A Sebum-Mimetic Lipid Monolayer and Its Interaction with (Bio)Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
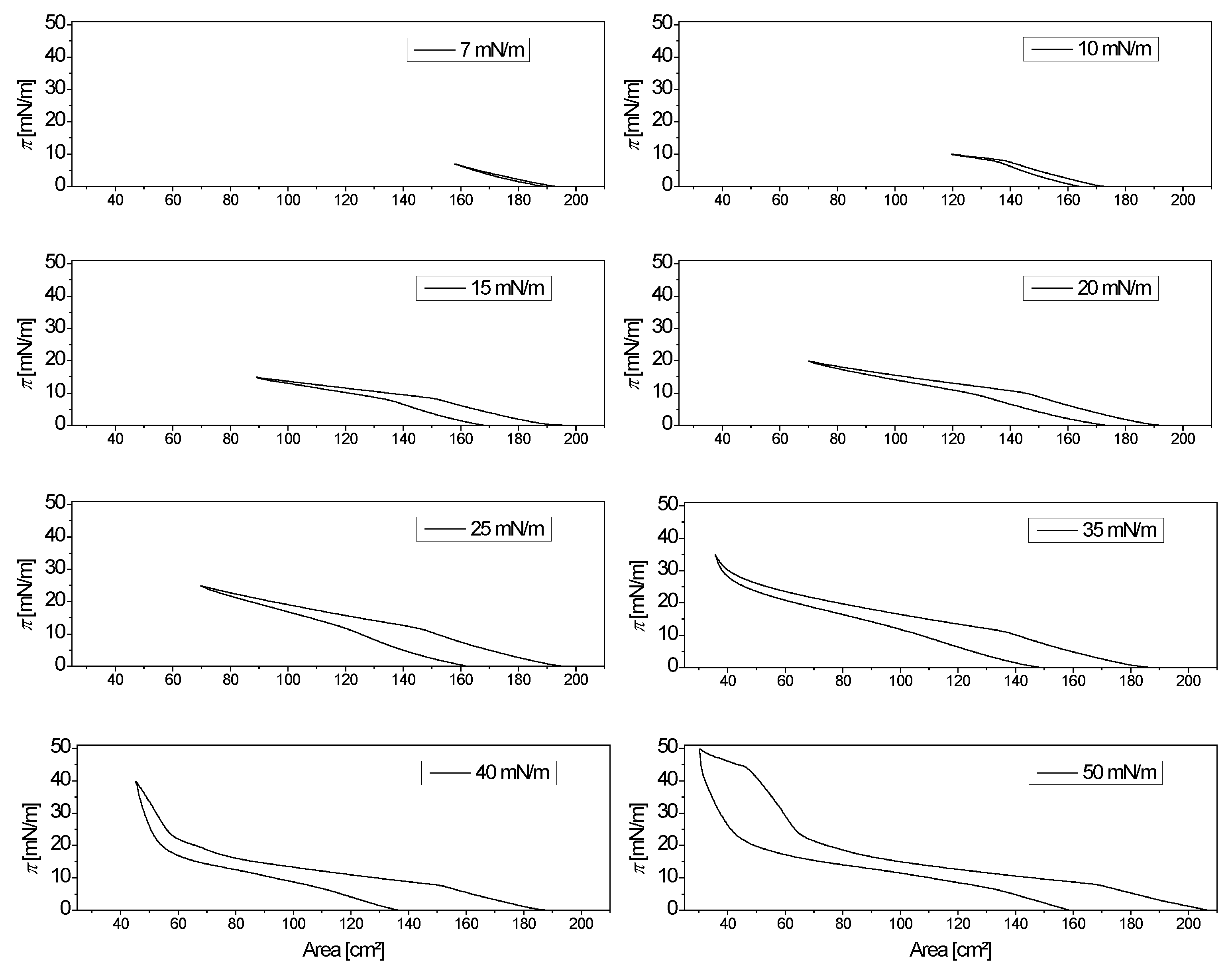
2.1. Synthetic Sebum Monolayer Characterization
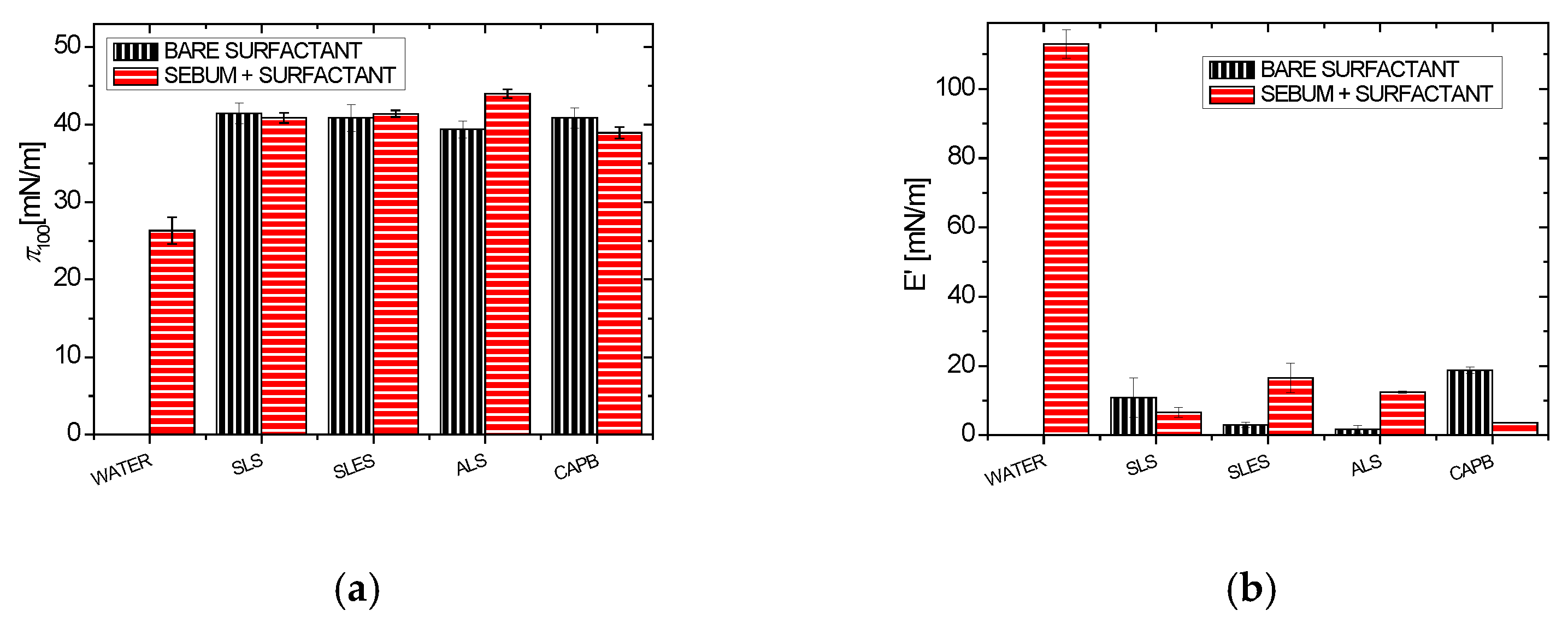
2.2. Effect of Surfactants on the Synthetic Sebum Monolayers
2.2.1. Synthetic Surfactants
2.2.2. Plant Extracts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Antunes, E.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Stratum corneum lipid matrix with unusual packing: A molecular dynamics study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, G.; Rapaka, S.; Koski, N.; Kearney, M.; Ortblad, K.; Tadlock, L. A robust sebum, oil, and particulate pollution model for assessing cleansing efficacy of human skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seweryn, A. Interactions between surfactants and the skin—Theory and practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenna, R.M.B.; Wheatley, V.R.; Wormall, A. The Composition of the Surface Skin Fat (‘Sebum’) from the Human Forearm. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1949, 15, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Moore, D.J.; Subramanyan, K.; Misra, M.; Meyer, F. Cleansing without compromise: The impact of cleansers on the skin barrier and the technology of mild cleansing. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D. The science behind skin care: Cleansers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, A.; Endo, K.; Ozawa, T.; Miyaki, M.; Matsuo, K.; Nozawa, K.; Manabe, M.; Takagi, Y. A cleanser based on sodium laureth carboxylate and alkyl carboxylates washes facial sebum well but does not induce dry skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2014, 13, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, V.S.; Sanadhya, N.; Sharma, P.; Parmar, A.; Datta, M. Biosurfactant characterization and its potential to remove sebum from hair. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Fontán, M.; Rodríguez-López, L.; Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Novel Multifunctional Biosurfactant Obtained from Corn as a Stabilizing Agent for Antidandruff Formulations Based on Zn Pyrithione Powder. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5704–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, K.G.O.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Saponins and microbial biosurfactants: Potential raw materials for the formulation of cosmetics. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B.; Rodrigues, L.R. Biosurfactants in cosmetic formulations: Trends and challenges. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varvaresou, A.; Iakovou, K. Biosurfactants in cosmetics and biopharmaceuticals. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, J.-P.; Heng, L.; de Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroos, K.; Vincken, J.-P.; van Koningsveld, G.A.; Gruppen, H.; Verstraete, W. Preparative chromatographic purification and surfactant properties of individual soyasaponins from soy hypocotyls. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü-Üstündağ, Ö.; Mazza, G. Saponins: Properties, Applications and Processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, A.B.; Harvey, C.J. Dissolution of materials in artificial skin surface film liquids. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 1265–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W.; Wertz, P.W. Human synthetic sebum formulation and stability under conditions of use and storage. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, C.A.M.; Zagury, G.J. Comparison of synthetic sweat and influence of sebum in the permeation of bioaccessible metal(loid)s from contaminated soils through a synthetic skin membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8215–8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lie, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, I.I. Development of aperture total internal reflection (A-TIR) for micro droplets and fingerprint patterns characterization. Opt. Commun. 2019, 453, 124414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, P.R.; Ran, L. The effect of calcium on the foam behaviour of aqueous sodium alkyl benzene sulphonate solutions. 2. In the Presence of triglyceride-based antifoam mixtures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 513, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrzębska, A.; Musiał, W. The Influence of Increasing Concentrations of AMPD on the Efficacy of Its Penetration into a Model Skin Sebum Layer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujak, T.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Ziemlewska, A. Amphiphilic cationic polymers as effective substances improving the safety of use of body wash gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujak, T.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Majtan, J.; Bucekova, M.; Jesenak, M. Complexes of ectoine with the anionic surfactants as active ingredients of cleansing cosmetics with reduced irritating potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, I.; Szuplewska, A.; Chudy, M.; Wojciechowski, K. Effect of the oat, horse chestnut, cowherb, soy, quinoa and soapwort extracts on skin-mimicking monolayers and cell lines. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, I.; Szuplewska, A.; Chudy, M.; Wojciechowski, K. Soapwort (Saponaria officinalis l.) extract vs. synthetic surfactants—Effect on skin-mimetic models. Molecules 2021, 26, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broniatowski, M.; Macho, I.S.; Miñones, J.; Dynarowicz-Łatka, P. Langmuir monolayers characteristic of (Perfluorodecyl)-alkanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13403–13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luviano, A.S.; Campos-Terán, J.; Langevin, D.; Castillo, R.; Espinosa, G. Mechanical Properties of DPPC-POPE Mixed Langmuir Monolayers. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16734–16744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, O.N.; Caseli, L.; Ariga, K. The Past and the Future of Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett Films. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6459–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, G.S.; Fameau, A.L.; Léonforte, F.; Greaves, A.J. Surface science of cosmetic substrates, cleansing actives and formulations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 290, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, V.C.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; Andersen, F.A. Final report of the amended safety assessment of sodium laureth sulfate and related salts of sulfated ethoxylated alcohols. Int. J. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 151S–161S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.; Orczyk, M.; Gutberlet, T.; Trapp, M.; Marcinkowski, K.; Kobiela, T.; Geue, T. Unusual penetration of phospholipid mono- and bilayers by Quillaja bark saponin biosurfactant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jurek, I.; Góral, I.; Mierzyńska, Z.; Moniuszko-Szajwaj, B.; Wojciechowski, K. Effect of synthetic surfactants and soapwort (Saponaria officinalis L.) extract on skin-mimetic model lipid monolayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.T.; Alexander, A.E. The application of monolayer techniques to a study of protein-surfactant interaction. I. Interactions in spread films at the air/water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 27, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezron, I.; Galet, L.; Clausse, D. Surface interaction between a protein monolayer and surfactants and its correlation with skin irritation by surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 180, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, N.C.; Gunning, A.P.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Wilde, P.J.; Morris, V.J. Probing the in situ competitive displacement of protein by nonionic surfactant using atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12560–12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, P.A. A review of shampoo surfactant technology: Consumer benefits, raw materials and recent developments. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, S.; Mishra, A.; Khushtar, M. Phytochemical, ethanomedicinal and pharmacological applications of escin from Aesculus hippocastanum L. Towards future medicine. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L. Escin: A review of its anti-edematous, antiinflammatory, and venotonic properties. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, R.; Dargel, C.; Hellweg, T. The biosurfactant β-aescin: A review on the physico-chemical properties and its interaction with lipid model membranes and langmuir monolayers. Molecules 2020, 25, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, R.; Pedersen, M.C.; Hannappel, Y.; Schweins, R.; Prévost, S.; Dattani, R.; Arleth, L.; Hellweg, T. Aescin-Induced Conversion of Gel-Phase Lipid Membranes into Bicelle-like Lipid Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16244–16255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargel, C.; Geisler, R.; Hannappel, Y.; Kemker, I.; Sewald, N.; Hellweg, T. Self-Assembly of the Bio-Surfactant Aescin in Solution: A Small-Angle X-ray Scattering and Fluorescence Study. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, I.; Góral, I.; Gęsiński, K.; Wojciechowski, K. Effect of saponins from quinoa on a skin-mimetic lipid monolayer containing cholesterol. Steroids 2019, 147, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, K.; Jurek, I.; Góral, I.; Campana, M.; Geue, T.; Gutberlet, T. Surface-active extracts from plants rich in saponins—Effect on lipid mono- and bilayers. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orczyk, M.; Wojciechowski, K.; Brezesinski, G. Disordering Effects of Digitonin on Phospholipid Monolayers. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3871–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Human Sebum | Content (% m/m) | Synthetic Sebum |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid triglycerides | 35 | Lard |
| Free fatty acids | 25 | Stearic acid |
| Waxes | 23 | Lanolin |
| Squalene | 13 | Squalane |
| Cholesterol | 4 | Cholesterol |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurek, I.; Wojciechowski, K. A Sebum-Mimetic Lipid Monolayer and Its Interaction with (Bio)Surfactants. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020037
Jurek I, Wojciechowski K. A Sebum-Mimetic Lipid Monolayer and Its Interaction with (Bio)Surfactants. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurek, Ilona, and Kamil Wojciechowski. 2022. "A Sebum-Mimetic Lipid Monolayer and Its Interaction with (Bio)Surfactants" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020037
APA StyleJurek, I., & Wojciechowski, K. (2022). A Sebum-Mimetic Lipid Monolayer and Its Interaction with (Bio)Surfactants. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020037