Levofloxacin and Amikacin Adsorption on Nanodiamonds: Mechanism and Application Prospects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanodiamond Characterization
2.3. Tritium-Labeled Antibiotics Preparation
2.4. Adsorption of Antibiotics on the Surface of DND
2.5. Desorption of Antibiotics from Nanodiamonds
2.6. Antimicrobal Analysis of DND–Antibiotics Composite Desposed on Collagen Matrices
3. Results and Discussion
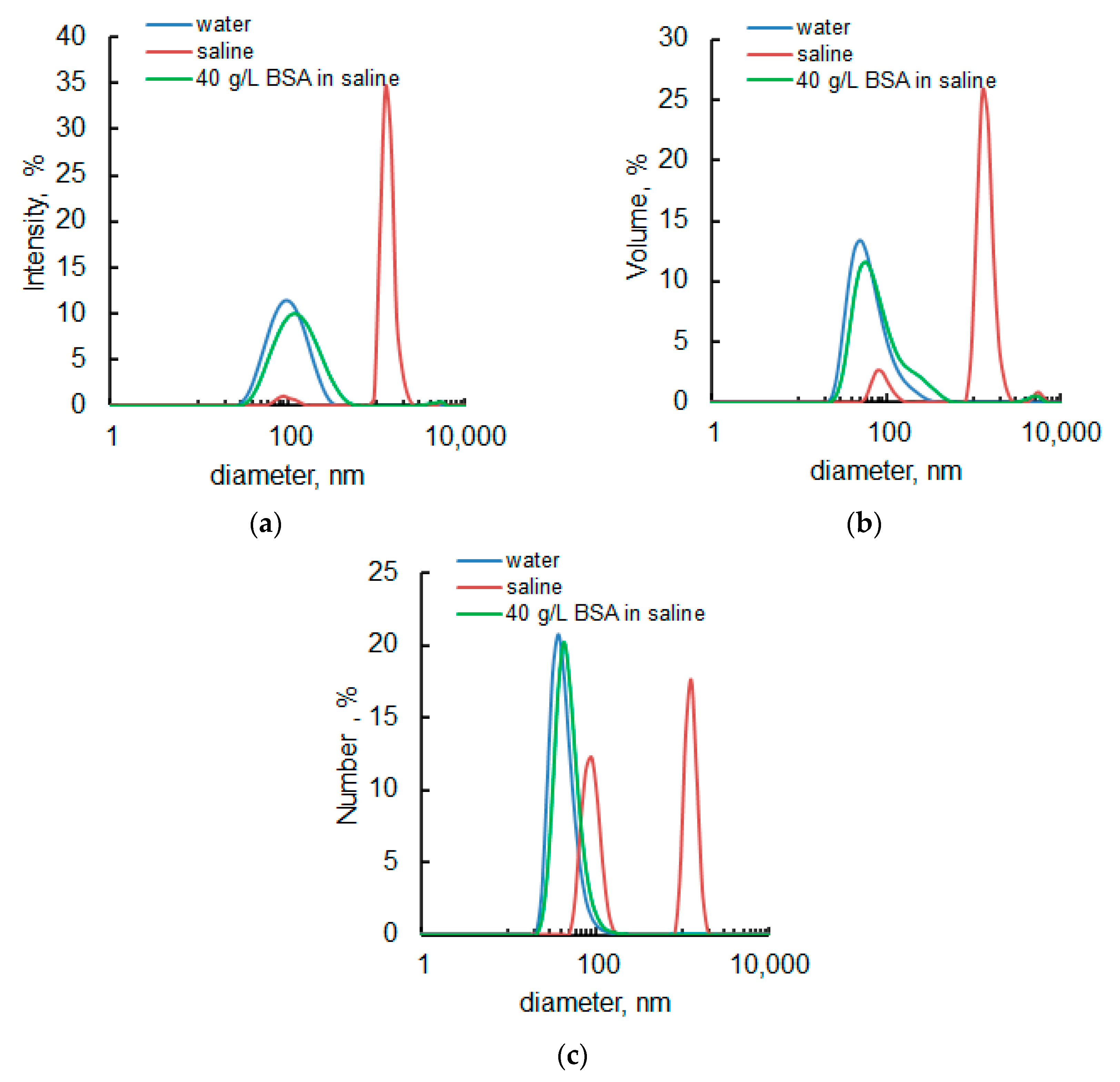
3.1. Initial Nanodiamonds Characterization: Size, Morphology and Specific Surface
3.2. DND–Antibiotics Adsorption Complexes Preparation and Characterization
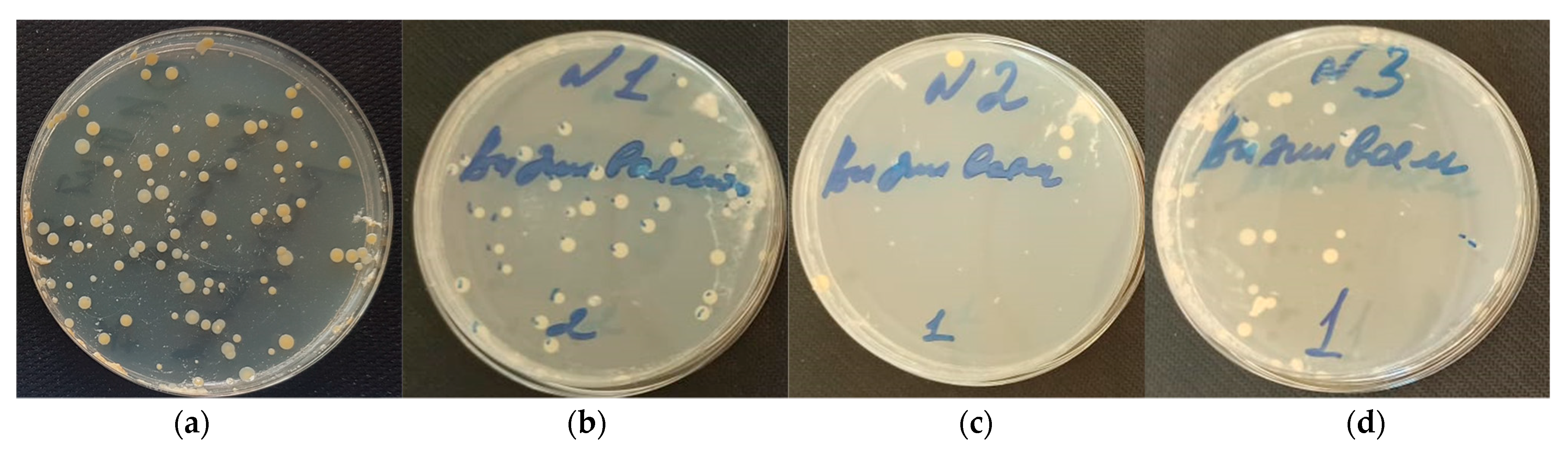
3.3. Antimicrobial Characterization of DND–Levofloxacin and DND–Amikacin Complexes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greiner, N.R.; Phillips, D.S.; Johnson, J.D.; Volk, F. Diamonds in detonation soot. Nature 1988, 333, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidelman, S.; Altshuler, A. Synthesis of nanoscale materials using detonation of solid explosives. Nanostruct. Mater. 1993, 3, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Jain, N.; Nagaich, U. Nanodiamonds with powerful ability for drug delivery and biomedical applications: Recent updates on in vivo study and patents. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.; Wang, C.-H.K.C.H.K.; Chow, E.K.-H.K.H. Nanodiamonds: The intersection of nanotechnology, drug development, and personalized medicine. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulakova, I.I. Surface chemistry of nanodiamonds. Phys. Solid State (Transl. Fiz. Tverd. Tela) 2004, 46, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaam, A.D.; Hwang, P.T.J.; Poonawalla, A.; Green, H.N.; Jun, H.W.; Dean, D. Nanodiamonds enhance therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in treating metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 425103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Su, W.; Ahmad, K.Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Chow, E.K.H.; Ho, D.; Ding, X. Safety evaluation of nanodiamond-doxorubicin complexes in a Naïve Beagle canine model using hematologic, histological, and urine analysis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3356–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Pentecost, A.; Li, X.-M.M.; Neitzel, I.; Nelson, M.; Wei, C.; He, T.; Guo, F.; Gogotsi, Y. Adsorption of drugs on nanodiamond: Toward development of a drug delivery platform. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3728–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.; Chen, M.; Pierstorff, E.; Huang, H.; Osawa, E.; Ho, D. Nanodiamond-Embedded Microfilm Devices for Localized Chemotherapeutic Elution. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Low, X.C.; Hou, W.; Abdullah, L.N.; Toh, T.B.; Mohd Abdul Rashid, M.; Ho, D.; Chow, E.K.H. Epirubicin-Adsorbed Nanodiamonds Kill Chemoresistant Hepatic Cancer Stem Cells. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12151–12166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.; Yang, P. Immobilization of enzyme on detonation nanodiamond for highly efficient proteolysis. Talanta 2010, 80, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimkunas, R.A.; Robinson, E.; Lam, R.; Lu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Huang, H.; Osawa, E.; Ho, D. Nanodiamond-insulin complexes as pH-dependent protein delivery vehicles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.C.L.; Chang, H.C. Adsorption and immobilization of cytochrome c on nanodiamonds. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5879–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Perevedentseva, E.; Tu, J.-S.; Chung, P.-H.; Cheng, C.-L.; Liu, K.-K.; Chao, J.-I.; Chen, P.-H.; Chang, C.-C. Direct and in vitro observation of growth hormone receptor molecules in A549 human lung epithelial cells by nanodiamond labeling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 163903/1–163903/3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kossovsky, N.; Gelman, A.; Hnatyszyn, H.J.; Rajguru, S.; Garrell, R.L.; Torbati, S.; Freitas, S.S.F.; Chow, G.-M. Surface-Modified Diamond Nanoparticles as Antigen Delivery Vehicles. Bioconjug. Chem. 1995, 6, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.-I.; Perevedentseva, E.; Chung, P.-H.; Liu, K.-K.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Cheng, C.-L. Nanometer-sized diamond particle as a probe for biolabeling. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adnan, A.; Lam, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, J.; Schaffer, D.J.; Barnard, A.S.; Schatz, G.C.; Ho, D.; Liu, W.K. Atomistic Simulation and Measurement of pH Dependent Cancer Therapeutic Interactions with Nanodiamond Carrier. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysheva, M.G.; Chaschin, I.S.; Sinolits, A.V.; Vasil’ev, V.G.; Popov, A.G.; Badun, G.A.; Bakuleva, N.P. Chitosan-nanodiamond composites for improving heart valve biological prostheses materials: Preparation and mechanical trial. Fullerenes, Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysheva, M.G.; Popov, A.G.; Tashlitsky, V.N.; Badun, G.A. Cationic surfactant coating nanodiamonds: Adsorption and peculiarities. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 565, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badun, G.A.; Myasnikov, I.Y.; Kazakov, A.G.; Fedorova, N.V.; Chernysheva, M.G. Noncovalent Modification of Nanodiamonds with Tritium-Labeled Pantothenic Acid Derivatives. Radiochem. (Moscow Russ. Fed.) 2019, 61, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badun, G.A.; Chernysheva, M.G.; Ksenofontov, A.L. Increase in the specific radioactivity of tritium-labeled compounds obtained by tritium thermal activation method. Radiochim. Acta 2012, 100, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomatin, A.S.; Yakovlev, R.Y.; Leonidov, N.B.; Badun, G.A.; Chernysheva, M.G.; Kulakova, I.I.; Stavrianidi, A.N.; Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Lisichkin, G.V. Obtaining Tritium-Labeled Amikacin and Its Adsorption Immobilization on Functionalized Nanodiamonds. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 73, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaschin, I.S.; Bakuleva, N.P.; Grigoriev, T.E.; Krasheninnikov, S.V.; Nikitin, L.N. Collagen tissue treated with chitosan solution in H2O/CO2 mixtures: Influence of clathrates hydrates on the structure and mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 67, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, W.M. Bacterial Adhesion: Seen Any Good Biofilms Lately? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavithra, D.; Doble, M. Biofilm formation, bacterial adhesion and host response on polymeric implants—Issues and prevention. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spormann, A.M.; Thormann, K.; Saville, R.; Shukla, S.; Entcheva, P. Nanoscale Technology in Biological Systems; Greco, R.S., Prinz, F.B., Smith, R.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780203500224. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, V.L.; Fang, G.D.; Keys, T.F.; Harris, A.A.; Gentry, L.O.; Fuchs, P.C.; Wagener, M.M.; Wong, E.S. Prosthetic valve endocarditis: Superiority of surgical valve replacement versus medical therapy only. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1994, 58, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, M.; Witchitz, S.; Chastang, C.; Regnier, B.; Vachon, F. Prosthetic valve endocarditis in the ICU. Prognostic factors of overall survival in a series of 122 cases and consequences for treatment decision. Chest 1995, 108, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krüger, A.; Kataoka, F.; Ozawa, M.; Fujino, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y.; Osawa, E. Unusually tight aggregation in detonation nanodiamond: Identification and disintegration. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Mohamed, A.S.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Soliman, A.T.A. Enhanced Adsorption of Toxic and Biologically Active Levofloxacin Residuals from Wastewater Using Clay Nanotubes as a Novel Fixed Bed: Column Performance and Optimization. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26195–26205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn 2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chabani, M.; Amrane, A.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetic modelling of the adsorption of nitrates by ion exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 125, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Application of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: A theoretical analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, 8th ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Badun, G.A.; Sinolits, A.V.; Chernysheva, M.G.; Popov, A.G.; Kulakova, I.I.; Lisichkin, G.V. Mechanism of formation of adsorption complexes amikacin–detonation nanodiamond. Mendeleev Commun. 2019, 29, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, T.; Puskar, L. FTIR spectroscopy of nanodiamonds: Methods and interpretation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 89, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-470-09307-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, S.Y.; Van Harmelen, R.J.J.; Norouzi, N.; Offens, F.; Venema, I.M.; Habibi Najafi, M.B.; Schirhagl, R. Interaction of nanodiamonds with bacteria. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17117–17124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kalimuthu, S.; Rajasekar, V.; Xu, F.; Yiu, Y.C.; Hui, T.K.C.; Neelakantan, P.; Chu, Z. Biofilm inhibition in oral pathogens by nanodiamonds. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5127–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, J.; Dringen, R.; Zare, R.N.; Maas, M.; Rezwan, K. Bactericidal activity of partially oxidized nanodiamonds. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6475–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumont, A.; Pitt, A.R.; Lambert, P.A.; Oggioni, M.R.; Ye, H. Properties, mechanism and applications of diamond as an antibacterial material. Funct. Diam. 2021, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Perevedentseva, E.; Jani, M.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Ye, Y.-S.; Chung, P.-H.; Cheng, C.-L. Antibacterial effect of ultrafine nanodiamond against gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 20, 051014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappeler, R.; Gillham, M.; Brown, N.M. Antibiotic prophylaxis for cardiac surgery. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallyamov, M.O.; Chaschin, I.S.; Bulat, M.V.; Bakuleva, N.P.; Badun, G.A.; Chernysheva, M.G.; Kiselyova, O.I.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Gallyamov, M.O.; Chaschin, I.S.; et al. Chitosan coatings with enhanced biostability in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wispelwey, B.; Schafer, K.R. Fluoroquinolones in the management of community-acquired pneumonia in primary care. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, C.; Wilcox, C. Susceptibility of Recently Isolated Bacteria to Amikacin In Vitro: Comparisons with Four Other Aminoglycoside Antibiotics Author (s): Maxwell Finland, Carol Garner, Clare Wilcox and Leon D. Sabath Source: The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Nov. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 134, S297–S307. [Google Scholar]
- Routledge, P.A.; Hutchings, A.D. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM). In The Immunoassay Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 945–962. ISBN 9780080970370. [Google Scholar]
- Broussou, D.C.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Toutain, P.L.; Woehrlé, F.; El Garch, F.; Bousquet-Melou, A.; Ferran, A.A. Differential activity of the combination of vancomycin and amikacin on planktonic vs. biofilm-growing Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in a Hollow Fiber infection model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perevedentseva, E.; Lin, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-L. A review of recent advances in nanodiamond-mediated drug delivery in cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.; Ho, D. Nanodiamonds as vehicles for systemic and localized drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Algar, W.R.; Berti, L.; Gemmill, K.B.; Casey, B.J.; Oh, E.; Stewart, M.H.; Medintz, I.L. Functionalizing Nanoparticles with Biological Molecules: Developing Chemistries that Facilitate Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1904–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrand, A.M.; Huang, H.; Carlson, C.; Schlager, J.J.; Ōsawa, E.; Hussain, S.M.; Dai, L. Are Diamond Nanoparticles Cytotoxic? J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.; Chow, E.K.-H.; Osawa, E.; Bishop, J.M.; Ho, D. Diamond-Lipid Hybrids Enhance Chemotherapeutic Tolerance and Mediate Tumor Regression. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3532–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Antibiotic | The Langmuir Model | The Freundlich Model | The Dubinin-Radushkevich Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Γmax1 | KL | R | KF | n | R | β | Γmax | E | r | |
| Levofloxacin | 145 | 0.27 | 0.983 | 32.2 | 1.8 | 0.951 | 1 × 10−2 | 244 | 7.2 | 0.970 |
| Amikacin | 99 | 1.3 | 0.979 | 48 | 3.2 | 0.978 | 5 × 10−3 | 159 | 11 | 0.987 |
| Antibiotic | Initial Adsorption, mg/g | After Desorption in Saline, mg/g | After Desorption in 40-g/L Albumin Solution in Saline, mg/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Levofloxacin | 132 ± 23 | 34 ± 6 | 17 ± 3 |
| Amikacin | 73 ± 13 | 58 ± 15 | 30 ± 8 |
| Coating Composition | No Coating | DND | DND–Amikacin | DND–Levofloxacin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adhesion (Log (CFU)) | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| Survivability (Log (CFU)) | 5.0 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, T.; Chernysheva, M.G.; Badun, G.A.; Popov, A.G.; Egorov, A.V.; Anuchina, N.M.; Chaschin, I.S.; Bakuleva, N.P. Levofloxacin and Amikacin Adsorption on Nanodiamonds: Mechanism and Application Prospects. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020035
Shen T, Chernysheva MG, Badun GA, Popov AG, Egorov AV, Anuchina NM, Chaschin IS, Bakuleva NP. Levofloxacin and Amikacin Adsorption on Nanodiamonds: Mechanism and Application Prospects. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Tianyi, Maria G. Chernysheva, Gennadii A. Badun, Andrey G. Popov, Alexander V. Egorov, Neli M. Anuchina, Ivan S. Chaschin, and Natalia P. Bakuleva. 2022. "Levofloxacin and Amikacin Adsorption on Nanodiamonds: Mechanism and Application Prospects" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020035
APA StyleShen, T., Chernysheva, M. G., Badun, G. A., Popov, A. G., Egorov, A. V., Anuchina, N. M., Chaschin, I. S., & Bakuleva, N. P. (2022). Levofloxacin and Amikacin Adsorption on Nanodiamonds: Mechanism and Application Prospects. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020035







