Study of the Effects of Alkali Treatment and Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Enset/Sisal Polymer Hybrid Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Fiber Treatment
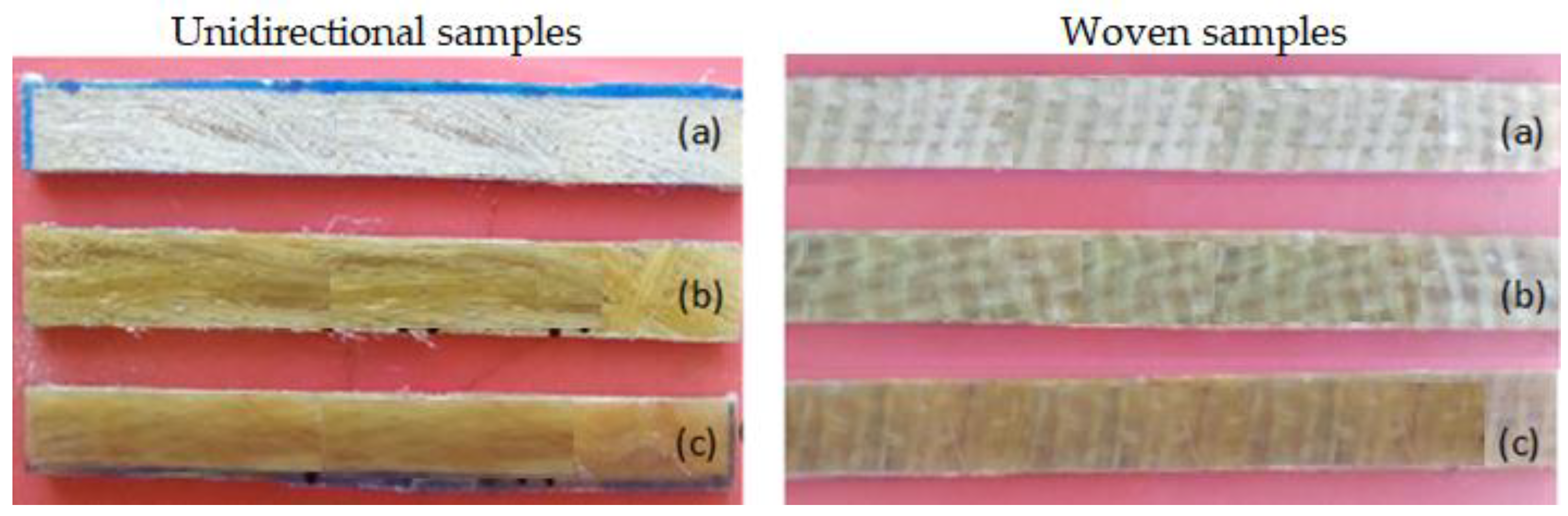
2.2.2. Composite Fabrications
2.2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Discussion of Results
3.1. Tensile Strength Test
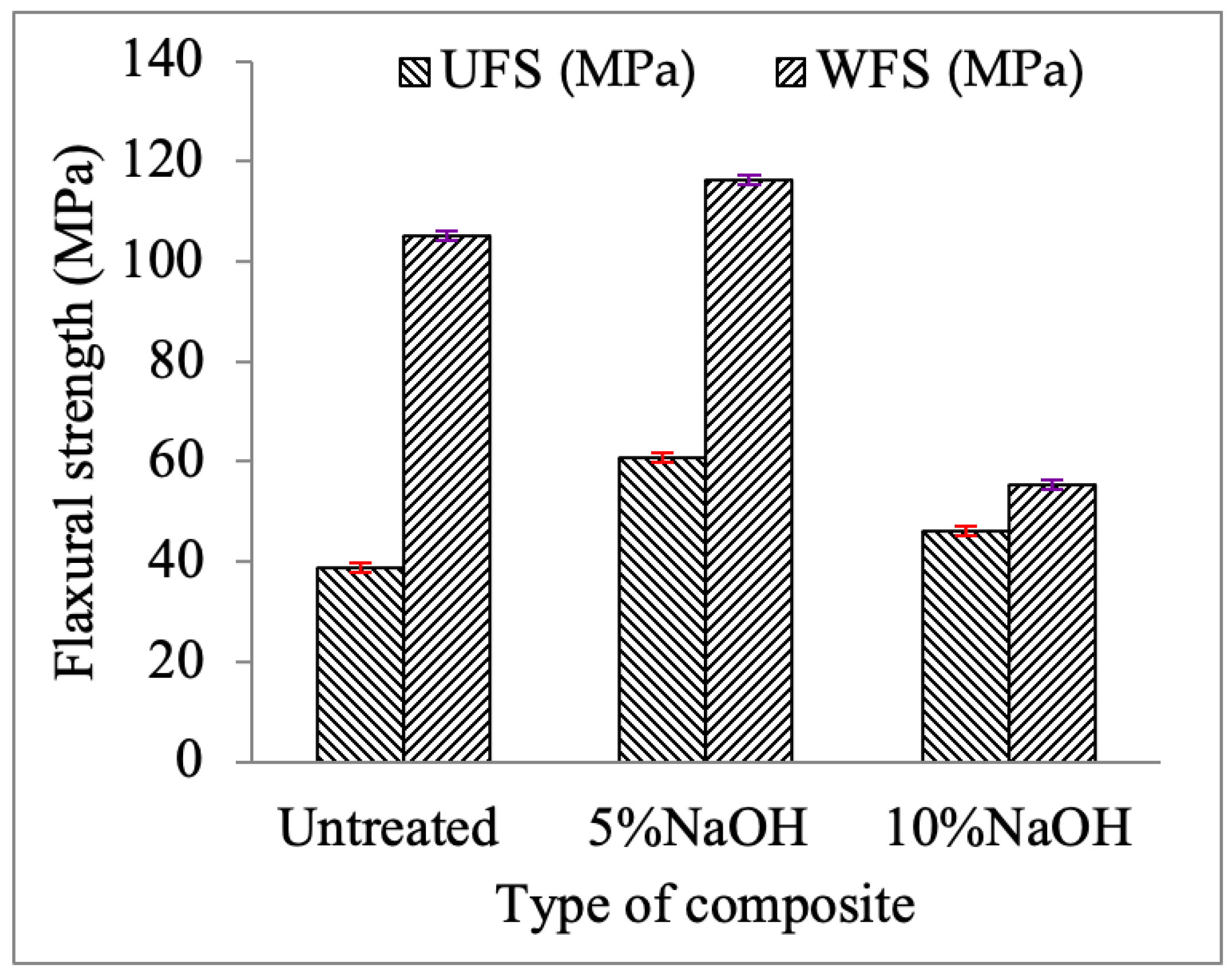
3.2. Flexural Strength Test
3.3. Impact Strength Test
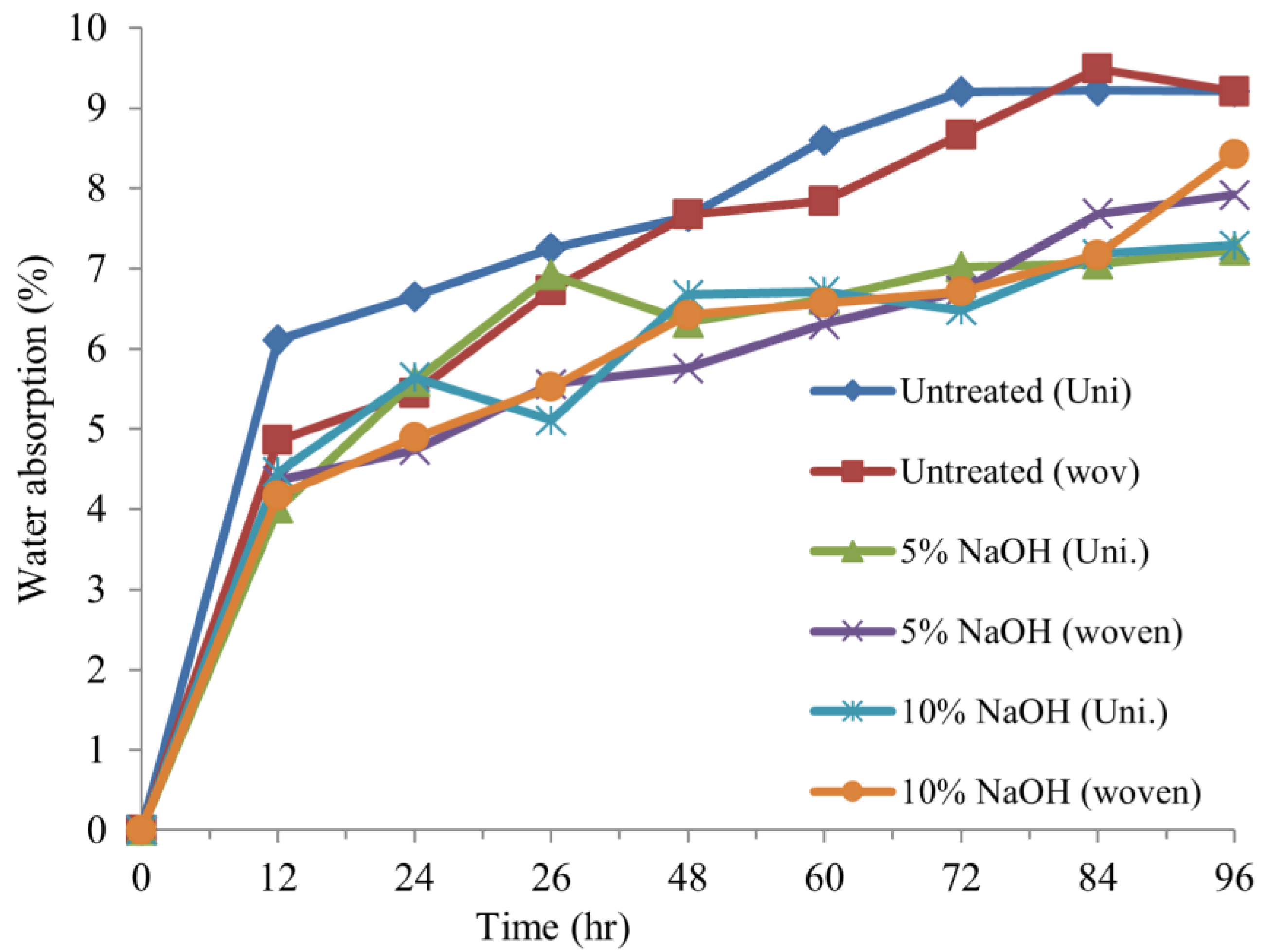
3.4. Water Absorption Test
3.5. Morphological Study of Composites
3.6. Promising Application Area of E/S Composite
4. Conclusions
- The mechanical properties of the hybrid composite are dependent on the interfacial bond between the fiber and matrix and on each lamina. So, fiber is one mechanism to improve the interfacial bond between fiber and matrix. The result of the study showed that treated fiber composites have better mechanical properties than untreated fiber hybrid composites.
- The woven type of fiber orientation has better mechanical properties than unidirectional fiber orientation in both untreated and treated hybrid composites.
- Tensile and flexural strengths of a 10% NaOH composite are similar to those of untreated fibers in unidirectional fiber orientation composites but less so in woven fiber orientation composites.
- The higher tensile and flexural strengths were obtained for 5% NaOH in both unidirectional and woven types of fiber orientation composites when compared with untreated and 10% NaOH-treated composites.
- The water absorption properties of treated E/S hybrid composites are less than those of untreated hybrid composites.
- The analysis of SEM images for unidirectional and woven types of composites revealed that the mode of failure of natural fibers and matrix during the tensile test was analyzed, and better surface interference was observed in woven fiber orientation composites with 5% NaOH treatment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammed, L.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Pua, G.; Jawaid, M.; Islam, M.S. A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 243947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.K.; Pagar, D.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Linul, E. Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elanchezhian, C.; Ramnath, B.V.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Rajendrakumar, M.; Naveenkumar, V.; Saravanakumar, M.K. Review on mechanical properties of natural fiber composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Madhu, P.; Jawaid, M.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Senthil, S.; Pradeep, S. Characterization and Properties of Natural Fiber Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clear. Prod. 2017, 172, 32394–32396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C. Review of natural fibre-reinforced hybrid composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupner, N.; Ziegmann, G.; Wilde, F.; Beckmann, F.; Müssig, J. Procedural influences on compression and injection moulded cellulose fibre-reinforced polylactide (PLA) composites: Influence of fibre loading, fibre length, fibre orientation and voids. Compos. Part A 2016, 81, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. Studies on mechanical and morphological characterization of developed jute /hemp /flax reinforced hybrid composites for structural applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 15, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochane, M.J.; Mokhena, T.C.; Mokhothu, T.H.; Mtibe, A.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S.; Ibrahim, I.D.; Daramola, O.O. Recent progress on natural fiber hybrid composites for advanced applications: A review, eXPRESS. Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 159–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.S.; Boopathy, S.R.; Sangeetha, D.; Ramnath, B.V. Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of banana-flax based natural fibre composite. J. Mater. 2014, 60, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swolfs, Y.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I. Fibre hybridisation in polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A 2014, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, D.K.K.; Banea, M.D.; Neto, J.S.S.; Lima, R.A.A.; Da Silva, L.F.M.; Carbas, R.J.C. Mechanical characterization of intralaminar natural fibre-reinforced hybrid composites. Compos. Part B 2019, 175, 107149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanarieswaran, V.P.; Kumaravel, A.; Saravanakumar, S.S. Characterization of new natural cellulosic fiber from Acacia leucophloea bark. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2015, 20, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Saxena, N.S.; Sharma, K.B.; Thomas, S.; Sreekala, M.S. Activation energy and crystallization kinetics of untreated and treated oil palm fibre reinforced phenol formaldehyde composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 277, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniyappan, S.; RajKumar, R.; Gnanavelbabu, A. Mechanical properties of Almond Shell-sugarcane leaves hybrid epoxy. Apppl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 852, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, D.; Thiruchitrambalam, M. Static and dynamic mechanical properties of alkali treated unidirectional continuous Palmyra Palm Leaf Stalk Fiber/jute fiber reinforced hybrid polyester composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogesha, B.; Arpitha, G.R.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Kathiresan, M. The hybrid effect of Jute/Kenaf/E-Glass woven fabric epoxy composites for medium load applications: Impact, inter-laminar strength, and failure surface characterization. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 16, 600–612. [Google Scholar]
- Yorseng, Y.; Mavinkere, S.; Pulikkalparambil, H.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Accelerated weathering studies of kenaf / sisal fiber fabric reinforced fully biobased hybrid bioepoxy composites for semi-structural applications: Morphology, thermo-mechanical, water absorption behavior and surface hydrophobicity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Palanikumar, K.; Reddy, K.H. Influence of fiber orientation and fiber content on properties of sisal-jute-glass fiber-reinforced polyester composites. J. Appl.-Polym. Sci. 2016, 42968, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Krishnaraj, V.; Sathish, S.; Gokulkumar, S.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S. Mechanical and acoustic properties of alkali-treated Sansevieria ehrenbergii/Camellia sinensis Fiber—Reinforced Hybrid Epoxy Composites: Incorporation of Glass Fiber Hybridization. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 9840–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawpan, M.A.; Pickering, K.L.; Fernyhough, A.A. Effect of fibre treatments on interfacial shear strength of hemp fibre reinforced polylactide and unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Misra, M.; Tripathy, S.S.; Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, A.K. Graft copolymerization of Acrylonitrile on chemically modified sisal fibers, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; Elayaperumal, A.; Alavudeen, A.; Thiruchitrambalam, M. Mechanical and water absorption behaviour of banana / sisal reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4017–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakandhan, C.; Murali, G.; Tamiloli, N.; Ravikumar, L. Studies on mechanical properties of sisal and jute fiber hybrid sandwich composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 21, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Gowda, B.S.K. Exploration of mechanical properties of banana / jute hybrid polyester composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 7171–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, I.S.; Zainudin, E.S.; Abdan, K.; Sapuan, S.M. Mechanical properties and water absorption behavior of hybridized kenaf / pineapple leaf fibre-reinforced high-density polyethylene composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effect of fiber surface treatment on structure, moisture absorption and mechanical properties of luffa sponge fiber bundles. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 123, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perremans, D.; Hendrickx, K.; Verpoest, I.; Van Vuure, A.W. Effect of chemical treatments on the mechanical properties of technical flax fibres with emphasis on stiffness improvement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 160, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shibata, S.; Fukumoto, I. Mechanical properties of biodegradable composites reinforced with bagasse fibre before and after alkali treatments. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Li, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial bonding in abaca fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Hybrid Composites | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unt. * | Trt. | Unt. | Trt. | Unt. | Trt. | ||
| Enset/Sisal unidirectional | 90.23 | 116.12 | 38.77 | 60.92 | 22.21 J/m2 | 23.33 J/m2 | Current Study |
| Enset/Sisal Woven | 115.67 | 122.56 | 105.23 | 116.30 | 22.77 J/m2 | 24.11 J/m2 | Current Study |
| Jute/Sisal | 70.39 | 74.78 | 67.56 | 54.67 | 332 J/m | 588 J/m | [11] |
| Jute/Curaua | 66.77 | 63.9 | 97.67 | 80.86 | 388 J/m | 288 J/m | [11] |
| Sisal/Jut | 42.45 | 53.7 4 | 39.8 | 44.58 | 19.5 J | 22.25 J | [29] |
| Bagasse aliphatic | 23.47 | 26.77 | 43.87 | 50.86 | 8.82 | 11.27 | [30] |
| Abaca epoxy | 717 | 773 | - | - | [31] | ||
| Sugarcane leaves/almond shell | 12.86 | 17.16 | 39.91 | 40.68 | 0.78 J | 1.05 J | [16] |
| sisal fiber epoxy composite unidirectional | 132.73 | 288.6 | [25] | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekele, A.E.; Lemu, H.G.; Jiru, M.G. Study of the Effects of Alkali Treatment and Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Enset/Sisal Polymer Hybrid Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7010037
Bekele AE, Lemu HG, Jiru MG. Study of the Effects of Alkali Treatment and Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Enset/Sisal Polymer Hybrid Composite. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekele, Abera E., Hirpa G. Lemu, and Moera G. Jiru. 2023. "Study of the Effects of Alkali Treatment and Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Enset/Sisal Polymer Hybrid Composite" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7010037
APA StyleBekele, A. E., Lemu, H. G., & Jiru, M. G. (2023). Study of the Effects of Alkali Treatment and Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Enset/Sisal Polymer Hybrid Composite. Journal of Composites Science, 7(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7010037






