Abstract
Cellular structures of metallic alloys are often made for various industrial applications by additive manufacturing. The permeability for fluid flow in these cellular structures is important. The current investigated the gas fluidity of cellular structures made by selective laser melting (SLM). The porosity and permeability of the SLM cellular structures were measured for 17-4 PH stainless steel, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. The relations between porosity and energy density are expressed using the power law. The characteristic molar energies were 1.07 × 105, 9.02 × 104, and 7.11 × 104 J/mole for 17-4 PH steel, Ti-6Al-4V, and Inconel 718 alloys, respectively. 17-4 PH steel gave rise to higher porosity at the same energy density when compared with Ti-6Al-4V and Inconel 718 alloy. The values of these molar energy density are related to the heat needed to melt the alloys, viscosity, and thermal conductivity. It was further shown that air permeability is not only concerned with the percentage of porosity in the cellular materials, but it also relates to the tortuosity of pore pathways formed in the cellular materials. At the same porosity, Inconel 718 demonstrates higher air permeability in comparison with that of Ti-6Al-4V and 17-4 PH alloys due to its smoother pore pathways. Ti-6Al-4V, on the other hand, demonstrates the highest specific surface areas due to powder sticking along the pore pathways and led to the lowest permeability among the three alloys.
1. Introduction
Cellular metal parts have been employed for many industrial applications [1,2], such as the in-growth of bone tissues [3], heat exchangers in high-temperature applications [4], and the vapor chamber for thermal management of electronics [5]. Another example is the porous mold inserts in plastic injection molding for gas escape to avoid flow lines, short shots, burn marks defects, etc. [6,7,8,9,10]. Among these applications, fluidity is critical inside the cellular parts. Traditionally, cellular metal parts are mainly made via metal foaming and powder metallurgy [1,2,11,12]. Pore arrangements in the cellular metals made by these processes cannot be controlled. Additive manufacturing becomes a reasonable candidate for manufacturing three-dimensional structures with desired cellular structures [10,13].
Additive manufacturing by power bed fusion such as selective laser melting (SLM) is capable of building cellular structures by controlling energy density to form gas pathways among pores [14,15,16]. The microstructures and anisotropic properties of SLM parts are also greatly affected by printing parameters and energy density [17,18]. The volumetric energy density [19], EDv (in J/mm3), has been formulated to express the energy input in unit volume by laser power (P), scanning speed (), hatch space (h) and layer thickness (t) according to Equation (1).
Olakanmi [20] pointed out that, for different alloys, the same EDv would give rise to different porosity. For example, in the case of Al alloys, silicon aids in the fluidity of the molten pools and thus increases the densification of SLM parts. Apparently, cellular parts of different alloys can give rise to different gas permeability depending on the melting and solidification characteristics of alloys [21,22].
Studies [21,22,23] have reported permeability (k) measurements of SLM porous steel parts with 5 to 50% porosity. The permeability ranging from 10−14 to 10−12 m2 is applicable for mold inert to release in-mold gas in plastic injection molding. Leong [24] then reported that, at the same level of porosity, metal foams with a pore density of 40 ppi display lower k than the ones with 20 or 10 ppi due to reduced pore size and higher surface area. It is apparent that the fluid flows with larger frictional force leading to higher pressure drop and thus lower permeability as it passes through the porous media [25]. Therefore, it is critical to look into the pore pathways in cellular structures to understand their effects on gas permeability.
Most of the studies on SLM cellular structures focus on single metal or alloy. There is lack of studies that discuss the variation of cellular structures made by different alloys. Among different alloys employed for making cellular structures, 17-4 PH stainless steel is often used to make porous mold inserts for injection molding purposes [26]. Inconel 718 porous parts are used for air flow in turbine components [27]. And Ti-6Al-4V porous pats are used extensively in biomedical applications, such as spinal cages [3]. The permeability of fluids in the porous parts made by these materials is apparently an important characteristic to understand for the design of porous parts.
As 17-4 PH stainless steel, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V alloys are three of the alloys most frequently fabricated by SLM, the current study intends to manufacture cellular parts using these alloys. The relation of porosity and permeability in cellular parts will be formulated to relate to SLM building process parameters for the three alloys. It will also aid to understand the effects of metal pools upon the formation of cellular parts when using different alloys. The characteristics of pore pathways due to the difference in materials’ thermophysical properties will be discussed. Gas fluidity in the cellular parts made by these alloys can then be controlled for various industrial applications.
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material and SLM Parameters
Table 1 lists the compositions and powder sizes of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V ELI (extra low interstitial) spherical powders made by EOS® (Krailling, Germany) to prepare cellular parts in this study. These are iron-, nickel-, and titanium-based alloys, respectively, and represent three major alloys used in SLM.

Table 1.
Compositions (in wt.%) and size of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V powders.
EOS M290 SLM equipment (Krailling, Germany, Figure 1a) is used in the current study, and Table 2 lists the SLM parameters for making cellular parts of the three alloys. As the three alloys have different melting points and thermophysical properties, different laser power (P), scan speed (), and layer thickness (t) were employed. Each layer is rotated by 66.7° to reduce anisotropy and local overheating. Hatch distances (h) from 300 to 1000 μm are selected to prepare cellular structures with varying porosity levels. The volumetric energy density calculated using Equation (1) ranges from 7.28 to 25.93 J/mm3. Figure 1b shows the designed 30 mm × 30 mm × 4 mm SLM cellular coupons.
Figure 1.
(a) EOS M290 SLM equipment and (b) schematics of SLM cellular parts.

Table 2.
SLM parameters of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V ELI porous material.
2.2. Porosity and Gas Permeability Measurement
Due to that, the pores printed in SLM cellular parts are mainly through pores, the Archimedean method is inapplicable for measuring the porosity of the cellular parts. We estimate the density based on the mass and volume of the cellular blocks. The porosity is then obtained by subtracting the ratio of relative density from unity as expressed in Equation (2), where mexp represents the mass, volume Vexp is estimated by the length, width, and thickness of the porous coupons, and is the theoretical density of the alloys.
The connectivity of pores in cellular structures cannot be expressed just by porosity. Gas permeability is also affected by pore size and the surfaces of the pore pathways. Therefore, other pore characteristics, such as pore size and surface area must also be characterized to relate with gas permeability, k.
The gas permeability of the SLM cellular coupons is measured using apparatus [14] set up according to Darcy’s Law or Equation (3) [28]. The inlet air pressure is kept constant at 20 psi (0.138 MPa or 1.36 atm) for permeability measurement. The pressure drop (ΔP) across the porous media (thickness, L) is proportional to the gas viscosity (μ), flow rate of gas (), and thickness of the porous media (L), while it is inversely proportional to gas permeability (k) [28].
Micromeritics AutoPore® IV 9520 (Norcross, GA, USA, Figure 2a) is used to measure the distribution of pore sizes in the cellular parts. As for the surface area, Micromeritics ASAP 2020 BET analyzer (Norcross, GA, USA, Figure 2b) and nitrogen gas are utilized to measure the specific surface area in the cellular parts.

Figure 2.
(a) Micromeritics AutoPore IV 9520 and (b) Micromeritics ASAP 2020 BET Analyzer for pore size and specific surface area measurements.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Porosity of SLM Cellular Parts
Figure 3 shows the porosity of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V ELI SLM cellular parts made by varying energy density. The largest porosity of the three materials are 67.67, 51.15, and 40.34%, respectively for 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V ELI at similar energy density. It is important to note that, at the same energy density, the three materials exhibit different levels of porosity. Apparently, different alloys require different energy to form a liquid pool. As energy density, or EDv, increases, the porosity of porous parts decrease since the powder bed absorbs higher energy and the material powder is molten more completely to form liquid pools.
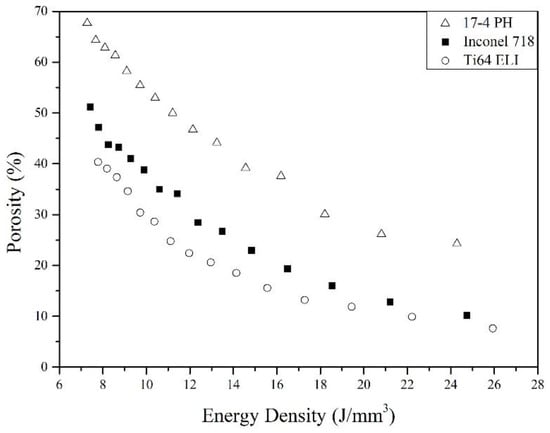
Figure 3.
Relation between porosity and volumetric energy density (EDv) of the three alloys.
To further discuss on the porosity of SLM cellular parts, molar energy density is introduced to substitute volumetric energy density. The molar energy density is employed to compare upon the same number of atoms in the three alloys. Due to the fact that three alloys have different theoretical density and molecular weight, molar energy density (EDmole) can be converted from volumetric energy density (EDv) according to Equation (4) where theoretical density () and molecular weight (MW) of each alloy are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Theoretical density and molecular weight of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V ELI.
Figure 4 demonstrates the new relationship between molar energy density and porosity of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718, and Ti-6Al-4V ELI SLM cellular parts. It is seen now, in contrast to those shown in Figure 3, 17-4 PH shows the highest porosity, followed by Ti-6Al-4V ELI and Inconel 718 at a similar molar energy density.
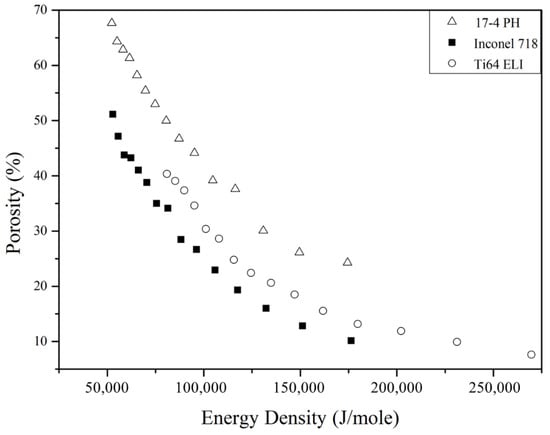
Figure 4.
Relation between porosity and molar energy density (EDmole) of the three alloys.
The formation of pores in cellular structures can be treated as the cause of thermal activities. The power law is used to relate molar energy density input with the porosity in cellular structures [20] or Equation (5)
In Equation (5), the exponent of negative molar energy density (EDmole) divided by “Eo” gives rise to a probability of pore formation. Therefore, the “Eo” term relates to the needed energy to form fully consolidated material (zero porosity), and “ϕo” represents the maximum porosity that can be achieved. Table 4 lists the fitted values of ϕo and Eo for the three alloys based on the data in Figure 4. It can be seen that ϕo has nearly the value of 100% which corresponds to 100% porosity or non-powder melting when zero energy input is applied.

Table 4.
ϕo and Eo of 17-4 PH, Ti-6Al-4V ELI and Inconel 718.
It is also noted that Eo differs greatly for the three alloys (Table 4). Among them, 17-4 PH has the highest Eo which requires higher energy than the other two alloys to form fully dense structures. Therefore, at the same molar energy input, 17-4 PH cellular parts give rise to the highest level of porosity (Figure 4) in comparison with the other two alloys. On the contrary, Inconel 718 with the lowest Eo needs the least energy to fabricate a fully dense solid, so the Inconel 718 cellular parts give rise to the lowest level of porosity in Figure 4 in the three alloys investigated.
It is interesting to discuss the plausible thermophysical properties that Eo comprises. According to Figure 5, during the melting and solidification of SLM parts from metal powders, activities including melting, vaporization, and the dissipation of heat all add to the needed energy from the entered laser power (ELaser). Therefore, the specific heat capacity and heat of melting of each material need to be considered to obtain the heat required for fusion (ΔHf). After the molten pool is formed, the heat dissipation by conduction (ECond) and the enthalpy of vaporization (EVap) are also supplied by the input laser power (ELaser) as shown in Figure 5.
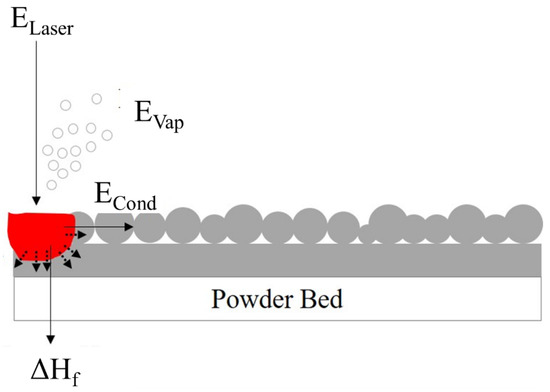
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of SLM process.
Table 4 [29] lists the enthalpy needed to heat and melt the three alloys starting from room temperature (ΔHf). It is seen that Ti-6Al-4V ELI powders need to absorb the highest energy for melting (54,137 J/mole). It is about 2086 J/mole higher than that for 17-4 PH stainless steel while Eo of Ti-6Al-4V is lower than that for 17-4 PH. According to Table 5, among the three major elements in the three alloys, Ti has the lowest viscosity and vapor pressure. In comparison, the solvent elements in 17-4 PH, or Fe, have the highest viscosity (η) and vapor pressure (PVap) when compared with Ni in Inconel 718 and Ti in Ti-6Al-4V. Molten pools with higher viscosity and higher vapor pressure can lead to reduced fluidity and higher vapor formation. Therefore, a high Eo value is attained for 17-4 PH alloy which leads to the highest porosity at the same energy density among the three alloys tested (Figure 4).

Table 5.
Physical properties of Fe, Ni, and Ti.
3.2. Air Permeability
Figure 6 exhibits the relation between air permeability (k) and porosity for cellular parts made by the three alloys. It is important to note that three materials have different permeability even at the same porosity level, which suggests that the amount of porosity is not the only factor that determines k. The fluid flow in the cellular parts must also depend on the arrangements of pores in cellular structures.
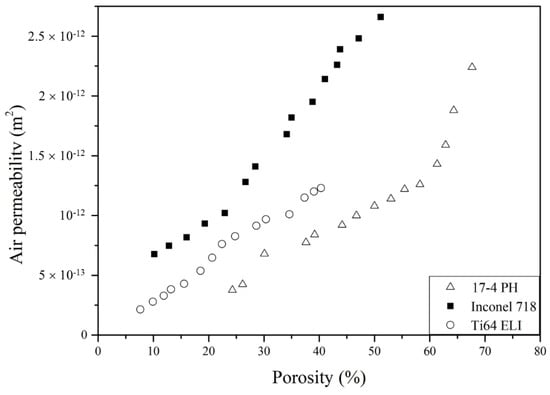
Figure 6.
The relation between air permeability and porosity of 17-4 PH, Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V ELI cellular parts.
We further selected three groups of porous materials (Table 6) to observe the difference in pore structures at similar porosity levels. The P2 (17-4 PH with h = 350 μm), I6 (Inconel 718 with h = 550 μm), and T10 (Ti-6Al-4V with h = 750 μm) samples all with 26.15~27.64% porosity are compared. According to Figure 6 and Table 6, Inconel 718 has the highest k, followed by Ti-6Al-4V ELI and 17-4 PH. The interconnection of pores, pore size, and specific surface areas are observed to explain the difference in k values.

Table 6.
Porosity and air permeability of 17-4 PH (P), Inconel 718 (I) and Ti-6Al-4V ELI (T) cellular parts.
Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 show the cross-section of the cellular samples selected in Table 6. In Figure 7, the samples have lower porosity compared to those in Figure 8 and Figure 9. Pores are less likely to interconnect when the porosity level is low, therefore lower permeability is obtained when compared with samples of higher porosity levels in Figure 8 and Figure 9. With increasing porosity (Figure 8 and Figure 9), through-pore paths dominate in Inconel 718 cellular samples, while 17-4 PH and Ti-6Al-4V ELI samples demonstrate more single-end pore paths. The Inconel 718 samples, therefore, demonstrate the highest permeability when compared with 17-4 PH and Ti-6Al-4V ELI.
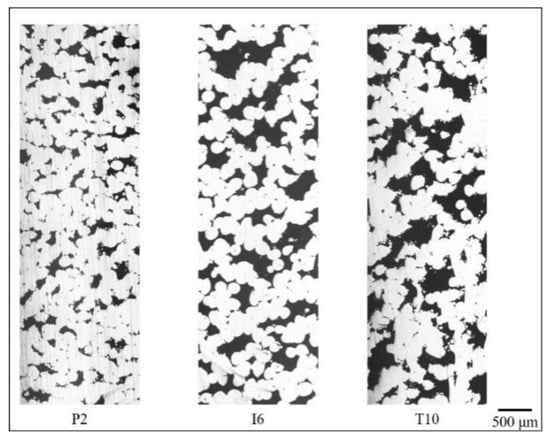
Figure 7.
Flow paths in P2, I6, and T10 samples (lateral direction corresponds to z or printing direction in SLM.).
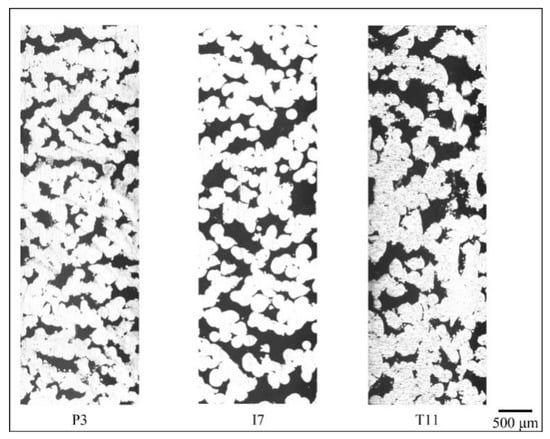
Figure 8.
Flow paths in P3, I7, and T11 (lateral direction corresponds to z or printing direction in SLM.).
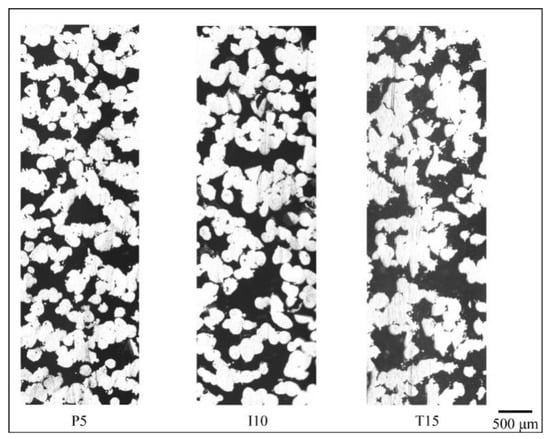
Figure 9.
Flow paths in P5, I10, and T15 (lateral direction corresponds to z or printing direction in SLM.).
According to Table 7, Ti-6Al-4V ELI porous material has the largest median pore size (d50) [32] and specific surface area (S) indicating that the pathways for gas are more tortuous and powders are partially sintered on the pathways. Even though Ti-6Al-4V samples have larger pore paths, the more complicated zigzagging paths can reduce their permeability when compared with Inconel 718 samples.

Table 7.
Median pore size (d50) and specific surface area (S) in SLM cellular samples.
On the other hand, the 17-4 PH samples have slightly smaller median pore sizes and higher specific surfaces than Inconel 718 alloy. It is also noted that 17-4 PH molten liquid is more viscous (Table 5) and uses smaller hatch spacings causing smaller paths to form at higher energy input which could thus lead to more closed pore paths and even lower permeability than Ti-6Al-4V.
By analyzing pore characteristics, the parametric studies explain how SLM cellular porous materials can have completely different permeability with similar porosity. Inconel 718 samples using the highest hatch distance to generate porosity of the same levels. More through holes for gas pathways are present to bear the highest permeability. Ti-Al-4V uses an even higher hatch distance, however, the tortuosity of pore pathways causes the specific area to increase greatly which limits the gas permeability. Lastly, 17-4 PH requires higher energy input to generate the same amount of porosity, indicating much smaller holes and the limited interconnectivity among pores lead to the lowest permeability when compared with the same levels of porosity in Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- SLM was employed to prepare 17-4 PH, Ti-6Al-4V ELI, and Inconel 718 cellular parts by adjusting hatch distance from 300 to 1000 μm. The relationship between energy density and porosity levels is expressed using power law. The Eo coefficients are 1.07 × 105, 9.09 × 104, and 7.14 × 104 J/mm3, respectively, for the three alloys;
- (2)
- 17-4 PH powders require higher energy to attain liquid states which are also more viscous and have higher vapor pressure. Therefore, 17-4 PH demonstrated the highest Eo and porosity level at the same energy density. In contrast, Inconel 718 requires lower enthalpy to melt, and the lowest porosity is obtained at the same energy density input;
- (3)
- Gas permeability relates not only to porosity level but also to the size and tortuosity of pore pathways in cellular parts. As Inconel 718 cellular parts contain more through-pores, a lower surface area gave rise to the highest permeability at a similar porosity. Pore pathways in Ti-6Al-4V were characterized by higher tortuosity with the highest specific surface area indicating many powders are partially adhered to the surface along the gas pathways. The lowest permeability was attained by 17-4 PH at a similar level of porosity among the three alloys investigated due to the reduced pore sizes.
The characterization of porosity formation and pore pathways reported in the current study can provide guidelines for understanding the fluid flow characteristics in the industry applications of cellular parts made by the three alloys.
Author Contributions
Data curation, T.-W.L. and T.-L.C.; Formal analysis, J.-K.C.; Funding acquisition, J.-K.C.; Investigation, T.-W.L.; Methodology, K.-C.C.; Resources, T.-W.L.; Supervision, J.-K.C.; Validation, J.-K.C.; Visualization, T.-W.L. and J.-K.C.; Writing—original draft, T.-W.L.; Writing—review & editing, J.-K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan under grant number MOST #108-2221-E-027-058-MY2.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the MSc thesis of Mr. Ting-Wei Liu under the supervision of Prof. Jhewn-Kuang Chen entitled “Pore Characteristics and Air Permeability of Porous Parts Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting” at National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, TAIWAN, 2021.
Acknowledgments
The financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology, TAIWAN under grant MOST #108-2221-E-027-058-MY2 is acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Atwater, M.A.; Guevara, L.N.; Darling, K.A.; Tschopp, M.A. Solid State Porous Metal Production: A Review of the Capabilities, Characteristics, and Challenges. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Liang, Y.; He, Y.; Shang, S.; Liu, Z.-K. Pore structure and gas permeability of high Nb-containing TiAl porous alloys by elemental powder metallurgy for microfiltration application. Intermetallics 2013, 33, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matassi, F.; Botti, A.; Sirleo, L.; Carulli, C.; Innocenti, M. Porous metal for orthopedics implants. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2013, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azizi, A.; Sammakia, B.G.; Daeumer, M.A.; Murray, B.T.; Simmons, J.C.; Schiffres, S.N. Additive laser metal deposition onto silicon for enhanced microelectronics cooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, Z.; Yan, Y.; Li, B. Experimental investigation of vapor chambers with different wick structures at various parameters. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 77, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavekar, R.; Vasudevan, H.; Ranka, D. Investigating red X parameter for short shot-type defect in plastic injection moulds using Shainin’s design of experiments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, Wuhan, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 533–541. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Ryu, K. Dual-Kernel-Based Aggregated Residual Network for Surface Defect Inspection in Injection Molding Processes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Kuroiwa, H.; Fukushima, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Terauchi, F. Detection of the burn mark on the plastic surface using image analysis: Fundamental study for reduction the environmental impact by unpainted plastic products. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century, Miyagi, Japan, 7–8 November 2013; pp. 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Crema, L.; Sorgato, M.; Lucchetta, G. Thermal optimization of deterministic porous mold inserts for rapid heat cycle molding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 109, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahara, H.; Takeshita, S.; Fukumaru, H.; Koresawa, H.; Suzuki, H. Permeability performance on porous structure of injection mold fabricated by metal laser sintering combined with high speed milling. Int. J. Auto. Techn. 2012, 6, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Dhakad, S. Preparation of metal foam by different methods: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, E.; Keleş, O. Open Cell Aluminum Foams Produced by Polymer Impregnation Method. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 125, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Narahara, H.; Nakao, Y.; Fukumaru, H.; Koresawa, H.; Suzuki, H.; Abe, S. Permeability characteristics and applications of plastic injection molding fabricated by metal laser sintering combined with high speed milling. Int. J. Auto. Techn. 2008, 2, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhinakar, A.; Li, B.-E.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chiu, K.-C.; Chen, J.-K. Air Permeability of Maraging Steel Cellular Parts Made by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2021, 14, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremen, S.; Meiners, W.; Diatlov, A. Selective laser melting: A manufacturing technology for the future? Laser Tech. J. 2012, 9, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Martinez, E.; Hernandez, J.; Collins, S.; Amato, K.N.; Gaytan, S.M.; Shindo, P.W. Microstructures and Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, A.; Shamsaei, N.; Thompson, S.M.; Elwany, A.; Bian, L. Effects of building orientation and heat treatment on fatigue behavior of selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.K.; Banerjee, M.; Sharma, A.; Singh, J.; Bansal, A.; Gupta, M.K.; Khanna, N.; Shahi, A.; Goyal, D.K. Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V alloy: Process parameters, defects and post-treatments. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakanmi, E.O. Selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM) of pure Al, Al–Mg, and Al–Si powders: Effect of processing conditions and powder properties. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 2013, 213, 1387–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furumoto, T.; Koizumi, A.; Alkahari, M.R.; Anayama, R.; Hosokawa, A.; Tanaka, R.; Ueda, T. Permeability and strength of a porous metal structure fabricated by additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 219, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, D.F.; German, R.M. Porous stainless steel parts using selective laser sintering. Adv. Powder Metall. Partic. Mater. 2001, 8, 8–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Tian, X.; Peng, G.; Cao, Y.; Li, D. Hierarchically porous materials prepared by selective laser sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, K.; Jin, L. Characteristics of oscillating flow through a channel filled with open-cell metal foam. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2006, 27, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhan, N.; Patel, P. Equivalent particle diameter and length scale for pressure drop in porous metals. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2008, 32, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.L.S.; Diegel, O.; Xu, X. Bonding integrity of hybrid 18Ni300-17-4 PH steel using the laser powder bed fusion process for the fabrication of plastic injection mould inserts. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2022, 120, 4963–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealy, B.; Calderon, L.; Wang, W.; Valetin, R.; Mingareev, I.; Richardson, M.; Kapat, J. Characterization of laser additive manufacturing fabricated porous superalloys for turbine components. J. Eng. Gas Turb. Power 2017, 139, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.T. Henry Darcy (1803–1858): Immortalised by his scientific legacy. Appl. Hydrogeol. 2008, 16, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, J.J.; Quested, P.N. Thermophysical Properties; ASM Handbook, Casting; ASM International: Ohio, OH, USA, 2013; Volume 15, pp. 468–481. [Google Scholar]
- Battezzati, L.; Greer, A. The viscosity of liquid metals and alloys. Acta Met. 1989, 37, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, A. Electrical transport properties of some liquid metals. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2008, 46, 800–810. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffregen, H.A.; Fischer, J.; Siedelhofer, C.; Abele1, E. Selective laser melting of porous structures. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2011; pp. 680–695. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).