Investigation of Metal Wire Mesh as Support Material for Dieless Forming of Woven Reinforcement Textiles †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
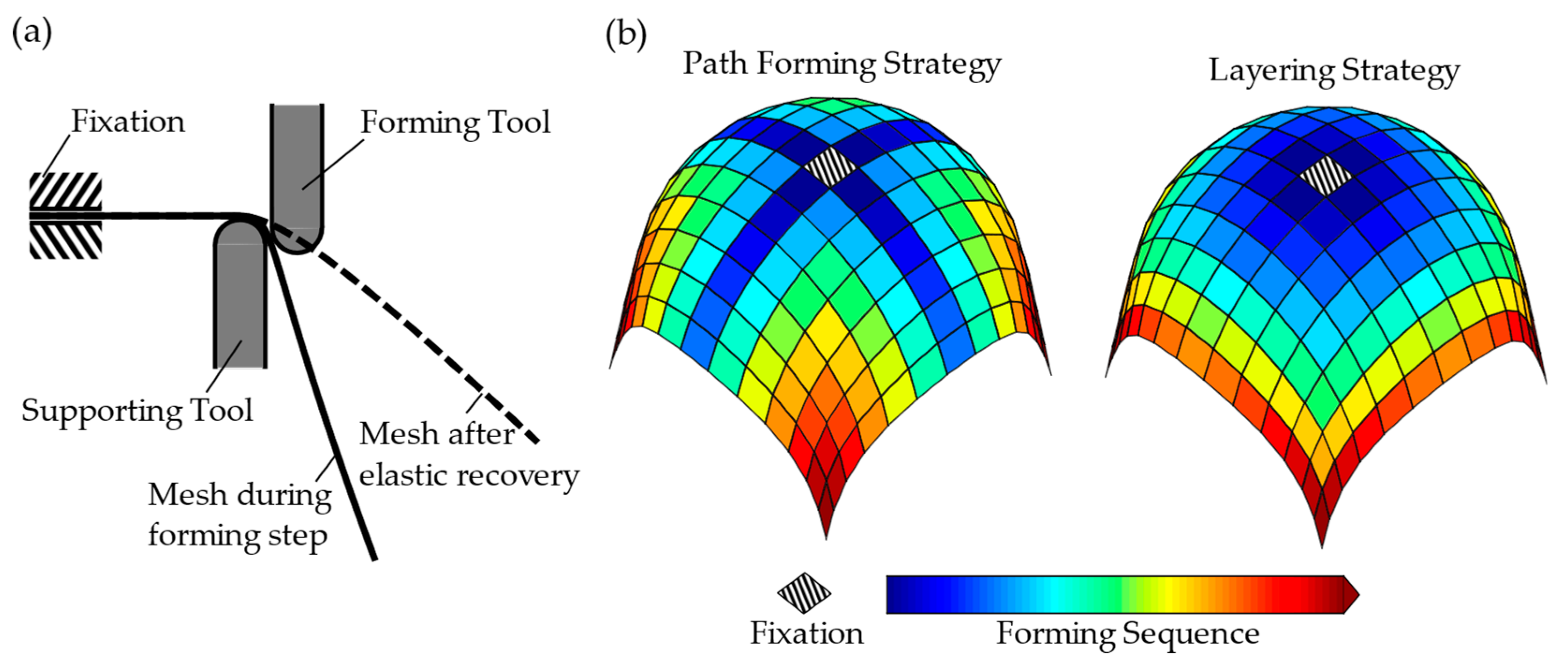
2.1. Forming Strategy
2.2. Materials
- Dry reinforcement fiber fabric;
- Thermoset prepregs;
- Woven commingled thermoplastic and reinforcement fiber yarns;
- Impregnated and consolidated thermoplastic organo sheets.
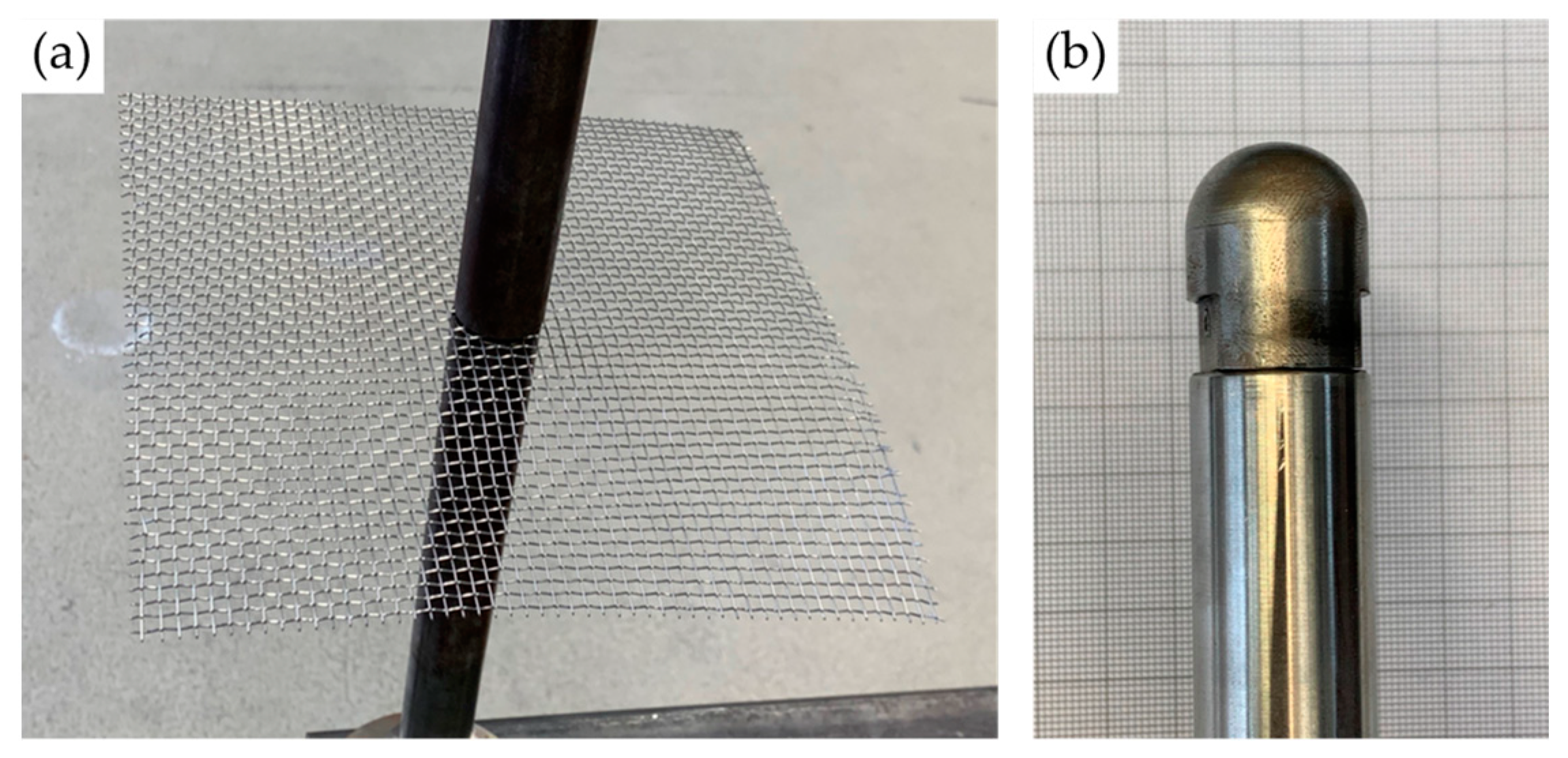
2.3. Investigation of Wire Mesh Forming
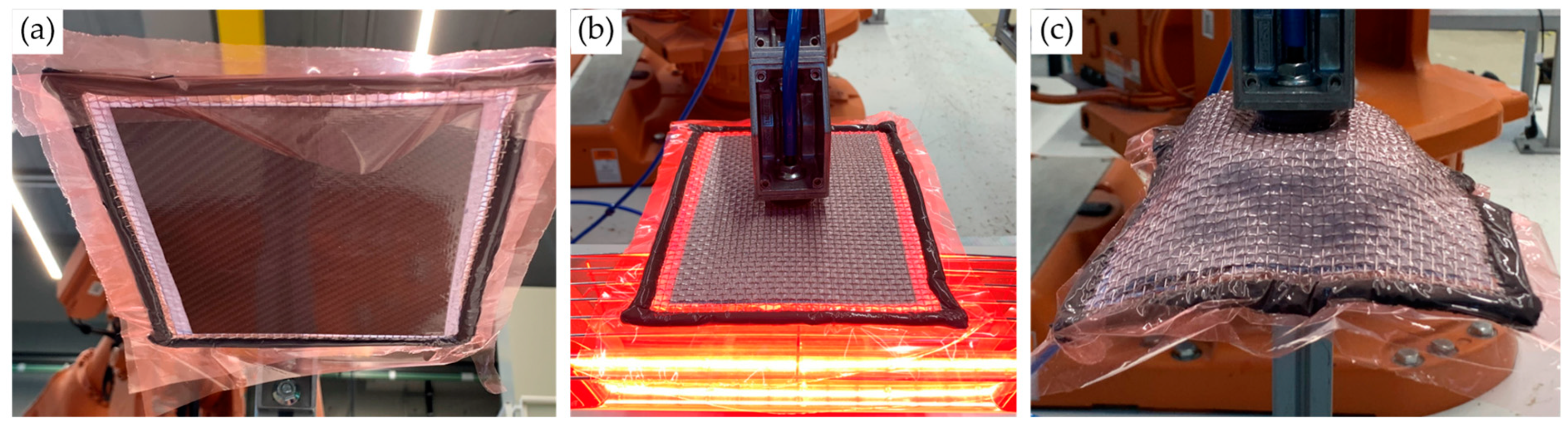
2.4. Investigation of Prepreg Forming
2.5. Investigation of Woven Commingled Yarn Forming
2.6. Investigation of Organo Sheet Forming
3. Results
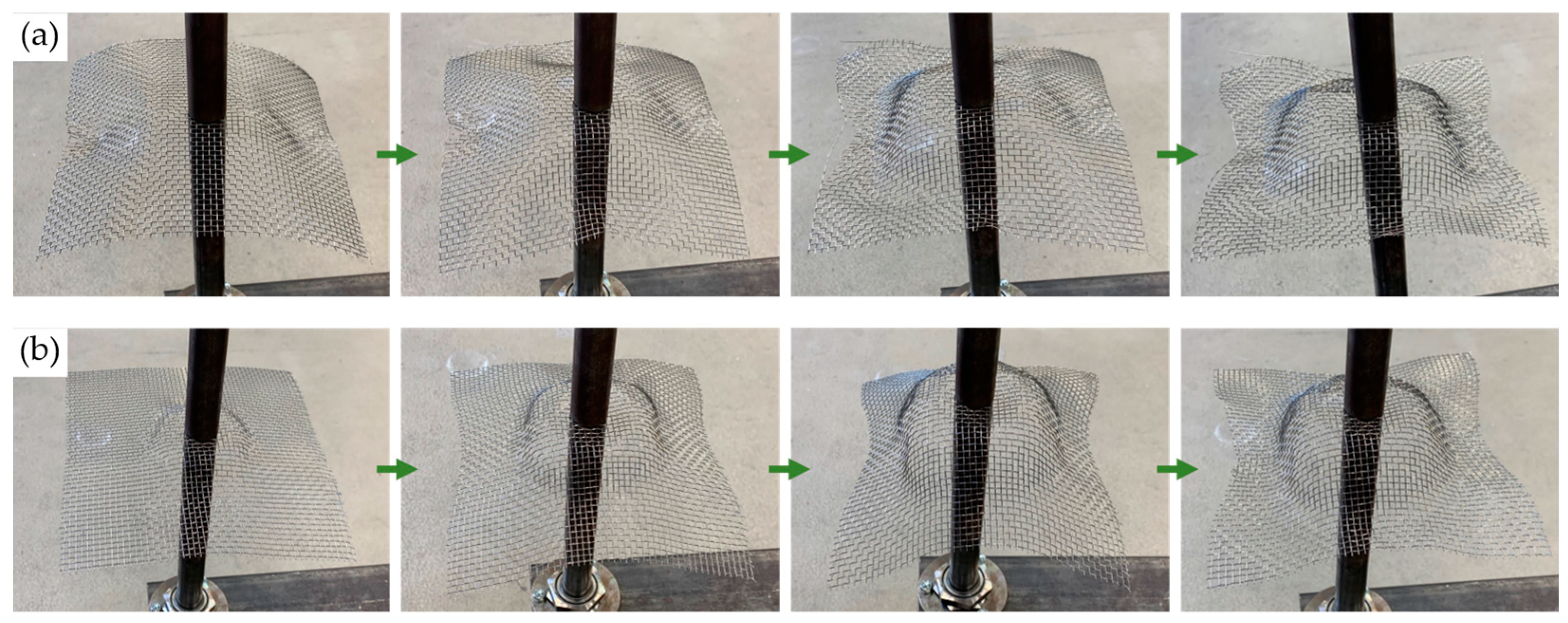
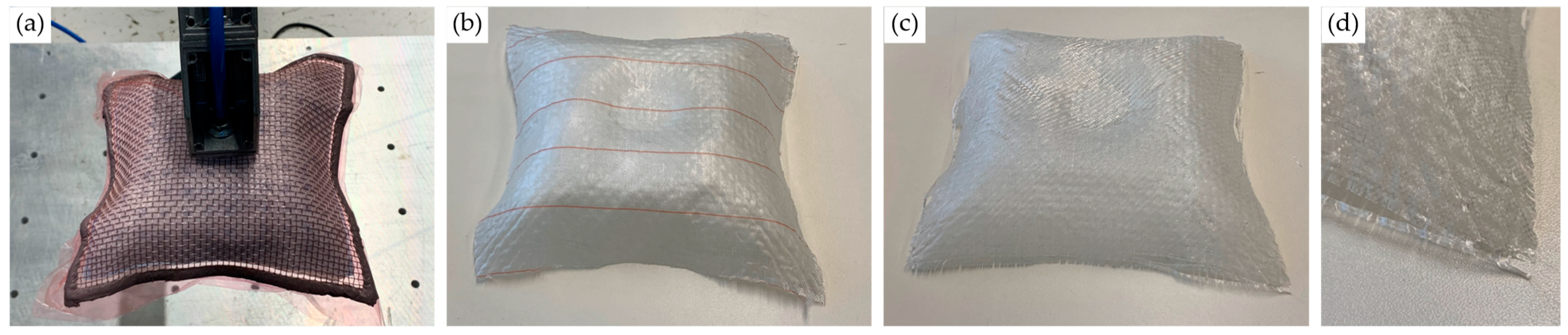
3.1. Wire Mesh Forming
3.2. Prepreg Forming
3.3. Woven Commingled Yarn Forming
3.4. Organo Sheet Forming
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flemming, M.; Ziegmann, G.; Roth, S. Faserverbundbauweisen: Fertigungsverfahren Mit Duroplastischer Matrix; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Biron, M. Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Composites: Technical Information for Plastics Users; Elsevier BH: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; ISBN 978-1-85617-478-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, P. Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Materials, Manufacturing and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein, G. Faserverbund-Kunststoffe; Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, I.; Del Saenz Castillo, D.; Fernandez, A.; Güemes, A. Advanced Thermoplastic Composite Manufacturing by In-Situ Consolidation: A Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitzel, M.; Mitschang, P.; Breuer, U. Handbuch Verbundwerkstoffe: Werkstoffe, Verarbeitung, Anwendung, 2nd ed.; Hanser: München, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783446436978. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, B.-A.; Raatz, A.; Hübner, S.; Bonk, C.; Bohne, F.; Bruns, C.; Micke-Camuz, M. Automated Stamp Forming of Continuous Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastics for Complex Shell Geometries. Procedia CIRP 2017, 66, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennige, T. Flexible Formgebung von Blechen Durch Laserstrahlumformen; Meisenbach: Bamberg, Germany, 2001; ISBN 3875251407. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.K.; Gur, M.; Peled, A.; Payne, A.; Menzel, E. Die-Less Forming of Thermoplastic- Matrix, Continuous-Fiber Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1990, 24, 346–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, M.P.; Sarkytbayev, A.; Ward, C. Automated composite draping: A review. In SAMPE 2017, Proceedings of the Washington State Convention Center, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–25 May 2017; SAMPE North America: Diamond Bar, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walczyk, D.F.; Hosford, J.F.; Papazian, J.M. Using Reconfigurable Tooling and Surface Heating for Incremental Forming of Composite Aircraft Parts. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2003, 125, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Said, L. The incremental sheet forming; technology, modeling and formability: A brief review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 2729–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, R.; Ambrogio, G.; Pulice, D.; Gagliardi, F.; Filice, L. Incremental Sheet Forming of a Composite Made of Thermoplastic Matrix and Glass-Fiber Reinforcement. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.; Ortega, R.; Acosta, P.; Calderón, E. Hot Incremental Forming of Biocomposites Developed from Linen Fibres and a Thermoplastic Matrix. SV-JME 2021, 67, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Kami, A.; Shakouri, M. Single point incremental forming of polyamide/30 wt% short glass fiber composite. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2022, 36, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorotto, M.; Sorgente, M.; Lucchetta, G. Preliminary studies on single point incremental forming for composite materials. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2010, 3, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Kim, J.-J.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Study on the incremental sheet forming of CFRP sheet. Compos.—A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 141, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogio, G.; Conte, R.; Gagliardi, F.; de Napoli, L.; Filice, L.; Russo, P. A new approach for forming polymeric composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.; Graf, A.; Kräusel, V.; Trautmann, M. Heat supported single point incremental forming of hybrid laminates for orthopedic applications. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 29, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.; Kunke, A.; Kräusel, V. Hot single-point incremental forming of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (PA6GF47) supported by hot air. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, R.; Mirnia, M.J.; Elyasi, M.; Zolfaghari, A. An experimental investigation into single point incremental forming of glass fiber-reinforced polyamide sheet with different fiber orientations and volume fractions at elevated temperatures. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2022, 36, 1893–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Su, X.; Peng, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, D. Thermal-Assisted Single Point Incremental Forming of Jute Fabric Reinforced Poly(lactic acid) Biocomposites. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, R.; Serratore, G.; Ambrogio, G.; Gagliardi, F. Numerical analyses of long fiber–reinforced polymeric sheets processed by Single Point Incremental Forming. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.-E.; Graupner, R.; Schüppstuhl, T. Processing Strategies for Dieless Forming of Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites. Machines 2023, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.-E.; Graupner, R.; Schüppstuhl, T. Die-Less Forming of Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites. In Flexible Automation and Intelligent Manufacturing: The Human-Data-Technology Nexus; Kim, K.-Y., Monplaisir, L., Rickli, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 3–14. ISBN 978-3-031-18325-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.-E.; Schwieger, L.-S.; Schüppstuhl, T. Robotic Die-Less Forming Strategy for Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites Production. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.-E.; Schüppstuhl, T. Die-less forming of fiber-reinforced thermoplastic sheets and metal wire mesh. In Sheet Metal 2023, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Sheet Metal, Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany, 2–5 April 2023; Merklein, M., Hagenah, H., Duflou, J.R., Fratini, L., Martins, P., Meschut, G., Micari, F., Eds.; Materials Research Forum LLC.: Millersville, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shankar, K.; Morozov, E.; Ram Ramakrishnan, K.; Fien, A. Characterization of Shear Behavior in Stainless Steel Wire Mesh Using Bias-Extension and Picture Frame Tests. J. Eng. Mech. 2020, 146, 04019127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagirusamy, R.; Fangueiro, R.; Ogale, V.; Padaki, N. Hybrid Yarns and Textile Preforming for Thermoplastic Composites. Text. Prog. 2006, 38, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Deformation Characteristic | Woven Fabric | Steel Wire Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Bending stiffness | - - - | o |
| Shear stiffness | - - | - |
| Tensile strength | + + + | + |
| Compressive strength | - - - | o |
| Material | Weave Type | Basis Weight | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel 1.4301 wire mesh 1 | plain | 3.15 × 0.56 mm | |
| Glass fiber fabric 2 | twill | 160 g/m2 | |
| GF/PP commingled yarn fabric 3 | twill | 700 g/m2, 60 wt% | |
| CF/SAN organo sheet 4 | twill | 245 g/m2, 45 vol% | 0.9 mm |
| Nylon peel ply 5 | plain | 85 g/m2 | |
| PP separating foil 5 | 25 µm | ||
| PE breather fleece 5 | nonwoven | 150 g/m2 | 1.6 mm |
| FEP bagging film 2 | 25 µm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rath, J.-E.; Schüppstuhl, T. Investigation of Metal Wire Mesh as Support Material for Dieless Forming of Woven Reinforcement Textiles. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050182
Rath J-E, Schüppstuhl T. Investigation of Metal Wire Mesh as Support Material for Dieless Forming of Woven Reinforcement Textiles. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2023; 7(5):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050182
Chicago/Turabian StyleRath, Jan-Erik, and Thorsten Schüppstuhl. 2023. "Investigation of Metal Wire Mesh as Support Material for Dieless Forming of Woven Reinforcement Textiles" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 7, no. 5: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050182
APA StyleRath, J.-E., & Schüppstuhl, T. (2023). Investigation of Metal Wire Mesh as Support Material for Dieless Forming of Woven Reinforcement Textiles. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 7(5), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050182











