Abstract
In recent years, the removal of dyes has emerged as a significant problem that attracted several researchers. The search for green and eco-friendly adsorbents has been a never-ending task in environmental protection to overcome this issue. Herein, almond shells (AS) were used as an adsorbent to remove methyl orange (MO) from aqueous solutions. The AS was characterized using several techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Adsorption experiments were carried out under different pH, temperature, and AS particle size conditions. Kinetic and isothermal studies revealed that MO adsorption on the AS reached equilibrium at 90 min, following the pseudo-second-order (PSO) kinetic model. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm was found the suitable adsorption model for MO adsorption on AS, showing a maximum adsorption capacity of 15.63 mg/g. Thermodynamic parameters such as the change in standard enthalpy (ΔH°), the change in standard entropy (ΔS°), and the change in standard free energy (ΔG°) indicated that the MO dye adsorption process is non-spontaneous, endothermic, and physical, which was further confirmed from FTIR analysis of AS samples after adsorption. The contaminated sludge was converted into biochar by slow pyrolysis at a temperature of 400 °C for 2 h. Biochar has been exploited for the manufacture of combustible briquettes.
1. Introduction
Organic and mineral pollutants such as aromatic compounds, concentrated detergents, dyes, metals, etc., are the primary discharged wastes into the environment by several industries [1,2,3]. The treatment of water contaminated by organic pollutants such as dyes generally necessitates costly techniques. Azo dyes are an important class of pollutants discharged from various industries such as textile, paper, leather, and plastic without treatment each year [4]. The discharge of wastewater containing azo dyes is harmful to the ecosystem and can cause poisoning, cancer, and deformity [5]. Methyl orange (MO) is a typical anionic dye for industrial products and laboratory research [5]. Therefore, the successful removal of MO from wastewater would be of significant importance in treating anionic-containing wastewater.
To meet both low cost and effectiveness, adsorption is one of the most chosen techniques to treat polluted water [6,7,8]. It is an easy execution and low-cost technique that can successfully be applied to eliminate dyes, especially if the selected adsorbent is made from a natural resource. According to previous research, several types of natural materials have been tested for the adsorption removal of different pollutants [9,10,11,12]. To only cite few, date pits activated carbon [13], bagasse, oil palm shell and pericarp of rubber fruit [14], Pinus pinaster bark [15], pistachio shells [16], activated sludge biomass [17], biopolymers (chitosan, cellulose and chitin) [18,19,20], polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) [21], acrylic ester [22], bentonite [23], clinoptilolite [24], silica/hydrotalcite [25], biochar [26], waste acorns [27], hematite and alumina [28], solid waste from the leather industry [29], biomass of fungi [30], montmorillonite [31], and poly(4-vinylpyridines) [32], etc.
Almond shells are agricultural residues produced abundantly in a Mediterranean climate, including Morocco, where tons of almond shells are incinerated or dumped. It is reported that almond shells account for more than 35% of the total fruit weight [33]. Therefore, millions of tons of shells are discharged globally every year [33]. This large quantity of almond shells requires extra attention for its valorization and implementation into the economic cycle. Almond shells composition includes a higher amount of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, making it an excellent option for adsorbing different kinds of chemical pollutants [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43].
Encouraged by the above successful applications, the present study reports the application of almond shells for adsorption removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions. The pH, adsorbent mass, the MO initial concentration, adsorbent particle size, and the temperature, along with pHPZC were all taken into consideration. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies were carried out to investigate the adsorption mechanism of MO on almond shells, which is further analyzed by FTIR analysis of AS after adsorption. Moreover, to prevent another type of pollution, the sludge generated from the treatment processes was dried and pyrolyzed to prepare combustible briquettes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The almond represents the second fruit species cultivated in Morocco after the olive tree. Meknes and Fez regions are distinguished by high productivity at the national level, with nearly 30% of national production in 2012. This important production of almonds generates a high quantity of wastes that are discharged without recycling. Herein, the studied biomass samples were collected from different regions of Meknes. The selected pollutant model is methyl orange, a water-soluble anionic azo dye used as a colored indicator in acid-base titrations.
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
For adsorption experiments, MO solutions introduced into Erlenmeyer flasks with constant amounts of the adsorbent were stirred at different periods of time. The temperature and pH were maintained at 25 °C and pH = 6, respectively. After a determined contact time, samples were filtered, and the final MO concentrations were measured via a UV spectrophotometer (U–2800, Hitachi, Japan) at the maximum absorption peak of MO (λmax = 464 nm). The following experimental conditions were maintained: A mass m = 100 mg of material and 25 mL of a solution of MO with concentration C = 10−4 mol/L. The effect of initial MO concentration was investigated for the isothermal study.
The removal rate R (%) and equilibrium adsorption capacity Qe (mg/g) were calculated using the following Equations (1) and (2), respectively:
where C0 is the initial MO concentration (in mg/L), and Ce is the MO concentration at equilibrium (in mg/L).
Kinetic and isotherm models analyzed in the present study are listed in Table 1, along with their equations and fitting parameters.

Table 1.
Equation of adsorption kinetic, isotherm models, and fitting parameters.
2.3. Biochar Production from Pyrolysis of Biomass
For slow pyrolysis of biomass samples, experiments were carried out under an inert atmosphere (N2) at a heating rate of 20 °C/min ranging from 40 to 900 °C.
2.4. Densification of Biomass into Briquettes
Briquettes were fabricated from the biochar obtained by the pyrolysis of almond shells using molasses as a binder (30%). Compaction forces are 4T. The compaction of the mixture (the biochar + the binder) was carried out using the STENHOJ hydraulic press and cylindrical steel die with a well-defined operating model.
2.5. Characterization Methods
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is based on the analyzed material’s absorption of infrared radiation (400–4000 cm−1). Via the detection of characteristic vibrations, it allows chemical functional groups to be identified. The FTIR spectra were collected using a Shimadzu spectrometer (JASCO 4100, Kyoto, Japan). The structural analysis by X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried out on a diffractometer type X-RD-6100-Shimadzu (λCu = 1.54 Å). The diffraction spectrum was produced for 2Ө value between 2° and 80°, at a scanning speed of 1°/min. The morphology of the biomass samples was studied using the Hitachi S-3400N scanning electron microscope (Tokyo, Japan), equipped with an energy dispersion spectroscopy (SEM–EDS) probe.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AS
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
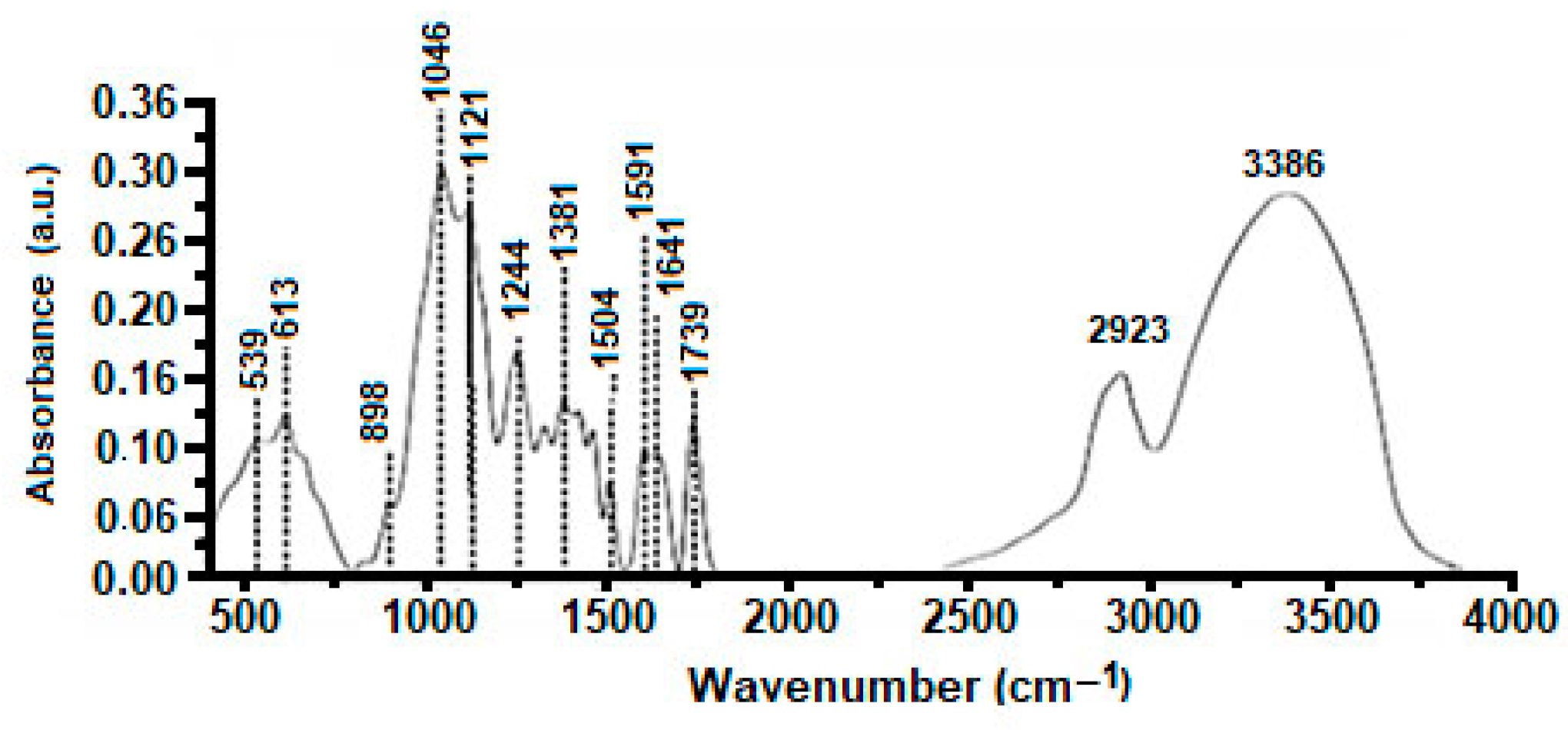
FTIR spectra of AS are represented in Figure 1. It shows two C-Cl elongations of alkyl chlorides and acids at 539 and 613 cm−1, respectively. The band located at 898 cm−1 corresponds to the deformation of the >N-H function of amines I and II. Intense CO-stretching for secondary alcohols >CH-OH at 1121–1244 cm−1 is due to CO stretching (1046 cm−1), and then the bond strain of OH phenols at 1381 cm−1. The tertiobutyl (–C(CH3)3) group appears at 1381 cm−1, while the deformation bond of -CH2 is located at 1430–1455 cm−1. A band at 1504 cm−1 indicates an elongation of the >C=C< aromatic group. In addition, a very intense elongation of the carboxylic acids occurs at 1739 cm−1, while the aromatic derivatives are shown between 2024 and 2371 cm−1. Asymmetric stretching of aliphatic CHs is apparent at 2923 cm−1, followed by OH phenols stretching with a broad and intense band due to hydrogen bonding at 3386 cm−1 (shell and water structure). These bands correspond to the main compositions of almond shells, which are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin [44].
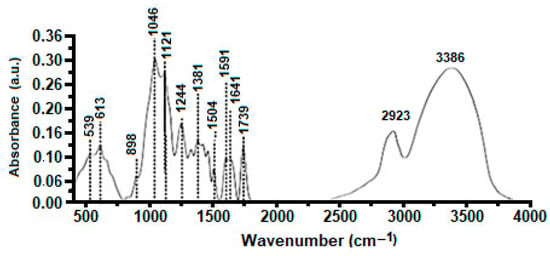
Figure 1.
FTIR analysis of AS.
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
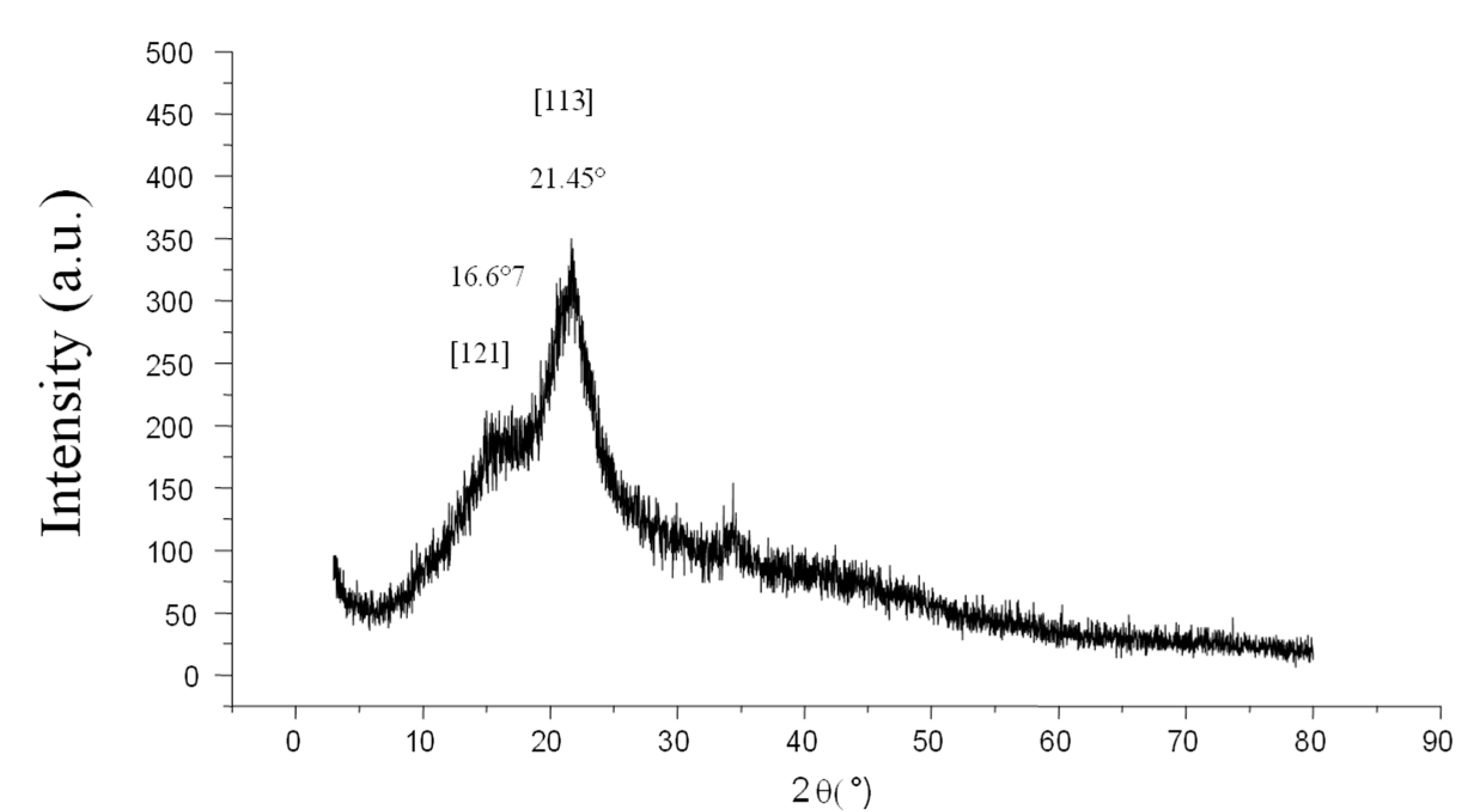
The XRD diffractogram of the almond shell is given in Figure 2. The two prominent peaks that are located at 2θ = 16.67° and 21.45° correspond to reflection plans in [121] and [113], which agree with previously published data [45]. The XRD analysis for agricultural waste also revealed two slightly narrow peaks detected at 2θ values around 16° and 22°, which is due to the semi-crystalline structure of the cellulose contained in the biomass [45]. In fact, according to a study by Amaury, cellulose has a semi-crystalline structure characterized by both disordered (amorphous) and very ordered (crystalline areas) areas [46]. The results of the XRD analysis showed that the crystallization index of the AS is 37.5%.
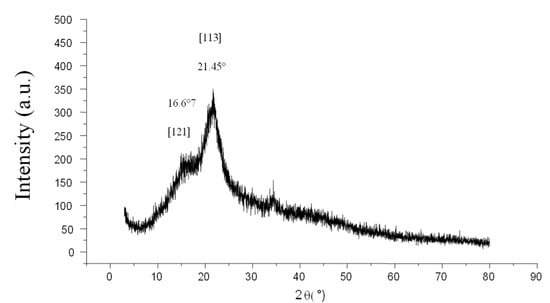
Figure 2.
XRD analysis of AS.
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
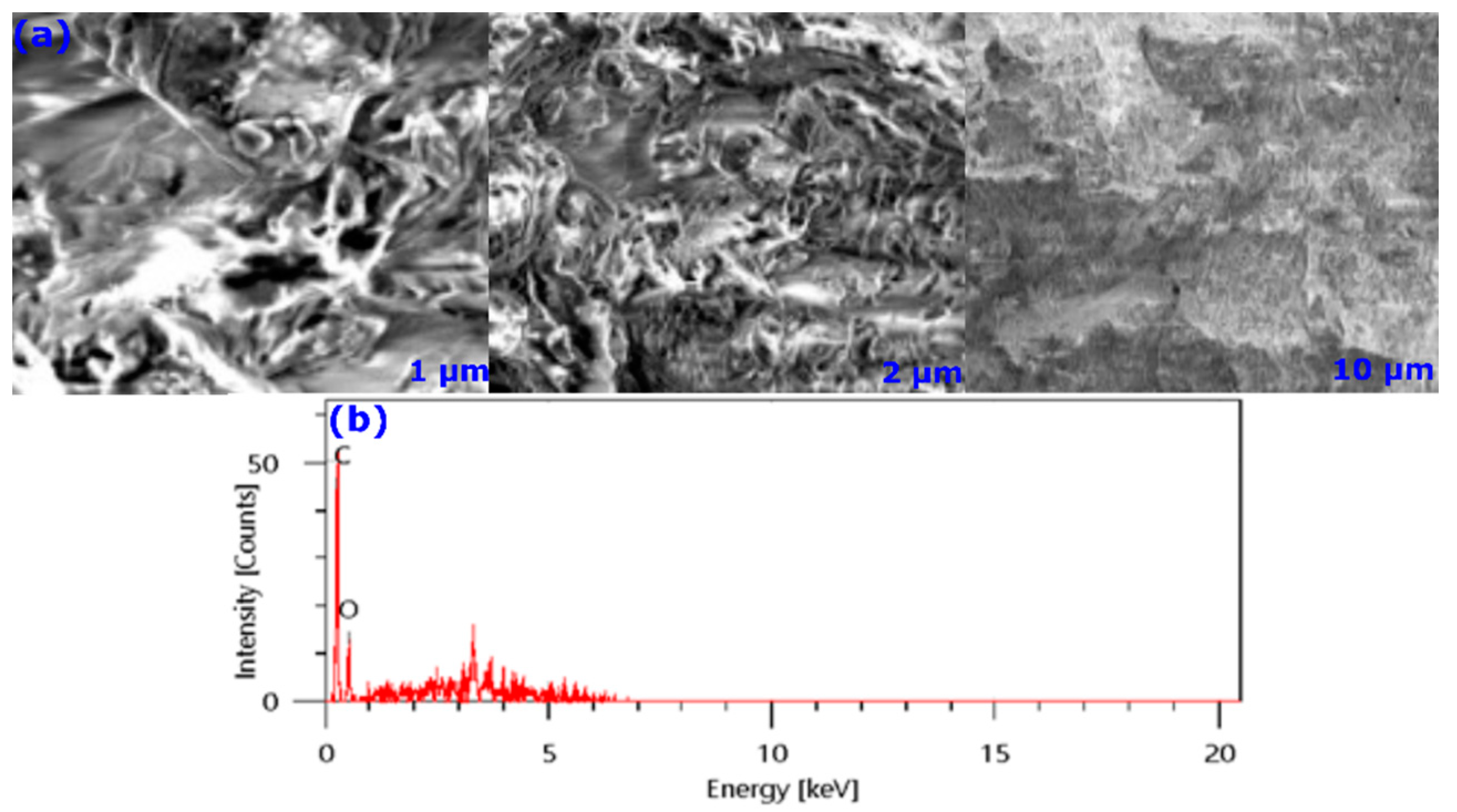
SEM analysis was carried out to investigate the morphology of the studied almond shell. Almond shell samples with 0.3–0.7 mm were considered for taking SEM images. By inspecting the SEM image in Figure 3a, one can notice that the AS is a naturally porous material. This indicates that it has natural bioabsorption abilities without further chemical or thermal activation.
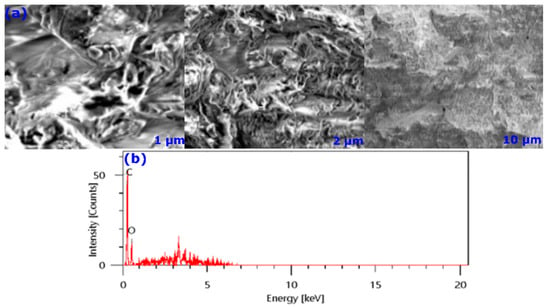
Figure 3.
SEM (a) and EDS (b) analyses of AS.
On the other hand, the EDS elemental analysis was conducted, the results of which are represented in Figure 3b. Peaks located between 0 and 1 keV are attributed to O, C, and N atoms, while those located above 1 keV indicate the presence of trace amounts of Cl, Ca, K, Al, and Mg. Results are in good agreement with those obtained from FTIR analysis, according to which a significant proportion of carbon and oxygen atoms characterize the biomass.
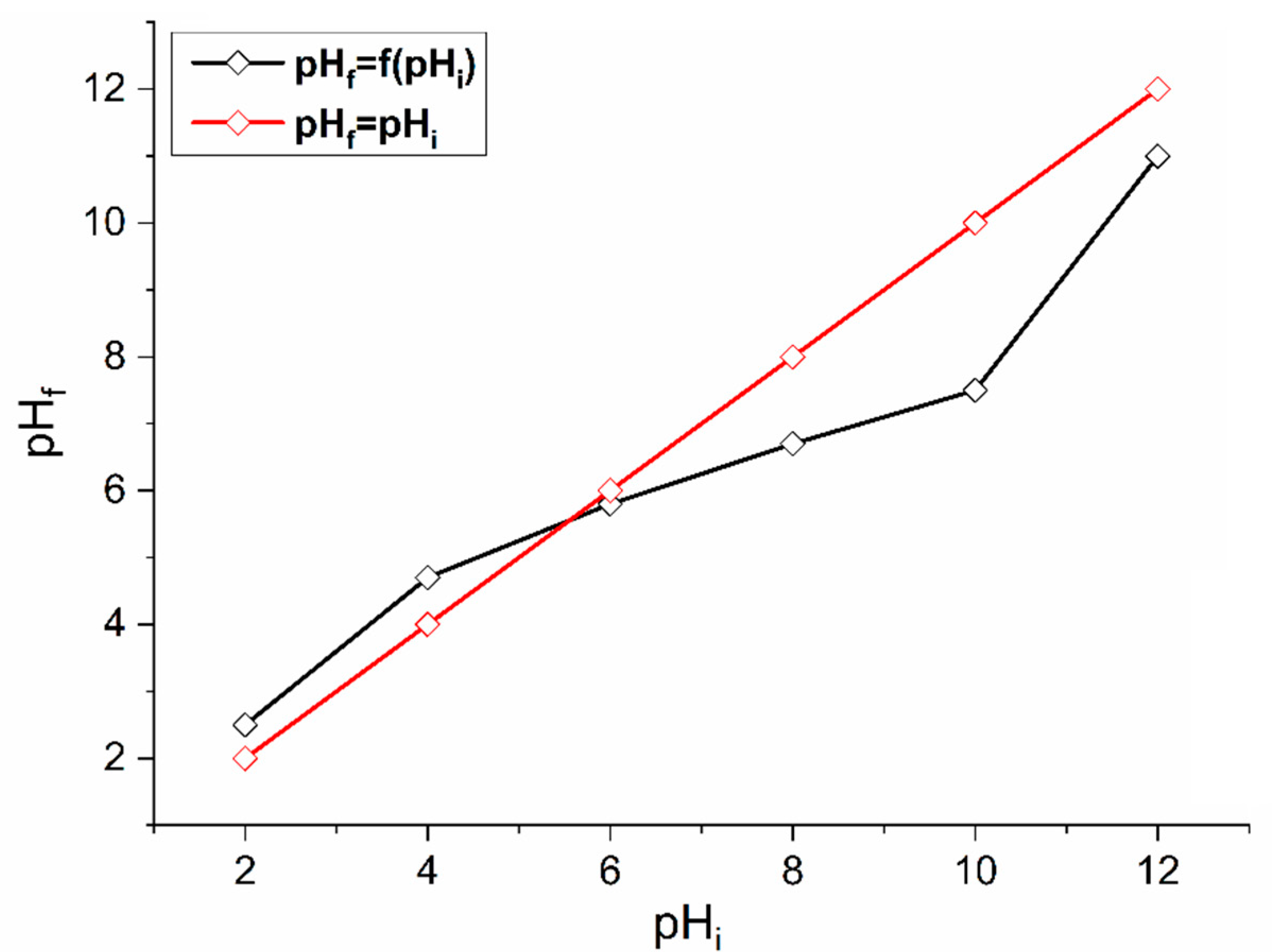
3.1.4. The pH at the Zero-Charge Point
The pH at the zero-charge point indicates the pH at which the surface of a solid reaches a zero charge [47,48]. According to Figure 4, the intersection point corresponds to a pHpzc = 6.2. Therefore, at pH values lower than this point, the global charge of the surface is positive and negative at pH values higher than pH = 6.2.
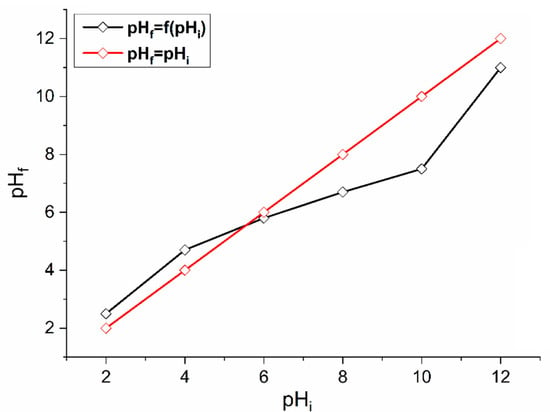
Figure 4.
pHpzc determination of AS.
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Effect of Adsorbent Mass
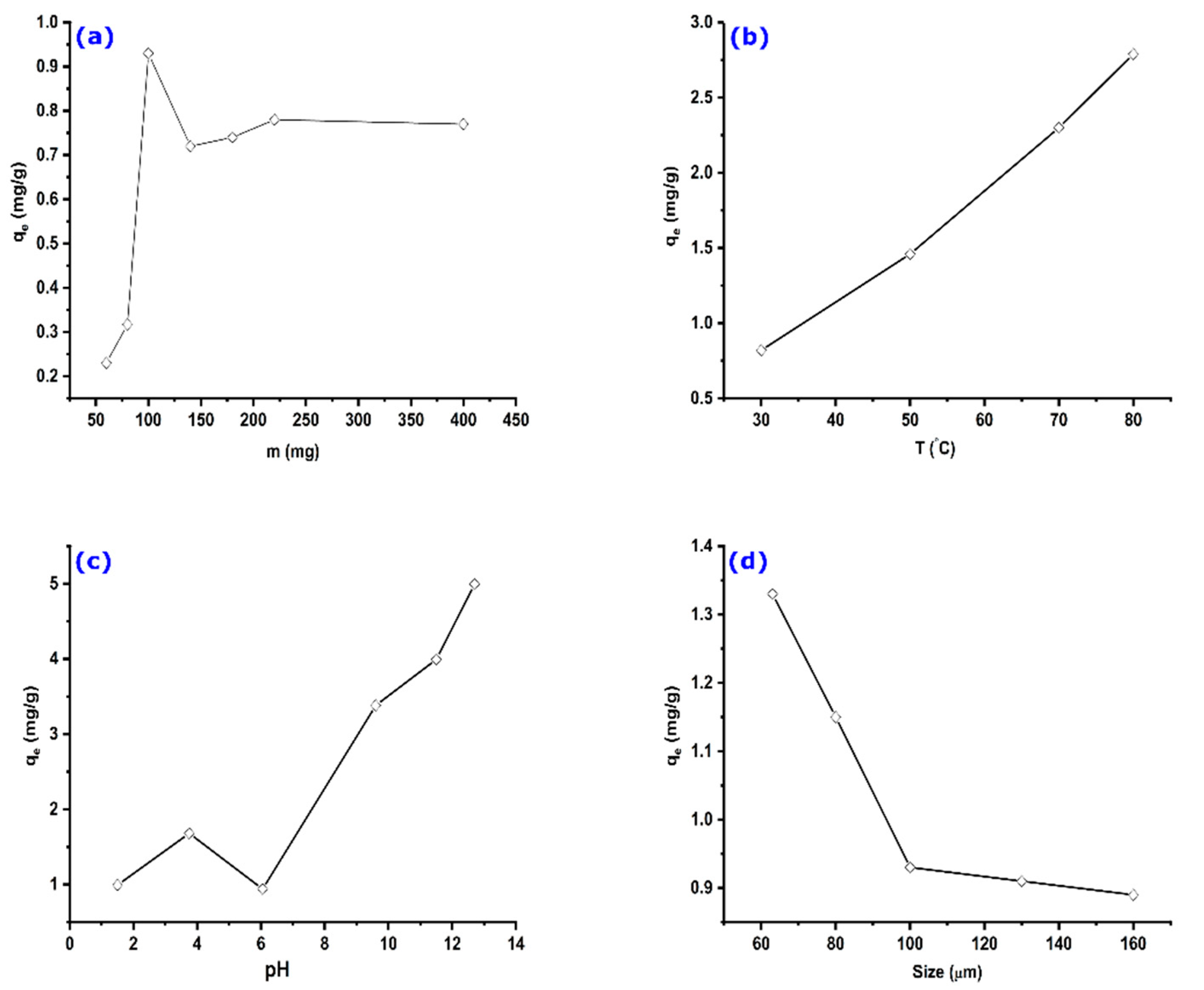
The influence of the AS mass on the adsorption capacity was examined for a fixed MO initial concentration. The obtained results are shown in Figure 5a. Results show that the adsorbed quantity of the methyl orange increases with the increase in the adsorbent mass up to 100 mg (considered optimal). This can be explained by the increase in the contact surface and the availability of active sites; then, the adsorbed quantity decreases slightly before reaching an equilibrium state. This variation is probably due to the competition between fibers retaining fractions of dye molecule and the free fibers of AS that attract it, making it return into the solution, or by the desorption of molecules because of the increase in the collisions inter-particle [49]. On the other hand, the stabilization may be due to the difficulty of reaching active sites by molecules of methyl orange because of the presence of adsorbent molecules in excess amount.
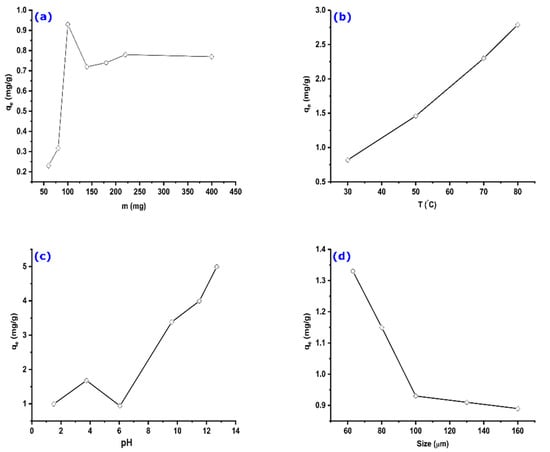
Figure 5.
The effect of different parameters on the adsorption capacity of AS: (a) adsorbent mass, (b) temperature, (c) pH, and (d) AS particle diameter. Experimental conditions: C0 = 32.7 mg/g, m = 100 mg, V = 25 mL, T = 25 °C, pH = 6.
3.2.2. Effect of Temperature
Temperature is one of the significant factors affecting the adsorption of adsorbates on adsorbents. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate its effect on the adsorption of MO on AS. Adsorption experiments were performed under the same conditions at temperatures of 30 °C, 50 °C, 70 °C, and 80 °C.
The obtained results are shown in Figure 5b. It can be observed that the amount of adsorbed MO increases slightly with the adsorption temperature, suggesting that the adsorption process is endothermic. Indeed, the increase in temperature would promote the mobility of dye molecules, resulting in a swelling effect on the internal structure of the adsorbent [50]. It would also allow dye molecules to easily penetrate into the adsorbent by favoring their diffusion through the external layer and the internal pores, consequently increasing the adsorption capacity.
3.2.3. Effect of Solution pH
Adjusting the solution pH is a critical step toward effective adsorption of dyes on different types of adsorbents. The analysis of results represented in Figure 5c shows a low adsorption rate at pH values between 2 and 6. In contrast, the adsorbed quantity of MO increases when the solution pH is at basic values. There should be a competition between MO molecules and H+ ions for the adsorbent’s active sites at low pH values, which occurs through ion exchange. Such effect is diminished when H+ concentration becomes low at near-neutral and basic solutions. These remarks reveal that the adsorption depends on phenomena other than electrostatic attractions. Similar results were found for the adsorption of a basic dye on sawdust [51].
3.2.4. Effect of AS Particle Diameter
The adsorbent particle size is an important factor that can influence the adsorption capacity. The adsorbed quantity was calculated for different grain sizes of the AS powder, ranging from 63 µm to 160 µm. Figure 5d shows a decrease in the adsorption capacity with an increase in AS diameter. This can be explained by reducing the specific surface (adsorbent–adsorbate contact surface). The reactivity depends, in general, on the solid–liquid contact surface, which is inversely proportional to the size of the particles [52].
3.2.5. Kinetic Study
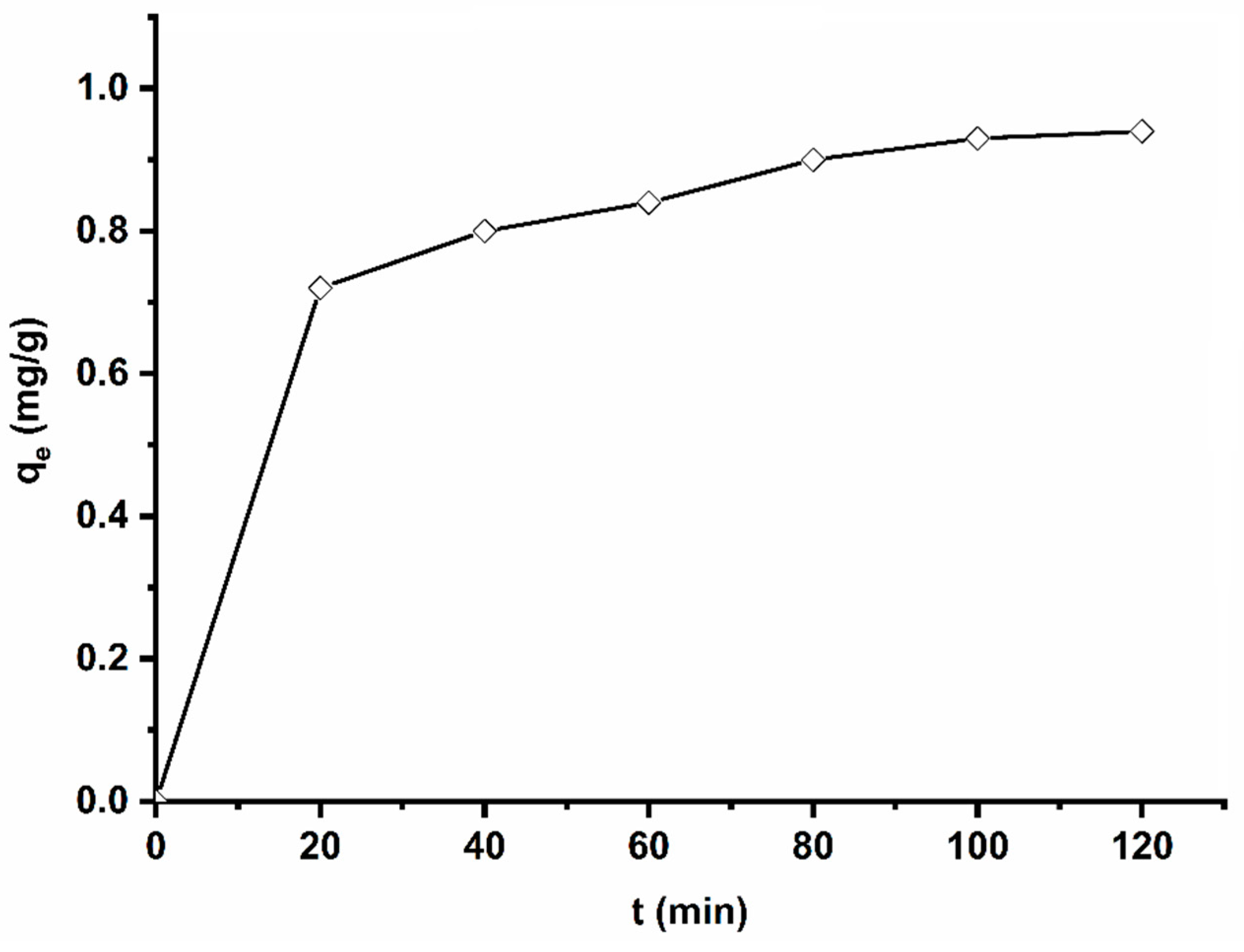
To determine the adsorption equilibrium time, adsorption experiments were performed at various stirring times, ranging from 20 min to 120 min. The obtained results are shown in Figure 6. It can be seen from this figure that the adsorbed quantity of methyl orange by the used adsorbent increases with time, up to a saturation level at 90 min, where the amount adsorbed is practically constant. However, one can notice that there is no significant difference between adsorption capacity after 20 min and adsorption capacity after 90 min, signifying the high affinity of MO to AS. In the first stage, there are many accessible adsorption sites; then, the adsorbate starts diffusing into less accessible adsorption sites before reaching an equilibrium state.
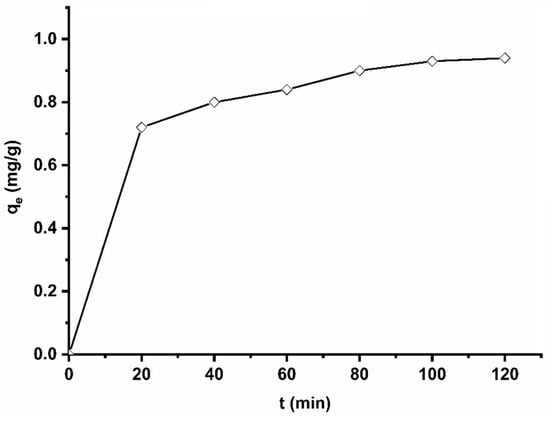
Figure 6.
Influence of contact time on MO adsorption on AS. Experimental conditions: C0 = 32.7 mg/g, m = 100 mg, V = 25 mL, T = 25 °C, pH = 6.
Different kinetic models were developed to model the adsorption of adsorbate onto a solid surface. These models help explain the mechanism by which the adsorbate is adsorbed on the adsorbent surface.
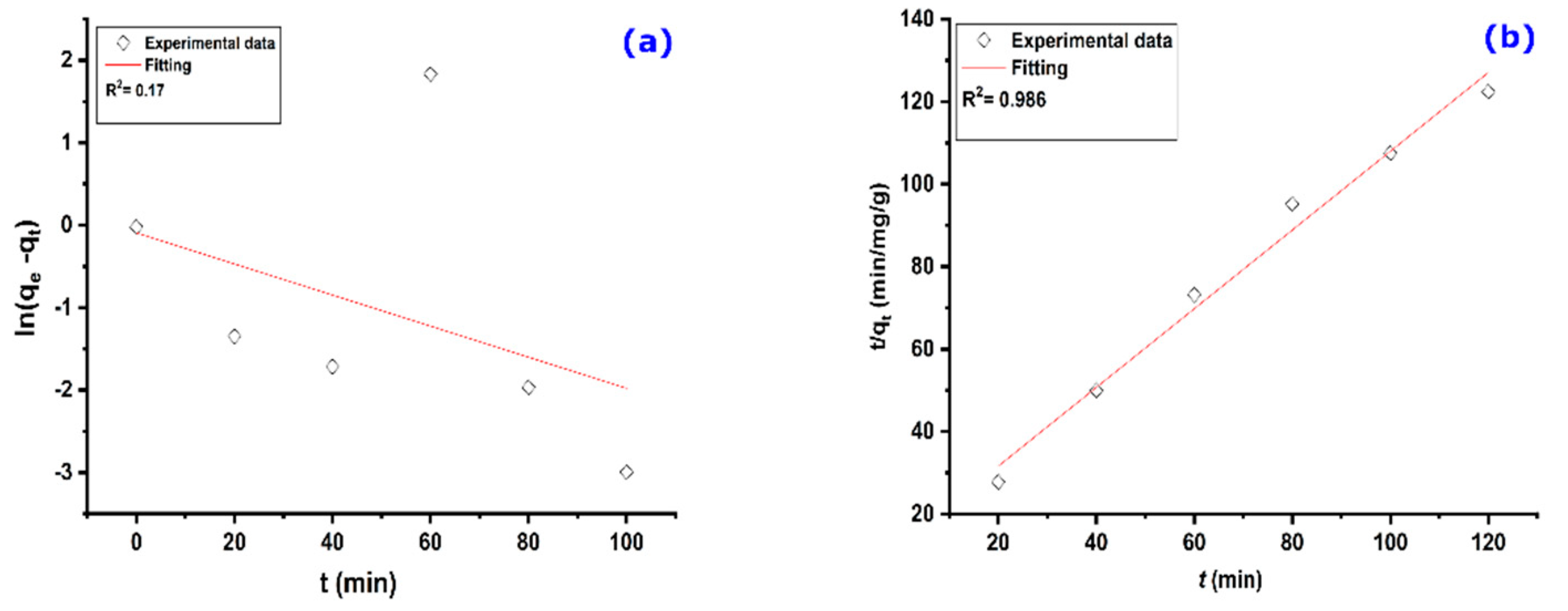
The plot of ln(qe–qt) as a function of (t), given in Figure 7a, represents the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. It shows a non-straight line with a low correlation coefficient, which signifies that the kinetics of adsorption of MO on AS does not follow the kinetics of the pseudo-first-order model.
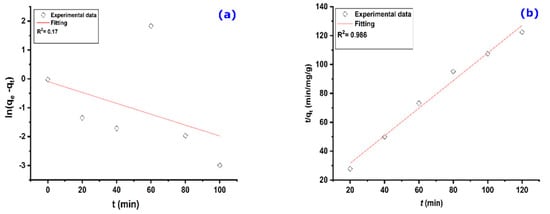
Figure 7.
Kinetic models relating to adsorption of MO on AS: (a) pseudo-first order and (b) pseudo-second order. Experimental conditions: C0 = 32.7 mg/g, m = 100 mg, V = 25 mL, T = 25 °C, pH = 6.
The pseudo-second-order kinetic model has been successfully used to describe the kinetics of pollutants’ adsorption on a given adsorbent [53]. It is one of the most suitable adsorption kinetic models because it depends on one second or two primary reactants in the solution [54]. The plot t/qt = f(t) representing the PSO kinetic model is shown in Figure 7b. A fitting of the plot gives a linear regression coefficient (R2) of 0.986. The parameters K2 and qe, determined from the same plot, are 0.072 g/mg min and 1.05 mg/g, respectively. The calculated qe value is in perfect agreement with the experimental value (0.95 mg/g), which indicates that the adsorption of MO on AS obeys the pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
3.2.6. Adsorption Isotherm
The adsorption isotherm study of MO on AS was carried out under the same experimental conditions used for the kinetic analysis, except that the adsorption time was fixed at 120 min, which is mainly a sufficient time to obtain the adsorbate–adsorbent equilibrium. The modeling of the MO adsorption on the AS was carried out using Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models.
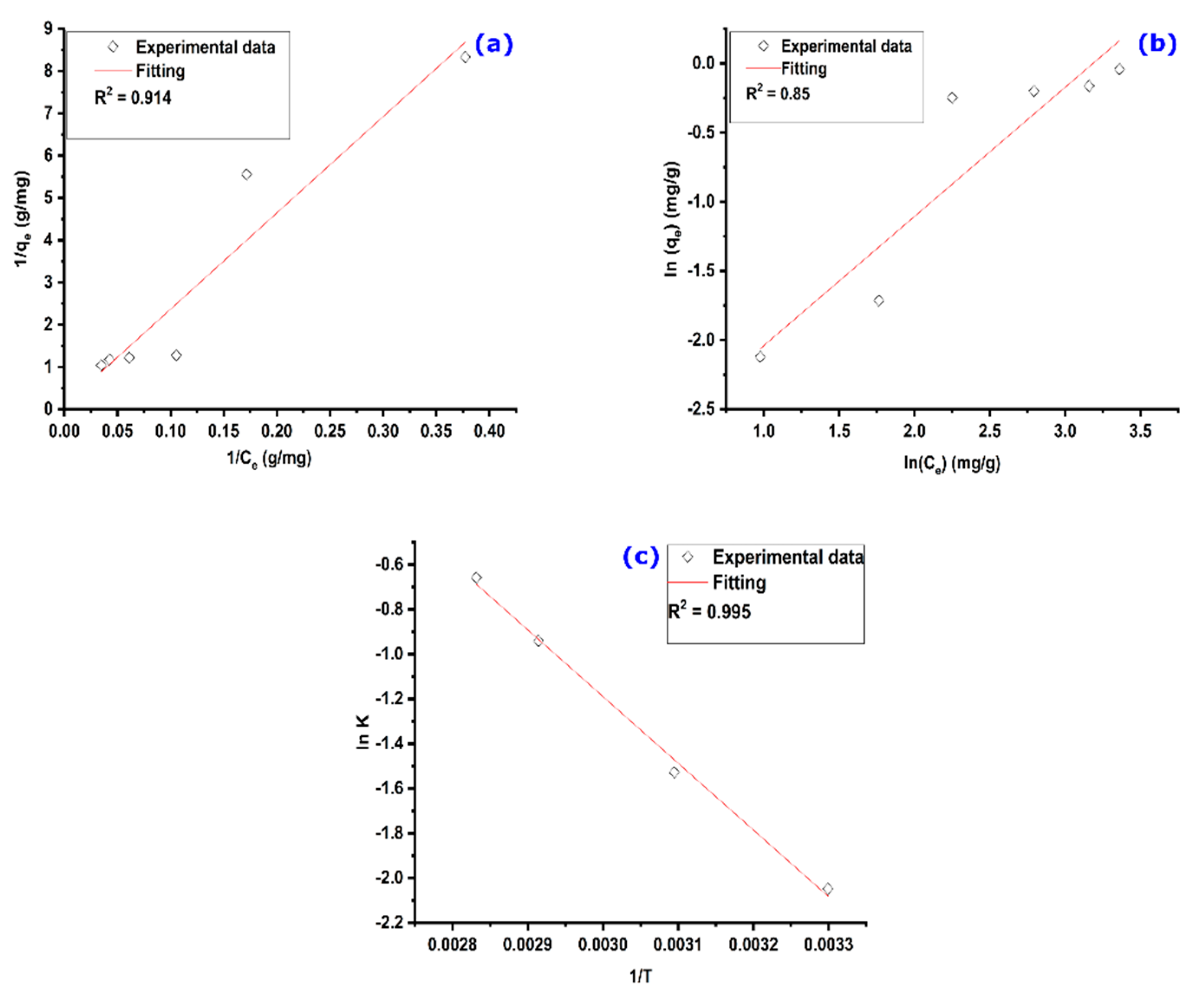
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm plot is represented in Figure 8a, in which a straight line is observed. In addition, the theoretical fitted line obtained by linear regression of the experimental points gives a correlation coefficient R2 equaling 0.958. The constants qm and KL are 15.63 mg/g and 0.0028 L mg−1, respectively.
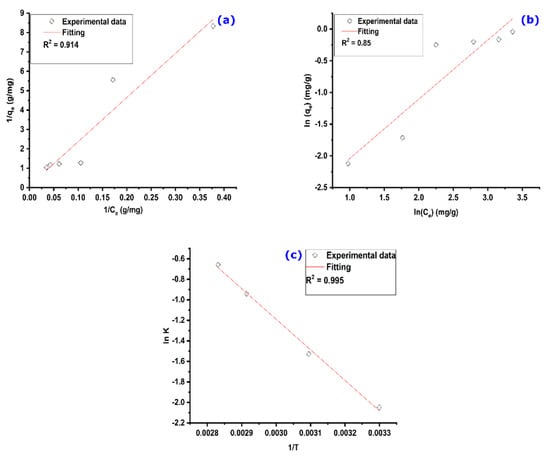
Figure 8.
(a) Langmuir and (b) Freundlich isotherm models, and (c) K vs. 1/T for MO adsorption on AS. Experimental conditions: C0 = Variable, m = 100 mg, V = 25 mL, T = 25 °C, pH = 6.
On the other hand, the Langmuir separation factor (RL) is a dimensionless parameter that can be used to estimate the adsorption preference of the adsorbate on the AS. RL is defined by the following equation:
where C0 is the initial dye concentration. It has been demonstrated that the adsorption can be classified into linear, unfavorable, favorable, or irreversible when RL value equals 1, greater than 1, between 0 and 1, or equals 0, respectively [55].
Taking this into consideration, the obtained RL value for C0 = 32.7 mg/L was found to be 0.916, which is within the interval of favorable adsorption. This finding further suggests the suitability of the Langmuir isotherm in describing the adsorption process of MO on the AS.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is another model that can be suitable for describing multilayer adsorption with the possibility of interaction between the adsorbed molecules [56]. It is based on the hypothesis of heterogeneity of the adsorption sites of the solid. Its linear form makes it possible to determine its KF and n parameters and, therefore, the model’s validity for the adsorption process under study.
From Figure 8b, which represents the Freundlich isotherm model with its fitting, it is clear that the model cannot be applied to describe the adsorption of MO on the AS since the theoretical straight line has a regression coefficient R2 that is very far from 1.
Adsorption isotherm parameters derived from Langmuir and Freundlich models are represented in Table 2. Comparing all parameters, it is evident that the Langmuir isotherm is the model that better describes the experimental results. This suggests that MO molecules are adsorbed on the material’s surface on energetically homogeneous sites and probably form a monolayer.

Table 2.
Fitting parameters of adsorption isotherm models for MO adsorption on AS.
Thermodynamic parameters such as the change in standard enthalpy (), change in standard entropy (), and change in standard free energy () can be determined from the following equations:
where T, Kd, and R denote the temperature, the adsorption equilibrium constant, and the universal gas constant.
The standard enthalpy and entropy values were determined from the linear fitting of experimental data, which are represented in Figure 8c. Calculated thermodynamic parameters are listed in Table 3. The positive values of free Gibbs energy changes () indicate that the MO adsorption onto the AS is not spontaneous at these temperatures [57]. Furthermore, values decrease with increasing temperatures, suggesting improved adsorption at higher temperatures [57]. The analysis of the listed results shows that the change in standard enthalpy is positive, indicating an endothermic adsorption process of MO on the AS [58]. In addition, its value is less than 40 KJ/mol, signifying that the physisorption process occurs [59]. In addition, the positive value of the entropy indicates that the adsorption is accompanied by an increase in the disorder of MO molecules; that is, MO molecules have many possibilities to find an adsorption site to be adsorbed.

Table 3.
Thermodynamic parameters for MO adsorption on AS.
3.2.7. Adsorption Mechanism
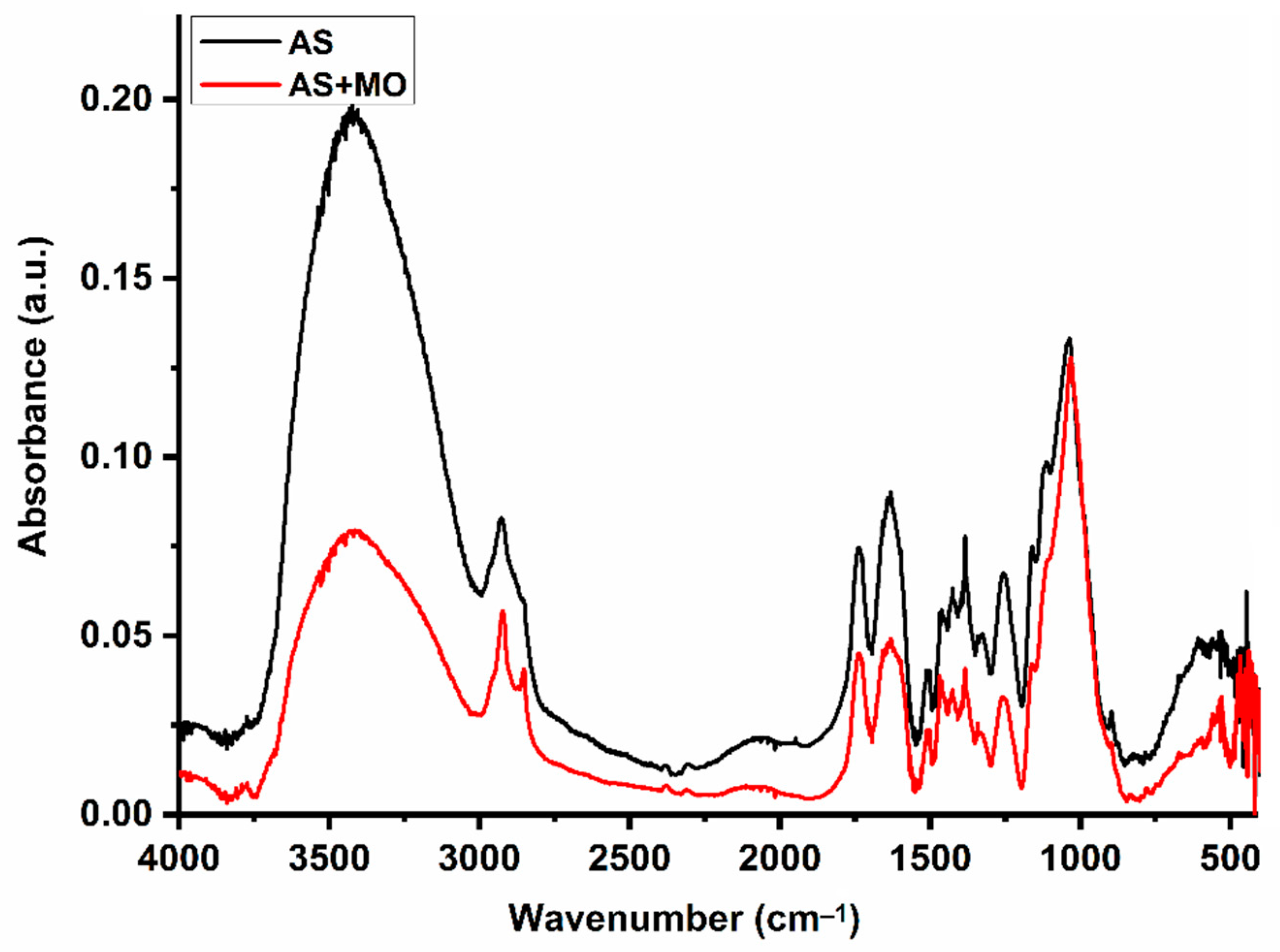
The almond shell is found to be effective in capturing MO molecules. However, further analysis is needed to figure out the adsorption mechanism. To this end, FTIR analysis was carried out for AS samples before and after the adsorption experiment. Results are shown in Figure 9.
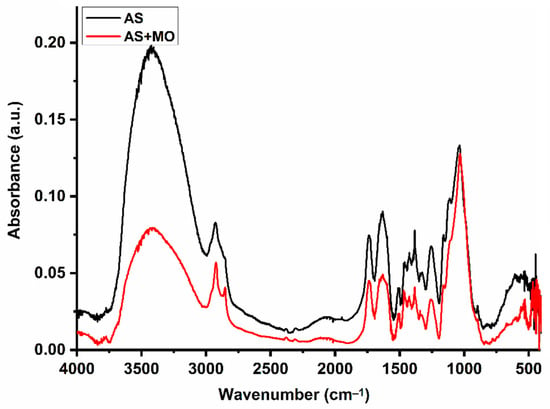
Figure 9.
FTIR analysis of AS before and after adsorption experiments.
A careful analysis of the results shows FTIR spectra with similar profiles for both AS samples but with different band intensities, especially the broadband at about 3420 cm−1, which corresponds to the stretching of the O-H groups. The position of the other bands remains unchanged after the adsorption process. On the other hand, the FTIR spectrum recorded for MO shows the same vibration bands as those reported by Parshetti et al. [60]. The most characteristic absorption bands for MO are located at 1605, 1520, 1411, 1381, 1357, 1200, 1115, 1002, 815, 691, and 620 cm−1. The band at 1605 cm−1 is associated with the C=C stretching vibration in the heterocycle [61,62,63], while that observed at 1381 cm−1 is associated with the -C stretching vibration –N of the dimethylamino terminal group [61,62,63,64]. The band at 1411 cm−1 can be assigned to the stretching vibration of -N=N- in azobenzene compounds [60]. The bands at 1357 and 1200 cm−1 can be attributed to asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of S(=O)2 in the group -SO32−, respectively [64]. The other peaks appearing at 1002, 815, 691, and 620 cm−1 are characteristic of the benzene ring [12,64].
The absence of new peaks in the AS + MO FTIR spectrum suggests that the adsorption process is taken effect through physical interactions without charge transfer or bond formation. The mechanism controlling the adsorption of MO on AS is mostly a combination of (1) non-dominant electrostatic interactions between MO molecules functional groups of the adsorbent, (2) π–π interactions between the aromatic rings of the dye molecules and those of the lignin, (3) the intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the surface hydroxyl groups and the nitrogen atoms of the dye, and (4) dye–hydrogen ion exchange process.
For comparison with some previously studied adsorbents, adsorption capacity and experimental conditions for adsorption of MO by different adsorbents are reported in Table 4. It can be deduced that there is a noticeable difference in the MO adsorption ability of reported adsorbents. Such difference is mainly attributed to the adsorbent’s surface area, functional groups, and experimental conditions, especially pH and equilibrium time. The chemical composition of an adsorbent is a critical factor in its adsorption performance. However, given the synthesis cost, the application of agro-wastes seems more beneficial than materials that require high resources.

Table 4.
MO adsorption capacity by different adsorbents in comparison with AS.
3.3. Preparation of Combustible Briquettes by Recycling AS Sludge
The energetic conversion of waste is a favorable alternative way to meet our energy needs and ensure good waste management. The biomass is neutral in terms of pollution compared with other fossil fuels. However, it contains much less carbon and more oxygen and has a low calorific value and energy density, which can cause undesirable problems related to the direct use of biomass as an energy source. Slow pyrolysis has been proposed as a biomass pretreatment process to overcome these gaps. It increases carbon content, removes oxygen, and increases energy density [69]. The manufactured biochar is very difficult to handle, transport, store and use in its original form. Thus, its densification into energetic briquettes in various forms is one of the attractive solutions. Densification increases the apparent density [70], ensures uniform combustion, and reduces dust generation, hence reducing transport, handling, and storage costs.
The fabricated combustible briquettes (Figure 10) require a drying time before characterization, which differs according to the nature of the binder. For molasses, the optimal value is 72 h at room temperature [71].

Figure 10.
Fabricated combustible briquettes.
The energy content of the biomass samples and their biochar is determined using the bomb calorimeter. The calorific values are 18.17 and 29.96 kJ/kg before and after pyrolysis. From the immediate analysis, as listed in Table 5, A400 has a volatile matter/fixed carbon ratio <1, much like fossil coal [72], and low ash content. Therefore, it can be a good option for cooking and raw material for existing coal-fired power plants.

Table 5.
Immediate analysis of the sludge generated in the treatment of the AS.
4. Conclusions
In the present paper, we presented an investigation of the MO adsorption on almond shells and the recycling of AS sludge into combustible briquettes. The AS was characterized using a variety of techniques such as XRD, FTIR, SEM, etc. The maximum adsorption of MO dye occurred at an optimal adsorbent mass of 100 mg and PH > pHPZC, confirming that its adsorption depends on phenomena other than electrostatic attractions. Results showed that MO adsorption on the AS reached an equilibrium state after 90 min. The kinetic study indicated that the adsorption process of methyl orange on almond shells followed a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm was found suitable in describing the adsorption process of MO on AS, showing an adsorption capacity of 15.63 mg/g. Moreover, the temperature and adsorbent particle size had a favorable effect on the MO adsorption capacity. Thermodynamic parameters indicated that the MO adsorption process is non-spontaneous, endothermic, and physical. The physical nature of adsorption was confirmed by FTIR analysis of AS after adsorption experiments. Furthermore, the biochar obtained by slow pyrolysis at a temperature of 400 °C for 2 h was used to manufacture combustible briquettes. Together, the present study revealed that almond shells could be used effectively as a low-cost adsorbent to remove real liquid effluent containing methyl orange and biofuels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, resources, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing, H.L., A.A.A., F.B. and M.S.; formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; investigation, writing—review and editing, A.A., A.E.-k., I.L., C.H. and M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yin, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication of Ceramsite Adsorbent from Industrial Wastes for the Removal of Phosphorus from Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8036961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiadi, N.; Dash, R.R.; Mohanty, C.R.; Patel, A.M. Comparative Studies of Adsorption of Chromium (VI) Ions onto Different Industrial Wastes. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2020, 24, 04020021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, S.; Karaman, Z.; Yalvac, M. Anionic and Cationic Textile Dyes Adsorption by Industrial Wastes: Pistachio Hull. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 7340–7351. [Google Scholar]
- Ayati, A.; Shahrak, M.N.; Tanhaei, B.; Sillanpää, M. Emerging Adsorptive Removal of Azo Dye by Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and Its Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; Arrieta, E.; Vicente, M.Á.; Korili, S.A. Application of Industrial Wastes from Chemically Treated Aluminum Saline Slags as Adsorbents. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 18275–18284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, Y.N.; Souza, E.S.; da Costa, H.S.C.; Melo, L.C.A.; Penido, E.S.; do Amarante, C.B.; Teixeira, O.M.M.; Fernandes, A.R. Biochar Produced from Amazonian Agro-Industrial Wastes: Properties and Adsorbent Potential of Cd 2+ and Cu 2+. Biochar 2019, 1, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Andrade, J.R.; Oliveira, M.F.; da Silva, M.G.; Vieira, M.G. Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Water and Wastewater Using Nonconventional Low-Cost Materials: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3103–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ji, G.; Li, A. Degradation of Antibiotic Pollutants by Persulfate Activated with Various Carbon Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Xu, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Khan, R.; Yue, Q.; Duan, P.; Dan, H.; Pan, J. Highly Efficient Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Media by Pomegranate Peel Co-Doping with Ferric Chloride and Lanthanum Hydroxide Nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 125311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Lai, S.; Sun, Y.; Yang, D. Recent Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Heavy Metal Oxoanions from Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Dai, G. Isotherm, Thermodynamic, Kinetics and Adsorption Mechanism Studies of Methyl Orange by Surfactant Modified Silkworm Exuviae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhachemi, M.; Belala, Z.; Lahcene, D.; Addoun, F. Adsorption of Phenol and Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Chemically Modified Date Pits Activated Carbons. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 7, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panumati, S.; Chudecha, K.; Vankhaew, P.; Choolert, V.; Chuenchom, L.; Innajitara, W.; Sirichote, O. Adsorption of Phenol from Diluted Aqueous Solutions by Activated Carbons Obtained from Bagasse, Oil Palm Shell and Pericarp of Rubber Fruit. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 30, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, G.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, J.; Garcia, A.I.; Freire, M.S.; Antorrena, G. Adsorption of Phenol on Formaldehyde-Pretreated Pinus Pinaster Bark: Equilibrium and Kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, K.-T.; Wu, F.-C.; Juang, R.-S. Kinetic Studies on the Adsorption of Phenol, 4-Chlorophenol, and 2,4-Dichlorophenol from Water Using Activated Carbons. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.N.; Martín, M.J.; Burguillo, F.J. A Comparative Study of the Adsorption of Humic Acid, Fulvic Acid and Phenol onto Bacillus Subtilis and Activated Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Meng, X.-G.; Hu, C.-W.; Du, J. Adsorption of Phenol, p-Chlorophenol and p-Nitrophenol onto Functional Chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhome, M.A.L.; Keukeleire, D.D.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Nascimento, R.F.; Carvalho, T.V.; Queiroz, D.C. Removal of Phenol and Conventional Pollutants from Aqueous Effluent by Chitosan and Chitin. Quím. Nova 2009, 32, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, A.Y.; Kalayci, C.S. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Phenol onto Chitin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala’a, H.; Ibrahim, K.A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Ali-Khashman, O.; Walker, G.M.; Ahmad, M.N. Remediation of Phenol-Contaminated Water by Adsorption Using Poly (Methyl Methacrylate)(PMMA). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S. Adsorptive Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Phase by Using a Porous Acrylic Ester Polymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dali-Youcef, Z.; Bouabdasselem, H.; Bettahar, N. Élimination Des Composés Organiques Par Des Argiles Locales. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Ligor, T.; Lebedynets, M.; Buszewski, B. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Phenol Adsorption by Natural and Modified Forms of the Clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.F.; Lin, W.G.; Gao, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Wei, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H. Low-Cost and Effective Phenol and Basic Dyes Trapper Derived from the Porous Silica Coated with Hydrotalcite Gel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Rajput, S.; Singh, V.K.; Steele, P.H.; Pittman Jr, C.U. Modeling and Evaluation of Chromium Remediation from Water Using Low Cost Bio-Char, a Green Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, E.; Nuhoglu, Y. Determination of Kinetic and Equilibrium Parameters of the Batch Adsorption of Cr (VI) onto Waste Acorn of Quercus Ithaburensis. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajouyed, O.; Hurel, C.; Ammari, M.; Allal, L.B.; Marmier, N. Sorption of Cr (VI) onto Natural Iron and Aluminum (Oxy) Hydroxides: Effects of PH, Ionic Strength and Initial Concentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.Q.; Gonçalves, M.; Oliveira, L.C.; Guilherme, L.R. Removal of As (V) and Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solutions Using Solid Waste from Leather Industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhab, K.; Addad, J.; Barr, S.; Goma, B. Thermodynamic of Chromium Sorption on Biomass Fungi from Aqueous Solution. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 2486–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Luo, H.; Chen, H.; Dong, T. Adsorption of Chromate and Para-Nitrochlorobenzene on Inorganic–Organic Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, V.; Mikhalovsky, S. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium by New Quaternized Crosslinked Poly (4-Vinylpyridines). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebringerová, A.; Hromádková, Z.; Košťálová, Z.; Sasinková, V. Chemical valorization of agricultural by-products: Isolation and characterization of xylan-based antioxidants from almond shell biomass. BioResources 2008, 3, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yüksel, Ş.; Orhan, R. The Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon Prepared from Apricot, Peach Stone and Almond Shell Mixture in a Fixed-Bed Column. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5345–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Ji, B.; Cui, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Luo, S.; Guo, D. Almond Shell-Derived, Biochar-Supported, Nano-Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Aqueous Hexavalent Chromium Removal: Performance and Mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahya, M.D.; Abubakar, H.; Obayomi, K.S.; Iyaka, Y.A.; Suleiman, B. Simultaneous and Continuous Biosorption of Cr and Cu (II) Ions from Industrial Tannery Effluent Using Almond Shell in a Fixed Bed Column. Results Eng. 2020, 6, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimi, N.; Tadjarodi, A. Adsorption of Rhodamine-B from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon from Almond Shell. Proceedings 2019, 41, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zbair, M.; Anfar, Z.; Ait Ahsaine, H.; El Alem, N.; Ezahri, M. Acridine Orange Adsorption by Zinc Oxide/Almond Shell Activated Carbon Composite: Operational Factors, Mechanism and Performance Optimization Using Central Composite Design and Surface Modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.K.; Giri, B.S.; Nath, Y.; Bajaj, H.; Soni, S.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N. Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon Prepared from Almond Shell: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics Study. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2018, 67, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsini, A.; Essekri, A.; Aarab, N.; Laabd, M.; Ait Addi, A.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Elaboration of Novel Polyaniline@Almond Shell Biocomposite for Effective Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Ions and Orange G Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15245–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ahsaine, H.; Zbair, M.; Anfar, Z.; Naciri, Y.; El haouti, R.; El Alem, N.; Ezahri, M. Cationic Dyes Adsorption onto High Surface Area ‘Almond Shell’ Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium Isotherms and Surface Statistical Modeling. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Basu, R.K.; Das, S.K. Cu(II) Removal Using Green Adsorbents: Kinetic Modeling and Plant Scale-up Design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11542–11557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari Moghaddam, N.; Lorestani, B.; Cheraghi, M.; Jamehbozorgi, S. Adsorption of Cd and Ni from Water by Graphene Oxide and Graphene Oxide–Almond Shell Composite. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homem, V.; Alves, A.; Santos, L. Amoxicillin Removal from Aqueous Matrices by Sorption with Almond Shell Ashes. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 1063–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertaş, M.; Alma, M.H. Pyrolysis of Laurel (Laurus Nobilis L.) Extraction Residues in a Fixed-Bed Reactor: Characterization of Bio-Oil and Bio-Char. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 88, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetit, A. Élaboration de Matériaux Composites à Base de Filaments de Cellulose et de Polyéthylène. PhD Thesis, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, Trois-Rivières, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Annab, H.; Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Essamri, A. A Proposal for the Sustainable Treatment and Valorisation of Olive Mill Wastes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Toledo, I.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Vegas Fernández, F.J. Bisphenol A Removal from Water by Activated Carbon. Effects of Carbon Characteristics and Solution Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6246–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouki, Z.; Hadri, M.; Nawdali, M.; Benzina, M.; Zaitan, H. Treatment of a Landfill Leachate from Casablanca City by a Coagulation-Flocculation and Adsorption Process Using a Palm Bark Powder (PBP). Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoğlu, M.H.; Doğan, M.; Alkan, M. Kinetic Analysis of Reactive Blue 221 Adsorption on Kaolinite. Desalination 2010, 256, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaid, K.; Kacha, S. Étude Cinétique et Thermodynamique de l’adsorption d’un Colorant Basique Sur La Sciure de Bois. Rev. Sci. L’eauJournal Water Sci. 2011, 24, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Guechi, E.-K.; Hamdaoui, O. Sorption of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution by Potato Peel: Kinetics and Equilibrium Modeling Using Non-Linear Analysis Method. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S416–S424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Sorption of Dye from Aqueous Solution by Peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayranli, B.; Gok, O.; Yilmaz, T.; Gok, G.; Celebi, H.; Seckin, I.Y.; Mesutoglu, O.C. Low-Cost Organic Adsorbent Usage for Removing Ni2+ and Pb2+ from Aqueous Solution and Adsorption Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; O’Hara, I.M.; Kent, G.A.; Doherty, W.O. Comparative Study on Adsorption of Two Cationic Dyes by Milled Sugarcane Bagasse. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 42, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, M.L.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H.; Parajó, J.C. Recovery, Concentration and Purification of Phenolic Compounds by Adsorption: A Review. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, H.; Ghaemi, A.; Ghanadzadeh Gilani, H.; Ramazanipour Penchah, H. Benzene-Based Hypercross-Linked Polymers as a Highly Efficient Adsorbent for Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, O.S.; Amodu, O.S.; Adubiaro, H.; Olutona, G.O.; Ebenezer, O.T.; Nelana, S.M.; Naidoo, E.B. Effectiveness of Termite Hill as an Economic Adsorbent for the Adsorption of Alizarin Red Dye. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2018, 9, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dall’Agnol, P.; Libardi, N.; da Silva, E.C.; da Costa, R.H.R. Biosorption of Phosphorus Using Alginate-Like Exopolymers: Investigation of Removal Mechanism, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshetti, G.K.; Telke, A.A.; Kalyani, D.C.; Govindwar, S.P. Decolorization and Detoxification of Sulfonated Azo Dye Methyl Orange by Kocuria Rosea MTCC 1532. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Ikeda, E.; Nagayasu, T.; Sakiyama, T.; Nakanishi, K. Adsorption Behavior of Methylene Blue and Its Congeners on a Stainless Steel Surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.-H.; Jiang, W.-T.; Jean, J.-S.; Hong, H. Mechanism of Methylene Blue Removal from Water by Swelling Clays. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, O.V.; Chernykh, S.V.; Smirnov, M.S.; Alpatova, D.V.; Vorob’eva, R.P.; Latyshev, A.N.; Evlev, A.B.; Utekhin, A.N.; Lukin, A.N. Analysis of Interaction between the Organic Dye Methylene Blue and the Surface of AgCl(I) Microcrystals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 74, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G.C. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds. J. Chem. Educ. 1962, 39, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, O.; Mehrez, I.; Younsi, M.; Nacef, M.; Affoune, A.M. Methyl orange adsorption on biosorbent derived from mango seed kernels. LARHYSS J. P-ISSN 1112-3680 E-ISSN 2521-9782 2018, 36, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Use of Cellulose-Based Wastes for Adsorption of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Malviya, A.; Kaur, D.; Mittal, J.; Kurup, L. Studies on the Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms for the Removal and Recovery of Methyl Orange from Wastewaters Using Waste Materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapan Kumar, S. Adsorption of Methyl Orange onto Chitosan from Aqueous Solution. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, H.; Wu, H. Biochar as a Fuel: 1. Properties and Grindability of Biochars Produced from the Pyrolysis of Mallee Wood under Slow-Heating Conditions. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 4174–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Thek, G. Physical Characterisation and Chemical Composition of Densified Biomass Fuels with Regard to Their Combustion Behaviour. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 27, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, M.J.; Miranda, J.L.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Moliner, R. Curing Temperature Effect on Mechanical Strength of Smokeless Fuel Briquettes Prepared with Molasses☆. Fuel 2003, 82, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, D.A. Biomass Cofiring: The Technology, the Experience, the Combustion Consequences. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).