Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Compared with the original neurons, the Rulkov neurons coupled with the LADM produce many novel firing patterns. Meanwhile, we show the coexisting firing behaviors of the neural network;
- (2)
- The synchronization transition behavior is explored;
- (3)
- The neural network exhibits the anti-phase synchronization of different firing patterns of homogeneous neurons, which has not been found in the previous literature.
2. Bistable LADM Model
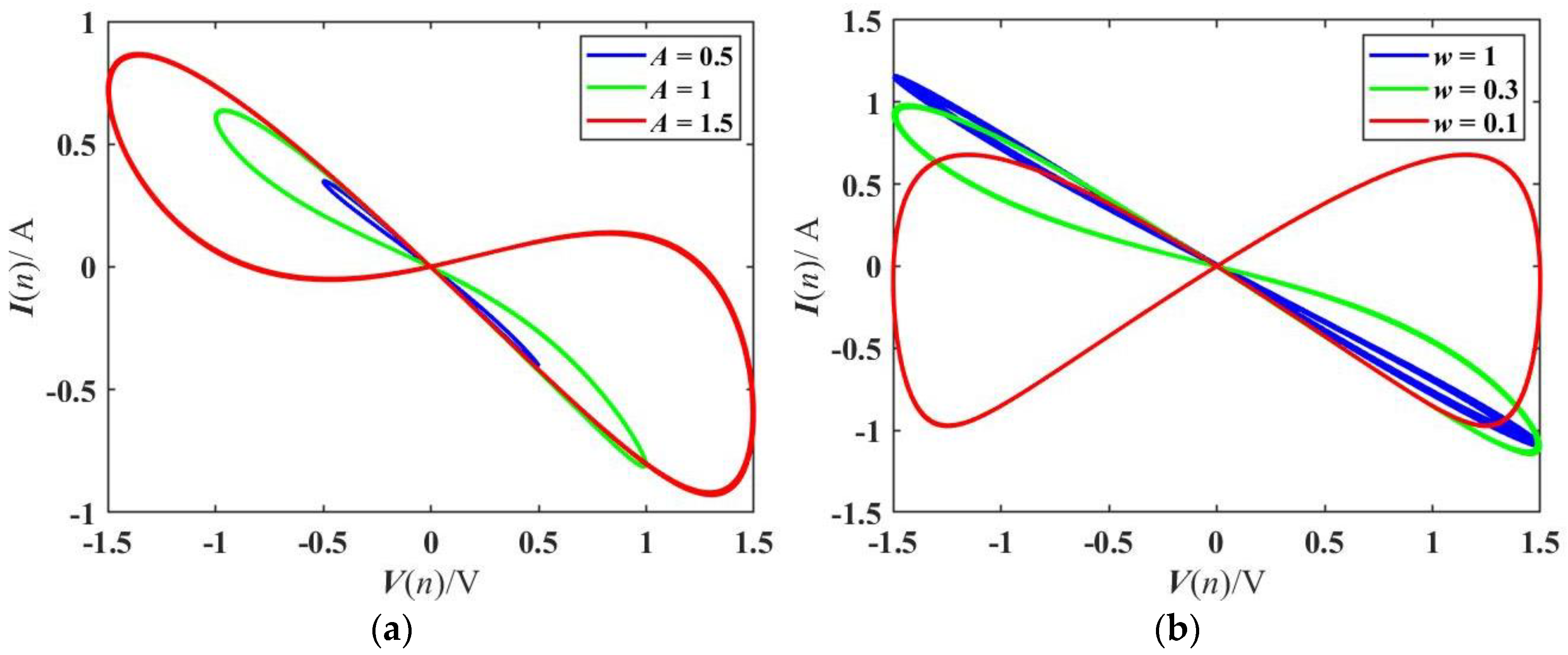
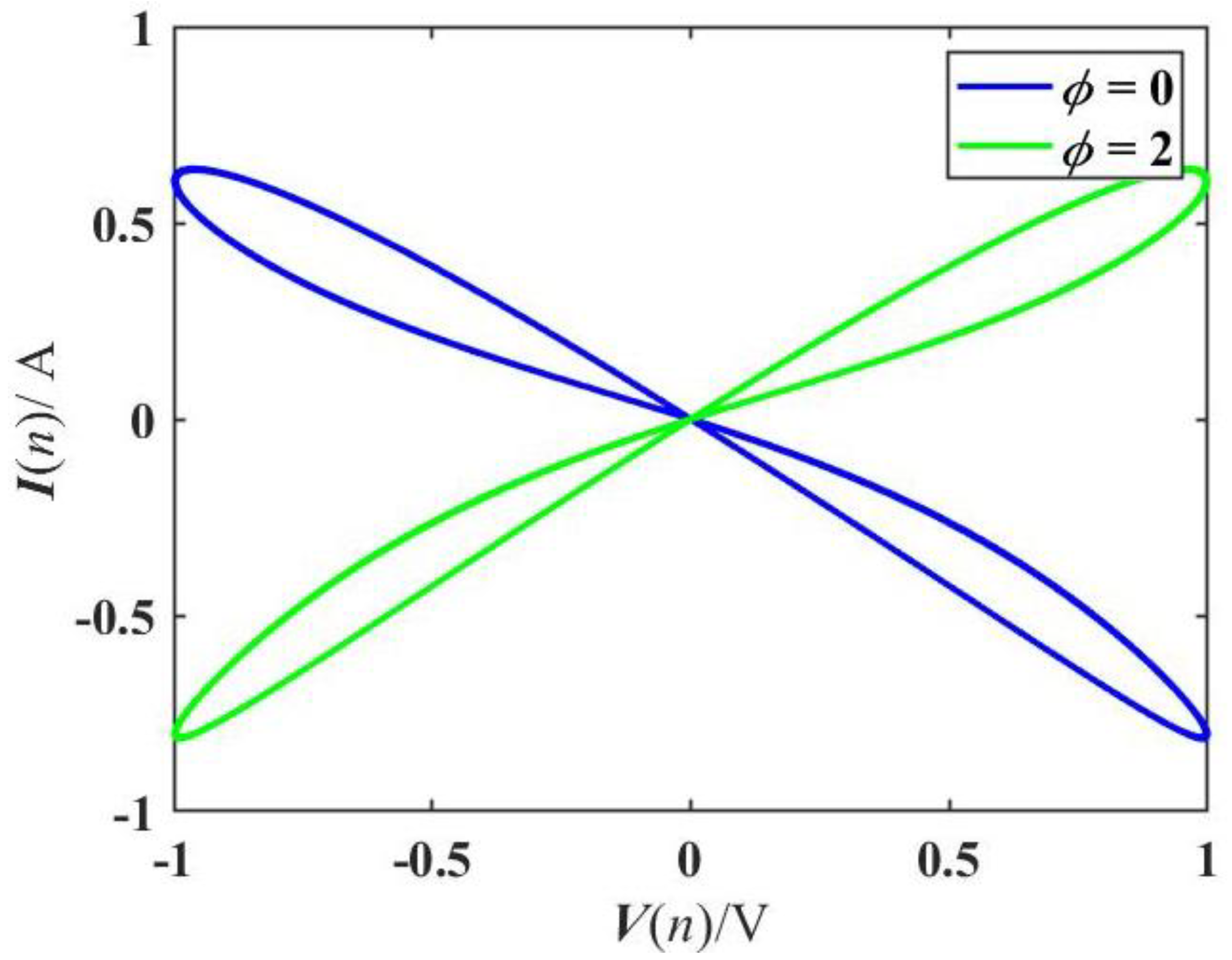
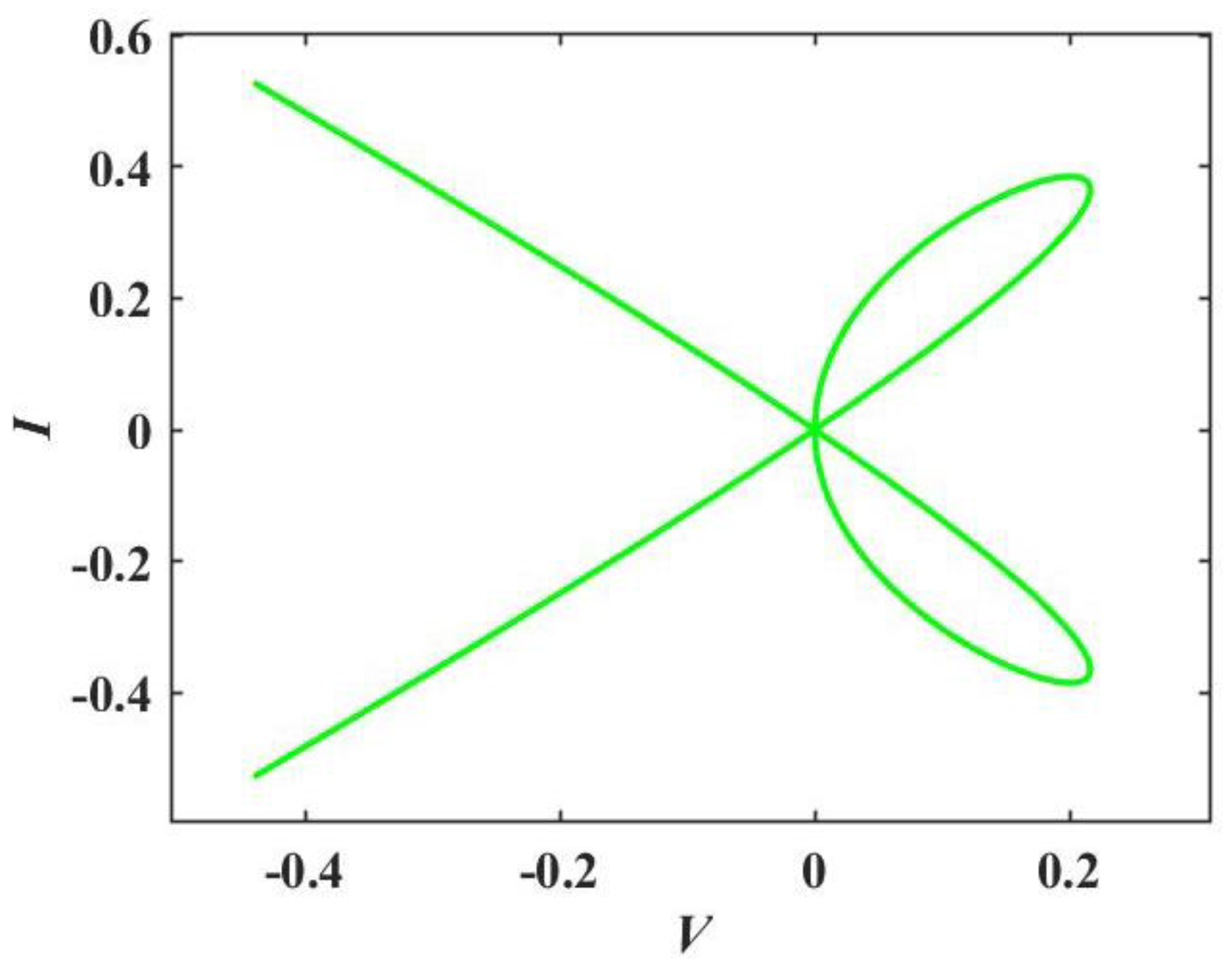
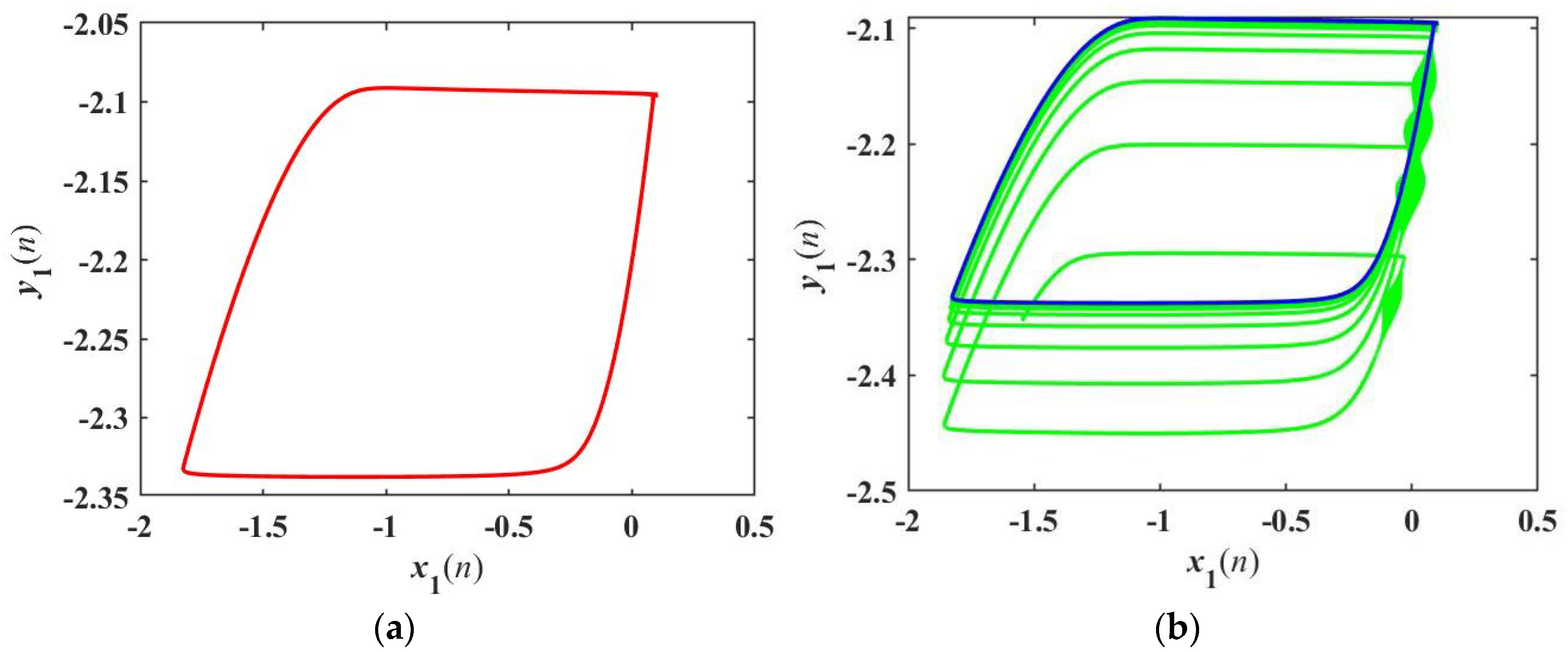
2.1. Pinched Hysteresis Loops and Bistability
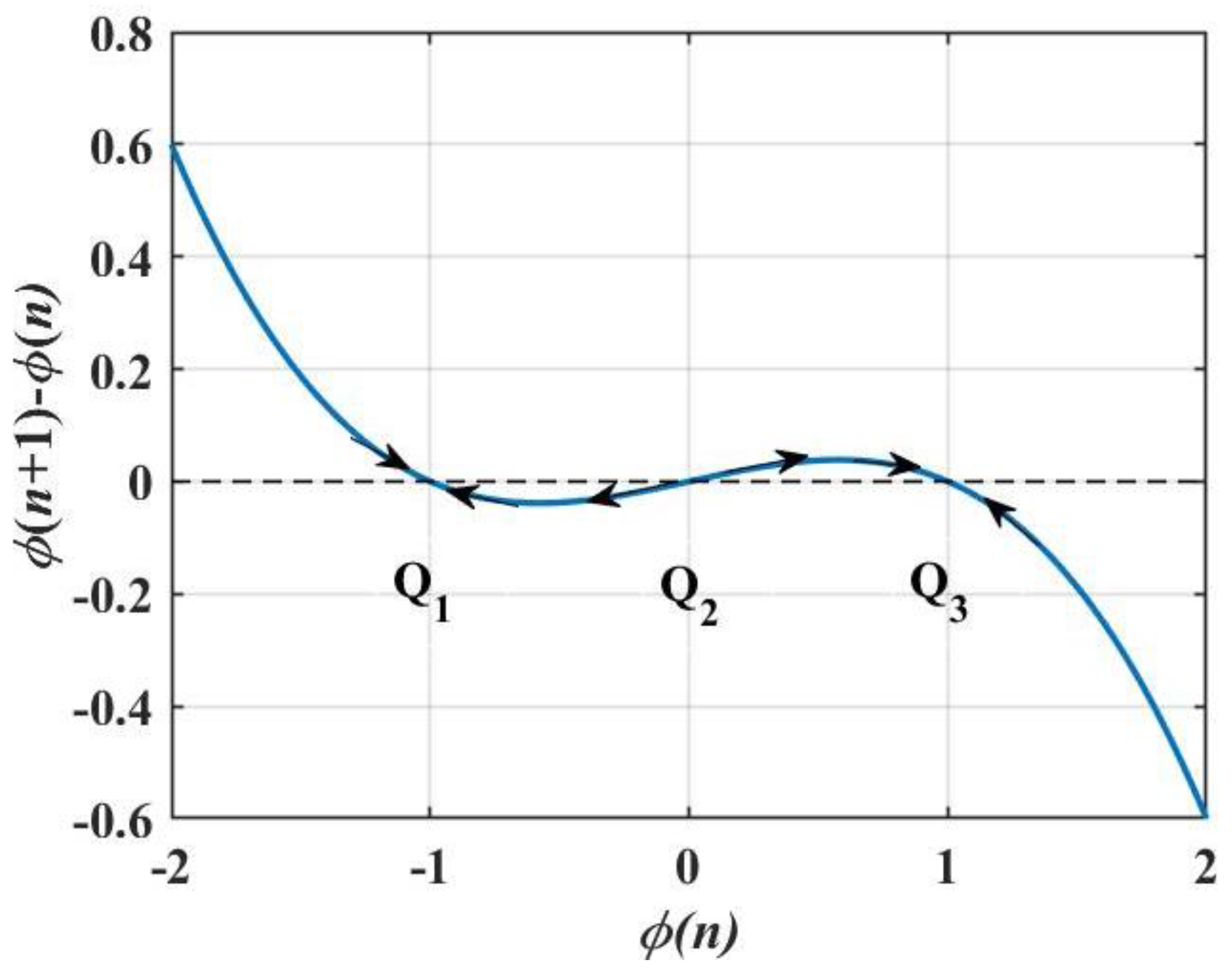
2.2. Nonvolatility and Local Activity
3. The Neural Network Model and Equilibrium Point Analysis
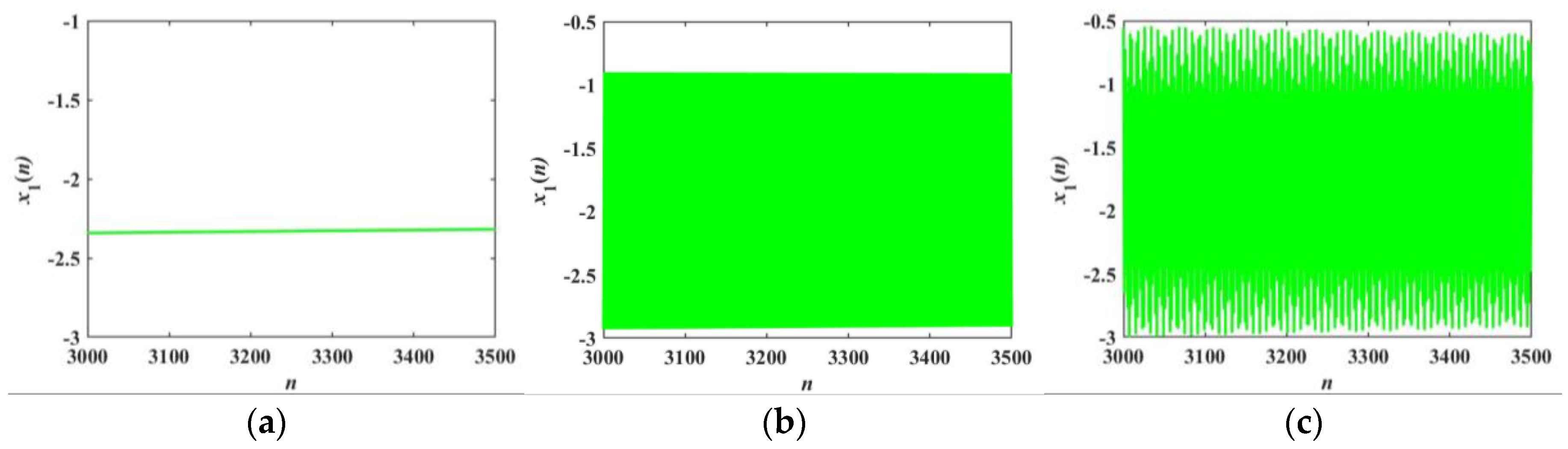
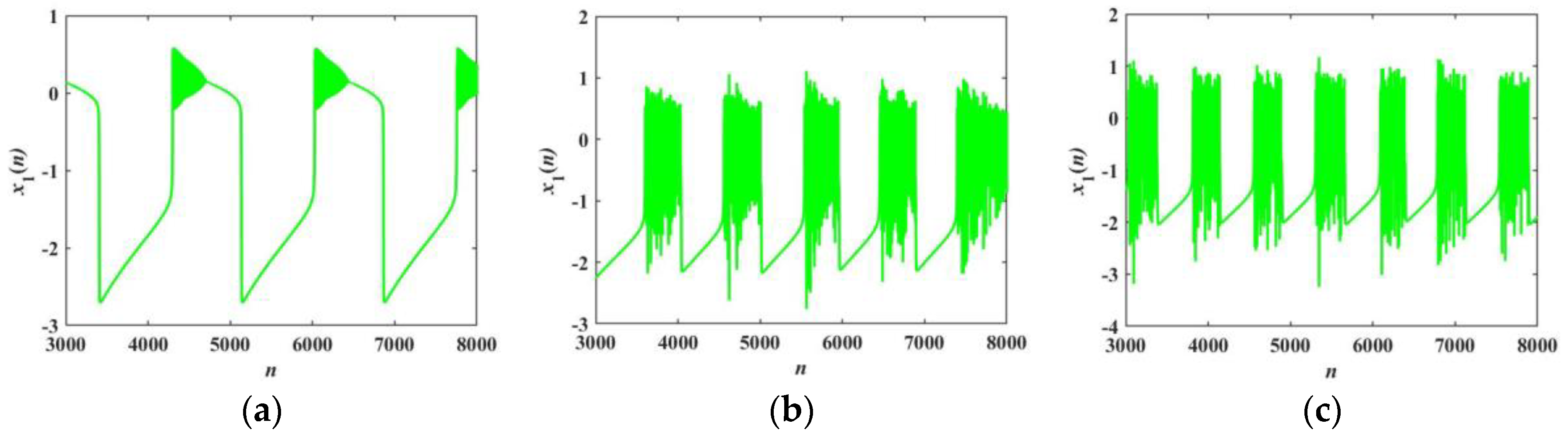
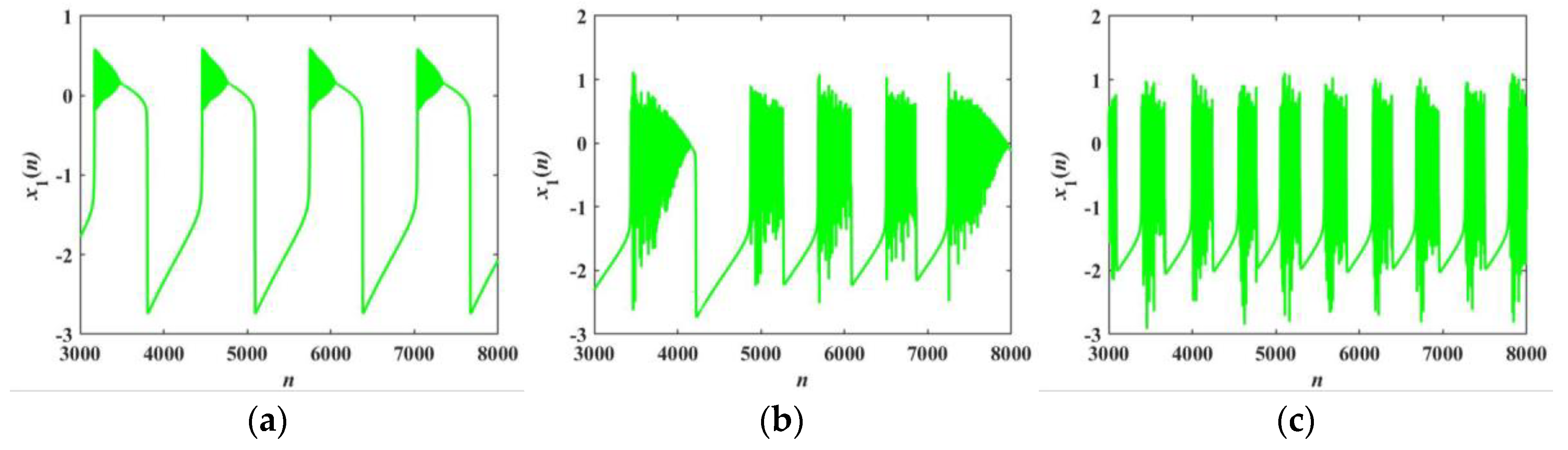
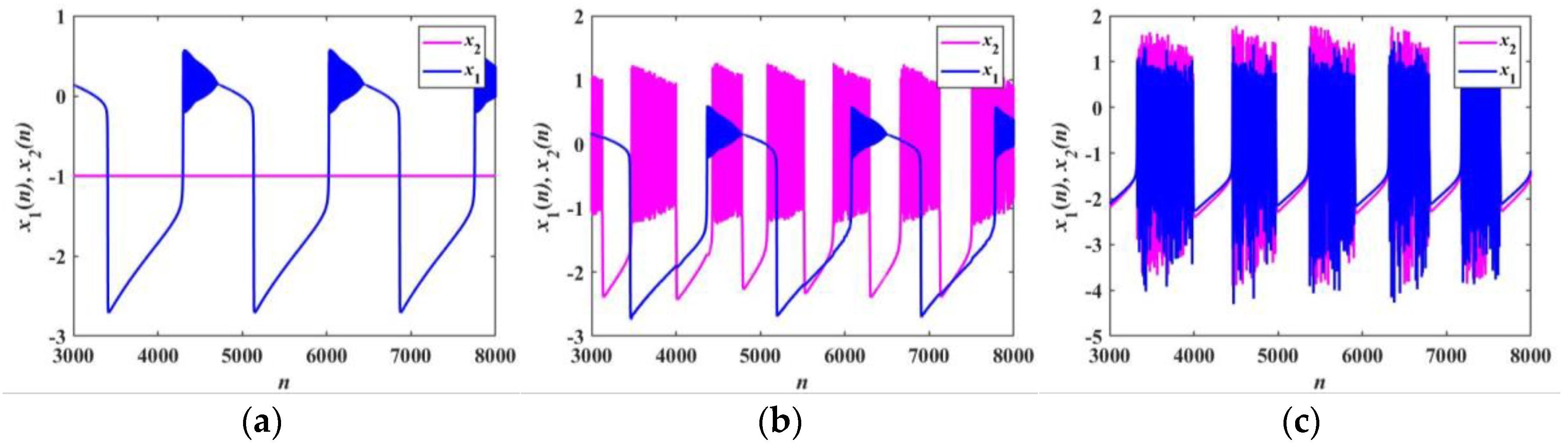
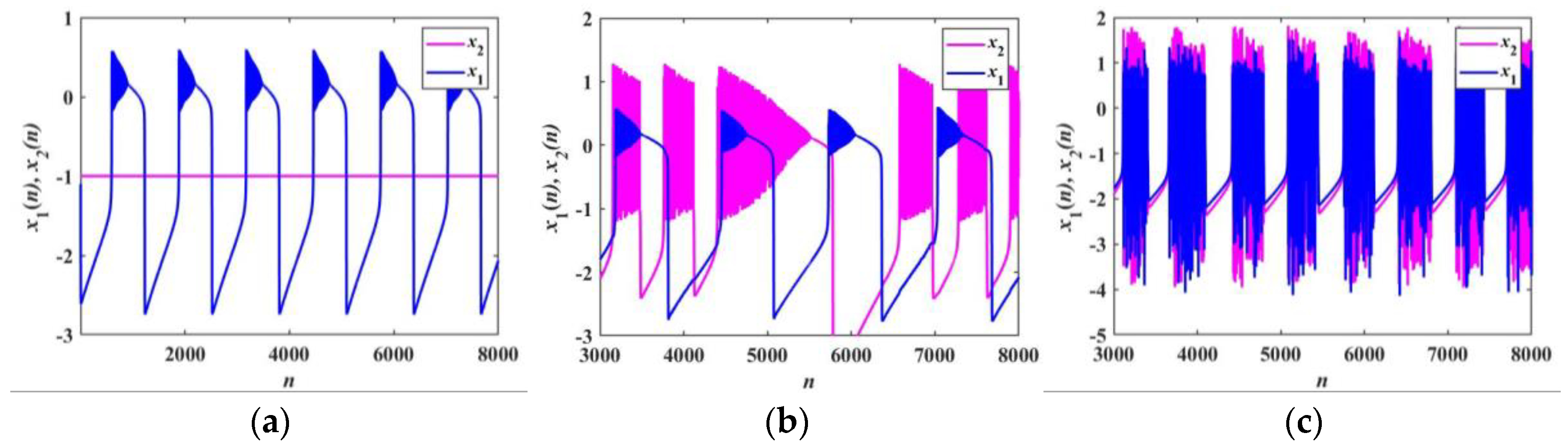
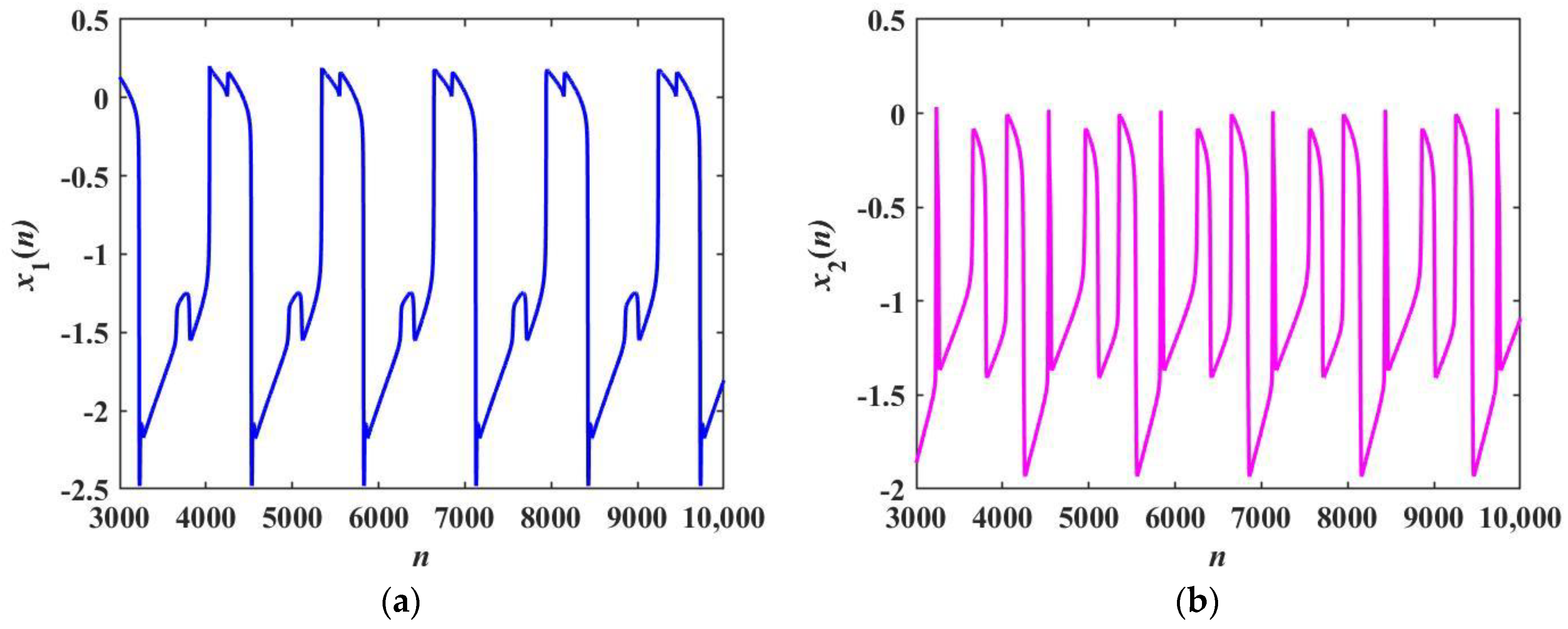
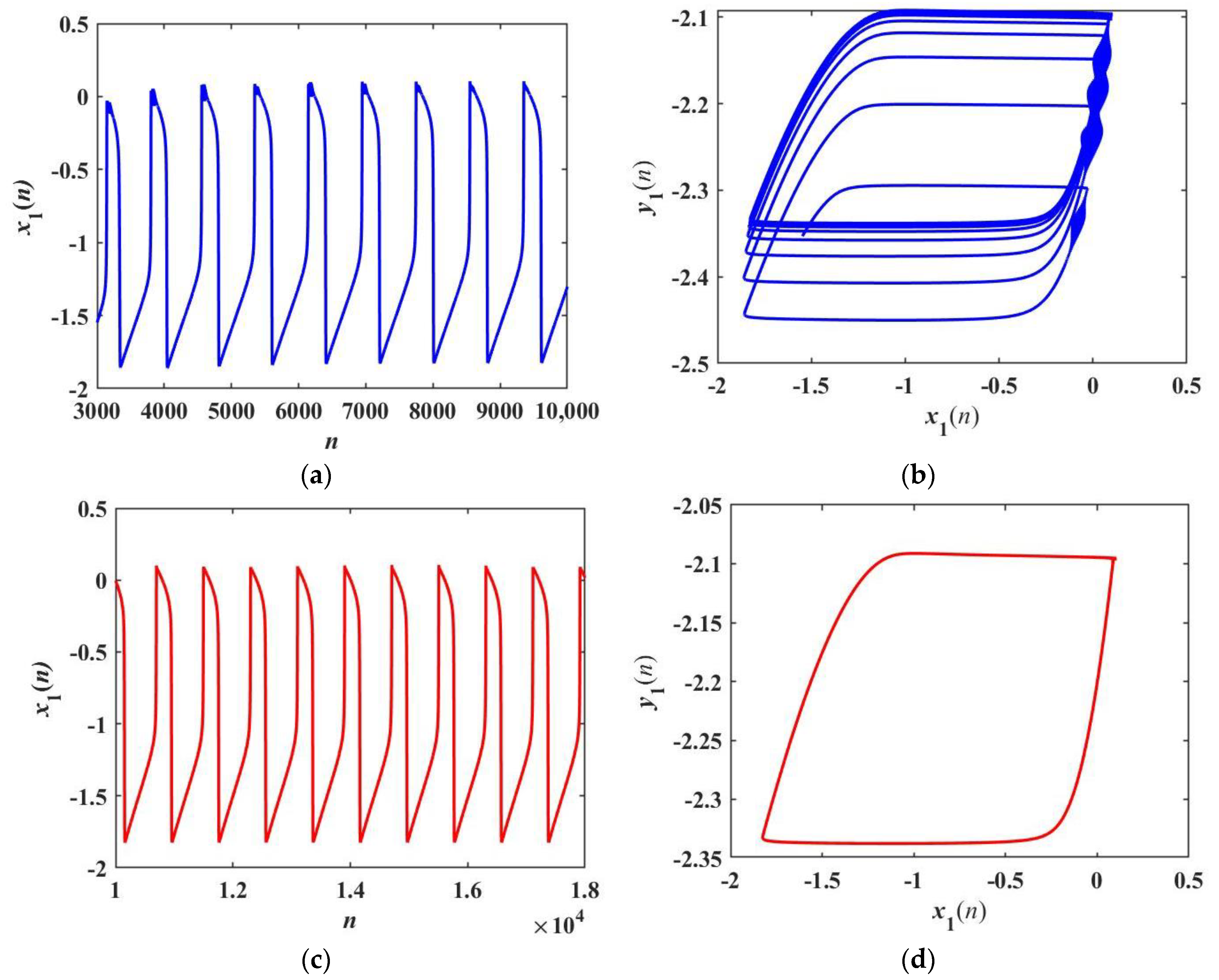
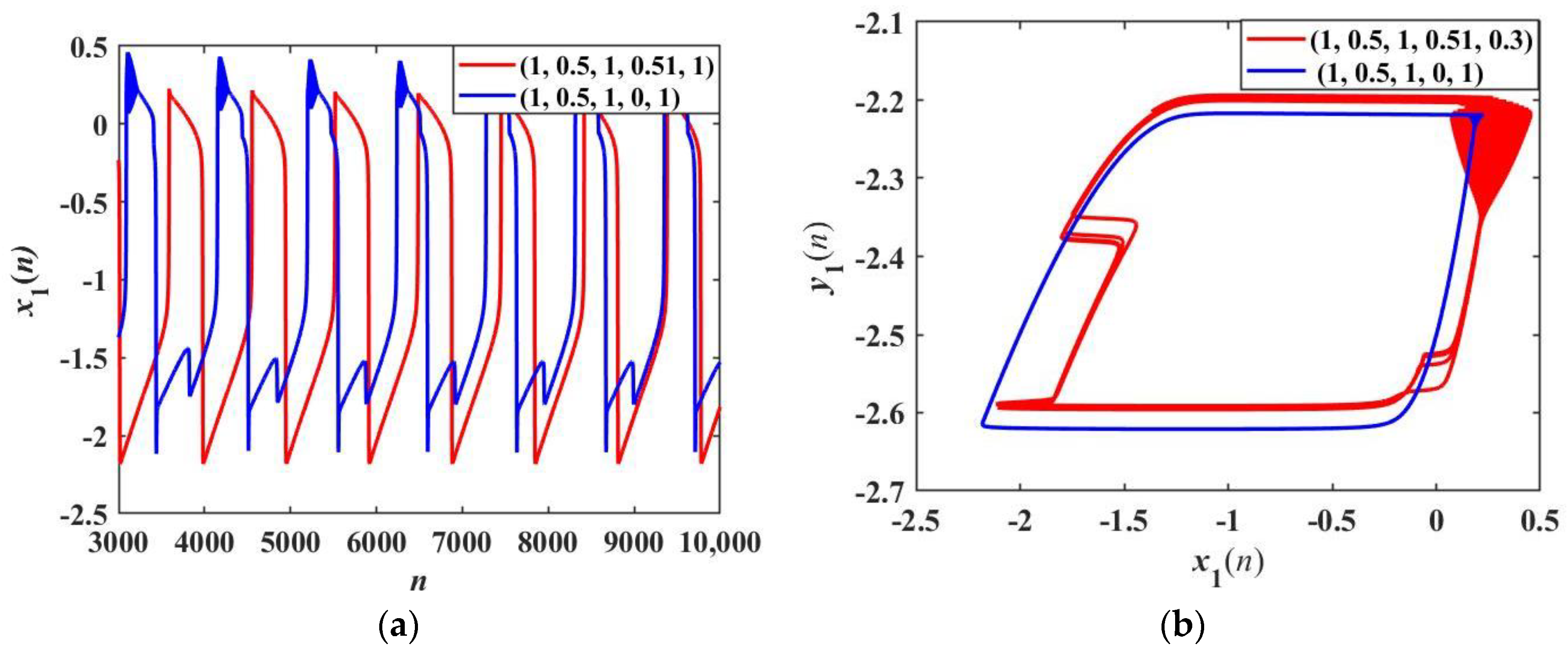
4. Multistability and Novel Firing Patterns
4.1. Transition of Firing Patterns
4.2. Novel Firing Patterns
4.3. Transient Chaotic Firing Behavior
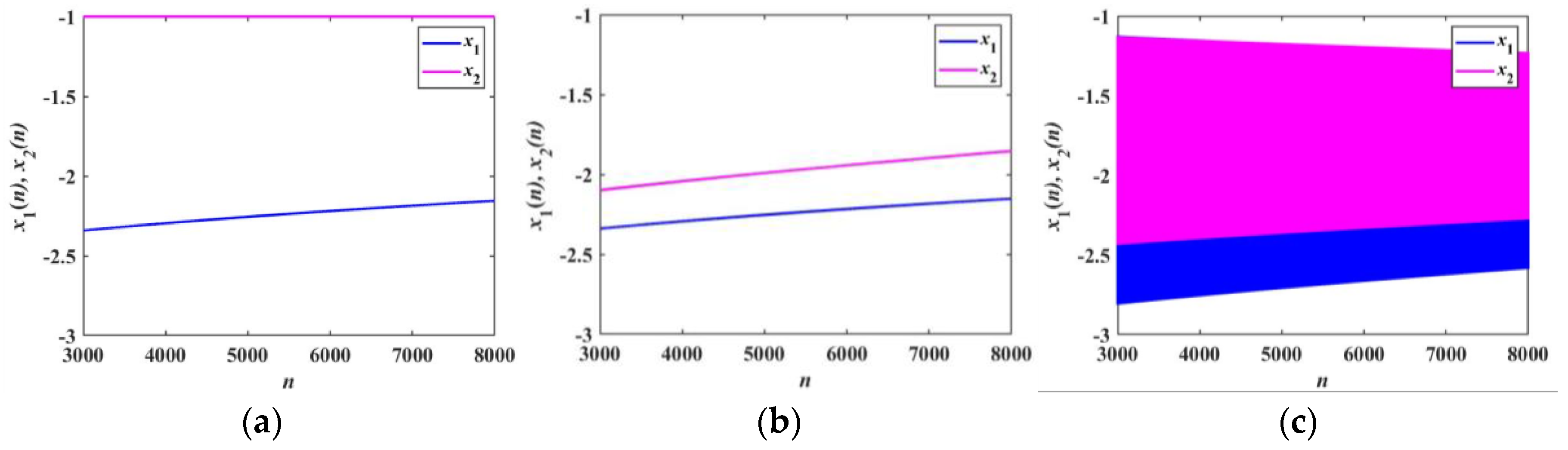
4.4. Coexisting Firing Patterns
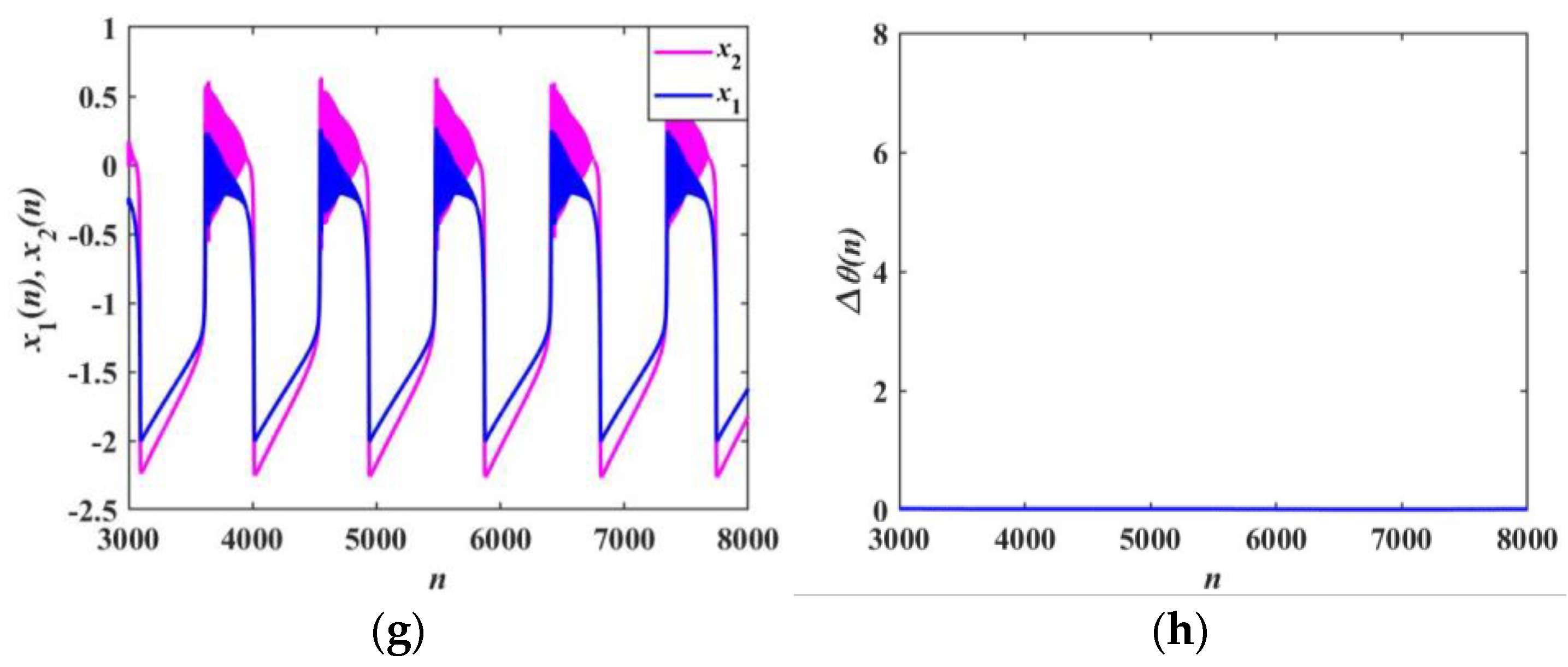
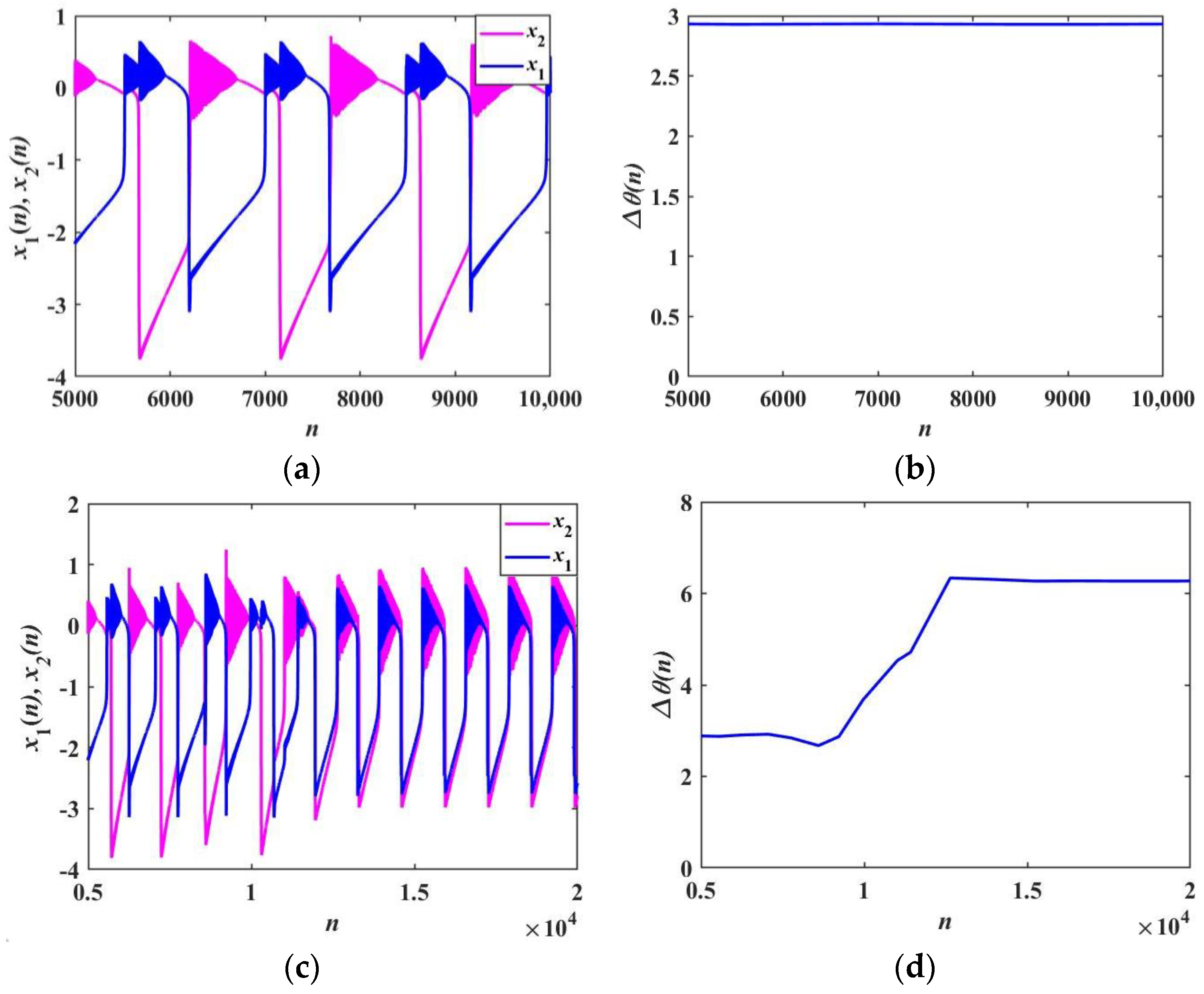
5. Phase Synchronization and Synchronization Transition
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Zamora-Lopez, G.; Moreno, Y.; Arenas, A. From Modular to Centralized Organization of Synchronization in Functional Areas of the Cat Cerebral Cortex. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Spinks, R.; Jackson, A.; Lemon, R.N. Synchronization in monkey motor cortex during a precision grip task. I. Task-dependent modulation in single-unit synchrony. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloni, L.; Molina, C.; Pena, M.; Torres, D.; Singer, W.; Rodriguez, E. Synchronization of neural activity across cortical areas correlates with conscious perception. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.G.; Greening, S.G. Conscious perception of emotional stimuli: Brain mechanisms. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiruska, P.; Csicsvari, J.; Powell, A.D.; Fox, J.E.; Chang, W.-C.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Li, X.; Palus, M.; Bujan, A.F.; Dearden, R.W.; et al. High-Frequency Network Activity, Global Increase in Neuronal Activity, and Synchrony Expansion Precede Epileptic Seizures In Vitro. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5690–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamoulis, C.; Gruber, L.J.; Chang, B.S. Network dynamics of the epileptic brain at rest. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; Volume 2010, pp. 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, W. Zero-Hopf bifurcation analysis in an inertial two-neural system with delayed Crespi function. Eur. Phys. J. -Spec. Top. 2020, 229, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njitacke, Z.T.; Doubla, I.S.; Kengne, J.; Cheukem, A. Coexistence of firing patterns and its control in two neurons coupled through an asymmetric electrical synapse. Chaos 2020, 30, 023101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Gong, J. A Robust Predefined-Time Convergence Zeroing Neural Network for Dynamic Matrix Inversion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yan, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, J. Complex dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. Chaos 2022, 32, 073107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, J. A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Sun, K.; He, S. Firing patterns in a fractional-order FithzHugh–Nagumo neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 1807–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhikevich, E.M. Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F.; Timofeev, I.; Bazhenov, M. Oscillations in large-scale cortical networks: Map-based model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2004, 17, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, G.; Ibarz, B.; Sanjuan, M.A.F.; Aihara, K. Synchronization and propagation of bursts in networks of coupled map neurons. Chaos 2006, 16, 013113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Ibarz, B. Hybrid discrete-time neural networks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 5071–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A. A discrete Huber-Braun neuron model: From nodal properties to network performance. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q. Rulkov neural network coupled with discrete memristors. Netw.-Comput. Neural Syst. 2022, 33, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cao, H. Stability and chaos of Rulkov map-based neuron network with electrical synapse. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 20, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Cao, H. Stability and synchronization of coupled Rulkov map-based neurons with chemical synapses. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2016, 35, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cao, H. Complete synchronization of coupled Rulkov neuron networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 84, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cao, H. Synchronization of two identical and non-identical Rulkov models. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2016, 40, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Cao, H. Synchronization of Rulkov neuron networks coupled by excitatory and inhibitory chemical synapses. Chaos 2019, 29, 023129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, F.A.S.; Viana, R.L.; Reis, A.S.; Iarosz, K.C.; Caldas, I.L.; Batista, A.M. A network of networks model to study phase synchronization using structural connection matrix of human brain. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 496, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, S.; Ray, A.; Bera, B.K.; Ghosh, D. Synchronization and firing patterns of coupled Rulkov neuronal map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yan, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Multistable dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic radiation and dual bias currents. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ju, Z.; Ding, S.; Feng, C.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Electromagnetic induction effects on electrical activity within a memristive Wilson neuron model. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2022, 16, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, F. Brain-Like Initial-Boosted Hyperchaos and Application in Biomedical Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q.; Lin, H. Regulating memristive neuronal dynamical properties via excitatory or inhibitory magnetic field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Shen, H.; Yu, Q.; Kong, X.; Sharma, P.K.; Cai, S. Privacy Protection of Medical Data Based on Multiscroll Memristive Hopfield Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Mou, J.; Yan, H.; Cao, Y. A new class of Hopfield neural network with double memristive synapses and its DSP implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Min, F.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, B. Memristive electromagnetic induction effects on Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 2559–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Deng, Q.; Hong, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. A memristor-based circuit design and implementation for blocking on Pavlov associative memory. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14745–14761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Kong, X.; Mokbel, A.A.M.; Yao, W.; Cai, S. Complex Dynamics, Hardware Implementation and Image Encryption Application of Multiscroll Memeristive Hopfield Neural Network With a Novel Local Active Memeristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 70, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yi, Z. A memristor-based associative memory circuit considering synaptic crosstalk. Electron. Lett. 2022, 58, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, G.; Nath, S.K.; Iu, H.H.-C.; Nandi, S.K.; Elliman, R.G. Universal Dynamics Analysis of Locally-Active Memristors and Its Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 69, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; You, Z.; Liang, X.; Li, X. A Memristor-Based Colpitts Oscillator Circuit. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M. Fractional-Order Heterogeneous Neuron Network With Hr Neuron and Fhn Neuron Based on Coupled Locally-Active Memristors: Super Coexisting Firing Behaviors, Bursting Behaviors and its Application. Bursting Behav. Its Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M. Initial-induced coexisting and synchronous firing activities in memristor synapse-coupled Morris-Lecar bi-neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 99, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H. A memristive synapse control method to generate diversified multi-structure chaotic attractors. IEEE Trans. Comput. -Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Cai, S. Firing mechanism based on single memristive neuron and double memristive coupled neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 3807–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liao, X. Synchronization and chaos in coupled memristor-based FitzHugh-Nagumo circuits with memristor synapse. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 75, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Bao, B. Memristor synapse-coupled memristive neuron network: Synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Min, F.; Cheng, Y.; Dou, Y. Dynamical analysis in dual-memristor-based FitzHugh-Nagumo circuit and its coupling finite-time synchronization. Eur. Phys. J. -Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, C. Organization of anti-phase synchronization pattern in neural networks: What are the key factors? Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Z. Design and analysis of a three-dimensional discrete memristive chaotic map with infinitely wide parameter range. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 065210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Lai, C. Design and Implementation of a New Hyperchaotic Memristive Map. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2331–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Xing, G.; Deng, Y. Flexible cascade and parallel operations of discrete memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 166, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Du, J. Discretized locally active memristor and application in logarithmic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, K. A novel discrete memristive chaotic map. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. A locally active discrete memristor model and its application in a hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 2935–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; An, M.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.-C. Two-variable boosting bifurcation in a hyperchaotic map and its hardware implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 111, 1871–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, S.; Sun, K. Parameter identification for discrete memristive chaotic map using adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhan, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Peng, Y. Discrete Memristor and Discrete Memristive Systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Lai, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Hidden coexisting hyperchaos of new memristive neuron model and its application in image encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 158, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hua, Z.; Liu, W.; Bao, B. Discrete memristive neuron model and its interspike interval-encoded application in image encryption. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Xiong, K.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y. Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-M.; Wang, C.-H.; Deng, Q.-L.; Xu, C. The dynamics of a memristor-based Rulkov neuron with fractional-order difference. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, T.; Feng, C.-T.; Bao, H.; Wu, H.-G.; Bao, B.-C. Continuous non-autonomous memristive Rulkov model with extreme multistability. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 128702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y. Application of discrete memristors in logistic map and Hindmarsh-Rose neuron. Eur. Phys. J. -Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 3209–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Sah, M.P.; Kim, H.; Chua, L.O. Three Fingerprints of Memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 3008–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, Q.; Sun, Y. A Multi-Stable Memristor and its Application in a Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3472–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Everything You Wish to Know About Memristors But Are Afraid to Ask. Radioengineering 2015, 24, 319–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. Local activity is the origin of complexity. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2005, 15, 3435–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F. Regularization of synchronized chaotic bursts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zeng, Z. Global Mittag-Leffler Stabilization of Fractional-Order Memristive Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-L.; Park, J.H.; Wu, G.-C.; Mo, Z.-W. Variable-order fractional discrete-time recurrent neural networks. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 370, 112633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, K.; Wang, H. Complexity Analysis and DSP Implementation of the Fractional-Order Lorenz Hyperchaotic System. Entropy 2015, 17, 8299–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C. Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7010082
Ma M, Lu Y, Li Z, Sun Y, Wang C. Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor. Fractal and Fractional. 2023; 7(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Minglin, Yaping Lu, Zhijun Li, Yichuang Sun, and Chunhua Wang. 2023. "Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor" Fractal and Fractional 7, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7010082
APA StyleMa, M., Lu, Y., Li, Z., Sun, Y., & Wang, C. (2023). Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor. Fractal and Fractional, 7(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7010082










