Sustainable Reprocessing of Thermoset Composite Waste into Thermoplastics: A Polymer Blend Approach for Circular Material Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Processing of Second-Generation Thermoplastic Composites
2.2.1. Fiber Recycling Process
2.2.2. Preparation of Second-Generation Thermoplastic Composites (STCs)
2.3. Analysis of EPG Thermoset Composite Scrap Materials
2.3.1. Particle Size Determination (Sieving)
2.3.2. Measurement of EPG Fiber Lengths
2.3.3. Burn-Off Test
2.4. Analysis of Second-Generation Thermoplastic Composite Materials
2.4.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.4.3. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analyses of STCs
2.4.4. Density and Water Absorption of the STCs
2.5. Mechanical Properties of the STCs
3. Results and Discussion
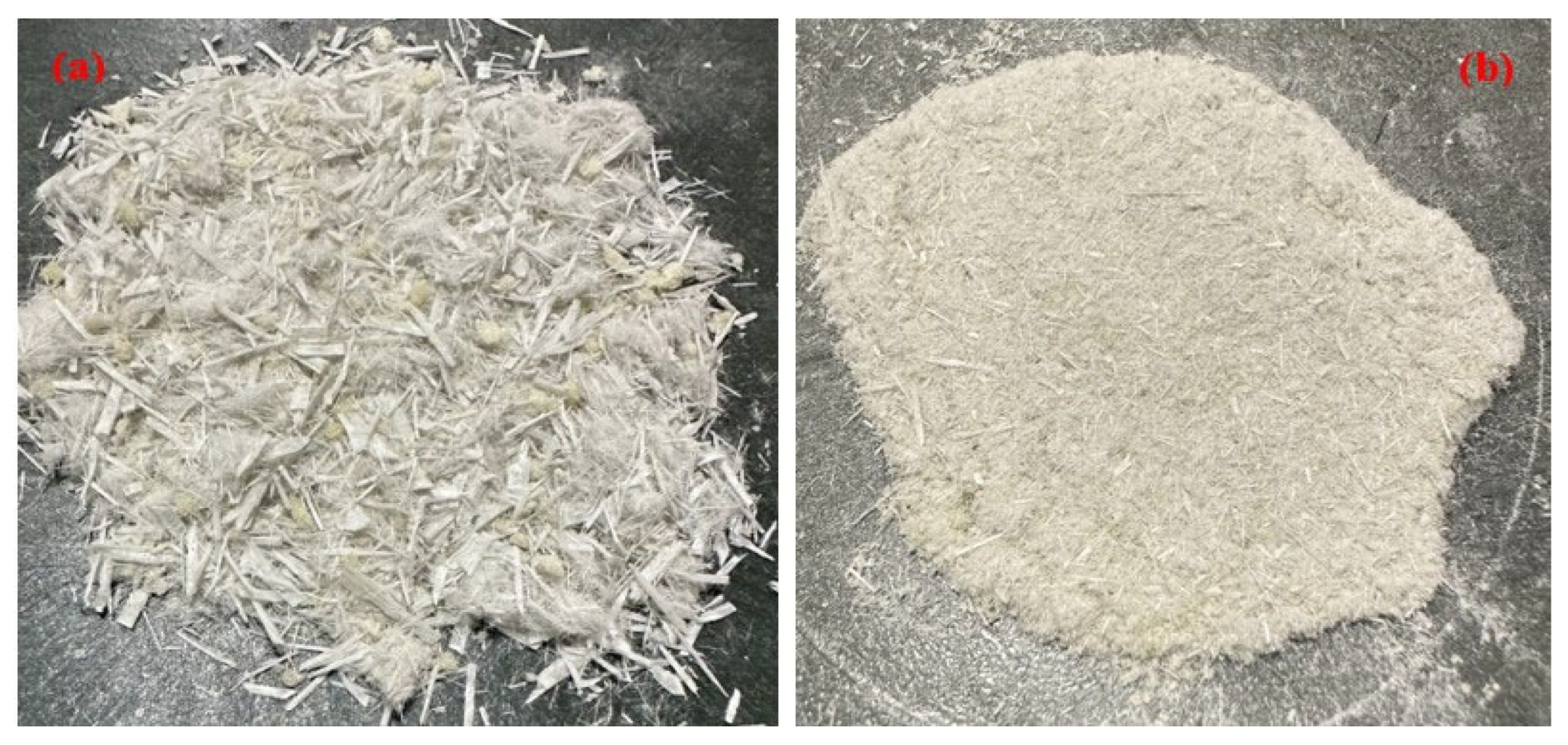
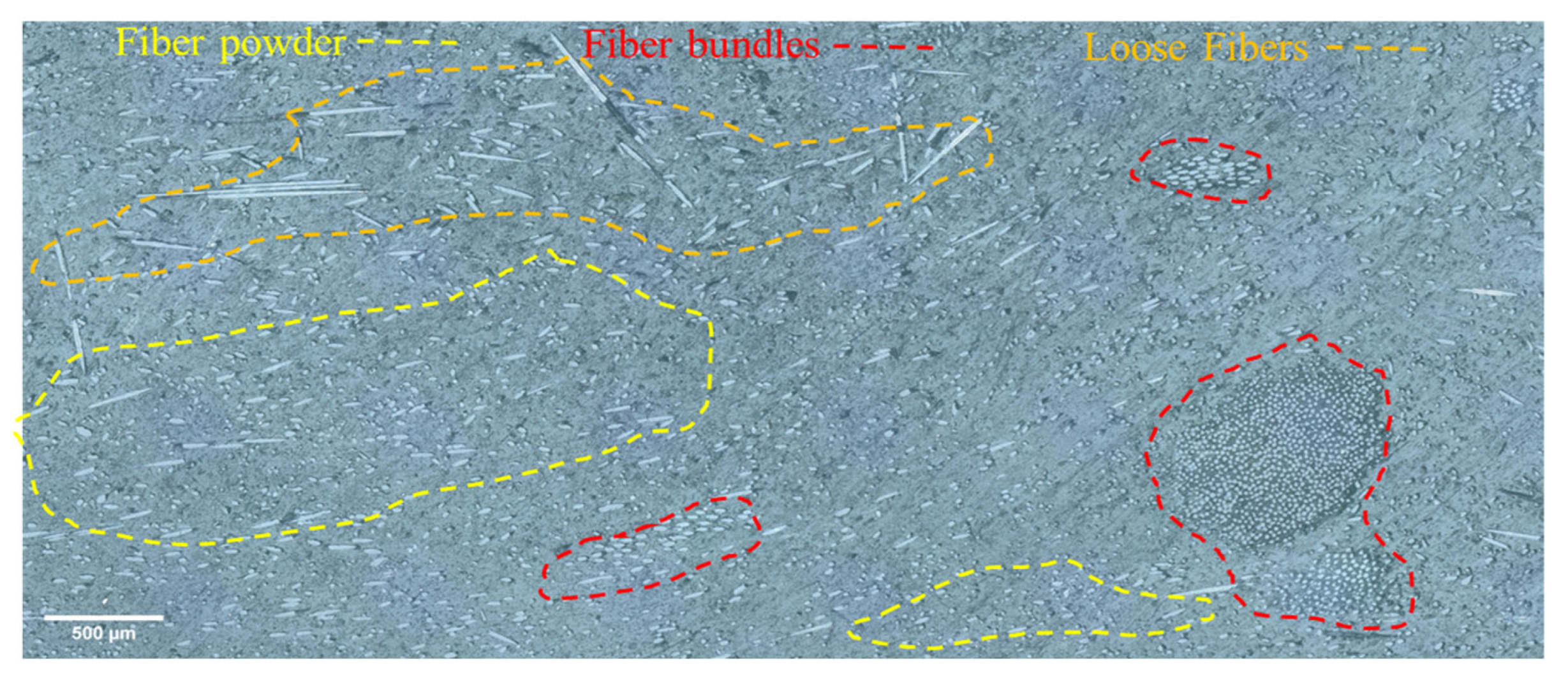
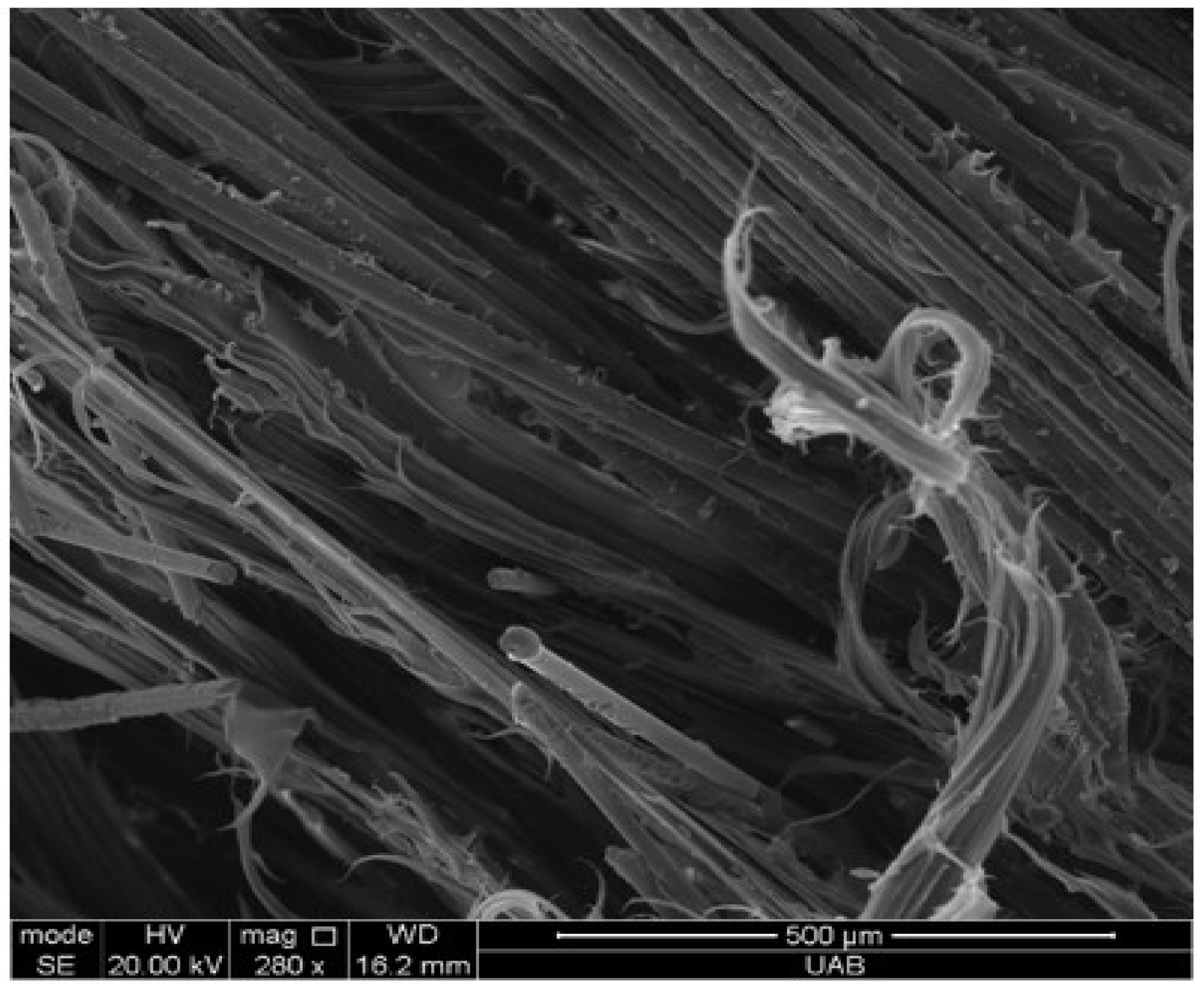
3.1. Assessment of Thermoset Composite Scrap Materials (EPG)
3.2. Assessment of Second-Generation Thermoplastic Composite Materials
3.2.1. Assessment of Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA/DTA)
3.2.2. Assessment of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.2.3. Assessment of the Density and Moisture Absorption of STCs
3.3. Assessment of the Morphological Characteristics of STCs
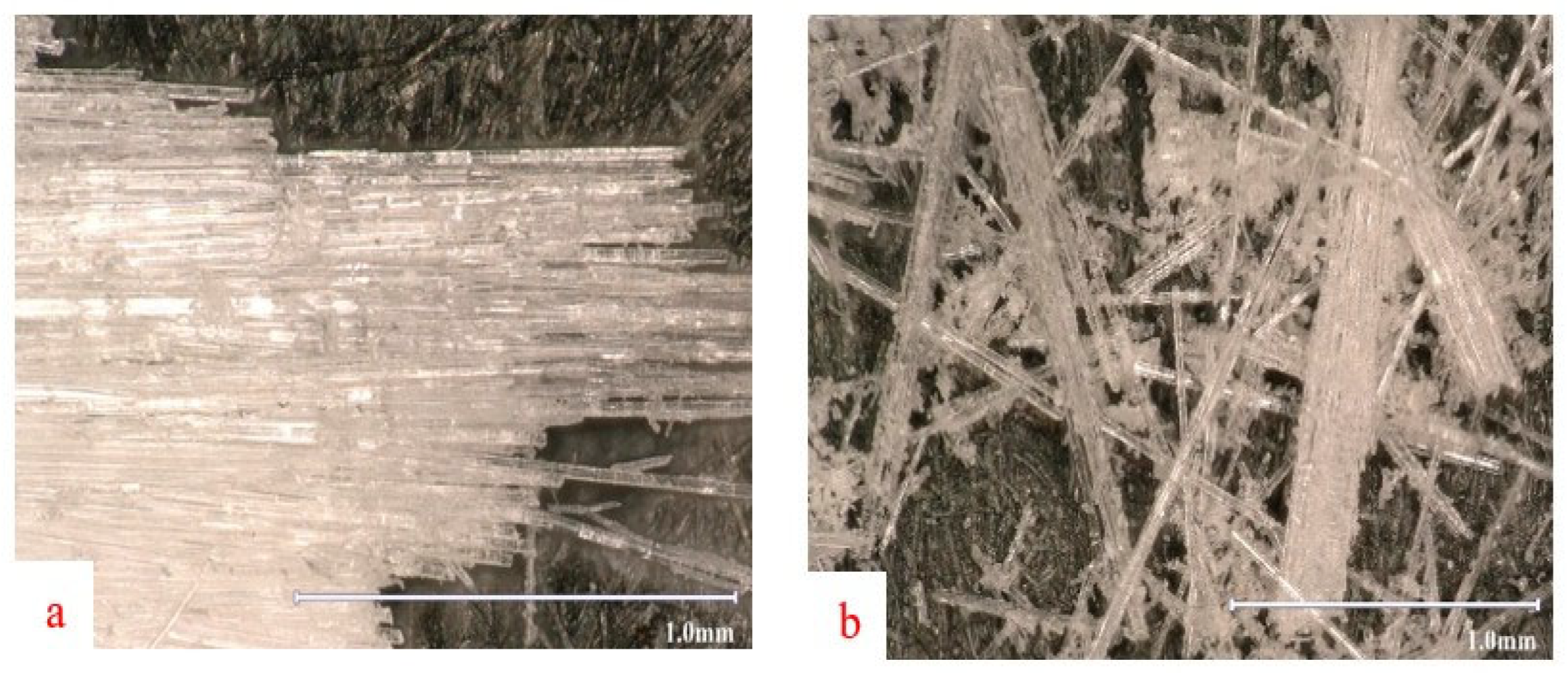
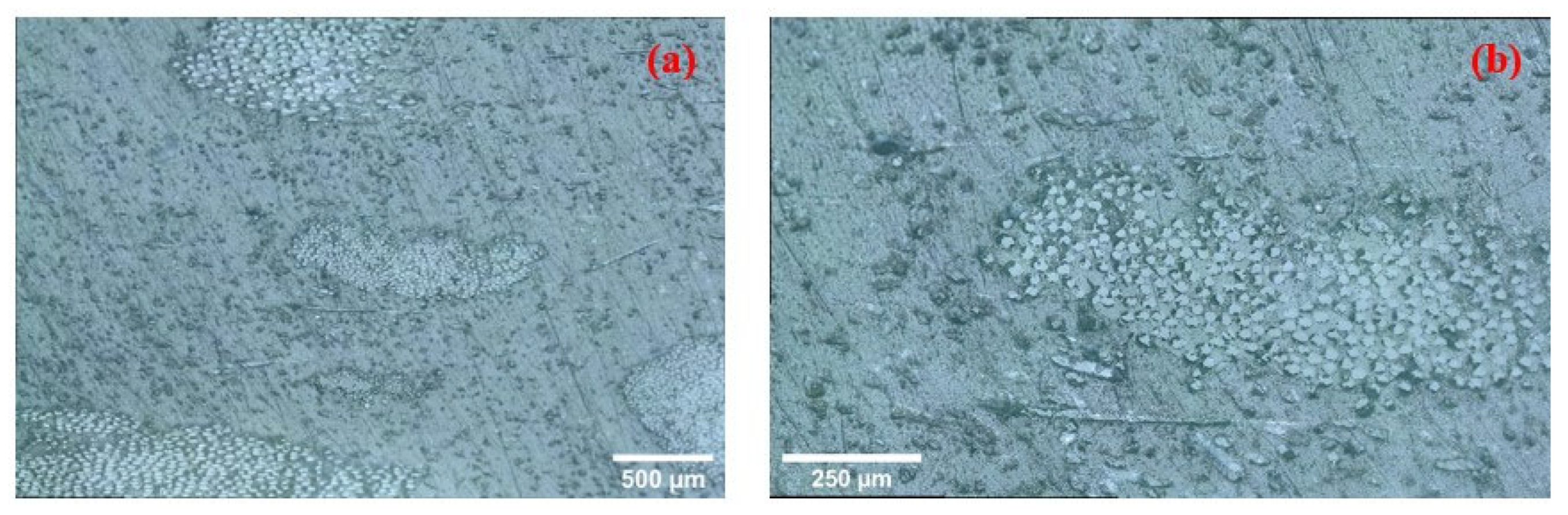
3.3.1. Optical Microscopy Analysis
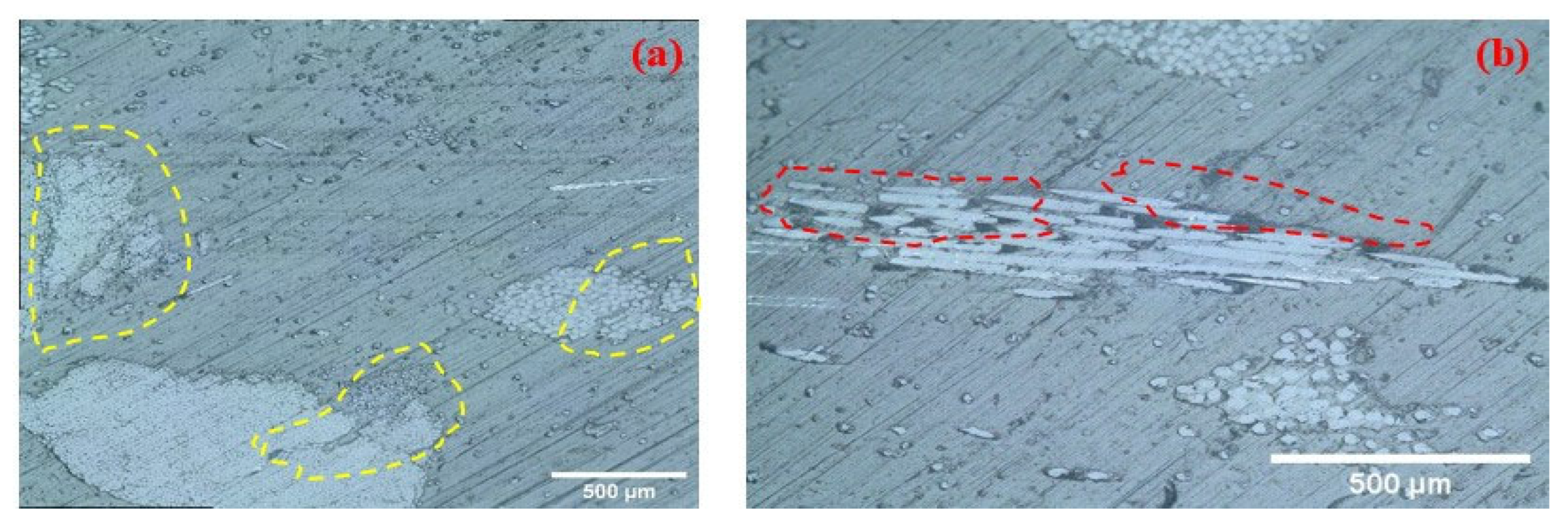
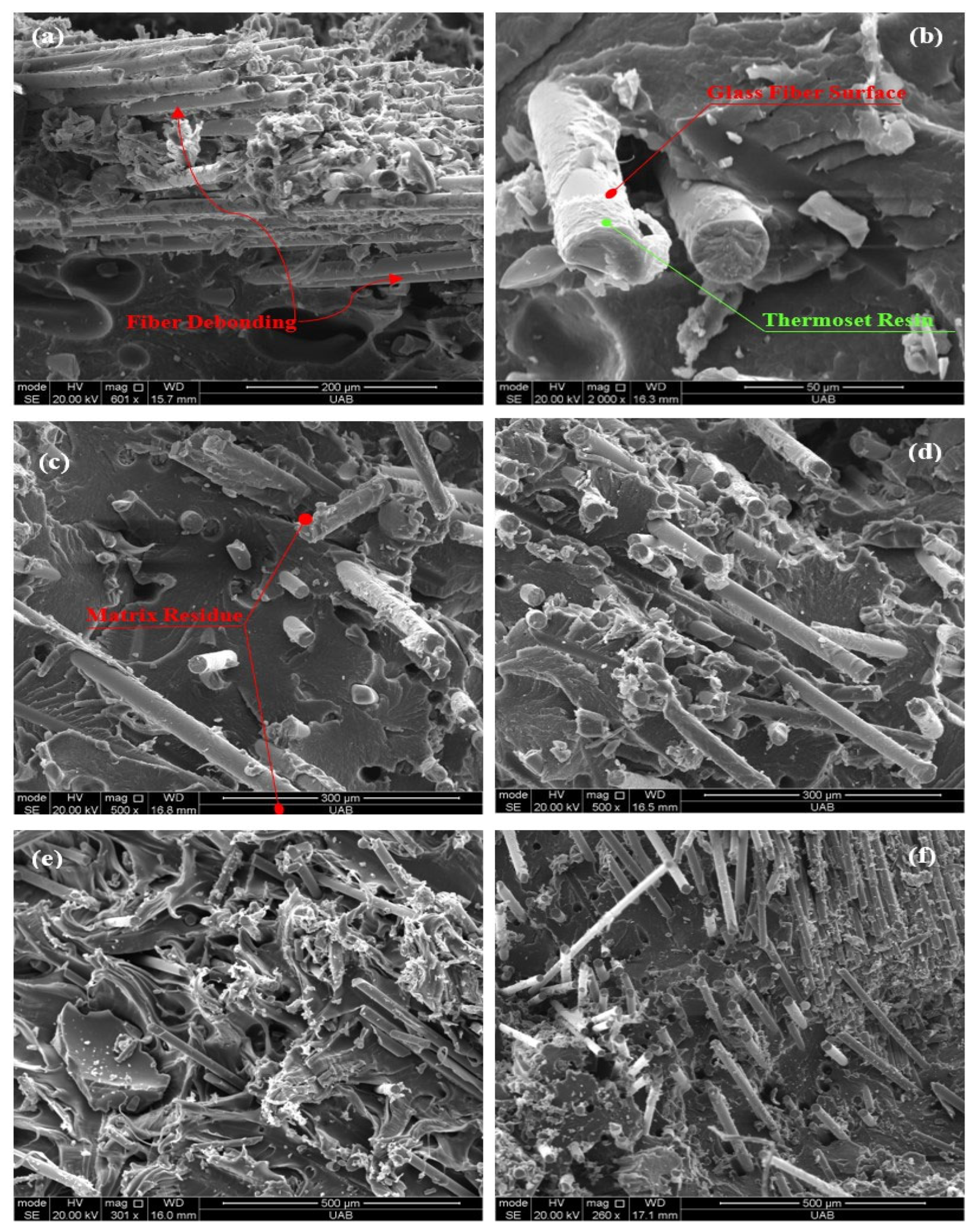
3.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.4. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of STCs
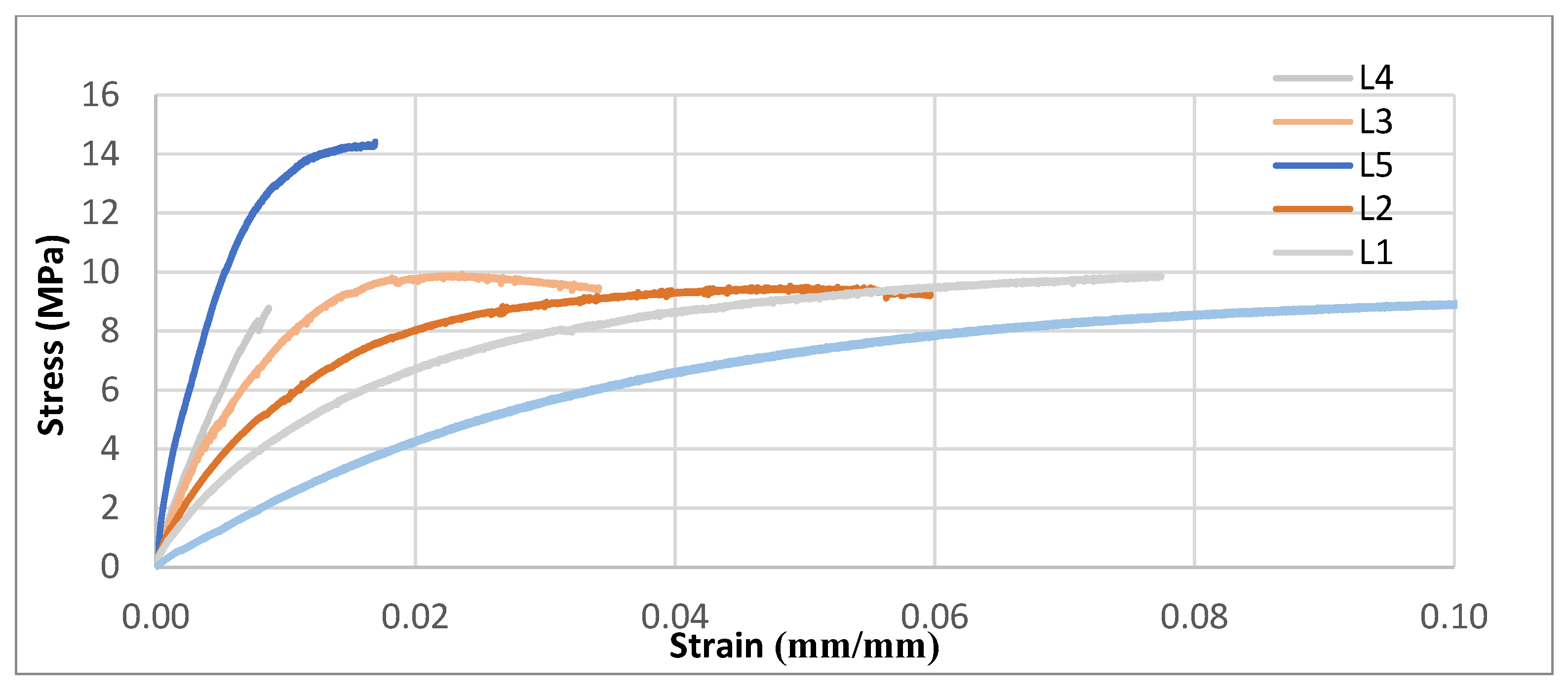
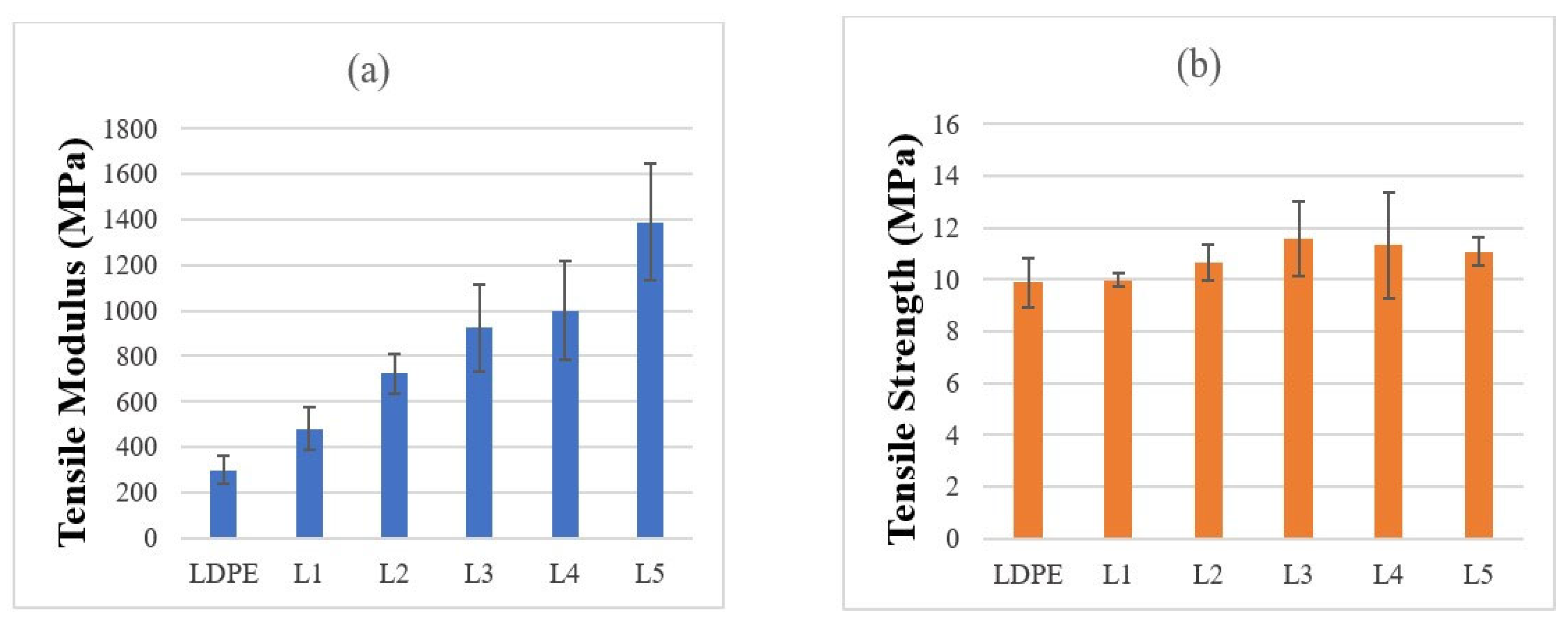
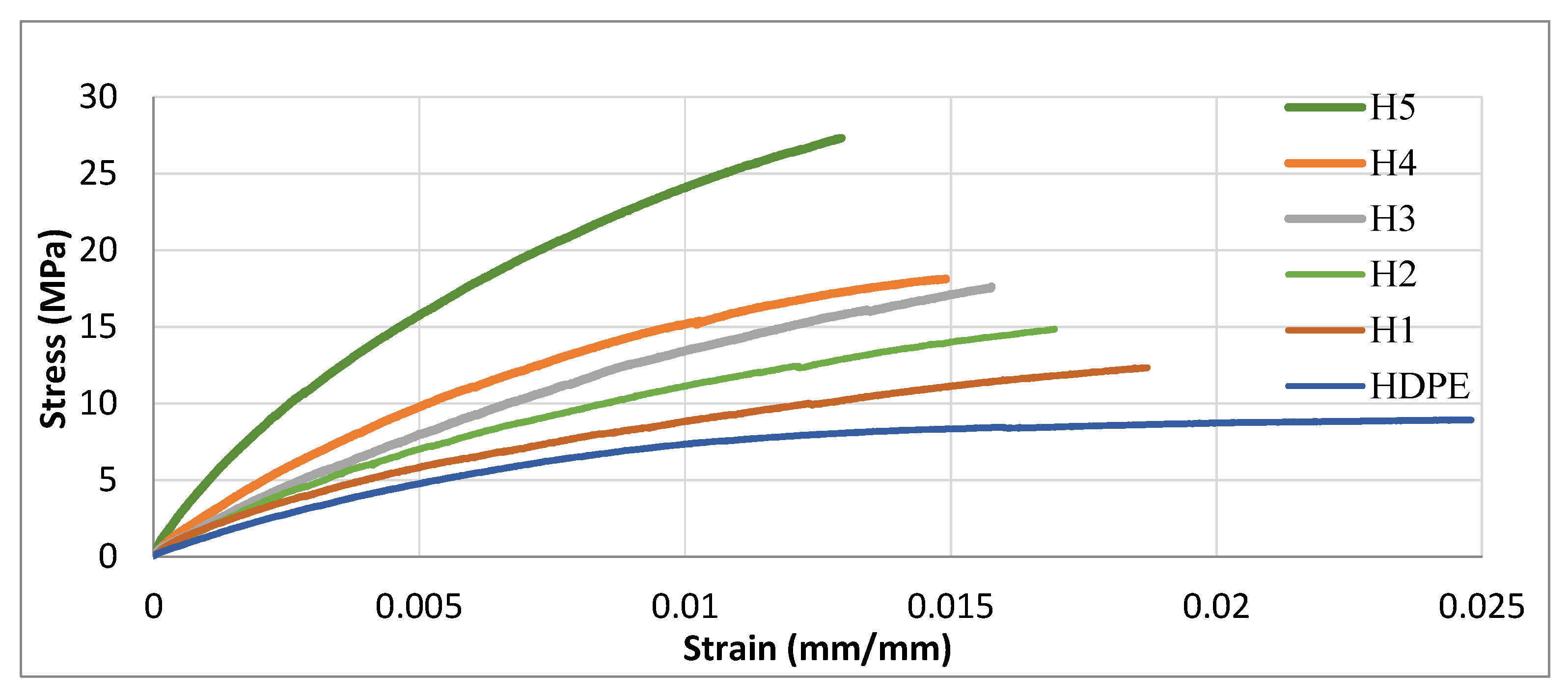
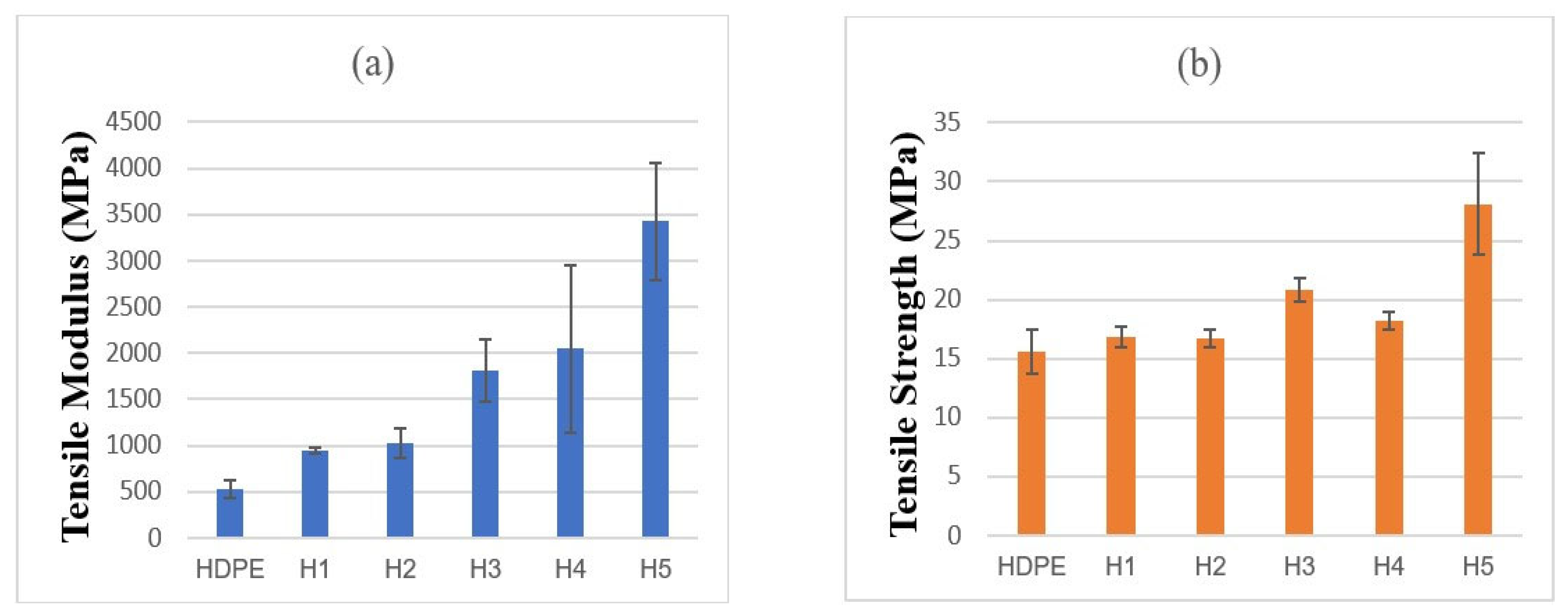
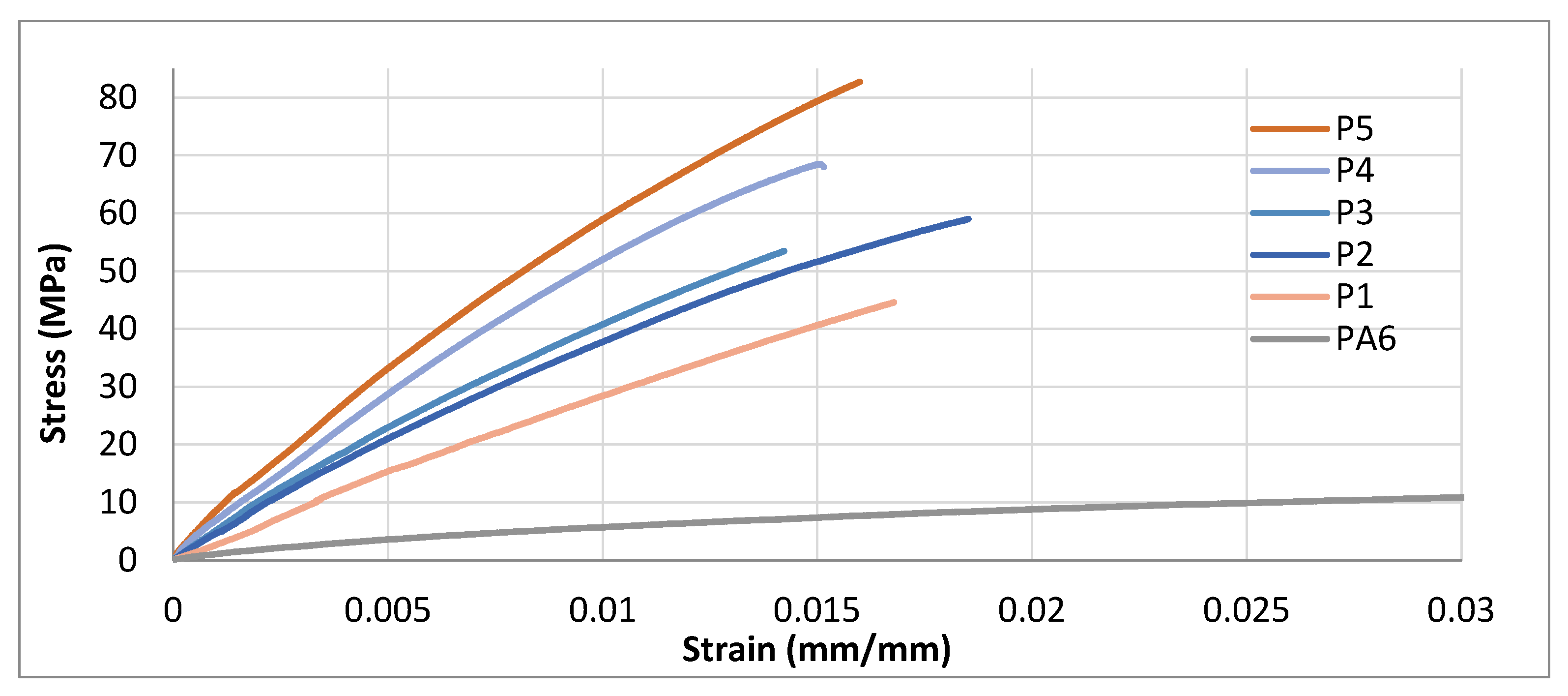
3.4.1. Tensile Properties of STCs
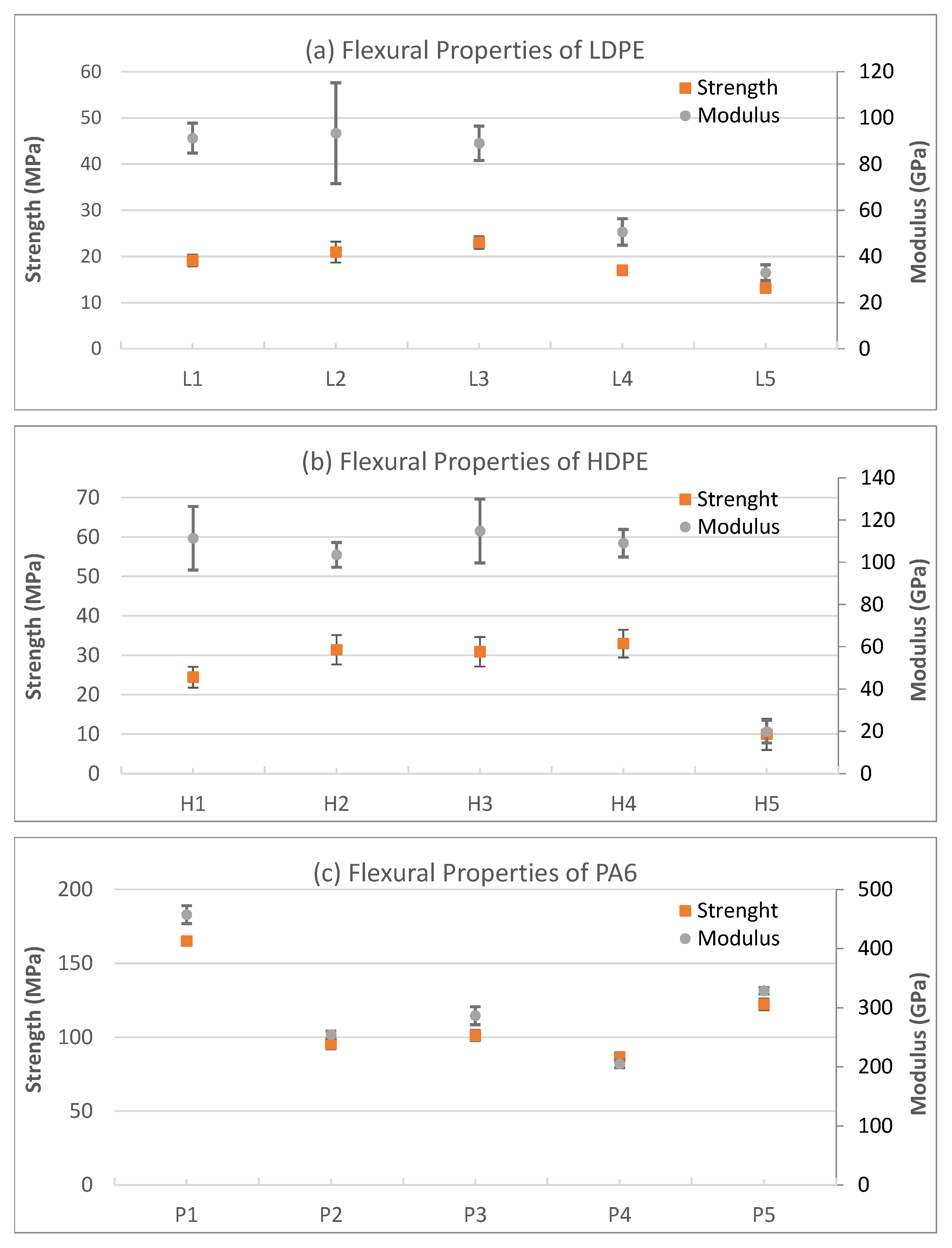
3.4.2. Flexural Properties of STCs
3.4.3. Izod Impact Properties of the STCs
4. Conclusions
- The mechanical recycling of epoxy–polyurethane–glass fiber (EPG) thermoset wastes has enabled their reuse as reinforcing fillers in LDPE, HDPE, and PA6 matrices, thereby providing a sustainable and cost-effective recycling pathway.
- The recycled epoxy–polyurethane–glass fiber (EPG) wastes used in this study were found to comprise two main morphological fractions: loosely bound fiber bundles and fine particulates. This heterogeneity in size distribution directly influenced fiber–matrix interactions; in particular, microfiber bundles tended to localize stresses, thereby limiting the efficiency of load transfer.
- The average fiber length of STCs was strongly affected by matrix viscosity and processing conditions; the recycled EPG, initially ~9 mm, was shortened to ~6.7 mm in LDPE, ~5.6 mm in HDPE, and ~5.0 mm in PA6 composites.
- Microstructural examinations (optical microscopy and SEM) revealed that at high filler loadings, EPG fiber bundles were not uniformly dispersed, leading to microvoids and localized stress concentrations that limited the mechanical performance. Partial wetting of the fibers by the residual thermoset phase and the thermoplastic matrix weakened interfacial bonding, thereby reducing load transfer efficiency. In particular, filler contents above 30% resulted in more pronounced heterogeneity and microstructural defects, which were directly associated with strength reductions.
- Among the matrices, LDPE composites exhibited the most pronounced increase in water absorption (+131%), while both LDPE and HDPE showed significant increases in density of ~45%. PA6, in contrast, displayed a more moderate increase in density (+27.5%).
- Thermal analyses further highlighted the influence of EPG incorporation. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed a substantial increase in the amount of char residue at 700 °C, rising from 2.5% to 33.5% in LDPE (+1240%), from 2.6% to 45.7% in HDPE (+1656%), and from 0.4% to 38.7% in PA6 (+9570%), confirming the strong contribution of the inorganic glass content to thermal stability. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that crystallinity decreased consistently with filler loading: from 62.2% to 23.7% in LDPE (−61.9%), from 56.4% to 44.3% in HDPE (−21.5%), and from 31.1% to 23.1% in PA6 (−25.9%). These findings demonstrate that while EPG waste increases thermal stability through char formation, it simultaneously reduces crystallinity, reflecting restricted polymer chain mobility in all matrices.
- Tensile results showed clear reinforcement effects across all matrices. In HDPE, the modulus increased from 523 MPa (neat) to 3424 MPa at 50 wt% (~6-fold), with strength peaking at +23.6% before declining at higher loadings. PA6 composites exhibited the highest stiffness, increasing from 3035 to ~5000 MPa, while tensile strength improved by ~25% at optimal filler levels. LDPE composites showed balanced improvements at 10–20 wt%, with modulus gains up to ~590% and strength increases of ~40–47%, though excessive loading reduced strength. Overall, moderate filler contents offered the best trade-off between stiffness and strength.
- Flexural tests confirmed significant stiffening with filler addition across all matrices. In LDPE composites, the flexural modulus increased by 286–589%, accompanied by ~40–47% improvement in flexural strength. HDPE composites showed a ~347% rise in the modulus and up to a 23.6% strength enhancement. PA6-based composites exhibited the highest rigidity, with flexural modulus gains exceeding 50% and strength improvements of ~25% at optimal filler loadings. However, at high filler levels (≥40 wt%), heterogeneity and fiber agglomeration led to limited reductions in strength.
- Izod impact tests showed contrasting trends depending on the matrix. LDPE composites exhibited improved toughness at low filler levels, with impact energy increasing by ~12–18% up to 20 wt%, before declining at higher loadings. HDPE composites, in contrast, showed a continuous decrease, with impact strength reductions of ~15–25% across the filler range. PA6-based composites experienced the most pronounced loss, with impact strength decreasing by ~30–40% at 50 wt% loading, reflecting the matrix’s higher polarity and brittleness. Overall, moderate filler contents in LDPE offered a balance between stiffness gains and acceptable toughness, whereas HDPE and especially PA6 were more sensitive to impact degradation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPG | Epoxy–Polyurethane–Glass Fiber |
| GFRP | Glass Fiber-Reinforced Plastic |
| STC | Second-Generation Thermoplastic Composites |
| LDPE | Low-Density Polyethylene |
| HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene |
| PA6 | Polyamide 6 |
| DMC | Dough Molding Compound |
| GWP | Woven Glass Phenolic Laminate |
| LGF/PBT | Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polybutylene Terephthalate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| BMC | Bulk Molding Compound |
| VARTM | Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding |
| MPAD | Materials Processing and Applications Development |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
References
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, E.; Dintcheva, N.T. Recycling of Thermoset Materials and Thermoset-Based Composites: Challenge and Opportunity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J. Recycling technologies for thermoset composite materials-current status. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kismet, Y.; Dogan, A.; Wagner, M.H. Thermoset powder coating wastes as filler in LDPE—Characterization of mechanical, thermal and morphological properties. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouparitsas, C.E.; Kartalis, C.N.; Varelidis, P.C.; Tsenoglou, C.J.; Papaspyrides, C.D. Recycling of the fibrous fraction of reinforced thermoset composites. Polym. Compos. 2022, 23, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bream, C.E.; Hornsby, P.R. Comminuted thermoset recyclate as a reinforcing filler for thermoplastics: Part I characterisation of recyclate feedstocks. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bream, C.E.; Hornsby, P.R. Comminuted thermoset recyclate as a reinforcing filler for thermoplastics: Part II Structure–Property effects in polypropylene compositions. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 2977–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, N.A.; Mativenga, P.T. Effect of Process Parameters on Mechanical Recycling of Glass Fibre Thermoset Composites. Procedia CIRP 2016, 48, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, M.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Effect of fiber length and dispersion on properties of long glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites based on poly(butylene terephthalate). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15439–15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröning, M.; Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A.C. Recycling of glass-fibre reinforced phenolic prepreg waste. Part 2. Milled prepreg as functional filler in PP and PA6. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2004, 12, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRosa, R.; Telfeyan, E.; Gaustad, G.; Mayes, S. Strength and microscopic investigation of unsaturated polyester BMC reinforced with SMC-recyclate. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2005, 18, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Adusumalli, R.B.; Doddipatla, P.; Venkateshan, K.C. Comparative study between dry and wet properties of thermoplastic PA6/PP novel matrix-based carbon fibre composites. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Kale, D.D. Effect of processing conditions and properties of PP/nylon 6 blends. J. Polym. Res. 2000, 7, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, R.S.; Ozcan, S. Recycling of commercial E-glass reinforced thermoset composites via two temperature step pyrolysis to improve recovered fiber tensile strength and failure strain. Recycling 2019, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Madsen, B.; Toncelli, C.; Brøndsted, P.; Ilsted Bech, J. Recycling of shredded composites from wind turbine blades in new thermoset polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.M.E.; Stonecipher, E.; Ning, H.; Pillay, S.B. Mixing rules for high density polyethylene-polypropylene blends. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 101, 5395–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatas, R.; Dagreou, S.; Despax-Ferreres, A.; Barasinski, A. Recycling of fiber reinforced composites with a focus on thermoplastic composites. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E11; Standard Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Lu, N.; Hassen, A.A.; Chawla, K.; Selim, M.; Pillay, S. A review of Long fibre thermoplastic (LFT) composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2020, 65, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3171-22; Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Preparation, microstructures, and properties of long-glass-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites based on polycarbonate/poly(butylene terephthalate) alloys. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D792-20; Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D5229/D5229M-20; Standard Test Method for Moisture Absorption Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D3039/D3039M-17; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D7264/D7264M-21; Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM D256; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Delli, E.; Giliopoulos, D.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Chrissafis, K. Fibre length and loading impact on the properties of glass fibre reinforced polypropylene random composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Wu, G.; Li, L. Effects of Fiber Volume Fraction and Length on the Mechanical Properties of Milled Glass Fiber/Polyurea Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Lauke, B. Effects of fiber length and fiber orientation distributions on the tensile strength of short-fiber-reinforced polymers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. The interface region in glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composites: 1. Sample preparation, void content and interfacial strength. Composites 1995, 26, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, F.; Ville, J.; Ghamri, N.; Pradel, J.L.; Durin, A.; Valette, R.; Vergnes, B. Correlation between processing conditions and fiber breakage during compounding of glass fiber-reinforced polyamide. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Solis, C.; Yan, N.; Zhang, S.Y. Effect of mixing conditions and initial fiber morphology on fiber dimensions after processing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, P.N.; AlMaadeed, M.A.A. Processing and characterization of polyethylene-based composites. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Compos. Sci. 2015, 1, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sáenz Juano-Arbona, V.; Vallés-Lluch, A.; Contat-Rodrigo, L.; Ribes-Greus, A. Chemical and thermal characterization of high- and low-density irradiated polyethylenes. J. App. Pol. Sci. 2002, 86, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Sain, M.M. Effects of Wood Fiber and Microclay on the Performance of Soy Based Polyurethane Foams. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.K.; Gao, W.J.; Chen, C.H.; Juang, T.Y.; Abu-Omar, M.M.; Lin, C.H. Degradation of Thermal-Mechanically Stable Epoxy Thermosets, Recycling of Carbon Fiber, and Reapplication of the Degraded Products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5304–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polińska, M.; Rozanski, A.; Galeski, A.; Bojda, J. The Modulus of the Amorphous Phase of Semicrystalline Polymers. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 9113–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.L.; Casem, D.T.; Bradley, J.M.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Brown, E.N.; Jordan, C.W. Mechanical Properties of Low Density Polyethylene. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2016, 2, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Zu, L.; Lan, T. The study on microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-component composite based on HDPE. Des. Monomers Polym. 2020, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, M.B.; Anstey, A.; Shaayegan, V.; Lee, P.C.; Park, C.B. Enhancing the mechanical performance of PA6 based composites by altering their crystallization and rheological behavior via in-situ generated PPS nanofibrils. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 195, 108067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzén, B.; Klason, C.; Kubát, J.; Kitano, T. Fibre degradation during processing of short fibre reinforced thermoplastics. Composites 1989, 20, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, K.; Nagai, C. Effects of temperature and water absorption on the interfacial mechanical properties of carbon/glass-reinforced thermoplastic epoxy hybrid composite rods. Compos. Struct. 2022, 282, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Luda, M.P.; Polishchuk, A.Y.; Revellino, M.; Blancon, R.; Merle, G.; Martinez-Vega, J. Kinetic aspects of water sorption in polyester-resin/glass-fibre composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1997, 57, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, G. Composite degradation due to fluid absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 2000, 31, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. The interface region in glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composites: 2. Water absorption, voids and the interface. Composites 1995, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Dong, S.; Xian, G.; Vedernikov, A.; Akhatov, I.; Safanov, A.; Yue, Q. Durability study on the interlaminar shear behavior of glass-fibre reinforced polypropylene (GFRPP) bars for marine applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Liang, C. The effects of strain rates on mechanical properties and failure behavior of long glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, G.; De Nicola, S.; Palomba, M.; Pullini, D.; Horsewell, A.; Hansen, T.W.; Nicolais, L. Mechanical properties of low-density polyethylene filled by graphite nanoplatelets. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 485705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Daly, M.; Geever, L.M.; Major, I.; Higginbotham, C.L.; Devine, D.M. Synthesis and characterization of high density polyethylene/peat ash composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 94, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heflin, D.G.; Mansson, J.A.E. Mechanisms for combining polyamide and epoxy and their effects on mechanical performance—A review. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2022, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, S.D.; Denchev, Z.; Dencheva, N.V.; Rocha, A.M.; Rosa, L.A.; Engesser, B. Development of polyamide 6 based single polymer composites reinforced by novel stitched plain fabrics. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, N.; Papila, M.; Özkoç, G. Overmolded hybrid composites of polyamide-6 on continuous carbon and glass fiber/epoxy composites: ‘An assessment of the interface’. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 131, 105771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, W.A.; El-Demerdash, A.G.M.; Abokhateeb, A.E.A.; Elessawy, N.A. Innovative high-density polyethylene/waste glass powder composite with remarkable mechanical, thermal and recyclable properties for technical applications. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Christéen, J.; Kalantar, A.; Skrifvars, M. Glass fibres recovered by microwave pyrolysis as a reinforcement for polypropylene. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2013, 21, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Lu, M.; Mai, Y.W. Thermal de-consolidation of thermoplastic matrix composites-I. Growth of voids. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 62, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, R.J.; Longana, M.L.; Yu, H.; Hamerton, I.; Potter, K.D. Development of a closed-loop recycling process for discontinuous carbon fibre polypropylene composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 146, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmare, S.; Yoseph, B.; Jamir, T.M. Investigating the impact resistance of E-glass/Polyester composite materials in variable fiber-to-matrix weight ratio composition. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2178110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinash, S.; Karunagaran, N. Izod impact behaviouron e-glass fibre reinforced with epoxy matrix addition of novel ButeaMonosperma filler in comparison with plain GFRP epoxy hybrid composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2822, 020187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Definition of STCs | Thermoplastic Matrix | Thermoset Scraps (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | wt% | ||
| L1 | LDPE | 90 | 10 |
| L2 | 80 | 20 | |
| L3 | 70 | 30 | |
| L4 | 60 | 40 | |
| L5 | 50 | 50 | |
| H1 | HDPE | 90 | 10 |
| H2 | 80 | 20 | |
| H3 | 70 | 30 | |
| H4 | 60 | 40 | |
| H5 | 50 | 50 | |
| P1 | PA6 | 90 | 10 |
| P2 | 80 | 20 | |
| P3 | 70 | 30 | |
| P4 | 60 | 40 | |
| P5 | 50 | 50 | |
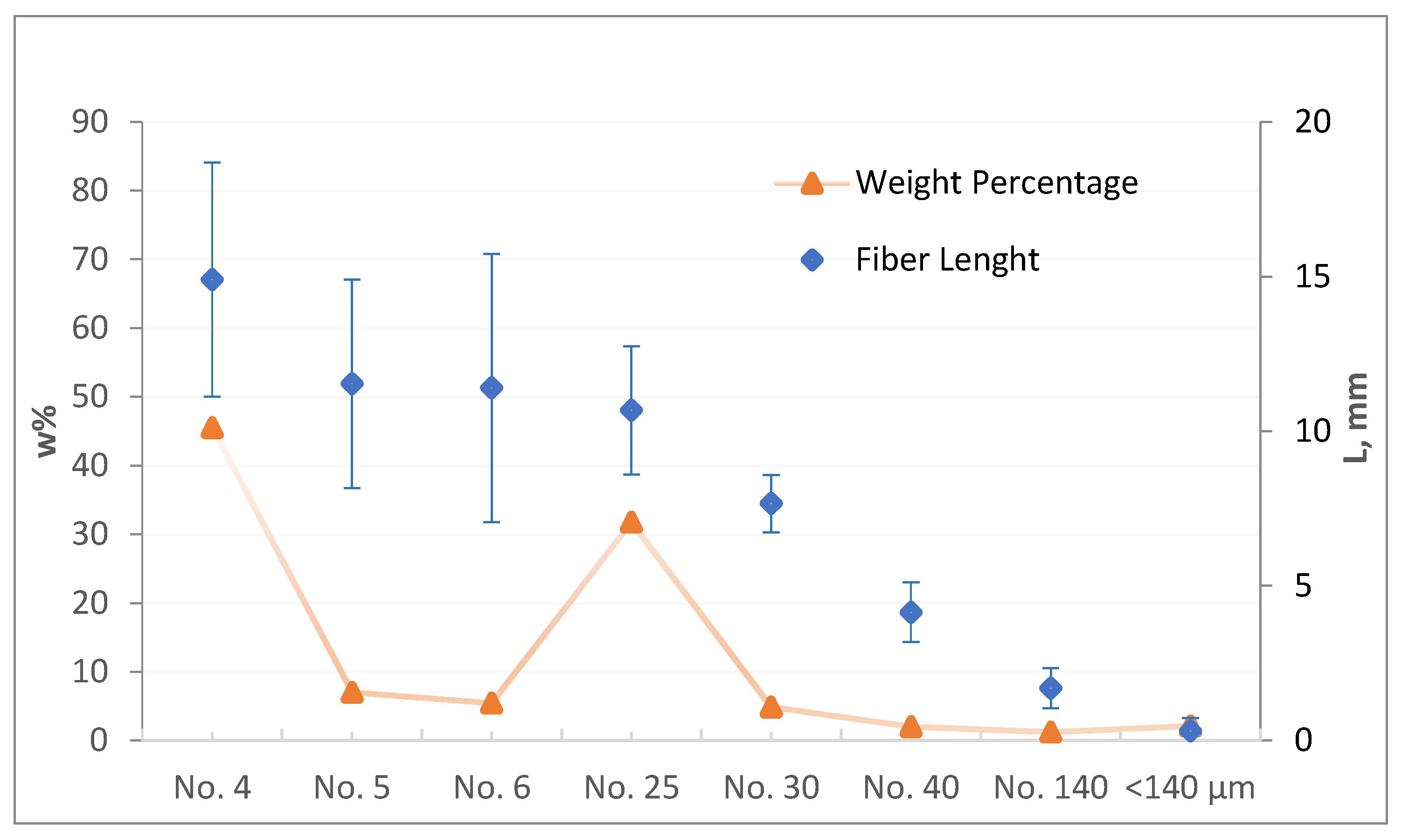
| Sieve Identification | Sieve Dimensions | Description of the Resulting EPG Materials | Weight Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| no. 4 | >4.75 mm | coarse fiber bundles | 45.53% |
| no. 5 | >4 mm | medium fiber bundles | 7.00% |
| no. 6 | >3.35 mm | small fiber bundles | 5.43% |
| no. 25 | >0.71 mm | dusty fiber bundles | 31.78% |
| no. 30 | >0.6 mm | coarse EPG powder | 4.88% |
| no. 40 | >0.425 mm | medium EPG powder | 2.03% |
| no. 140 | >0.106 mm | small EPG powder | 1.22% |
| under sieve | <0.106 mm | fine EPG powder | 2.13% |
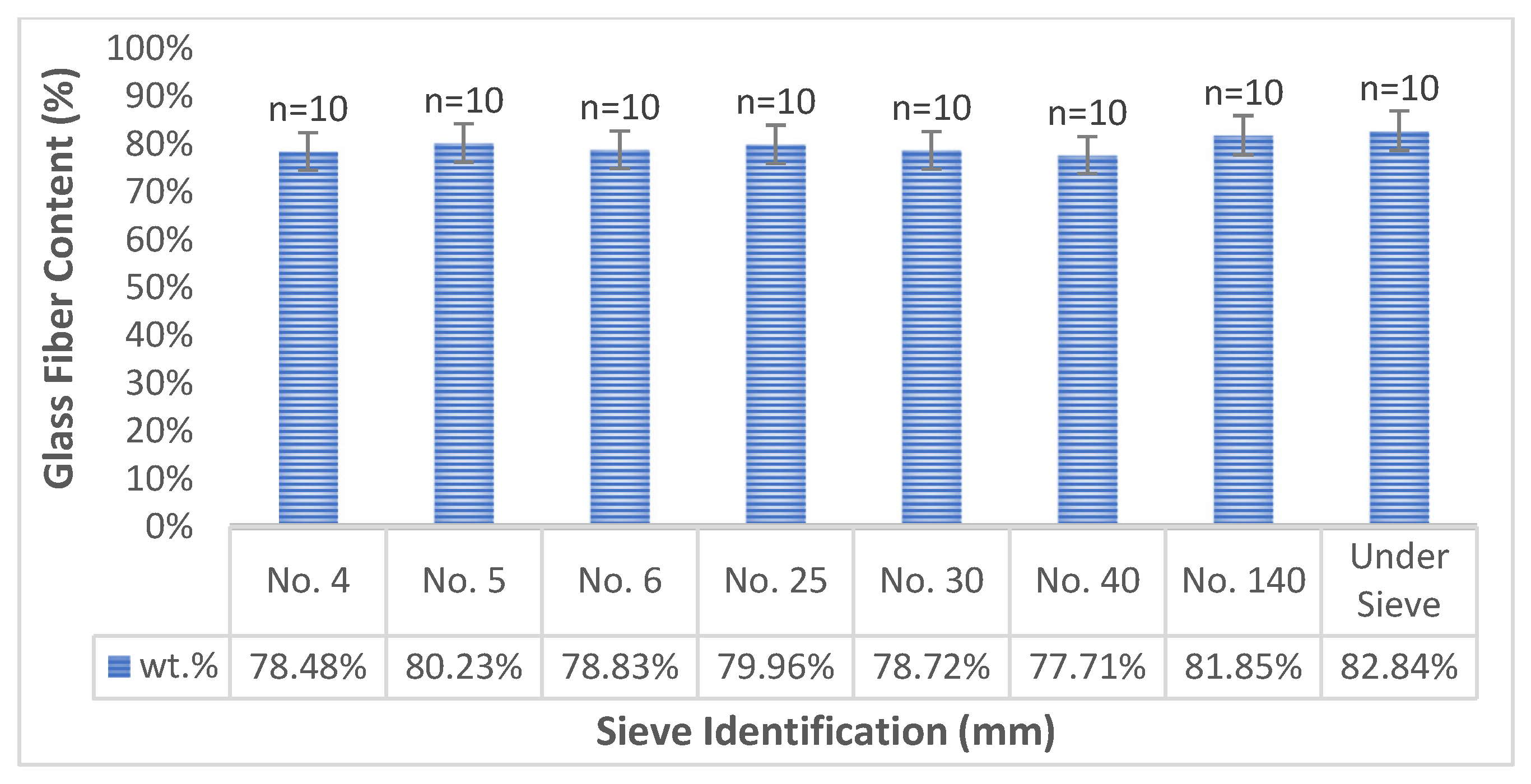
| Definition of STCs | Loading Fraction | Post-Test Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix (wt%) | EPG Scraps (wt%) | Matrix (wt%) | Glass Fiber (wt%) | σSD 1 | |
| L1 | 90 | 10 | 92.04 | 7.96 | 0.47 |
| L2 | 80 | 20 | 84.16 | 15.84 | 0.66 |
| L3 | 70 | 30 | 76.39 | 23.61 | 0.66 |
| L4 | 60 | 40 | 68.90 | 31.10 | 1.65 |
| L5 | 50 | 50 | 59.63 | 40.37 | 2.05 |
| H1 | 90 | 10 | 92.02 | 7.98 | 0.33 |
| H2 | 80 | 20 | 84.05 | 15.95 | 0.59 |
| H3 | 70 | 30 | 76.26 | 23.74 | 0.77 |
| H4 | 60 | 40 | 68.14 | 31.86 | 1.70 |
| H5 | 50 | 50 | 59.71 | 40.29 | 1.44 |
| P1 | 90 | 10 | 91.99 | 8.01 | 0.26 |
| P2 | 80 | 20 | 84.06 | 15.94 | 0.69 |
| P3 | 70 | 30 | 75.95 | 24.05 | 1.44 |
| P4 | 60 | 40 | 67.95 | 32.05 | 1.51 |
| P5 | 50 | 50 | 59.84 | 40.16 | 2.54 |
| Definition of STCs | T5%/°C | Tmax1%/°C | Tmax2%/°C | Residues at 700 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 394.74 | 458 | - | 2.5 |
| L4 | 357.4 | 321.8 | 487.2 | 26.71 |
| L5 | 343.4 | 331.1 | 491.1 | 33.48 |
| HDPE | 420 | 490.8 | - | 2.6 |
| H4 | 400.3 | 417.2 | 485.6 | 23.58 |
| H5 | 399.7 | 421.2 | 484.3 | 45.67 |
| PA6 | 391.6 | 456 | - | 0.4 |
| P4 | 322.3 | 341.4 | 453.4 | 26.66 |
| P5 | 312.4 | 347.6 | 451.7 | 38.68 |
| Definition of STCs | Tom (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 117.1 | 130.6 | 110.85 | 62.20% |
| L4 | 118.5 | 129.6 | 111 | 30.56% |
| L5 | 120.3 | 130.5 | 110.9 | 23.73% |
| HDPE | 126.3 | 134.25 | 114.95 | 56.40% |
| H4 | 120.5 | 130.3 | 115.9 | 47.42% |
| H5 | 121.4 | 130.2 | 115.3 | 44.29% |
| PA6 | 213.1 | 227.4 | 189 | 31.10% |
| P4 | 204.3 | 218.8 | 186.7 | 27.18% |
| P5 | 198.2 | 213.9 | 178 | 23.07% |
| Definition of STCs | Loading Fraction | Post-Test Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix (wt%) | EPG Scraps (wt%) | Density g/cm3 | σSD (*) | |
| L1 | 90 | 10 | 0.96 | 0.021 |
| L2 | 80 | 20 | 1.07 | 0.020 |
| L3 | 70 | 30 | 1.09 | 0.021 |
| L4 | 60 | 40 | 1.19 | 0.032 |
| L5 | 50 | 50 | 1.20 | 0.051 |
| H1 | 90 | 10 | 0.98 | 0.016 |
| H2 | 80 | 20 | 1.04 | 0.031 |
| H3 | 70 | 30 | 1.09 | 0.013 |
| H4 | 60 | 40 | 1.19 | 0.035 |
| H5 | 50 | 50 | 1.21 | 0.064 |
| P1 | 90 | 10 | 1.18 | 0.007 |
| P2 | 80 | 20 | 1.24 | 0.004 |
| P3 | 70 | 30 | 1.31 | 0.014 |
| P4 | 60 | 40 | 1.38 | 0.008 |
| P5 | 50 | 50 | 1.44 | 0.009 |
| Definition of STCs | Initial Mass (g) | Saturated Mass (g) | Coefficient of Determination | Diffusion Coefficient (m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 5.6383 | 5.6398 | 0.993 | 5.13 × 10−13 |
| L2 | 5.4202 | 5.4218 | 0.955 | 4.97 × 10−13 |
| L3 | 5.8803 | 5.8819 | 0.968 | 6.15 × 10−13 |
| L4 | 5.7457 | 5.7474 | 0.965 | 9.92 × 10−13 |
| L5 | 5.5709 | 5.5725 | 0.965 | 1.33 × 10−12 |
| H1 | 5.3843 | 5.3856 | 0.933 | 3.58 × 10−13 |
| H2 | 5.9685 | 5.9702 | 0.981 | 5.26 × 10−13 |
| H3 | 6.0245 | 6.0262 | 0.910 | 7.51 × 10−13 |
| H4 | 5.7465 | 5.7483 | 0.935 | 9.43 × 10−13 |
| H5 | 5.4122 | 5.4139 | 0.962 | 1.24 × 10−12 |
| P1 | 6.144 | 6.2389 | 0.932 | 8.35 × 10−13 |
| P2 | 5.9998 | 6.0937 | 0.866 | 8.12 × 10−13 |
| P3 | 6.1459 | 6.2434 | 0.848 | 7.09 × 10−13 |
| P4 | 6.2374 | 6.3391 | 0.881 | 9.61 × 10−13 |
| P5 | 6.4753 | 6.5818 | 0.897 | 1.05 × 10−12 |
| Definition of STCs | Test Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Break Energy (J) | σSD (*) | Izod Impact Strength (kJ/m2) | σSD (*) | |
| L1 | 1.65 | 0.06 | 40.58 | 1.34 |
| L2 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 34.93 | 1.51 |
| L3 | 1.08 | 0.02 | 22.37 | 0.77 |
| L4 | 0.79 | 0.07 | 19.63 | 1.36 |
| L5 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 16.90 | 2.87 |
| H1 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 14.78 | 3.94 |
| H2 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 13.48 | 2.85 |
| H3 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 10.92 | 1.88 |
| H4 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 12.50 | 1.62 |
| H5 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 5.16 | 0.86 |
| P1 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 16.95 | 4.46 |
| P2 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 13.78 | 2.03 |
| P3 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 7.49 | 3.39 |
| P4 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 8.20 | 1.20 |
| P5 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 4.60 | 1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasim, H.; Shih, Y.-C.; Pillay, S.; Ning, H. Sustainable Reprocessing of Thermoset Composite Waste into Thermoplastics: A Polymer Blend Approach for Circular Material Design. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100565
Kasim H, Shih Y-C, Pillay S, Ning H. Sustainable Reprocessing of Thermoset Composite Waste into Thermoplastics: A Polymer Blend Approach for Circular Material Design. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(10):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100565
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasim, Hasan, Yu-Chao Shih, Selvum Pillay, and Haibin Ning. 2025. "Sustainable Reprocessing of Thermoset Composite Waste into Thermoplastics: A Polymer Blend Approach for Circular Material Design" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 10: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100565
APA StyleKasim, H., Shih, Y.-C., Pillay, S., & Ning, H. (2025). Sustainable Reprocessing of Thermoset Composite Waste into Thermoplastics: A Polymer Blend Approach for Circular Material Design. Journal of Composites Science, 9(10), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100565







