Nanofluid Structural Forces Alter Solid Wetting, Enhancing Oil Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory of the Oscillatory Structural Forces
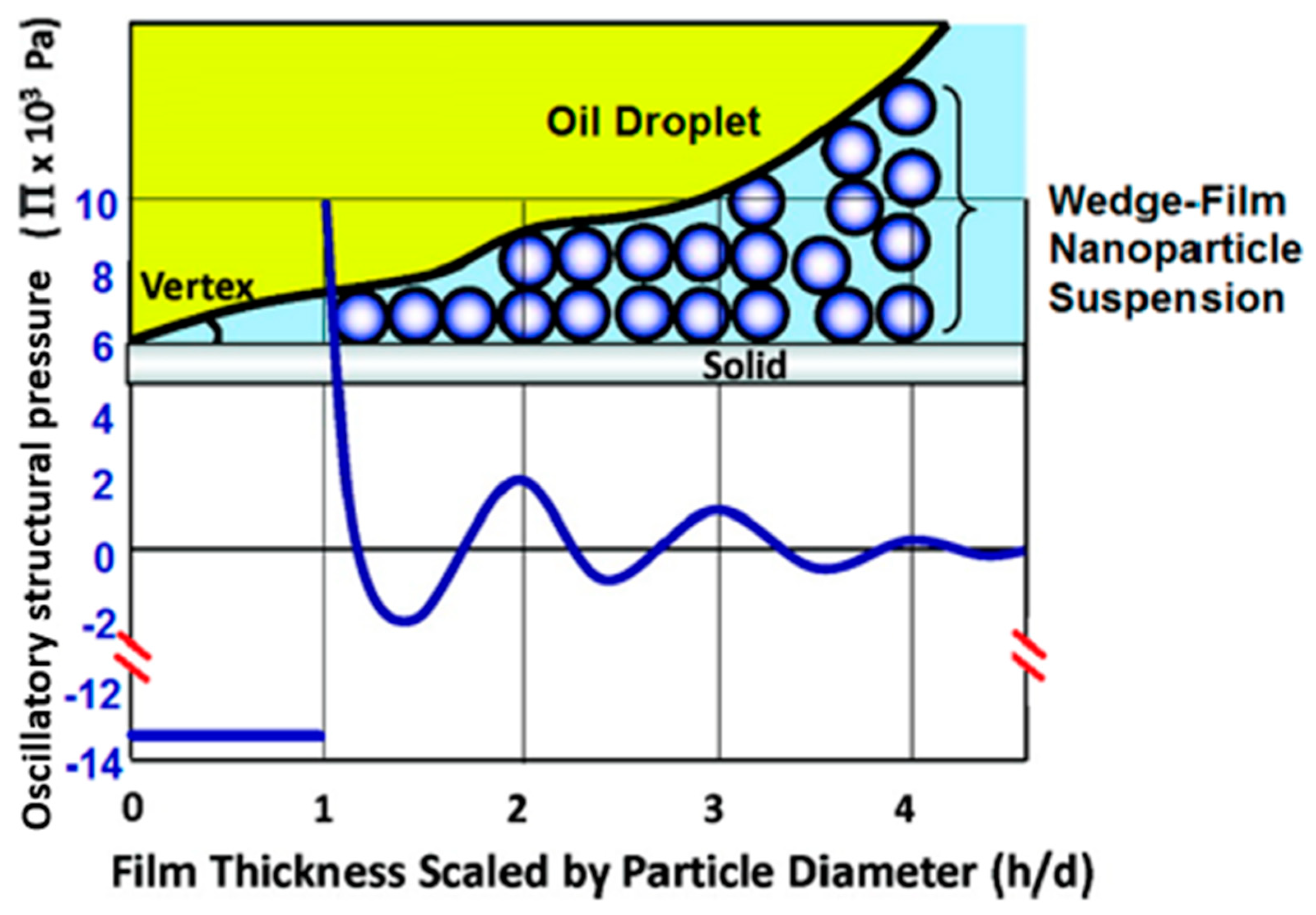
2.1. Origin of the Oscillatory Structural Pressure
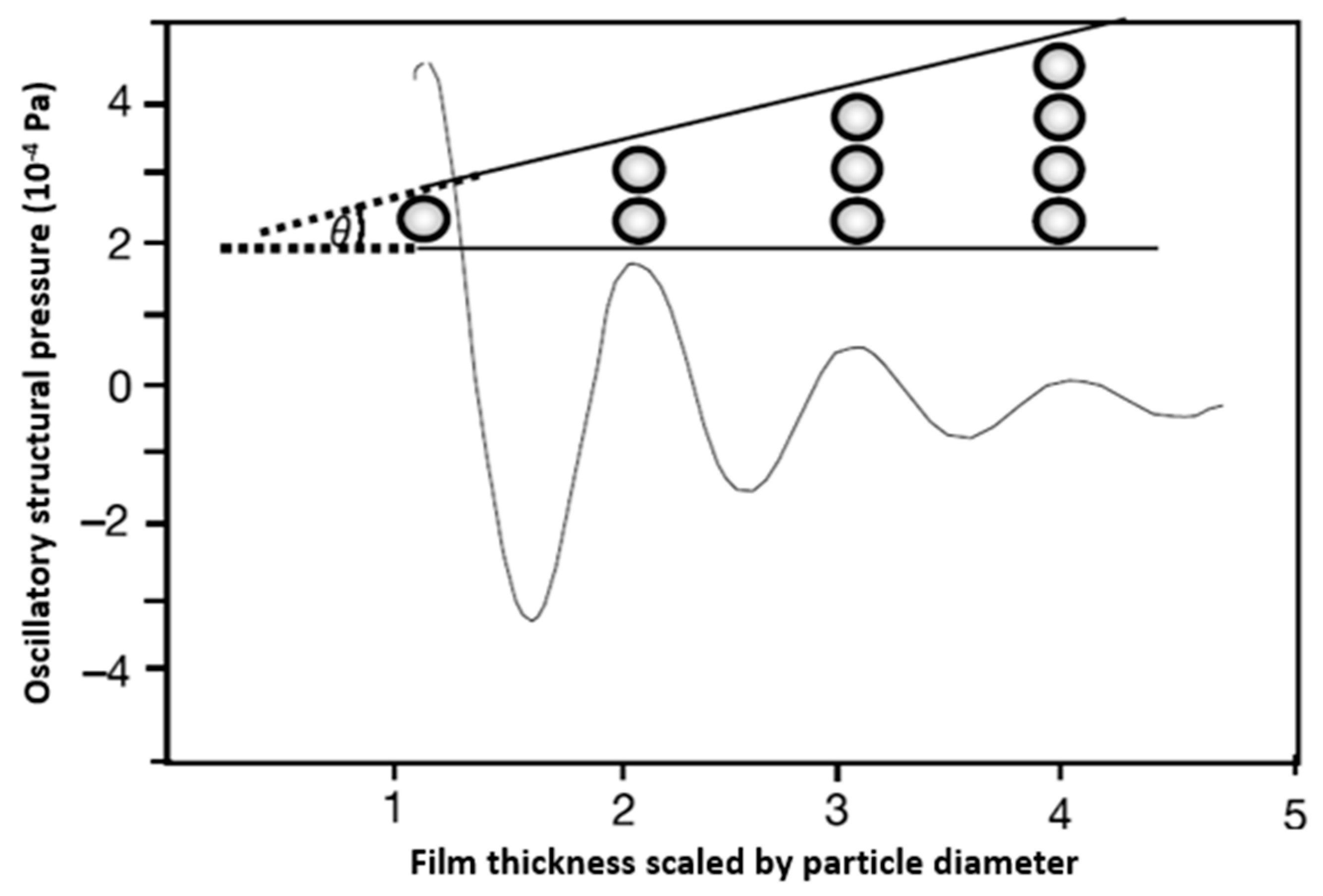
2.2. Theoretical Calculation of the Oscillatory Structural Pressure
2.2.1. Analytical Expressions Derived from the Radial Distribution Function
2.2.2. Contact Angle Approach
2.2.3. Relationship between the Film Energy and the Oscillatory Structural Pressure
2.3. Factors Affecting the Oscillatory Structural Pressure
2.3.1. Effect of the Nanoparticle Volume Fraction
2.3.2. Effect of Nanoparticle Diameter and Polydispersity
2.3.3. Effect of the Interfacial Tension and Three-Phase Contact Angle
2.3.4. Effect of Film Size
3. Experiments Demonstrating the Oscillatory Structural Pressure
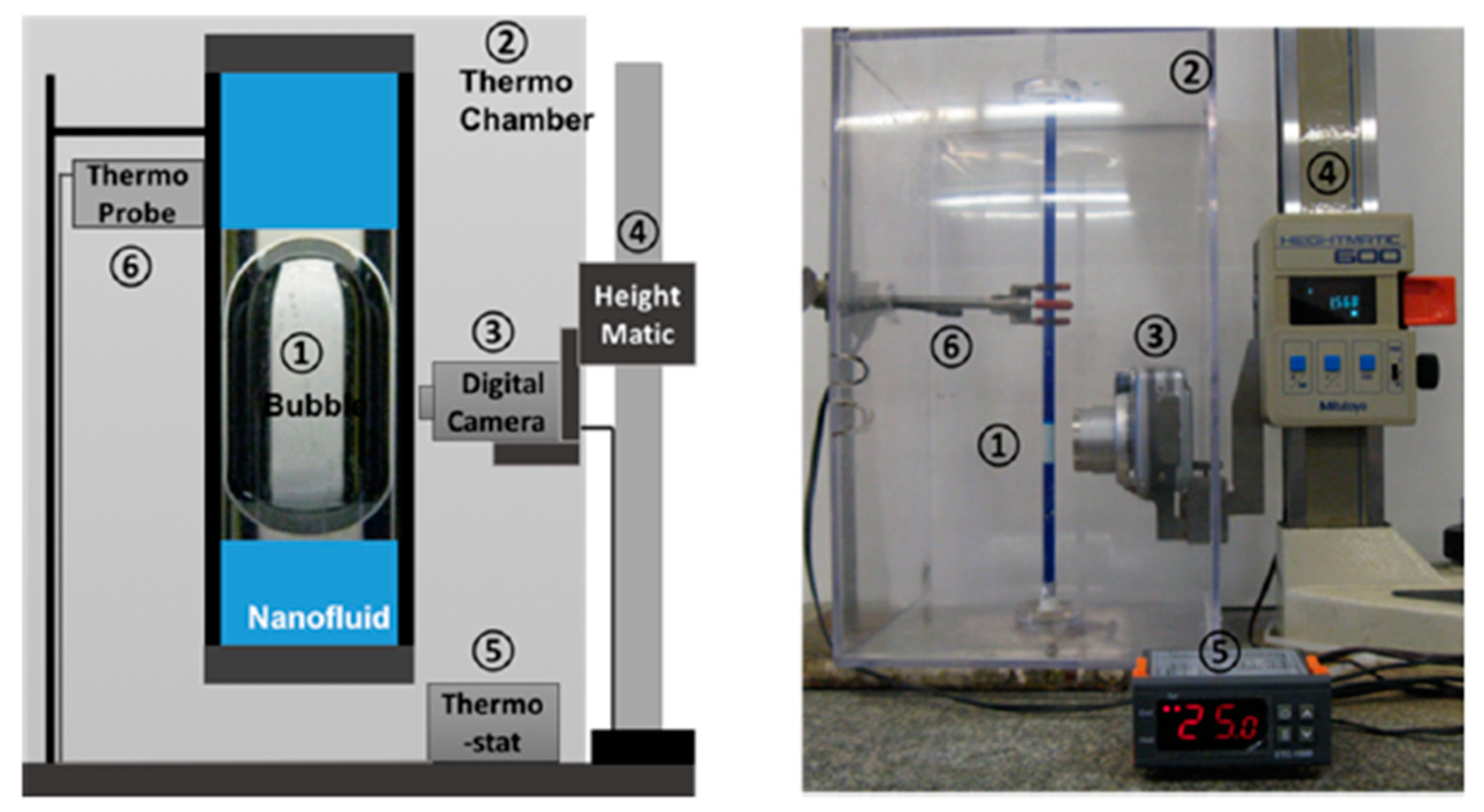
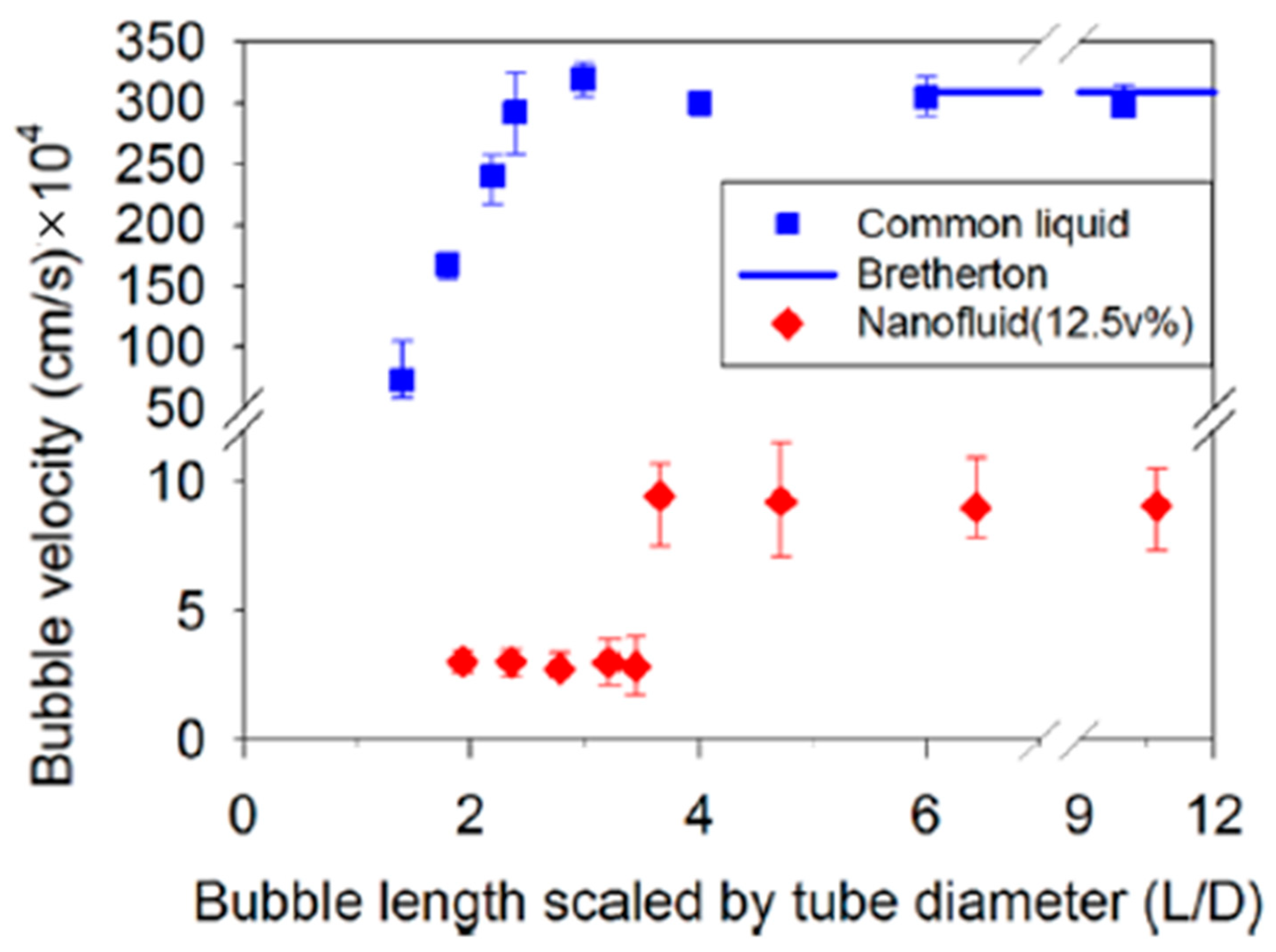
3.1. Moving Bubble Inside a Vertical Circular Tube
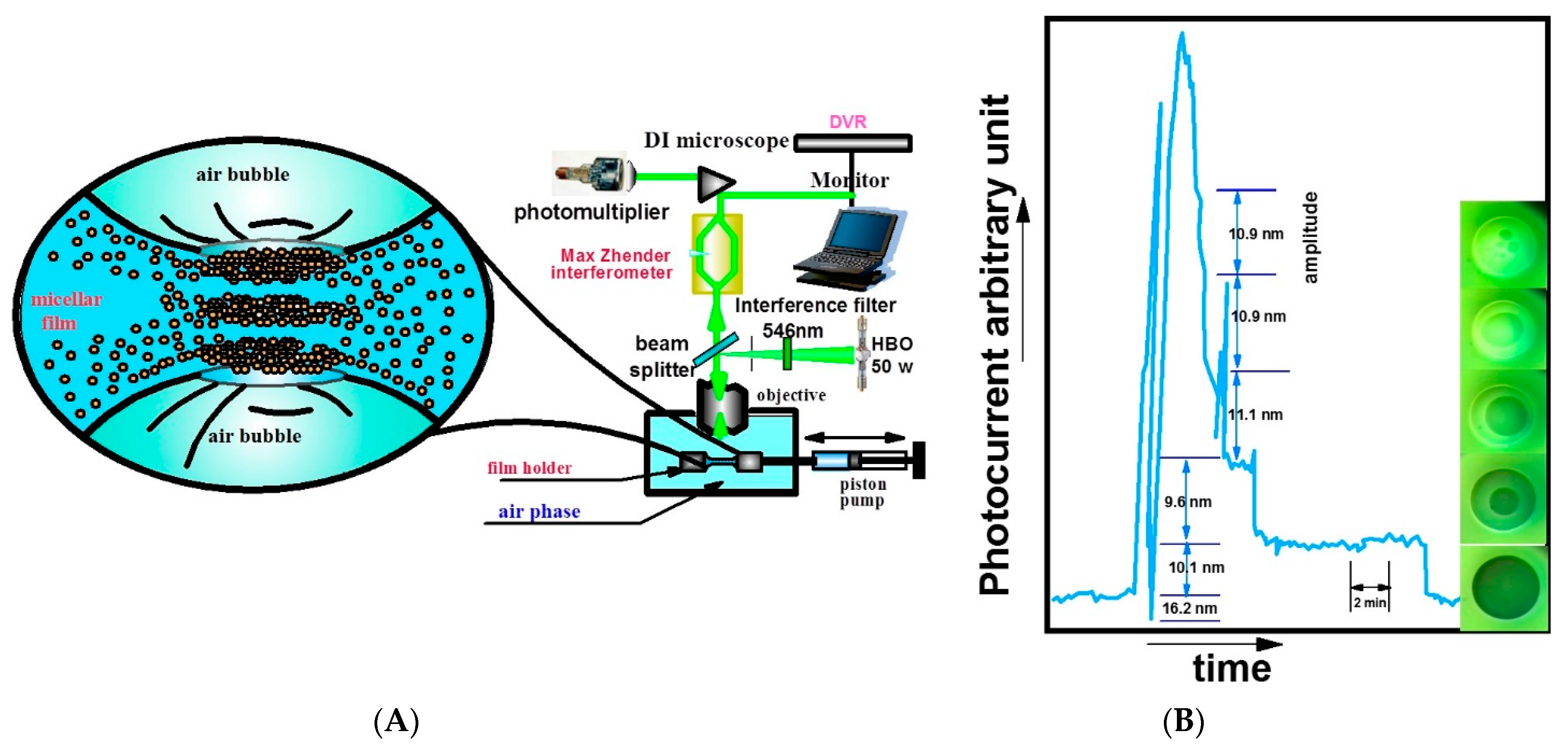
3.2. Stepwise Film Thinning under Reflected-Light Interferometry
3.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) for the Measurement of the Oscillatory Structural Force
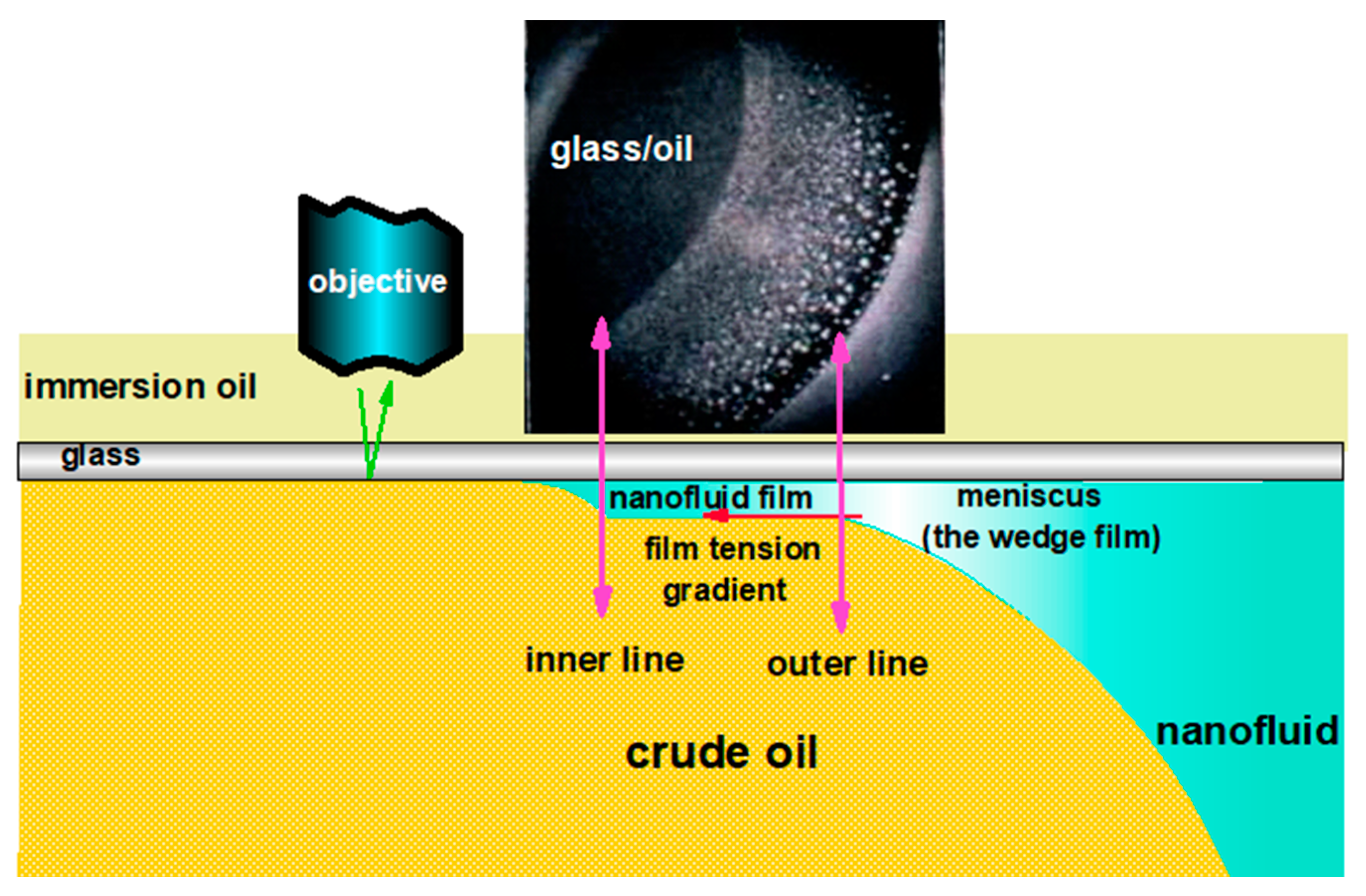
3.4. Nanofluid Displacing an Oil Droplet on a Solid Surface under Reflected-Light Interferometry
4. Experiments Visualizing the Effects of a Nanofluid in Enhanced Oil Recovery
4.1. Oil Displacement in a 2D Glass Pore
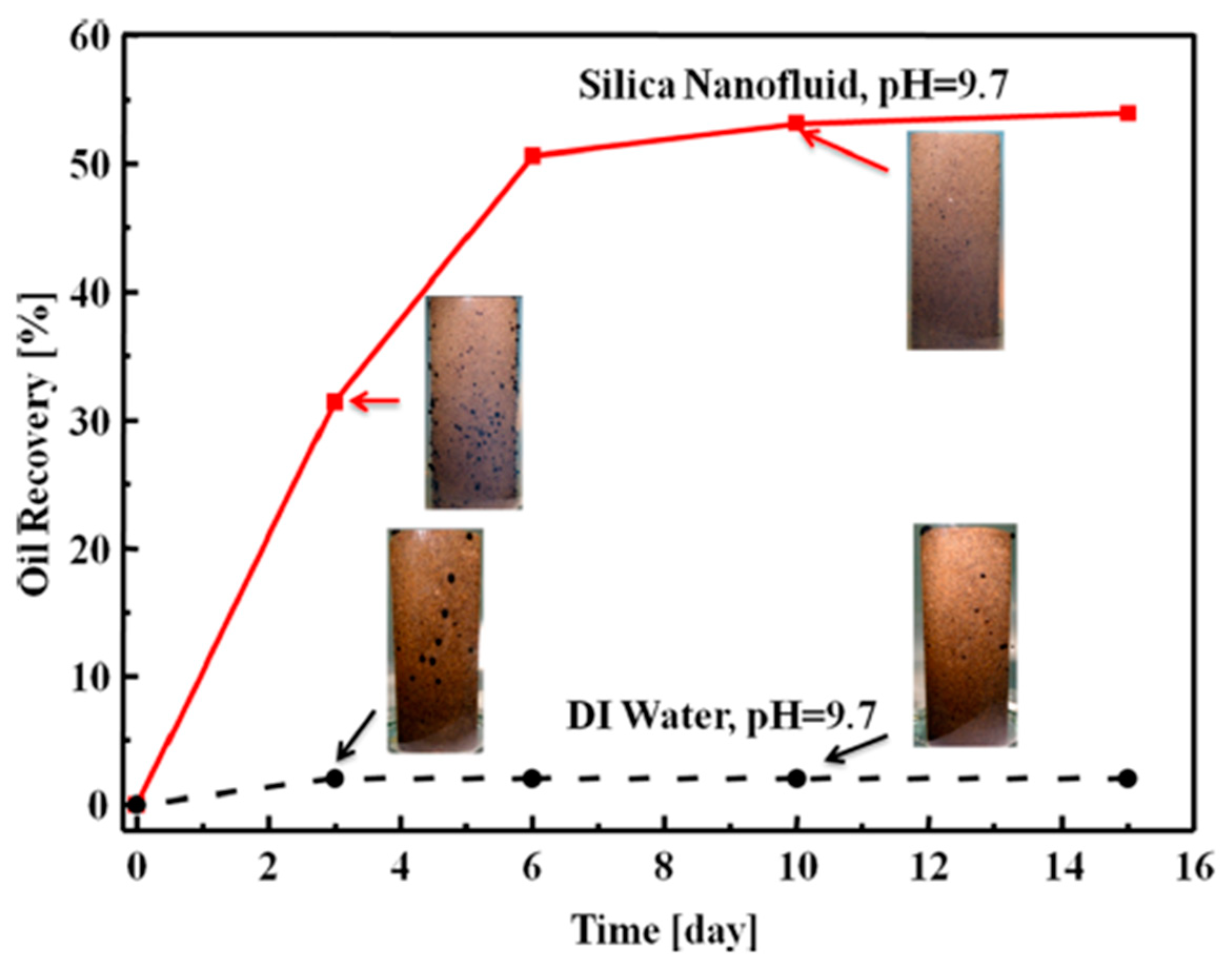
4.2. Imbibition of the Nanofluid into a Crude-Oil-Pre-Saturated Sandstone Core
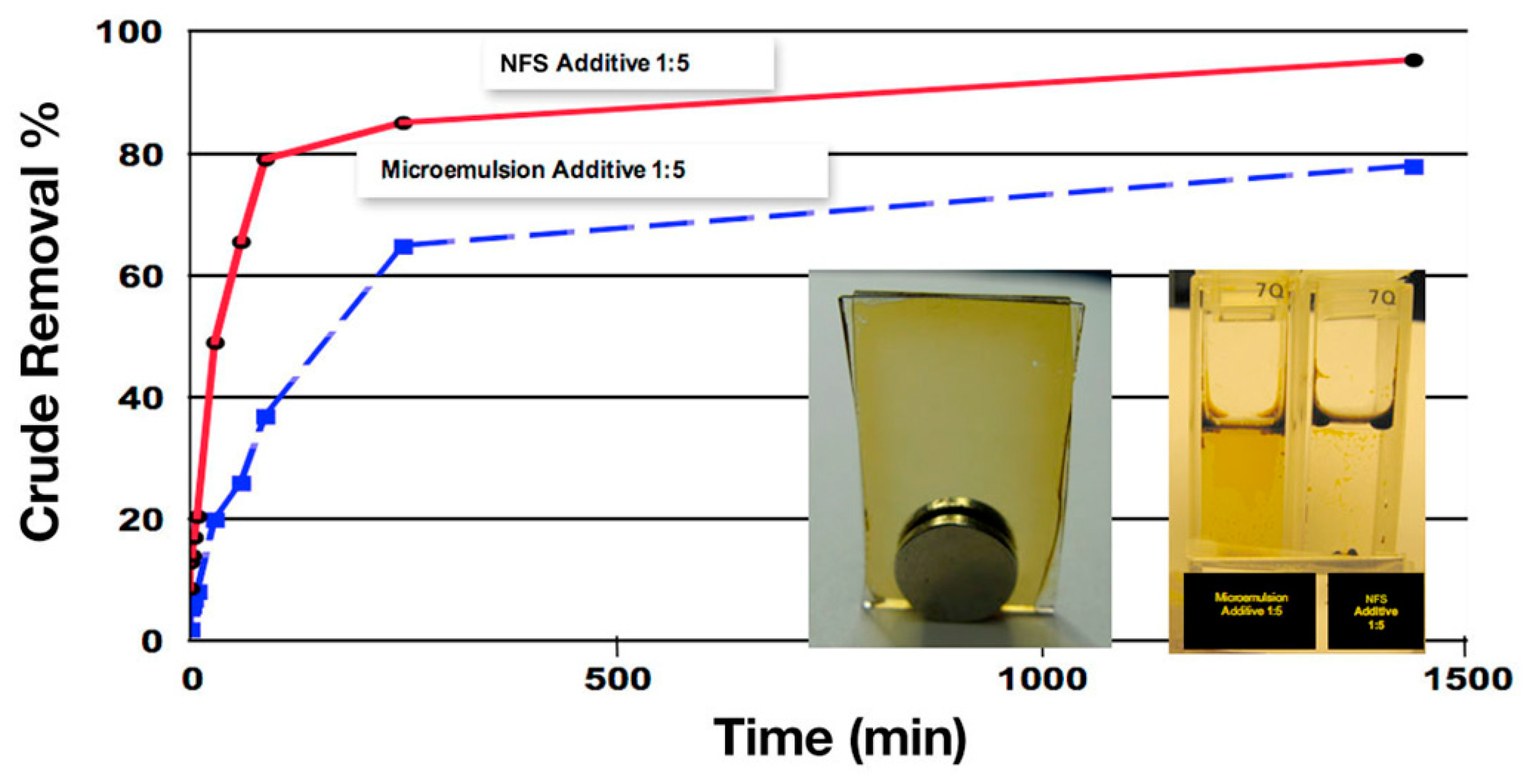
4.3. Nanofluids Displacing Oil in a Single Capillary
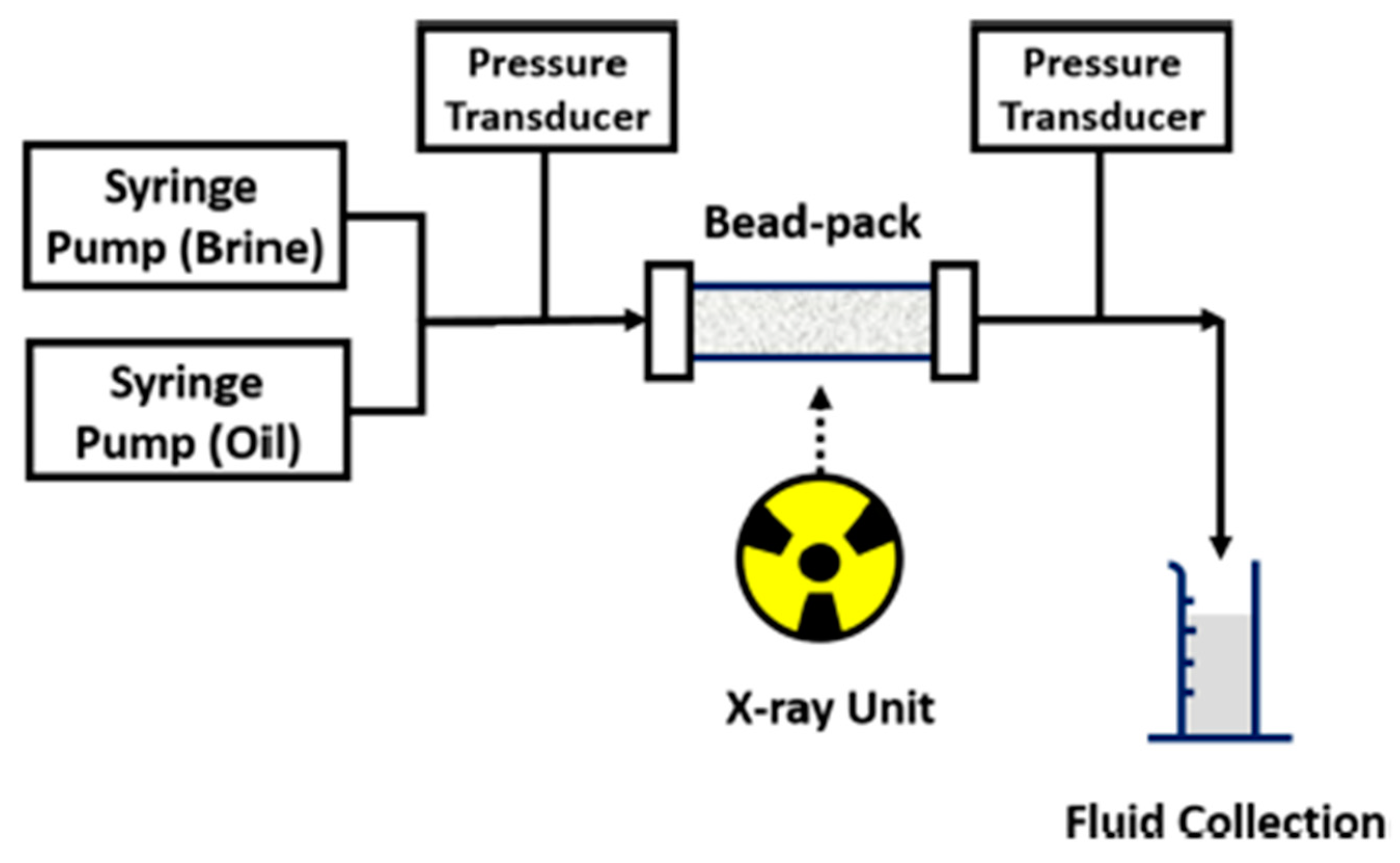
4.4. Microvisualization of Nanofluid Flooding Displacing Oil from a Bead Pack Using X-ray Microtomography
5. Conclusions
- Nanoparticle self-layering under confinement and the performance of oscillatory structural forces depend on the nanoparticle volume fraction, diameter, polydispersity, interfacial tension, contact angle, and film size. The higher the nanoparticle volume fraction, the smaller the nanoparticles’ size, polydispersity, interfacial tension, and contact angle, and the greater the oscillatory structural force.
- Bubbles rising in a nanofluid in a tube reveal the nanoparticle layering and structuring in the confined nanofluid film. The oscillatory structural forces increase the viscosity of the nanofluid film.
- The stepwise thinning of the nanofilm observed under reflected-light interferometry is an informative experiment evidencing the nanoparticles’ layering in the confined nanofluid film.
- The oscillatory decay nature of the oscillatory structural pressure is directly evidenced by the AFM measurement of the forces between two surfaces surrounded by a nanofluid. However, since in AFM measurements the nanofluid film is thinned under external force, this method offers limited information on the stability of the nanofluid film, mechanism, and dynamics of the nanofluid film’s stepwise thinning.
- The nanofluid displacing the oil droplet on a solid surface under reflected-light interferometry shows the enhanced nanofluid spreading and wetting on solid surfaces caused by the oscillatory structural forces.
- The imbibition tests in 2D glass pores, cores, and flooding, as well as on a nanofluid displacing oil in a single capillary, all imply the immense benefit of nanofluids in enhanced oil recovery as a result of the oscillatory structural forces.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassar, N.N.; Cortés, F.B.; Franco, C.A. Nanoparticles: An Emerging Technology for Oil Production and Processing Applications; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghian, G.; Rostami, S.; Afrand, M. Nanotechnology in enhanced oil recovery. Processes 2020, 8, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Babadagli, T. Wettability alteration: A comprehensive review of materials/methods and testing the selected ones on heavy-oil containing oil-wet systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 220, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzobaidi, S.; Wu, P.K.; Da, C.; Zhang, X.; Hackbarth, J.; Angeles, T.; Rabat-Torki, N.J.; MacAuliffe, S.; Panja, S.; Johnston, K.P. Effect of surface chemistry of silica nanoparticles on contact angle of oil on calcite surfaces in concentrated brine with divalent ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Johnson, S.J.; Liang, J.-T. Mechanistic study of wettability alteration using surfactants with applications in naturally fractured reservoirs. Langmuir 2008, 24, 14099–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan Monfared, A.; Ghazanfari, M.H.; Jamialahmadi, M.; Helalizadeh, A. Potential Application of Silica Nanoparticles for Wettability Alteration of Oil–Wet Calcite: A Mechanistic Study. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 3947–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, D.T.; Nikolov, A.D. Spreading of nanofluids on solids. Nature 2003, 423, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) using nanoparticle dispersions: Underlying mechanism and imbibition experiments. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.; Zhang, X.; Alzobaidi, S.; Hu, D.; Wu, P.; Johnston, K.P. Tuning Surface Chemistry and Ionic Strength to Control Nanoparticle Adsorption and Elastic Dilational Modulus at Air-Brine Interface. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5795–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, D.; Nikolov, A. Thin liquid films containing micelles or nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 13, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.; Daigle, H. Manipulation of Pickering emulsion rheology using hydrophilically modified silica nanoparticles in brine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzobaidi, S.; Da, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Rabat-Torki, N.J.; Harris, J.M.; Hackbarth, J.E.; Lu, C.; Hu, D.; Johnston, K.P. Tuning Nanoparticle Surface Chemistry and Interfacial Properties for Highly Stable Nitrogen-In-Brine Foams. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5408–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestro, A.; Rio, E.; Drenckhan-Andreatta, W.; Langevin, D.; Salonen, A. Foams stabilised by mixtures of nanoparticles and oppositely charged surfactants: Relationship between bubble shrinkage and foam coarsening. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6975–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Micellar films: Thinning and structure. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 4297–4312. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Monte Carlo simulation of inlayer structure formation in thin liquid films. Langmuir 1994, 10, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trokhymchuk, A.; Henderson, D.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D.T. A simple calculation of structural and depletion forces for fluids/suspensions confined in a film. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4940–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D. An explicit expression for the solvent contribution to the force between colloidal particles using a hard sphere model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 121, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, P.; Bérard, D.R.; Ursenbach, C.P.; Patey, G.N. Interaction free energy between planar walls in dense fluids: An Ornstein-Zernike approach with results for hard-sphere, Lennard-Jones, and dipolar systems. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.-P.; McDonald, I.R. Theory of Simple Liquids: With Applications to Soft Matter; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan, N.F.; Starling, K.E. Equation of state for nonattracting rigid spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, D.; Razouk, R. Adsorption and the wettability of solid surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1937, 33, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A. On the wetting phenomena and attachment of bubbles. Zhur. Fiz. Khim. (J. Phys. Chem.) 1938, 12, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Derjaguin, B. Theory of capillary condensation and related capillary effects. Calculation of spreading action of polymolecular liquid films. Zh. Fiz. Khim 1940, 14, 137. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.-G. Wetting: Statics and dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churaev, N.V.; Sobolev, V.D. Prediction of Contact Angles on the Basis of the Frumkin-Derjaguin Approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Wu, P.; Wasan, D. Structure and stability of nanofluid films wetting solids: An overview. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 264, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, D.; Lozada-Cassou, M. A simple theory for the force between spheres immersed in a fluid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 114, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Wu, P.; Wasan, D. Novel approach for calculating the equilibrium foam nanofilm-meniscus contact angle and the film free energy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Kondiparty, K.; Wasan, D. Nanoparticle self-structuring in a nanofluid film spreading on a solid surface. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7665–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. The foam film’s stepwise thinning phenomenon and role of oscillatory forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 303, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Effects of film size and micellar polydispersity on film stratification. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 128, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralchevski, P.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D.T.; Ivanov, I. Formation and expansion of dark spots in stratifying foam films. Langmuir 1990, 6, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Step-Wise Velocity of an Air Bubble Rising in a Vertical Tube Filled with a Liquid Dispersion of Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2920–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Prediction of the rate of the rise of an air bubble in nanofluids in a vertical tube. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 525, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Stepwise thinning dynamics of a foam film formed from an anionic micellar solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 487, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Effects of surfactant on multiple stepwise coalescence of single drops at liquid-liquid interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheva, E.S.; Nikolov, A.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ivanov, I.B.; Wasan, D.T. Multi-stepwise drainage and viscosity of macroscopic films formed from latex suspensions. In Surfactants in Solution; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, C.; Gao, S.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, V. Foam film stratification studies probe intermicellar interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024805118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilixiati, S.; Rafiq, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sharma, V. Influence of salt on supramolecular oscillatory structural forces and stratification in micellar freestanding films. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sharma, V. Nanoridge formation and dynamics of stratification in micellar freestanding films. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Ordered micelle structuring in thin films formed from anionic surfactant solutions: I. Experimental. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, A.S.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Contact angles of thin liquid films: Interferometric determination. Colloids Surf. 1990, 47, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, L.A.; Nikolov, A.; Dimitrov, A.; Kralchevski, P.; Wasan, D.T. Contact angle of air bubbles attached to an air-water surface in foam applications. Langmuir 1990, 6, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetti, P.; Kekicheff, P. Direct measurement of depletion and structural forces in a micellar system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, M.; von Klitzing, R. Recent progress in measurements of oscillatory forces and liquid properties under confinement. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 47, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, S.; von Klitzing, R. Experimental evaluation of additional short ranged repulsion in structural oscillation forces. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Schön, S.; von Klitzing, R. Silica nanoparticle suspensions under confinement of thin liquid films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 449, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christov, N.C.; Danov, K.D.; Zeng, Y.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; von Klitzing, R. Oscillatory Structural Forces Due to Nonionic Surfactant Micelles: Data by Colloidal—Probe AFM vs. Theory. Langmuir 2010, 26, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondiparty, K.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.; Liu, K.-L. Dynamic spreading of nanofluids on solids. Part I: Experimental. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14618–14623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. The dynamic spreading of nanofluids on solid surfaces—Role of the nanofilm structural disjoining pressure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Liu, S.; Puerto, M.; Miller, C.A.; Hirasaki, G.J. Wettability alteration and spontaneous imbibition in oil-wet carbonate formations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 52, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Two-phase Displacement Dynamics in Capillaries-Nanofluid Reduces the Frictional Coefficient. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Capillary dynamics driven by molecular self-layering. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 243, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Capillary Rise: Validity of the Dynamic Contact Angle Models. Langmuir 2017, 33, 7862–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiasa, M.; Ralston, J.; Fetzer, R.; Sedev, R. Contact Line Friction in Liquid–Liquid Displacement on Hydrophobic Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 24975–24986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ramakrishnan, T.S.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Enhanced Oil Recovery Driven by Nanofilm Structural Disjoining Pressure: Flooding Experiments and Microvisualization. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ramakrishnan, T.S.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D. Enhanced oil displacement by nanofluid’s structural disjoining pressure in model fractured porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, N.K.; Lebedev, M.; Iglauer, S.; Ali, M.; Roshan, H.; Barifcani, A.; Sangwai, J.S.; Sarmadi-valeh, M. Pore scale investigation of low salinity surfactant nanofluid injection into oil saturated sandstone via X-ray micro-tomography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 562, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Zhao, M. Investigation of spontaneous imbibition by using a surfactant-free active silica water-based nanofluid for enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssif, M.I.; El-Maghraby, R.M.; Saleh, S.M.; Elgibaly, A. Silica nanofluid flooding for enhanced oil recovery in sandstone rocks. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Khodabakhshi, A.; Esmaeili, A.; Razavifar, M. Effects of initial wettability and different surfactant-silica nanoparticles flooding scenarios on oil-recovery from carbonate rocks. Petroleum, 2021, in press.








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Nanofluid Structural Forces Alter Solid Wetting, Enhancing Oil Recovery. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020033
Wu P, Nikolov AD, Wasan DT. Nanofluid Structural Forces Alter Solid Wetting, Enhancing Oil Recovery. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Pingkeng, Alex D. Nikolov, and Darsh T. Wasan. 2022. "Nanofluid Structural Forces Alter Solid Wetting, Enhancing Oil Recovery" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020033
APA StyleWu, P., Nikolov, A. D., & Wasan, D. T. (2022). Nanofluid Structural Forces Alter Solid Wetting, Enhancing Oil Recovery. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020033




