Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites Reinforced with Silane-Modified Al2O3 Nanoparticles: An Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
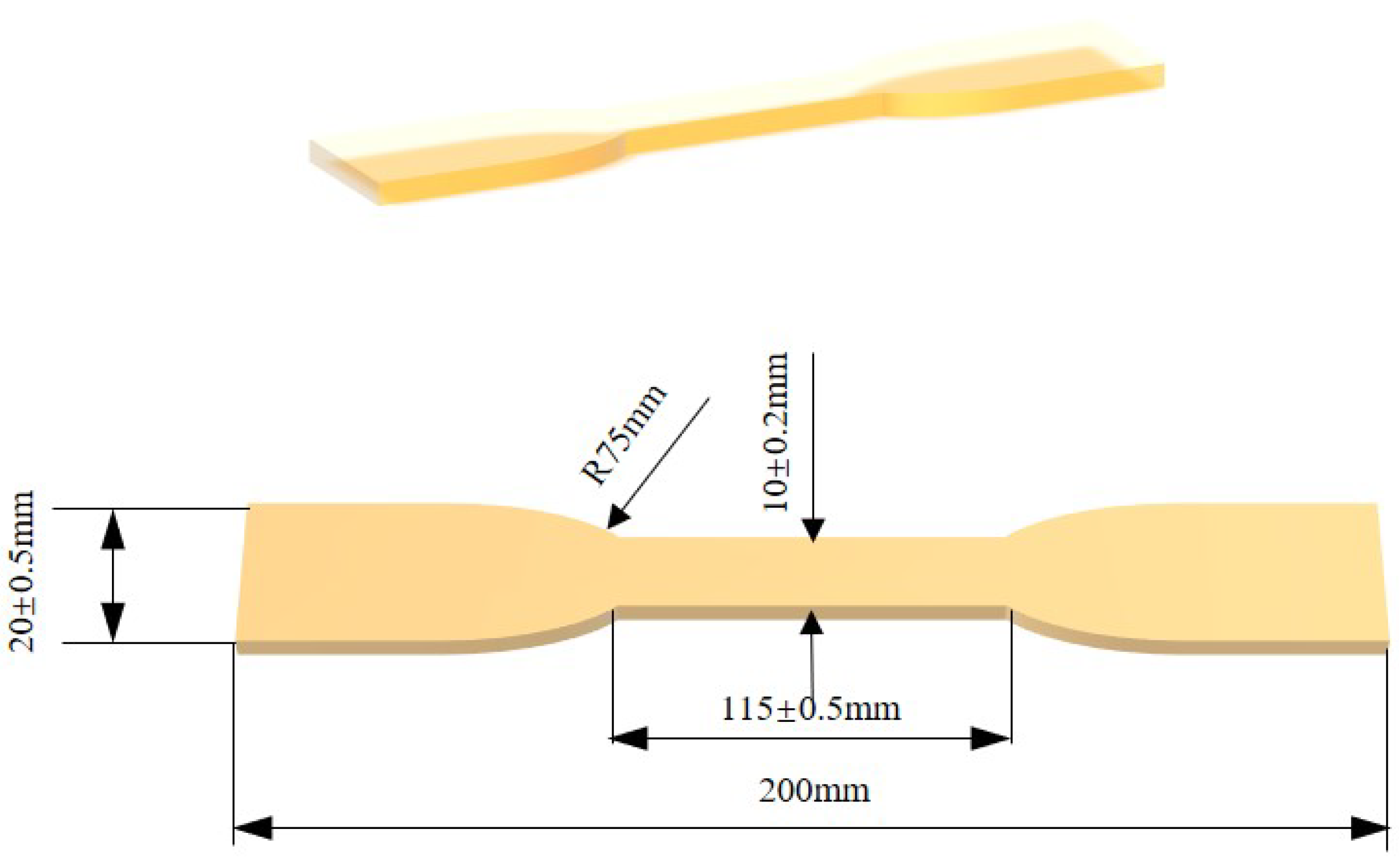
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Surface Modification of Nano-Al2O3
- (1)
- Pretreatment of Nano-Al2O3:
- Raw nanoparticles (50 g) were thermally treated at 200 °C for 1 h to eliminate surface adsorbates, followed by ultrasonic cleaning in acetone (5 min) and drying at 60 °C.
- (2)
- Silane Grafting:
- Hydrolysis: A~5 wt% silane/ethanol solution was acidified to pH 4 with acetic acid, then hydrolyzed at 30–35 °C for 2 h under stirring.
- Grafting: 5 g of pretreated Al2O3 was dispersed in the hydrolyzed solution, and the reaction proceeded at 60 °C for 4 h.
- Purification: Modified particles were collected by centrifugation (2000 RCF, 1 min), washed with ethanol to remove physiosorbed silanes, and vacuum-dried at 70 °C (4 h).

2.3. Preparation of m-Nano-Al2O3/Epoxy Composites
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Analyses of Surface Modification
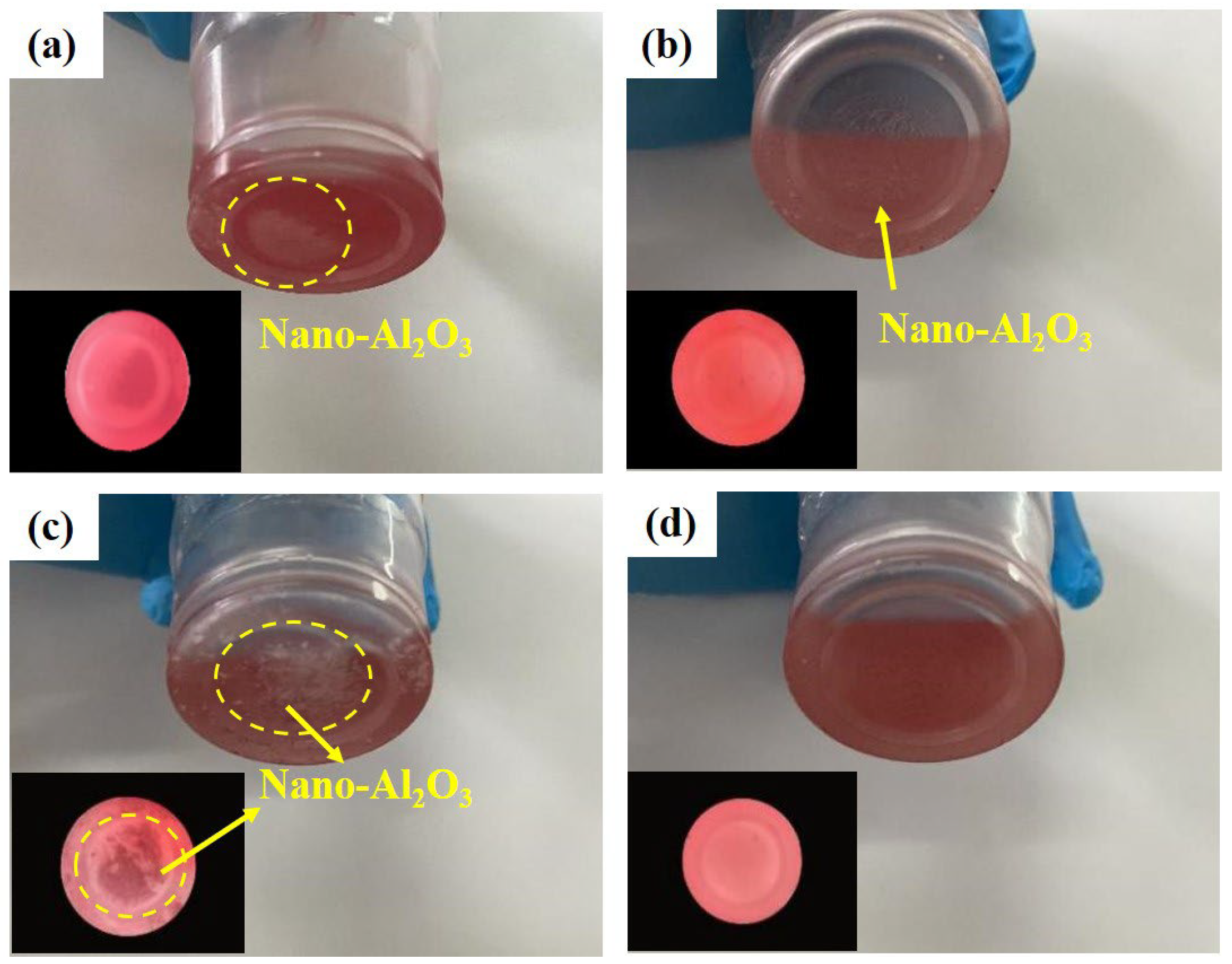
3.2. Dispersion Behavior
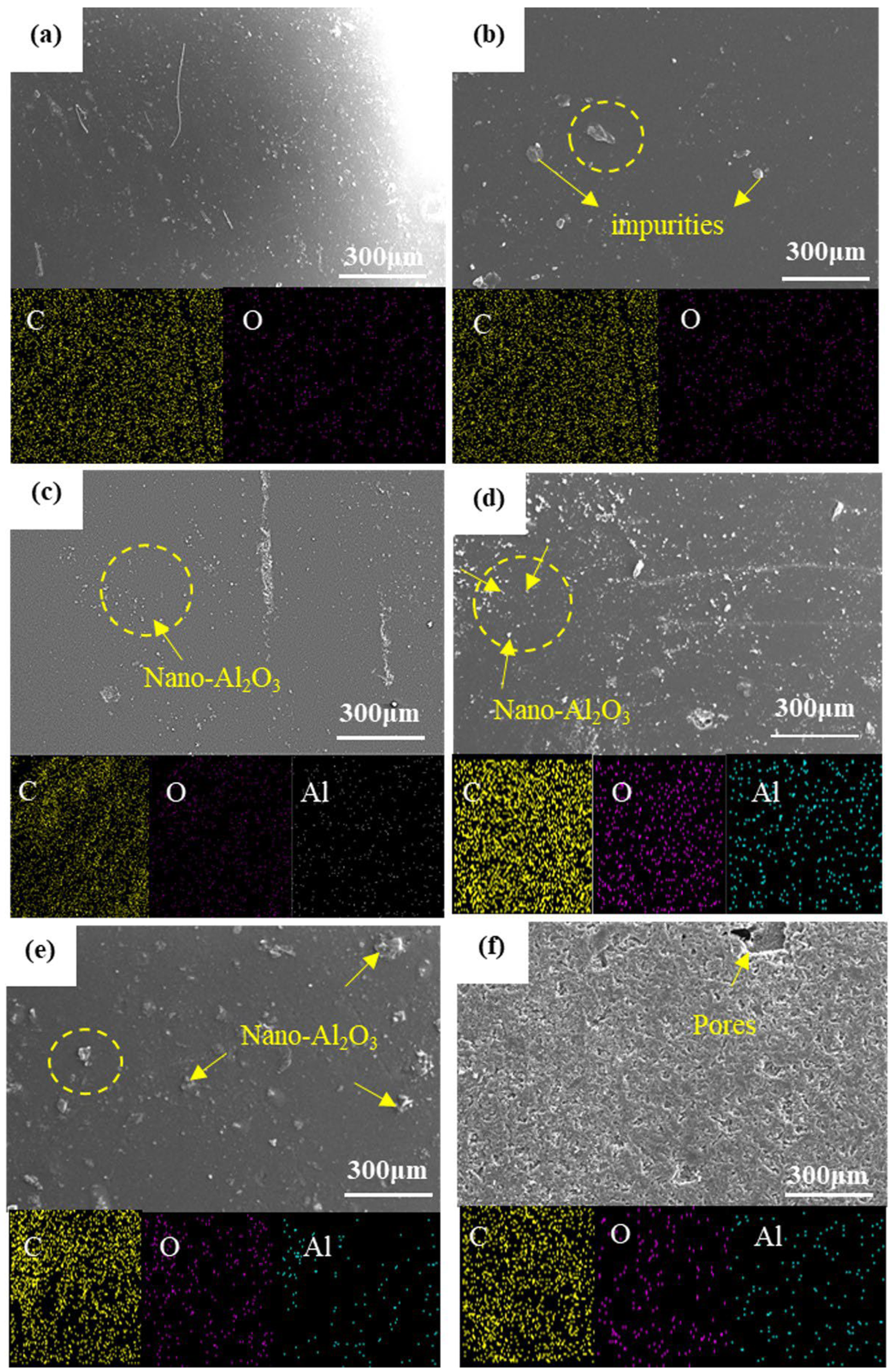
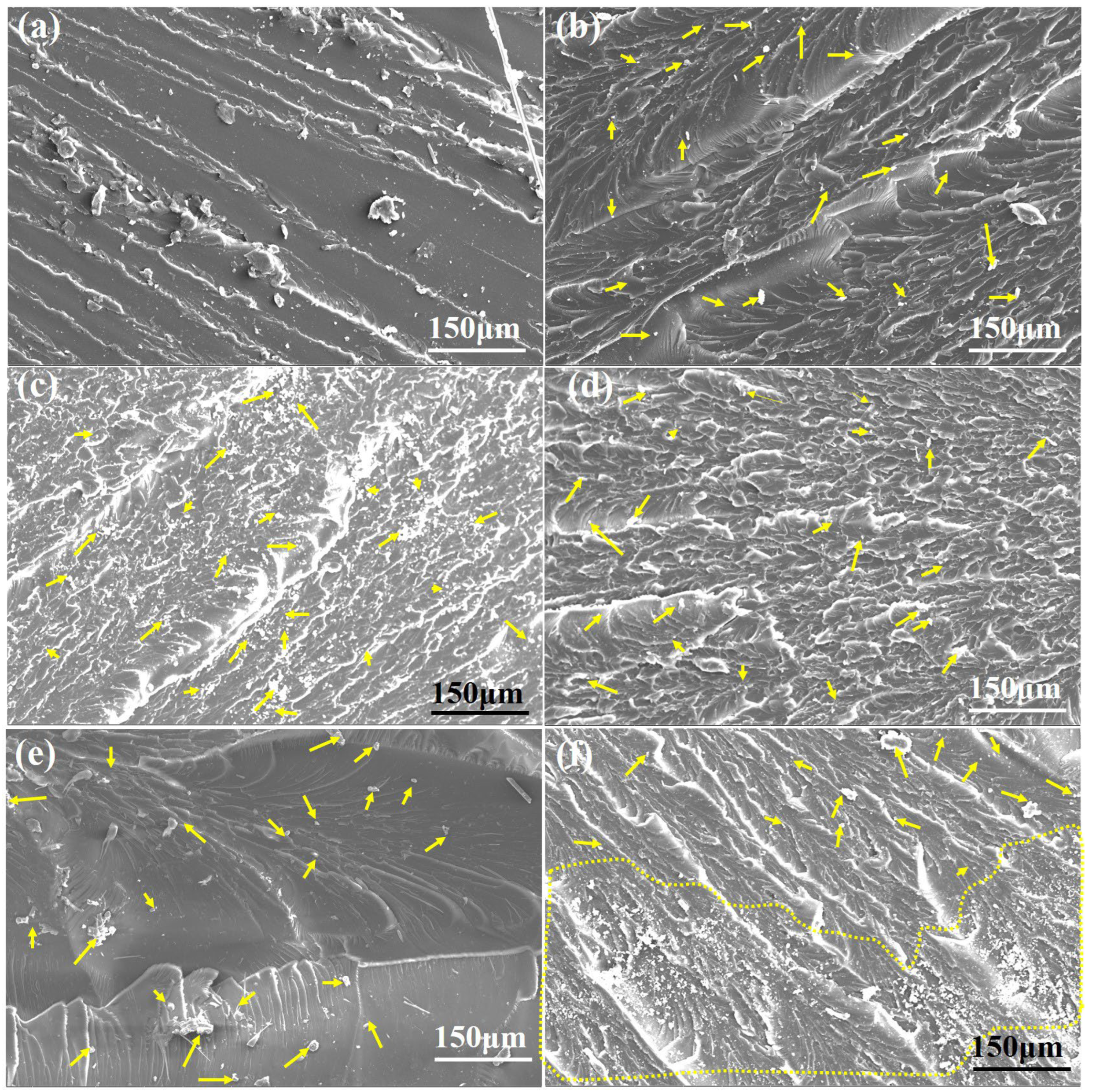
3.3. Microstructural Evaluation
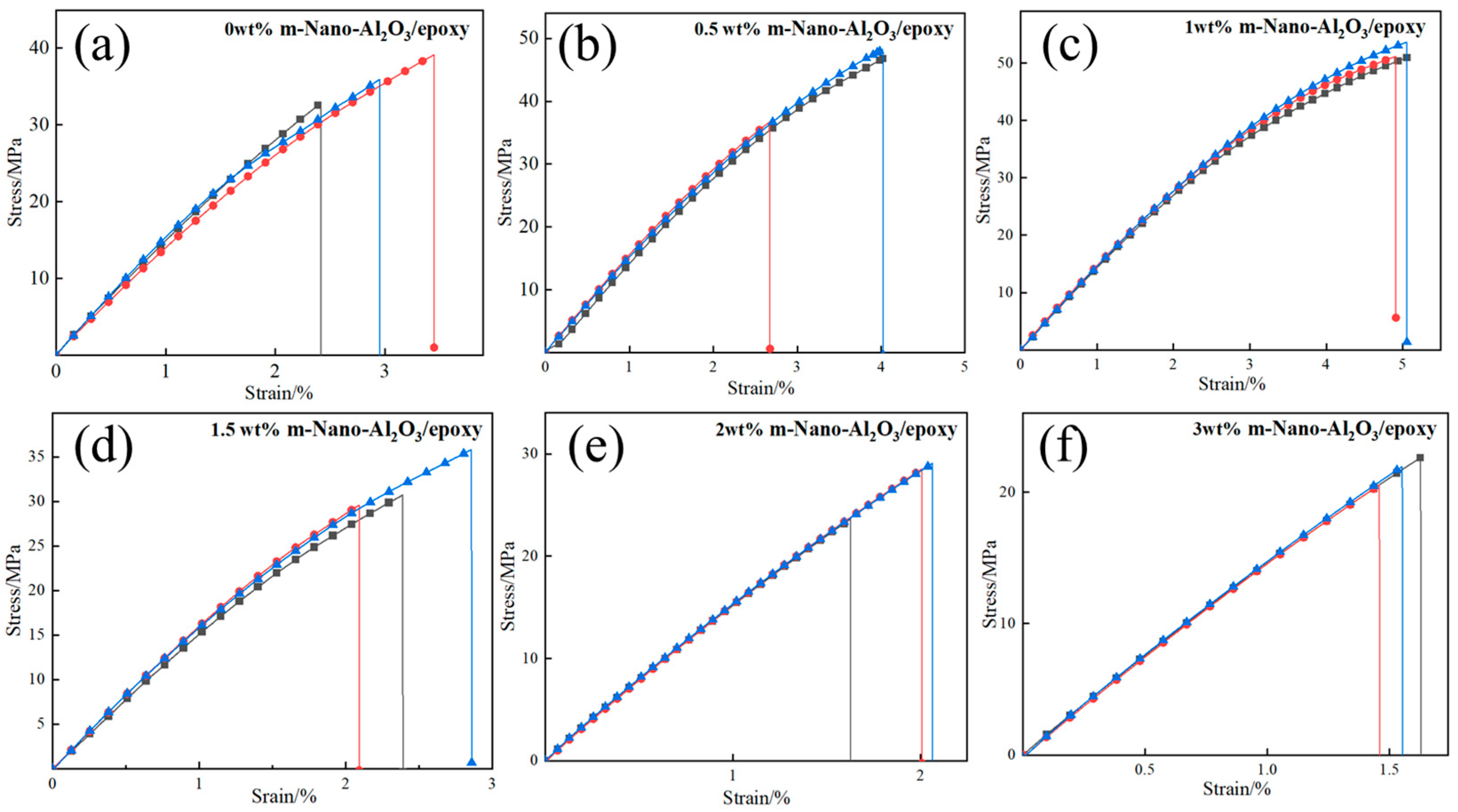
3.4. Mechanical Performance Optimization
3.5. Tensile Fracture Analysis
3.6. Distribution of m-Nano-Al2O3
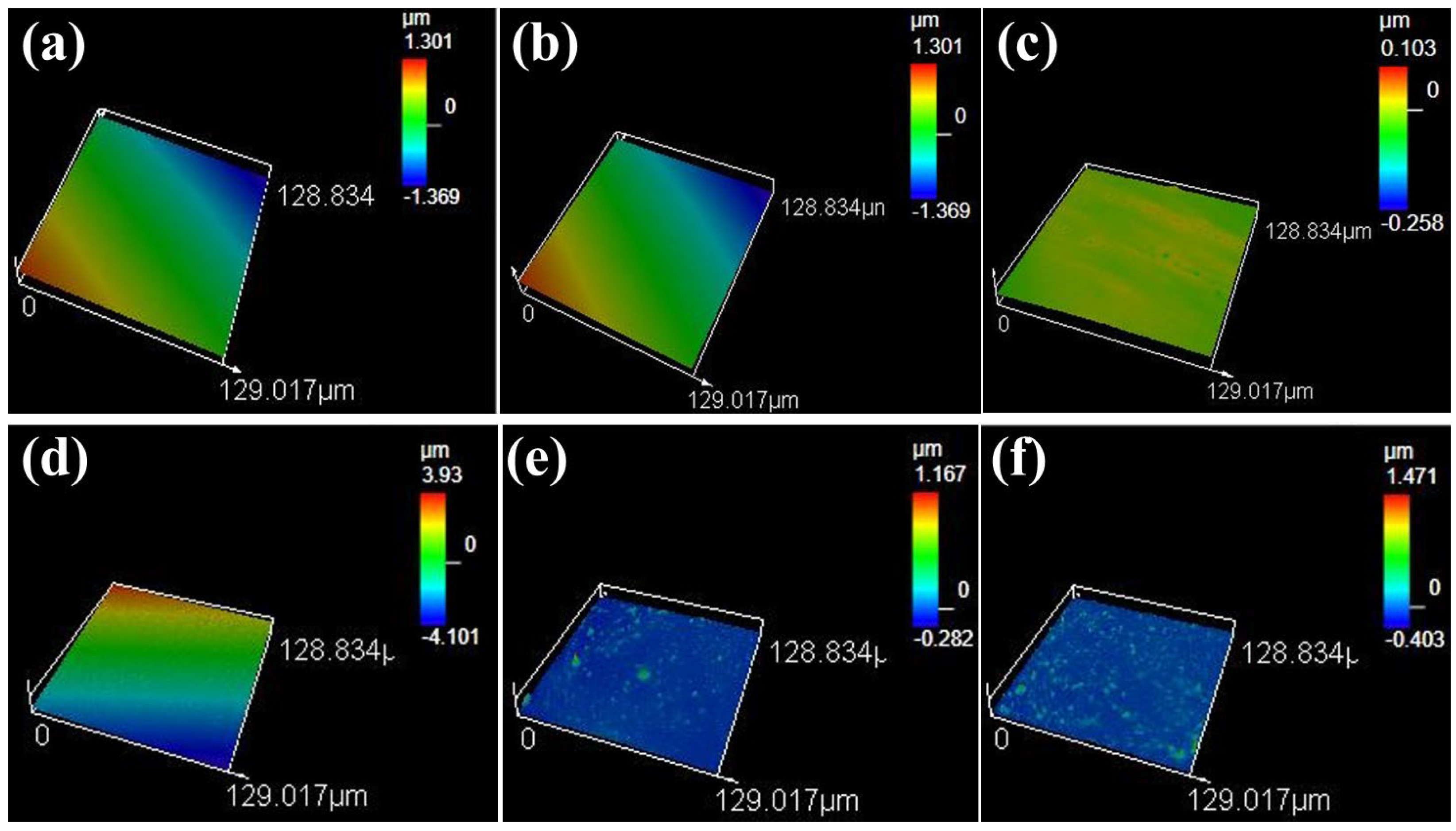
3.7. Surface Roughness Analysis
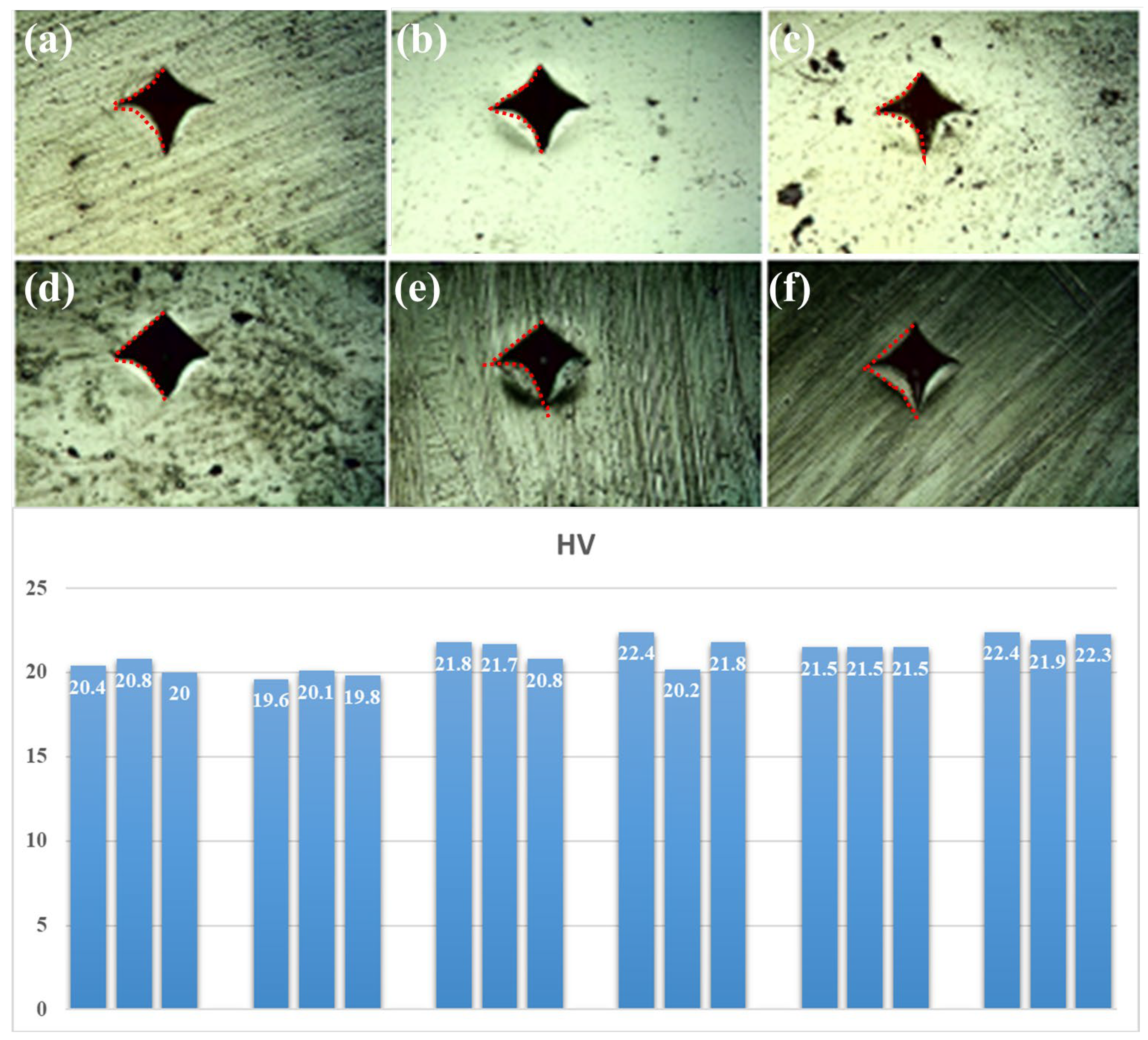
3.8. Hardness Test Analyses
4. Conclusions
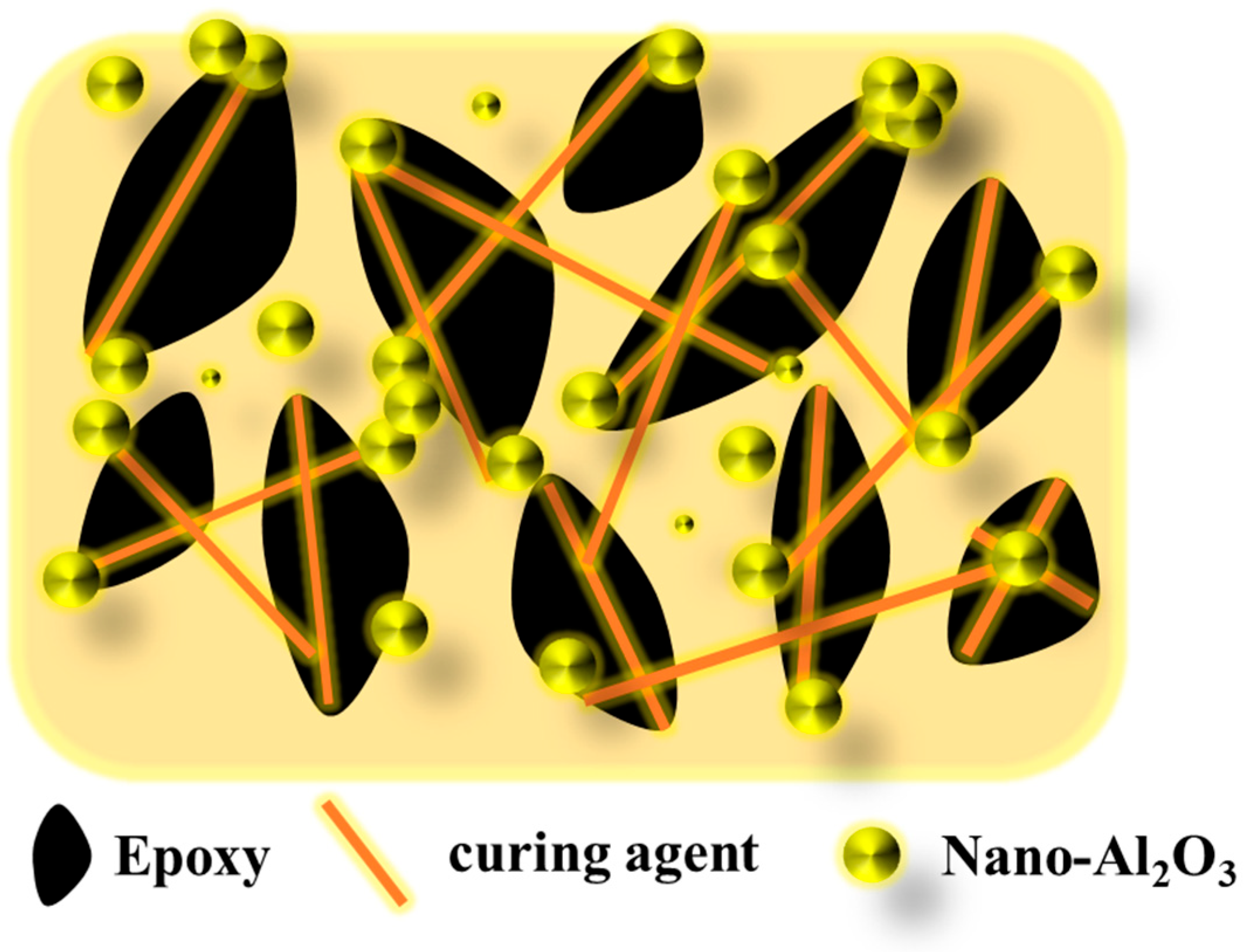
- The dispersion and stability of Nano-Al2O3 modified by the KH570 coupling agent in epoxy resin are the best. The KH570 modified Nano-Al2O3 contains active groups, such as Si-O-Si, which can combine better with epoxy groups and enhance the dispersion and stability of Al2O3 particles in the epoxy.
- The dispersibility of nanoparticles is optimal when the content of Nano-Al2O3 is 1 wt%, and the tensile strength is 51.9 MPa, which is 49.1% higher than that of pure epoxy resin. When the content exceeds 1 wt%, the nanoparticles gradually accumulate, causing agglomeration and defects in the m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy composites, and result in damage to the mechanical properties.
- The addition of m-Nano-Al2O3 in the matrix can increase the hardness of the epoxy resin. The 3wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy has the highest hardness among all the samples because of the inherent high hardness of alumina, which is an 8.8% increase compared to pure epoxy resin.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.-X.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. The influence of high content nano-Al2O3 on the properties of epoxy resin composites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2009, 48, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrgari, D.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Sabbagh-Alvani, A.; Rasoulianboroujeni, M.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L. Mechanical properties and tribological performance of epoxy/Al2O3 nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.N.; Alithari, A.S.; Hasan, H.S. Influence of adding tungsten carbide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the impact strength of epoxy based composite materials used in marine applications. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Li, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Nan, D. Enhancing mechanical properties of epoxy resin composites with aluminum oxide-modified graphene oxide. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 151, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Rhee, K.Y.; Alfantazi, A. Functionalized epoxy resins for enhanced interface properties and corrosion resistance: Tailoring of surface and interface properties and performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2025, 25, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naous, W.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.X.; Naito, K.; Kagawa, Y. Morphology, tensile properties, and fracture toughness of epoxy/Al2O3 nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ning, R.; Zheng, Y. Study of SiO2 nanoparticles on the improved performance of epoxy and fiber composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2005, 24, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protyai, M.I.H.; Adib, F.M.; Taher, T.I.; Karim, M.R.; Rashid, A.B. Performance evaluation of kevlar fiber reinforced epoxy composite by depositing graphene/SiC/Al2O3 nanoparticles. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Xue, K.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Huang, Y. Epoxy composites with satisfactory thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding yet electrical insulation enabled by Al2O3 platelet-isolated MXene porous microsphere networks. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 248, 110425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeshev, A.; Mostovoy, A.; Shcherbakov, A.; Tastanova, L.; Akhmetova, M.; Apendina, A.; Orynbassar, R.; Lopukhova, M. The influence of pristine and aminoacetic acid-treated aluminum nitride on the structure, curing processes, and properties of epoxy nanocomposites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirbeygi, H.; Khosravi, H.; Tohidlou, E. Reinforcing effects of aminosilane-functionalized graphene on the tribological and mechanical behaviors of epoxy nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Bae, J.; Lee, K.J. Enhancement of adhesion between inorganic nanoparticles and polymeric matrix in nanocomposite by introducing polymeric thin film onto nanoparticles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1906–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kango, S.; Kalia, S.; Celli, A.; Njuguna, J.; Habibi, Y.; Kumar, R. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic–inorganic nanocomposites—A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1232–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.-Y.; Baek, J.-B. Nanocomposites derived from polymers and inorganic nanoparticles. Materials 2010, 3, 3654–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowski, T.; Krysztafkiewicz, A. Influence of silane coupling agents on surface properties of precipitated silicas. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 172, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.R.; Yu, Z.M.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, Y. Study on surface modification of nano-alumina with silicane coupling agent KH550. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 528, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Albano, C.; Ichazo, M.; Díaz, B. Effects of coupling agents on mechanical and morphological behavior of the PP/HDPE blend with two different CaCO3. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Deng, J.; Guan, X. Surface modification of nano-zinc oxide by silane coupling agents. Nat. Sci. J.-Xiangtan Univ. 2006, 28, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Varley, R.J.; Mathys, Z.; Cheng, Y.B.; Simon, G.P. Effect of organo-phosphorus and nano-clay materials on the thermal and fire performance of epoxy resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 1233–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, X.; Thomann, R.; Mülhaupt, R.; Finter, J.; Berglund, L. Synthesis of amine-cured, epoxy-layered silicate nanocomposites: The influence of the silicate surface modification on the properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tjiu, W.C.; Tong, Y.; He, C.; Goh, S.S.; Chung, T.S. Morphology and fracture behavior of intercalated epoxy/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gu, A.; Liang, G.; Ji, L.; Yuan, L. Preparation and properties of novel resins based on cyanate ester and hyperbranched polysiloxane. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, R.H.; Sadeq, A.S.; Fares, M.N.; Salahshour, S.; Sabetvand, R. Modeling the thermal performance of hybrid paraffin-air nanostructure in a heat sink: Effect of atomic ratio of Al2O3 nanoparticles. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Tian, W.; Chao, X. Nanomaterial textiles for personal thermal management: Perspectives of the processes and properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.; Aval, H.J.; Jamaati, R. Influence of Al2O3 addition on microstructure, mechanical strength, and wear behavior of AA7075-Al2O3 matrix composites fabricated using deformation-driven metallurgy. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1040.2-2006, GB/T 1040.2, 2006/1S0527-2:1993; Plastics-Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Cui, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, W. Effect of alumina on the structure and properties of polyimide matrix films. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2016, 45, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Bai, L.; Du, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G. Effect of micro-Al2O3 contents on mechanical property of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 91, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Bao, C.; Cao, Y. Effect of the addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the magnetic properties of Fe soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 399, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.P.; Yan, J.; Liu, J. Surface modification of superfine aluminum oxide powders. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 3963–3966. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Huang, Z.; Jin, G.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y. Preparation of Inorganic Filler Modified Epoxy Resin Adhesive and Study on Its Compatibility with UDMH. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1802, 022046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.-K.; Cheung, H.-y.; Lau, K.-t.; Zhou, L.-m.; Ho, M.-w.; Hui, D. Cluster size effect in hardness of nanoclay/epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2005, 36, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
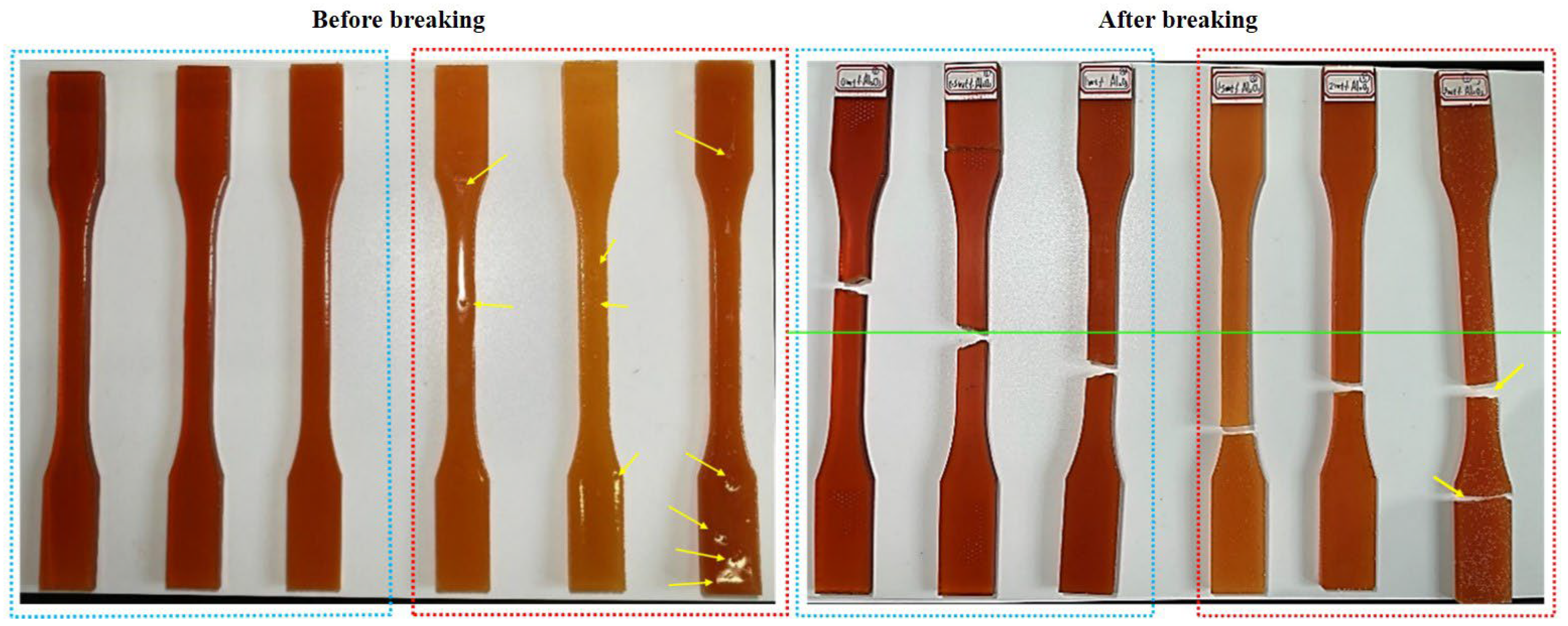





| m-Nano-Al2O3 Content/wt% | 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 32.7 | 36.3 | 51.2 | 30.7 | 23.7 | 20.5 |
| II | 32.9 | 48.1 | 50.9 | 33.6 | 28.4 | 21.9 |
| III | 38.8 | 45.8 | 53.6 | 35.8 | 29.1 | 22.6 |
| Average value | 34.8 | 43.4 | 51.9 | 33.4 | 27.1 | 21.7 |
| Standard deviations | 2.83 | 5.11 | 1.21 | 2.09 | 2.40 | 0.87 |
| Enhanced strength | 0 | 24.7 | 49.1 | −4.0 | −22.1 | −37.6 |
| Samples | D1 (μm) | D2 (μm) | HV | HV Average | Standard Deviations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat epoxy | 212.462 | 213.99 | 20.4 | 20.4 | 0.4 |
| 205.583 | 217.047 | 20.8 | |||
| 210.933 | 220.104 | 20 | |||
| 0.5 wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy | 219.34 | 215.519 | 19.6 | 19.8 | 0.255 |
| 216.283 | 213.226 | 20.1 | |||
| 214.754 | 217.811 | 19.8 | |||
| 1 wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy | 203.291 | 209.405 | 21.8 | 21.4 | 0.543 |
| 206.348 | 207.112 | 21.7 | |||
| 210.169 | 212.462 | 20.8 | |||
| 1.5 wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy | 207.112 | 200.234 | 22.4 | 21.5 | 1.136 |
| 217.047 | 210.933 | 20.2 | |||
| 207.876 | 204.819 | 21.8 | |||
| 2 wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy | 207.876 | 207.876 | 21.5 | 21.5 | 0 |
| 215.519 | 200.234 | 21.5 | |||
| 200.998 | 214.754 | 21.5 | |||
| 3 wt% m-Nano-Al2O3/epoxy | 201.762 | 204.819 | 22.4 | 22.2 | 0.255 |
| 206.348 | 205.583 | 21.9 | |||
| 202.526 | 205.583 | 22.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Chao, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, M. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites Reinforced with Silane-Modified Al2O3 Nanoparticles: An Experimental Study. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050252
Zhang T, Chao X, Liang J, Wang B, Sun M. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites Reinforced with Silane-Modified Al2O3 Nanoparticles: An Experimental Study. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(5):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050252
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ting, Xujiang Chao, Junhao Liang, Bin Wang, and Mengmeng Sun. 2025. "Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites Reinforced with Silane-Modified Al2O3 Nanoparticles: An Experimental Study" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 5: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050252
APA StyleZhang, T., Chao, X., Liang, J., Wang, B., & Sun, M. (2025). Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites Reinforced with Silane-Modified Al2O3 Nanoparticles: An Experimental Study. Journal of Composites Science, 9(5), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050252








