Influence of Steel Fiber and Rebar Ratio on the Flexural Performance of UHPC T-Beams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mix Ratio Design
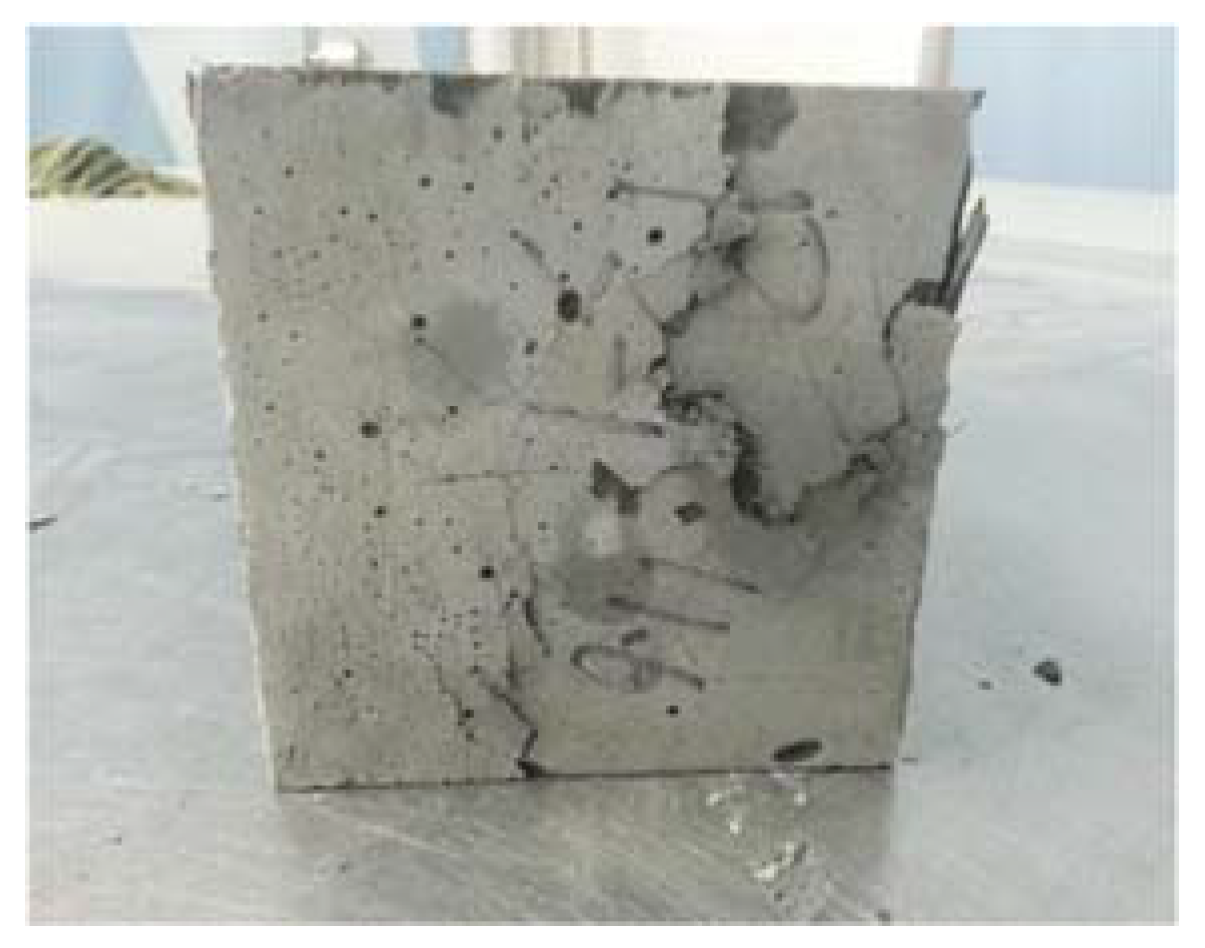
3. UHPC Compressive Strength
4. Design of Flexural Test for T-Beams
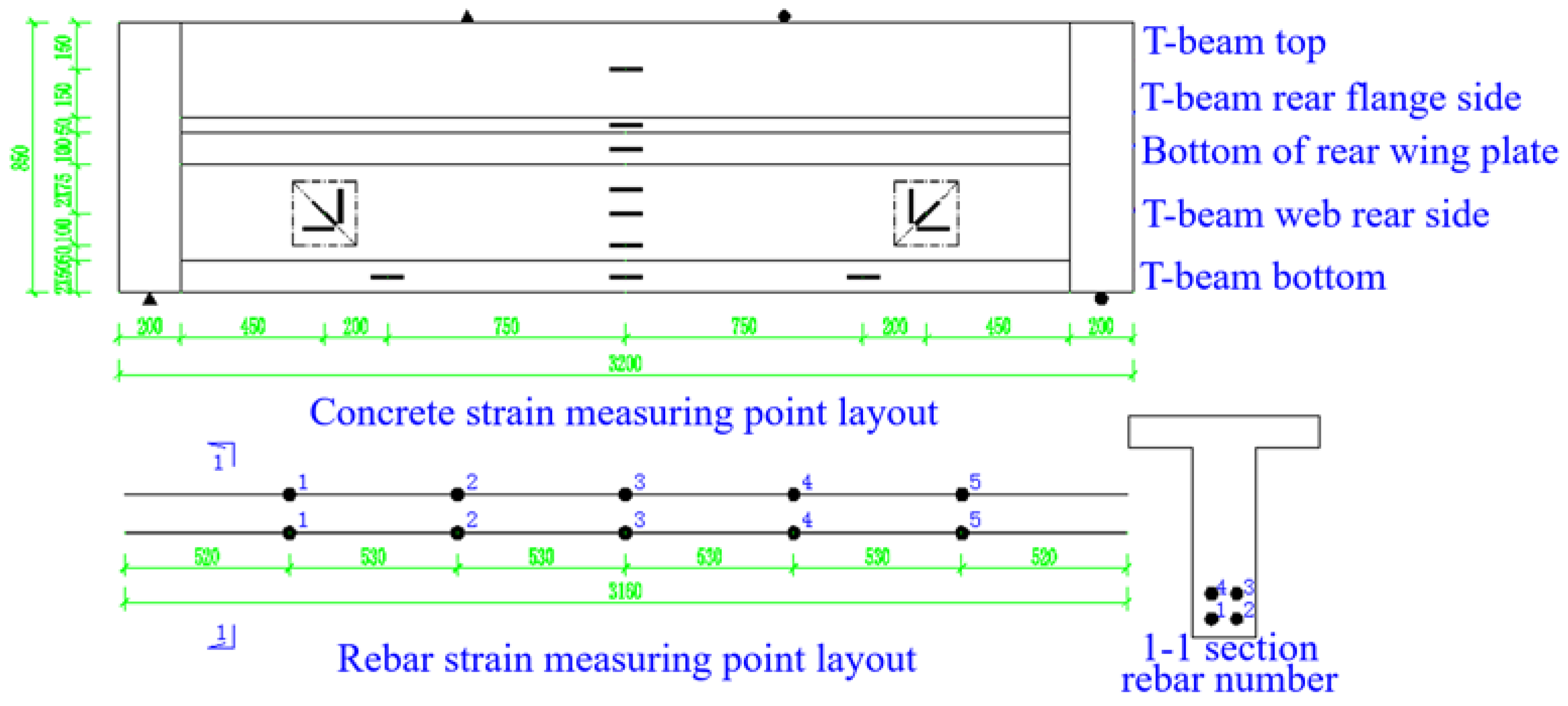
4.1. Test Purpose and Scope
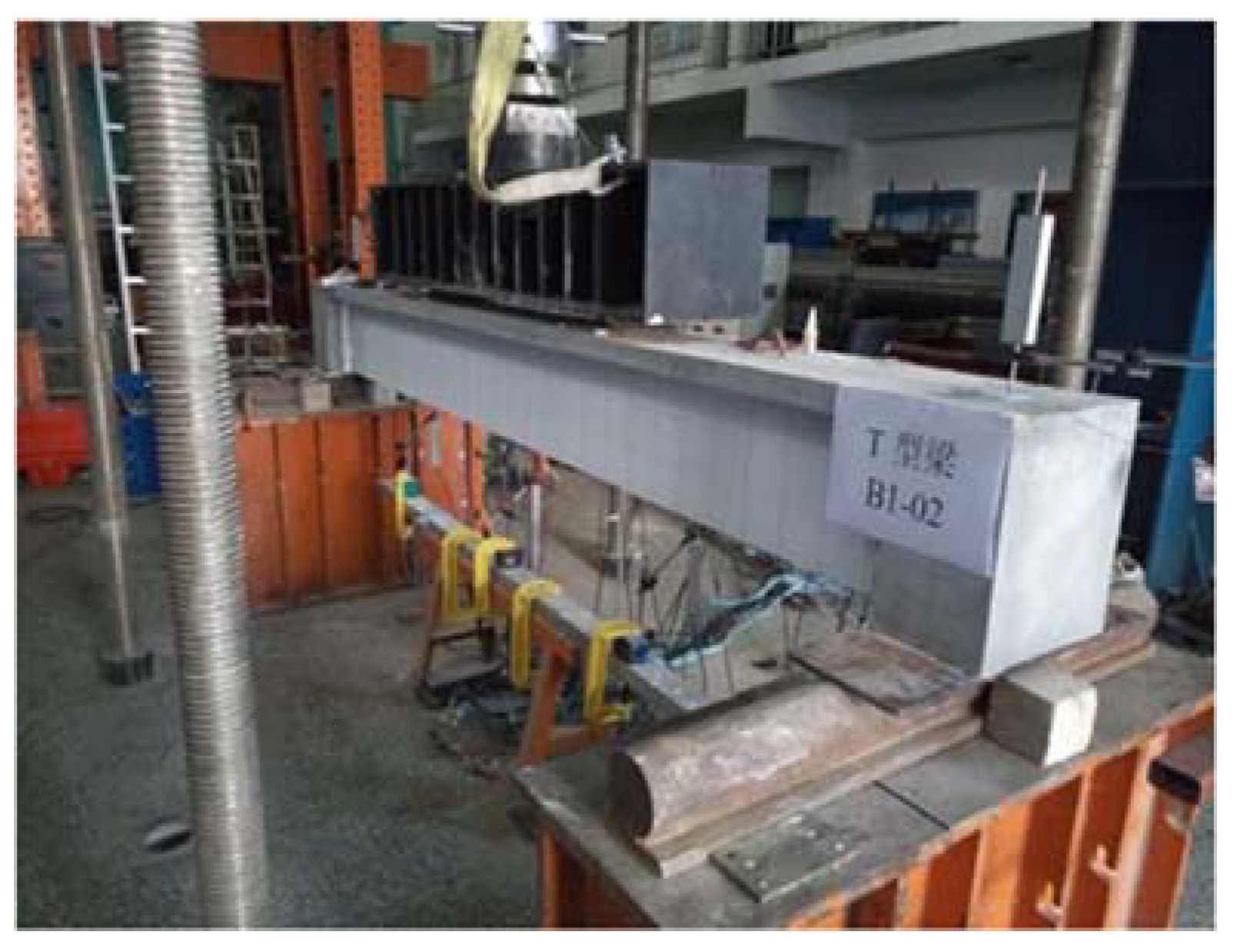
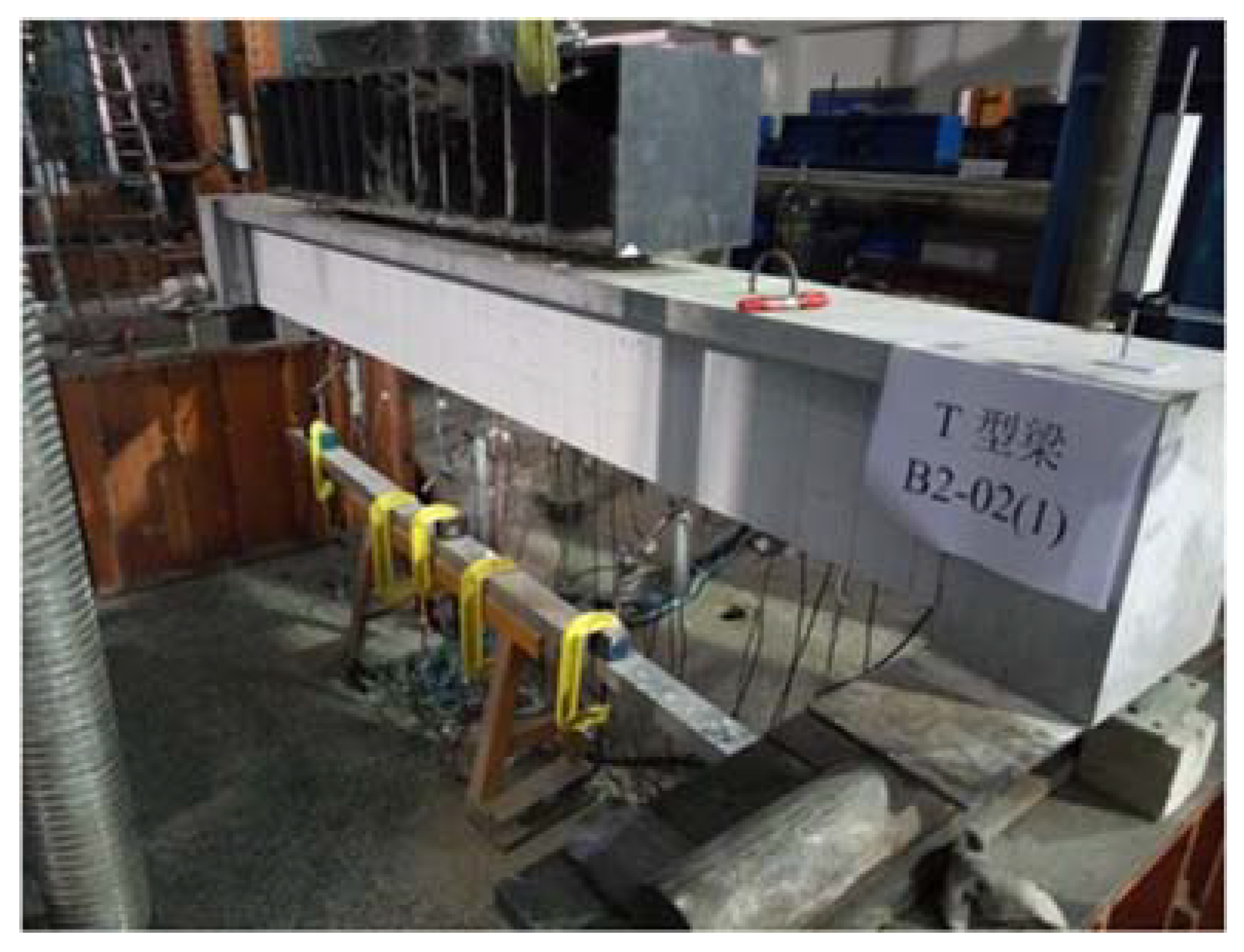
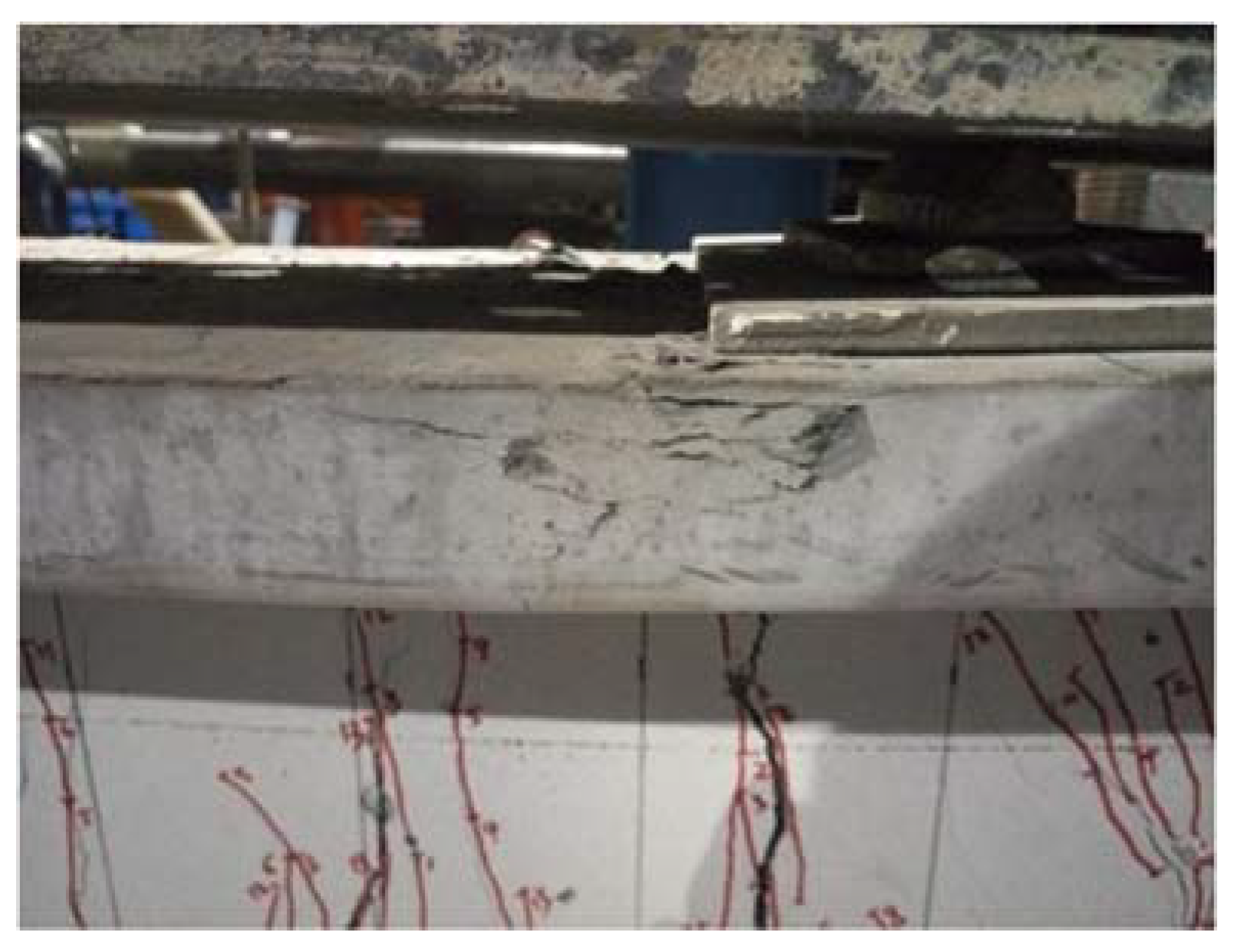
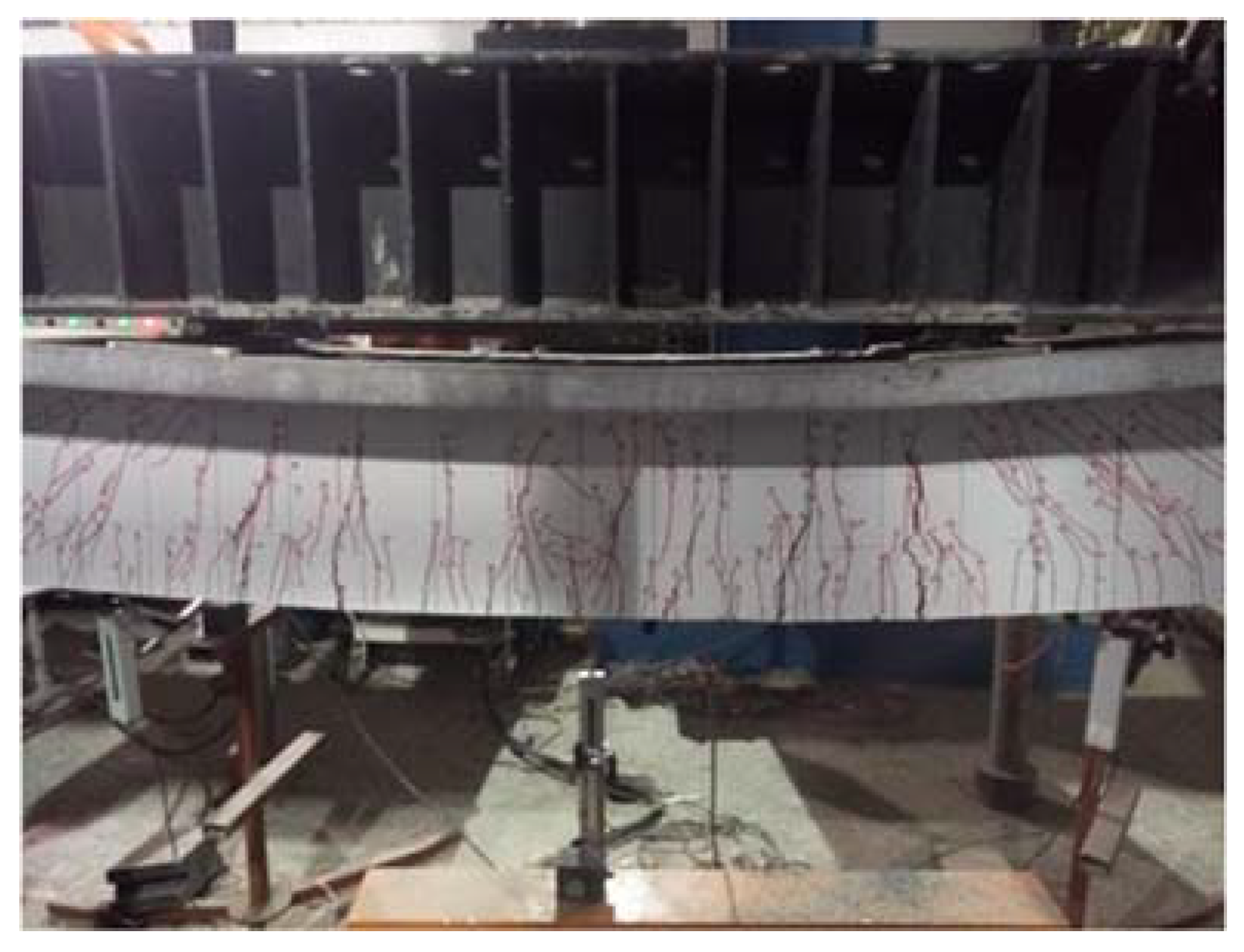
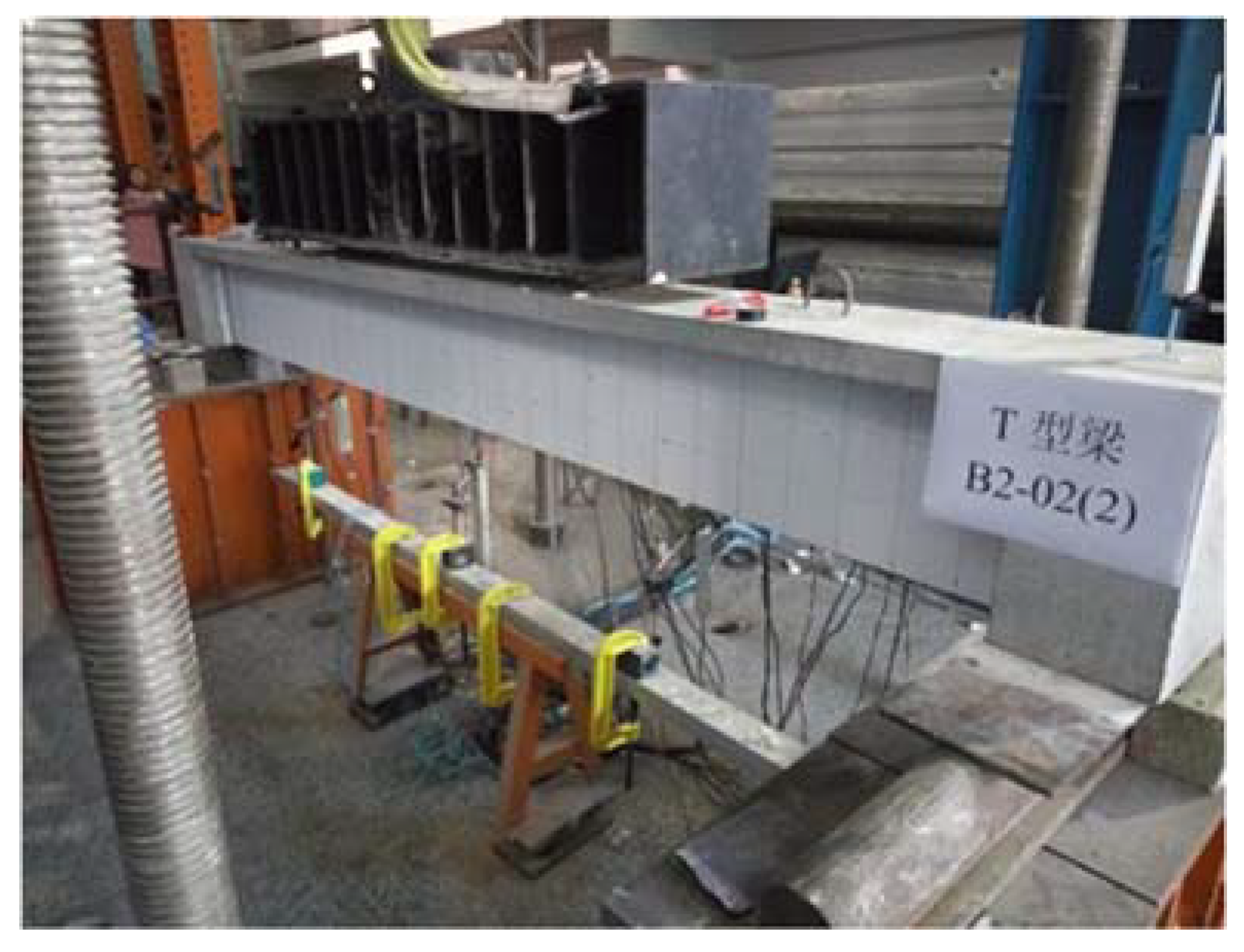
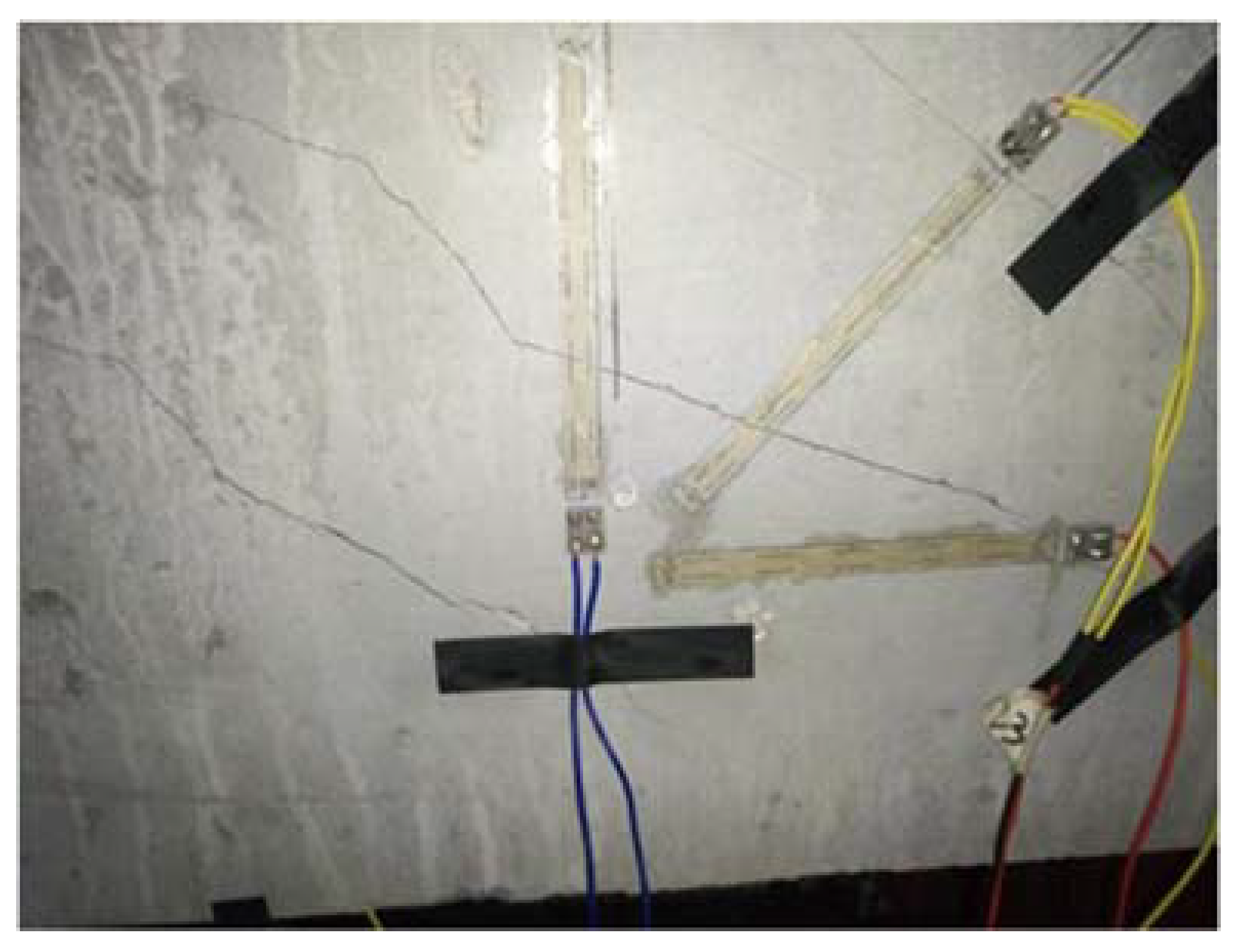
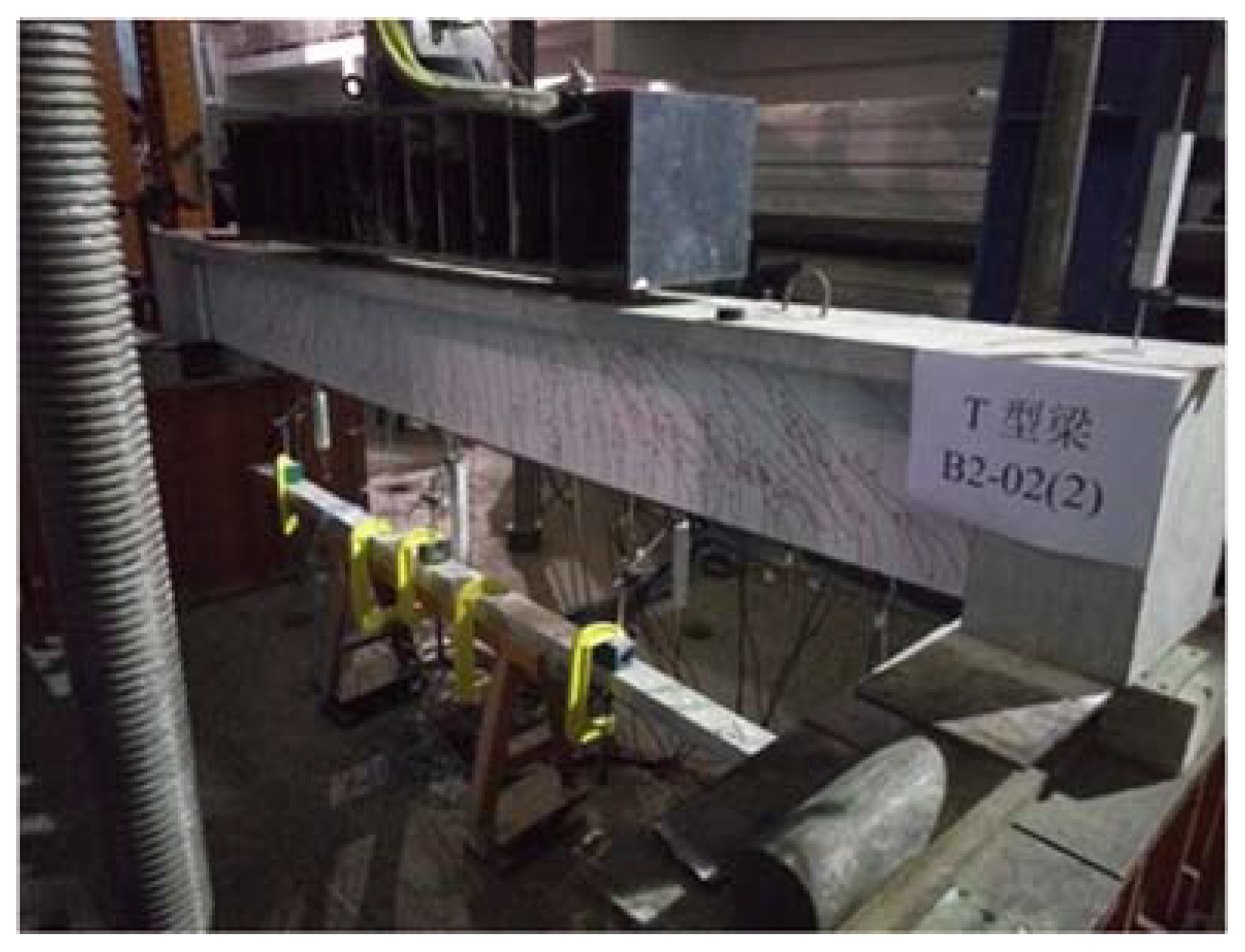
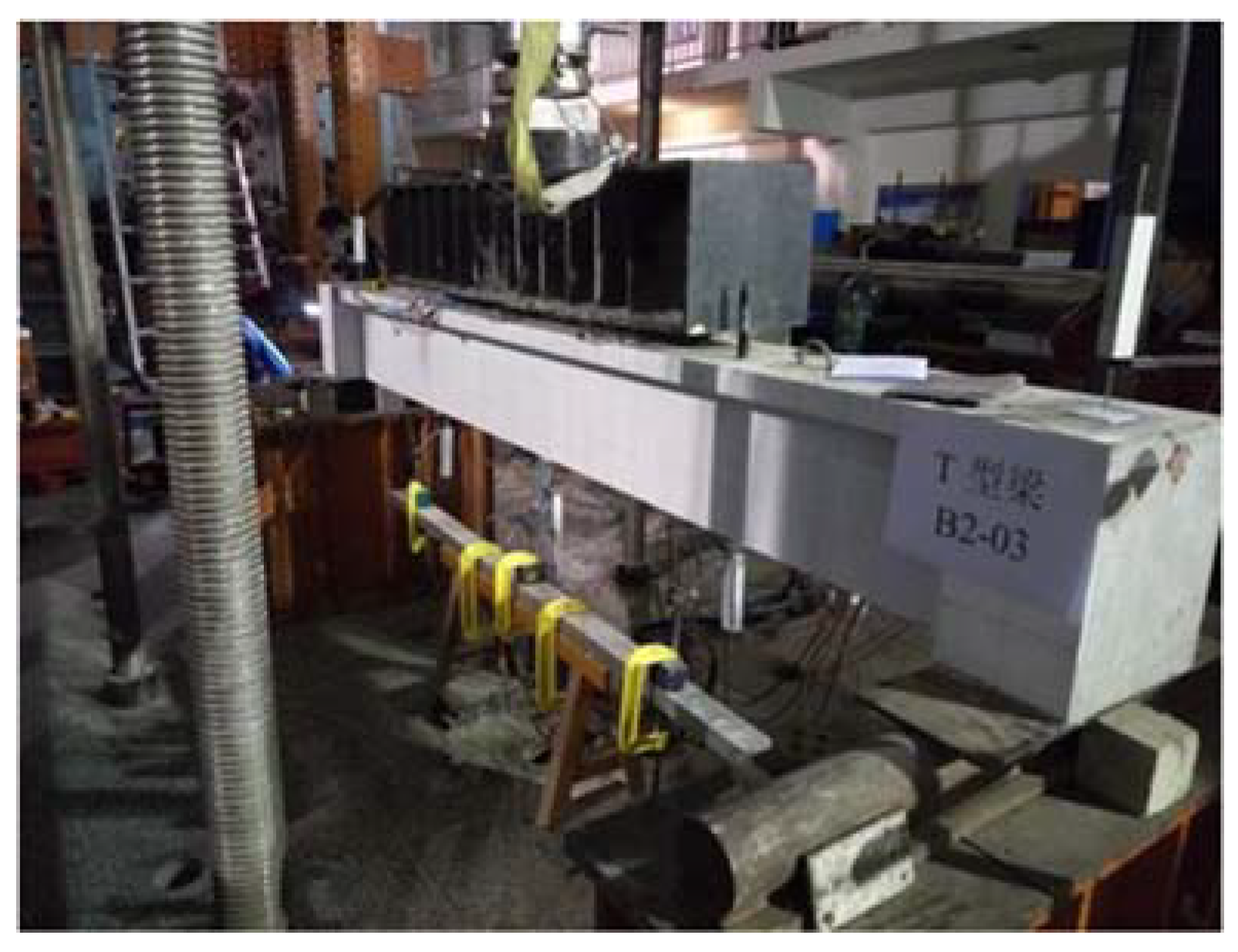
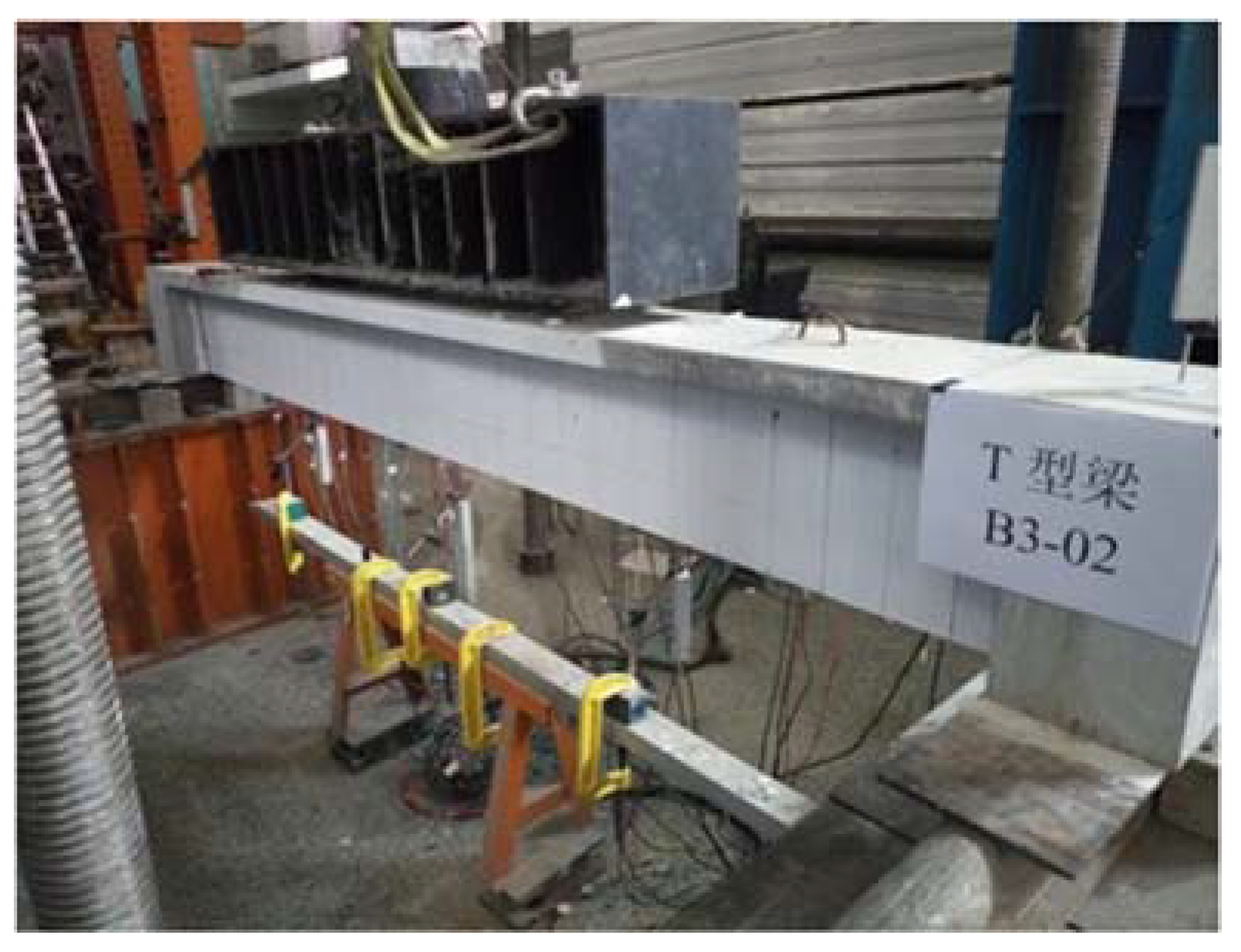
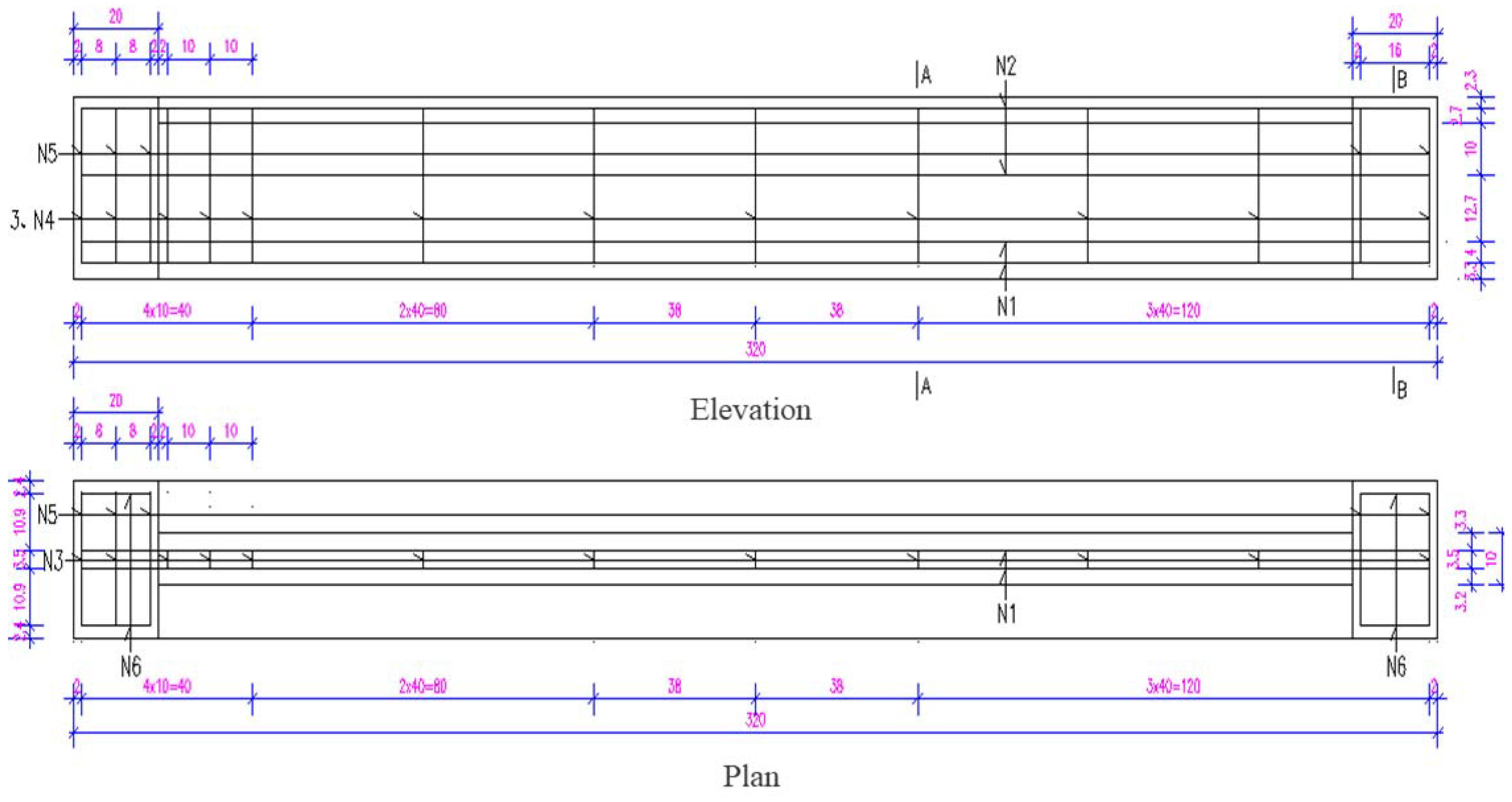
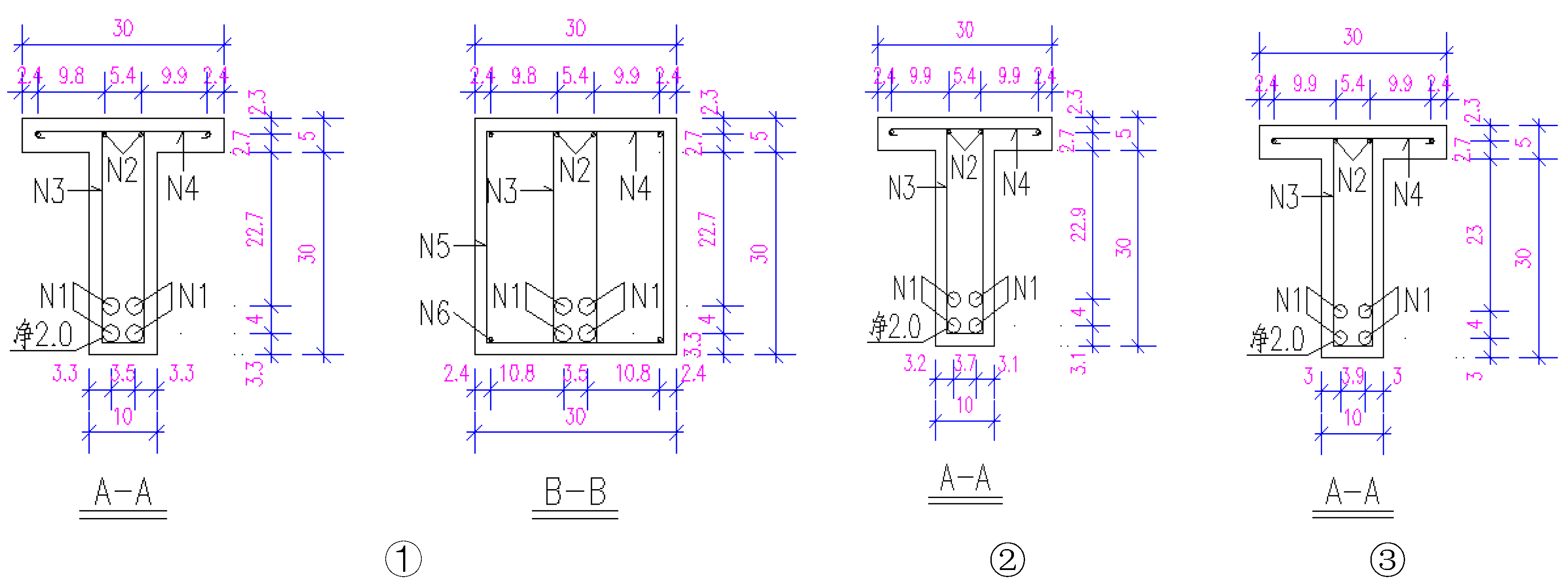
4.2. Specimen Preparation Process
4.3. Load Scheme
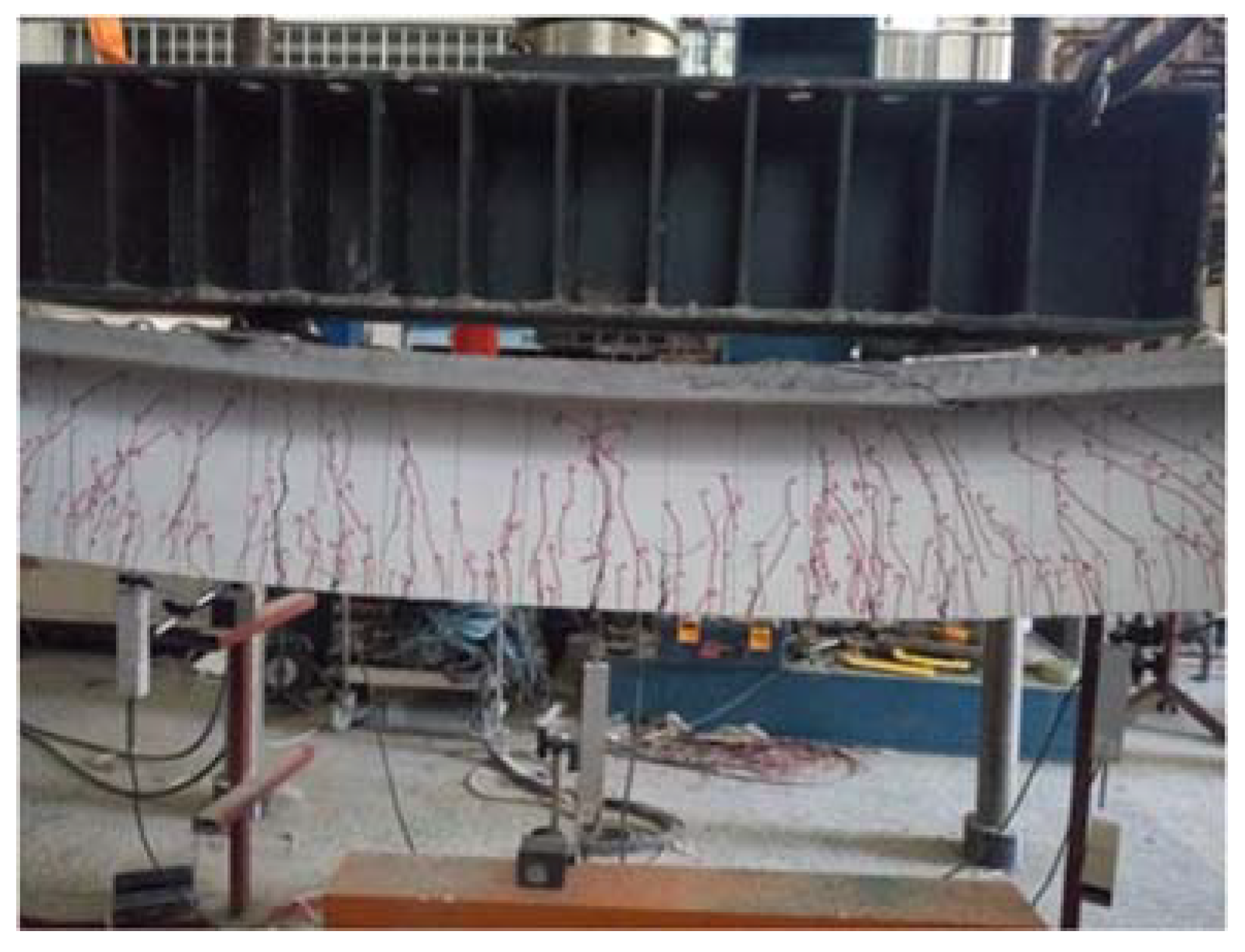
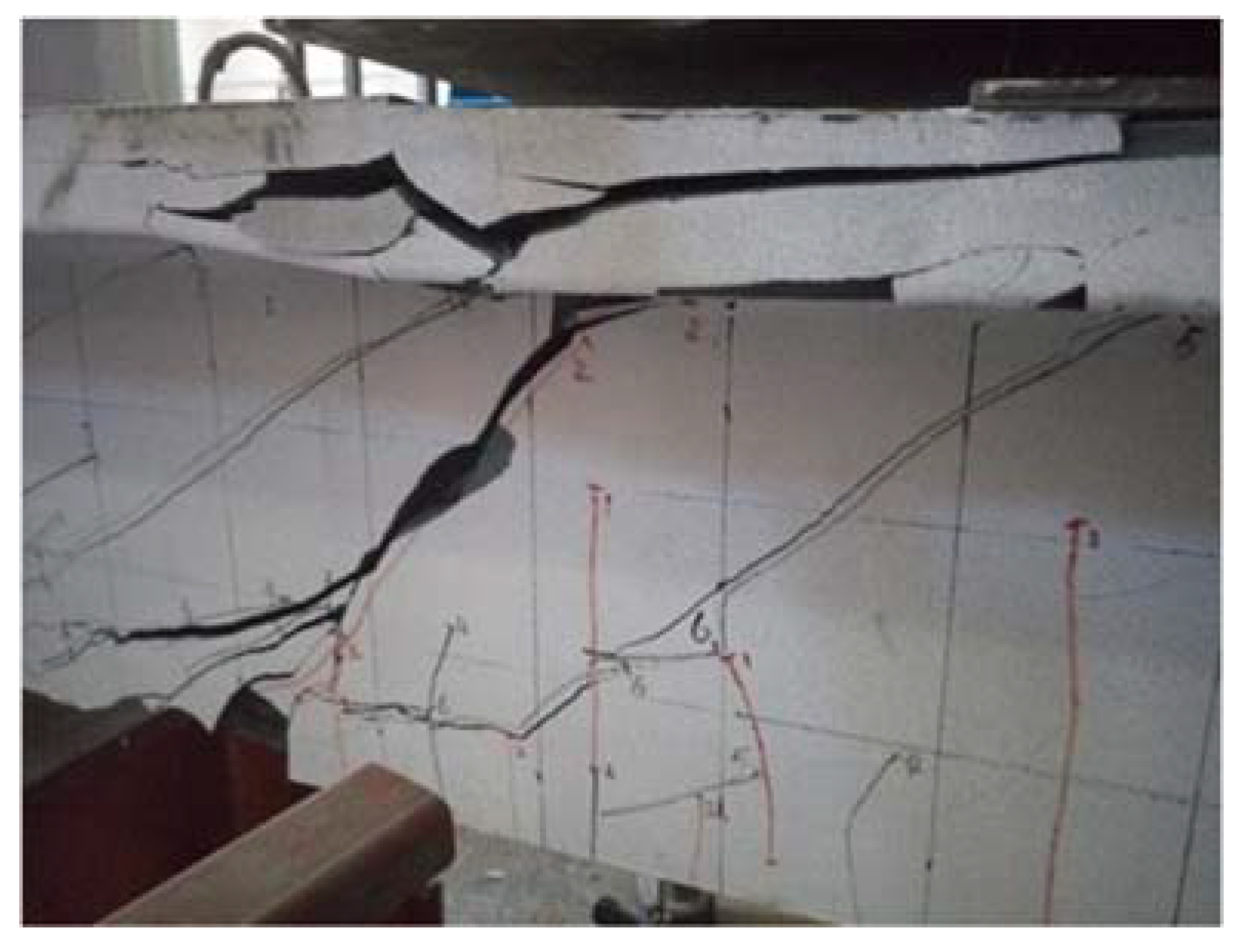
5. T-Beam Flexural Test Results
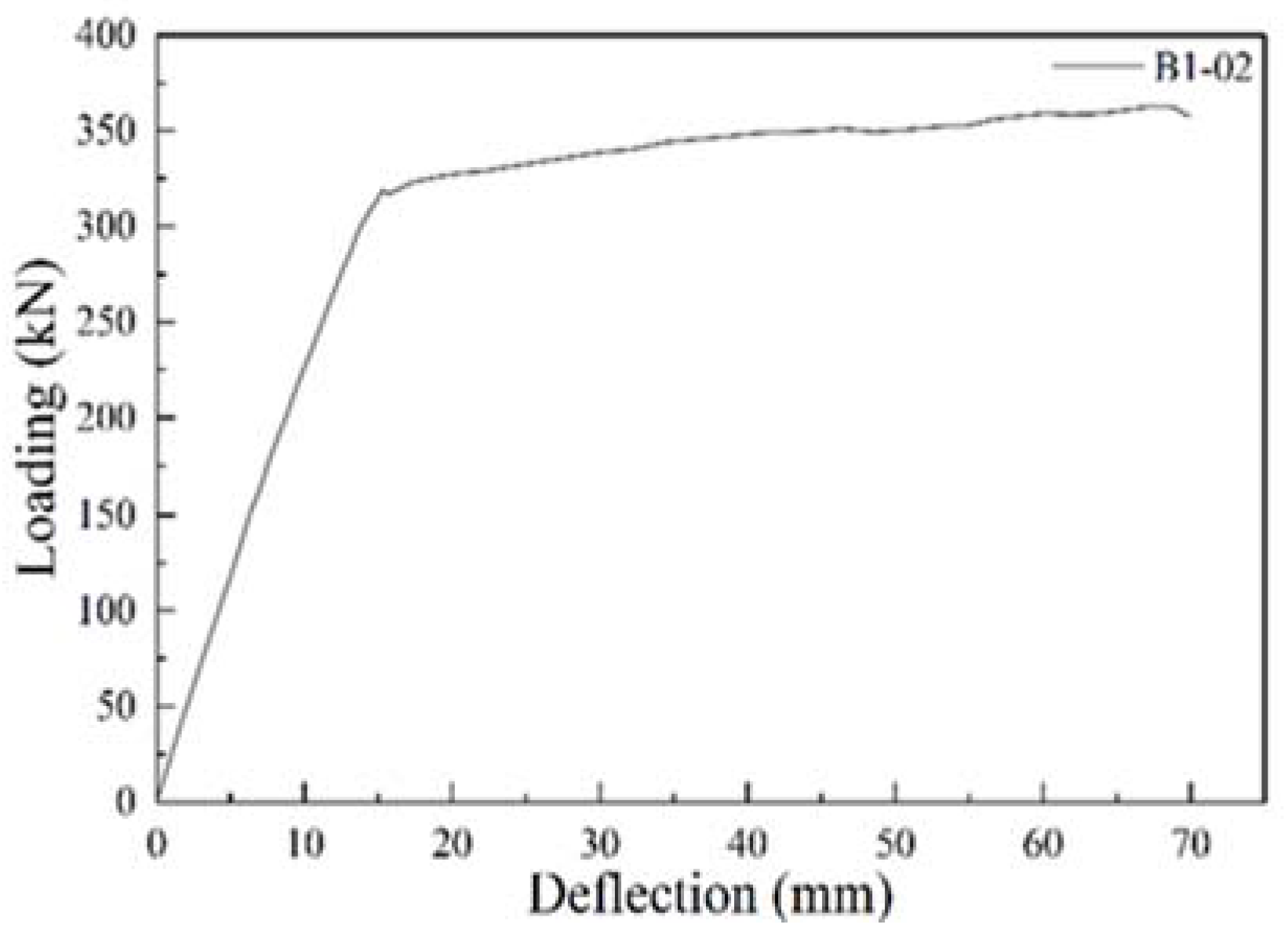
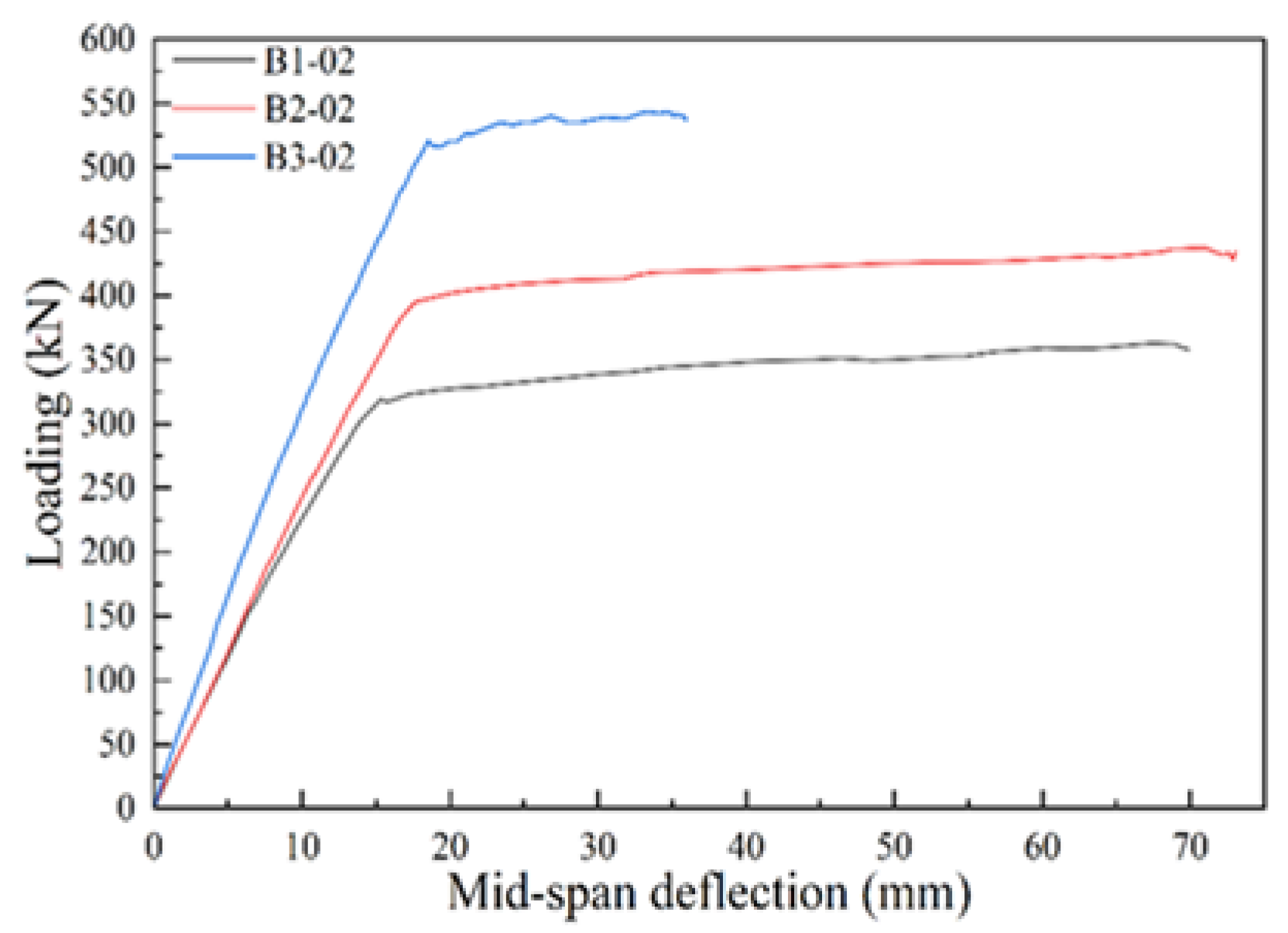
5.1. B1-02 T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
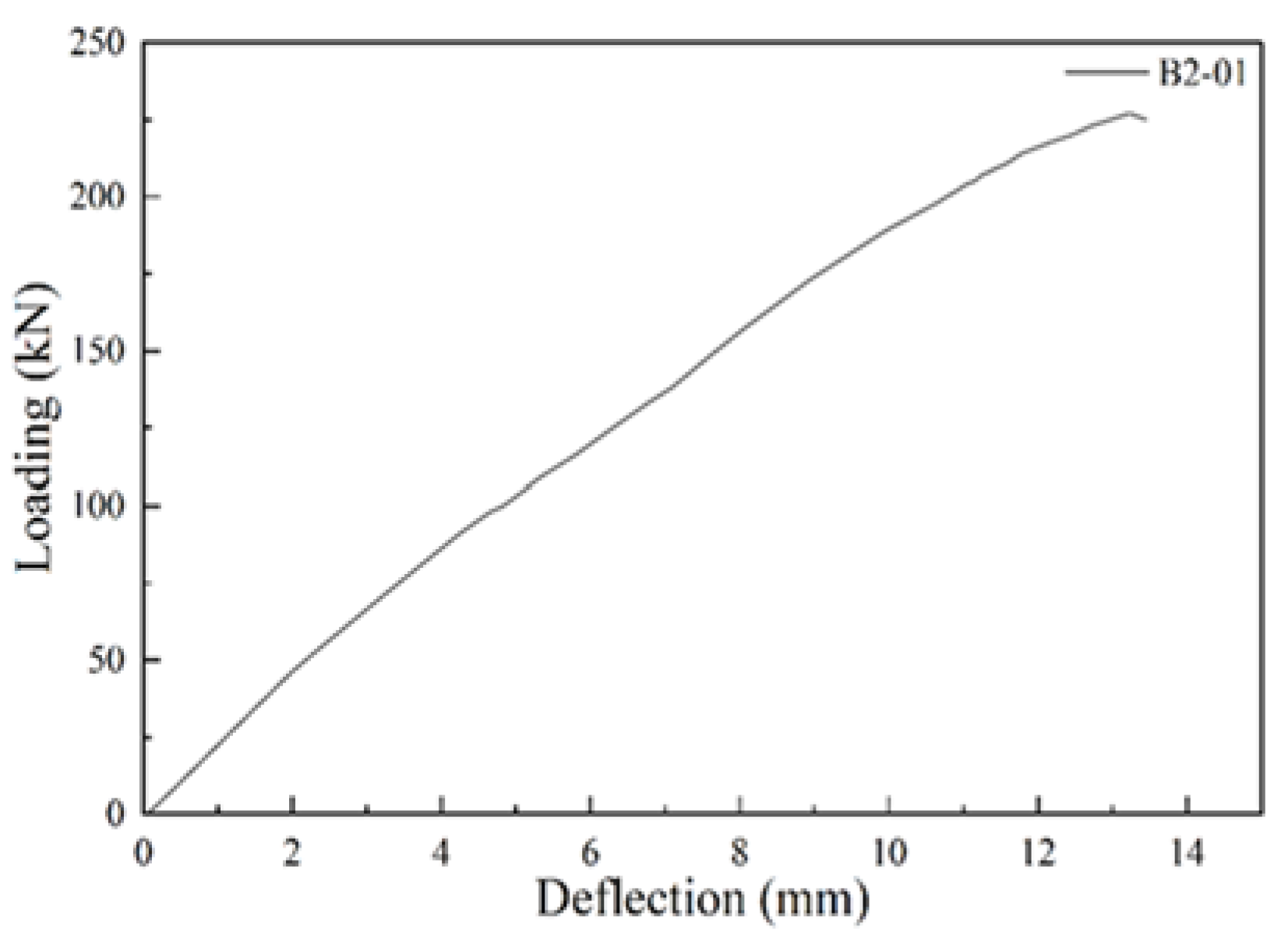
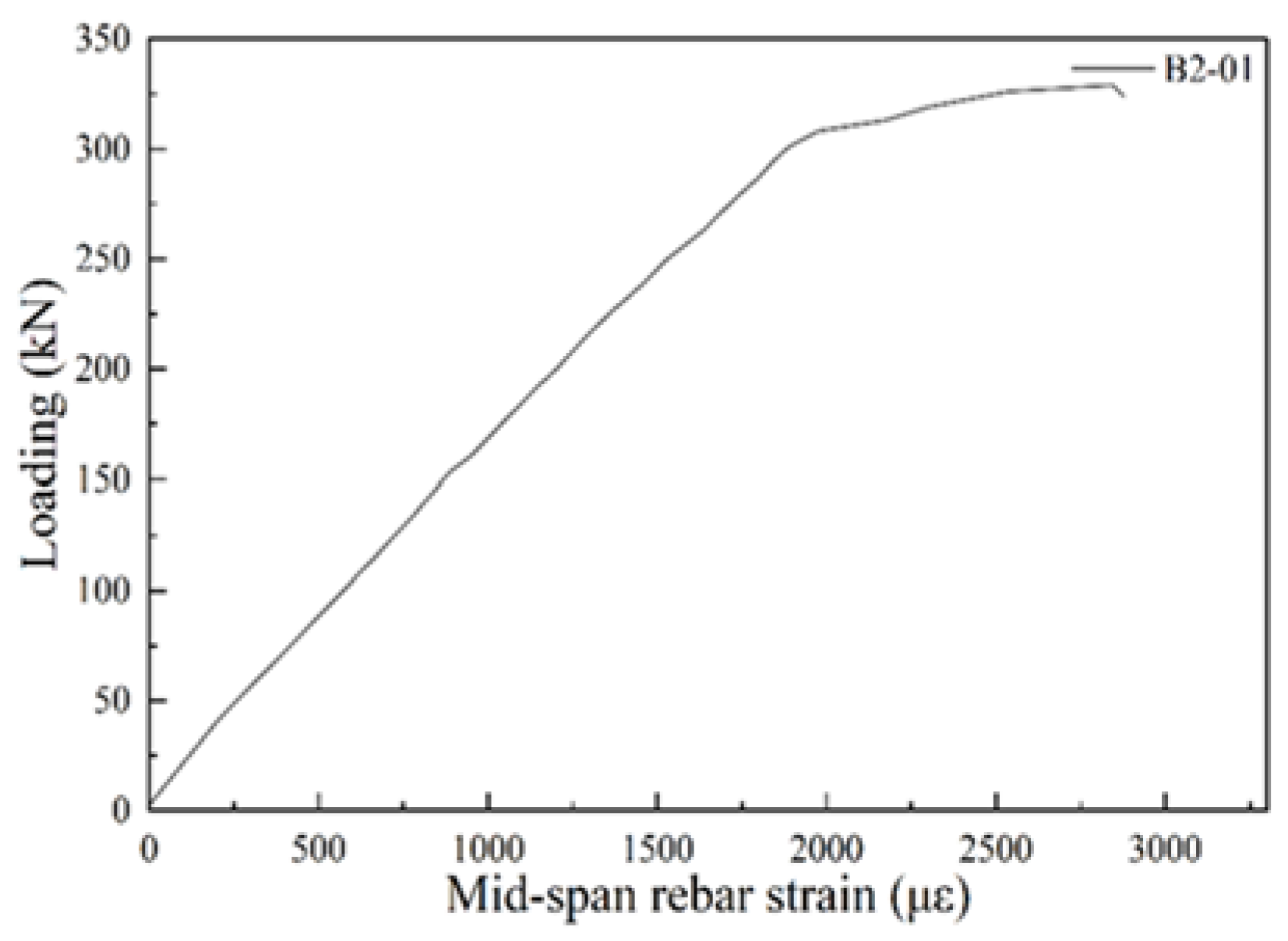
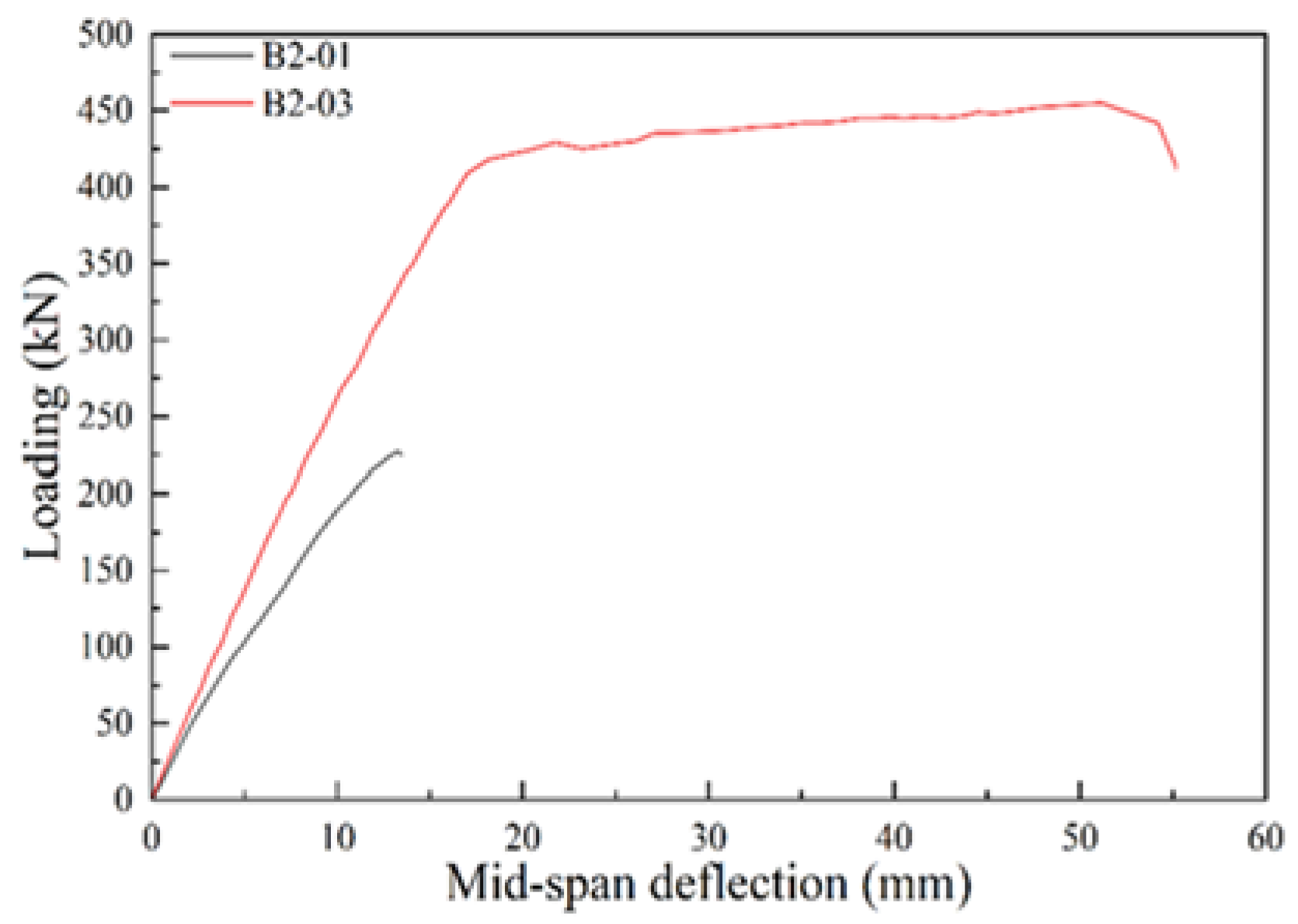
5.2. B2-01 T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
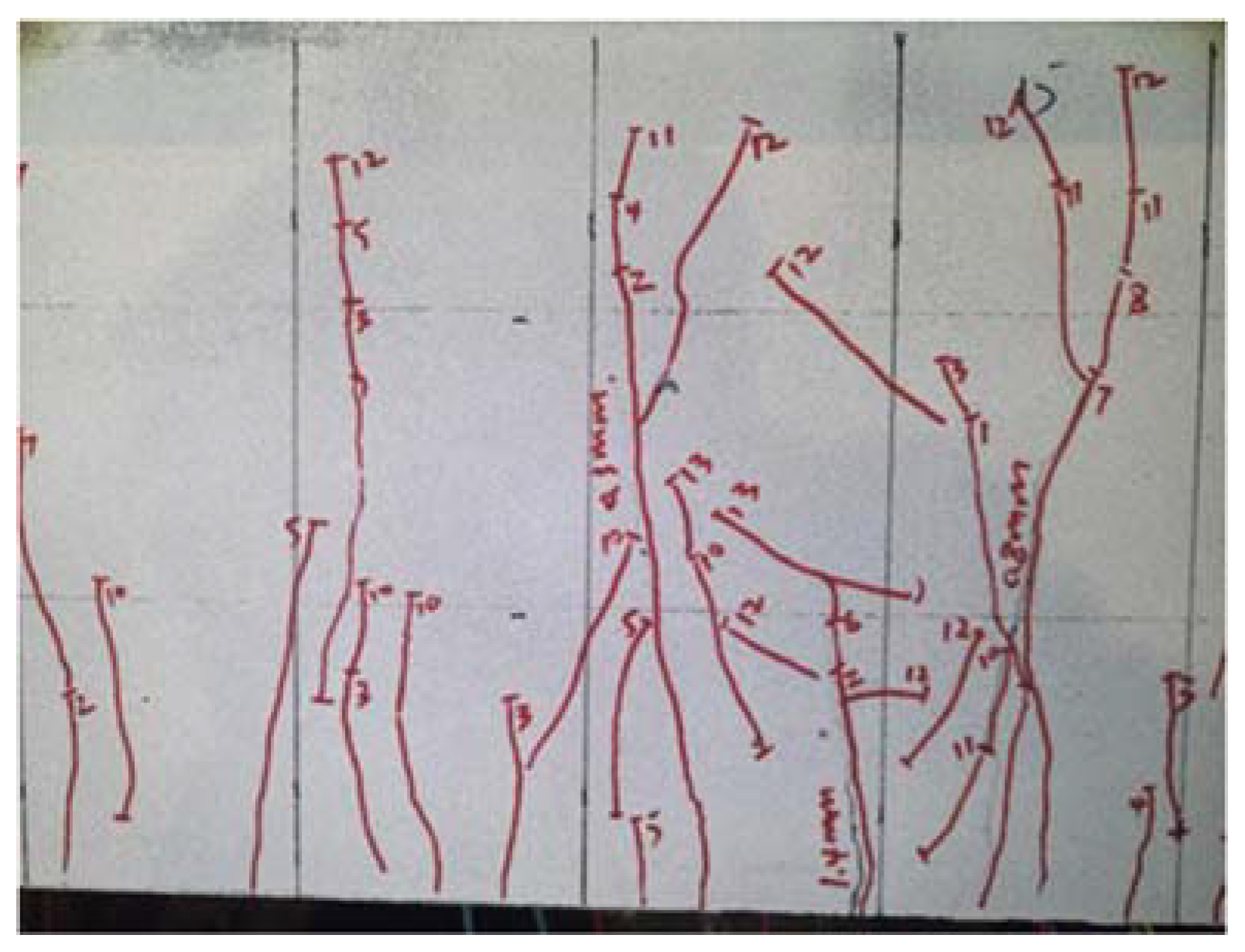
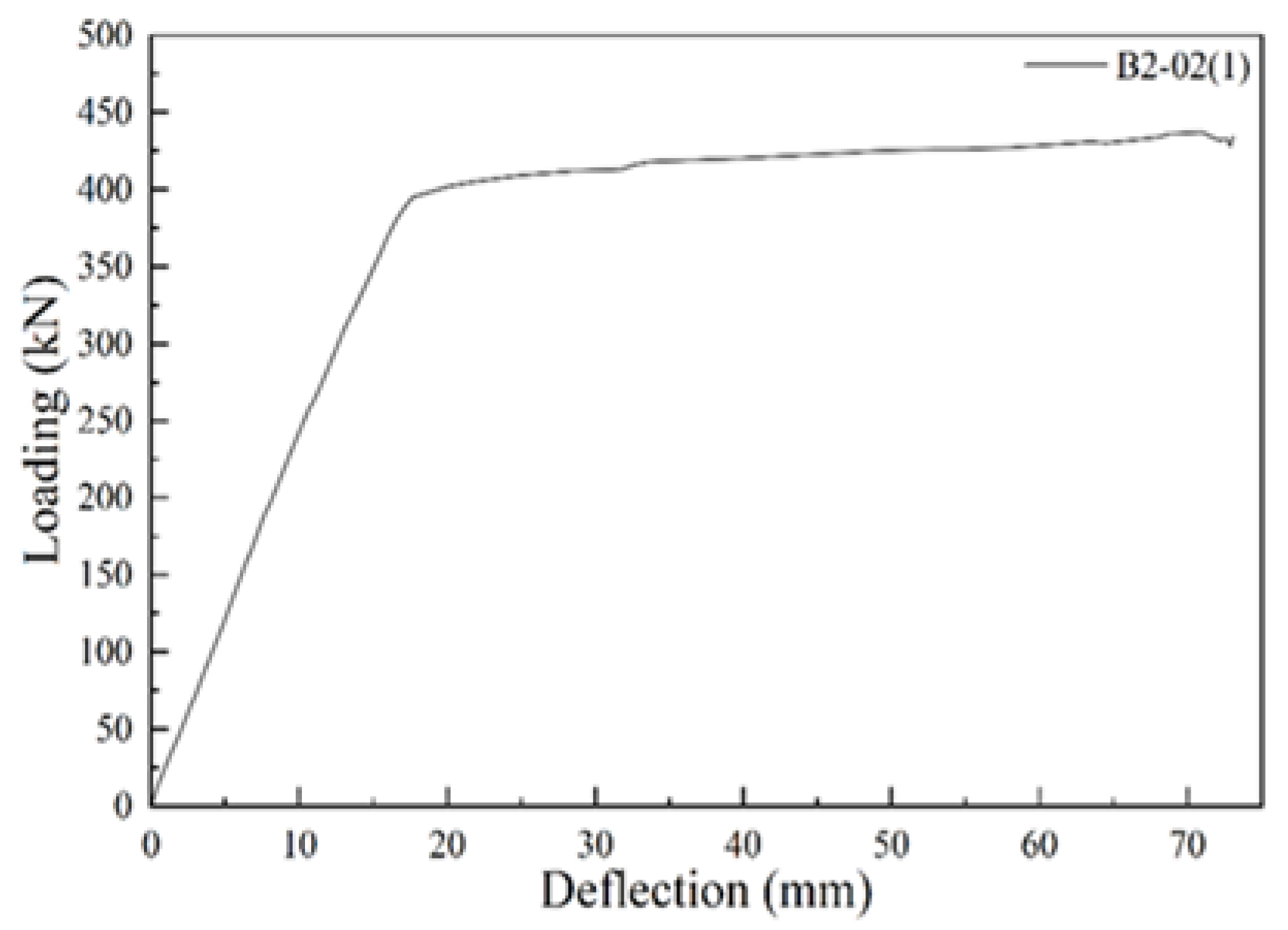
5.3. B2-02(1) T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
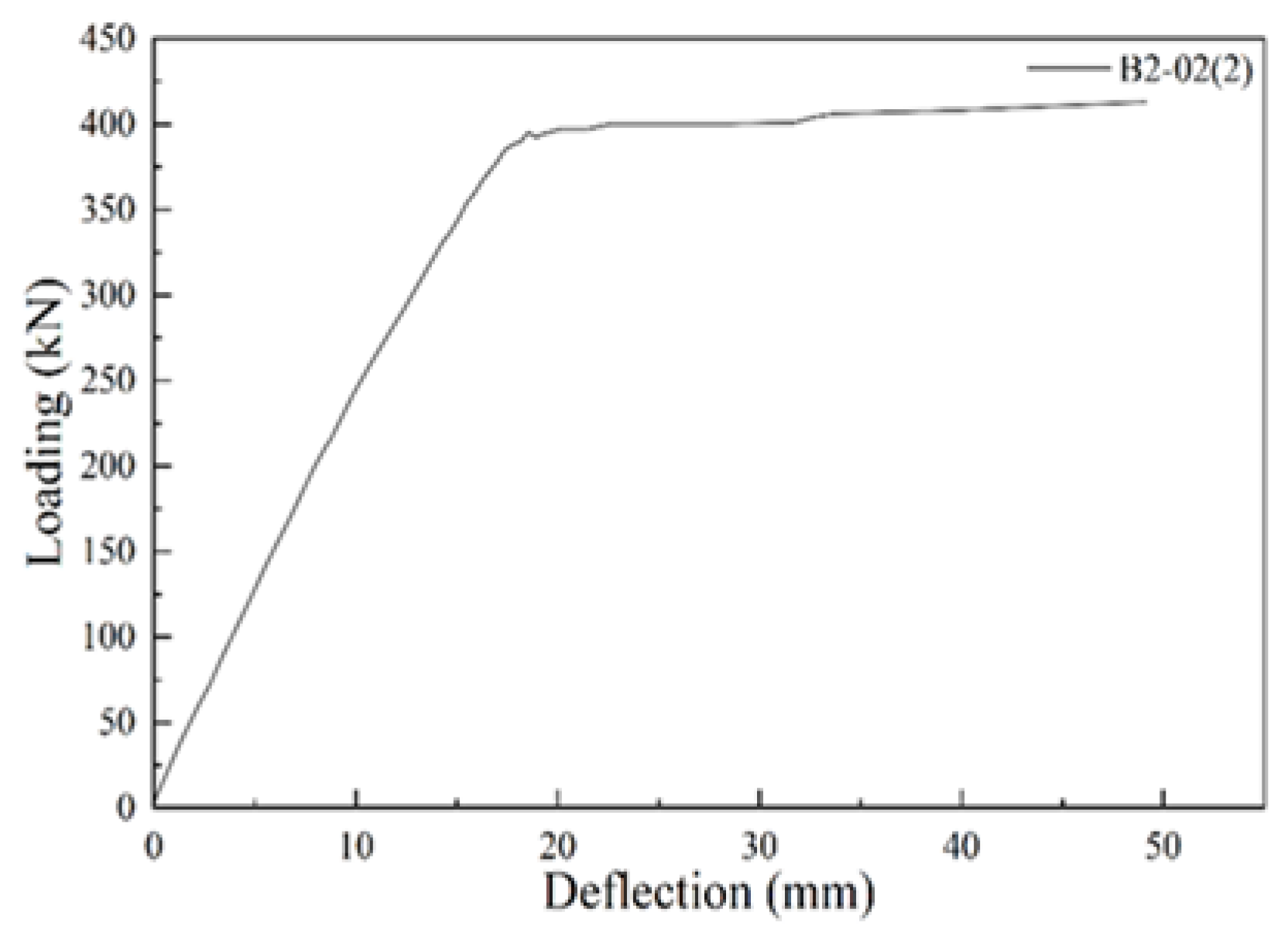
5.4. B2-02(2) T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
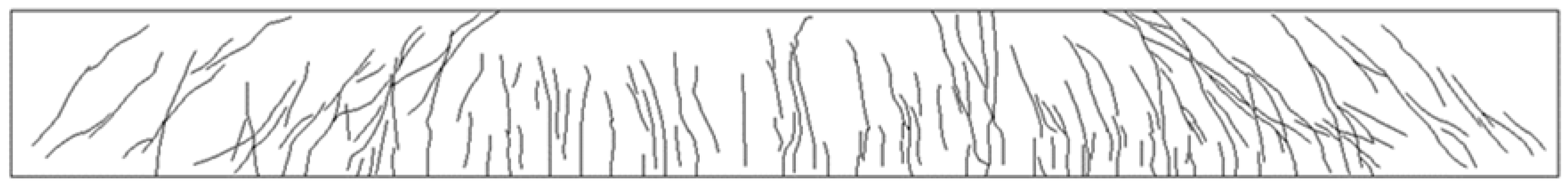
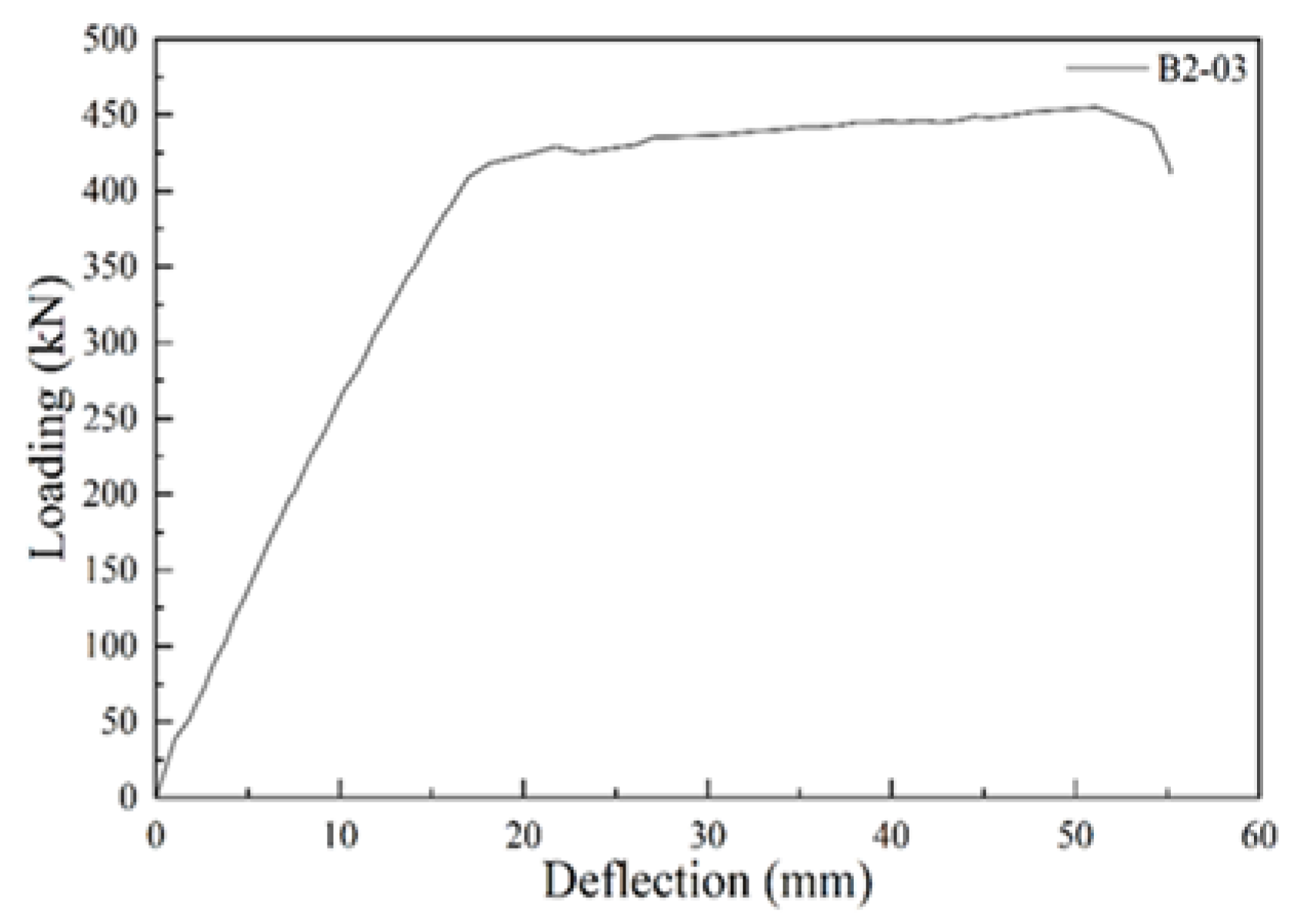
5.5. B2-03 T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
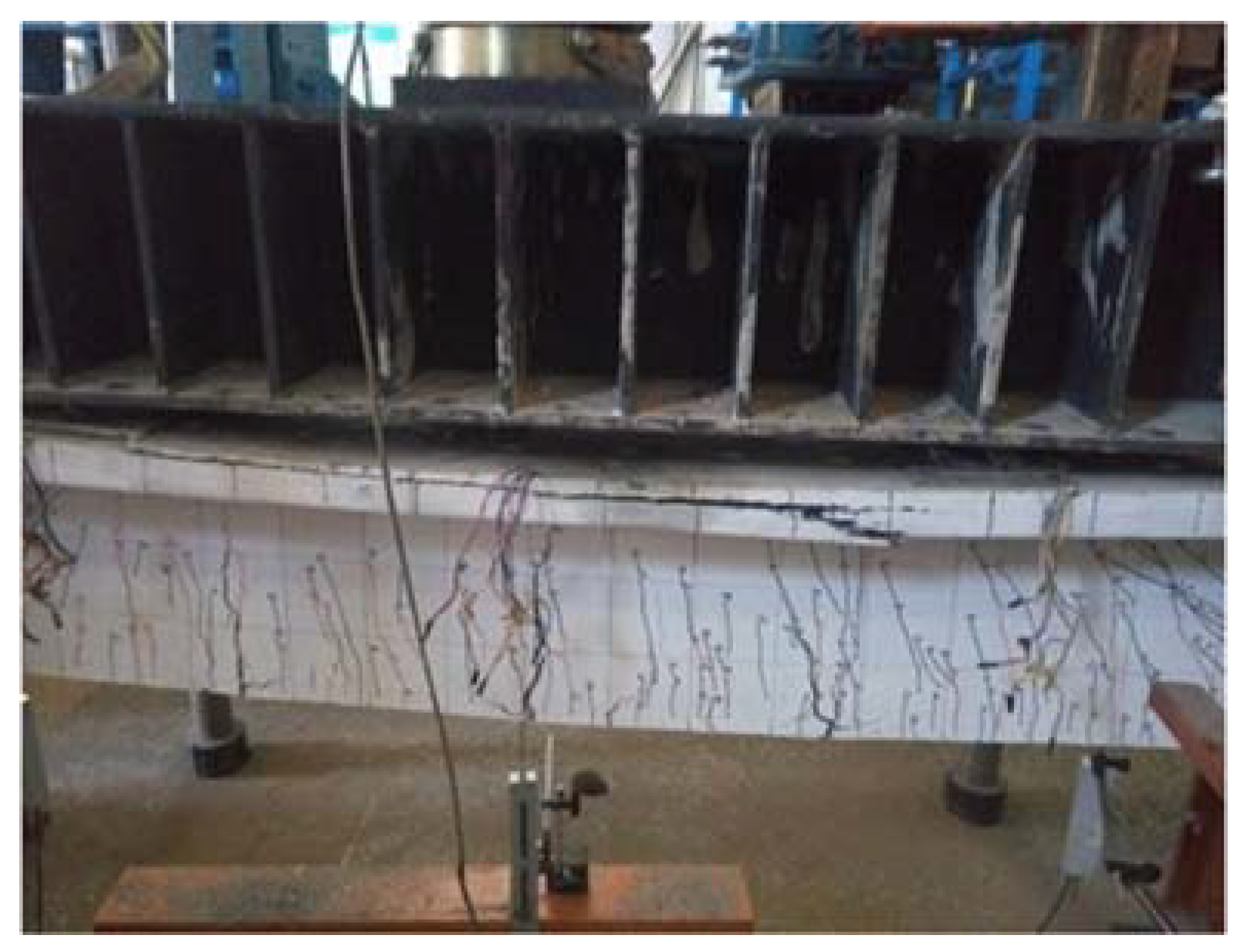
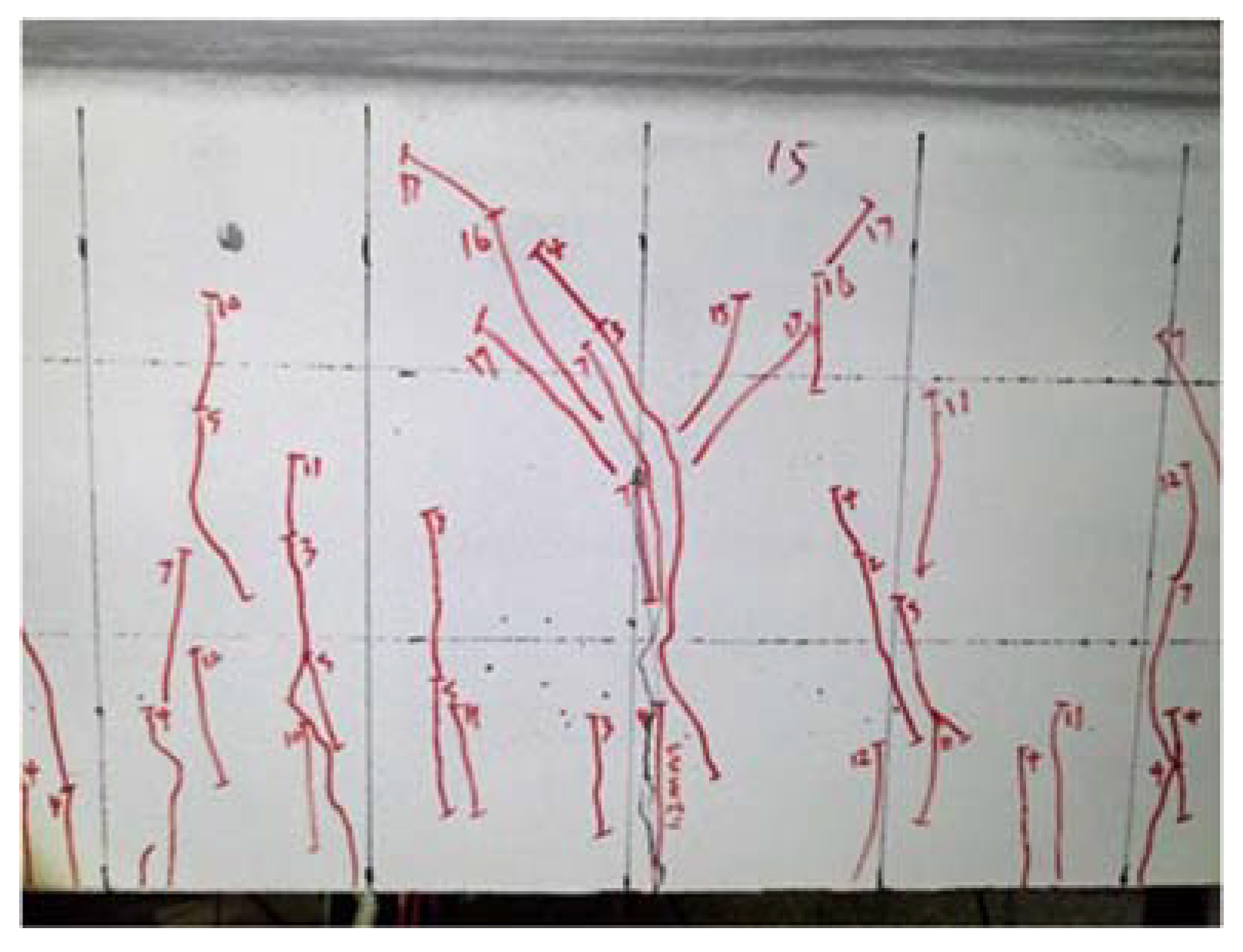
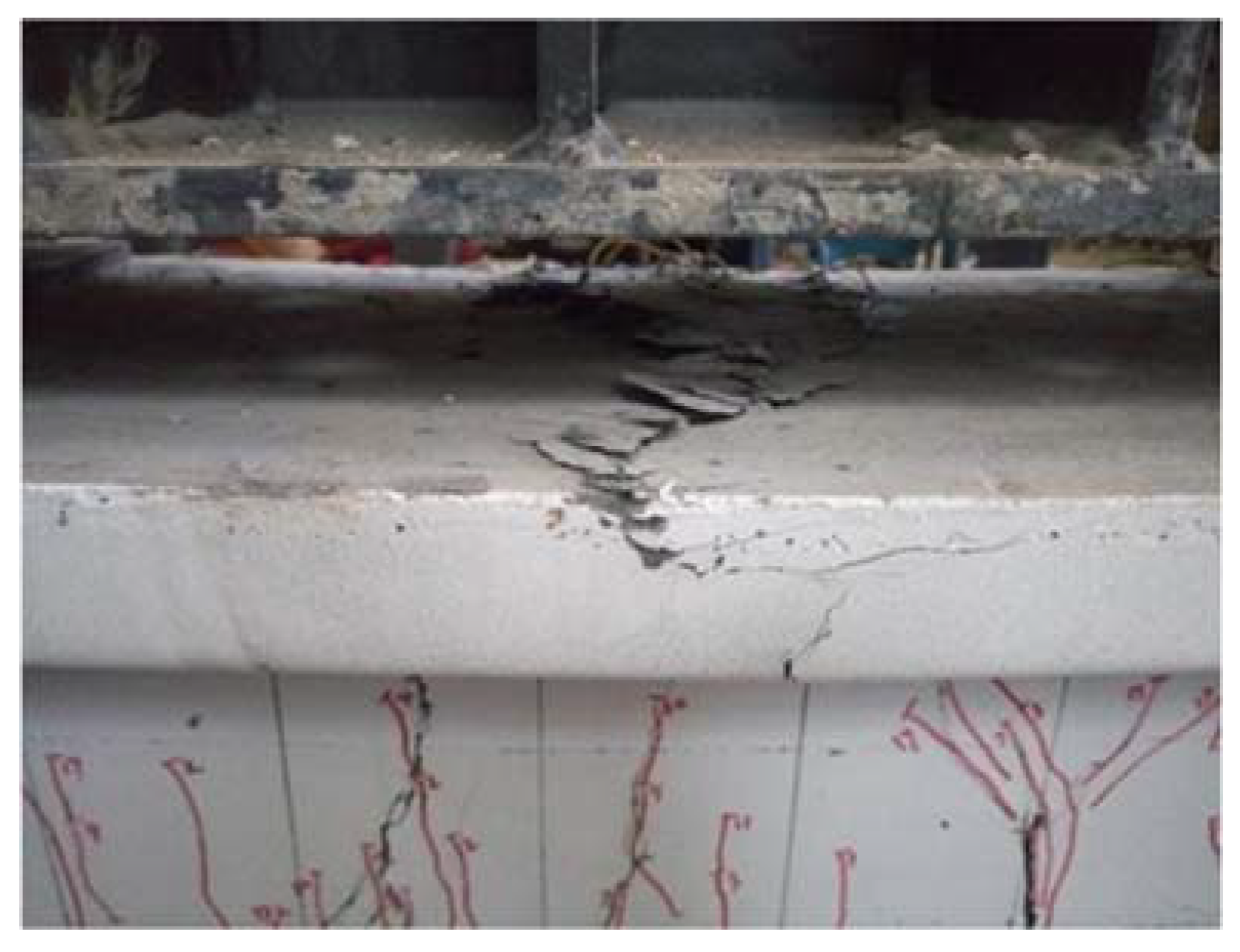
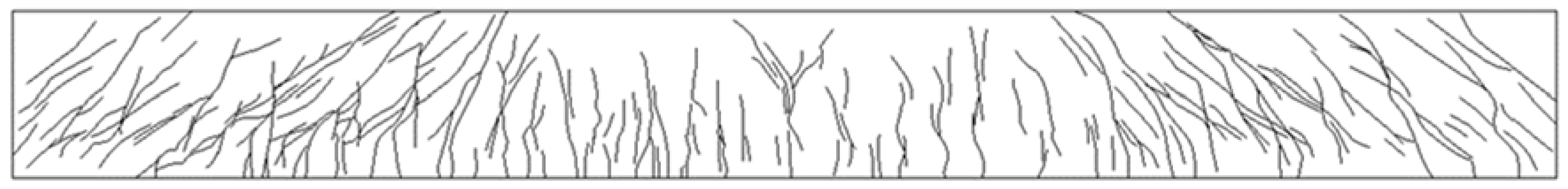
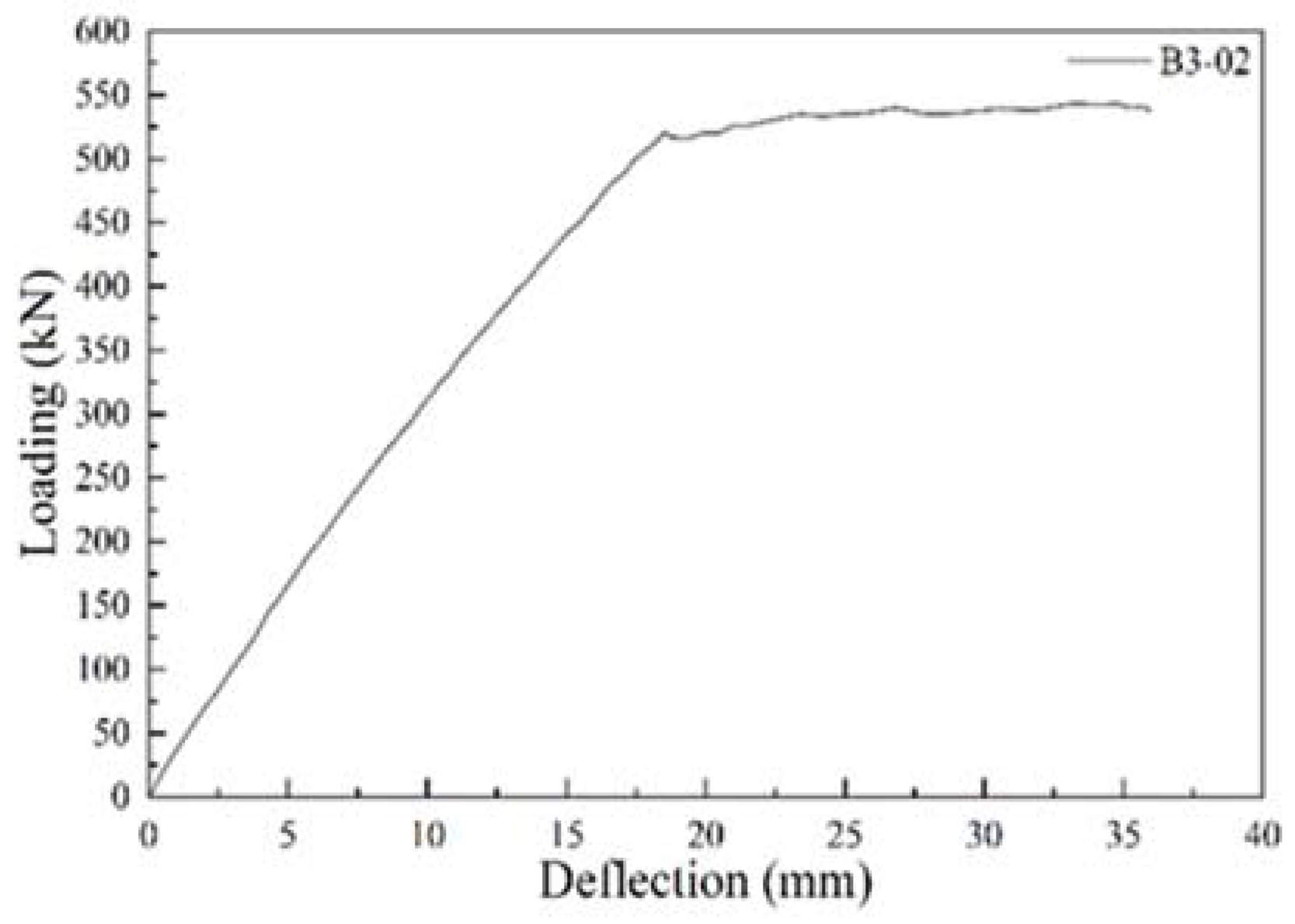
5.6. B3-02 T-Beam Test Procedure and Results
6. T-Beam Flexural Test Analysis
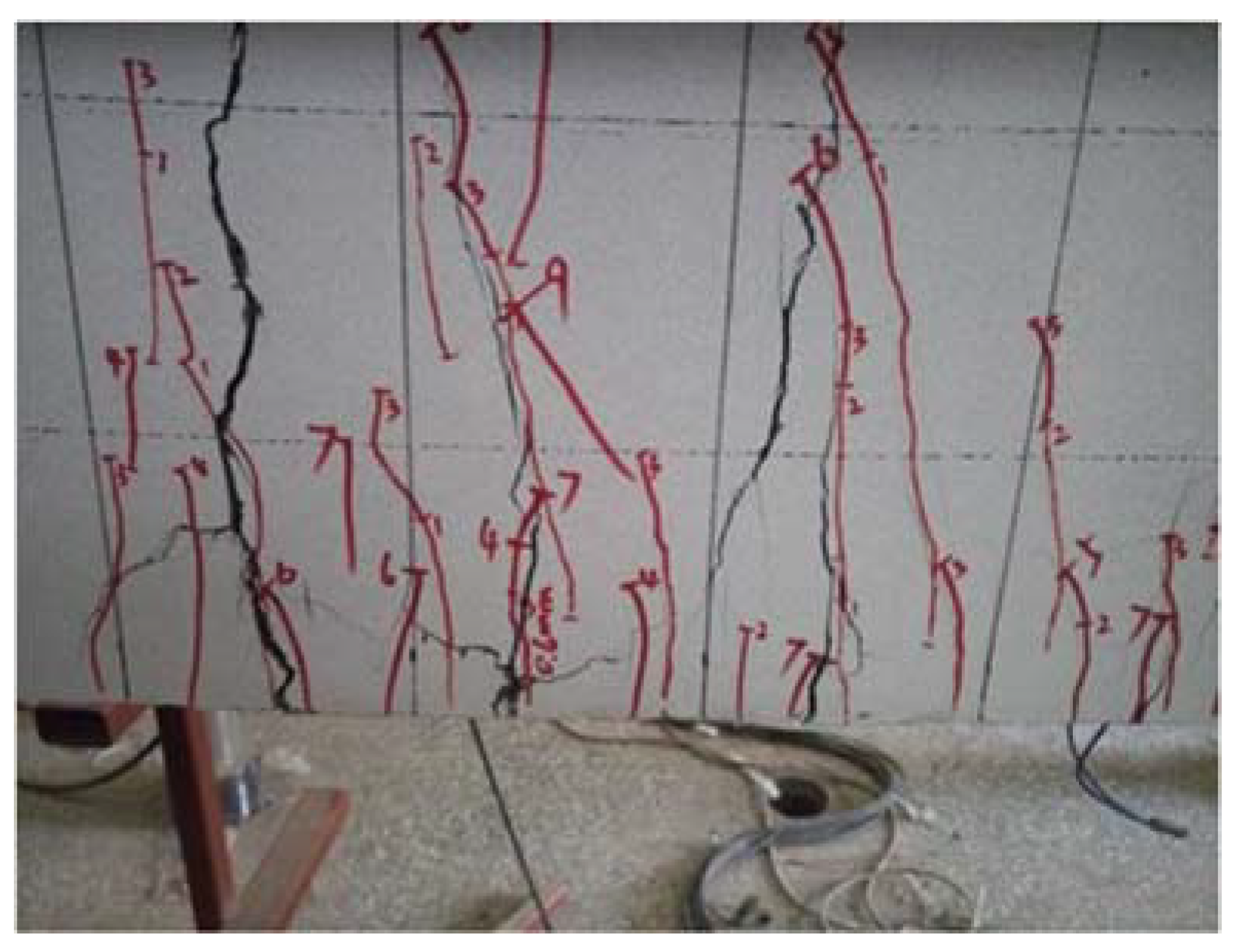
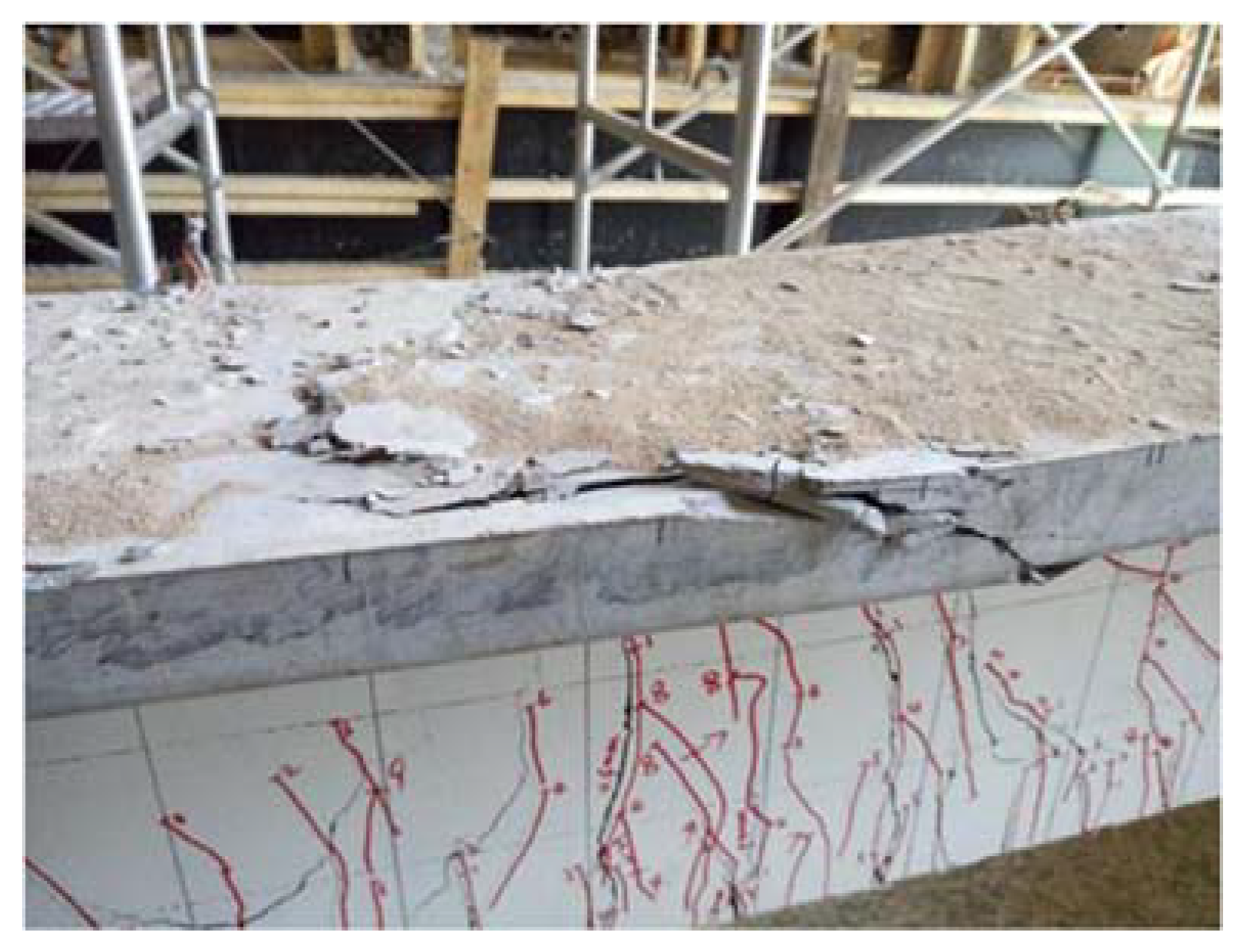
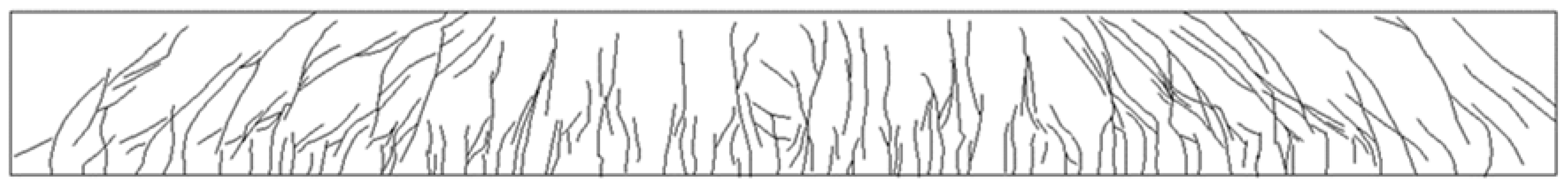
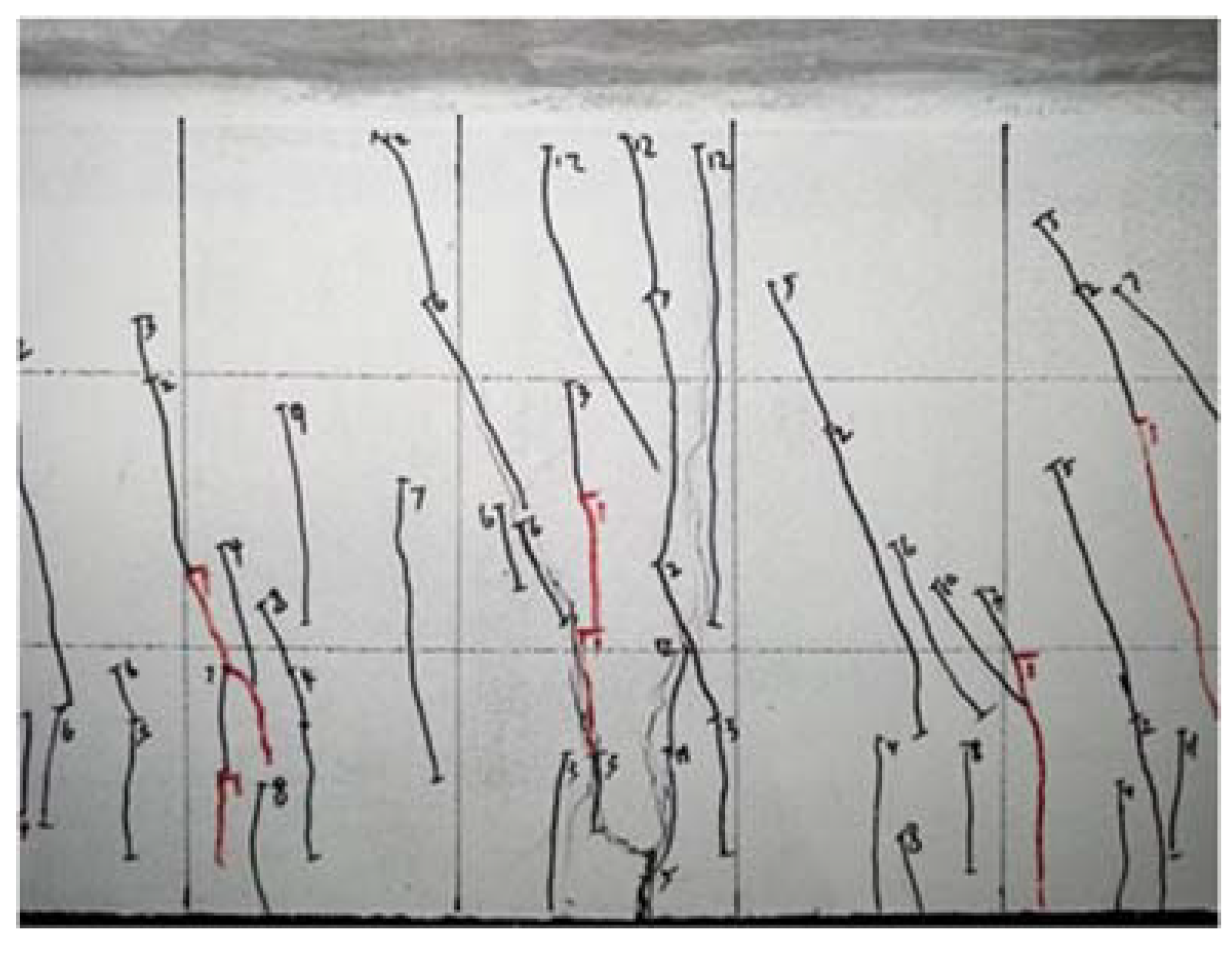
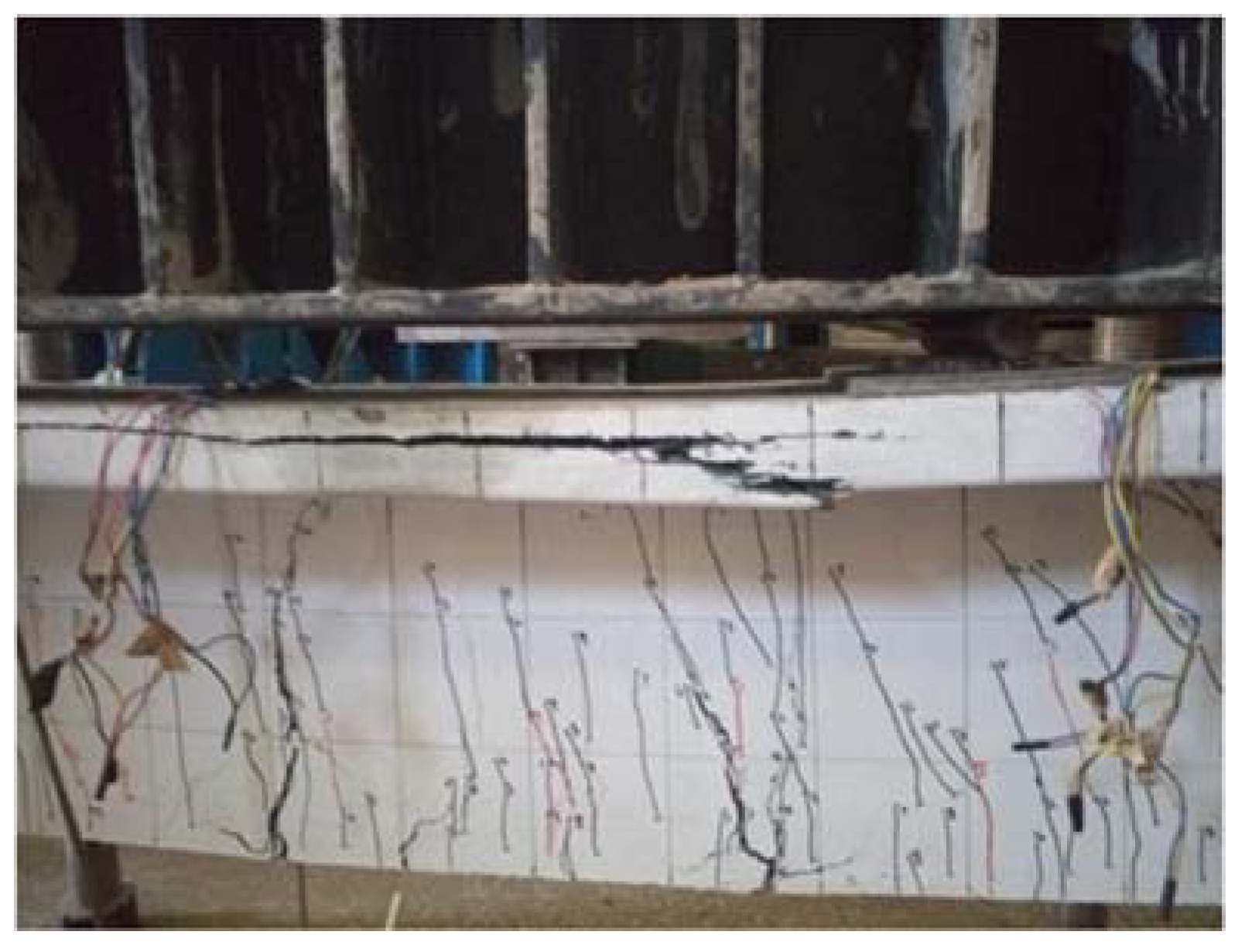
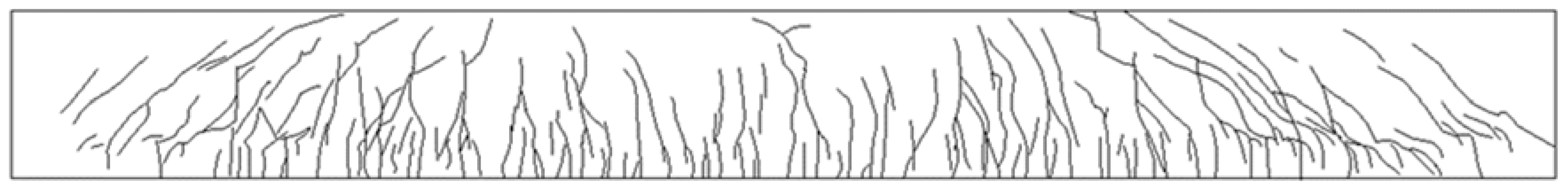
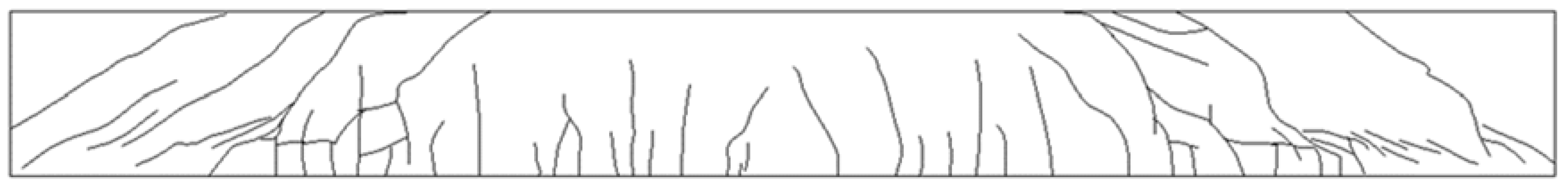
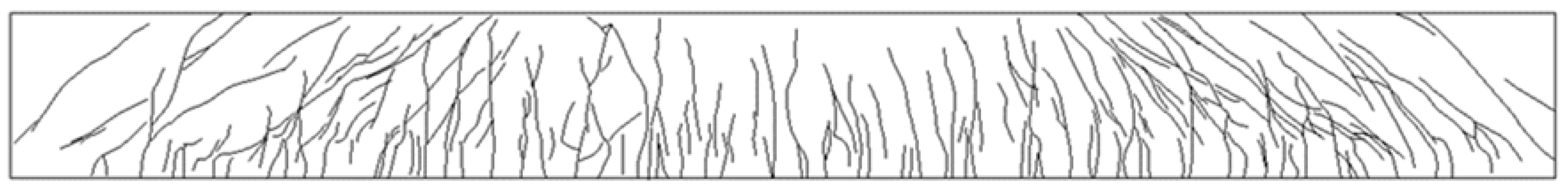
6.1. Flexural Failure Mode
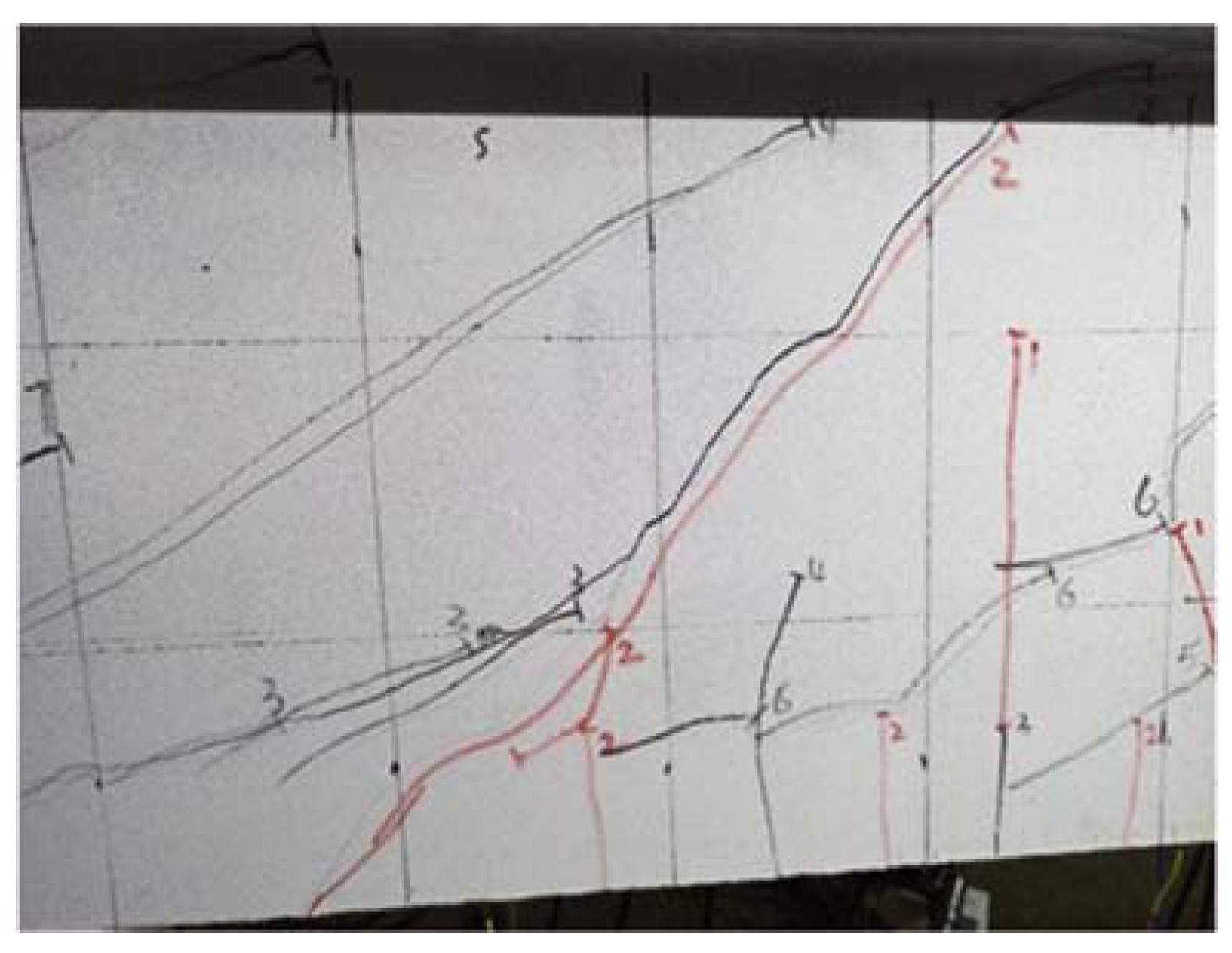
6.2. Rebar Strain Analysis
6.3. Initial Stiffness Analysis
6.4. Comparative Analysis of Different Rebar Ratios
6.5. Comparative Analysis of Different Steel Fiber Addition Rates
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, D. Vulnerability analysis of high-strength steel-reinforced UHPC frame structures. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2024, 45, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, J. Study on seismic damage and control measures of the long-span continuous rigid frame bridge with high piers. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2025, 46, 720–726. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Xue, X.; Hou, D.; Li, W.; Han, H.; Han, Y. Effect of Polyethylene and Steel Fibers on the Fracture Behavior of Coral Sand Ultra-High Performance Concrete. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Vaidyan, J.A.P. Optimisation of Fibre-Reinforced Hybrid Composites Under Combined Loading. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, S. High-Performance construction materials: Latest advances and prospects. Buildings 2022, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Ma, M. The research progress and Hotspot analysis of polymer cement mortar based on bibliometrics. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1401816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fuhaid, A. Effects of Recycled and Supplemented Cementitious Materials on Corrosion Resistance and Mechanical Properties in Reinforced Concrete. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Carr, L.; Zia, A.; Khan, M.; McNally, C. Advancing 3D Printable Concrete with Nanoclays: Rheological and Me-chanical Insights for Construction Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, S. Flexural toughness and impact behavior of hybrid fibers reinforced UHPC. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2025, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Deng, Z. Investigation of tensile cracking characteristics of high strength and toughness ECC (HST-ECC) and CFRP reinforced HST-ECC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 159, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaber, M.A.; Hakeem, I.Y. UHPC evolution, development, and utilization in construction: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1058–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yuan, S.; Jia, S. Bond Behavior Between Fabric-Reinforced Cementitious Ma-trix (FRCM) Composites and Different Substrates: An Experimental Investigation. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Jang, J.G.; Bansal, P.P. A comprehensive review on effects of mineral admixtures and fibers on engineering properties of ultra-high-performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 45, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, I.Y.; Amin, M.; Agwa, I.S.; Rizk, M.S.; Abdelmagied, M.F. Effect of using sugarcane leaf ash and granite dust as partial replacements for cement on characteristics of ultra-high performance concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçioğlu, A.Ö.; Kazemi, F.; Shafighfard, T. Grey wolf optimizer integrated within boosting algorithm: Application in mechanical properties prediction of ultra high-performance concrete including carbon nanotubes. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 42, 102601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçioğlu, A.Ö.; Delikanlı, A.; Shafighfard, T.; Bagherzadeh, F. Machine learning based shear strength prediction in reinforced concrete beams using Levy flight enhanced decision trees. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Asgarkhani, N.; Shafighfard, T.; Jankowski, R.; Yoo, D.Y. Machine-learning methods for estimating performance of structural concrete members reinforced with fiber-reinforced polymers. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025, 32, 571–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, N.M.; Mirrashid, M.; Naderpour, H.; Ciftcioglu, A.O.; Meddage, D.P.P.; Ezami, N. Machine learning approach to predict the mechanical properties of cementitious materials containing carbon nanotubes. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 19, 100494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıok, T.Y.; Üstüner, B.; Özyüksel, Ç.A.; Demir, A. Enhancing Structural Evaluation: Machine Learning Approaches for Inadequate Reinforced Concrete Frames. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2024, 48, 3027–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Xue, H. Flexural toughness of hybrid fiber-reinforced ultra-high performance concrete. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2023, 44, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Kang, S.T.; Yoon, Y.S. Enhancing the flexural performance of ultra-high-performance concrete using long steel fibers. Compos. Struct. 2016, 147, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wie, B.; Yue, N.; Yu, P.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, L. Experimental and numerical study on honeycomb T-beam bridge deck. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 164, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamari, A.; Thongchom, C.; Zapris, A.G.; Kytinou, V.K. Novel Ductile Moment-Resisting Frame Compound of Steel Gusset Plate for Beam-to-Column Connections and I-Shaped FRP Profile Sections. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Gutub, S.A.; Wafa, M.A. A review on FRP composites applications and durability concerns in the construction sector. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1966–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Brenkus, N.R.; Tatar, J. Strategies for prevention, protection, and repair of bridge girders vulnerable to over-height vehicle impacts: A state-of-the-art review. Structures 2022, 44, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hag-Elsafi, O.; Almpalli, S.; Kunin, J. Application of FRP laminates for strengthening of a reinforced-concrete T-beam bridge structure. Compos. Struct. 2001, 52, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deifalla, A.; Awad, A.; Seleem, H.; Abdekrahman, A. Investigating the behavior of lightweight foamed concrete T-beams under torsion, shear, and flexure. Eng. Struct. 2020, 219, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Mao, J.Y.; Dong, K.; Miao, J.J.; Gu, Z.J.; Li, L.H. Calculation method of the residual bearing capacities of concrete T-shaped beams considering the effect of fire cracks. Fire Technol. 2023, 59, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lu, W.; Song, J.; Lee, G.C. Application of ultra-high performance concrete in bridge engineering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Yang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xu, L.; Feng, S.; Sun, X. Shear performance of deep partially precast high-strength steel reinforced UHPC T-beam: Experimental study and a novel shear model. Eng. Struct. 2025, 323, 119256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, X.; Cao, J.; Fu, Y. Experimental and analytical investigations into flexural behavior of composite beams with UHPC T-section and HRS H-section. Eng. Struct. 2024, 315, 118445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T50081; Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China and Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Zeng, J.J.; Pan, B.Z.; Fan, T.H.; Zhuge, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, L.J. Shear behavior of FRP-UHPC tubular beams. Compos. Struct. 2023, 307, 116576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Lin, R.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Ren, J.; Liu, F.; Xiong, Z. The mechanical and microstructural study on the cement pastes adding various cementitious capillary crystalline waterproof materials. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.H.; Zeng, J.J.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.D.; Wu, P.P.; Liu, H.T.; Zhuge, Y. Flexural fatigue behavior of FRP-reinforced UHPC tubular beams. Eng. Struct. 2025, 330, 119848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Zeng, J.J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhang, L. Constitutive models of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) under true tri-axial compression and an analysis-oriented model for FRP-confined UHPC. Eng. Struct. 2024, 305, 117656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Liu, F.; Zhuge, Y.; Zeng, J.J.; Liao, J.J. ECCs/UHPFRCCs with and without FRP reinforcement for structural strengthening/repairing: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 316, 125824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



























| Mix Ratio ID | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Steel Fiber Content (%) | Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 130 | 0 | The base material remains unchanged without adding steel fibers |
| 02 | 130 | 1.5 | Adjust the base material composition by adding 1.5% steel fibers |
| 03 | >130 | 1.5 | Based on mix ratio 1, add 1.5% steel fibers |
| SP | Water | Cement | Powdered Slag | 100–200 Mesh Quartz Sand | 40–70 Mesh Quartz Sand | Steel Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36.7 | 173 | 700 | 250 | 800 | 200 | 0 |
| 40 | 170 | 700 | 250 | 960 | 240 | 117 |
| 36.7 | 173 | 700 | 250 | 800 | 200 | 117 |
| Cube Size | Mix Ratio 1 | Mix Ratio 2 | Mix Ratio 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-40 mm | 146.6 | 138.3 | 147.5 |
| C-70 mm | 143.8 | 135.6 | 144.5 |
| C-100 mm | 133.8 | 132.1 | 135.7 |
| ID | Steel Fiber Content | Specimen Rebar Placement | Number of Specimens |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1-02 | 1.5% | 4D18 | 1 |
| B2-01 | 0.0% | 4D20 | 1 |
| B2-02(1) | 1.5% | 4D20 | 2 |
| B2-02(2) | |||
| B2-03 | 1.5% | 4D20 | 1 |
| B3-02 | 1.5% | 2D20 + 2D25 | 1 |
| ID | Rebar Ratio | Cracking Load | Yielding Load | Ultimate Load Capacity | Maximum Deflection at Mid-Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1-02 | 2.26 | 76 | 319 | 360 | 70 |
| B2-01 | 2.79 | 45 | Rebar not yielded | 225 | Brittle shear failure |
| B2-02 | 2.79 | 69 | 395 | 434 | 72 |
| B2-03 | 2.79 | 70 | 418 | 455 | 55 |
| B3-02 | 4.58 | 59 | 517 | 543 | 36 |
| B1-02 | 2.26 | 76 | 319 | 360 | 70 |
| ID | Load Range in the Elastic Stage (kN) | Corresponding Deflection Range (mm) | Initial Stiffness |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1-02 | 0–319 | 0–16 | 19.94 |
| B2-01 | 0–225 | 0–12 | 18.75 |
| B2-02 | 0–395 | 0–17 | 23.24 |
| B2-03 | 0–389 | 0–18 | 21.61 |
| B3-02 | 0–418 | 0–18 | 23.22 |
| B1-02 | 0–517 | 0–18.7 | 27.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, H.; Mao, S.; Wang, L.; Deng, Z. Influence of Steel Fiber and Rebar Ratio on the Flexural Performance of UHPC T-Beams. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100545
Xue H, Mao S, Wang L, Deng Z. Influence of Steel Fiber and Rebar Ratio on the Flexural Performance of UHPC T-Beams. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(10):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100545
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Huiqing, Shichun Mao, Liyang Wang, and Zongcai Deng. 2025. "Influence of Steel Fiber and Rebar Ratio on the Flexural Performance of UHPC T-Beams" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 10: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100545
APA StyleXue, H., Mao, S., Wang, L., & Deng, Z. (2025). Influence of Steel Fiber and Rebar Ratio on the Flexural Performance of UHPC T-Beams. Journal of Composites Science, 9(10), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100545





