Numerical Investigation of the Fatigue Behavior of Lattice Structures Under Compression–Compression Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Analysis
2.1. Design Setup
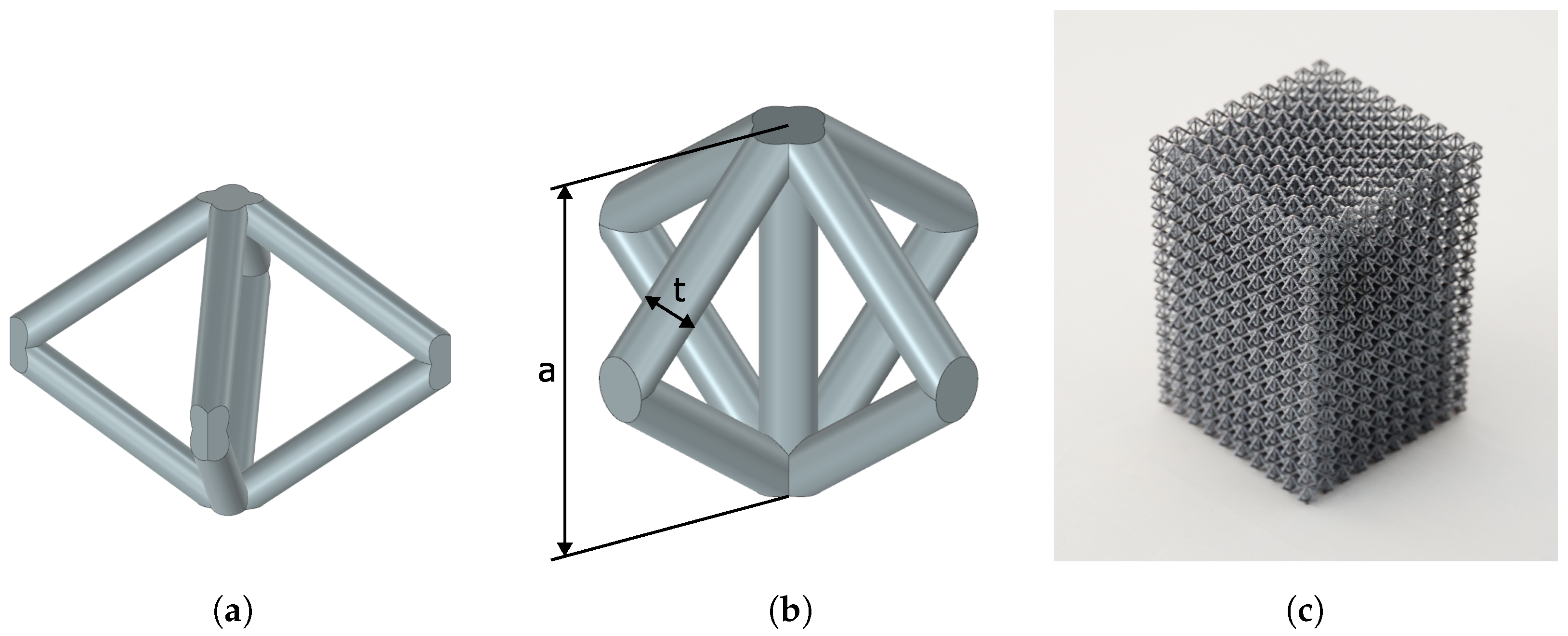
2.2. Finite Element Model

| Unit Cell | in W | in mm/s | in m | in m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bcc | 250 | 2500 | 373.67 | 49.54 |
| f2ccz | 250 | 2500 | 374.82 | 31.57 |
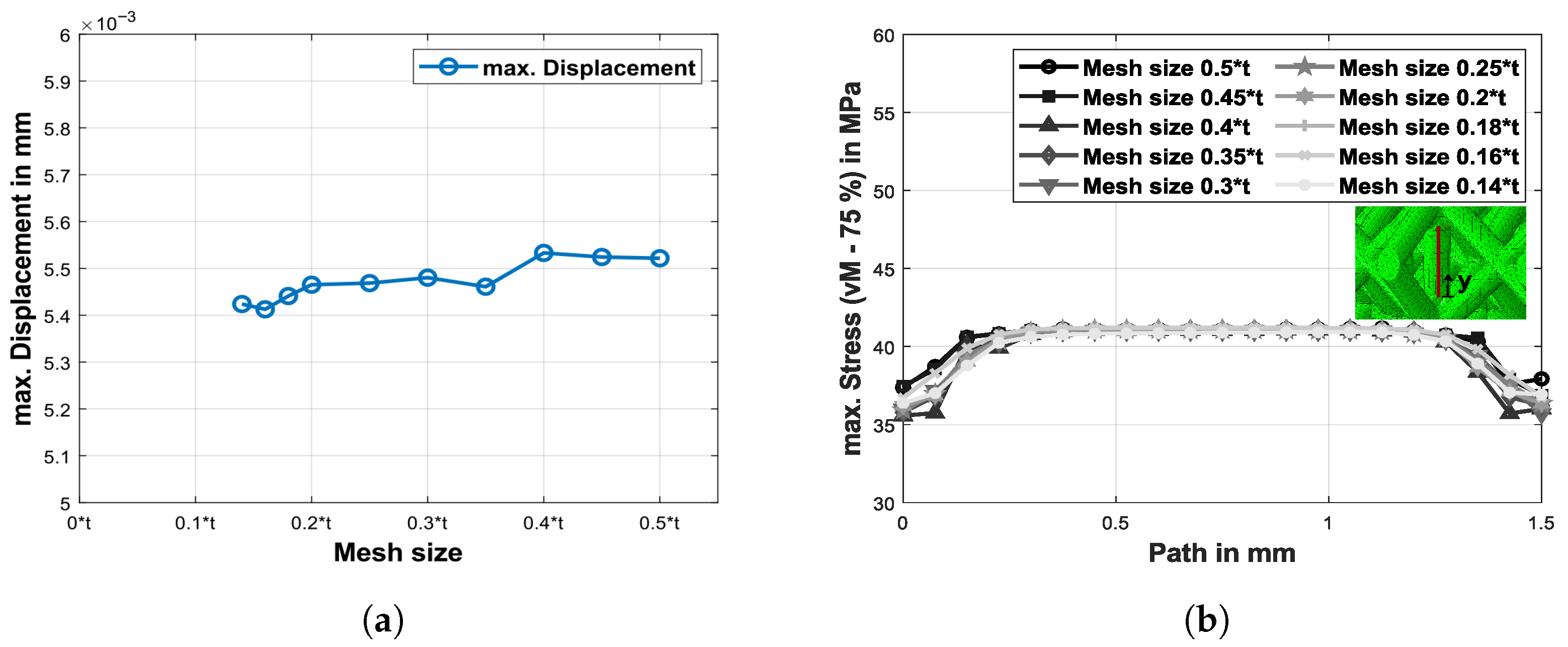
2.3. Convergence Study
3. Experimental Mechanical Testing
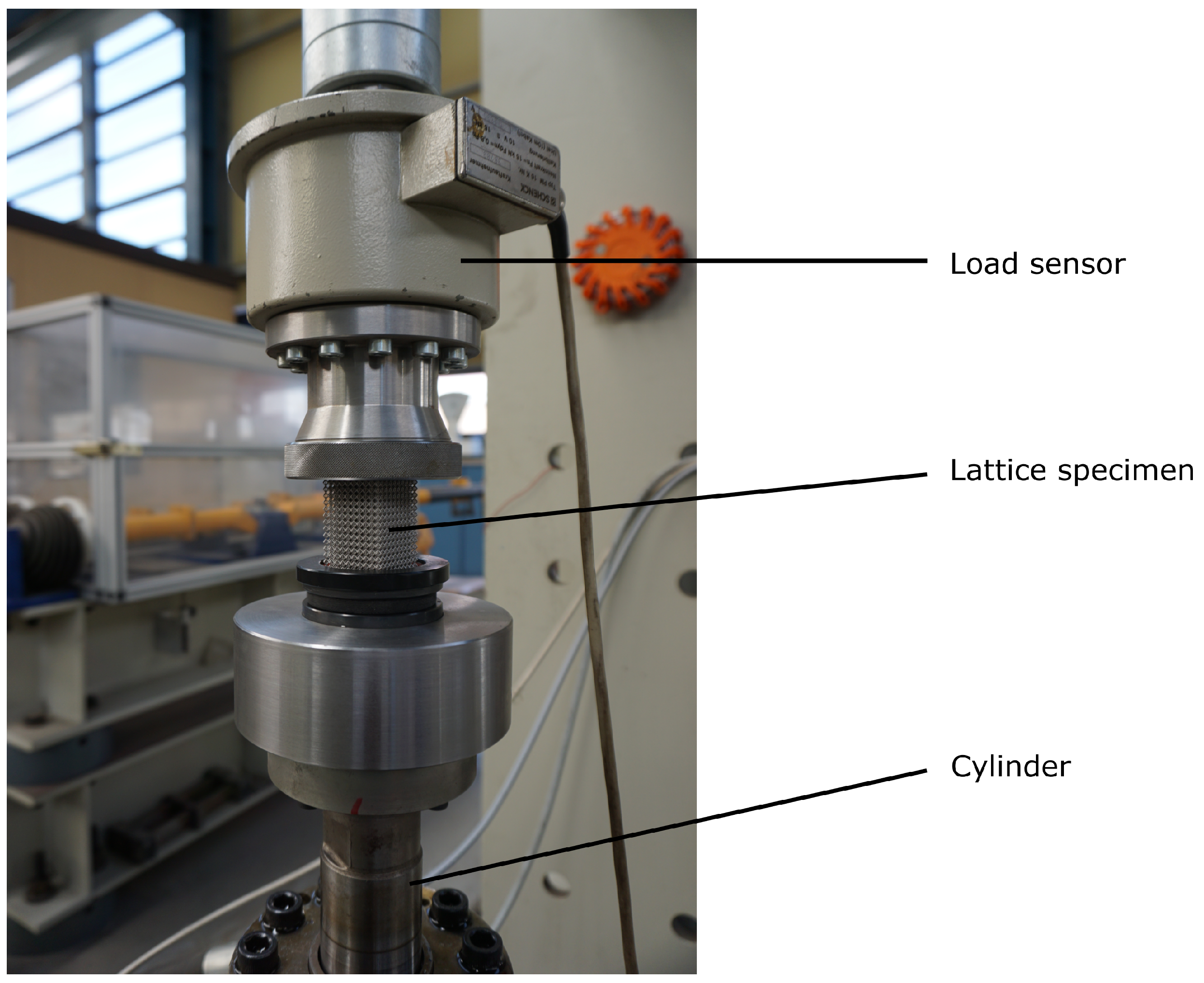
3.1. Material and Machine
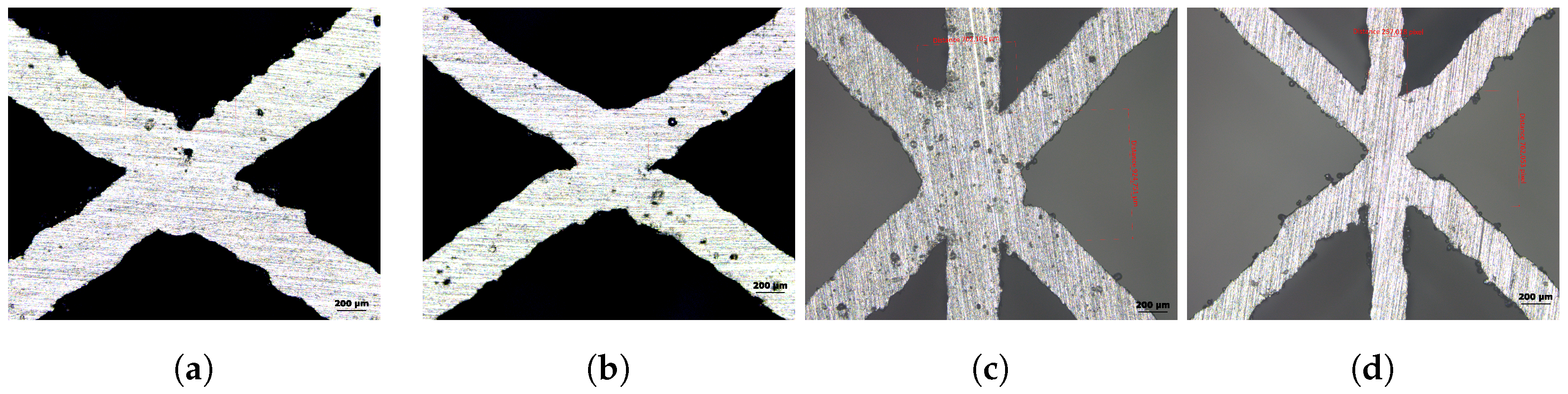
3.2. Specimen Fabrication
3.3. Compression–Compression Testing
4. Discussion of Results
4.1. Stress Distribution of the Finite Element Model
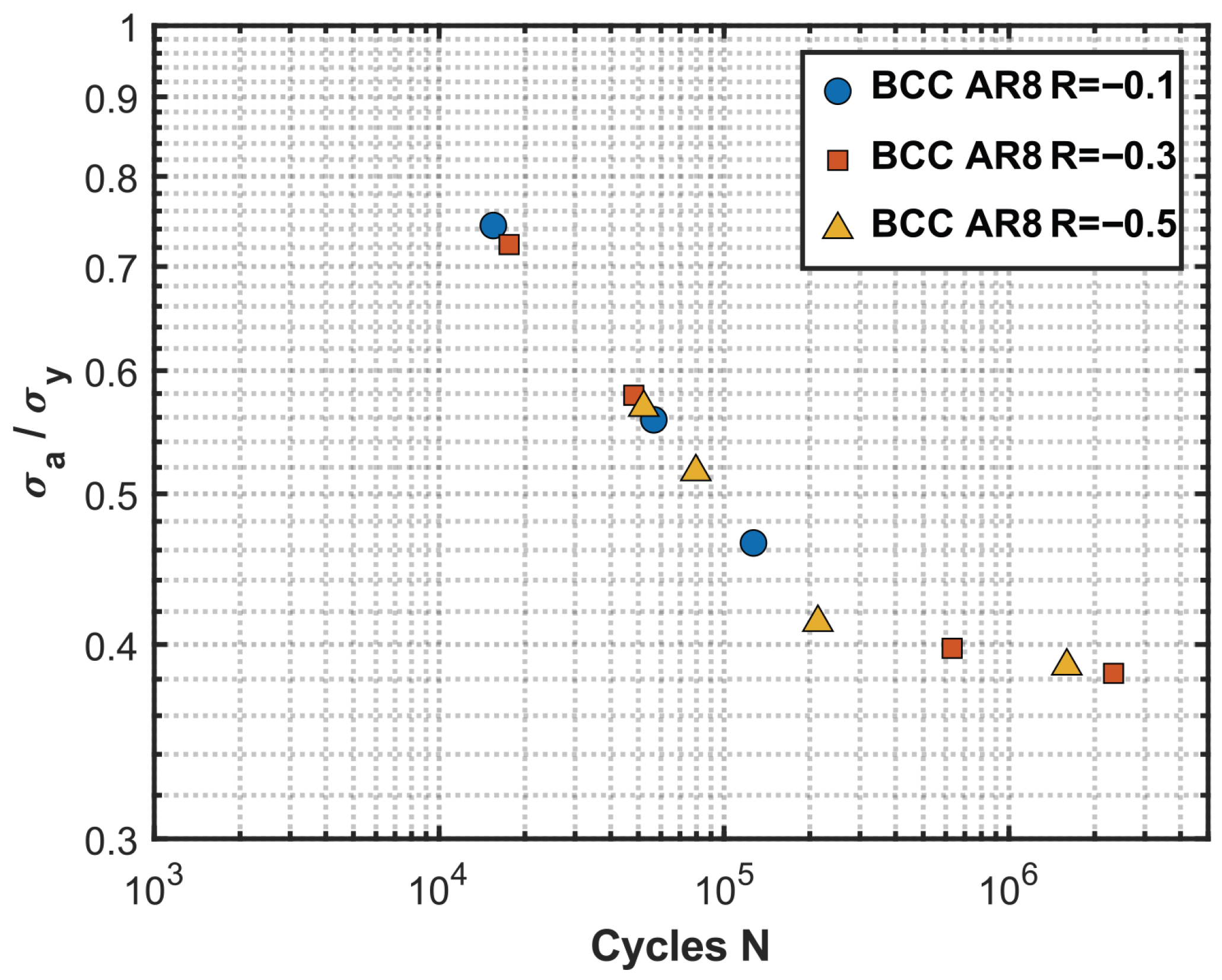
4.2. Fatigue Life Prediction
4.3. Influence of the Aspect Ratio
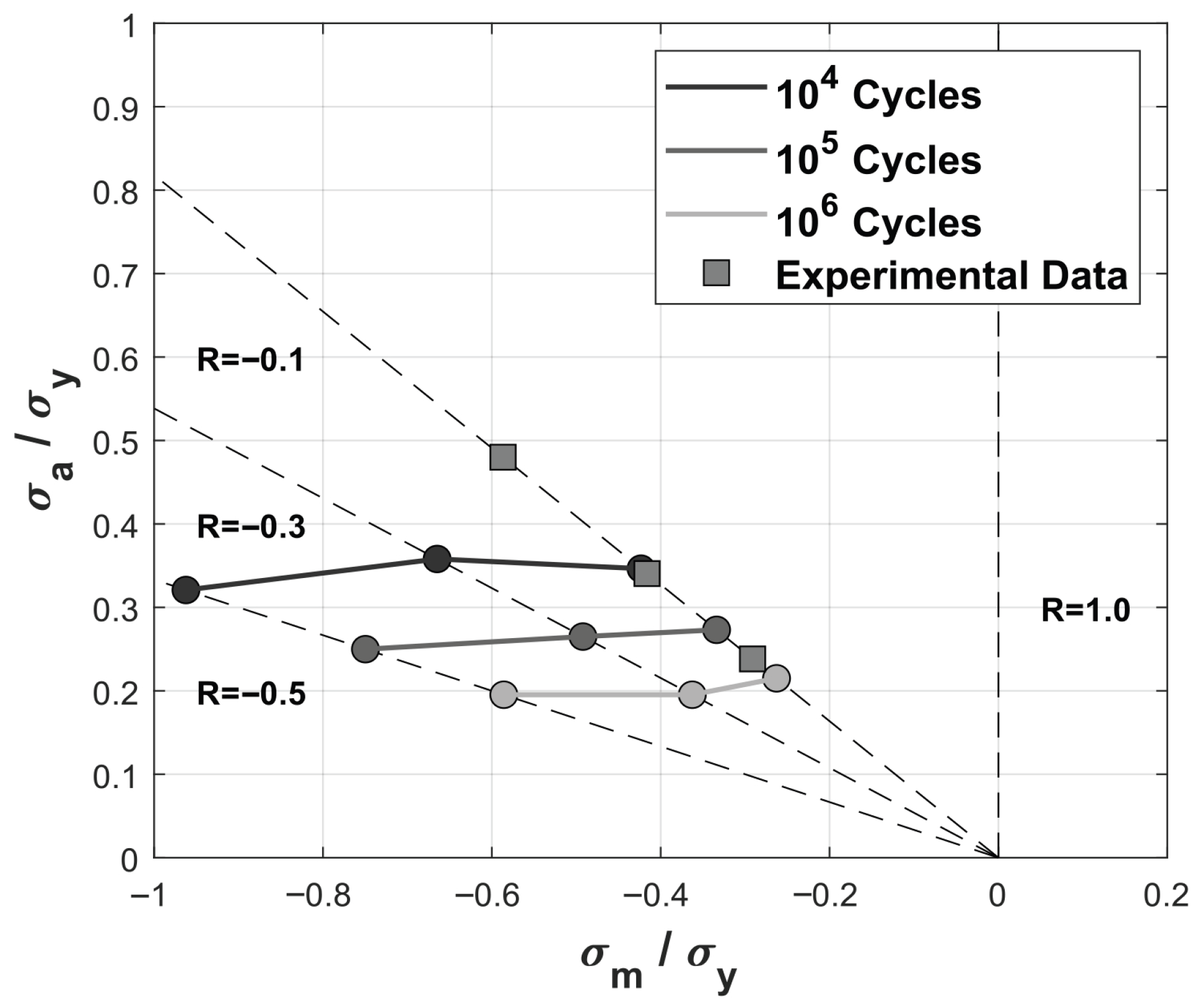
4.4. Mean Stress Influence and Correction
4.5. Experimental Data Evaluation
| bcc | f2ccz | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR | Sim. | Exp. | Error | Sim. | Exp. | Error | |
| 6 | k | −0.136 | −0.151 | −9.93% | −0.059 | - | - |
| [MPa] | 0.297 | 0.363 | −18.18% | 1.748 | - | - | |
| 8 | k | −0.137 | −0.150 | −8.67% | −0.075 | −0.091 | −17.58% |
| [MPa] | 0.201 | 0.207 | −2.90% | 0.925 | 1.456 | −36.47% | |
| 10 | k | −0.133 | - | - | −0.085 | −0.071 | 19.72% |
| [MPa] | 0.093 | - | - | 0.725 | 0.747 | −2.95% | |
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.P.; Masrurotin; Wibisono, A.T.; Macek, W.; Ramezani, M. Enhancing Internal Cooling Channel Design in Inconel 718 Turbine Blades via Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A Comprehensive Review of Surface Topography Enhancements. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2025, 26, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehly, C.; Neuberger, H.; Bühler, L. Fabrication of thin-walled fusion blanket components like flow channel inserts by selective laser melting. Fusion Eng. Des. 2019, 143, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, M.E.; Culhaoglu, A.; Ozgul, O.; Tekin, U.; Atıl, F.; Taze, C.; Yasa, E. Biomimetic dental implant production using selective laser powder bed fusion melting: In-vitro results. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 151, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spickler, B.; Gray, J.; Nicolaisen, D.; Schiefelbein, B.; Depcik, C. Surface roughness and dimensional evaluation of laser powder bed fusion additively manufactured shell and tube heat exchangers. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 65, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Bodemer, J.; Kabelac, S. Experimental investigation of additively manufactured high-temperature heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 218, 124774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, A.; Yadroitsava, I.; Yadroitsev, I.; Le Roux, S.G.; Blaine, D.C. Numerical comparison of lattice unit cell designs for medical implants by additive manufacturing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Liu, J. Study on fatigue crack initiation behavior of two types of lattice structures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3009, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, P.; Fang, D. Architecture design of periodic truss-lattice cells for additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.; Großmann, A.; Mittelstedt, C. Micromechanical analysis of the effective properties of lattice structures in additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Mazur, M.; Elambasseril, J.; McMillan, M.; Chirent, T.; Sun, Y.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.; Brandt, M. Selective laser melting (SLM) of AlSi12Mg lattice structures. Mater. Des. 2016, 98, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Du Plessis, A.; Ritchie, R.O.; Dallago, M.; Razavi, N.; Berto, F. Architected cellular materials: A review on their mechanical properties towards fatigue-tolerant design and fabrication. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 144, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tankasala, H.C.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. Tensile response of elastoplastic lattices at finite strain. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 109, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, N.A.; Deshpande, V.S.; Ashby, M.F. Micro-architectured materials: Past, present and future. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 466, 2495–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarian, A.; Esfahanian, M.; Kadkhodapour, J.; Ziaei-Rad, S. Effect of solid distribution on elastic properties of open-cell cellular solids using numerical and experimental methods. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, Z.; Concli, F. A Review of the Selective Laser Melting Lattice Structures and Their Numerical Models. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, Y.F. A Survey of Modeling of Lattice Structures Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing. J. Mech. Des. 2017, 139, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Yánez, A.; Martel, O.; Deviaene, S.; Monopoli, D. Influence of load orientation and of types of loads on the mechanical properties of porous Ti6Al4V biomaterials. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodapour, J.; Montazerian, H.; Darabi, A.C.; Anaraki, A.P.; Ahmadi, S.M.; Zadpoor, A.A.; Schmauder, S. Failure mechanisms of additively manufactured porous biomaterials: Effects of porosity and type of unit cell. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 50, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Li, Q. Additively manufactured materials and structures: A state-of-the-art review on their mechanical characteristics and energy absorption. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 246, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Martínez, C.; Piedra, S.; Perez-Barrera, J.; González-Carmona, J.M.; Franco Urquiza, E.A.; Gómez-Ortega, A. Lightweighting and performance analysis of a spur gear by implementing cellular structures and additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarian, A.; Esfahanian, M.; Kadkhodapour, J.; Ziaei-Rad, S. Numerical simulation of the fatigue behavior of additive manufactured titanium porous lattice structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 60, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, E.; Cerri, E. Work Hardening of Heat-Treated AlSi10Mg Alloy Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting: Effects of Layer Thickness and Hatch Spacing. Materials 2021, 14, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Riccio, A. A systematic review of design for additive manufacturing of aerospace lattice structures: Current trends and future directions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2024, 149, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.L.; Li, X. An overview of residual stresses in metal powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, P.; Silva, M.B.; Moita de Deus, A.; Cláudio, R.; Carmezim, M.; Santos, C.; Magrinho, J.; Reis, L.; Lino, J.; Oliveira, L.; et al. Evaluation of the roughness of lattice structures of AISI 316 stainless steel produced by laser powder bed fusion. Eng. Manuf. Lett. 2024, 2, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarik Hasib, M.; Ostergaard, H.E.; Li, X.; Kruzic, J.J. Fatigue crack growth behavior of laser powder bed fusion additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V: Roles of post heat treatment and build orientation. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 142, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchio, S.; Dallago, M.; Rigatti, A.; Luchin, V.; Berto, F.; Maniglio, D.; Benedetti, M. On the effect of the node and building orientation on the fatigue behavior of L–PBF Ti6Al4V lattice structure sub–unital elements. Mater. Des. Process. Commun. 2021, 3, e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tvenning, T.; Wu, T.; Razavi, N. Evaluating quasi-static and fatigue performance of IN718 gyroid lattice structures fabricated via LPBF: Exploring relative densities. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 178, 108028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, N.; Saintier, N.; Merzeau, J.; Veidt, M.; Dargusch, M.S. Quasi-static and fatigue properties of graded Ti–6Al–4V lattices produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF). Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, A.; Razavi, N.; Berto, F. The effects of microporosity in struts of gyroid lattice structures produced by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Vaghefi, E.; Mirkoohi, E. The role of defect structure and residual stress on fatigue failure mechanisms of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured via laser powder bed fusion: Effect of process parameters and geometrical factors. J. Manuf. Processes 2023, 102, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, G.; Carraturo, M.; Korshunova, N.; Kollmannsberger, S. Numerical evaluation of high cycle fatigue life for additively manufactured stainless steel 316L lattice structures: Preliminary considerations. Mater. Des. Process. Commun. 2021, 3, e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.M.; Hedayati, R.; Li, Y.; Lietaert, K.; Tümer, N.; Fatemi, A.; Rans, C.D.; Pouran, B.; Weinans, H.; Zadpoor, A.A. Fatigue performance of additively manufactured meta-biomaterials: The effects of topology and material type. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, A.; van Hooreweder, B. Fatigue behaviour of diamond based Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures produced by laser powder bed fusion: On the effect of load direction. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Tang, D.; Dang, L.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, B.; He, X.; Zhan, Z. Fatigue failure mechanisms and life prediction of additive manufactured metallic lattices: A comprehensive review. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2025, 20, e2451124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Tang, X.; Zhang, D.; Dai, Y.; Lin, J.; Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Wen, C. Compression fatigue behavior of gyroid porous titanium scaffolds manufactured by laser powder bed fusion for bone-implant applications. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 201, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, P.; Kesavan, D.; Jayaganthan, R. High-cycle fatigue analysis in dumbbell-shaped lattice structure of Ti6Al4V through additive manufacturing: Experimental and numerical simulation. J. Mater. Res. 2025, 40, 1838–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, D.; Voshage, M.; Burkamp, K.; Kunz, J.; Bezold, A.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Broeckmann, C. Mechanical behaviour of additive manufactured 316L f2ccz lattice structure under static and cyclic loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, C.; Mohr, D. Large deformation response of additively-manufactured FCC metamaterials: From octet truss lattices towards continuous shell mesostructures. Int. J. Plast. 2017, 92, 122–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerappan, S. Finite Element-Based Modeling of Stress Distribution in 3D-Printed Lattice Structures. J. Appl. Math. Model. Eng. 2025, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kamranfard, M.R.; Darijani, H.; Rokhgireh, H.; Khademzadeh, S. Analysis and optimization of strut-based lattice structures by simplified finite element method. Acta Mech. 2023, 234, 1381–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Tran, P.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Ferreira, A. Mechanical performance and fatigue life prediction of lattice structures: Parametric computational approach. Compos. Struct. 2020, 235, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniotti, L.; Dancette, S.; Gavazzoni, M.; Lachambre, J.; Buffiere, J.Y.; Foletti, S. Experimental and numerical investigation on fatigue damage in micro-lattice materials by Digital Volume Correlation and μCT-based finite element models. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 266, 108370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Attallah, M.M.; Coules, H.; Martinez, R.; Pavier, M. Fatigue of octet-truss lattices manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 170, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Biasi, R.; Yasin, M.S.; Perini, M.; Benedetti, M.; Berto, F. Compensated beam model for efficient and accurate FE elastic simulation of strut-based lattice structures. Mater. Des. 2025, 255, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Biasi, R.; Oztoprak, O.; Zanini, F.; Carmignato, S.; Kollmannsberger, S.; Benedetti, M. Predicting fatigue life of additively manufactured lattice structures using the image-based Finite Cell Method and average strain energy density. Mater. Des. 2024, 246, 113321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarian, A.; Esfahanian, M.; Kadkhodapour, J.; Ziaei-Rad, S.; Zamani, D. On the fatigue behavior of additive manufactured lattice structures. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 100, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, A.; Persenot, T.; Doutre, P.T.; Buffiere, J.Y.; Lhuissier, P.; Martin, G.; Dendievel, R. A numerical framework to predict the fatigue life of lattice structures built by additive manufacturing. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 139, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozanovski, B.; Leary, M.; Tran, P.; Shidid, D.; Qian, M.; Choong, P.; Brandt, M. Computational modelling of strut defects in SLM manufactured lattice structures. Mater. Des. 2019, 171, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Pantidis, P.; Bertoldi, K.; Gerasimidis, S. Correlation between topology and elastic properties of imperfect truss-lattice materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 124, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, R.; Hosseini-Toudeshky, H.; Sadighi, M.; Mohammadi-Aghdam, M.; Zadpoor, A.A. Computational prediction of the fatigue behavior of additively manufactured porous metallic biomaterials. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 84, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, F.; Temizer, I. Computational homogenization of fatigue in additively manufactured microlattice structures. Comput. Mech. 2023, 71, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavitabrizi, D.; Ekberg, A.; Mousavi, S.M. Computational model for low cycle fatigue analysis of lattice materials: Incorporating theory of critical distance with elastoplastic homogenization. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2022, 92, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, A.; de Pasquale, G. Strain-based method for fatigue failure prediction of additively manufactured lattice structures. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, G.; Curtarello, A.; Rosso, S.; Meneghello, R.; Concheri, G. Homogenization driven design of lightweight structures for additive manufacturing. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. IJIDeM 2019, 13, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauß, L.; Löwisch, G. Prediction of fatigue lifetime and fatigue limit of aluminum parts produced by PBF-LB/M using a statistical defect distribution. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EOS Aluminium AlSi10Mg—Material Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.eos.info/var/assets/03_system-related-assets/material-related-contents/metal-materials-and-examples/metal-material-datasheet/aluminium/material_datasheet_eos_aluminium-alsi10mg_en_web.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Großmann, A.; Gosmann, J.; Mittelstedt, C. Lightweight lattice structures in selective laser melting: Design, fabrication and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13314:2011; Mechanical Testing of Metals—Ductility Testing—Compression Test for Porous and Cellular Metals. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- DIN 50100; Schwingfestigkeitsversuch—Durchführung und Auswertung von Zyklischen Versuchen mit Konstanter Lastamplitude für Metallische Werkstoffproben und Bauteile. DIN-Normenausschuss Materialprüfung: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- Alaña, M.; Cutolo, A.; Ruiz de Galarreta, S.; van Hooreweder, B. Influence of relative density on quasi-static and fatigue failure of lattice structures in Ti6Al4V produced by laser powder bed fusion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Krijger, J.; Rans, C.; van Hooreweder, B.; Lietaert, K.; Pouran, B.; Zadpoor, A.A. Effects of applied stress ratio on the fatigue behavior of additively manufactured porous biomaterials under compressive loading. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 70, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmuller, P.; Favre, J.; Piotrowski, B.; Kenzari, S.; Laheurte, P. Stress Concentration and Mechanical Strength of Cubic Lattice Architectures. Materials 2018, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.G.; Varetti, S.; Maggiore, P. Experimental Evaluation of Fatigue Strength of AlSi10Mg Lattice Structures Fabricated by AM. Aerospace 2023, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanning, D.; Nicholas, T.; Haritos, G. On the use of critical distance theories for the prediction of the high cycle fatigue limit stress in notched Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2005, 27, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozanovski, B.; Downing, D.; Tran, P.; Shidid, D.; Qian, M.; Choong, P.; Brandt, M.; Leary, M. A Monte Carlo simulation-based approach to realistic modelling of additively manufactured lattice structures. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozanovski, B.; Downing, D.; Tino, R.; Du Plessis, A.; Tran, P.; Jakeman, J.; Shidid, D.; Emmelmann, C.; Qian, M.; Choong, P.; et al. Non-destructive simulation of node defects in additively manufactured lattice structures. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenne, F.; Niendorf, T. Load distribution and damage evolution in bending and stretch dominated Ti-6Al-4V cellular structures processed by selective laser melting. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 121, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Takata, N.; Suzuki, A.; Kobashi, M. Effect of Heat Treatment on Gradient Microstructure of AlSi10Mg Lattice Structure Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Materials 2020, 13, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallago, M.; Winiarski, B.; Zanini, F.; Carmignato, S.; Benedetti, M. On the effect of geometrical imperfections and defects on the fatigue strength of cellular lattice structures additively manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Property | Detailed Property | Result |
|---|---|---|
| PSD | d [µm] | 25–70 |
| Chemical Composition [wt%] | Al | Balance |
| Si | 9.0–11.0 | |
| Fe | ≤0.55 | |
| Mn | ≤0.45 | |
| Mg | 0.20–0.45 | |
| Ti | ≤0.15 | |
| Zn | ≤0.10 | |
| Sn | ≤0.05 | |
| Cu | ≤0.05 | |
| Ni | ≤0.05 | |
| Pb | ≤0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Greiner, M.; Kappel, A.; Röder, M.; Mittelstedt, C. Numerical Investigation of the Fatigue Behavior of Lattice Structures Under Compression–Compression Loading. J. Compos. Sci. 2026, 10, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs10010028
Greiner M, Kappel A, Röder M, Mittelstedt C. Numerical Investigation of the Fatigue Behavior of Lattice Structures Under Compression–Compression Loading. Journal of Composites Science. 2026; 10(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs10010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreiner, Matthias, Andreas Kappel, Marc Röder, and Christian Mittelstedt. 2026. "Numerical Investigation of the Fatigue Behavior of Lattice Structures Under Compression–Compression Loading" Journal of Composites Science 10, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs10010028
APA StyleGreiner, M., Kappel, A., Röder, M., & Mittelstedt, C. (2026). Numerical Investigation of the Fatigue Behavior of Lattice Structures Under Compression–Compression Loading. Journal of Composites Science, 10(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs10010028








