotropic anchoring and a mesogen with negative dielectric anisotropy, this protocol breaks the in-plane degeneracy of the LC director upon application of the driving electric field between the glass plates. Particles move parallel to , which is itself aligned with the magnetic field due to the positive value of the magnetic susceptibility anisotropy of the used mesogens. Moreover, the presence of the orienting magnetic field does not have any apparent impact on the velocity of the driven particles.
Replacing the uniform in-plane magnetic field generated by a Halbach array of magnets with a ring magnet featuring a toroidal magnetic field, we are able to generate point defects from which a spiral arrangement of the LC director emanates. When driven by the AC electric field, this configuration leads to the condensation of particle clusters around the central singularity, forming a steady-state rotating mill with a velocity and vorticity profile that we have analyzed, offering a more straightforward particle-condensing strategy than other protocols reported in the literature.
We have further demonstrated the versatility of our control with magnetic fields by transporting swarms of particles when the ring magnet is displaced or when it is replaced by the homogeneous magnetic field once the particle assembly has been formed. While the former method is less straightforward and versatile, since it involves displacing the magnet over the sample, the latter allows continuous steering simply by rotating the magnetic field, although it is more severely affected by irregularities in the particles’ shape or surface inhomogeneities. Interestingly, these experiments suggest the existence of coupling between moving particles within a swarm, as most of them move with the same heading, rather than being equally distributed parallel or antiparallel to the direction dictated by .
The demonstrated particle-steering method could be further generalized for the controlled motion of colloids within microfluidic environments, micro-cargo transport, or the generation of new metamaterials, or as a model system to address other relevant issues such as the clogging of particle swarms. Thus, the simple experimental realization we have unveiled bears strong potential to become a powerful tool for other studies in which the controlled motion of micro-particles is required.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/colloids9030027/s1, Movie S1: Colloidal particles steered by changing magnetic field; Movie S2: Assembly of a rotating mill of colloidal particles; Movie S3: Collective displacement of a rotating mill to a new defect location; Movie S4: Collective displacement of particles along a homogeneous magnetic field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.I.-M. experiments and data analysis, J.T.-A. and G.C.; supervision: F.S. and J.I.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.T.-A.; writing—review and editing: all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Authors acknowledge funding from MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 (Grant No. PID2022-137713NB-C21). J.T.-A. acknowledges support and funding from a FPU fellowship FPU22/1916 from MICIU.
Data Availability Statement
All data is included in the main text or as supplementary videos.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| AC | Alternate current |
| DC | Direct current |
| DI-LCEEP | Directron-induced liquid crystal-enabled electrophoresis |
| LC | Liquid crystal |
| LCEEP | Liquid crystal-enabled electrophoresis |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Experiments with active and driven synthetic colloids in complex fluids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 62, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, P.; Nsamela, A.; Lesher-Pérez, S.C.; Simmchen, J. Microfluidics for Microswimmers: Engineering Novel Swimmers and Constructing Swimming Lanes on the Microscale, a Tutorial Review. Small 2021, 17, 2007403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunea, A.I.; Taboryski, R. Recent advances in microswimmers for biomedical applications. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Solovev, A.A.; Huang, G.; Cui, J.; Mei, Y. Soft microswimmers: Material capabilities and biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 61, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, A.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Yeomans, J.M.; Sagués, F. Active nematics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, B.M.; Jü, F. Chemotaxis of sperm cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13256–13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottori, S.; Zhang, L.; Peyer, K.E.; Nelson, B.J. Assembly, disassembly, and anomalous propulsion of microscopic helices. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4263–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Manesh, K.M.; Weihs, D.; Wang, J. Magnetically powered flexible metal nanowire motors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14403–14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricard, A.; Caussin, J.B.; Desreumaux, N.; Dauchot, O.; Bartolo, D. Emergence of macroscopic directed motion in populations of motile colloids. Nature 2013, 503, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, R.; Parola, A. Thermophoresis in colloidal suspensions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2008, 20, 153102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogishi, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Sohn, W.Y.; Katayama, K. Optically induced motion of liquid crystalline droplets. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 8085–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, P.; Feldmann, D.; Kopyshev, A.; Lomadze, N.; Santer, S. Light driven guided and self-organized motion of mesoporous colloidal particles. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuri, J.; Ma, X.; Stanton, M.M.; Sánchez, S. Designing micro-and nanoswimmers for specific applications. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Wei, F.; Yin, C.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y. Biomimetic soft micro-swimmers: From actuation mechanisms to applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleman, M.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Soft Matter Physics: An Introduction, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, P.; Pieranski, P. The Liquid Crystals Book Series Nematic and Cholesteric Liquid Crystals the Liquid Crystals Book Series, 1st ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, I.; Peng, C.; Xiang, J.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Liquid crystal-enabled electro-osmosis through spatial charge separation in distorted regions as a novel mechanism of electrokinetics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Liquid crystals-enabled AC electrokinetics. Micromachines 2019, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Active colloids in liquid crystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 21, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.X.; Xiao, R.L.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Soliton-induced liquid crystal enabled electrophoresis. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 013178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Li, C.Y.; Pan, J.T.; Ji, Y.E.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.X.; Lu, Y.Q. Self-assembled liquid crystal architectures for soft matter photonics. Light. Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Xiong, J.; He, Z.; Wu, S.T. Patterning Liquid-Crystal Alignment for Ultrathin Flat Optics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31485–31489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Kumar, A.; Chauhan, S. Aligning Liquid Crystal Materials through Nanoparticles: A Review of Recent Progress. Liquids 2022, 2, 50–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.R.O.; Liu, C.D.; Voinescu, R.; Chen, Z.; Smalyukh, I.I. Optically enriched and guided dynamics of active skyrmions. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.W.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H. Micro-contact printing method for patterning liquid crystal alignment layers. J. Inf. Disp. 2006, 7, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodič, U.; Vellaichamy, M.; Škarabot, M.; Muševič, I. Surface alignment of nematic liquid crystals by direct laser writing of photopolymer alignment layers. Liq. Cryst. 2023, 50, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamat, P.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Control of active liquid crystals with a magnetic field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5498–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümler, P.; Soltner, H. Practical Concepts for Design, Construction and Application of Halbach Magnets in Magnetic Resonance. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2023, 54, 1701–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasselet, E. Tunable High-Resolution Macroscopic Self-Engineered Geometric Phase Optical Elements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 033901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Prat, B.; Arteaga, O.; Sagués, F.; Ignés-Mullol, J. Multimodal fluorescence microscope with fast adaptive polarimetry. HardwareX 2023, 16, e00480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmini, H.N.; Rajabi, M.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Azimuthal anchoring strength in photopatterned alignment of a nematic. Crystals 2021, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Liu, S.F.; Chao, C.Y. Eliminating optical bounce of homeotropic liquid crystal cells with sputtered silicon dioxide alignment films by rubbing treatment. Displays 2011, 32, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernàndez-Navarro, S.; Tierno, P.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. AC electrophoresis of microdroplets in anisotropic liquids: Transport, assembling and reaction. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 7999–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernàndez-Navarro, S.; Tierno, P.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Nematic colloidal swarms assembled and transported on photosensitive surfaces. IEEE Trans. Nanobioscience 2015, 14, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrentovich, O.D.; Lazo, I.; Pishnyak, O.P. Nonlinear electrophoresis of dielectric and metal spheres in a nematic liquid crystal. Nature 2010, 467, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernàndez-Navarro, S.; Tierno, P.; Farrera, J.A.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Reconfigurable swarms of nematic colloids controlled by photoactivated surface patterns. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10696–10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, A.V.; Pagès, J.M.; Tierno, P.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Collective dynamics and conformal ordering in electrophoretically driven nematic colloids. Phys. Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 022008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, J.M.; Straube, A.V.; Tierno, P.; Ignés-Mullol, J.; Sagués, F. Inhomogeneous assembly of driven nematic colloids. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford O’Neill, J.J.; Salter, P.S.; Booth, M.J.; Elston, S.J.; Morris, S.M. Electrically-tunable positioning of topological defects in liquid crystals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, R.; Bortolozzo, U.; Assanto, G.; Vidal-Henriquez, E.; Clerc, M.G.; Residori, S. Harnessing optical vortex lattices in nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawale, T.; Swain, J.; Hashemi, M.R.; Tierra, G.; Li, X. Dynamic Motions of Topological Defects in Nematic Liquid Crystals under Spatial Confinement. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2300136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Marshall, O.; Wright, J.; Bulleid, N. Annihilation dynamics of umbilical defects in nematic liquid crystals under applied electric fields. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 71, 061709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierno, P.; Johansen, T.H.; Fischer, T.M. Magnetically driven colloidal microstirrer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3077–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).