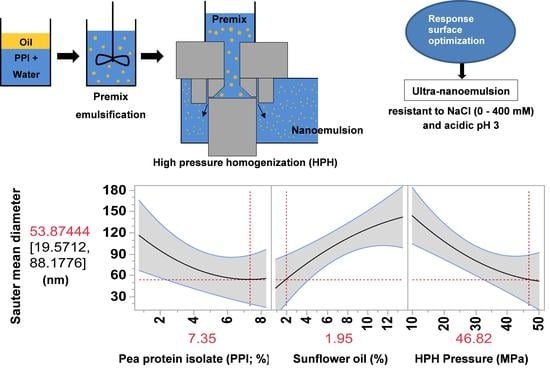
Optimization of Pea Protein Isolate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Ultra-Nanoemulsions by Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Electrolytes on Optimized Nanoemulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Evaluation
2.3. Aqueous Phase, Coarse Emulsion, and Nanoemulsion Preparation
2.4. Emulsion Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
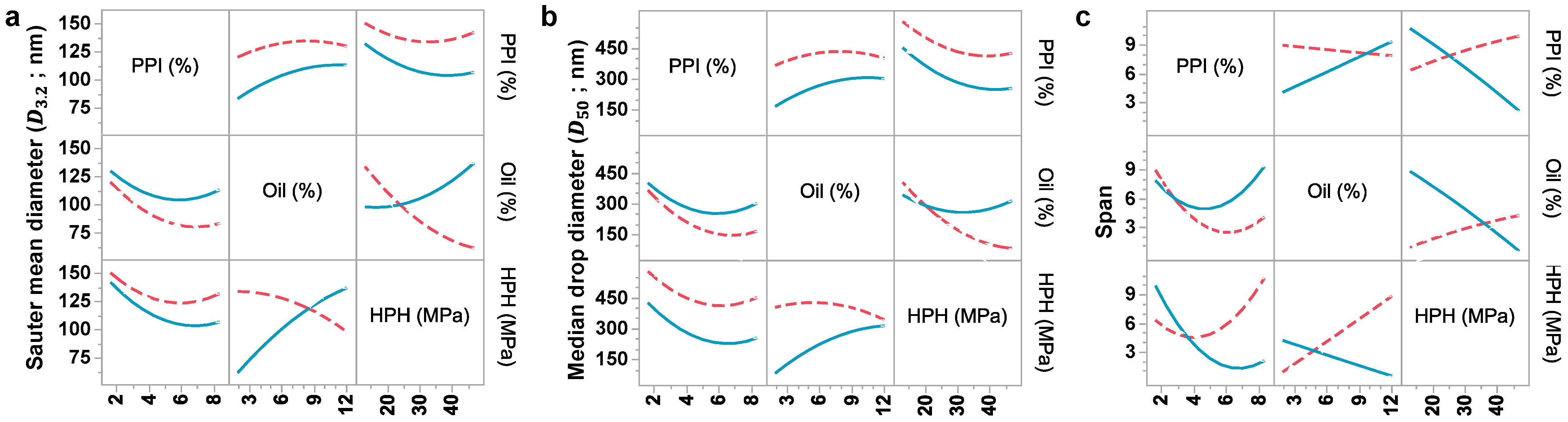
3.1. Response Surface Evaluation
3.1.1. Effect of PPI Concentration
3.1.2. Effect of Oil Content
3.1.3. Effect of HPH Pressure
3.2. Prediction and Validation
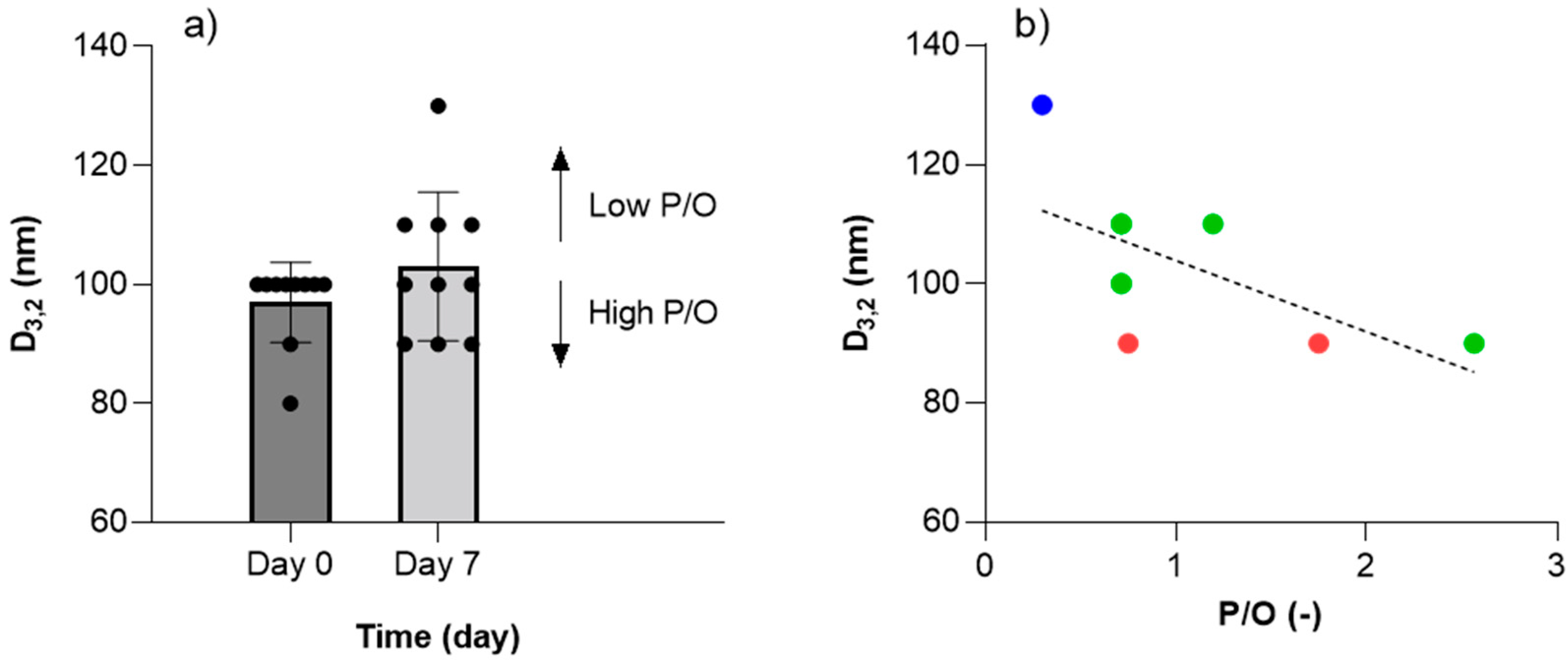
3.3. Emulsion Stability
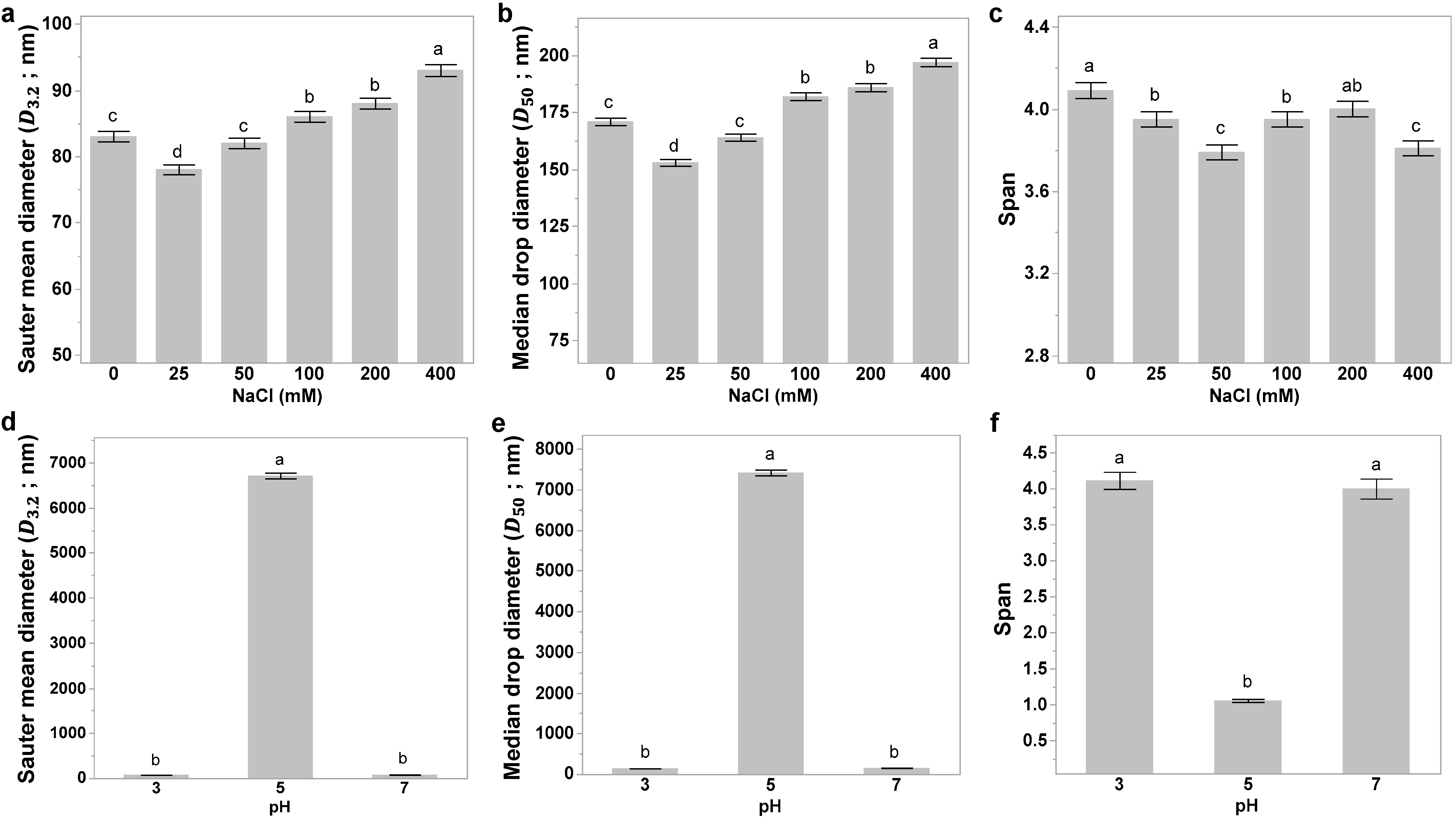
3.4. Effect of Salt on Optimized Conditions
3.5. Effect of pH on Optimized Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santiago, J.S.J.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Palomo, A.; Niroula, A.; Xu, F.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E. Process-induced water-soluble biopolymers from broccoli and tomato purées: Their molecular structure in relation to their emulsion stabilizing capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, A.; Gamot, T.D.; Ooi, C.W.; Dhital, S. Biomolecule-based pickering food emulsions: Intrinsic components of food matrix, recent trends and prospects. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 112, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; McClements, D.J. Structure–function relationships in food emulsions: Improving food quality and sensory perception. Food Struct. 2013, 1, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Khalid, N.; Shu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Tuwo, A.; Nakajima, M. Fucoxanthin-Loaded Oil-in-Water Emulsion-Based Delivery Systems: Effects of Natural Emulsifiers on the Formulation, Stability, and Bioaccessibility. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 10502–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, R.; Mehmood, Z.; Baig, A.; Khalid, N. Formulation and characterization of food grade O/W nanoemulsions encapsulating quercetin and curcumin: Insights on enhancing solubility characteristics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaade, W.; Méndez-Sánchez, C.; Güell, C.; De Lamo-Castellví, S.; Mestres, M.; Ferrando, M. Complexed Biopolymer of Whey Protein and Carboxymethyl Cellulose to Enhance the Chemical Stability of Lemon Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure–function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapala, K.P.; Mulvihill, D.M.; O’Mahony, J.A. A review of the analytical approaches used for studying the structure, interactions and stability of emulsions in nutritional beverage systems. Food Struct. 2018, 16, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Emulsion Formation, Stability, and Rheology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Biopolymers in Food Emulsions; Kasapis, S., Norton, I.T., Ubbink, J.B., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Izquierdo, P.; Nolla, J.; Azemar, N.; Garcia-Celma, M. Nano-emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Marshall-Breton, C.; Leser, M.E.; Sher, A.A.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of ultrafine edible emulsions: Comparison of high-energy and low-energy homogenization methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikov, K.P.; Pelan, E. Colloidal delivery systems for micronutrients and nutraceuticals. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Akhtar, M.; Sarkar, A. Recent advances in emulsion-based delivery approaches for curcumin: From encapsulation to bioaccessibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Lipid-Based Emulsions and Emulsifier. In Food Lipids, 4th ed.; Akoh, C.C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 64–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tenorio-Garcia, E.; Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Simone, E.; Sarkar, A. Recent advances in design and stability of double emulsions: Trends in Pickering stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Xue, C.; Wei, Z. Physicochemical characteristics, applications and research trends of edible Pickering emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 107, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Schroën, K. Pickering Emulsions for Food Applications: Background, Trends, and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Gao, S.; Li, X.; Liang, H.; Li, S. Antioxidant Pickering emulsions stabilised by zein/tannic acid colloidal particles with low concentration. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.; Ioannidis, M.A.; Henneke, D.E. Effects of temperature, pH, and ionic strength on the adsorption of nanoparticles at liquid–liquid interfaces. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 27, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güell, C.; Ferrando, M.; Trentin, A.; Schroën, K. Apparent Interfacial Tension Effects in Protein Stabilized Emulsions Prepared with Microstructured Systems. Membranes 2017, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Santana, A.S.; Braisch, B.; Preis, R.; Schuchmann, H. High pressure emulsification with nano-particles as stabilizing agents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donsì, F.; Senatore, B.; Huang, Q.; Ferrari, G. Development of Novel Pea Protein-Based Nanoemulsions for Delivery of Nutraceuticals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10653–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, E.; Burgos-Díaz, C.; Zúñiga, R.; Jorkowski, J.; Quilaqueo, M.; Rubilar, M. Effect of Interfacial Ionic Layers on the Food-Grade O/W Emulsion Physical Stability and Astaxanthin Retention during Spray-Drying. Foods 2021, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, Y.N.; Tan, C.P.; Tan, P.Y.; Khalid, N.; Tan, T.B. Fabrication of oil-in-water emulsions as shelf-stable liquid non-dairy creamers: Effects of homogenization pressure, oil type, and emulsifier concentration. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Graaf, S.; Schroen, K.; Boom, R. Preparation of double emulsions by membrane emulsification—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Tang, C.-H. Gel-like pea protein Pickering emulsions at pH3.0 as a potential intestine-targeted and sustained-release delivery system for β-carotene. Food Res. Int. 2016, 79, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-N.; Tang, C.-H. Pea protein exhibits a novel Pickering stabilization for oil-in-water emulsions at pH 3.0. LWT 2014, 58, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderink, E.B.; Münch, K.; Sagis, L.; Schroën, K.; Berton-Carabin, C. Synergistic stabilisation of emulsions by blends of dairy and soluble pea proteins: Contribution of the interfacial composition. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderink, E.B.A.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Schroën, K.; Riaublanc, A.; Houinsou-Houssou, B.; Boire, A.; Genot, C. Conformational Changes of Whey and Pea Proteins upon Emulsification Approached by Front-Surface Fluorescence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6601–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xia, S.; Huang, Q. High internal phase pickering emulsions stabilized by pea protein isolate-high methoxyl pectin-EGCG complex: Interfacial properties and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, W.; Wang, R. Protein networks and starch nanocrystals jointly stabilizing liquid foams via pickering-type coverages and steric hindrance. Food Chem. 2021, 370, 131014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded pea protein-pectin ternary complex for the stabilization and delivery of β-carotene emulsions. Food Chem. 2019, 313, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yolmeh, M.; Jafari, S.M. Applications of Response Surface Methodology in the Food Industry Processes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouli, M.; Polychniatou, V.; Tzia, C. Optimization of water in olive oil nano-emulsions composition with bioactive compounds by response surface methodology. LWT 2018, 89, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviadaran, R.; Chandran, D.; Shin, L.H.; Manickam, S. Optimization of palm oil in water nano-emulsion with curcumin using microfluidizer and response surface methodology. LWT 2018, 96, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsumpun, P.; Iwamoto, S.; Siripatrawan, U. Response surface methodology for optimization of cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsion with improved stability and antifungal activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 60, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, D. Stability of oil-in-water emulsions performed by ultrasound power or high-pressure homogenization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.B.; Drzymala, J. Physical meaning of the Sauter mean diameter of spherical particulate matter. Part. Sci. Technol. 2015, 34, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelichowska, J.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Chevalier, Y. Effects of solid particle content on properties of o/w Pickering emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yan, X.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, L.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Weitz, D.A. Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal surfactants: Role of solid particles. Particuology 2022, 64, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Lips, A. Comparison of solid particles, globular proteins and surfactants as emulsifiers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 1608–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E.; Mofolasayo, O.A.; Watts, B.M. Emulsifying and foaming properties of commercial yellow pea (Pisum sativum L.) seed flours. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9793–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Xu, B.-C.; Zhang, B. Simple method for fabrication of high internal phase emulsions solely using novel pea protein isolate nanoparticles: Stability of ionic strength and temperature. Food Chem. 2021, 370, 130899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Campbell, B. Coalescence stability of emulsions containing globular milk proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123–126, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, A.; Schroën, K.; Boom, R. High-throughput premix membrane emulsification using nickel sieves having straight-through pores. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Characterization of surimi particles stabilized novel pickering emulsions: Effect of particles concentration, pH and NaCl levels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brösel, S.; Schubert, H. Investigations on the role of surfactants in mechanical emulsification using a high-pressure homogenizer with an orifice valve. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 1999, 38, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadnađev, T.D.; Dokić, P.; Krstonošić, V.; Hadnađev, M. Influence of oil phase concentration on droplet size distribution and stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 115, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkestelli, H.I.; El, S.N. Preparation and characterization of double emulsions for saltiness enhancement by inhomogeneous spatial distribution of sodium chloride. LWT 2018, 101, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, A.; Agyei, D.; Wang, Q. Formulation of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions containing trans-resveratrol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35917–35927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lu, X.; Huang, Q. Double emulsion derived from kafirin nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsion: Fabrication, microstructure, stability and in vitro digestion profile. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-F.; He, Z.-Y.; Li, G.-Y.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Su, D.-X.; Zhang, J.-L.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; He, S. The formation and characterization of antioxidant pickering emulsions: Effect of the interactions between gliadin and chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 90, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-S.; Luo, Z.-G.; Li, X.-L. An enhanced pH-sensitive carrier based on alginate-Ca-EDTA in a set-type W1/O/W2 double emulsion model stabilized with WPI-EGCG covalent conjugates for probiotics colon-targeted release. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 113, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkestelli, H.I.; El, S.N. Development and characterization of double emulsion to encapsulate iron. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Vladisavljević, G.T. Droplet breakup mechanisms in premix membrane emulsification and related microfluidic channels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 290, 102393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, S.; Wagner, G.; Urban, K.; Ulrich, J. High-Pressure Homogenization as a Process for Emulsion Formation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, M.E.; Nikiforidis, C.V.; van der Goot, A.J.; van der Padt, A. Protein nativity explains emulsifying properties of aqueous extracted protein components from yellow pea. Food Struct. 2017, 14, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primozic, M.; Duchek, A.; Nickerson, M.; Ghosh, S. Formation, stability and in vitro digestibility of nanoemulsions stabilized by high-pressure homogenized lentil proteins isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Du, M. Physicochemical properties and oil/water interfacial adsorption behavior of cod proteins as affected by high-pressure homogenization. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 100, 105429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z. Impact of high-pressure homogenization on physico-chemical, structural, and rheological properties of quinoa protein isolates. Food Struct. 2022, 32, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, Z.-Y.; Othman, N.; Choo, C.-L. The Role of Internal Droplet Size on Emulsion Stability and the Extraction Performance of Kraft Lignin Removal from Pulping Wastewater in Emulsion Liquid Membrane Process. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 37, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, T.; Schroën, C.; Boom, R. Coalescence kinetics of oil-in-water emulsions studied with microfluidics. Fuel 2013, 106, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.R.; Davis, R.H. Modeling of collision and coalescence of droplets during microgravity processing of Zn-Bi immiscible alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1990, 21, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Folter, J.W.J.; van Ruijven, M.W.M.; Velikov, K.P. Oil-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal particles from the water-insoluble protein zein. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6807–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Sidzhakova, D.; Campbell, B. Effect of Thermal Treatment, Ionic Strength, and pH on the Short-Term and Long-Term Coalescence Stability of β-Lactoglobulin Emulsions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6042–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, T.; Liu, C. Fabrication and characterization of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by macadamia protein isolate/chitosan hydrochloride composite polymers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; de Campo, L.; Gilbert, E.P.; Knott, R.; Cheng, L.; Storer, B.; Lin, X.; Luo, L.; Patole, S.; Hemar, Y. Effect of NaCl and CaCl2 concentration on the rheological and structural characteristics of thermally-induced quinoa protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 124, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Sarkar, A. Pickering emulsion stabilized by protein nanogel particles for delivery of curcumin: Effects of pH and ionic strength on curcumin retention. Food Struct. 2019, 21, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.; Vieira, J.; Wolf, B. Cocoa particles for food emulsion stabilisation. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurukji, D.; Pichot, R.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I. Interfacial behaviour of sodium stearoyllactylate (SSL) as an oil-in-water pickering emulsion stabiliser. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 409, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Tu, S.; Ghosh, S.; Nickerson, M. Effect of pH on the inter-relationships between the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties for pea, soy, lentil and canola protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-N.; Tang, C.-H. pH-dependent emulsifying properties of pea [Pisum sativum (L.)] proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.R.; Williams, P.A.; Sharif, M.K.; Abbas, S.; Majeed, H.; Masamba, K.G.; Safdar, W.; Zhong, F. Current progress in the utilization of native and modified legume proteins as emulsifiers and encapsulants—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Experimental Run | PPI % | Sunflower Oil % | Pressure (MPa) | D3,2 (nm) | D50 (nm) | Span (δ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 4 | 40 | 90 | 200 | 3.95 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 40 | 97 | 220 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 108 | 279 | 3.34 |
| 4 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 106 | 275 | 4.09 |
| 5 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 100 | 245 | 3.91 |
| 6 | 7 | 10 | 40 | 114 | 268 | 3.07 |
| 7 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 104 | 258 | 3.76 |
| 8 | 7 | 4 | 20 | 107 | 288 | 4.14 |
| 9 | 5 | 1.95 | 30 | 85 | 181 | 4.07 |
| 10 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 102 | 259 | 3.99 |
| 11 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 103 | 298 | 4.69 |
| 12 | 5 | 7 | 13.18 | 135 | 488 | 4.03 |
| 13 | 3 | 10 | 40 | 131 | 328 | 4.72 |
| 14 | 5 | 7 | 30 | 104 | 262 | 3.71 |
| 15 | 5 | 12.05 | 30 | 110 | 298 | 3.85 |
| 16 | 3 | 4 | 20 | 125 | 368 | 3.71 |
| 17 | 1.64 | 7 | 30 | 144 | 521 | 11.62 |
| 18 | 5 | 7 | 46.82 | 102 | 227 | 3.31 |
| 19 | 8.36 | 7 | 30 | 101 | 239 | 3.66 |
| 20 | 7 | 10 | 20 | 109 | 329 | 11.77 |
| Optimization Setting | Optimized Factors Value | Predicted Value (nm) | Actual Value (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sauter Mean Diameter (D3,2) | Values (nm) | Desirability | PPI (%) | Oil (%) | HPH Pressure (MPa) | ||
| High | 150 | 0.06 | 7.35 | 1.95 | 46.82 | 53.87 ± 34.23 | 80.53 ± 2.45 |
| Middle | 100 | 0.90 | |||||
| Low | 80 | 0.98 | |||||
| Factors | Constant | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | R2 (%) | Model p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3,2 | 125.11 *** | −3.97 *** | 1.95 ** | −0.49 * | 1.43 ** | −0.35 | 0.04 * | 0.29 | −0.08 | 0.33 *** | 83 | <0.005 |
| D50 | 471.15 *** | −22.09 ** | 8.39 | −5.17 ** | 8.13 * | −1.91 | 0.25 | 1.48 | −0.19 | 0.85 | 77 | <0.05 |
| Span | 5.895 | −0.26 | 0.21 | −0.08 | 0.33 | 0.00 | −0.00 | 0.09 | −0.05 | −0.03 | 55 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niroula, A.; Alshamsi, R.; Sobti, B.; Nazir, A. Optimization of Pea Protein Isolate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Ultra-Nanoemulsions by Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Electrolytes on Optimized Nanoemulsions. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030047
Niroula A, Alshamsi R, Sobti B, Nazir A. Optimization of Pea Protein Isolate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Ultra-Nanoemulsions by Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Electrolytes on Optimized Nanoemulsions. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiroula, Anuj, Rodah Alshamsi, Bhawna Sobti, and Akmal Nazir. 2022. "Optimization of Pea Protein Isolate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Ultra-Nanoemulsions by Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Electrolytes on Optimized Nanoemulsions" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030047
APA StyleNiroula, A., Alshamsi, R., Sobti, B., & Nazir, A. (2022). Optimization of Pea Protein Isolate-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Ultra-Nanoemulsions by Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Electrolytes on Optimized Nanoemulsions. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030047