Proving Partial Miscibility in Poly(L-lactic acid)/Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Blends Using the Spherulite Observation Method
Abstract
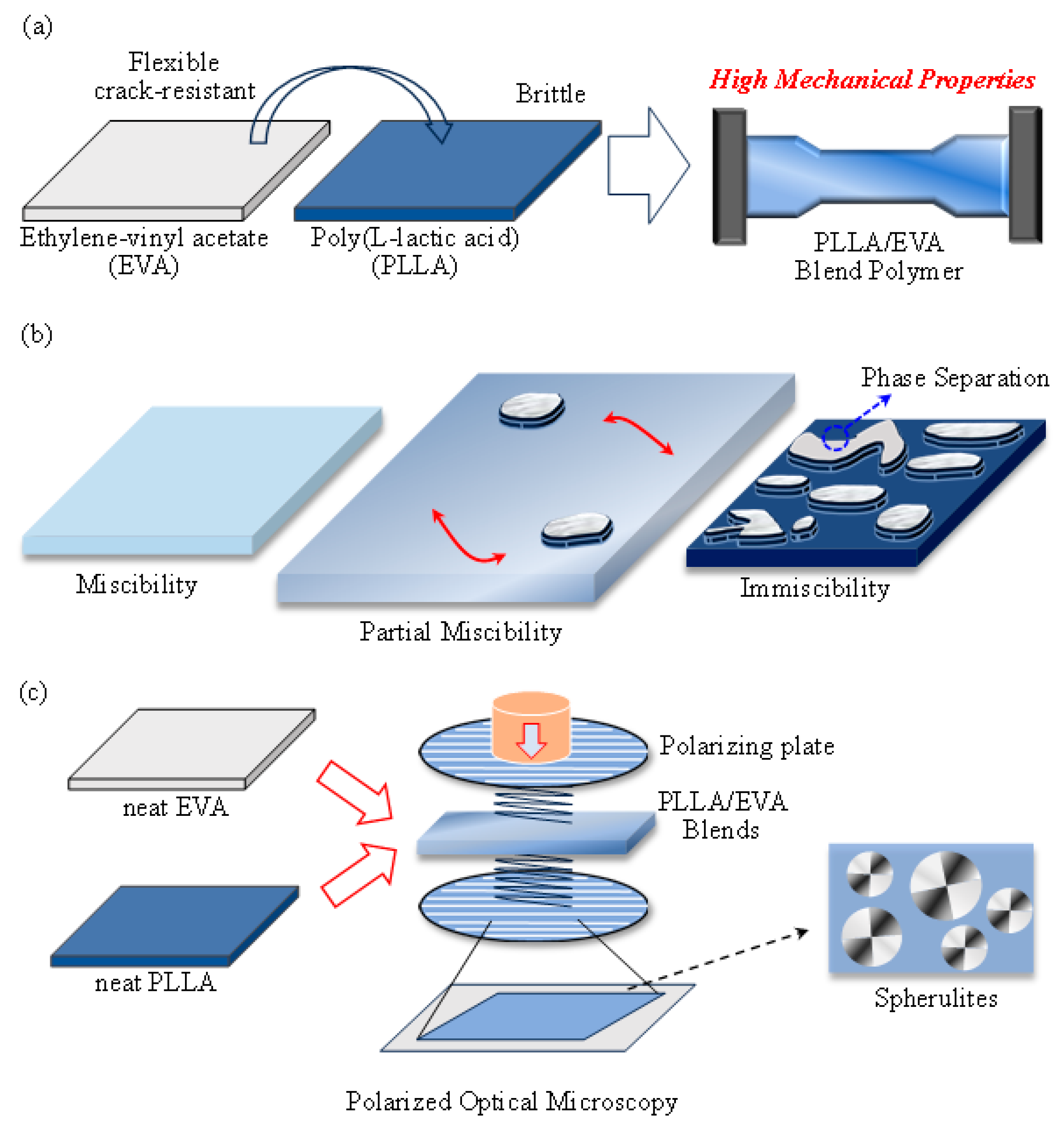
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
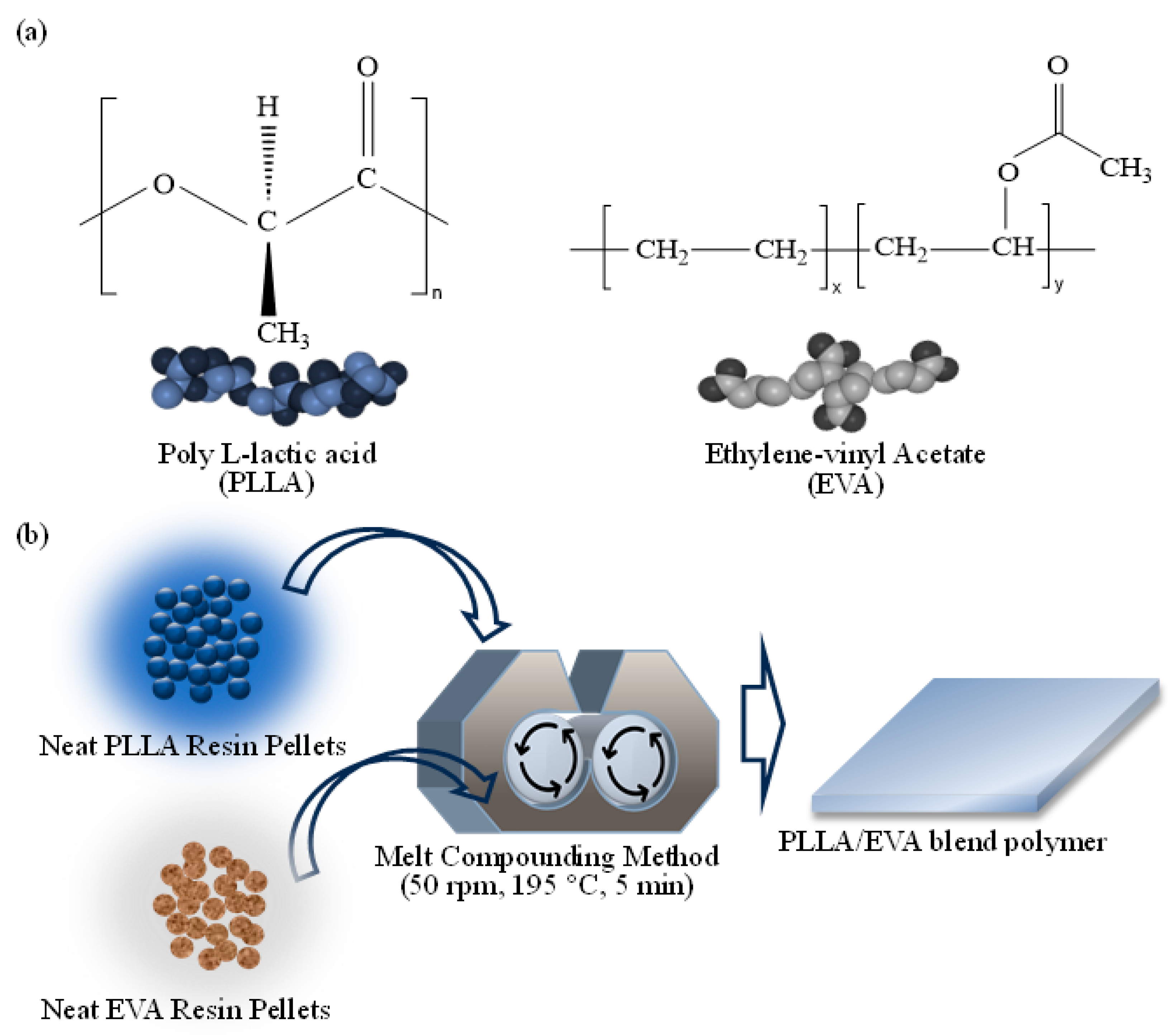
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Blends
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
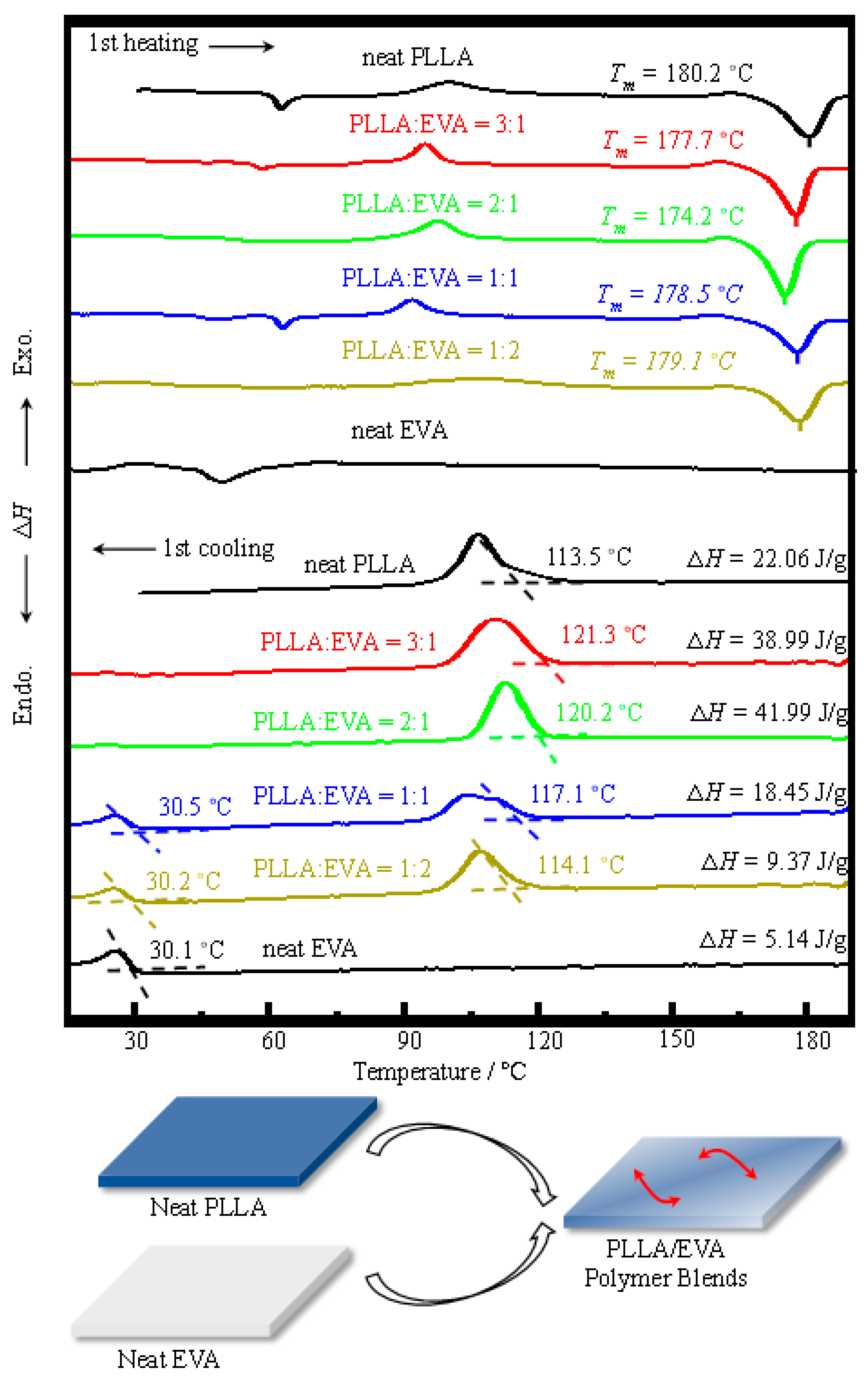
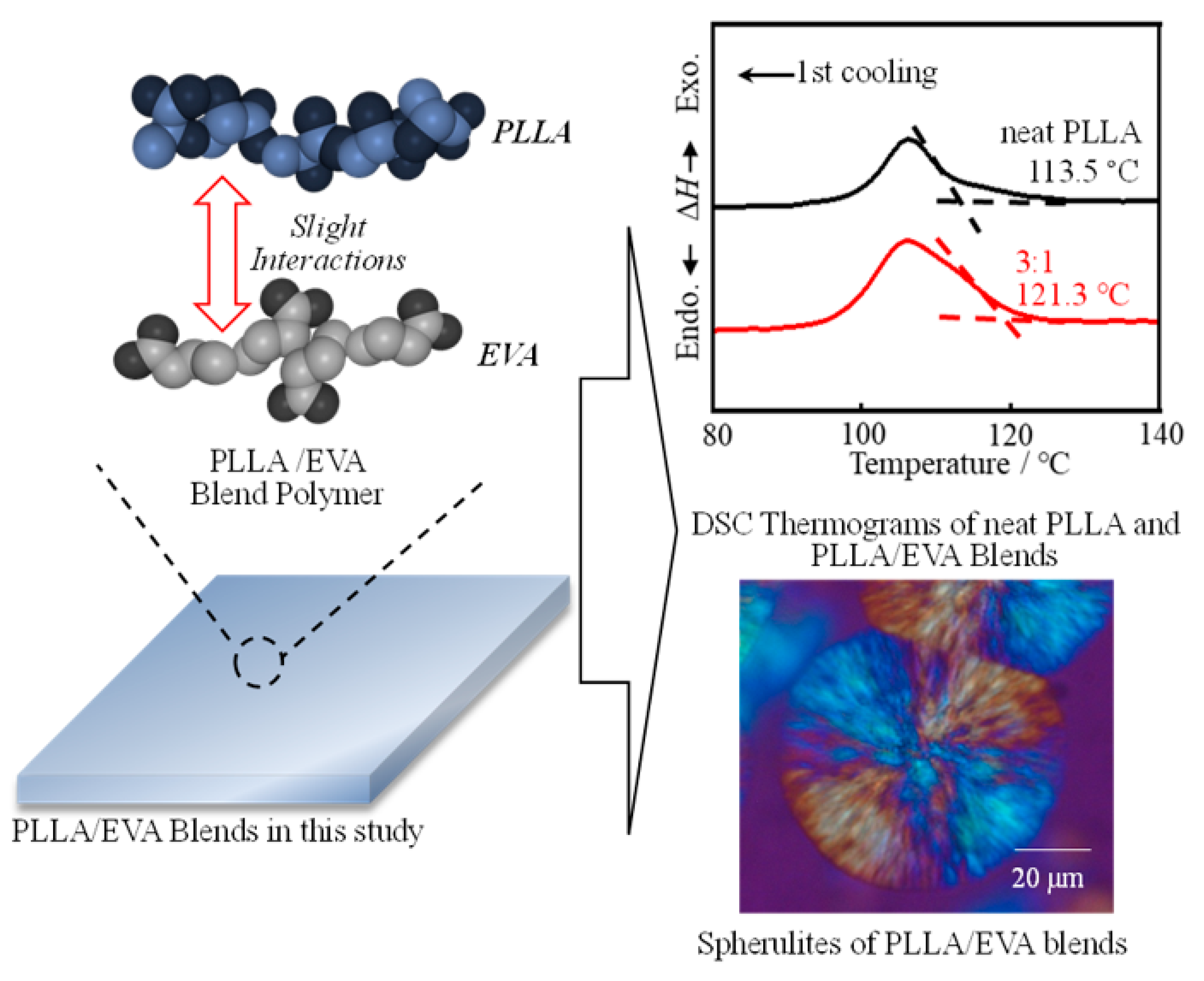
3.1. Thermal Behavior of PLLA:EVA Polymer Blends
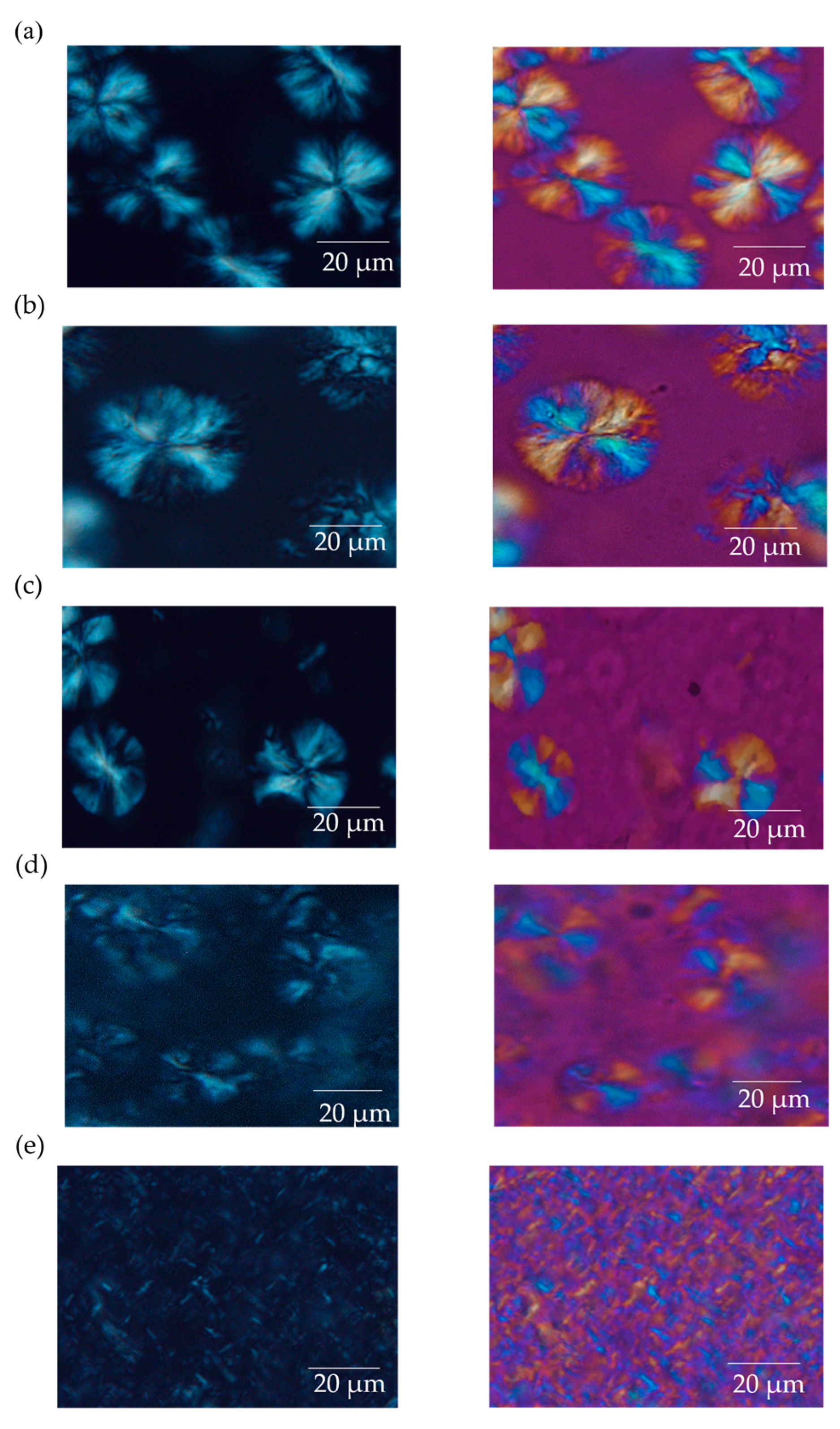
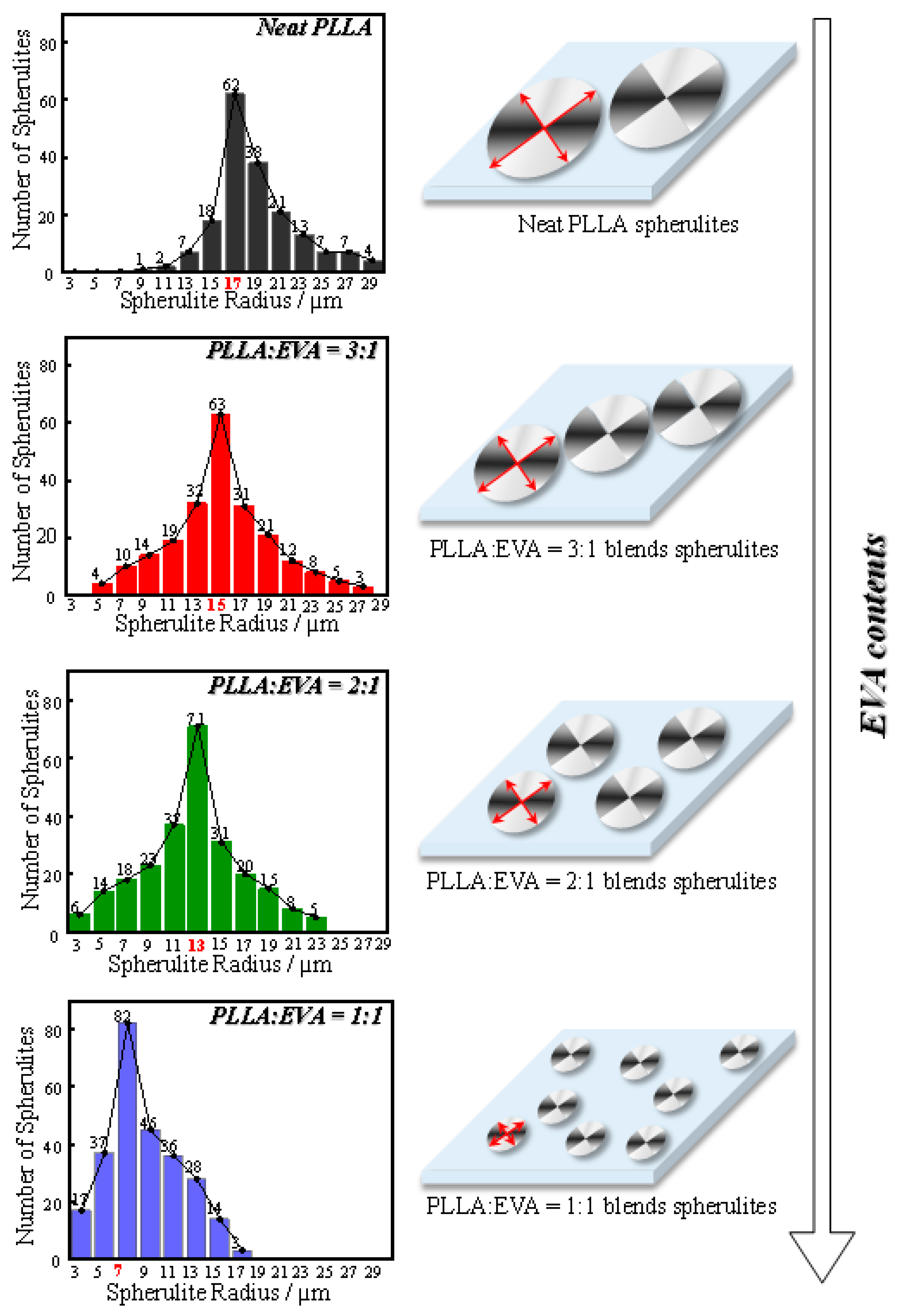
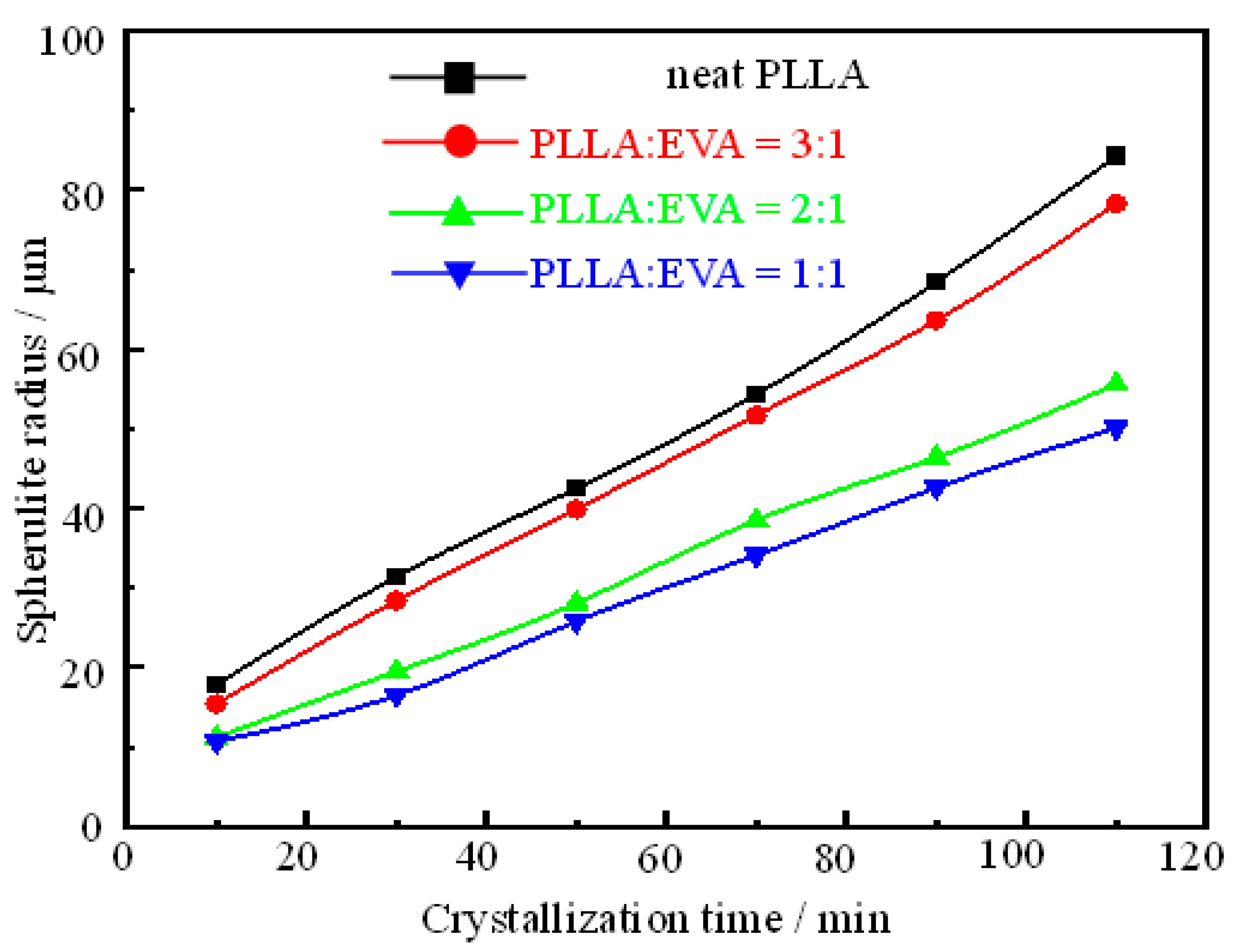
3.2. Spherulite Formation and Size Distribution in PLLA:EVA Polymer Blends
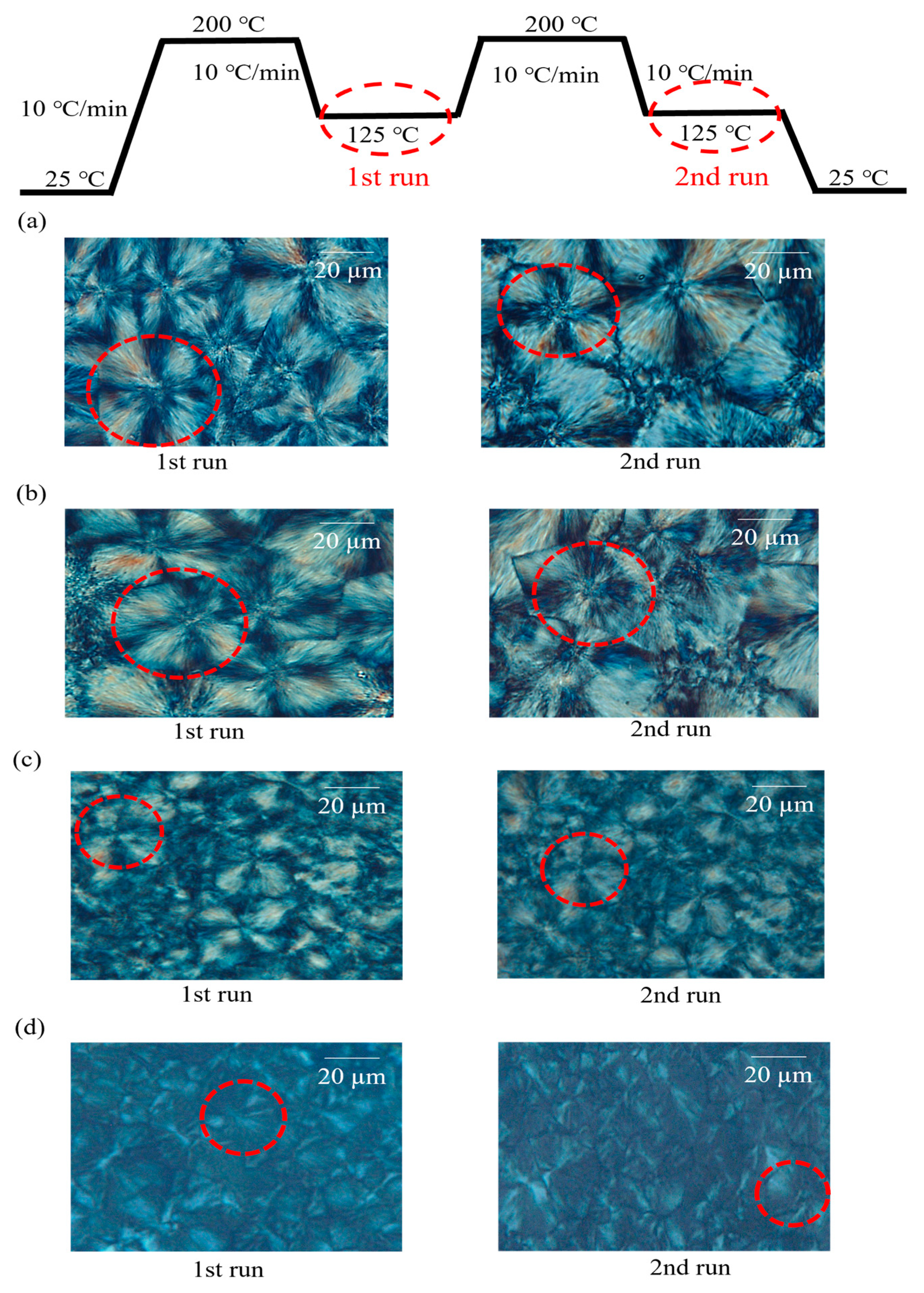
3.3. Characterization of Spherulite Formation/Growth Behavior in PLLA:EVA Polymer Blends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, W.; Shishehbor, M.; Guarín-Zapata, N.; Kirchhofer, N.D.; Li, J.; Cruz, L.; Wang, T.; Bhowmick, S.; Stauffer, D.; Manimunda, P.; et al. A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Niu, C.; Wang, R. Natural composite hydrogel regulated interface polymerization to prepare high performance nanofiltration membranes with wrinkled structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 717, 123567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, T.W.; Hull, D. An Introduction to Composite Materials, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.M. Mechanics of Composite Materials; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, K.K. Composite Materials: Science and Engineering, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A. A Concise Encyclopedia of Composite Materials; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.F.V. Structural Biomaterials, 3rd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Noe, M.M.; Sugawara, A.; Asoh, T.A.; Takashima, Y.; Harada, A.; Uyama, H. Composite hydrogels with host–guest interaction using cellulose nanocrystal as supramolecular filler. Polymer 2023, 277, 125979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, X.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Molecular Orientation-Regulated Bioinspired Multilayer Composites with Largely Enhanced Mechanical Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 21467–21475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrburger, P.; Ubbelohde, A.R.J.P.; Scott, R.A.M.; Johnson, J.W.; Richardson, M.O.W.; Watt, W.; Harris, B.; Ham, A.C. Interface in composite materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1980, 294, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F.; Wennerström, H. The Colloidal Domain: Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Technology Meet, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lyu, J.; Kim, M.; Ahn, H.; Lim, S.; Jang, H.W.; Chung, H.-J.; Lee, J.H. Quantitative Determination of Charge Transport Interface at Vertically Phase Separated Soluble Acene/Polymer Blends. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2215221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, T. Unlocking enhanced thermal conductivity in polymer blends through active learning. npj Comput. Mater. 2024, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathna, S.; Andersson, M.; Andersson, R. Recent Advances in Starch-Based Blends and Composites for Bioplastics Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uramatsu, T.; Morinaga, S.; Shibatsuka, T.; Kawauchi, T. Polymer alloys with high thermal properties consisting of polyfunctional benzoxazine derived from an oligonuclear phenolic compound and bismaleimide. Polym. J. 2024, 56, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sango, T.; Koubaa, A.; Ragoubi, M.; Yemele, M.C.N.; Leblanc, N. Insights into the functionalities of cellulose acetate and microcrystalline cellulose on water absorption, crystallization, and thermal degradation kinetics of a ternary polybutylene succinate-based hybrid composite. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, M.; Torlak, Y.; Choi, H.; Ak, M. Designed hybrid organic−inorganic nanocomposite film based on synergistic effect of conducting polymer and keggin type polyoxometalate clusters. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 167, 112406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, E.; Ma, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Kwon, J.; Evans, K.M.; Tang, X.; Tovmasyan, V.L.; Jan, J.; Arias, A.C.; et al. Functional composites by programming entropy-driven nanosheet growth. Nature 2023, 623, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, W.J. Physical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, B.D.; Broutman, L.J. Analysis and Performance of Fiber Composites, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, Y.; He, B. Preparation and properties of self-reinforced polypropylene composites modified with β-nucleating agents. Polymer 2024, 313, 127723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Oaki, Y.; Imai, H. Phase separation of composite materials through simultaneous polymerization and crystallization. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.A.; Wang, L.; Yao, J.; Lv, X.; Xu, Y.; Dou, W.; Zhang, H.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.-C. Characterizing microstructural patterns within the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuit in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 135, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, G. The Physics of Polymers: Concepts for Understanding Their Structures and Behavior; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yang, R.; Guo, Z.; Chen, K.; Feng, H.; Lu, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H.; Shui, L. Dynamic photomask directed lithography based on electrically stimulated nematic liquid crystal architectures. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmanis, E.; Nalamasu, O.; Houlihan, F.M. Materials Challenges and Alternatives for Advanced Photolithographic Patterning: From 193 to 157 nm and Beyond. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2000, 636, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wan, G. Technologies for studying phase-separated biomolecular condensates. Adv. Biotechnol. 2024, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Sarikaya, M.; Ritchie, R.O. Nano- and Microstructural Design of Advanced Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K.; Chu, P.; Xu, K.; Fujimori, A. Polypropylene-based nanocomposite with improved mechanical properties: Effect of cellulose nanofiber and polyrotaxane with partial miscibility. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, L.S.; Mofokeng, J.P. Morphology and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/graphene oxide polymeric composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 5329–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; Lichtenthaler, R.N.; de Azevedo, E.G. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Tan, J.; Fang, S.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, N. A biodegradable, osteo-regenerative and biomechanically robust polylactide bone screw for clinical orthopedic surgery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, J.; Liang, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Peng, S. Crystallization behaviors regulations and mechanical performances enhancement approaches of polylactic acid (PLA) biodegradable materials modified by organic nucleating agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banpean, A.; Sakurai, S. Confined crystallization of Poly(ethylene glycol) in spherulites of Poly(L-lactic acid) in a PLLA/PEG blend. Polymer 2021, 215, 123370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chu, P.; Rumon, R.H.; Fujimori, A. Enhancing in-plane elasticity of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic multilayer films with polyrotaxane and nanocellulose composites. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaziri, M.; Kossentini Kallel, T.; Mbarek, S.; Elleuch, B. Morphology development in polyethylene/polystyrene blends: The influence of processing conditions and interfacial modification. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Li, X.; Eerdunbayaer; Cheng, P.; Pan, P.; Dong, T. Controllable Poly(L-lactic acid) Soft Film with Respirability and Its Effect on Strawberry Preservation. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2021, 63, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Gazzano, M.; Delpouve, N.; Saiter, A. Contribution of the rigid amorphous fraction to physical ageing of semi-crystalline PLLA. Polymer 2017, 125, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.D.; Wagener, K.B. Ethylene/Vinyl Acetate Copolymers via Acyclic Diene Metathesis Polymerization. Examining the Effect of “Long” Precise Ethylene Run Lengths. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 5411–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.J.A.; Rahmatabadi, D.; Baghani, M.; Baniassadi, M. Experimental Evaluation of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Analysis, Morphology, Printability, and Shape Memory Performance of the Novel 3D Printed PETG-EVA Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2400069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Dong, Y.; Islam, M.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Fu, S.Y. Excellent triple-shape memory effect and superior recovery stress of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 203, 108609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.J.; Rejinold, N.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Long, Y.-Z.; Choi, G.; Choy, J.-H. Nano-enhanced thermo-mechanical properties of ethylene vinyl acetate with intumescent agent and organoclays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 262, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, N.; Korkmaz, E. Structural, thermal, mechanical and viscoelastic properties of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)/olefin block copolymer (OBC) blends. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Chen, M.; Che, Q.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xu, K. A novel ethylene-vinyl acetate-impact hardening polymers composite with impact-resistance ability, strain-rate sensitivity and enhanced mechanical performance. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.H.; Choi, M.C.; Nagappan, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.S. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blends and their foams. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 707, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, V.H.; Valapa, R.B.; Nayak, S.K.; Varghese, T.O. Investigation on the Influence of EVA Content on the Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Poly(lactic acid) Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, S.H. Synergistic effect of TiO2 nanoparticles and poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) on the morphology and crystallization behavior of polylactic acid. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Nara, C.; Rumon, R.H.; Xu, K.; Fujimori, A. Introduction of organo-modified carbon nanotubes into fluoropolymer-based hybrids containing polyrotaxane and cellulose nanofibers as organic fillers and their drawn orientation effects. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Zafar, M.T.; Maiti, S.N.; Ghosh, A.K. Physical blends of PLA with high vinyl acetate containing EVA and their rheological, thermo-mechanical and morphological responses. Polym. Test. 2017, 63, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Duarte, M.E.; Estrada-Moreno, I.A.; García-Casillas, P.E.; Vega-Rios, A. Stiff-Elongated Balance of PLA-Based Polymer Blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, M.N.; Chin, I.J.; Kim, Y.H. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(l-lactic acid)–poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Shioda, Y.; Fujimori, A. Creation of Quasi-DNA Origami at the Air/Water Interface Using the Collapsed Mechanism of Langmuir Monolayer. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202400063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Hasunuma, Y.; Fujimori, A. Characterization of Langmuir Monolayers for Nanodiamonds Surface-Modified with 12-Hydroxystearyl Chains and the Occurrence of Structural Colors. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202403262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasunuma, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamagishi, Y.; Fujimori, A. Preparation and Structural Properties of Gel Coating Films Containing Lipophilized Nanocarbon Particles Functionalized with Thixotropic Chains. J. Oleo Sci. 2025, 74, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Maiti, S.N.; Ghosh, A.K. Mechanical, morphological, and solid-state viscoelastic responses of poly(lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate super-tough blend reinforced with halloysite nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10278–10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábi, T. The application of the synergistic effect between the crystal structure of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and the presence of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) to produce highly ductile PLA/EVA blends. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, M.H.; Alharby, T.S.; Alamri, S.N. Enhancement of structural, morphological, thermal, optical and mechanical characteristics of PVA/PEO blends based on acetate fillers and infrared laser irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2025, 229, 112488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, Y.; Terui, R.; Hoshino, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Fujimori, A. Spherulitic Characterization and Hierarchical Structural Evaluation of Azacalixarene-Polyethylene Glycol Copolymers Containing s-Triazine Rings. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2300117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Sato, H.; Tsuji, H.; Ozaki, Y. Crystal modifications and thermal behavior of poly(L-lactic acid) revealed by infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8012–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rumon, R.H.; Nara, C.; Xu, K.; Fujimori, A. Proving Partial Miscibility in Poly(L-lactic acid)/Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Blends Using the Spherulite Observation Method. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030130
Rumon RH, Nara C, Xu K, Fujimori A. Proving Partial Miscibility in Poly(L-lactic acid)/Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Blends Using the Spherulite Observation Method. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(3):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030130
Chicago/Turabian StyleRumon, Rokibul Hasan, Chisato Nara, Kai Xu, and Atsuhiro Fujimori. 2025. "Proving Partial Miscibility in Poly(L-lactic acid)/Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Blends Using the Spherulite Observation Method" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 3: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030130
APA StyleRumon, R. H., Nara, C., Xu, K., & Fujimori, A. (2025). Proving Partial Miscibility in Poly(L-lactic acid)/Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Blends Using the Spherulite Observation Method. Journal of Composites Science, 9(3), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9030130






