Dielectric Properties of All-Organic Coatings: Comparison of PEDOT and PANI in Epoxy Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
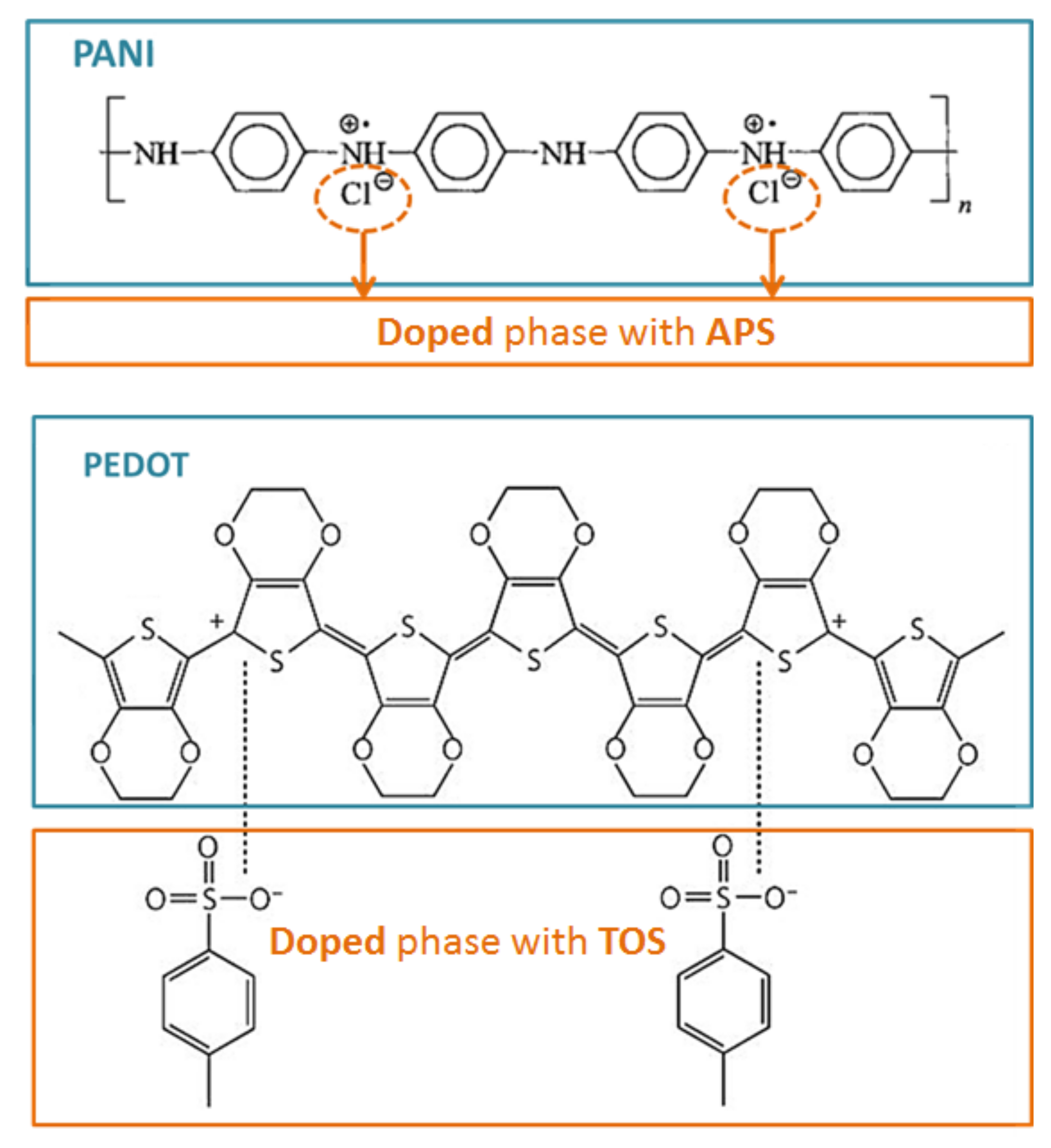
2.1. Synthesis of the Conductive Polymers
2.2. Sample Preparation
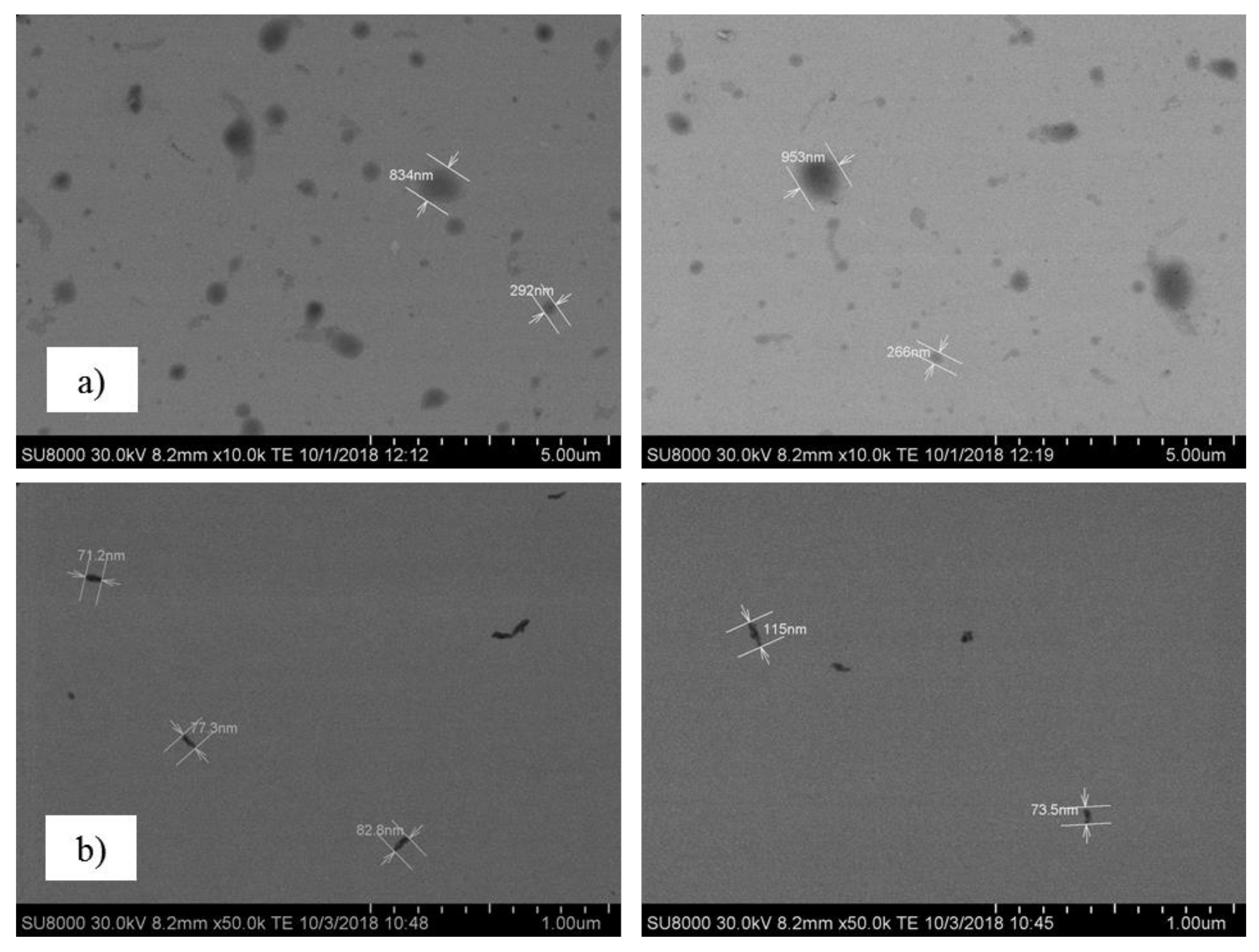
2.3. Characterization
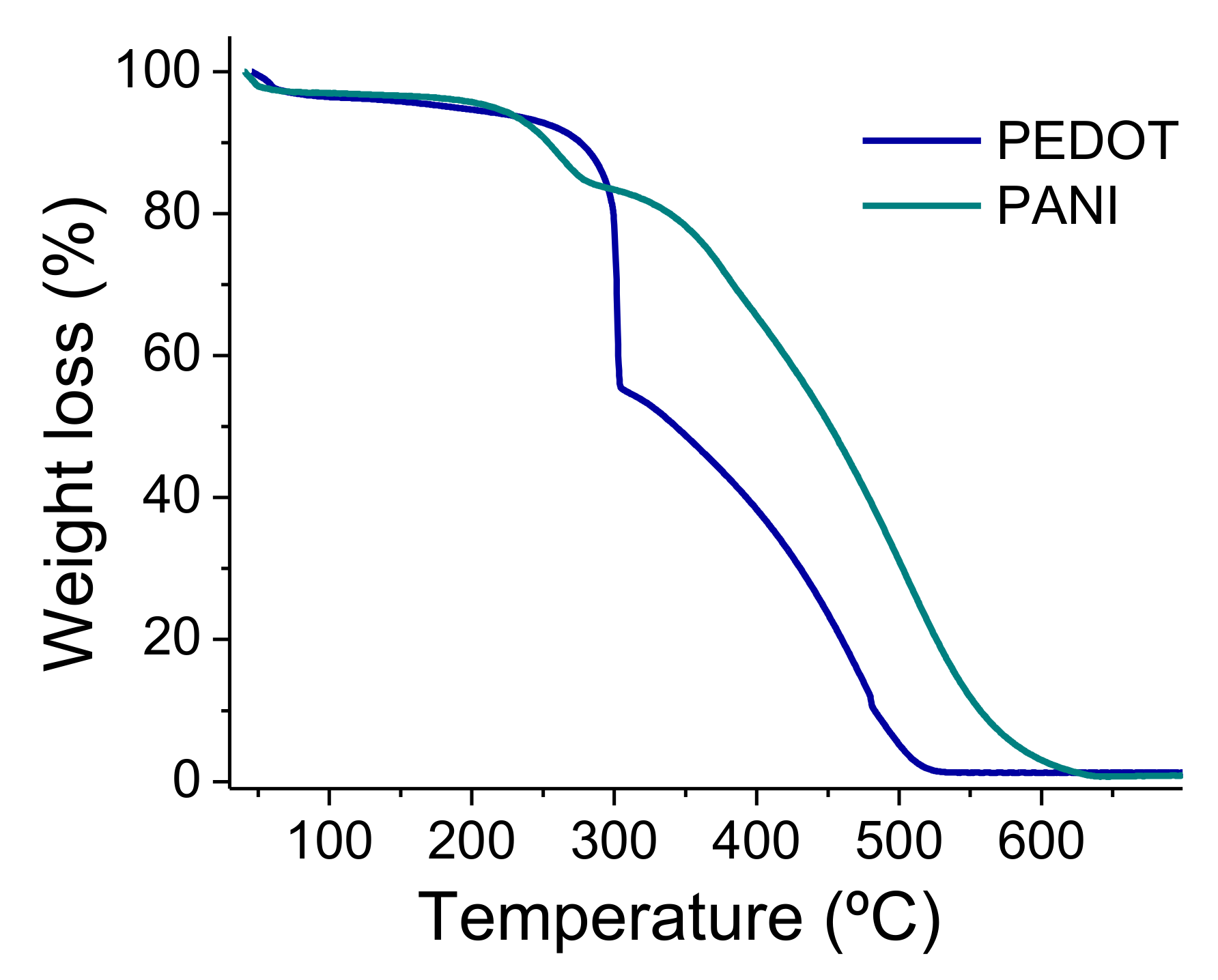
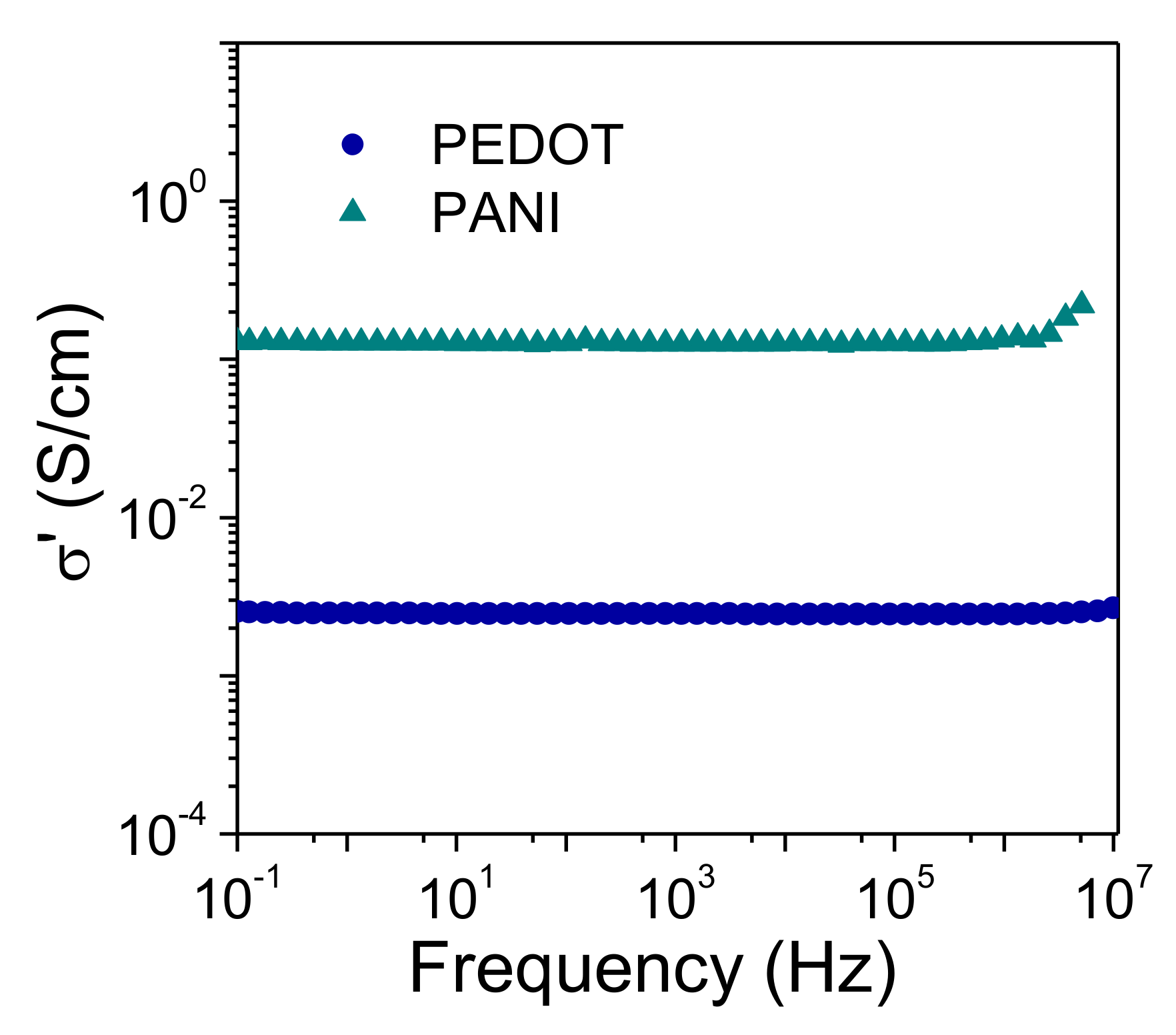
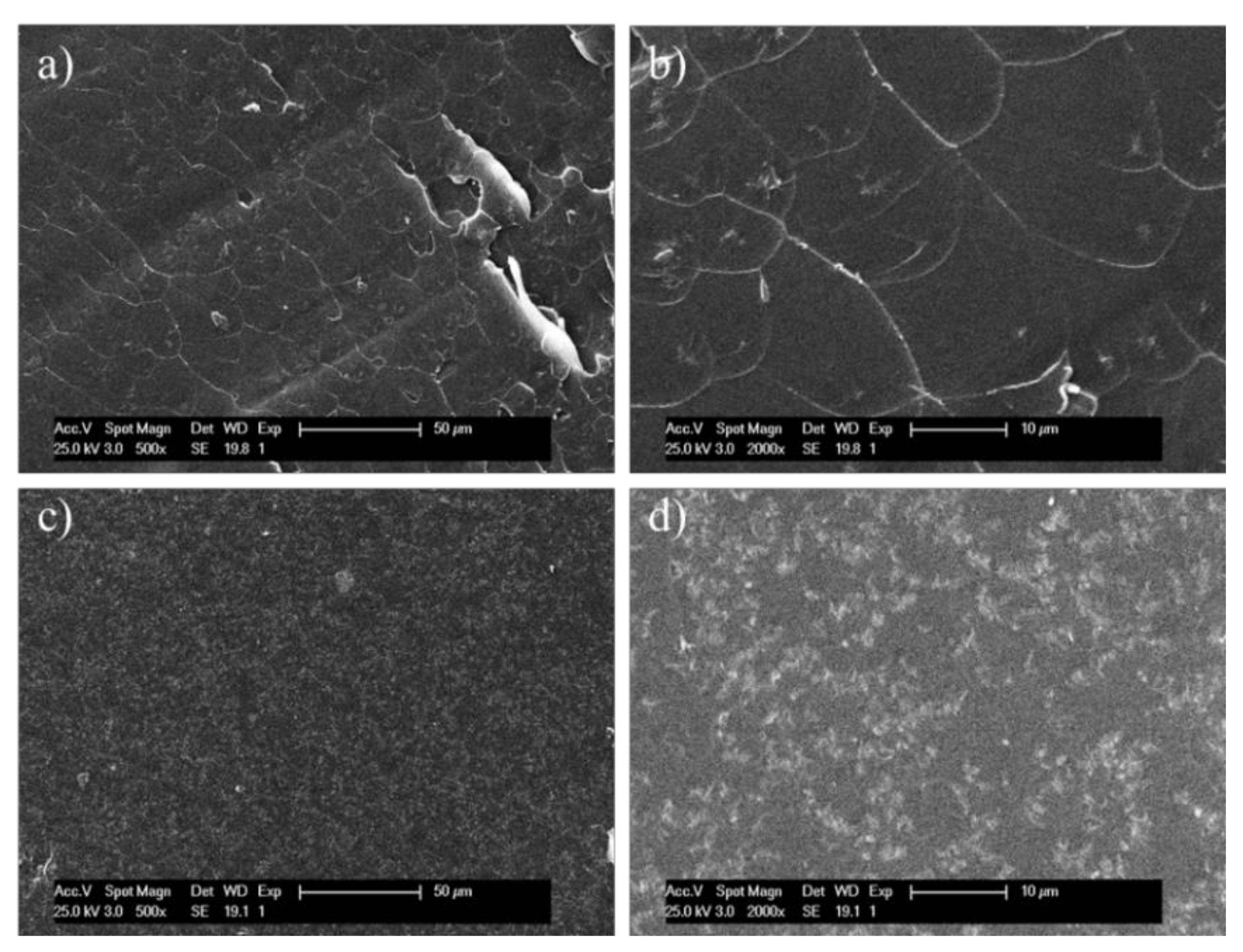
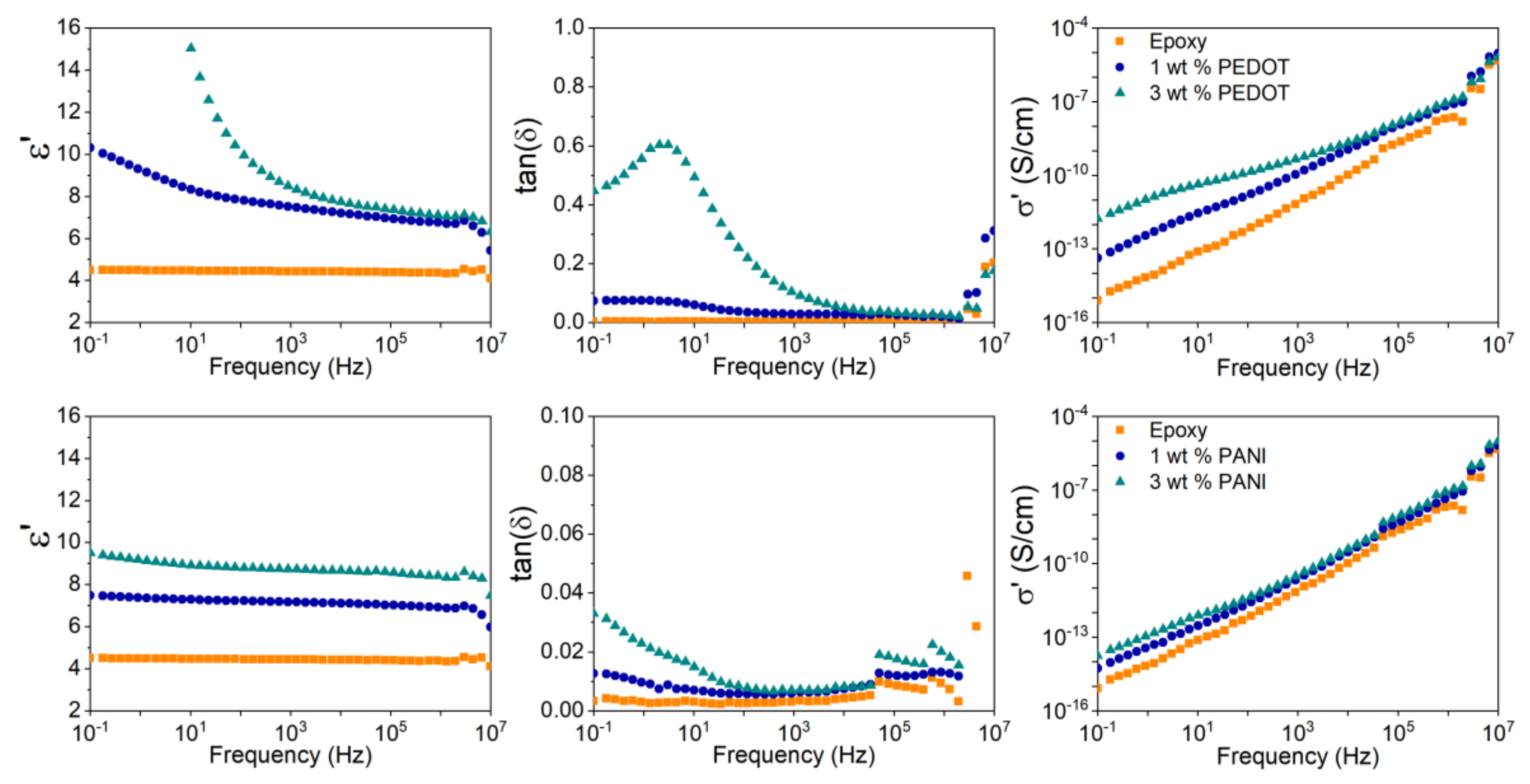
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catterson, V.M.; Castellon, J.; Pilgrim, J.A.; Saha, T.K.; Ma, H.; Vakilian, M.; Moradnouri, A.; Gholami, M.; Sparling, B.D. The impact of smart grid technology on dielectrics and electrical insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 3505–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markard, J. The next phase of the energy transition and its implications for research and policy. Nature Energy 2018, 3, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleşa, I.; Noţingher, V.P.; Schlögl, S.; Sumereder, C.; Muhr, M. Properties of Polymer Composites Used in High-Voltage Applications. Polymers 2016, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, F.X.; Oueiny, C. Polyaniline thermoset blends and composites. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, S.; Kausar, A.; Iqbal, T. Trends in Conducting Polymer and Hybrids of Conducting Polymer/Carbon Nanotube: A Review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1416–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.; Yadav, B. Conducting polymers: Synthesis, properties and applications. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Elschner, A.; Kirchmeyer, S.; Lovenich, W.; Merker, U.; Reuter, K. PEDOT: Principles and Applications of an Intrinsically Conductive Polymer; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z. The chemical modification of polyaniline with enhanced properties: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 126, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J. Conducting polymers are not just conducting: A perspective for emerging technology. Polym. Intern. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoumi, B.; Farjadbeh, F.; Mohammadi, R.; Entezami, A.A. Synthesis of conductive adhesives based on epoxy resin/nanopolyaniline and chloroprene rubber/nanopolyaniline: Characterization of thermal, mechanical and electrical properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wei, S.; Cheng, G. Preparation of conductive polyaniline/epoxy composite. Polym. Compos. 2006, 27, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.A.; Kumar, D. Development of Polyaniline/Epoxy Composite as a Prospective Solder Replacement Material. Int. J. Polymer. Mater. 2010, 59, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.A.; Kumar, D. Nanocomposites of Polyaniline as Conductive Adhesives. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 25, 2731–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvergne, S.; Gasse, A.; Pron, A. Electrical characterization of polyaniline-based adhesive blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Karpoormath, R.; Radha, S.; Singh, S.K.; Mutthukannan, R.; Bharate, G.; Vijayan, M. Corrosion resistant hydrophobic coating using modified conducting polyaniline. High Performance Polym. 2018, 30, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Performance of corrosion protective epoxy blend-based nanocomposite coatings: A review. Polym. Plastics Technol. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Q.; Gu, H.; Colorado, H.A.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z. Flame-retardant electrical conductive nanopolymers based on bisphenol F epoxy resin reinforced with nano polyanilines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Improving the flame retardancy and electrical conductivity of epoxy resin composites by multifunctional phosphorus-containing polyaniline. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 127092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros, L.F.; Soares, B.G.; Barra, G.M.O. DBSA-CTAB mixture as the surfactant system for the one step inverse emulsion polymerization of aniline: Characterization and blend with epoxy resin. Synth. Met. 2017, 226, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyharçabal, M.; Olinga, T.; Foulc, M.-P.; Lacomme, S.; Gontier, E.; Vigneras, V. Influence of the morphology of polyaniline on the microwave absorption properties of epoxy polyaniline composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 74, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokozeki, T.; Goto, T.; Takahashi, T.; Qian, D.; Itou, S.; Hirano, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Ogasawara, T. Development and characterization of CFRP using a polyaniline-based conductive thermoset matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yokozeki, T.; Okada, T.; Hirano, Y.; Goto, T.; Takahashi, T.; Hassen, A.A.; Ogasawara, T. Polyaniline-based all-polymeric adhesive layer: An effective lightning strike protection technology for high residual mechanical strength of CFRPs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 172, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueye, M.N.; Carella, A.; Faure-Vincent, J.; Demadrille, R.; Simonato, J.-P. Progress in understanding structure and transport properties of PEDOT-based materials: A critical review. Prog. Mater Sci. 2020, 108, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Kine, A.; Nelson, R.D.; LaRue, J.C. Impedance spectroscopy study of conducting polymer blends of PEDOT: PSS and PVA. Synth. Met. 2015, 206, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, M.J.; Redondo-Foj, B.; Carsí, M.; Ortiz-Serna, P.; Culebras, M.; Gómez, C.M.; Cantarero, A.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Controlling dielectrical properties of polymer blends through defined PEDOT nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 62024–62030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesa, F.; Ocampo, C.; Alemán, C.; Armelin, E.; Oliver, R.; Estrany, F. Application of electrochemically produced and oxidized poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) as anticorrosive additive for paints: Influence of the doping level. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Gilbert, R.G. Polyaniline. Preparation of a conducting polymer(IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Suh, K.S. Effects of alcoholic solvents on the conductivity of tosylate-doped poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)(PEDOT-OTs). Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeu, M.A.C.; Faria, L.K.; Cardoso, A.d.M.; Gama, A.M.; Baldan, M.R.; Gonçalves, E.S. Structural and Morphological Characteristics of Polyaniline Synthesized in Pilot Scale. J. Aerospace Technol. Manag. 2017, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Su, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Synthesis of water-free PEDOT with polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilizer in organic dispersant system. Org. Electron. 2018, 53, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Cai, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L. Synthesis of water-free PEDOT with polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilizer in organic dispersant system. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.M.; Li, J.B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.W.; Zheng, M. Electrically conductive epoxy resin composites containing polyaniline with different morphologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 448, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedvig, P. Dielectric Spectroscopy of Polymers; Adam Hilger Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]

| Step | Gap 1 (μm) | Gap 2 (µm) | Speed (rpm) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | 100 | 50 | 200 | 10 |
| Step 2 | 50 | 25 | 250 | 10 |
| Step 3 | 30 | 15 | 300 | 30 |
| Material | ε’ | σ’ (S/cm) | tan(δ) | λ (W/mK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 4.5 | 8.0 × 10−16 | 0.003 | 0.12 |
| 1 wt % PEDOT/epoxy | 10.3 | 4.2 × 10−14 | 0.072 | 0.13 |
| 3 wt % PEDOT/epoxy | 68.9 | 1.7 × 10−12 | 0.450 | 0.16 |
| 1 wt % PANI/epoxy | 7.5 | 5.3 × 10−15 | 0.013 | 0.12 |
| 3 wt % PANI/epoxy | 9.5 | 1.7 × 10−14 | 0.033 | 0.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuste-Sanchez, V.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, F.; Hoyos, M.; López Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Dielectric Properties of All-Organic Coatings: Comparison of PEDOT and PANI in Epoxy Matrices. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010026
Yuste-Sanchez V, Gonzalez-Gonzalez F, Hoyos M, López Manchado MA, Verdejo R. Dielectric Properties of All-Organic Coatings: Comparison of PEDOT and PANI in Epoxy Matrices. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuste-Sanchez, Vanesa, Francisco Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Mario Hoyos, Miguel A. López Manchado, and Raquel Verdejo. 2020. "Dielectric Properties of All-Organic Coatings: Comparison of PEDOT and PANI in Epoxy Matrices" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010026
APA StyleYuste-Sanchez, V., Gonzalez-Gonzalez, F., Hoyos, M., López Manchado, M. A., & Verdejo, R. (2020). Dielectric Properties of All-Organic Coatings: Comparison of PEDOT and PANI in Epoxy Matrices. Journal of Composites Science, 4(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010026








