Dimensional Quality and Distortion Analysis of Thin-Walled Alloy Parts of AlSi10Mg Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
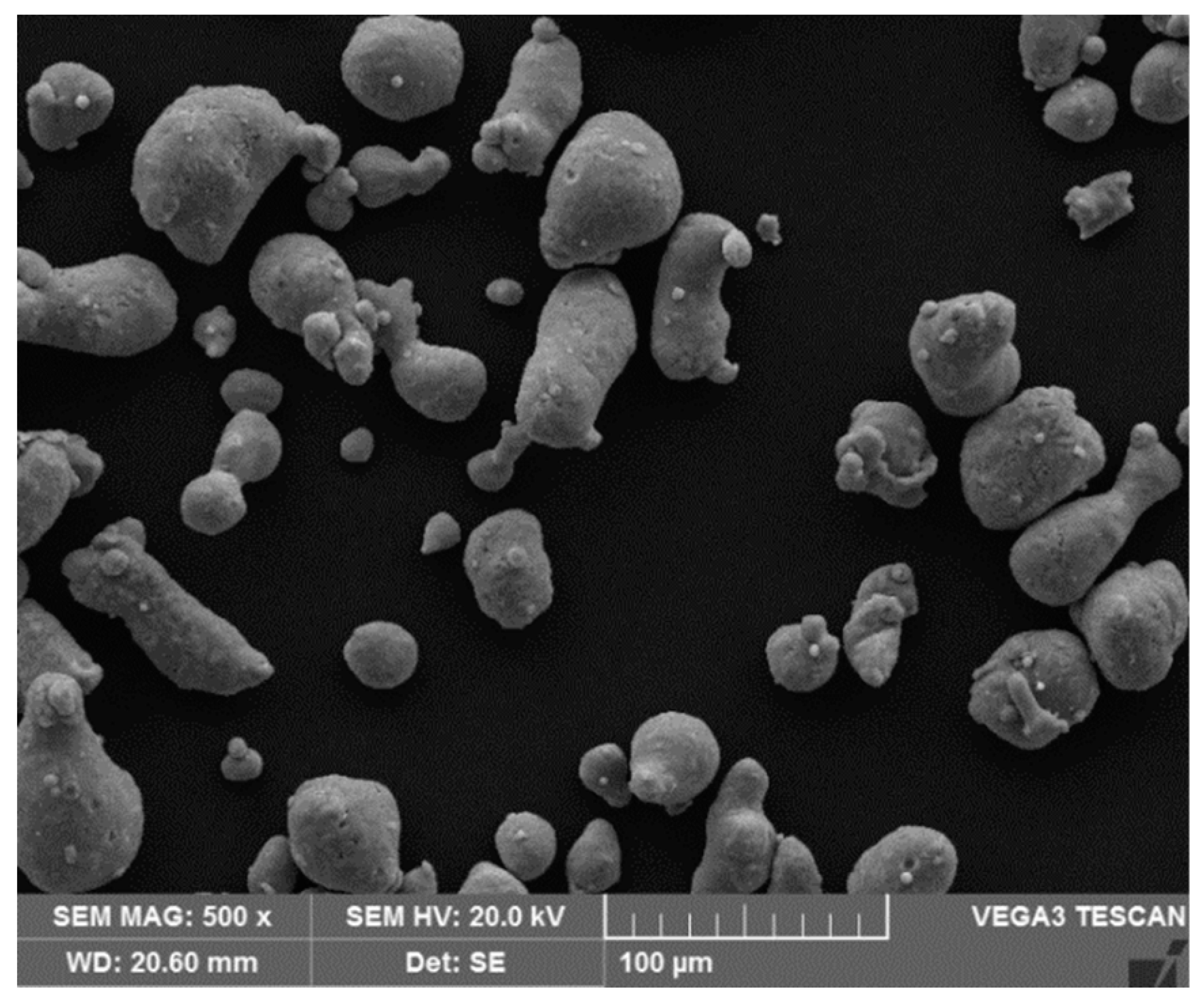
2. Material and Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
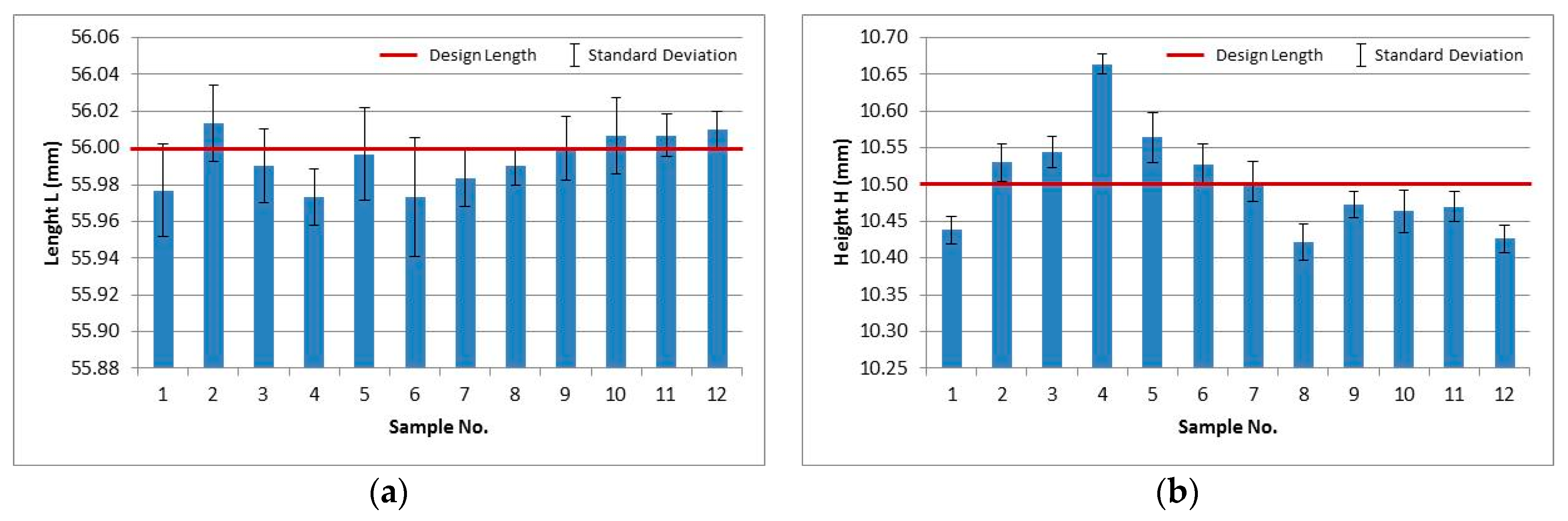
3.1. Dimensional Quality under Repeatability (Process Variability)
3.2. Dimensional Quality under Reproducibility (Process Variability)
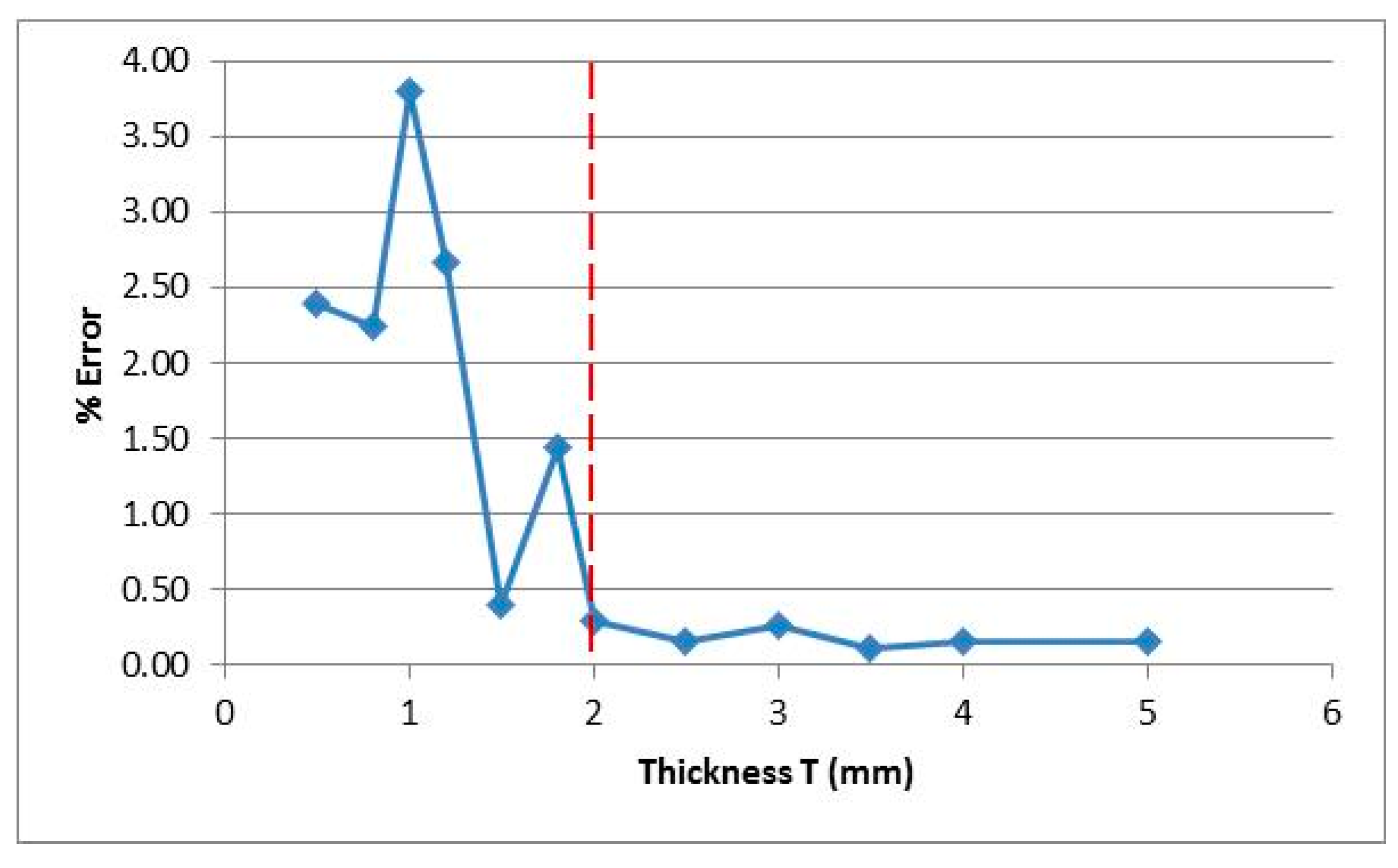
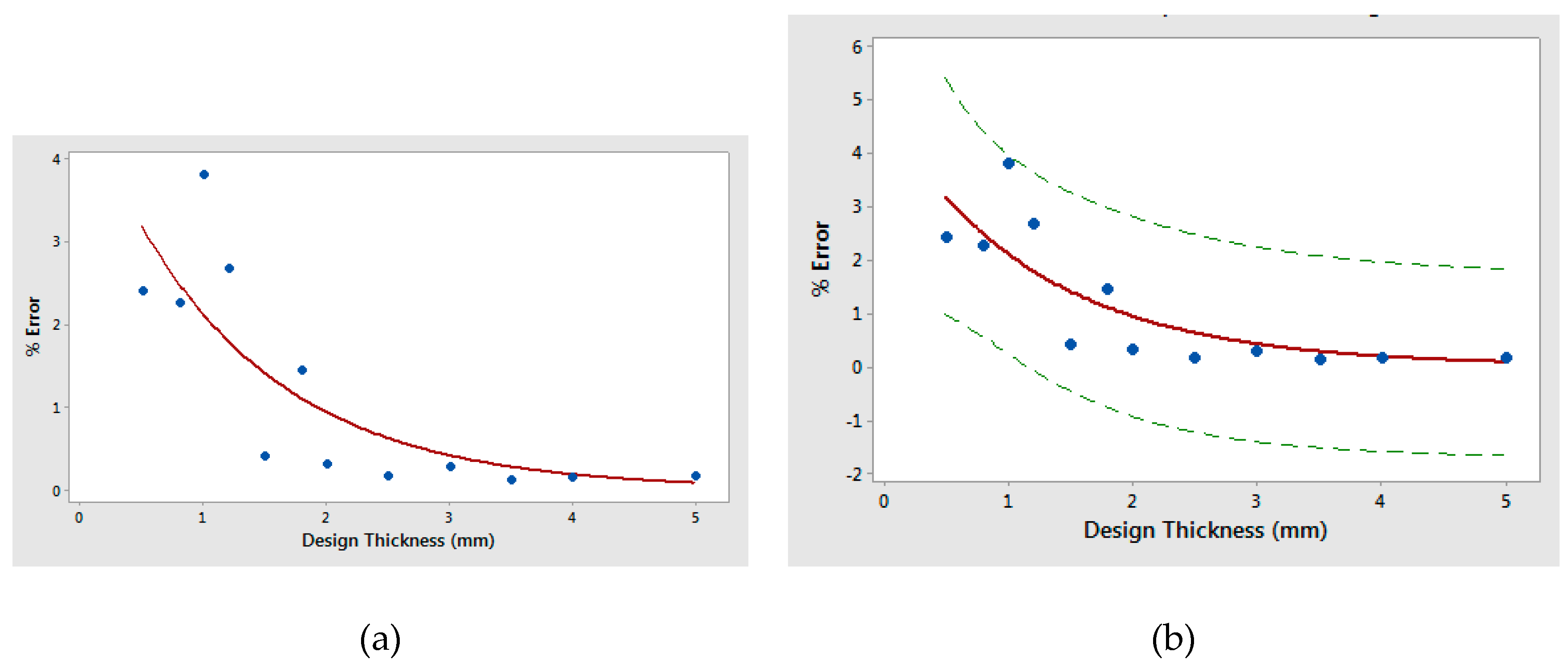
3.3. Dimensional Quality with Variable Dimension
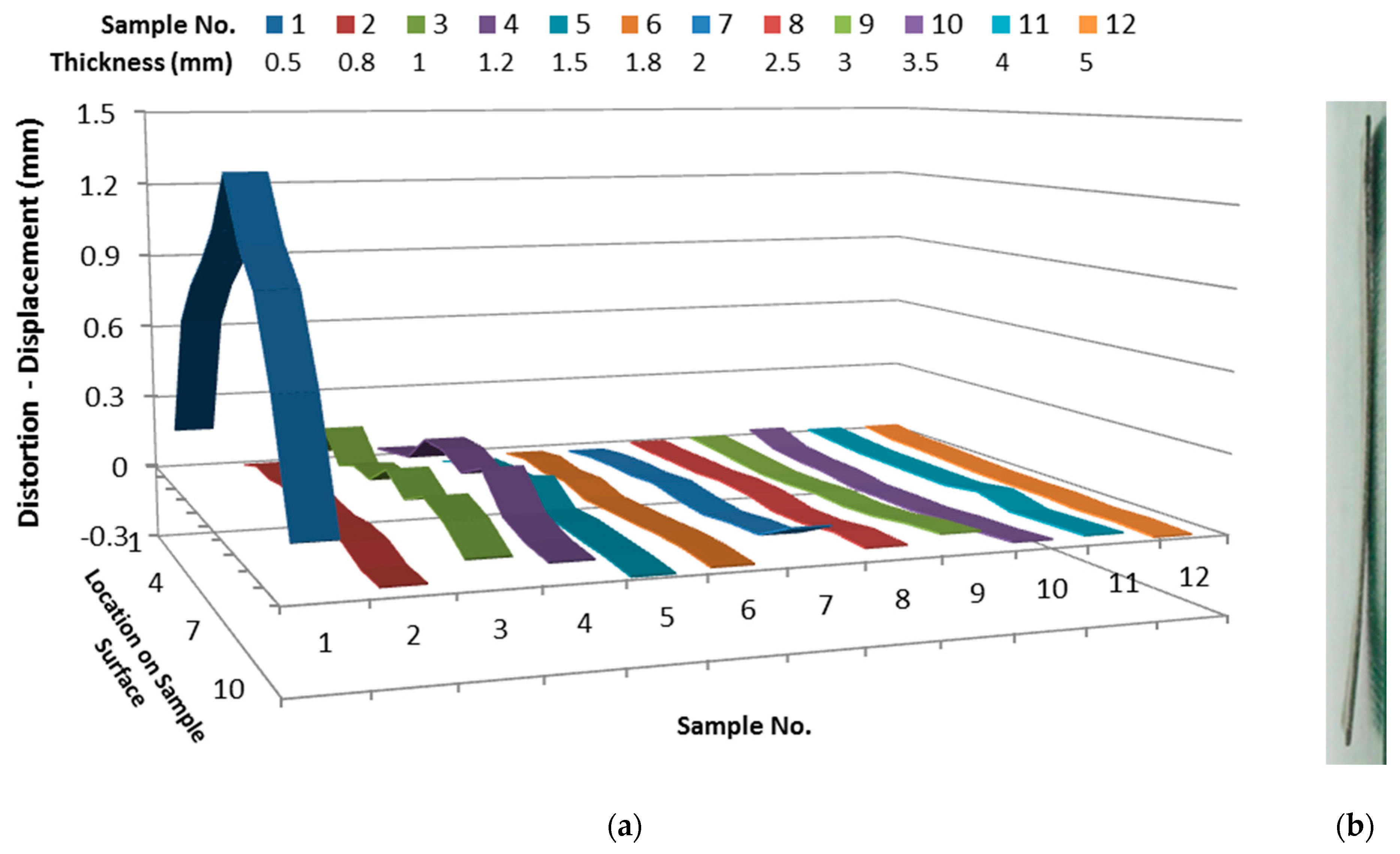
3.4. Distortion Analysis
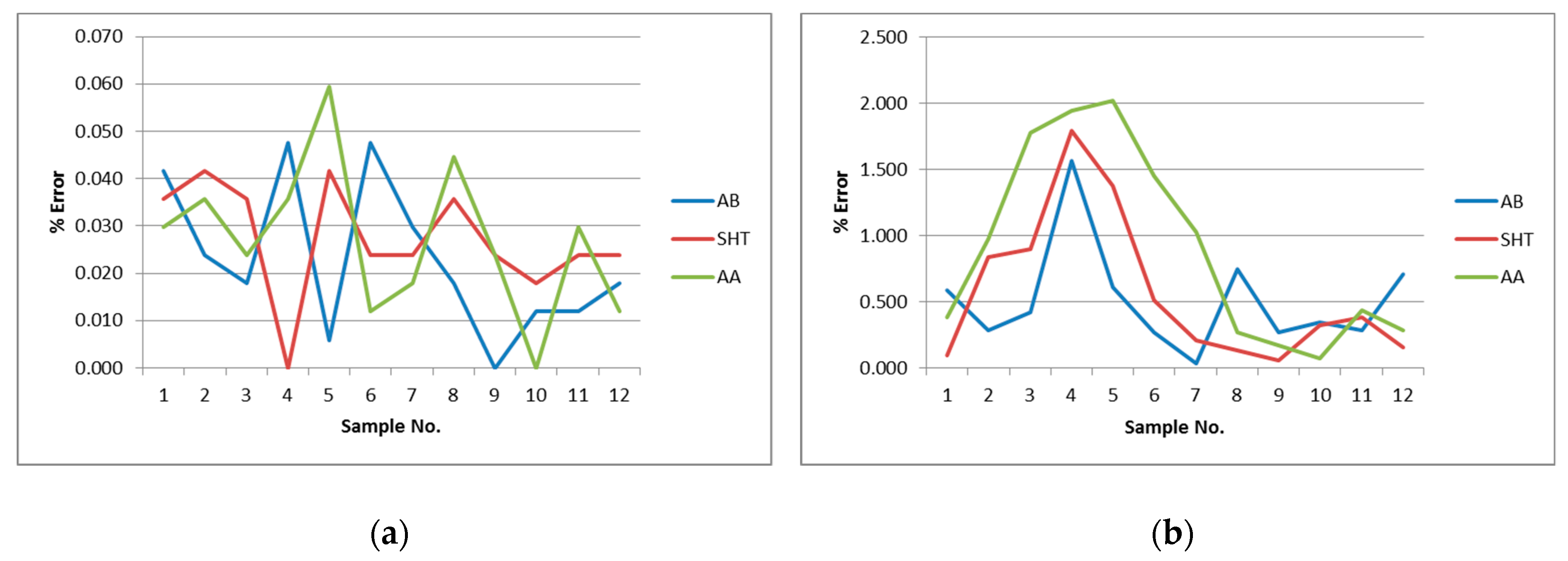
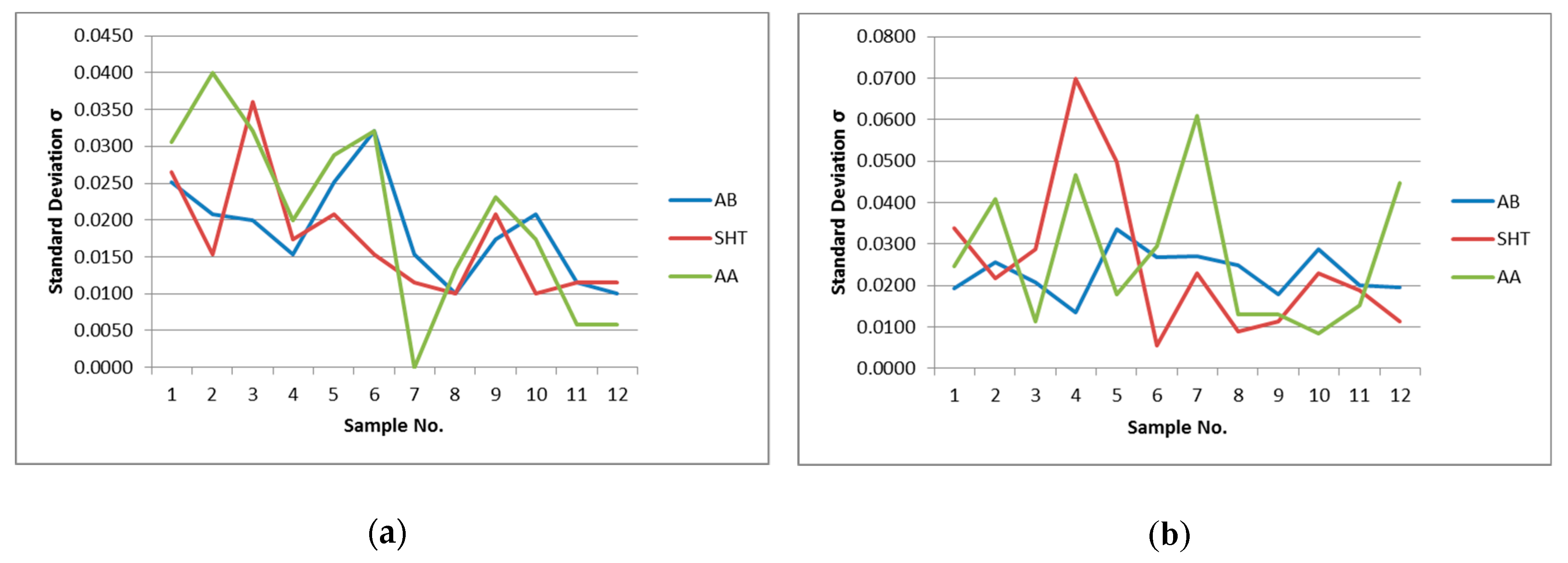
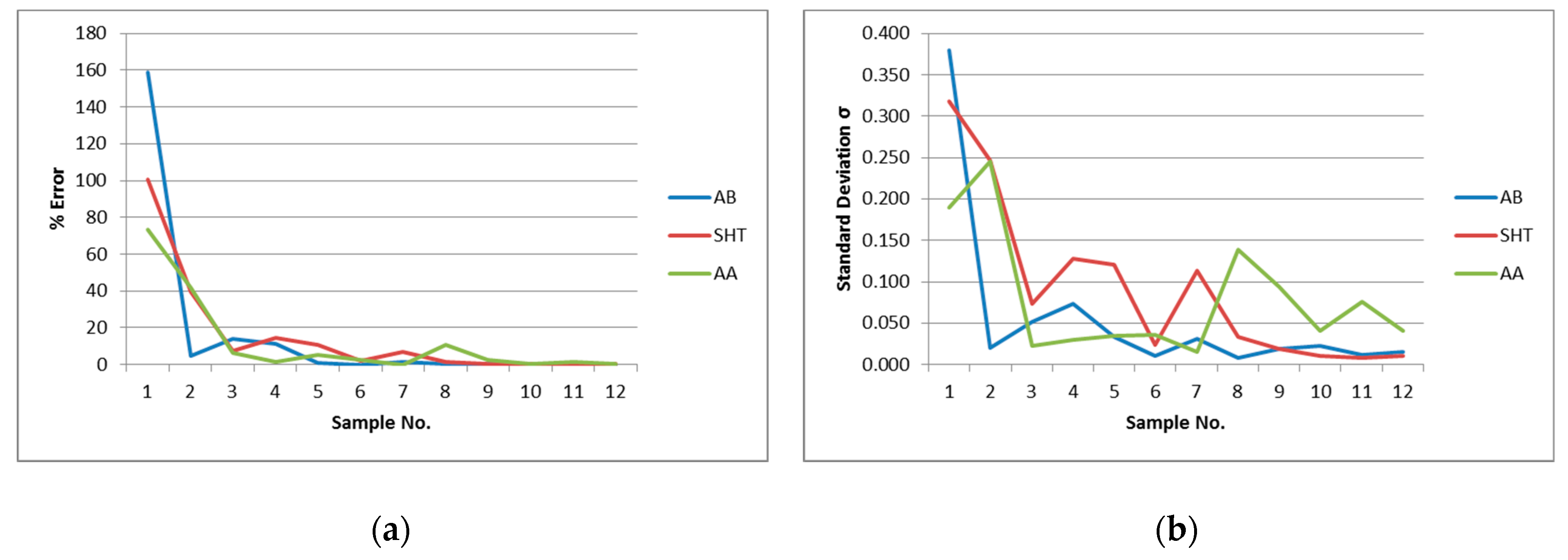
3.5. Effect of Heat Treatments (SHT and AA)
4. Conclusions
- The manufacturing process has shown instability and random variations under repeatability condition, which is due to the inherent variability or random errors in the system.
- The dimensional quality results revealed that in sample length (horizontal dimension), 0.05 mm maximum dimensional error, 0.0197 mm repeatability (σr), and 0.0169 mm reproducibility (σR) observed. Similarly, in sample height (vertical dimension), 0.258 mm maximum error, 0.0237 mm repeatability (σr), and 0.0863 mm reproducibility (σR) observed.
- The ANOVA results revealed that length means (horizontal dimension) is not statistically significantly different under repeatability and reproducibility conditions. Whereas, the height means (vertical dimension) are statistically significantly different under repeatability and reproducibility conditions.
- The results show the variation of dimensional quality in horizontal and vertical directions. The dimensions created in xy-plane (horizontal direction) observed more accurate and precise as compared to the z-axis dimension (vertical direction).
- The dimensional error decreased with increasing sample thickness. The error reduces to less than 0.3% for thickness greater than 2 mm. The correlation analysis has revealed a negative correlation (r = −0.73) between % error and sample thickness. The regression model revealed an exponential decrease of %error with increasing thickness, Rsq = 0.6348 (63.48%), and p-value 0.0006 (<0.05), which shows the significance of the relationship.
- The sample distortion decreased with increasing sample thickness. The 0.5 mm thickness sample has shown very high distortion, whereas, the distortion reduced significantly for the 0.8–1.5 mm thickness samples.
- The solution heat treatment and artificial aging did not give any advantage in improving dimensional quality or reducing distortion in comparison with as-built condition results. It is not proven suitable for improvement purpose, but these HT conditions may improve other mechanical properties of parts like tensile strength, elongation, etc.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colosimo, B.M.; Huang, Q.; Dasgupta, T.; Tsung, F. Opportunities and challenges of quality engineering for additive manufacturing. J. Qual. Technol. 2018, 50, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.C.; Sheikh, A.A. 3D printing in aerospace and its long-term sustainability. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2015, 10, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.; Ho, J.Y.; Leong, K.C.; Wong, T.N. Wong Fabrication of heat sinks by Selective Laser Melting for convective heat transfer applications. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2016, 11, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vončina, M.; Kores, S.; Mrvar, P.; Medved, J. Effect of Ce on solidification and mechanical properties of A360 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 7349–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Wang, X.J.; Saunders, M.; Suvorova, A.; Zhang, L.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Fang, M.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Sercombe, T.B. A selective laser melting and solution heat treatment refined Al–12Si alloy with a controllable ultrafine eutectic microstructure and 25% tensile ductility. Acta Mater. 2015, 95, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Yahata, B.D.; Hundley, J.M.; Mayer, J.A.; Schaedler, T.A.; Pollock, T.M. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys. Nature 2017, 549, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shamim, K.; Qureshi, M.E.; Muzamil, M.; Zafar, F.; Waqas, A. An investigation into the influence of processing parameters on the surface quality of AlSi10Mg parts by SLM process. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST-2019), Islamabad, Pakistan, 8–12 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kempen, K.; Thijs, L.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Kruth, J.P. Processing AlSi10Mg by selective laser melting: Parameter optimisation and material characterisation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.G.; Ahn, T.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.M. Synergistic effect of ultrasonic melt treatment and fast cooling on the refinement of primary Si in a hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 148, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, C.H.; Davidson, C.J.; Griffiths, J.R. The deformation and fracture behaviour of an Al-Si-Mg casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 197, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.D.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: Materials, processes and mechanisms. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, D.; Seyda, V.; Wycisk, E.; Emmelmann, C. Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakanmi, E.O.; Cochrane, R.F.; Dalgarno, K.W. A review on selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM) of aluminium alloy powders: Processing, microstructure, and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 74, 401–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.B.; Pham, Q.C. Selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg: Effects of scan direction, part placement and inert gas flow velocity on tensile. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, F.; Calignano, F.; Lorusso, M.; Pakkanen, J.; Aversa, A.; Ambrosio, E.; Lombardi, M.; Fino, P.; Manfredi, D. On the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of the AlSi10Mg Alloy: Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2017, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M.; Atzeni, E.; Canali, R.; Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Iuliano, L. On the effect of process parameters on properties of AlSi10Mg parts produced by DMLS. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, N.; Wang, W.; Essa, K.; Attallah, M.M. Selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg alloy: Process optimisation and mechanical properties development. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, G.; Hao, L.; Everson, R.M.; Evans, K.E. Surface roughness analysis, modelling and prediction in selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Bai, Y.; Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Song, C. Characteristics of typical geometrical features shaped by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 022007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Singamneni, S. Selective Laser Melting of Duplex Stainless Steel Powders: An Investigation. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calignano, F.; Lorusso, M.; Pakkanen, J.; Trevisan, F.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Manfredi, D.; Fino, P. Investigation of accuracy and dimensional limits of part produced in aluminum alloy by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calignano, F. Investigation of the accuracy and roughness in the laser powder bed fusion process. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Sing, S.L.; Dikshit, V.; Yeong, W.Y.; Wei, J. Material jetting additive manufacturing: An experimental study using designed metrological benchmarks. Precis. Eng. 2017, 50, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, N.; Pandey, P.M. Improving accuracy through shrinkage modelling by using Taguchi method in selective laser sintering. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Wang, G.; Zeng, X. Investigation on Selective Laser Melting AlSi10Mg Cellular Lattice Strut: Molten Pool Morphology, Surface Roughness and Dimensional Accuracy. Materials 2018, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, A.; Lv, J.; Peng, T. A framework for big data driven process analysis and optimization for additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2019, 25, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.H.; Lu, L.; Fuh, J.Y.H. Study on shrinkage behaviour of direct laser sintering metallic powder. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2006, 220, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Sing, S.L.; Chua, C.K.; Tian, X. Influence of re-melting on surface roughness and porosity of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.-P.; Badrossamay, M.; Yasa, E.; Deckers, J.; Thijs, L.; Van Humbeeck, J. Part and Material Properties in Selective Laser Melting of Metals. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Electromachining (ISEM–XVI), Shanghai, China, 19–23 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi, M.; Osakada, K.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Abe, F. Residual Stress within Metallic Model Made by Selective Laser Melting Process. CIRP Ann. 2004, 53, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, E.; Deckers, J.; Craeghs, T.; Badrossamay, M.; Kruth, J.P. Investigation on occurrence of elevated edges in selective laser melting. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, SFF 2009, Austin, TX, USA, 3–5 August 2009; pp. 673–685. [Google Scholar]
- Beal, V.E.; Erasenthiran, P.; Hopkinson, N.; Dickens, P.; Ahrens, C.H. Scanning strategies and spacing effect on laser fusion of H13 tool steel powder using high power Nd: YAG pulsed laser. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 46, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, C.H.; Guo, Y.B.; Fang, F.Z. Fast Prediction and Validation of Part Distortion in Selective Laser Melting. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 1, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Afazov, S.; Denmark, W.A.; Toralles, B.L.; Holloway, A.; Yaghi, A. Distortion Prediction and Compensation in Selective Laser Melting. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Ploshikhin, V. New method for fast predictions of residual stress and distortion of AM parts. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 4–6 August 2014; Volume 25, pp. 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, A.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, J.; Peng, T.; Waqar, S.; Atta, Z. Study the effect of heat treatment on the relative density of SLM built parts of AlSi10Mg alloy. In Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering (CIE 2018), Auckland, New Zealand, 2–5 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Tuck, C.; Ashcroft, I.; Maskery, I.; Everitt, N.M. On the Precipitation Hardening of Selective Laser Melted AlSi10Mg. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3337–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Q.; Yan, C.; Shi, Y. Effect of heat treatment on AlSi10Mg alloy fabricated by selective laser melting: Microstructure evolution, mechanical properties and fracture mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 663, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


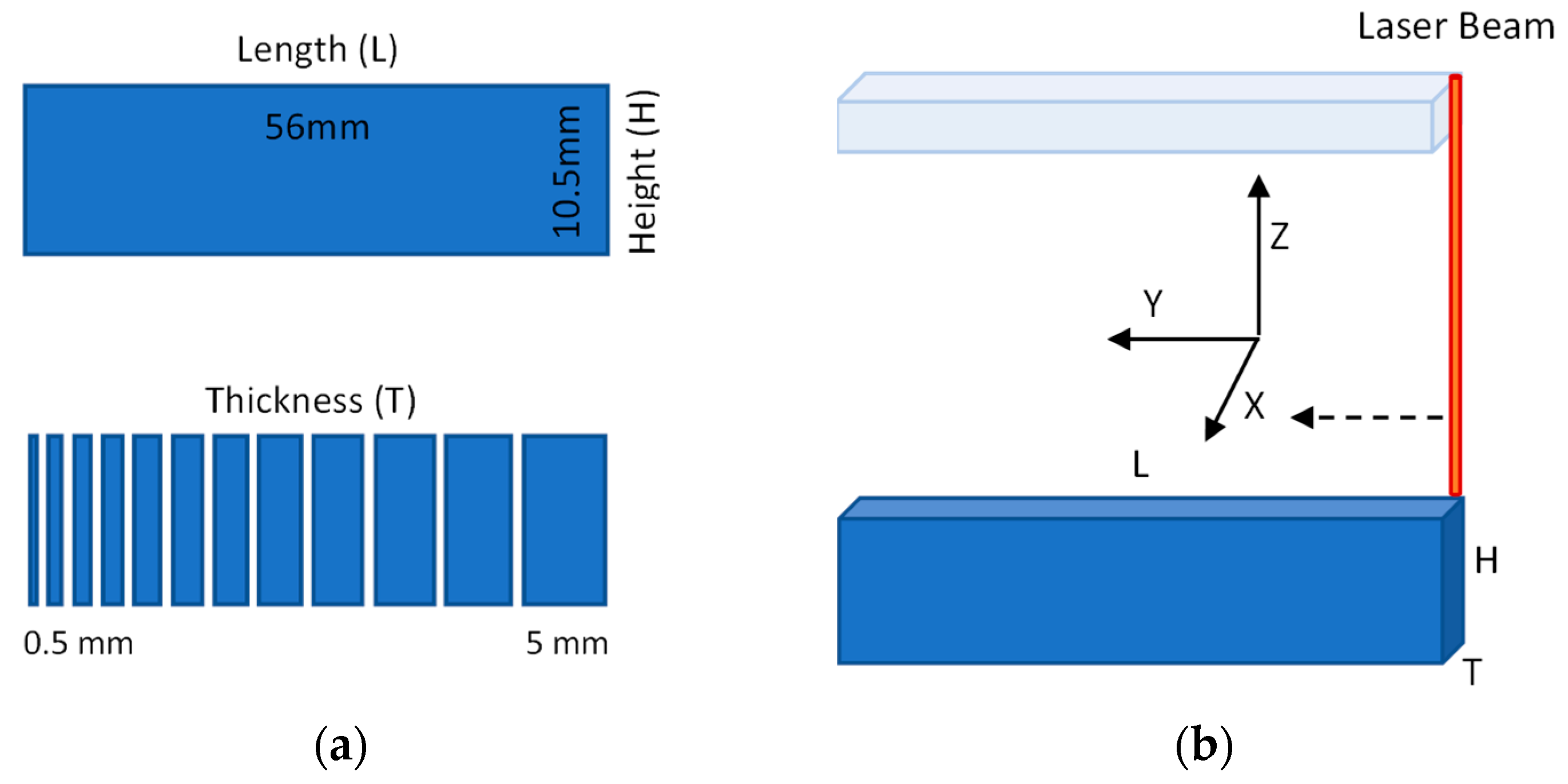
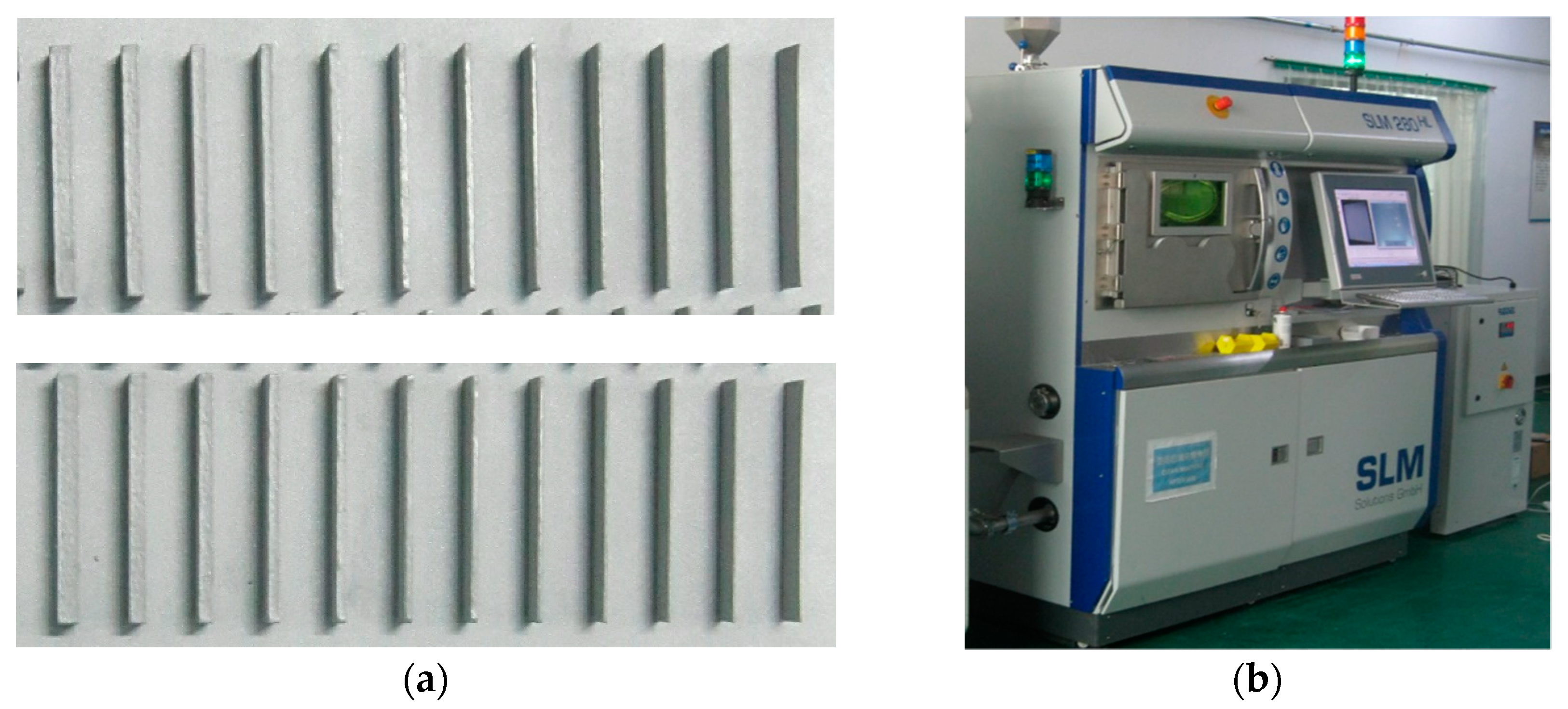
| Sample Length (L) | Sample Height (H) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No | Design Length (mm) | Actual Mean Length (mm) | % Error | Sample No | Design Height (mm) | Actual Mean Height (mm) | % Error |
| 1 | 56 | 55.977 | 0.042 | 1 | 10.5 | 10.438 | 0.590 |
| 2 | 56 | 56.013 | 0.024 | 2 | 10.5 | 10.530 | 0.286 |
| 3 | 56 | 55.990 | 0.018 | 3 | 10.5 | 10.544 | 0.419 |
| 4 | 56 | 55.973 | 0.048 | 4 | 10.5 | 10.664 | 1.562 |
| 5 | 56 | 55.997 | 0.006 | 5 | 10.5 | 10.564 | 0.610 |
| 6 | 56 | 55.973 | 0.048 | 6 | 10.5 | 10.528 | 0.267 |
| 7 | 56 | 55.983 | 0.030 | 7 | 10.5 | 10.504 | 0.038 |
| 8 | 56 | 55.990 | 0.018 | 8 | 10.5 | 10.422 | 0.743 |
| 9 | 56 | 56.000 | 0.000 | 9 | 10.5 | 10.472 | 0.267 |
| 10 | 56 | 56.007 | 0.012 | 10 | 10.5 | 10.464 | 0.343 |
| 11 | 56 | 56.007 | 0.012 | 11 | 10.5 | 10.470 | 0.286 |
| 12 | 56 | 56.010 | 0.018 | 12 | 10.5 | 10.426 | 0.705 |
| Overall Mean Length (mm) | 55.993 | Overall Mean Height (mm) | 10.502 | ||||
| Max. Error (mm) | 0.027 | Max Error (mm) | 0.164 | ||||
| Repeatability σr (mm) | 0.0197 | Repeatability σr (mm) | 0.0237 | ||||
| p-value | 0.160 | p-value | 0.000 | ||||
| F-value | 1.61 | F-value | 42.73 | ||||
| Parameter | Length (L) | Height (H) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set 1 | Set 4 | Set 1 | Set 4 | |
| Design Value (mm) | 56 | 56 | 10.5 | 10.5 |
| Mean Value (mm) | 55.993 | 56.006 | 10.502 | 10.591 |
| Max. Error in any sample (mm) | 0.027 (0.048%) | 0.050 (0.089%) | 0.164 (1.564%) | 0.258 (2.457%) |
| Reproducibility σR (mm) | 0.0169 | 0.0863 | ||
| p-value | 0.086 (>0.05) | 0.019 (<0.05) | ||
| F-value | 3.23 | 6.39 | ||
| Sample No | Design Thickness (mm) | Actual Thickness T (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Thickness (mm) | % Error | Max Error (mm) | Standard Deviation σ | ||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.488 | 2.40 | 0.038 | 0.0130 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.782 | 2.25 | 0.0045 | |
| 3 | 1 | 0.962 | 3.80 | 0.0179 | |
| 4 | 1.2 | 1.168 | 2.67 | 0.0084 | |
| 5 | 1.5 | 1.494 | 0.40 | 0.0089 | |
| 6 | 1.8 | 1.774 | 1.44 | 0.0055 | |
| 7 | 2 | 1.994 | 0.30 | 0.0089 | |
| 8 | 2.5 | 2.496 | 0.16 | 0.0089 | |
| 9 | 3 | 3.008 | 0.27 | 0.0084 | |
| 10 | 3.5 | 3.504 | 0.11 | 0.0055 | |
| 11 | 4 | 4.006 | 0.15 | 0.0055 | |
| 12 | 5 | 5.008 | 0.16 | 0.0045 | |
| Sample No | Design Thickness (mm) | Distortion (Displacement Measurement) mm | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Mean | Std. Dev. | % Distorted | ||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.174 | 0.663 | 0.833 | 0.949 | 1.09 | 1.312 | 1.074 | 0.935 | 0.618 | 0.172 | 0.782 | 0.380 | 158.62 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.011 | 0.05 | 0.044 | 0.062 | 0.044 | 0.035 | 0.051 | 0.047 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.0362 | 0.020 | 4.54 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.055 | 0.191 | 0.082 | 0.125 | 0.116 | 0.199 | 0.135 | 0.192 | 0.154 | 0.079 | 0.1328 | 0.051 | 13.89 |
| 4 | 1.2 | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.101 | 0.213 | 0.215 | 0.17 | 0.232 | 0.103 | 0.063 | 0.048 | 0.127 | 0.073 | 11.20 |
| 5 | 1.5 | -0.023 | 0.022 | 0.034 | 0.04 | 0.087 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.001 | -0.006 | -0.021 | 0.0149 | 0.033 | 1.04 |
| 6 | 1.8 | -0.003 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.014 | -0.015 | -0.009 | -0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | -0.009 | 0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.01 |
| 7 | 2 | -0.008 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 0.033 | 0.015 | 0.006 | 0.025 | 0.033 | 0.108 | 0.0262 | 0.031 | 1.36 |
| 8 | 2.5 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.025 | 0.02 | -0.001 | 0.004 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.0146 | 0.008 | 0.60 |
| 9 | 3 | 0.022 | 0.013 | 0.002 | -0.008 | -0.004 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.037 | 0.05 | 0.0134 | 0.018 | 0.45 |
| 10 | 3.5 | 0.043 | -0.001 | -0.013 | -0.016 | -0.034 | -0.031 | -0.031 | -0.018 | -0.012 | 0.001 | -0.0112 | 0.023 | 0.33 |
| 11 | 4 | 0.029 | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.025 | -0.007 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.23 |
| 12 | 5 | 0.029 | 0.011 | 0.007 | -0.001 | -0.008 | -0.01 | -0.009 | -0.017 | -0.012 | -0.019 | -0.0029 | 0.015 | 0.06 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.; Majeed, A.; Atta, Z.; Jia, G. Dimensional Quality and Distortion Analysis of Thin-Walled Alloy Parts of AlSi10Mg Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3020051
Ahmed A, Majeed A, Atta Z, Jia G. Dimensional Quality and Distortion Analysis of Thin-Walled Alloy Parts of AlSi10Mg Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2019; 3(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Altaf, Arfan Majeed, Zahid Atta, and Guozhu Jia. 2019. "Dimensional Quality and Distortion Analysis of Thin-Walled Alloy Parts of AlSi10Mg Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 3, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3020051
APA StyleAhmed, A., Majeed, A., Atta, Z., & Jia, G. (2019). Dimensional Quality and Distortion Analysis of Thin-Walled Alloy Parts of AlSi10Mg Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 3(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3020051






