Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Impact of the Electromagnetic Properties of the Die Materials in Electromagnetic Forming of Thin Sheet Metal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Die Material
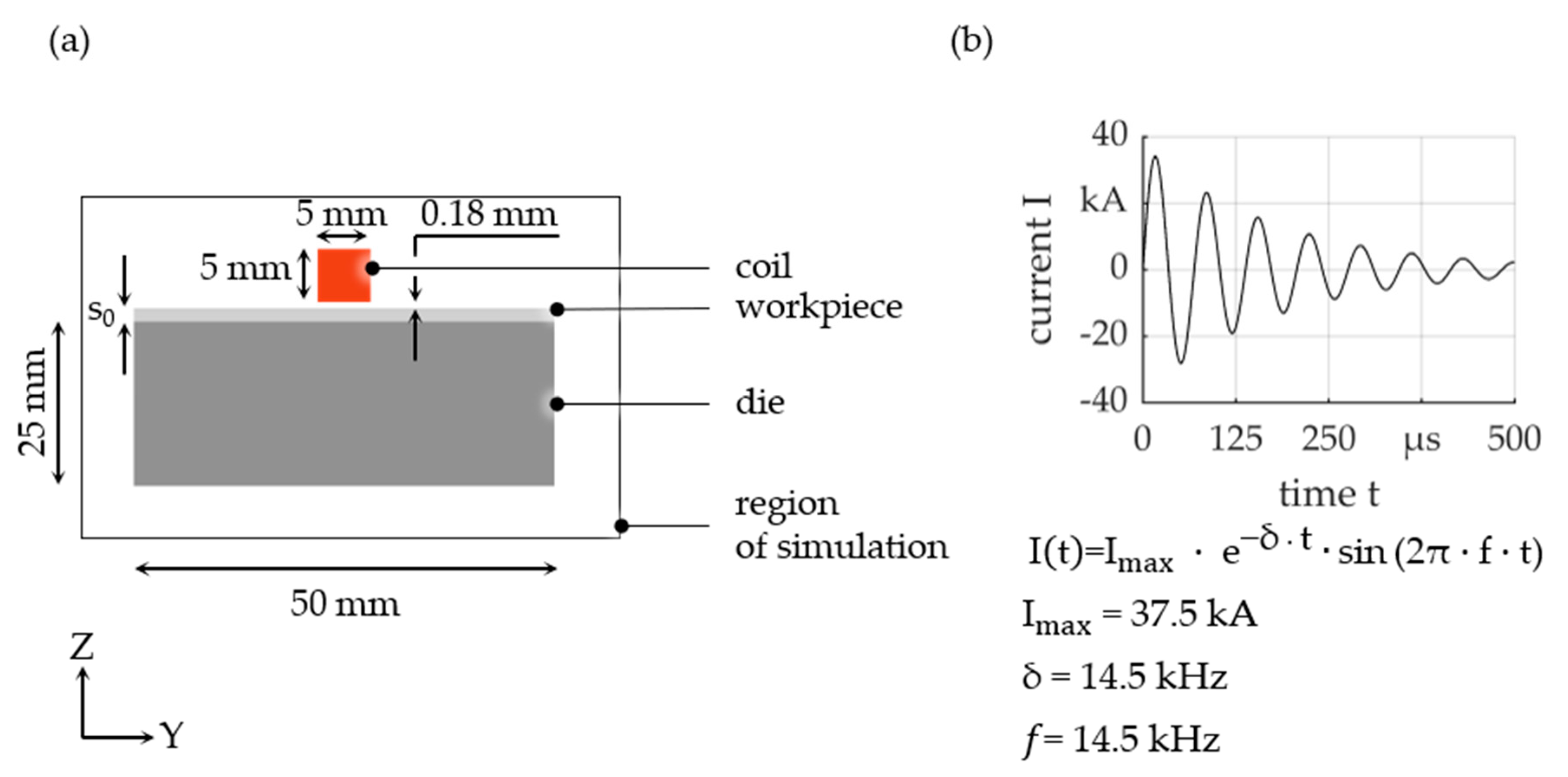
2.2. Simulation Model
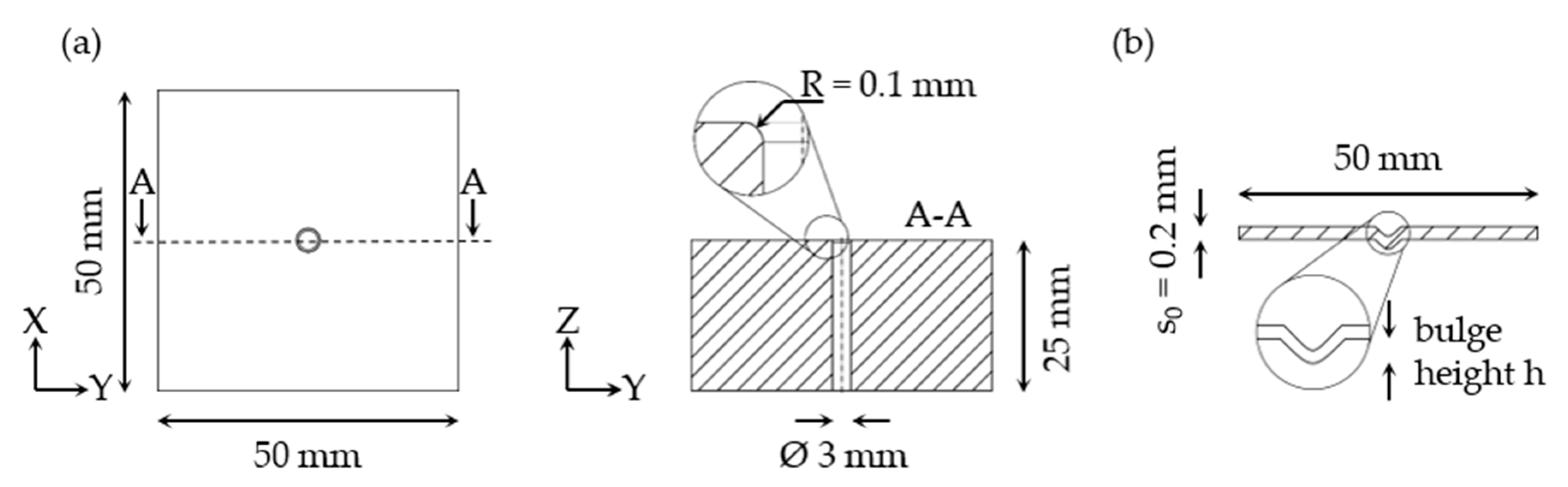
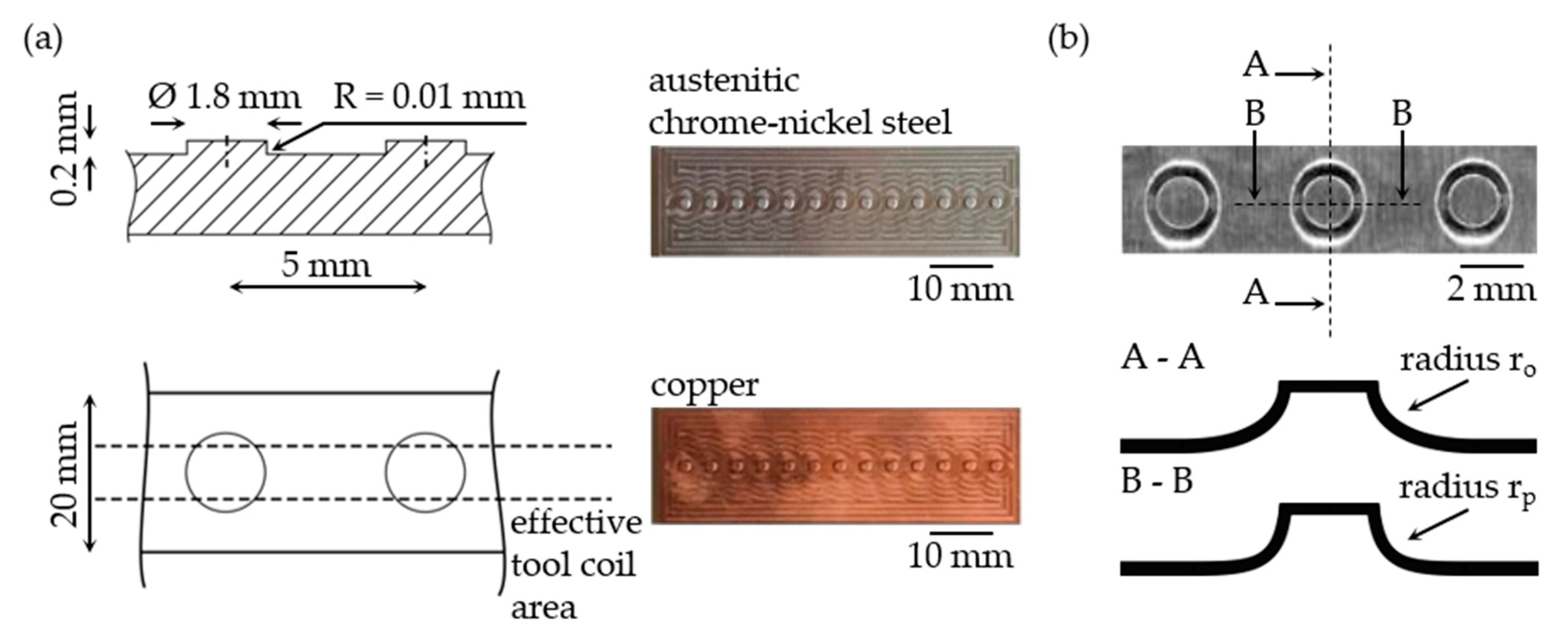
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results
3.1. Simulation Results
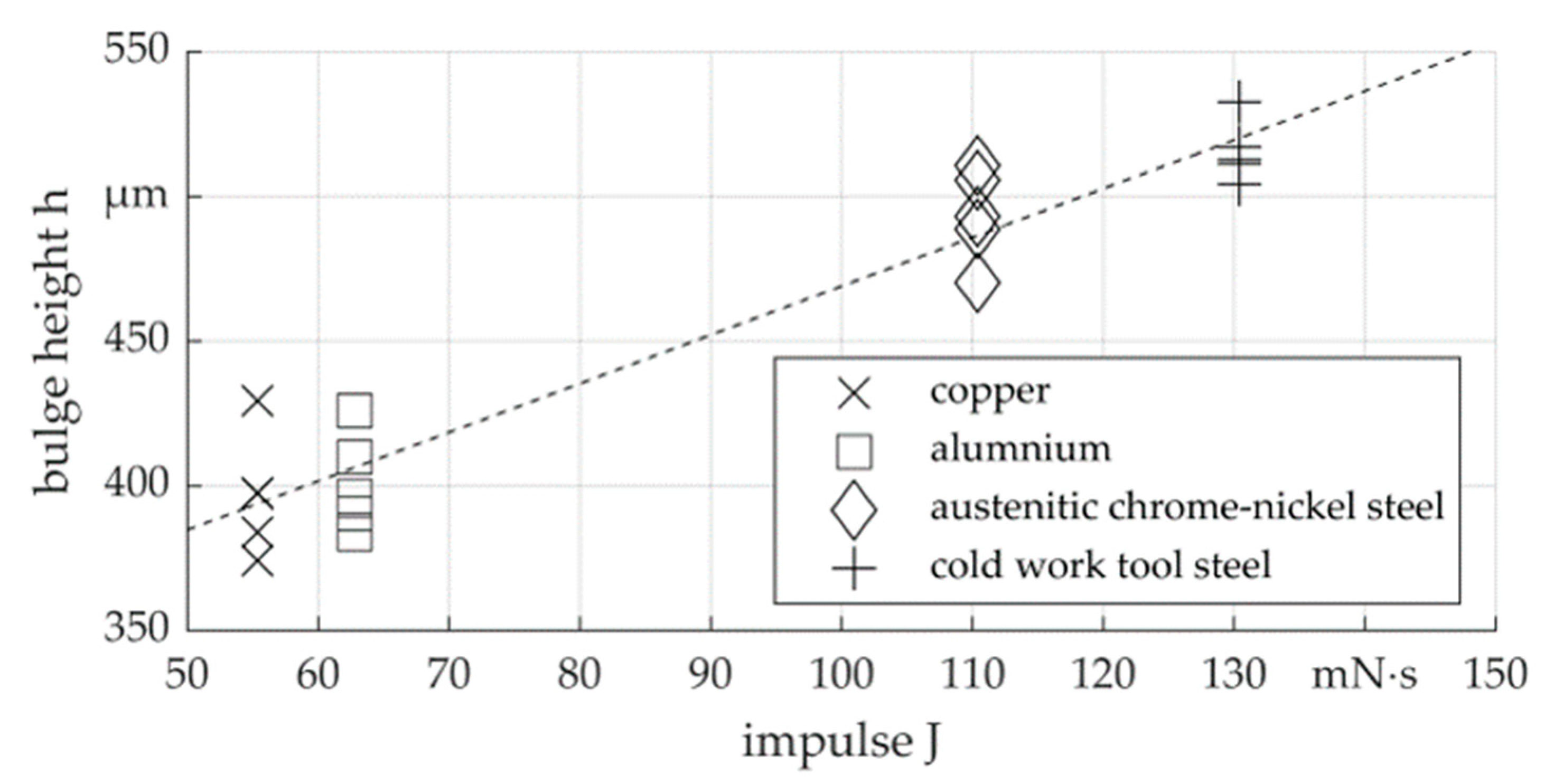
3.2. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
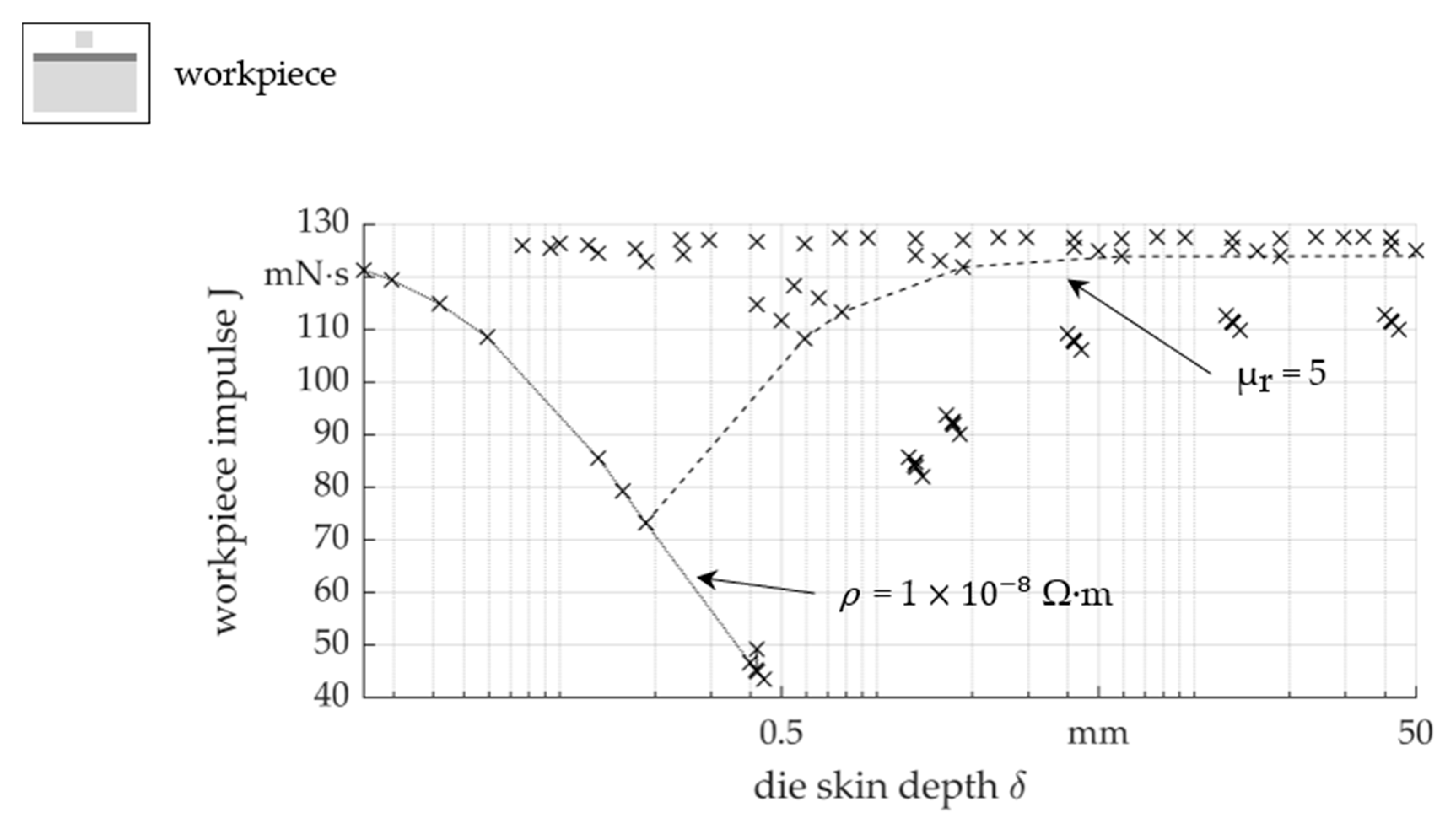
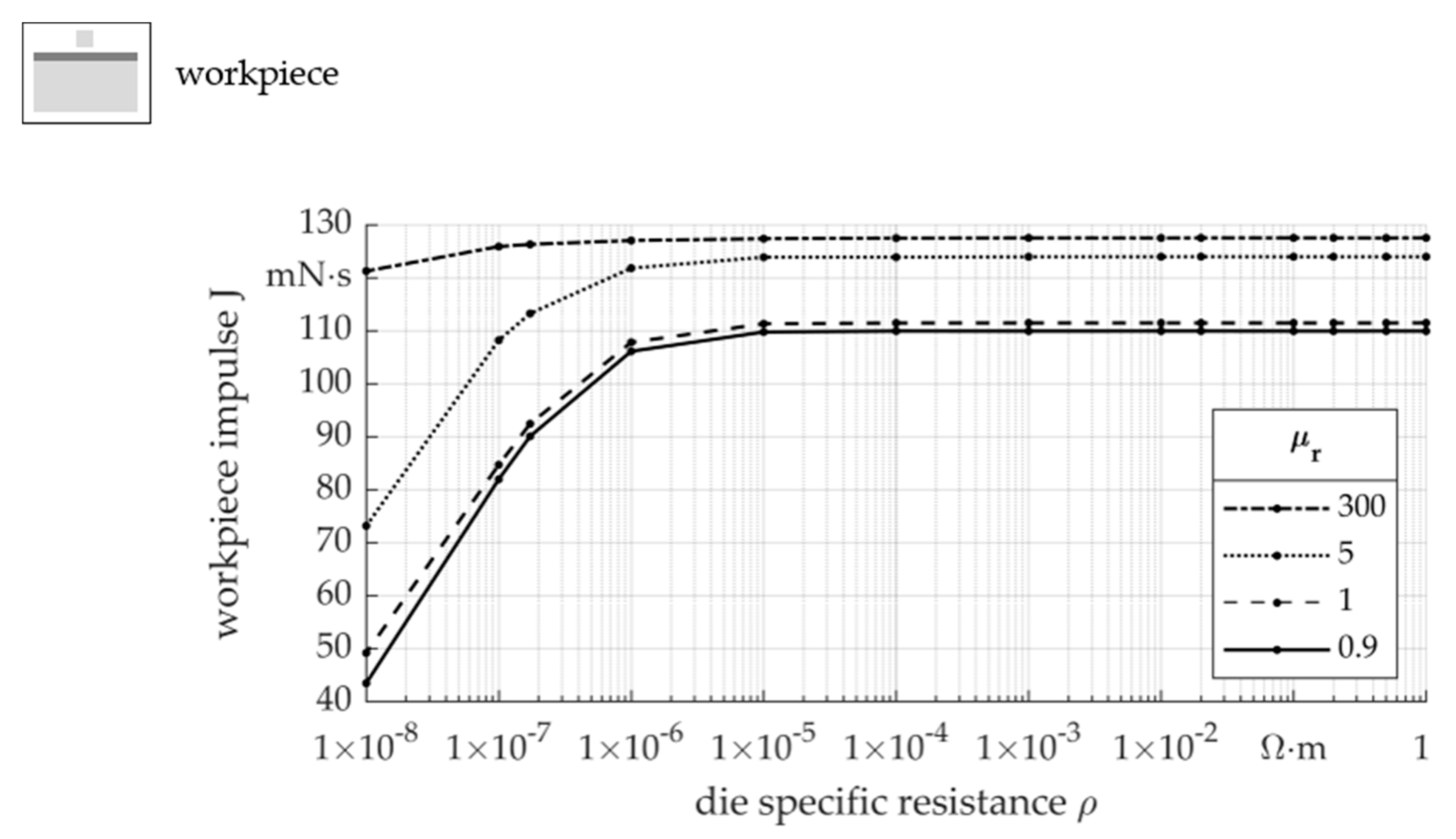
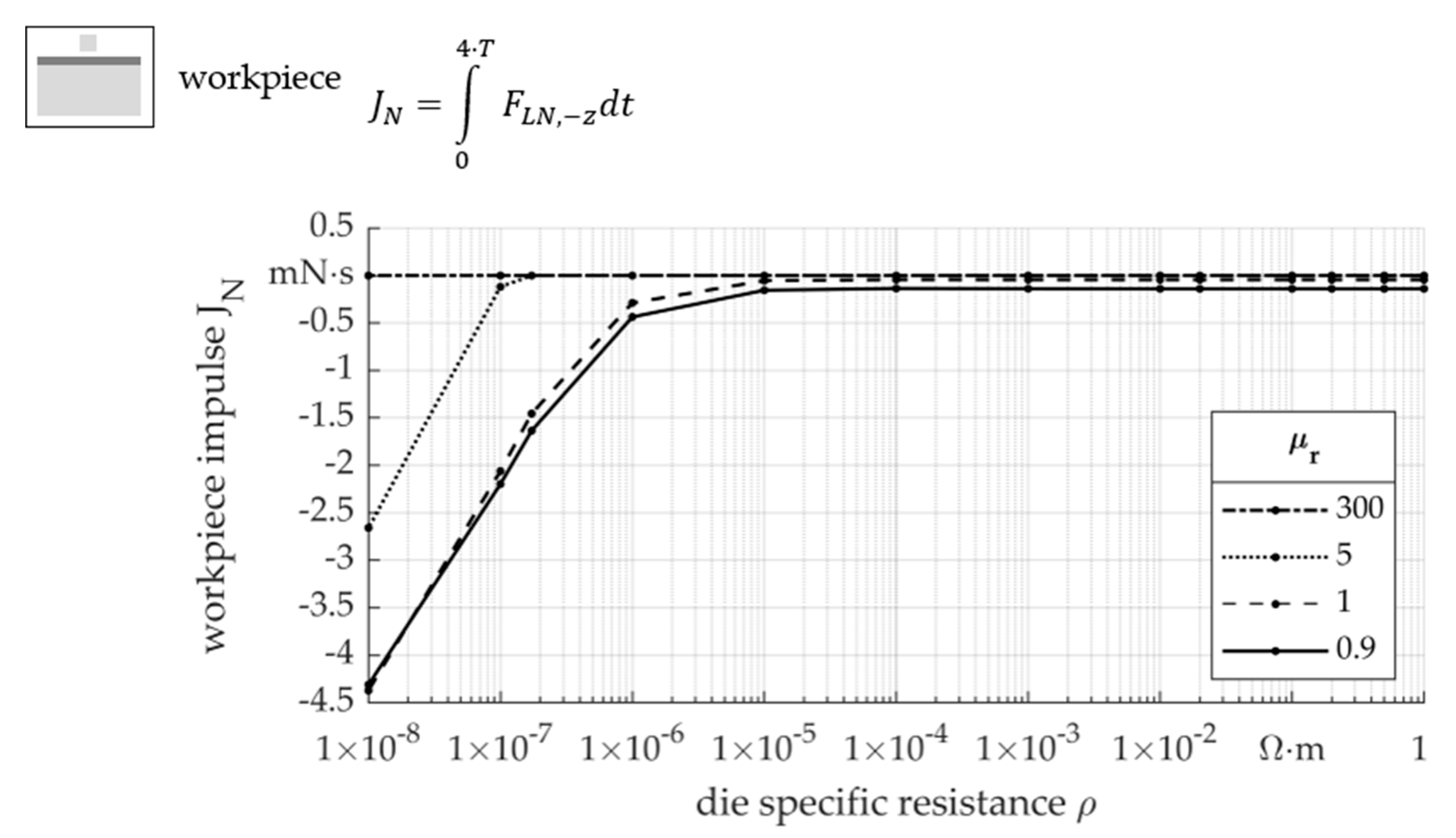
- Below a specific resistance ρ of around 10−5 Ω·m, a decrease in the workpiece impulse during electromagnetic forming can be expected. To increase forming efficiency, the die material should have a higher specific resistance ρ.
- The relative permeability influences the impulse up to a relative permeability μr of 5, whereby the influence decreases with higher relative permeability μr. A high relative permeability μr is positive regarding process efficiency.
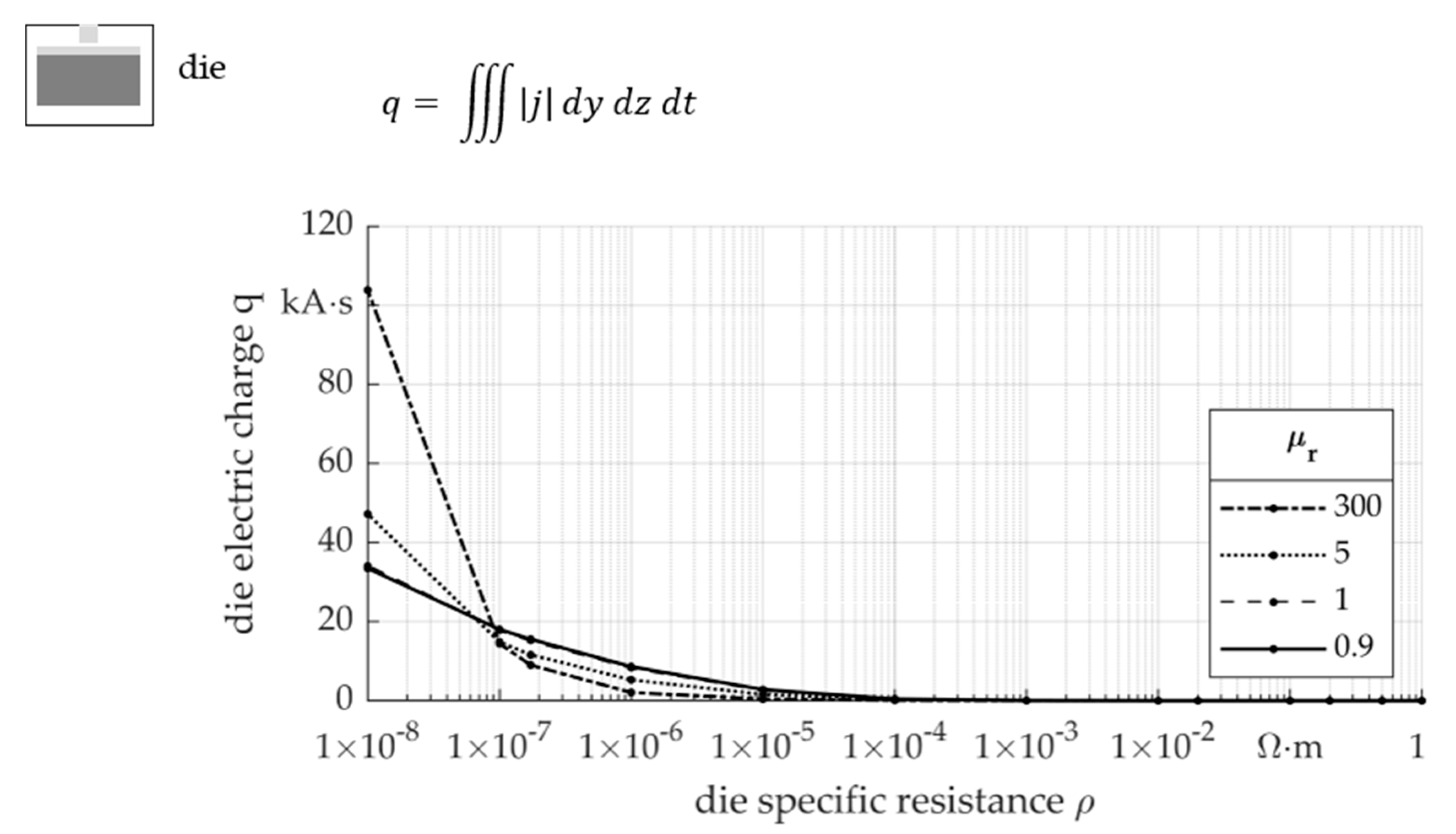
- The influence of the die material on the impulse J is due to the current density j in the workpiece. A high specific resistance ρ and relative permeability μr cause higher current densities j, which increases the impulse J on the workpiece.
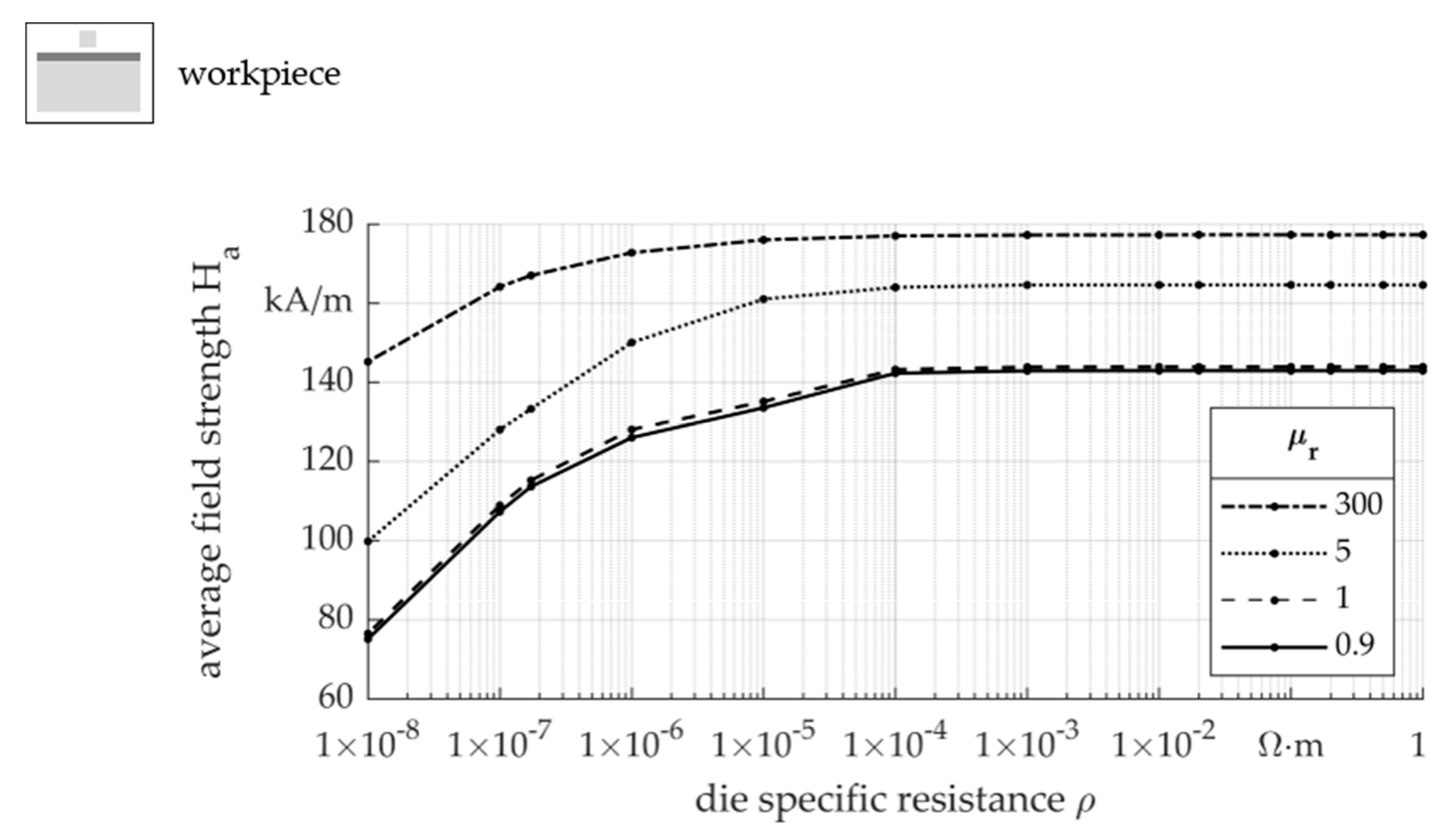
- The properties of the die material influence the field, which can be seen in the change of the distribution and level of the field strength H. A high specific resistance ρ and relative permeability μr lead to a magnetic field concentration.
- The results of the simulation confirmed by forming experiments using free forming of bulge structures.
- The results of the simulation and free forming could be transferred to electromagnetic embossing and it could be shown that an improvement of the impression is possible due to the die material influence.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleiner, M.; Beerwald, C.; Homberg, W. Analysis of Process Parameters and Forming Mechanisms within the Electromagnetic Forming Process. CIRP Ann. 2005, 54, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyk, V.; Kurka, P.; Kimme, S.; Werner, M.; Landgrebe, D.; Ebert, A.; Schwarzendahl, M. Structuring by electromagnetic forming and by forming with an elastomer punch as a tool for component optimisation regarding mechanical stiffness and acoustic performance. Manuf. Rev. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhfuss, B.; Schenck, C.; Wilhelmi, P.; Langstädtler, L. Magnetic pulse cutting of micro metal foils. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference of Micromanufacturing, ICOMM, Victoria, BC, Canada, 25–28 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jimbert, P.; Pérez, I.; Eguia, I.; Daehn, G. Straight Hemming of Aluminum Sheet Panels Using the Electromagnetic Forming Technology: First Approach. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 344, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Shang, J.; Cheng, V.; Hatkevich, S.; Daehn, G.S. Agile manufacturing of a micro-embossed case by a two-step electromagnetic forming process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 190, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taebi, F.; Demir, O.K.; Stiemer, M.; Psyk, V.; Kwiatkowski, L.; Brosius, A.; Blum, H.; Tekkaya, A.E. Dynamic forming limits and numerical optimization of combined quasi-static and impulse metal forming. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 54, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langstädtler, L.; Schönemann, L.; Schenck, C.; Kuhfuss, B. Electromagnetic embossing of optical microstructures. J. Micro Nano Manuf. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Yao, X.; Yan, S.; He, J.; Zhan, M.; Huang, L. Analysis of forming defects in electromagnetic incremental forming of a large-size thin-walled ellipsoid surface part of aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 255, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo, E.; Gutiérrez, M.A.; González, B.; Alcaraz, J.L.; Daehn, G.S. Electromagnetic impulse calibration of high strength sheet metal structures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, G.W.; Brower, D.F. General Dynamics Corp. Metal Forming Device and Method. U.S. Patent 2,976,907, 28 March 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Psyk, V.; Risch, D.; Kinsey, B.L.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Kleiner, M. Electromagnetic forming—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 787–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, C. Effects of current frequency on electromagnetic tube compression. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, D.; Beerwald, C.; Brosius, A.; Kleiner, M. On the Significance of the Die Design for Electromagnetic Sheet Metal Forming. In Proceedings of the International Conference on High Speed Forming, ICHSF, Dortmund, Germany, 31 March–1 April 2004; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaudeau, E.; Kinsey, B.L. Analytical design and experimental validation of uniform pressure actuator for electromagnetic forming and welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 215, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paese, E.; Geier, M.; Homrich, R.P.; Rossi, R. A coupled electric–magnetic numerical procedure for determining the electromagnetic force from the interaction of thin metal sheets and spiral coils in the electromagnetic forming process. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langstädtler, L.; Schenck, C.; Kuhfuss, B. Effective electromagnetic forces in thin sheet metal specimen. MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 21, 11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Li, Z.; Lai, Z.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Li, L. Analysis of the effect of an electrically conductive die on electromagnetic sheet metal forming process using the finite element-circuit coupled method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, V.Y. Effect of directed electron beam on moving dislocations. Sov. Phys. JETP 1967, 24, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Sánchez Egea, A.J.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, B.; Cao, J. Bio-Inspired Functional Surface Fabricated by Electrically Assisted Micro-Embossing of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, J.; Stiemer, M.; Walden, L.; Bach, F.; Blum, H.; Svendsen, B. On the effect of current pulses on the material behavior during electromagnetic metal forming. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on High Speed Forming, Dortmund, Germany, 20–21 March 2006; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, F.; Satapathy, S.; Ravi-Chandar, K. Plastic deformation in electrical conductors subjected to short-duration current pulses. Mech. Mater. 2012, 55, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Egea, A.J.; Peiró, J.J.; Signorelli, J.W.; González Rojas, H.A.; Celentano, D.J. On the microstructure effects when using electropulsing versus furnace treatments while drawing inox 308L. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2269–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sánchez Egea, A.J.; Xu, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Cao, J. Current-Induced Ductility Enhancement of a Magnesium Alloy AZ31 in Uniaxial Micro-Tension Below 373 K. Materials 2018, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANSYS. Material Database; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Langstädtler, L. Elektromagnetisches und Elektrohydraulisches Umformen in der Mikroproduktion. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Material | Specific Resistance ρ [Ω·m] | Relative Permeability μr [-] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| die | austenitic chrome-nickel steel X5CrNi18-10/AISI 304 | 9.0909 × 10−7 | 1.000000 |
| cold work tool steel 90MnCrV8/AISI O2 | 5 × 10−7 | ~300 | |
| copper E-Cu57/C11000/ETP | 1.7241 × 10−8 | 0.999991 | |
| aluminium AlCuMgPb/AA2007 | 2.6316 × 10−8 | 1.000021 | |
| workpiece | aluminium Al99.5/AA1050A | 2.6316 × 10−8 | 1.000021 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beckschwarte, B.; Langstädtler, L.; Schenck, C.; Herrmann, M.; Kuhfuss, B. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Impact of the Electromagnetic Properties of the Die Materials in Electromagnetic Forming of Thin Sheet Metal. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5010018
Beckschwarte B, Langstädtler L, Schenck C, Herrmann M, Kuhfuss B. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Impact of the Electromagnetic Properties of the Die Materials in Electromagnetic Forming of Thin Sheet Metal. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2021; 5(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeckschwarte, Björn, Lasse Langstädtler, Christian Schenck, Marius Herrmann, and Bernd Kuhfuss. 2021. "Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Impact of the Electromagnetic Properties of the Die Materials in Electromagnetic Forming of Thin Sheet Metal" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 5, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5010018
APA StyleBeckschwarte, B., Langstädtler, L., Schenck, C., Herrmann, M., & Kuhfuss, B. (2021). Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Impact of the Electromagnetic Properties of the Die Materials in Electromagnetic Forming of Thin Sheet Metal. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 5(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5010018





