Thermal Analysis Tools for Physico-Chemical Characterization and Optimization of Perfluorocarbon Based Emulsions and Bubbles Formulated for Ultrasound Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Emulsion Formulation and Preparation
2.3. Emulsion Characterization
2.3.1. Size Measurement
2.3.2. Number of Droplets
2.3.3. Localization of Fluorinated Surfactant in the Formulation
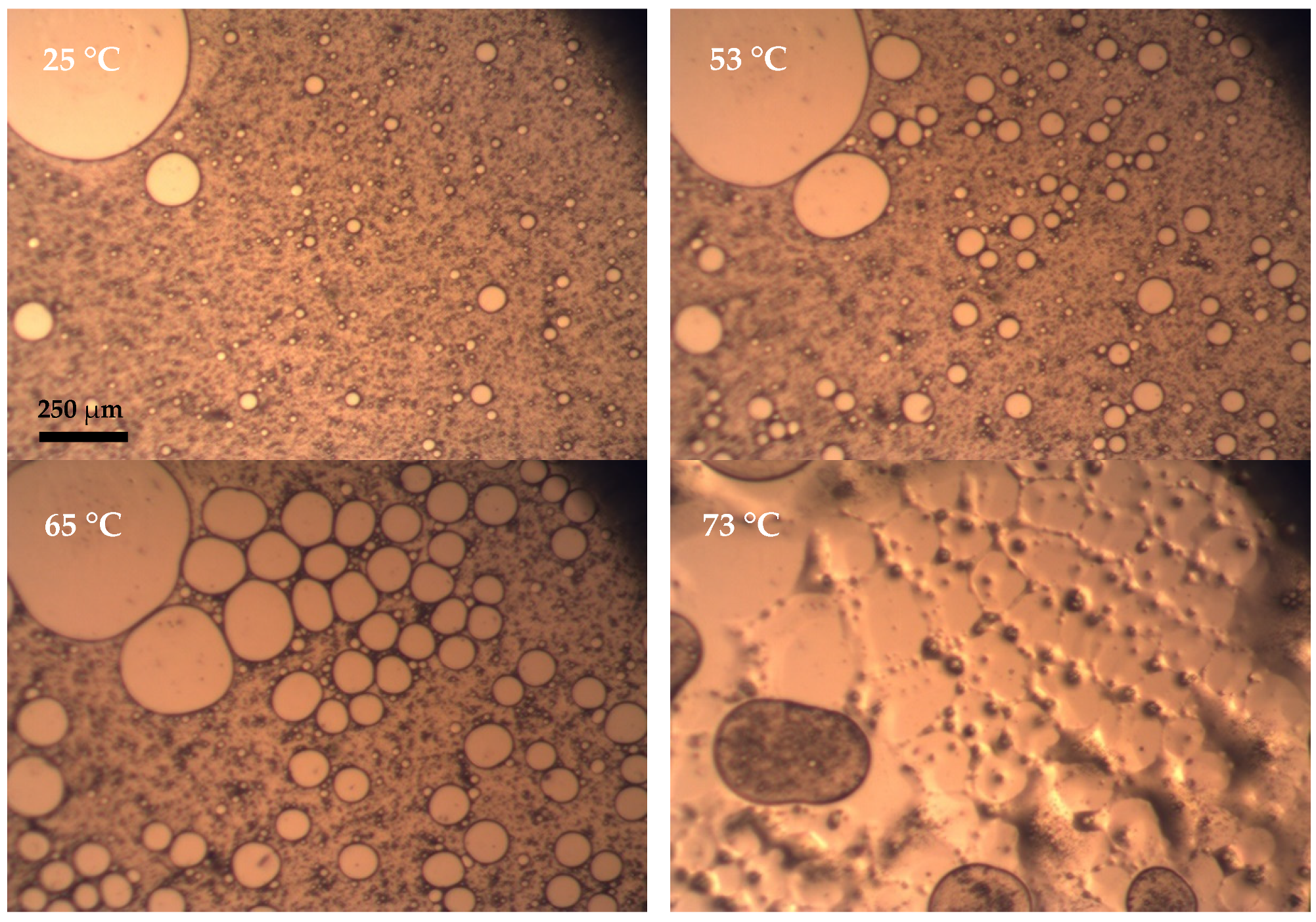
2.3.4. Visual Evaluation of the Emulsion Stability upon Heating by Thermal Microscopy
2.3.5. Thermal Analysis
2.3.6. Ultrasound Imaging Assessment of the Emulsions
2.3.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
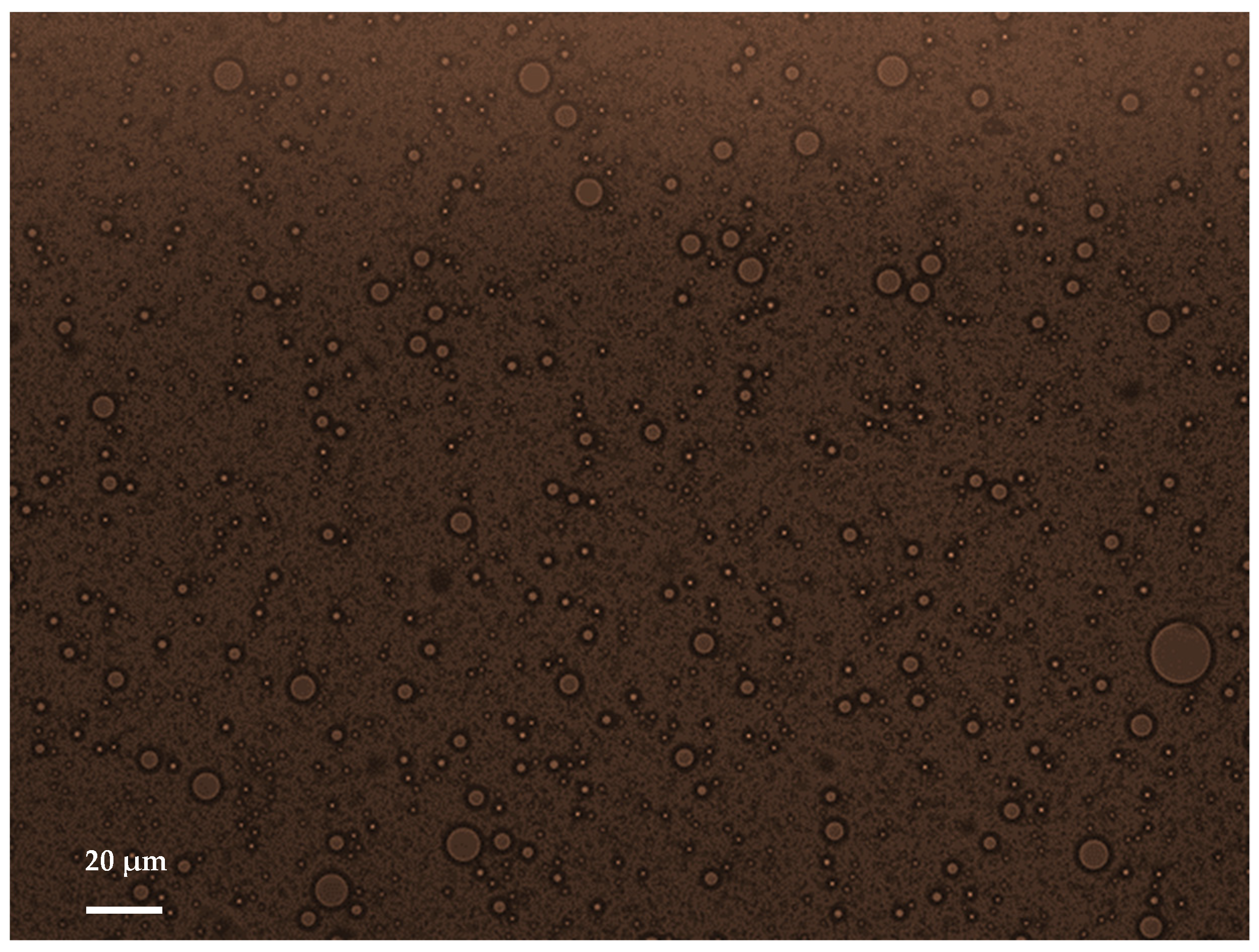
3.1. Characterization of the Droplets by Diffusion Light Scattering and Optical Imaging
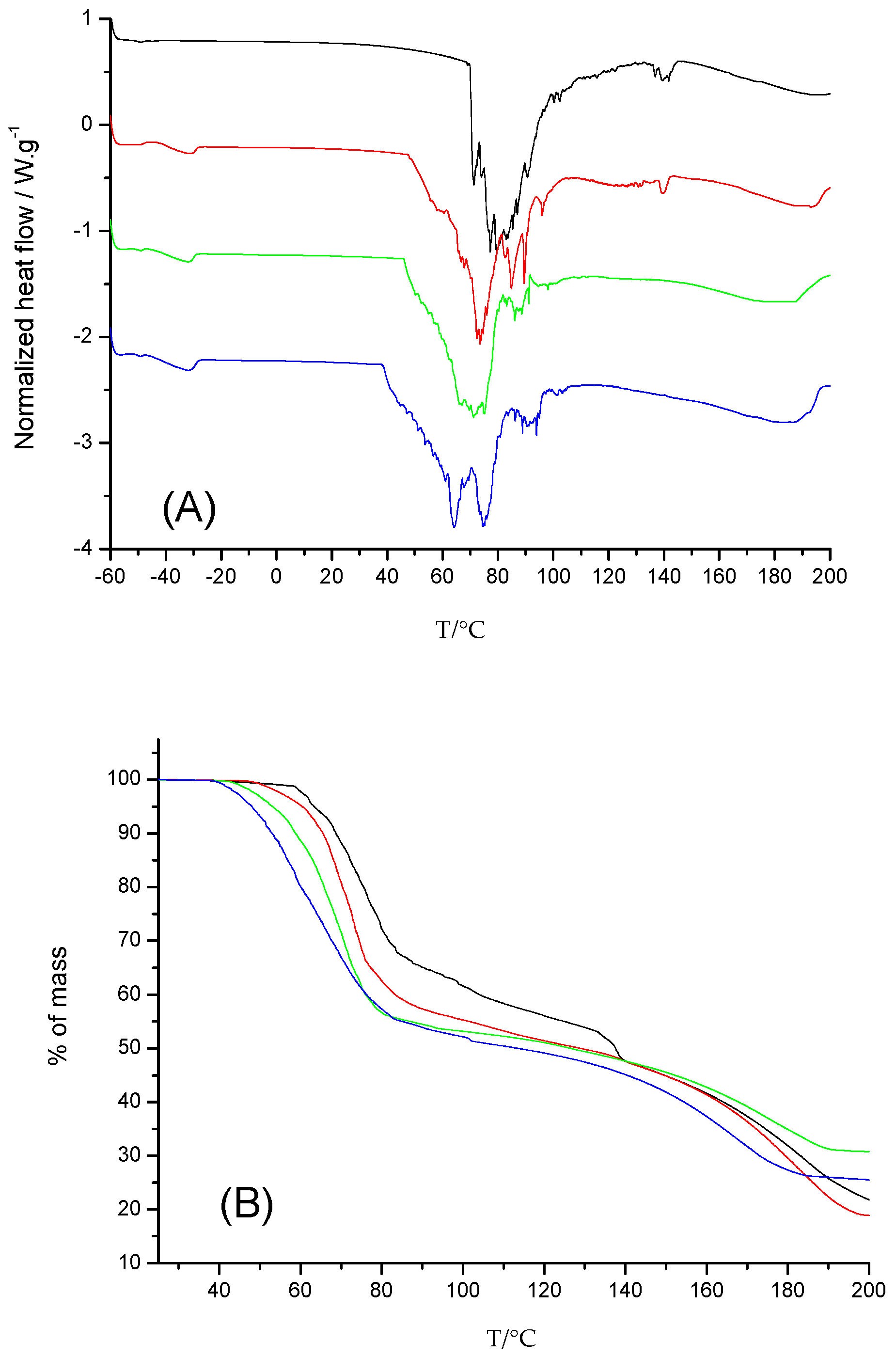
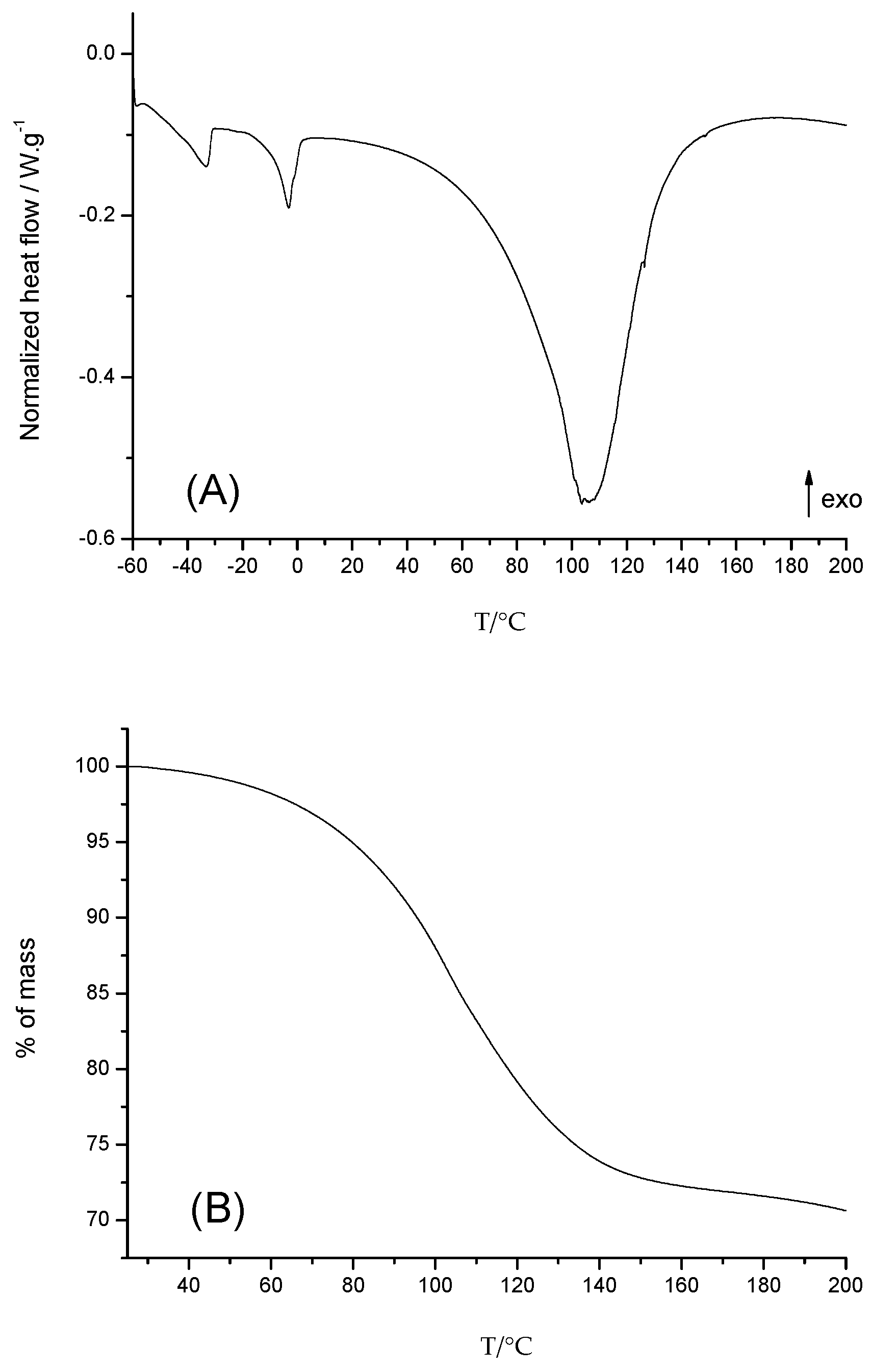
3.2. Characterization of the Microbubbles Using Thermal Analyses
- i/ The water/glycerol interactions manifested themselves with endothermic signals from −60 to −30 °C, as obtained with the PFH based emulsions.
- ii/ The wide peak due to the bursting of microbubbles is noisy but shifted to lower temperatures compared to emulsions containing PFH due to a lower vaporization temperature for PFP.
3.3. In Vitro Evaluation of Echogenicity of the Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gramiak, R.; Shah, P.M. Echocardiography of the aortic root. Investig. Radiol. 1968, 3, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaia, E. Microbubble ultrasound contrast agents: An update. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.; Lorton, O.; Guillemin, P.C.; Desgranges, S.; Contino-Pépin, C.; Salomir, R. Perfluorocarbon emulsion contrast agents: A mini review. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 810029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernot, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabiilli, M.L.; Haworth, K.J.; Sebastian, I.E.; Kripfgans, O.D.; Carson, P.L.; Fowlkes, J.B. Delivery of chlorambucil using an acoustically-triggered perfluoropentane emulsion. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Hung, C.-F.; Hua, S.-C.; Hwang, T.-L. Acoustically active perfluorocarbon nanoemulsions as drug delivery carriers for camptothecin: Drug release and cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Ultrasonics 2009, 49, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, E.C.; Porter, T.; Culp, W.; Labell, R.; Matsunaga, T.; Zutshi, R. Therapeutic applications of lipid-coated microbubbles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1291–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvis, Y.; Manta, S.; Thebault, C.; Couture, O.; Dhotel, H.; Michel, J.-P.; Seguin, J.; Bessodes, M.; Espeau, P.; Pichon, C.; et al. Novel perfluorinated triblock amphiphilic copolymers for lipid-shelled microbubble stabilization. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9744–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, N.; Nam, K.-H.; Gupta, R.; Gao, Z.; Mohan, P.; Payne, A.; Todd, N.; Liu, X.; Kim, T.; Shea, J.; et al. Ultrasound-mediated tumor imaging and nanotherapy using drug loaded block copolymer stabilized perfluorocarbon nanoemulsion. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, P.; Kiran, S.; Han, S.; Dwivedi, M.; Khatik, R.; Fan, R.; Mangrio, F.A.; Du, K.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.; et al. Magnetic Targeting and Ultrasound activation of liposome-microbubble conjugate for enhanced delivery of anticancer therapies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23737–23751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snipstad, S.; Vikedal, K.; Maardalen, M.; Kurbatskaya, A.; Sulheim, E.; de Lange Davies, C. Ultrasound and microbubbles to beat barriers in tumors: Improving delivery of nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 117, 113847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, N.; Bouakaz, A.; Frinkerg, P. Basic acoustic properties of microbubbles. Echocardiography 2002, 19, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouton, C.W. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 25, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtze, C.; Rowat, A.C.; Agresti, J.J.; Hutchison, J.B.; Angilè, F.E.; Schmitz, C.H.J.; Köster, S.; Duan, H.; Humphry, K.J.; Scanga, R.A.; et al. Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausse, D.; Gomez, F.; Pesron, I.; Komunjer, L.; Dalmazzone, C. Morphology characterization of emulsions by differential scanning calorimetry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 117, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Chavhan, S.; Sawant, K.K. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for adefovir dipivoxil: Design characterization in vitro and ex vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 392, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, F.; Puglia, C.; Grazia Sarpietro, M.; Rizza, L.; Bonina, F. Characterization of indomethacin-loaded lipid nanoparticles by differential scanning calorimetry. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 304, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Duan, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, D.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of oridonin-loaded long circulating nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigward, E.; Mignet, N.; Rat, P.; Dutot, M.; Muhamed, S.; Guigner, J.-M.; Scherman, D.; Brossard, D.; Crauste-Manciet, S. Formulation and cytotoxicity evaluation of new self-emulsifying multiple W/O/W nanoemulsions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 611–625. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, G.; Sheth, B.B. A novel self emulsifying parenteral drug delivery system. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1999, 53, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E., Eds.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sigward, E.; Corvis, Y.; Doan, B.-T.; Kindisko, K.; Seguin, J.; Scherman, D.; Brossard, D.; Mignet, N.; Espeau, P.; Crauste-Manciet, S. Preparation and Evaluation of Multiple Nanoemulsions Containing Gadolinium (III) Chelate as a Potential Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contrast Agent. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melich, R.; Valour, J.-P.; Urbaniak, S.; Padilla, F.; Charcosset, C. Preparation and characterization of perfluorocarbon microbubbles using Shirasu Porous Glass (SPG) membranes. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, S.; Bessodes, M.; Bureau, M.-F.; Scherman, D.; Delalande, A.; Pichon, C.; Mignet, N. Characterization of positively charged lipid shell microbubbles with tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS) method: A technical note. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-T.; Yeh, C.-K. Ultrasound Microbubble Contrast Agents for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: Current Status and Future Design. Chang Gung Med. J. 2012, 35, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Podell, S.; Burrascano, C.; Gaal, M.; Golec, B.; Maniquis, J.; Mehlhaff, P. Physical and biochemical stability of Optison®, an injectable ultrasound contrast agent. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1999, 30, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varshni, Y.P. Critical temperatures of organic compounds from their boiling points. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2009, 47, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postelnek, W. Boiling points of normal perfluoroalkanes. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 746–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of vitamin E-enriched nanoemulsions: Factors affecting particle size using spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 391, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.S.; Bruxel, F.; Teixeira, H.F. Physicochemical properties of lecithin-based nanoemulsions obtained by spontaneous emulsification or high-pressure homogenization. Quím. Nova 2014, 37, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Miner, C.S.; Dalton, N.N. Glycerol, 1st ed.; Reinhold Publishing Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Leffingwell, G.; Lesser, M.A. Glycerin: Its Industrial and Commercial Applications, 1st ed.; Chemical Publishing Co., Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]


| PFH Emulsion | PFP Emulsion | Control Emulsion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfluorohexane | 20 | - | - |
| Perfluoropentane | - | 20 | - |
| Medium chain triglyceride | - | - | 20 |
| Sorbitan monooleate (Span 80) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Polysorbate 85 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Poloxamer 188 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Water | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Zonyl® | 0.5;1;2;3 | 0.5;1;2;3 | 0.5;1;2;3 |
| Glycerol qs | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Perfluorohexane/Water Emulsions | Perfluoropentane/Water Emulsions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % of Zonyl® | 1% | 2% | 3% | 1% | 2% | 3% |
| Mean diameter (µm) | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 |
| DV50 (µm) | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.2 |
| Number of droplets/mL | 7.6 × 107 | 7.1 × 107 | 7.1 × 107 | 8.7 × 107 | 8.0 × 107 | 10.0 × 107 |
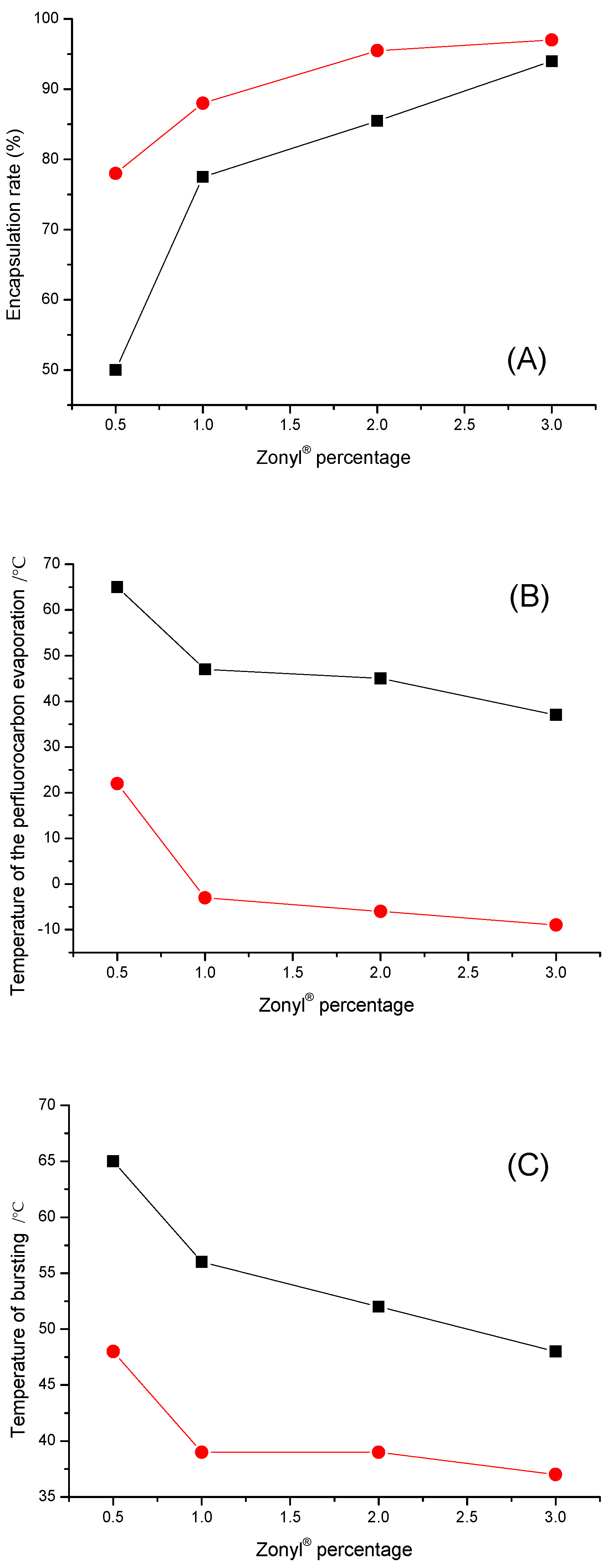
| Zonyl (%) | Encapsulated PFH (%) | Onset PFH Evaporation Temperature (°C) | Onset PFH Bursting Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 50 | 65 | 65 |
| 1 | 77.5 | 47 | 56 |
| 2 | 85.5 | 45 | 52 |
| 3 | 94 | 37 | 48 |
| Zonyl® (%) | Encapsulated PFP (%) | Onset PFP Evaporation Temperature (°C) | Onset PFP Bursting Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 78 | 22 | 48 |
| 1 | 88 | −3 | 39 |
| 2 | 95.5 | −6 | 39 |
| 3 | 97 | −9 | 37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corvis, Y.; Rosa, F.; Tran, M.-T.; Renault, G.; Mignet, N.; Crauste-Manciet, S.; Espeau, P. Thermal Analysis Tools for Physico-Chemical Characterization and Optimization of Perfluorocarbon Based Emulsions and Bubbles Formulated for Ultrasound Imaging. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020021
Corvis Y, Rosa F, Tran M-T, Renault G, Mignet N, Crauste-Manciet S, Espeau P. Thermal Analysis Tools for Physico-Chemical Characterization and Optimization of Perfluorocarbon Based Emulsions and Bubbles Formulated for Ultrasound Imaging. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorvis, Yohann, Frédéric Rosa, Minh-Tien Tran, Gilles Renault, Nathalie Mignet, Sylvie Crauste-Manciet, and Philippe Espeau. 2022. "Thermal Analysis Tools for Physico-Chemical Characterization and Optimization of Perfluorocarbon Based Emulsions and Bubbles Formulated for Ultrasound Imaging" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020021
APA StyleCorvis, Y., Rosa, F., Tran, M.-T., Renault, G., Mignet, N., Crauste-Manciet, S., & Espeau, P. (2022). Thermal Analysis Tools for Physico-Chemical Characterization and Optimization of Perfluorocarbon Based Emulsions and Bubbles Formulated for Ultrasound Imaging. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6020021










