Application of BiVO4 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of Bismuth Vanadate
2.2. Preparation of the BiVO4–Graphene Nanocomposite
3. Results and Discussion
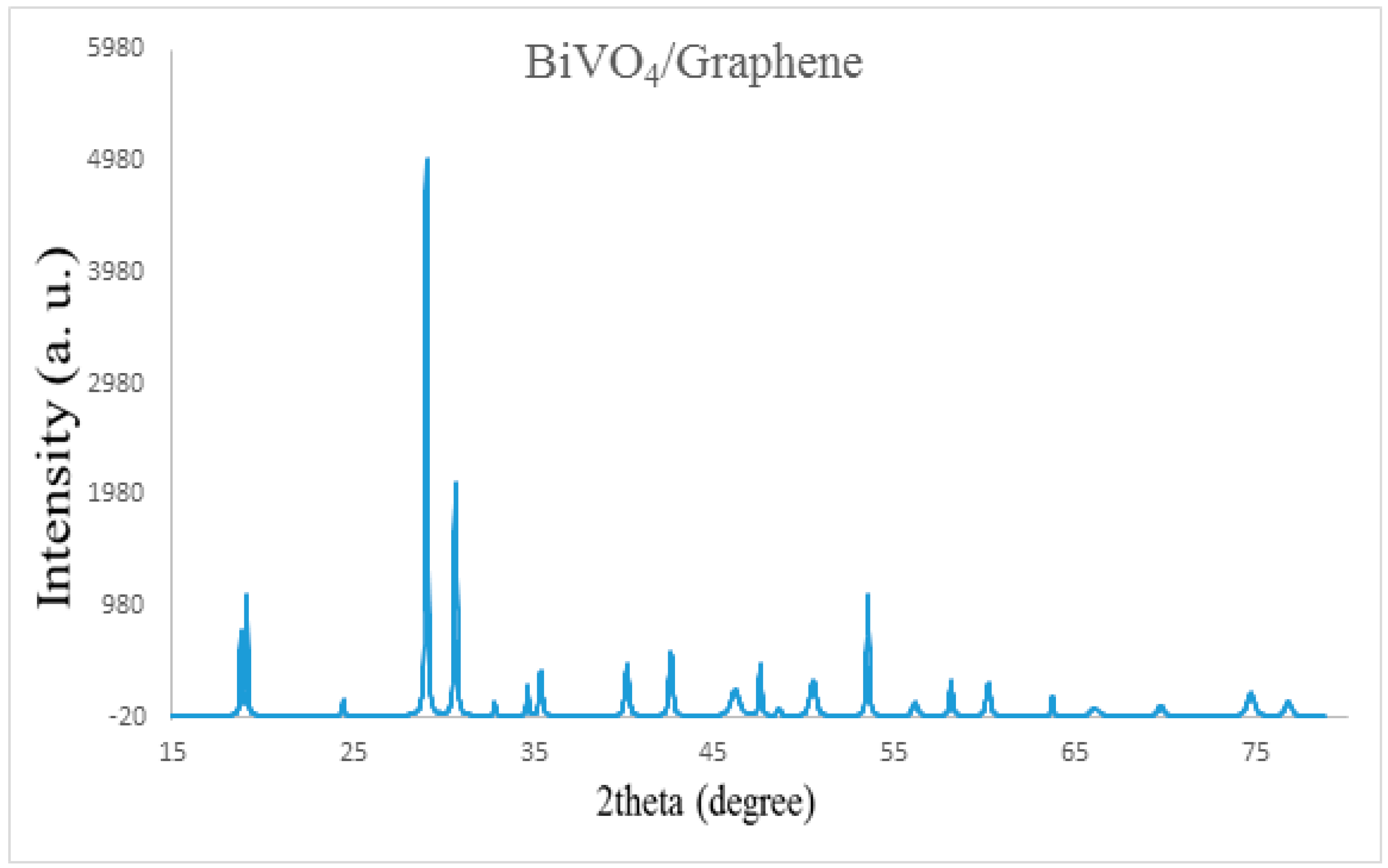
3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction
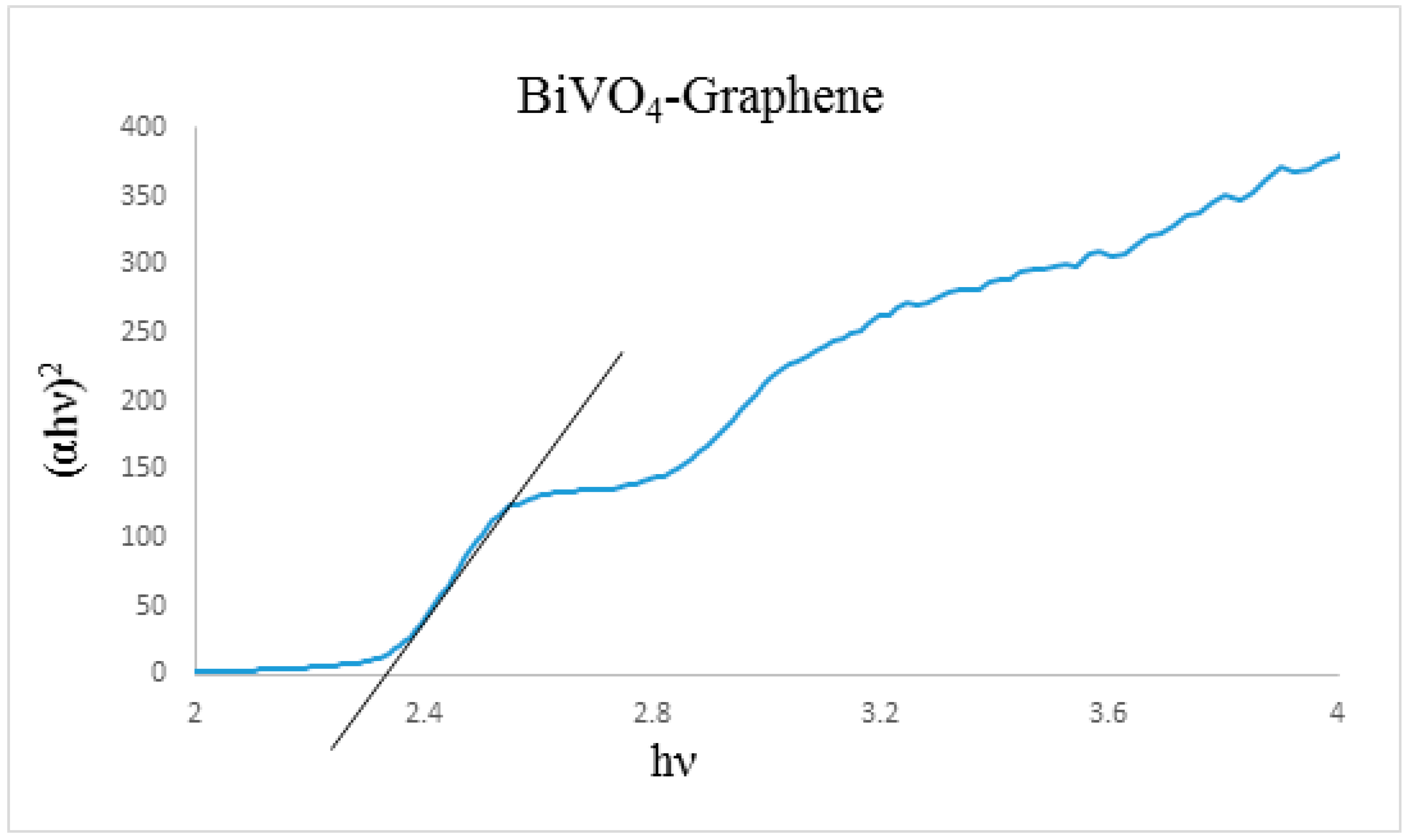
3.2. DRS Analysis of the Prepared Sample
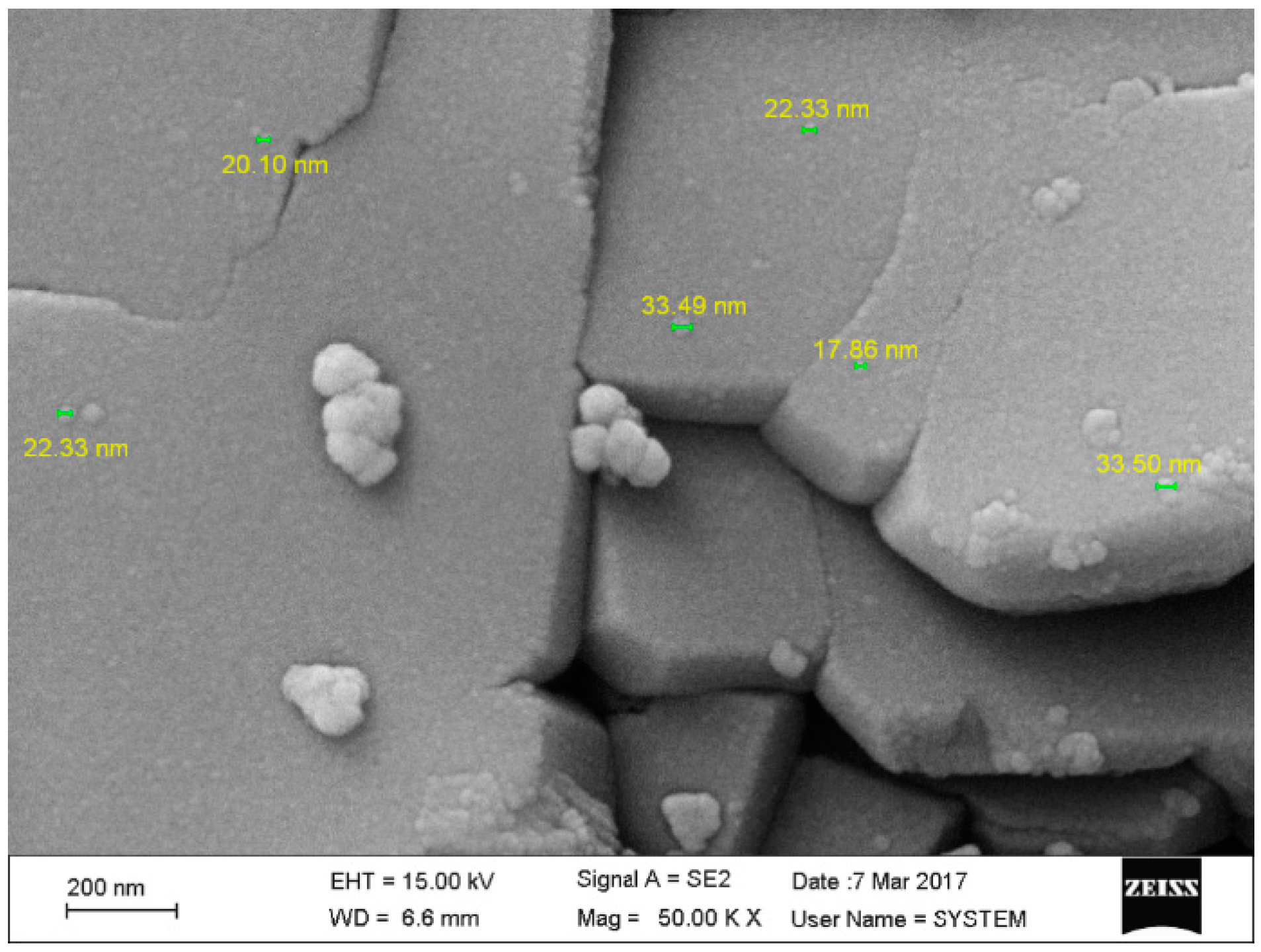
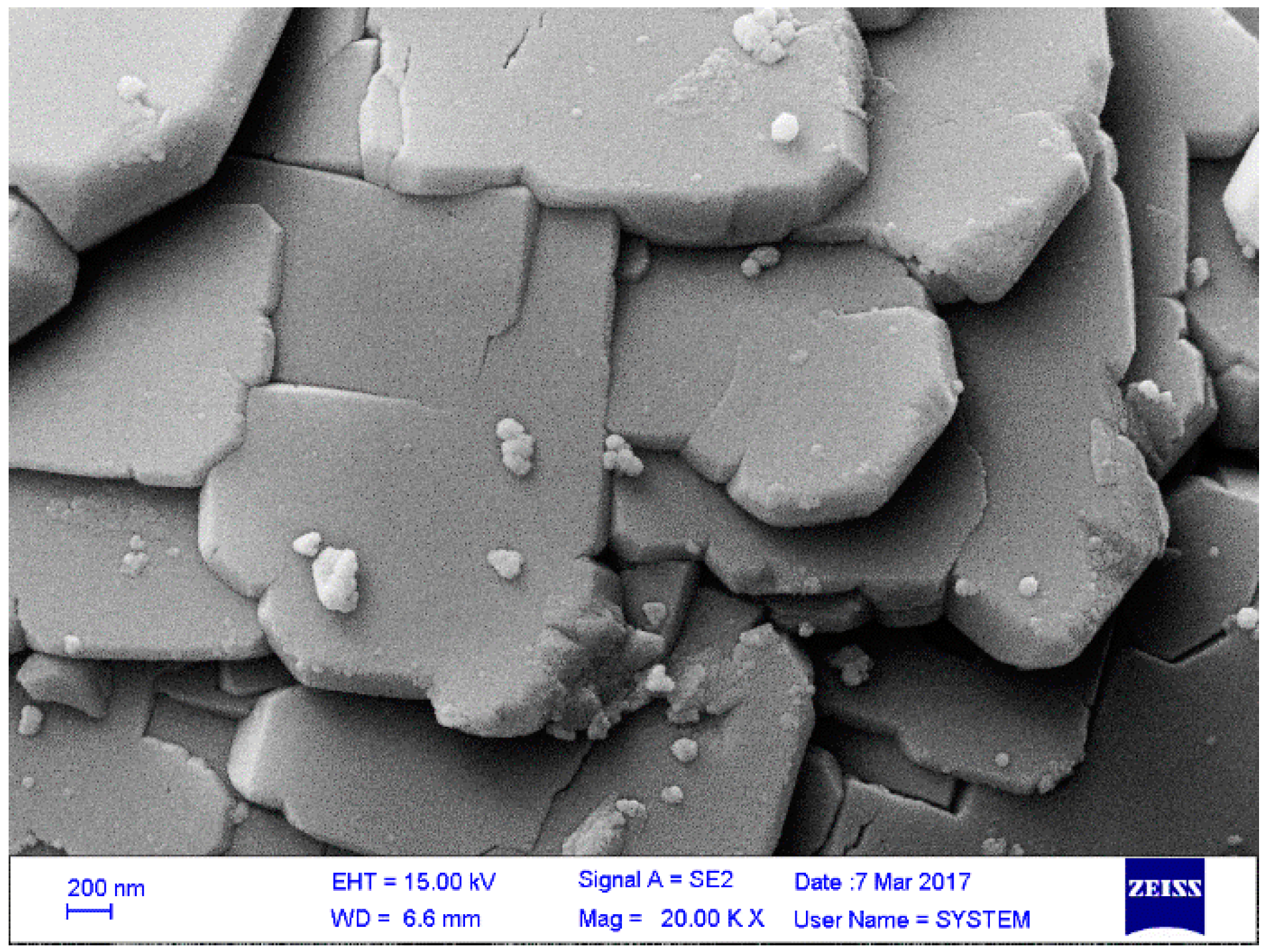
3.3. Morphological Characterization
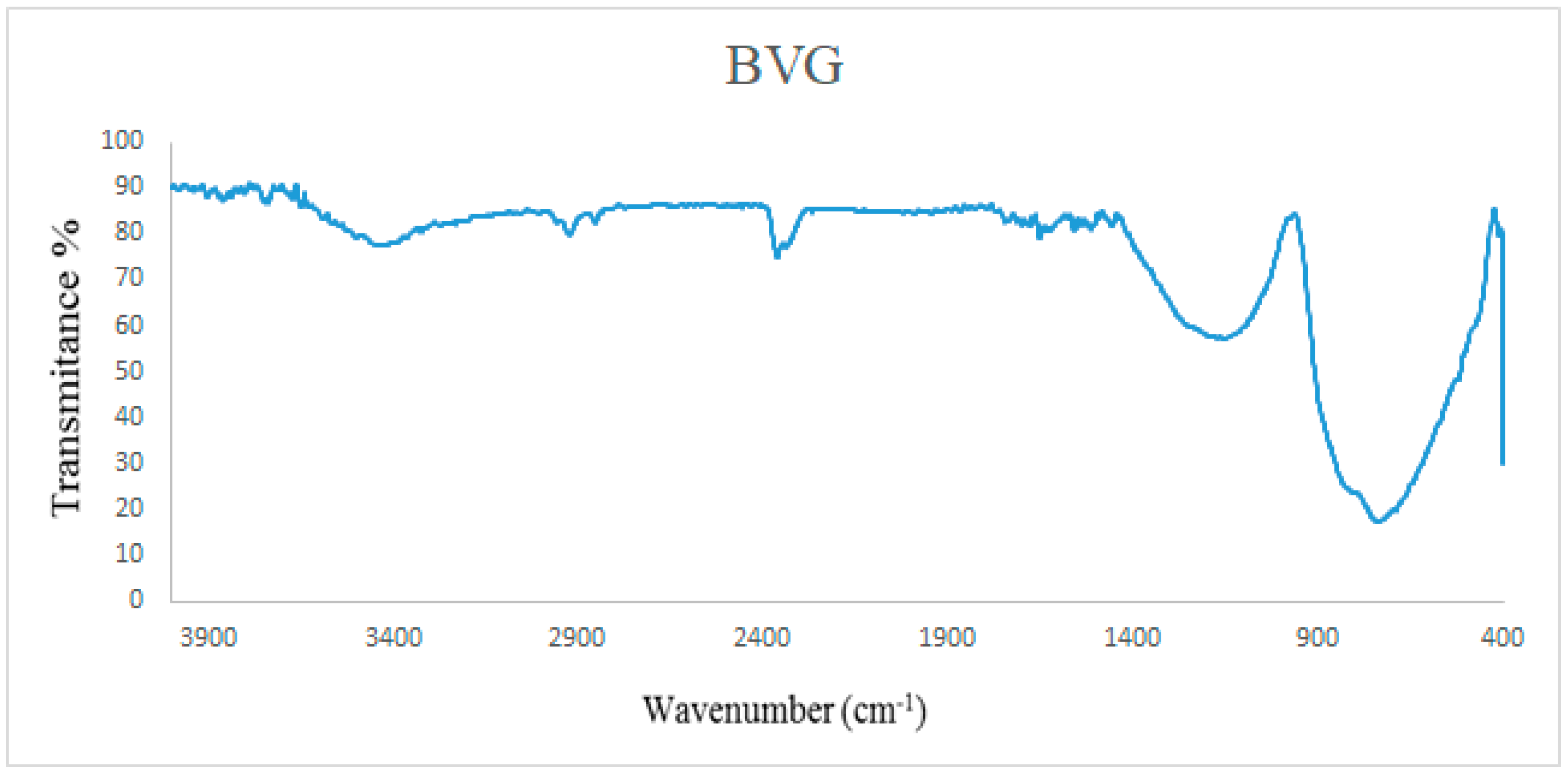
3.4. IR Spectrum of the Prepared Sample
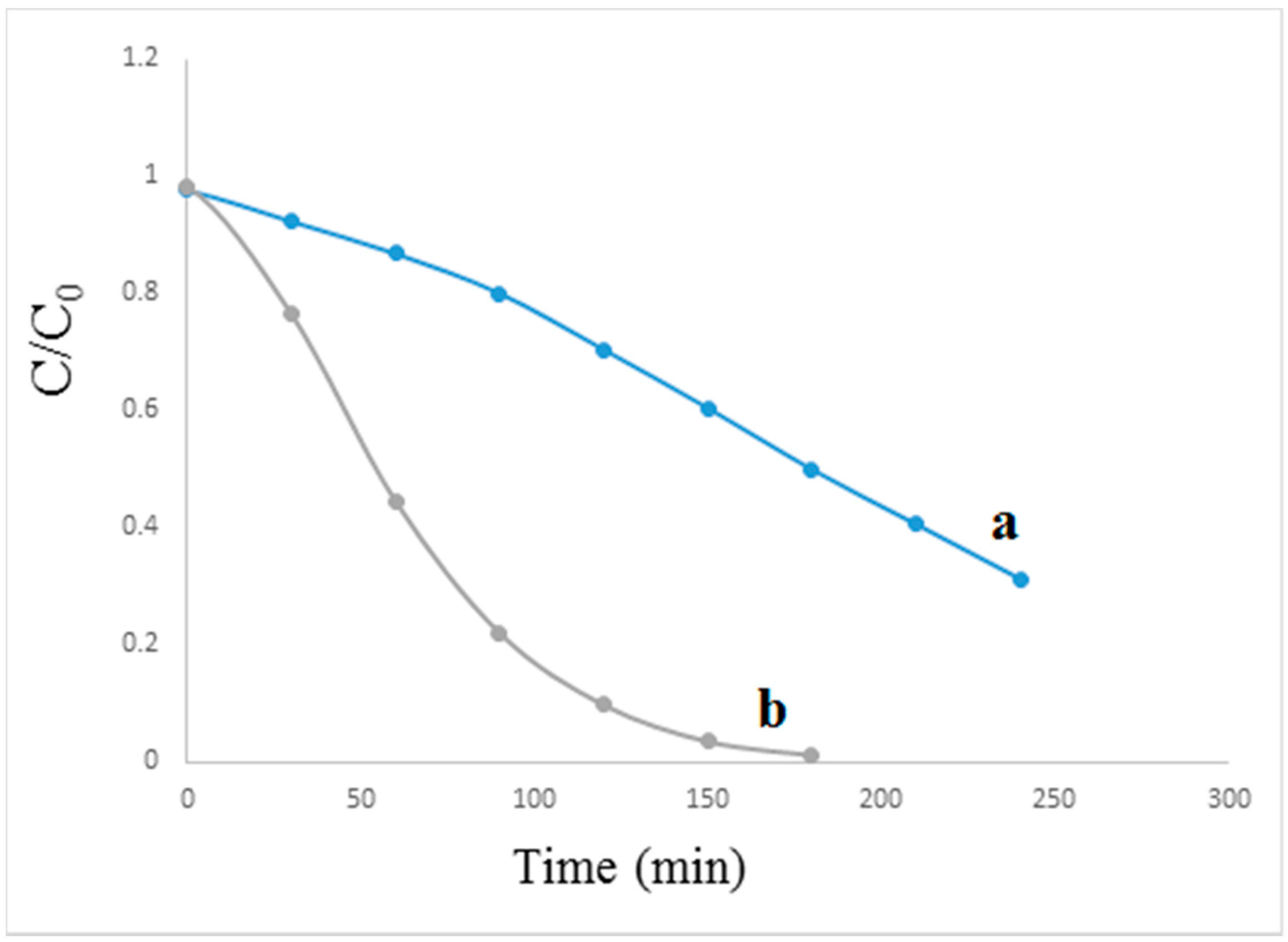
3.5. Photocatalytic Activity of the Prepared Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.J. TiO2 photocatalyst for water treatment applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woan, K.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Sigmund, W. Photocatalytic carbon- nanotube–TiO2composites. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.M.; Liu, W.S. Surface doping is more beneficial than bulk doping to the photocatalytic activity of vanadium doped TiO2. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2011, 101, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ye, J. Hierarchical WO3 hollow shells: dendrite, sphere, dumbbell, and their photocatalytic properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Mu, L.; Li, C. Significance of crystal morphology con- trolling in semiconductor-based photocatalysis: A case study on BiVO4 photocatalyst. Crystal Growth Des. 2017, 17, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mao, H.; Lu, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, J.; Ye, Z.; Lu, B. Electrostatic self-assembly of BiVO4–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for highly efficient visible light photocatalytic activities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12698–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsnelson, M.I. Graphene: Carbon in two dimensions. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Biswas, K.; Subrahmanyam, K.; Govindaraj, A. Graphene, the new nanocarbon. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2457–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Mehrehjedy, A.; Zargari, S. BiVO4/Mn3O4 a novel p–n heterojunction photocatalyst functionalized with metalloporphyrins: Synthe- sis, charge transfer mechanism, and enhanced visible-light photocatalysis for degradation of dye pollutant. Environ. Progress Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aghakhaninejad, S.; Rahimi, R.; Zargari, S. Application of BiVO4 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange. Proceedings 2019, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05666
Aghakhaninejad S, Rahimi R, Zargari S. Application of BiVO4 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange. Proceedings. 2019; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05666
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghakhaninejad, Sarah, Rahmatollah Rahimi, and Solmaz Zargari. 2019. "Application of BiVO4 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange" Proceedings 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05666
APA StyleAghakhaninejad, S., Rahimi, R., & Zargari, S. (2019). Application of BiVO4 Nanocomposite for Photodegradation of Methyl Orange. Proceedings, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05666



