Abstract
We propose an adaptive fractional multi-scale optimization optical flow algorithm, which for the first time improves the over-smoothing of optical flow estimation under the total variation model from the perspective of global feature and local texture balance, and solves the problem that the convergence of fractional optical flow algorithms depends on the order parameter. Specifically, a fractional-order discrete L1-regularization Total Variational Optical Flow model is constructed. On this basis, the Ant Lion algorithm is innovatively used to realize the iterative calculation of the optical flow equation, and the fractional order is dynamically adjusted to obtain an adaptive optimization algorithm with strong search accuracy and high efficiency. In this paper, the flexibility of optical flow estimation in weak gradient texture scenes is increased, and the optical flow extraction rate of target features at multiple scales is greatly improved. We show excellent recognition performance and stability under the MPI_Sintel and Middlebury benchmarks.
1. Introduction
The TV-L1 optical flow estimation algorithm is a method for estimating the optical flow field that combines the noise reduction advantage of L1 regularization and the global-scale smoothing performance of the total variation model [1]. The variation-based optical flow estimation unifies the calculation of optical flow quantities in a standard equation framework and reduces it to minimizing a global energy function, which consists of data terms and smoothness terms. Due to its standardized construction for computing models, it has quickly become the mainstream optical flow algorithm over the past two decades. Ant Lion optimization is a swarm intelligence optimization algorithm. In recent years, research on image processing optimization has focused on leveraging the advantages of Ant Lion swarm intelligence optimization in global optimization range, high convergence accuracy, and minimal parameter requirements [2,3]. Researchers have utilized Ant Lion optimization to improve search accuracy and robustness in various visual tasks. However, its application in optical flow estimation remains unexplored.
While studies [4,5] demonstrate that using the TV-L1 optical flow algorithm yields higher accuracy in weak texture regions compared to other methods, it can also lead to excessive smoothing and blurring of targets as well as contour edges. This cumulative error significantly impacts subsequent recognition results. Reference [6] employed multi-channel sampling interpolation to restore texture in motion-blurred images while reference [7] proposed a pixel-weight-based smoothing operation aimed at reducing edge blur caused by variational light path equations. Based on the work of Demetz O et al., reference [8] proposed the anisotropic smoothness constraint. However, this work presented a significant challenge for researchers. The graph-based method suggested for improving edge blurring can result in excessive segmentation of the foreground and background, leading to a loss in optical flow estimation. Consequently, penalty functions based on flow fields have been proposed to emphasize smooth edges and enhance them in order to mitigate excessive smoothing [9]. In addition, reference [10] employs super-resolution techniques to enhance contour edges and thereby increase the detection of displacement feature points at the edge. Generally speaking, projects aimed at improving Variational Optical Flow data seek to make their algorithms more robust against disturbances such as noise and illumination changes or enhance their ability to handle large motion displacements. The purpose behind enhancing the smoothing parameter is finding an optimal weight that is balanced between the data term and smoothing term. A reasonable choice of this parameter ensures stable results by appropriately considering each constituent term’s contribution. Nevertheless, previous works completely overlook local-scale optical flow estimation while few researchers address the issue of multi-scale feature imbalance that hampers motion features’ detection. Therefore, this work holds significance in terms of improvement within this field. The contributions made by this work are as follows:
- •
- The TV-L1 optical flow objective function is discretized by the fractional-order differential operator, which makes the model pay extra attention to the local texture-scale optical flow features, increases the participation of effective optical flow, and improves the robustness of the model in multi-scale computation.
- •
- The fractional order is regarded as one of the objects of the optimization problem, and the Ant Lion algorithm is used to realize the local sampling search, and the global smoothness advantage of the TV-L1 optical flow model is retained. The multi-scale objective function is optimized by multi-parameter optimization of the smoothness term weight and fractional order.
- •
- The significant performance of our proposed model is verified on the MPI_Sintel and Middleburry datasets.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, we propose an optical flow estimation algorithm based on the fractional order and the Ant Lion optimizer. As shown in Figure 1, the proposed optical flow model consists of the following main modules: a fractional-order TV-L1 optical flow estimation part to realize basic learning tasks, and an Ant Lion optimizer part responsible for adaptive parameters.
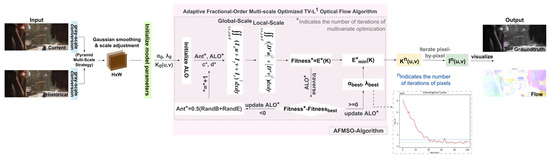
Figure 1.
AFMSO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm’s overall framework.
In Section 2.1, we first review the construction process of the TV-L1 optical flow model, and we carry out reasonable fractional discretization of it in Section 2.2. Next, we describe the iterative process of the Ant Lion optimization in detail in Section 2.3. Finally, we carry out the experimental analysis in Section 3, and give the discussion and conclusion in Section 4 and Section 5.
2.1. Construction Process of TV-L1 Optical Flow Model
The conventional TV-L1 optical flow model is established and solved under the brightness constant constraint, which is as follows (1):
where is the brightness function of the input image pixel, and are the components of the optical flow vector in the and directions, respectively, and and represent the change in the number of frames. Based on the assumption of uniform velocity, the L1 regularization Total Variational Optical Flow equation can be obtained as Equation (2):
where represents the weight of the smoothing term and is determined by the characteristics of the input data. Specifically, the smoothing term weight should be inversely proportional to the image quality. In Total Variational Optical Flow estimation tasks, the problem of solving the optical flow equation can be reformulated as an energy functional minimization problem, as represented by Equation (3). By solving the first derivative of the energy function using the Euler–Lagrange equation [11], Equations (3) and (4) can be obtained.
where , , , and respectively represent the mean velocity in the and directions in the neighborhood; then, the components of the optical flow vector in the and directions can be obtained as Equations (5) and (6).
After simplifying the components of the optical flow field, the optical flow field can finally be obtained as Equation (7):
The iterative process of the optical flow field corresponds to the optimization process of the optical flow energy function. In this work, we employ the Ant Lion optimization algorithm to enhance the fractional-order Variational Optical Flow estimation model. This enhancement manifests in the iterative evolution of the optical flow field, representing the optimization of the energy functional associated with optical flow.
2.2. Subsection
The fractional order is derived on the basis of the integer order. Assuming that the function is differentiable, the th derivative of with respect to is as follows (8):
where . According to the above derivation, the discretization expression of the objective function is shown in Equation (9).
As outlined in the introduction, the utilization of fractional-order optimization has been prevalent in various fields such as control systems, image enhancement, and restoration tasks within the realm of image processing. This preference is attributed to the historical correlation advantages and overall smoothing capabilities offered by fractional-order methods. Notably, research has extensively explored the application of fractional-order optimization in image processing tasks [12]. For instance, in the context of image data processing, the discrete brightness function derived from the image pixel serves as a prominent example, with denoting the total number of image pixels. From the definition of the G-L fractional-order differential derived in the previous subsection [13], it can be seen that its meaning is as follows: pixels are sampled equidistantly in at intervals of , the object function is a continuous function, and the domain of independent variable is ,,. Thus, the -order differential discretization of the brightness function can be obtained as Equations (10)–(12) [14].
In this section, drawing inspiration from the enhancements brought about by fractional-order methods in variational image denoising models [15], as illustrated in Equation (13), we incorporate fractional-order discretization to establish the L1 smoothness constraint based on fractional-order principles. This approach culminates in the derivation of the fractional TV-L1 optical flow. Equation (14) is finally obtained [16].
The TV-L1 optical flow equation can be derived from the Euler–Lagrange equation as Equation (15):
where , , the optical flow components and have deviations and , respectively, and the deviation parameter is ; then, the current optical flow component is shown in Equations (16) and (17).
Therefore, the energy function can be reformulated as Equation (18):
If , and at the same time the first derivative of the independent variable in the above equation is taken, then
where ; thus, the simplified equation can be obtained as Equation (20):
After obtaining the simplified optical flow equation, the next step involves continuing the fractional-order differential solution based on the aforementioned approach. This further demonstrates that the functions acquired through the calculations mentioned above are discrete in nature. Assuming the number of pixels , then , , and in the processing of the optical flow vector; according to the Grünwald–Letnikov definition, the fractional-order differential discretization Equation (22) of optical flow can be derived as follows (22):
where ; can be obtained from the discrete fractional-order differential properties as follows (23):
Thus, the following is true:
where is the neighborhood of the current pixel point participating in the computation, . Then, the component can be obtained as follows:
Finally, the iterative calculation formula of the fractional TV-L1 optical flow equation can be obtained as Equations (27) and (28):
From the iterative formula, it is evident that when the order is an integer (1 in this case), the proposed fractional-order TV-L1 optical flow model simplifies into the original L1 regularization optical flow. Therefore, the iterative formula exhibits certain versatility in the choice of a termination criterion.
2.3. Iterative Calculation of Fractional TV-L1 Optical Flow Based on Ant Lion Optimization
The Ant Lion algorithm is applied to facilitate the numerical iteration for calculating fractional optical flow. While the Ant Lion algorithm is designed for discrete optimization problems, optical flow estimation involves continuous problem solving. However, since the fractional-order TV-L1 optical flow itself relies on pixel-level discretization, employing the Ant Lion algorithm for minimizing the function for the fractional-order TV-L1 optical flow model is theoretically viable.
In Ant Lion optimization [17], the following entities are defined: the Ant Lion, representing the candidate’s better solution, and the Ant, which conducts a random walk around the candidate’s better solution to explore the neighborhood for potential improvements. The Ant algorithm operates by updating the current optimal solution based on the fitness value of the solution. This can be seen as the Ant randomly occupying points within the neighborhood of the pixel. By obtaining fitness information from these points, the Ant Lion leverages the information returned by the Ants. The selection probability is determined using the roulette wheel method and weights. As the number of iterations increases, the Ants’ territory narrows down, leading to more accurate searches in the Ant Lion neighborhood.
In this chapter, the Ant Lion algorithm is employed to replace the iterative method used in traditional optical flow algorithms for computing TV-L1 optical flow based on fractional-order theory discretization. Prior to this, it is essential to address two key points as the foundation of the entire problem [18]: defining the objective that must be accomplished during the numerical iteration process of fractional-order optical flow calculation and determining the desired outcome.
The numerical iterative process of the optical flow field is aimed at computing the motion of pixels between two images over a specific time interval. By modeling the intensity changes in each pixel in the input image sequence, the fractional TV-L1 algorithm can calculate the displacement vector of each pixel, representing its movement between the two images. During the iteration, the fractional TV-L1 algorithm computes the optical flow field by minimizing the overall error, which comprises three components: the luminance error, the fractional smoothness term that penalizes regions with large fractional gradients [19], and the L1-norm term, which effectively eliminates noise. Through iterative optimization of these three errors, the fractional TV-L1 algorithm accurately calculates the optical flow field. Ultimately, the TV-L1 algorithm with fractional iteration generates the optical flow vector for each individual pixel [20], signifying the displacement of that specific pixel between the two given images. These vectors can be utilized to calculate the motion of the entire image or to implement other computer vision applications such as object tracking, scene reconstruction, and virtual reality.
The parameters utilized in ALO optimization primarily involve the solution vector within the fractional TV-L1 algorithm, along with other parameters that affect the performance of the algorithm, such as the penalty parameter and the number of iterations. ALO adjusts the solution vector by updating the positions of the Ant colony and the Ant Lion, and applies the updated solution vector to the numerical iterative computation in the fractional TV-L1 algorithm. The movement process of the Ant colony and the Ant Lion is affected by the fractional TV-L1 energy function value and the current solution vector, aiming to search for a solution vector with a lower energy function value. By simulating the behavior of an ant colony searching for food and ant lion predation, ALO optimizes the solution vector by combining the requirements of the fractional TV-L1 energy function. The movement of the Ant colony is affected by the pheromone concentration and the attraction of the solution vector, and the Ant colony will randomly choose the next position. The pheromone concentration in the Ant colony is updated according to the distance between the current optimal solution vector and the current position. The Ant Lion, on the other hand, chooses the predation position according to the energy function value of the current solution vector, and adjusts the solution vector by modeling the behavior of the Ant Lion in expectation of finding a better solution.
Overall, the objective of ALO is to optimize the solution vector within the fractional TV-L1 algorithm by leveraging the movement of the Ant colony and Ant Lion, aiming to enhance the convergence rate and achieve superior optimization outcomes. In summary, in this chapter, the pixel point and optical flow vector are used as the initial position and initial velocity of the Ant and the Ant Lion. Following the Ant Lion’s flow involves these steps:
- The initial values of pixels and optical flow vectors are initialized in the two populations, and the pheromone matrix of the Ants is established to record the pheromone concentration between each pixel. The search space of the Ants is defined as follows (29):
- 2
- The second step is to randomly initialize the positions of Ants and Ant Lions on the solution space, calculate the fitness value of each pixel, and take the pixel corresponding to the lowest value as the Ant Lion.
During the individual random walk process, the initial configuration of the trap and the selection of the Ant Lion significantly influence the outcome as follows:
where represents the Ant Lion, represents the position of the -th Ant Lion in the -th iteration, represents the vector of all ’s in the -th iteration, and represents the vector of all ’s in the -th iteration. The motion space of the Ant was centered around the position of the Ant Lion, gradually shrinking as the number of iterations increased, ultimately converging towards the optimal solution and yielding the final computation result. The minimization process is detailed in Equations (32) and (33):
where is the parameter of iteration termination times set by initialization, and is the relevant parameter, whose value is determined by ; when , ; when , ; when , ; and when , .
- 3
- For each Ant, a roulette wheel is used to select an Ant Lion as the target. Concurrently, the Ant will randomly move around the chosen Ant Lion as the best solution, and update its position and speed, calculate the position and speed of the next moment and the pheromone increment of the current position, and update the pheromone, that is, the path that the Ant has passed and the local optimal pixel solution.
- 4
- When the fitness value of an Ant exceeds the optimal value from the previous iteration, the position is then updated to match the position of that particular Ant. In the selection and update of the Ant Lion, assuming that the random walk of goes to and the random walk of goes to , the movement of the individual Ant around the Ant Lion trap domain is as follows (34):
- 5
- The fifth step is to determine whether the convergence condition is satisfied, output the fractional order , penalty parameter , and solution vector corresponding to the current optimal solution, and stop the iteration, or otherwise return to step 3.
3. Experiments and Analysis
The algorithm in this chapter is based on the L1 regularization Total Variational Optical Flow model, which is improved by fractional discretization and numerical iteration. Therefore, the convergence performance of the new algorithm and the influence of the fractional-order parameter of the smoothing term on the optical flow tracker, that is, the index performance of the optical flow task, are two important criteria for investigating the algorithm. The following experiments are established on the conventional optical flow datasets known as the MPI_Sintel and MiddleBury sequences, and the optical flow performance indicators AEPE, AAE, PSNR, SSIM, and the visual coding map are selected. The proposed adaptive fractional multi-scale tracker was validated qualitatively and quantitatively in a Pytorch environment on a laptop with Intel(R) i7-12700F CPU, 16 GB RAM, and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060Ti. This was used to evaluate the feasibility and reliability of the algorithm in this chapter.
3.1. Ablation Experiment
In order to verify the improved performance of the TV-L1 optical flow energy function by introducing fractional discretization, the empirical interval was used to sample the order at 0.1 intervals, and the two optical flow error indexes AEPE and AAE, PSNR, and SSIM were calculated. Table 1 shows the setting of the necessary default parameters of AFMSO-TVL1 in the following experiments. The results of the ablation experiments are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio) and SSIM (Structural Similarity Index) were selected to measure the stability and accuracy of pixel calculation in the process of optical flow calculation.

Table 1.
The setting of fixed parameter values involved in the experimental analysis.

Table 2.
Under the MPI_Sintel random sequence, , AEPE and AAE indexes are obtained by the FO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm traversing fractional order alpha in the interval .

Table 3.
Under the MiddleBury random sequence, , AEPE and AAE indexes are obtained by the FO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm traversing fractional order alpha in the interval .
In order to verify and analyze the contribution of the introduction of the fractional differential theory of the Grünwald–Letnikov method discretization to the TVL1 algorithm using the gradient descent method for numerical iteration, two ablation experiments were carried out, as shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3.
(1) A fixed smoothing term parameter is set and the fractional order acting on the objective function is changed. The fractional order is in the interval with a step of 0.1. Table 2 and Table 3 intercept the results within the interval for presentation.
When the smoothing parameter is 79.4, the evaluation results of the FO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm under the MPI_Sintel sequence significantly reflect that the fractional-order TV-L1 algorithm reduces the values of two error evaluation indexes compared with the integer-order TV-L1 algorithm. In terms of the AEPE index, the optical flow errors of eight test sequences in the optimal fractional order are reduced compared with the integer order: 6.7409, 9.8112, 1.1759, 0.7221, 1.1107, 20.6276, 3.1123, and 0.6305. In the AAE index, the optical flow angle error is decreased compared with the integer order: 0.061, 0.509, 0.1335, 0.0116, 0.1843, 0.0113, 0.0017, and 0.1259. For sequences with different attribute challenges, the fractional-order parameters to obtain the best results are different, which is due to the feature of fractional-order discretization based on image gradient calculation.
According to the principle of AEPE and AAE evaluation of optical flow algorithms [18], when the two error values reach the minimum value in balance, the optical flow algorithm can obtain ideal parameters. In the results shown in Table 2, taking the Shaman2 sequence as an example, even if AEPE and AAE achieve ideal results when alpha = 0.6 and alpha = 0.8, respectively, the optimization parameters cannot be simply determined on this basis. The two evaluation indexes must be considered at the same time; otherwise, it is difficult to avoid the algorithm falling into local optimality during the convergence process. Therefore, it is necessary to further use the ALO method for parameter optimization to obtain the ideal optical flow estimation results.
It can be seen from Table 3 that when the fractional-order value is from 0.7 to 1, the optical flow error increases with a high growth rate, and when the fractional-order value is from 0.4 to 0.7, the optical flow error shows a steady downward trend. The optical flow calculation under fractional-order differentiation is better than that under integer-order differentiation as a whole. And in the interval , the best value is ; in this time flow error index, AEPE and AAE are overall low, indicating that the model in this interval performs well and has high accuracy under the influence of fractional-order differentials.
From the analysis of the challenging attributes of the test data, in the Army and Grove sequences with rich texture and clear edges, has the best comprehensive performance and the smallest error in time flow estimation. The Ambush2 sequence has rich contours, and the optimal order is . The Market1 sequence has rich and complex scenes and targets with dramatic changes in motion state, and the optimal fractional order of data items is . For the Mequn and Wall sequences with relatively simple motion and texture, the optimal orders are and , respectively, and the comprehensive error result is the lowest. The Cave4 sequence is not rich in texture details, and the optimal order is . The Wooden, Ambush2, and Market4 sequence have simple rules and sufficient illumination in the texture, and the optimal fractional order is .
In summary, the following hypotheses can be obtained from the above experimental results: The optimal performance interval of the fractional order has a strong correlation with the data themselves, and the higher the complexity of the motion scene, texture, and lighting conditions, the higher the value of the optimal fractional order, and there is a concentrated law. After performing the above experiments on two optical flow datasets with completely different scene elements and target states, it can be obtained that the value of the optimal fractional order is closely related to the complexity of the scene and the target texture conditions of the input image.
(2) To validate the efficacy of the ALO module in optimizing parameters for TV-L1 energy function minimization during numerical iteration, this chapter involves conducting ablation experiments using the gradient descent method (GD, gradient descent), conjugate gradient method (CG, conjugate gradient), and ALO method as ablation components under different methods and compares the optical flow evaluation results. Additionally, convergence experiments are carried out with AFMSO-TVL1’s smooth term parameters and fractional-order parameters.
From the analysis of the results in Table 3, when the smoothing parameter is fixed to 23.6, for the integer-order TVL1 algorithm, the AEPE of TVL1(ALO) using the ALO method for numerical iteration is reduced by 2.4614 and 0.4978, respectively, compared with TVL(GD) and TVL1(CG) using the gradient descent method and the conjugate gradient method. PSNR increased by 0.19% and 0.85%, while the SSIM index increased by 0.1017% and slightly decreased by 0.186%. Similarly, with the introduction of the ALO algorithm, the AEPE index of the FO-TVL1 algorithm is reduced by 3.0026 and 1.3616, the SSIM index is increased by about 0.9077% and 0.4059%, and the PSNR value is increased by about 0.0185 and 0.1446.
At the same time, it can be concluded from the statistical analysis results in Table 4 that the introduction of fractional differentiation or ALO alone can only lead to a maximum of two improvements in the evaluation results, which also confirms the necessity of the simultaneous contribution of fractional differentiation and ALO components based on the discretization of the Grünwald–Letnikov method.

Table 4.
Based on integer-order TVL1 and fractional-order TVL1 algorithms, different iterative methods were used for ablation experiments.
(3) The next step involves conducting an ablation experiment on the FO-TVL1 optical flow estimation algorithm to analyze the impact of the smoothing term parameter . Initially, various disturbance factors such as the number of iterations, population size, and initial parameters were determined (values provided in Table 1). The ablation component refers to the weight assigned to the smoothing term. The experimental optimization object is the objective function of optical flow estimation, and the fitness function is set as the error calculation function. The iteration process stops after reaching a predefined number (). Throughout the experiment, convergence values for three evaluation indexes were recorded. In Table 5, fractional order alpha is set at a fixed value (), and statistical analysis was performed on three evaluation results obtained from FO-TVL1 under different smoothing parameters.

Table 5.
When the fixed fractional order alpha is 1.5, the optical flow error index, PSNR index, and SSIM index are obtained when the smoothing coefficient value is traversed with the step of 0.1 in the interval .
In the experimental analysis results in Table 4, under the influence of different image scene attributes and image quality, the optical flow estimation results under different smoothing parameter values are different, but the data show that when the beta value is within the interval , the three evaluation results perform well.
Figure 2 shows a convergence process curve drawn in the control variable experiment.
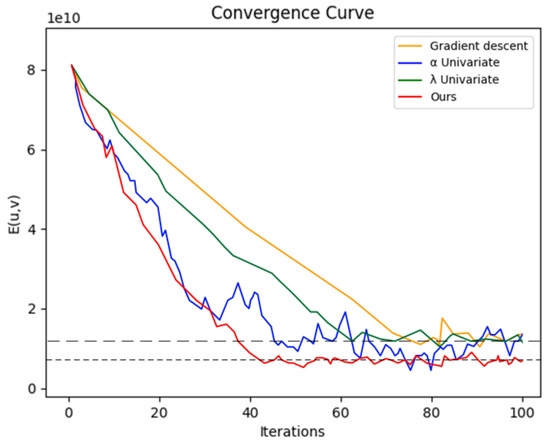
Figure 2.
Comparison plots of convergence curves of numerical iterations using gradient descent method, univariate iteration ( or ), and multivariate iteration (ours) based on the objective function of this paper when the number of iterations is set to 100 for random pixels.
3.2. Comparative Experiments
In order to verify the superiority of the algorithm in this chapter for the dataset performance, this chapter uses AFMSO-TVL1 to compare with TVL1-Flow, HS, FO-FFlow (the Fractional Order Farneback Flow Algorithm), FOTVL1-Flow, FOVOFM, and ADFOVOFM, and obtains the following optical flow performance of random sequences in the MPI_Sintel and Middlebury datasets under different algorithms.
As can be seen from the data in Table 5, the performance of the AFMSO-TVL1 algorithm proposed in this chapter for complex scenes is comprehensive and as fully able as possible to retain and estimate the moving optical flow from the texture information. In the scenes with complex texture structure and lighting conditions, the advantages of the algorithm in this chapter are stronger. The comparative experimental results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Optical flow error indexes obtained from parameter optimization experiments performed on MPI_Sintel sequences.
In Table 7, the AFMSO-TVL1 algorithm shows better results than the five contrasted algorithms in complex scenes, especially in scenes containing low light and high texture features (such as the Wall and Market sequences). Compared with the fractional-order moving optical flow estimation algorithm FOVOFM, the AEPE errors estimated by AFMSO-TVL1 in the four sequences are reduced by 2.4237, 0.3107, 0.2746, and 0.8499, respectively. In the Ambush sequence, the fractional-order parameter of AFMSO-TVL1 achieving the lowest convergence value is 2.1486, and the optimal value of the smoothing parameter is 67.9466.

Table 7.
Optical flow error indexes derived from Middlebury sequence parameter optimization experiments.
When considering the average endpoint error indexes of the optical flow, PSNR, and SSIM indexes at the same time, the proposed work can provide 6.45% and 4.76% lower error rates than TVL1-Flow and FOVOFM in the Mequn and Yosemite sequences from MiddleBury. The accuracy of the Grove and Teddy sequences is slightly lower than that of FOVOFM and FO-FFlow at 55.67% and 48.89%.
As shown in Figure 3, (a), (b), and (c) respectively represent three random sequences, (1) represents the original input image, and (2), (3), (4), and (5) respectively represent the visual results of optical flow estimation by the four algorithms HS, TVL1-Flow, FOVOFM, and AFMSO-TVL1 for the four random data. It can be seen that in group (1), the estimation of optical flow mainly focuses on the contour with distinct features, and hardly involves the extraction of texture, and even the edge of the moving target cannot be accurately extracted. In (2), the visualization image obtained by the TVL1 group obviously increases the pixel participation in the estimation of complex texture regions, but the performance is not ideal, and excessive smoothing on the global scale causes serious texture blur. According to the statistical analysis conclusion in Section 3.1, this is caused by the difficulty in achieving optimal convergence of parameter values. In (4b), the general outline of human facial features can be displayed more clearly, but because the algorithm is difficult to adapt to adjust the fractional order according to the pixel gradient, the details of the hair and the details of the wall in the background cannot be estimated. It can be seen from (5c) and (5a) that the algorithm in this chapter fairly restores and preserves the complex textures of the front and back scenes, and the details of the necklace, head shadow texture, and background fence are richly estimated. The shell decoration in the background with very poor lighting conditions, the details of the figure’s clothing, and the shape of the hand skeleton are all things that the previous works did not pay attention to or show. In this chapter, we make full use of pixel texture information and participate in optical flow calculation. The region selected by the red box in the image can highlight the improvements of our proposed AFMSO-TVL1 algorithm in texture detail and global feature extraction.
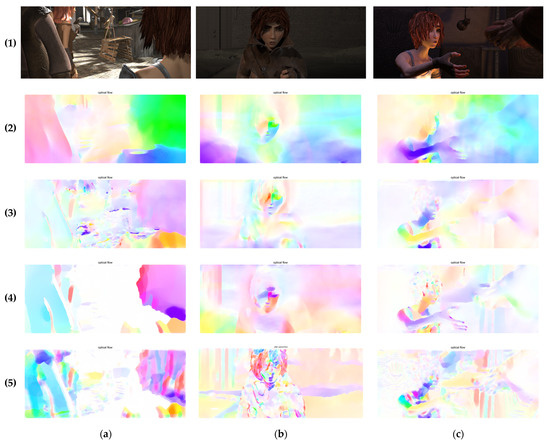
Figure 3.
Visualization of optical flow estimation. (a) Sequence 1; (b) Sequence 2; (c) Sequence 3.
4. Discussion
Multiple sets of experimental data in Section 3 show that the robustness and accuracy of our proposed optical flow estimation model for dynamic feature capture and estimation of texture details in complex attribute scenes are clear. Ant Lion optimization plays an important role in the minimization of fractional-order optical flow equations, and it can realize the global optical flow estimation while preserving texture details in contrast to the estimation methods under the fractional-order differential. The proposed optimization method for the Variational Optical Flow model avoids to a large extent the local optimal problem, which is easy to fall into when using the bionic population optimization method to optimize the optical flow estimation model. This method does not affect the advantage of fractional-order differentials in texture feature mining in the optical flow estimation model, whereas our proposed AFMSO-TVL1 deftly improves the accuracy and robustness of the optical flow estimation model at multiple scales through a multi-parameter optimization strategy but inevitably sacrifices the real-time operation of the model. Compared with the previous work, the optical flow estimation time of the AFMSO-TVL1 model is longer, which is also something that future researchers can pay attention to and improve.
In the TVL1 optical flow algorithm, the fractional differential is used to replace the traditional integer differential, and the ALO algorithm is used for numerical iteration of optical flow estimation. It can be seen from the results of experiment 3 in Section 3.1 that such a design can better capture the local correlation and global distribution of pixels in the sequence. The optical flow estimation based on pixel features can generalize input data and avoid optical flow estimation errors caused by sequence scene complexity and unpredictability of target motion. This makes the proposed algorithm more widely applicable to scenarios. At the same time, the enhancement effect of the fractional order on texture and the characteristics of historical memory make the total variable spectral flow estimation result more robust after optimization by the ALO algorithm with global search ability. The test optical flow graphs of the three sequences in Figure 3 can be analyzed as follows: To a certain extent, the proposed algorithm effectively solves the over-smoothing problem of the total variable spectral flow estimation, and the local optimal problem that the fractional-order optical flow algorithm is easy to produce. However, since the fractional order is calculated based on the per-pixel gradient, the calculation amount is much higher than that of the integer order. Moreover, the computational update of pheromones and the search for solution space in the ALO iterative search are complicated. This is despite the fact that ALO has improved speed relative to other swarm intelligence algorithms. However, for some carriers requiring real-time performance, the proposed algorithm has the limitation of slow operation speed.
5. Conclusions
In the previous experiments and theoretical studies, we found that the optical flow estimation algorithm has a relatively large estimation loss for the target texture in some dynamic scenes. In fact, not all objects are suitable for tracking by extracting salient contours. When it is necessary to estimate the moving target from the texture characteristics, the existing optical flow estimation algorithms are difficult to adapt to real-world application. In order to solve the shortcomings of the previous optical flow algorithms in the generalized scenario, we present the work in this paper.
The fractional-order theory of the Grünwald–Letnikov method is introduced into the TV-L1 optical flow algorithm, and a new fractional-order TV-L1 optical flow objective function is reconstructed. The Ant Lion optimization method is used for the first time to optimize the new objective function with multiple parameters, so that two parameters affect the final optical flow estimation error: the fractional order for enhancing the local features and the smoothing term for smoothing the global features are balanced and optimized. It can be found that the introduction of fractional differentiation reduces the convergence value of the objective function of optical flow, and the visualized optical flow results are more fully displayed in the processing of texture region information than in previous work.
In this work, we design a novel AFMSO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm from the perspective of balancing global and texture features. The TV-L1 optical flow equation involves fractional-order discretization, and the Ant Lion algorithm is innovatively introduced to realize the optimization of adaptive multi-scale algorithm parameters. Our algorithm performs well in scenes with complex lighting and rich textures. This improvement adds flexibility to dynamic optical flow estimation in scene fitness, while greatly improving the optical flow extraction rate of multi-scale features. However, the AFMSO-TVL1 optical flow algorithm may lead to increased background interference in some dynamic tracking tasks, such as target localization in SLAM tasks. Since the information is fully utilized in the calculation process, the sampling area should be carefully segmented into special tasks to ensure operation accuracy and efficiency.
At the same time, the random walk of the Ant population around the elite Ant Lion ensures the convergence of the optimization process, and the roulette wheel strategy helps to improve the global search ability of the algorithm to a certain extent. However, the phasic contraction of the Ant Lion’s predation radius with the increase in the number of iterations will lead to a gradual decrease in population diversity, and the convergence speed of the algorithm will be reduced under the leadership of a single elite. At the same time, compared with other optimization methods, the computational complexity of ALO optimization is relatively high. Therefore, future research can focus on how to improve the population renewal strategy and reduce the computational complexity of the algorithm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Y. and Y.W.; data curation, Y.W.; formal analysis, L.L.; funding acquisition, Q.Y.; investigation, X.Z.; methodology, Y.W.; project administration, X.Z.; resources, Q.Y.; software, Y.W.; supervision, Q.Y.; validation, Q.Y.; visualization, L.L.; writing—original draft, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Q.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52371339 and 12172283), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program under Grant JCYJ20210324122010027, Research Project of Key Laboratory of Underwater Acoustic Adversarial Technology (Grant No. JCKY2023207CH02), State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures (Nanjing University of Aeronautics and astronautics) (Grant MCMS-E-0122G02), Research Project of State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Vibration (Grant No. MSV202310), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2020M673484, National Research and Development Project under Grant 2021YFC2803000, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61971118), in part by the first batch of major science and technology projects in Liaoning Province unveiled and launched under Grant 2021020430-JH/104.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Bolme, D.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Yang, T.; Chai, T. Neural Network Control of Underactuated Surface Vehicles With Prescribed Trajectory Tracking Performance. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Xu, K.-D.; Wang, Q.-G. Prescribed performance tracking control of time-delay nonlinear systems with output constraints. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 67, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Luo, C.; Sun, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zeng, W. Tracking by Instance Detection: A Meta-Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6288–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. ECO: Efficient Convolution Operators for Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6638–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Qian, Z.; Bo, Q.; Yang, Y. Research on HS Optical Flow Algorithm Based on Motion Estimation Optimization. J. Comput. Commun. 2018, 6, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brox, T.; Bruhn, A.; Papenberg, N.; Weickert, J. High Accuracy Optical Flow Estimation Based on a Theory for Warping. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Boutat, D.; Liu, D. Applications of Fractional Operator in Image Processing and Stability of Control Systems. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Chai, T. Proportional-integral funnel control of unknown lower-triangular nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 69, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Yuan, J. Optical flow forvideo super-resolution: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 6505–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Yang, G.-H. Fault-Tolerant Output-Constrained Control of Unknown Euler–Lagrange Systems with Prescribed Tracking Accuracy. Automatica 2020, 111, 108606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Boutat, D. A Unified Framework of Stability Theorems for LTI Fractional Order Systems with 0 < alpha < 2. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3237–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.-X. Adaptive Sliding Mode Consensus Control Based on Neural Network for Singular Fractional Order Multi-Agent Systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 434, 127442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y. Fractional calculus in image processing: A review. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2016, 19, 1222–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Wang, Q.-G.; Ding, W. Global Output-Feedback Prescribed Performance Control of Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Virtual Control Coefficients. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2022, 67, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-M.; Hu, Q.; Guo, L.-J. Medical image non-rigid registration based on adaptive fractional order. Acta Autom. Sin. 2020, 46, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Research and Application of Antlion Optimization Algorithm Based on Distance; Hunan University: Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Raman, B. A fractional order variational model for the robust estimation of optical flow from image sequences. Optik 2016, 127, 8710–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Kumar, P. A nonlinear modeling of fractional order based variational model in optical flow estimation. Optik 2022, 261, 169136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. A duality based approach for fractional order Tv-model in optical flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), Patna, India, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).