Filler Migration after Facial Injection—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
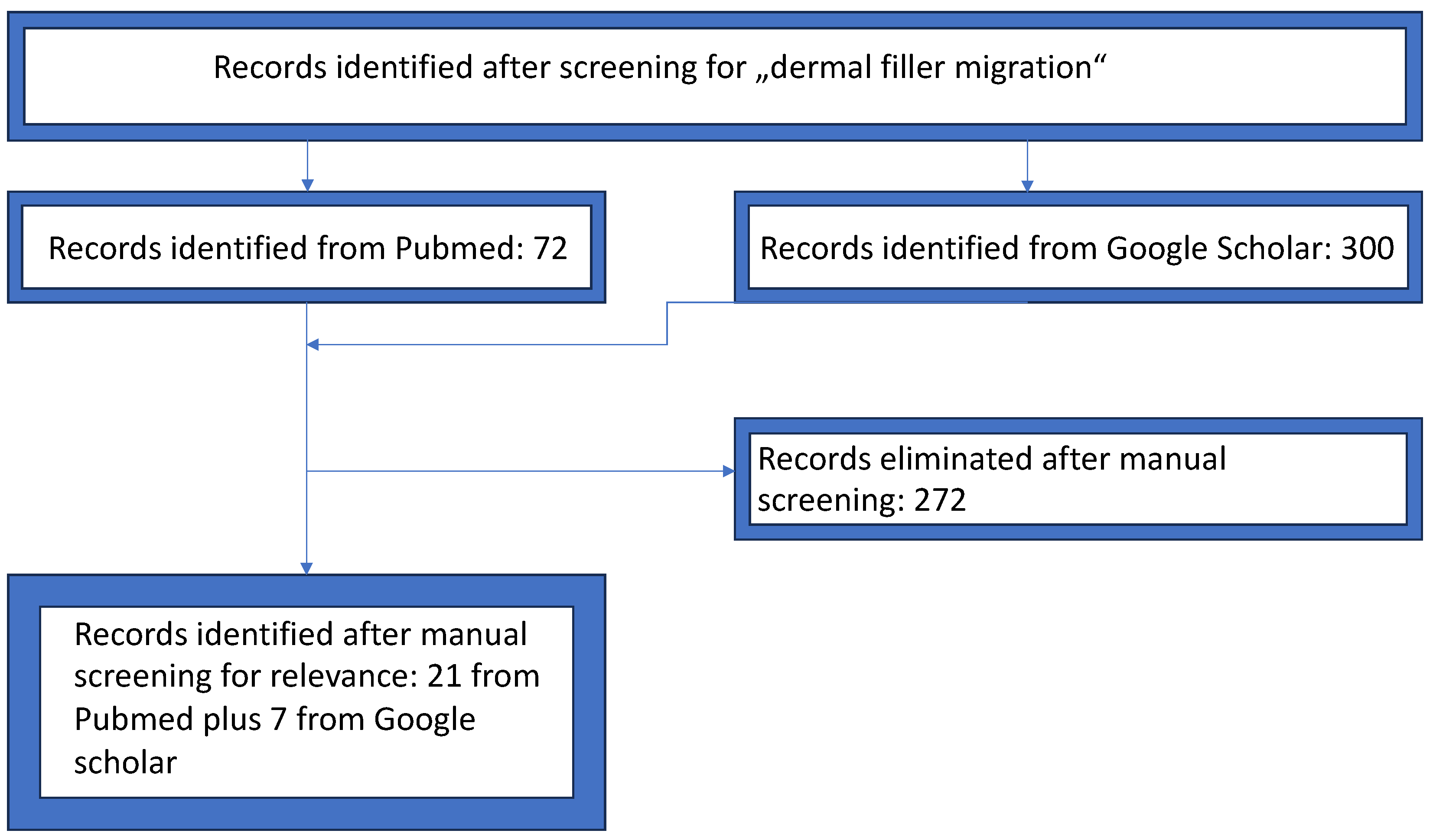
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, B.; Ramirez, M.; Ranjit-Reeves, R.; Baumann, L.; Woodward, J. Noncollagen dermal fillers: A summary of the clinical trials used for their FDA approval. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.H.; Beynet, D.P.; Gharavi, N.M. Overview of deep dermal fillers. Facial Plast. Surg. 2019, 35, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: Safety and efficacy for the treatment of wrinkles, aging skin, body sculpturing and medical conditions. Clin. Med. Rev. Ther. 2011, 3, 107–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Ryu, S.I.; Kim, N.Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Ro, Y.S.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, J.E. New classification of late and delayed complications after dermal filler: Localized or generalized? J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2020, 22, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, J.; Walker, L.; Ali, S.R.; Whitaker, I.S. An illustrated anatomical approach to reducing vascular risk during facial soft tissue filler administration—A review. JPRAS Open 2022, 36, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Facial vascular danger zones for filler injections. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, L.; Requena, C.; Christensen, L.; Zimmermann, U.S.; Kutzner, H.; Cerroni, L. Adverse reactions to injectable soft tissue fillers. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolotskiy, R.; Oleck, N.C.; Hatzis, C.M.; Paskhover, B. Adverse events associated with aesthetic dermal fillers: A 10-year retrospective study of FDA data. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 2018, 35, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadari, H.; Krompouzos, G.; Kassir, M.; Gupta, M.; Wollina, U.; Katsambas, A.; Lotti, T.; Jafferany, M.; Navarini, A.A.; Berg, R.V.; et al. Complication of soft tissue fillers: Prevention and management review. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2020, 19, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelke, L.W.; Van Den Elzen, H.J.; Canninga, M.; Neumann, M.H.A. Complications after treatment with polyalkylimide. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35 (Suppl. 2), 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, Z.; Trikha, S.; Etemad-Shahidi, S.; Virmani, S.; Denning, C.; Al-Mukhtar, Y.; Rennie, C.; Penny, A.; Jamali, Y.; Parrish, N.C.E. Case series and review on managing abscesses secondary to hyaluronic acid soft tissue fillers with recommended management guidelines. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Balassiano, L.K.A.; Cavallieri, F.A.; Munhoz, G.; Tembra, M.F.; Ramos-E-Silva, M. Not so “happy bump”: A complication due to hyaluronic acid. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6308–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.; Lopez-Gehrke, I.; Villarica-Hayano, W.; Suwanchinda, A.; Galadari, H. Nonscarring alopecia after temporal lifting technique with dermal fillers. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 37, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.; Shiuey, E.; Briceño, C.A.; Lee, V. Acute diplopia after glabellar hyaluronic acid filler injection. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2023, 31, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colon, J.; Mirkin, S.; Hardigan, P.; Elias, M.J.; Jacobs, R.J. Adverse events reported from hyaluronic acid dermal filler injections to the facial region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soares, D.; Bowhay, A.; Blevins, L.W.; Patel, S.M.; Zuliani, G.F. Patterns of filler-induced facial skin ischemia: A systematic review of 243 cases and introduction of the FOEM scoring system and grading scale. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 151, 592e–608e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.M.; Mueller, M.A.; Hu, A.C.; Evans, G.R.D. Asymptomatic stroke after hyaluronic acid filler injection: Case report and literature review. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP602–NP608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convery, C.; Davies, E.; Murray, G.; Walker, L. Delayed-onset nodules (DONs) and considering their treatment following use of hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2021, 14, E59–E67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trinh, L.N.; McGuigan, K.C.; Gupta, A. Delayed complications following dermal filler for tear trough augmentation: A systematic review. Facial Plast. Surg. 2022, 38, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, J. Dizziness and pain after temporal augmentation with hyaluronic acid. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.K.; Maeng, M.M.; Khzam, R.A.; Dubovy, S.R.; Johnson, T.E. Recurrent periorbital edema associated with retained foreign body after filler injection. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 39, e30–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Xie, H.; Wang, G.; An, Y. Risk comparison of filler embolism between polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hyaluronic acid (HA). Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, C.; Lossos, C.; Ali, S.Z. Polymethylmethacrylate-induced foreign body reaction presenting as bilateral parotid lesions: A case report of dermal filler adverse reaction diagnosed on fine needle aspiration. Cytopathology 2023, 34, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland-Warmann, M.J. Hypersensitivity reaction to Hyaluronic Acid Dermal filler following novel Coronavirus infection—A case report. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.A.; Oliveira, L.Q.; Martelli-Júnior, H.; Pires, F.R.; Carvas, J.B.; Rogerio, V.E.; Rabelo, V.D.; Coletta, R.D. Adverse reactions to the injection of face and neck aesthetic filling materials: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2023, 28, e278–e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.; Nieto-Lopez, F.; Rueda-Carrasco, J. Lipoteichoic acid and molecular weight of hyaluronic acid could explain the late inflammatory response trigger by hyaluronic acid fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 5610–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Lee, J.J.; Patton, T.; Choudhary, S. Facial sclerosing lipogranuloma after self-injection of homemade tissue filler: An alarming new practice. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Álvarez, J.; Lebrón-Martín, J.A.; Fernández-Freire, L.R.; Dorado, T.Z.; Morillo, J.S.G. Cutaneous and ganglion sarcoidosis induced by polycaprolactone facial filler: A new expression of ASIA syndrome? Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 002652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mario, M.; Ettore, L.; Bernardi, S.; Becelli, R.; Filippo, G. Vascular complications with necrotic lesions following filler injections: Literature systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023; 101499, epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, N.W.M.; Dhar, A.; Cameron-Strange, A. The perils of penile enhancement: Case report of a fulminant penile infection. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasarnaksorn, W.; Thanyavuthi, A.; Prasertvit, P.; Rattanakuntee, S.; Jitaree, B.; Suwanchinda, A. Case series of tongue necrosis from vascular complications after chin augmentation with hyaluronic acid: Potential pathophysiology and management. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.M.; Matayoshi, S. Visual loss after aesthetic facial filler injection: A literature review on an ophthalmologic issue. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2022, 85, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Ng, C.Y. Vitiligo associated with polycaprolactone-based collagen stimulator filler. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 24, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Kollipara, R.; Hoss, E.; Goldman, M.P. Lower eyelid xanthelasma following hyaluronic acid filler injections to the tear troughs. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3190–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Buhren, B.A.; Bölke, E.; Philipp-Dormston, W.G.; Homey, B.; Schrumpf, H. Time- and dose-dependent effects of hyaluronidase on the degradation of different hyaluronan-based fillers in vitro. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 151, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, L.; Ulrich, F.; Raffoul, W.; Rossi, S.A. Management of a large quantity of permanent gluteal copolyamide fillers (Aqualift/Activegel): Literature review and algorithm. Aesthet. Surg. J. Open Forum. 2022, 4, ojac051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, A.; Staub, H.; Wollina, U. Hypercalcemia due to polymethylmethacrylate injections? (Literature review and case reports). Georgian Med. News. 2018, 282, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chayangsu, O.; Wanitphakdeedecha, R.; Pattanaprichakul, P.; Hidajat, I.J.; Evangelista, K.E.R.; Manuskiatti, W. Legal vs. illegal injectable fillers: The adverse effects comparison study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydenrych, I.; De Boulle, K.; Kapoor, K.M.; Bertossi, D. The 10-Point Plan 2021: Updated concepts for improved procedural safety during facial filler treatments. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 779–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltzer, A.; Geeroms, M.; Antoniazzi, E.; Giunta, G.; De Baerdemaeker, R.; Hendrickx, B.; Hamdi, M. The “ART” of facial filler injections: Avoid, recognize, and treat hyaluronic acid-induced complications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.H.; Fitzgerald, R.; Cox, S.E.; Butterwick, K.; Murad, M.H.; Humphrey, S.; Carruthers, J.; Dayan, S.H.; Donofrio, L.; Solish, N.; et al. Preventing and treating adverse events of injectable fillers: Evidence-based recommendations from the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Multidisciplinary Task Force. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magacho-Vieira, F.N.; Santana, A.P. Displacement of hyaluronic acid dermal filler mimicking a cutaneous tumor: A case report. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Di Carmine, M.; Marchetti, M.; Lorusso, F.; Amore, R.; Amuso, D. Dermal cosmetic migration after lip augmentation procedure: Clinical management and histological analysis in a case report with review of the literature. Surgeries 2023, 4, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, H.; Masarwa, D.; Sapir, S.; Kaiserman, I. Subconjuctival mobile mass after hyaluronic acid filler injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 30, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed-Azzam, S.; Burkat, C.; Mukari, A.; Briscoe, D.; Joshi, N.; Scawn, R.; Alon, E.; Hartstein, M. Filler migration to the orbit. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP559–NP566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almukhtar, R.; Fitzgerald, R.; Cotofana, S.; Fabi, S. Migration of hyaluronic acid–based soft tissue filler from the temples to the cheeks—An anatomic explanation. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 1526–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, S.C.; Gabbard, R.D.; Meador, A.G.; Stoner, A.E.; Klippenstein, K.A.; Wesley, R.E. A case of orbital granuloma secondary to dermal filler injection. Cureus 2021, 13, e20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorowski, M.; Nelke, K.; Łuczak, K.; Hałoń, A. Filler migration and florid granulomatous reaction to hyaluronic acid mimicking a buccal tumor. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, e78–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlHarbi, Z.A.; Alkatan, H.M.; Alsuhaibani, A.H. Long-term outcomes of surgically removed migrated polyalkylimide (Bio-Alcamid) filler to the periorbital area. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 33, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, R.; Mukari, A.; Krausz, J.; Hartstein, M.E.; Azzam, S.H. Orbit mass secondary to migration of dermal hyaluronic acid filler. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi-Naeini, B.; Faghihi, G.; Shahmoradi, Z.; Saffaei, A. Filler migration and extensive lesions after lip augmentation: Adverse effects of polydimethylsiloxane filler. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chiang, C.P.; Wu, B.Y.; Gao, H.W. Filler migration to the forehead due to multiple filler injections in a patient addicted to cosmetic fillers. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2017, 19, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Delayed onset filler complication: Two case reports and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, W.J. A case of the migration of hyaluronic acid filler from nose to forehead occurring as two sequential soft lumps. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.R.; Stoica, B. Filler migration: A number of mechanisms to consider. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 31, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, O.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Clinical implications of ultrasound artifacts in the cervicofacial area following injection of permanent facial fillers. J. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 42, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippaudo, F.R.; Di Girolamo, M.; Mattei, M.; Pucci, E.; Grippaudo, C. Diagnosis and management of dermal filler complications in the perioral region. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J. Pseudocyst of the neck after facial augmentation with liquid silicone injection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, e474–e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, Y.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Periorbital lipogranuloma related to filler migration: A rare complication of facial fillers. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadouch, J.A.; Nolthenius, C.J.T.; Kadouch, D.J.; van der Woude, H.J.; Karim, R.B.; Hoekzema, R. Complications after facial injections with permanent fillers: Important limitations and considerations of MRI evaluation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014, 34, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrabi-Farahani, S.; Lerman, M.A.; Noonan, V.; Kabani, S.; Woo, S.-B. Granulomatous foreign body reaction to dermal cosmetic fillers with intraoral migration. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, S.; Lawrence, N.; Donofrio, L.; Cox, S.E. Delayed migration of hyaluronic acid fillers: A new complication? Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathoo, N.A.; Rassmussen, S.; Dolman, P.J.; Rossman, D.W. Periocular mass lesions secondary to dermatologic fillers: Report of 3 cases. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 49, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Mehta, P.; Adesanya, O.; Ahluwalia, H.S. Migrated periocular filler masquerading as arteriovenous malformation: A diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, J.M.; High, W.A.; Goldenberg, G. Evidence of calcium hydroxylapatite migration: Distant nodule formation in the setting of concurrent injection with nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, e65–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.H.; Malhotra, R. Long-term orbitofacial complications of polyalkylimide 4% (Bio-Alcamid). Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 25, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Sung, M.S.; Kim, N.J.; Choung, H.K.; Khwarg, S.I. Eyelid mass secondary to injection of calcium hydroxylapatite facial filler. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 24, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, K.R. Radiesse nodule of the lips from a distant injection site: Report of a case and consideration of etiology and management. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2007, 6, 846–847. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, R.B.; Hage, J.J.; van Rozelaar, L.; Lange, C.A.; Raaijmakers, J. Complications of polyalkylimide 4% injections (Bio-Alcamid): A report of 18 cases. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2006, 59, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda-Lari, A. Augmentation of the malar area with polyacrylamide hydrogel: Experience with more than 1300 patients. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2008, 28, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, A.; Gray, M.L.; Westra, W.H.; Teng, M.S.; Rosenberg, J.D. Dermal filler presenting as parotid mass: A case report. Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 15, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syunyaeva, Z.; Kahnert, K.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Huber, R.M.; Tufman, A. Dermal filler injections mimic tumor activity during immune checkpoint inhibition. Respiration 2018, 95, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, K.; Prabhu, I.S.; Bradley, K.M. Fluorodeoxyglucose activity associated with a cosmetic poly-L-lactide filler: A potential confounder on positron emission tomography and computed tomography. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginat, D.T.; Schatz, C.J. Imaging features of midface injectable fillers and associated complications. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. THP-1 cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Jennen, D.; Keizers, P.H.J.; Hodemaekers, H.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; Bakker, F.; Schwillens, P.; van Herwijnen, M.; Jetten, M.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; et al. Evaluation of adverse effects of resorbable hyaluronic acid fillers: Determination of macrophage responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennen, D.G.J.; van Herwijnen, M.; Jetten, M.; Vandebriel, R.J.; Keizers, P.; Geertsma, R.E.; de Jong, W.H.; Kleinjans, J.C.S. Transcriptomic analysis in human 3D skin model injected with resorbable hyaluronic acid fillers reveals foreign body response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneke, E. Adverse effects of fillers. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, L.G.; Stolz, W.; Schroeder, J.A. Electron microscopic documentation of late changes in permanent fillers and clinical management of granulomas in affected patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35 (Suppl. 2), 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenblätter, M.; Ehrchen, J.; Varga, G.; Sunderkötter, C.; Heindel, W.; Roth, J.; Bremer, C.; Wall, A. In vivo optical imaging of cellular inflammatory response in granuloma formation using fluorescence-labeled macrophages. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christensen, J.M.; Brat, G.A.; Johnson, K.E.; Chen, Y.; Buretta, K.J.; Cooney, D.S.; Brandacher, G.; Lee, W.P.; Li, X.; Sacks, J.M. Monocytes loaded with indocyanine green as active homing contrast agents permit optical differentiation of infectious and non-infectious inflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Filler, T. Static and dynamic anatomy of the face, in particular eyebrows, eyelids and lips. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2022, 56, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Master, M.; Roberts, S. Long-term MRI follow-up of hyaluronic acid dermal filler. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2022, 10, e4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Correction of tear trough deformity by hyaluronic acid soft tissue filler placement inferior to the lateral orbital thickening. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruglikov, I.; Trujillo, O.; Kristen, Q.; Isac, K.; Zorko, J.; Fam, M.; Okonkwo, K.; Mian, A.; Thanh, H.; Koban, K.; et al. The facial adipose tissue: A revision. Facial Plast. Surg. 2016, 32, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranges, C.M.; Brucato, D.; Schaefer, D.J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Harder, Y. Complications of nonpermanent facial fillers: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2021, 9, e3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Tran, T.; Cibulas, A.T.; Warden, D.; Danger, F.J.; Scherer, K.; Wasyliw, C. Filler migration and granuloma formation after gluteal augmentation with free-silicone injections. Cureus 2018, 10, e3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, H.L.; Wang, I.; Meehan, S.; Sanchez, M.; Smith, G.P. Gluteal silicone injections leading to extensive filler migration with induration and arthralgia. Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 21, 13030/qt4xf2m886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, I.S.; Song, Y.S.; Choi, K.U.; Ahn, H.Y. Distant migration of gel filler: Imaging findings following breast augmentation. Skeletal. Radiol. 2022, 51, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.V.; Urman, D.S.; Cabral, E.S.; Shim, E.K.; Bennett, R.G. Hyaluronic acid filler incidentally found during Mohs micrographic surgery: Observations in 36 patients regarding skin depth, degradation size, and estimated persistence time. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzany, B.; Becker-Wegerich, P.; Bachmann, F.; Erdmann, R.; Wollina, U. Hyaluronidase in the correction of hyaluronic acid-based fillers: A review and a recommendation for use. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliyeva, G.; Huayllani, M.T.; Kraft, C.; Lehrman, C.; Kraft, M.T. Allergic complications of hyaluronidase injection: Risk factors, treatment strategies, and recommendations for management. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.; Wollina, U.; Machado, D.; Marionwic, D. Laser in the treatment of granulomas on the nose produced by polymethylmethacrylate: A case series. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A.; Wollina, U. Polymethylmethacrylate-induced nodules of the lips: Clinical presentation and management by intralesional neodymium: YAG laser therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Hu, J.; Chai, H. High-frequency ultrasound of facial filler materials in the nasolabial groove. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, H.; Su, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Dou, M.; Hu, J. High-frequency ultrasound imaging findings of different mental injectable soft tissue fillers. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelke, L.W.; Cassuto, D.; Velthuis, P.; Wortsman, X. Nomenclature proposal for the sonographic description and reporting of soft tissue fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.G.; Jardim, L.C.; Schuch, L.F.; Silveira, F.M.; Wagner, V.P.; Pires, F.R.; Santos, J.N.D.; Martins, M.D. Foreign body reactions related to orofacial esthetic fillers: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Qi, Z. The histologic reaction and permanence of hyaluronic acid gel, calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres, and extracellular matrix bio gel. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Adverse Events | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Abscess | Needs microbial confirmation and identification of responsible microorganisms, treatment mostly surgical | [11] |
| “Angry red bump” | Indurated painful, petrified nodule or plaque, may occur within the first month after injection or later | [12] |
| Alopecia, non-scarring | After temporal injection | [13] |
| Acute diplopia | Vascular compromise after temporal injection, severe pain | [14] |
| Bruising | More often around the eyes | [15] |
| Cerebral infarction and stroke | Most common after accidental injection in the ophthalmic angiosome | [16,17] |
| Delayed-onset nodules | Various pathologies for inflammatory to infectious or filler migration | [18] |
| Discoloration | More often seen around the eyes, sometimes due to Tyndall effect, sometimes due to post-inflammatory pigmentary changes | [19] |
| Dizziness and pain | Vascular compromise after temporal injection, severe pain | [20] |
| Edema, recurrent | Inflammatory granulomatous reaction | [21] |
| Erythema | Mostly temporary, common | [15] |
| Filler embolism | Risk depending on anatomical area, filler volume, and type | [22] |
| Foreign body granuloma | Needs histologic confirmation, may be delayed for years, can be due to filler migration | [23] |
| HA—hypersensitivity | Seen occasionally after SARS-CoV-2 infection | [24] |
| Inflammatory granuloma | Needs histologic confirmation, may be delayed for years, can be due to filler migration | [25] |
| Infectious granuloma | Needs histologic and microbial confirmation | [26] |
| Lipogranuloma | Needs histologic confirmation, can be delayed for years | [27] |
| Sarcoidosis | Reported after polycaprolactone injection | [28] |
| Soft tissue necrosis | Vascular compromise by embolization or extravascular pressure on blood vessels | [29] |
| Soft tissue infection and sepsis | Unmeet hygienic standards, contaminated filler material | [30] |
| Tongue necrosis | After injection into the chin, vascular compromise | [31] |
| Visual loss | Most often after injection into glabella or nose with acute ocular pain, lid ptosis, and ophthalmoplegia due to vascular compromise | [32] |
| Vitiligo | Reported after polycaprolactone injection | [33] |
| Xanthelasma | Mostly seen on eyelids after multiple injections over time | [34] |
| Ref. | Patient | Filler | Clinical Findings | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forehead and glabella | ||||
| [64] | 52-y; f | Polylakylimide, 10 y | Swelling of left brow, temple, and glabella | Surgery |
| after injection into the | ||||
| glabella | ||||
| Tempel | ||||
| [46] | 34-y, f | HA, 2 weeks after | Bipolar buccal masses | Hyaluronidase |
| temporal injection | ||||
| Nose | ||||
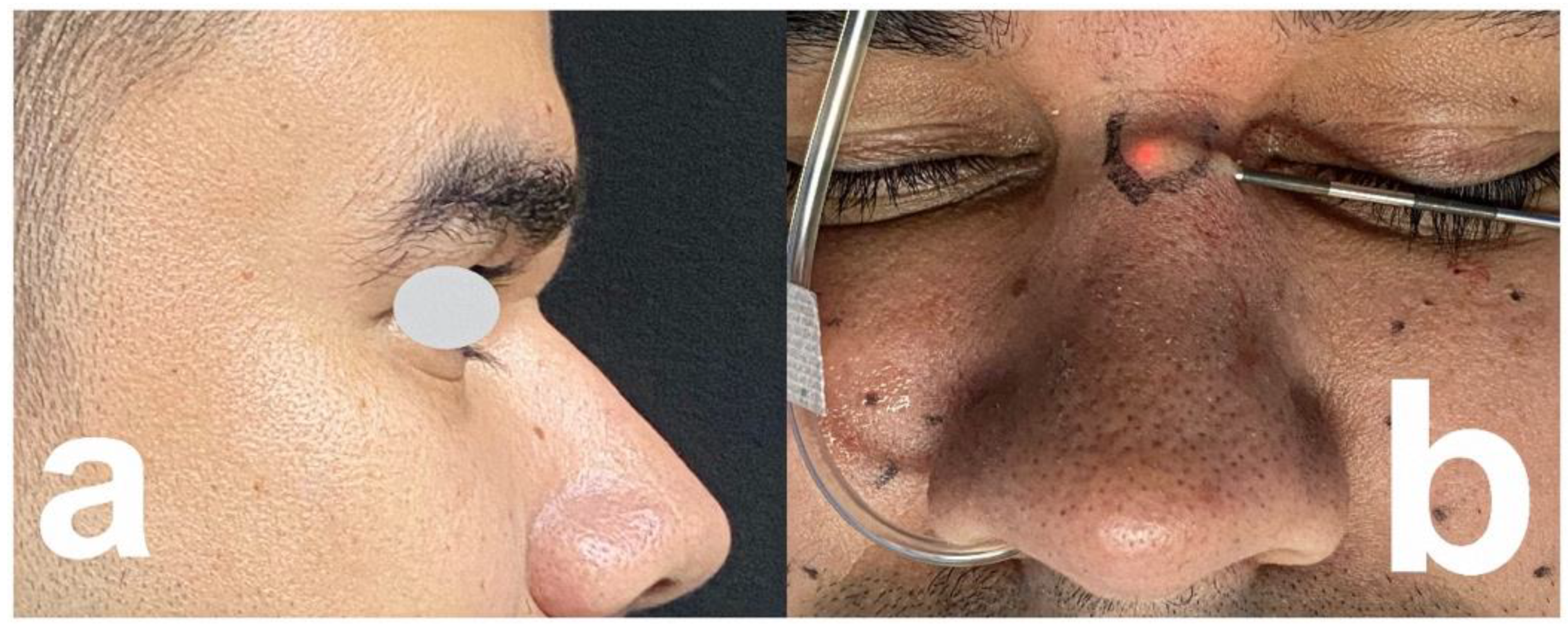
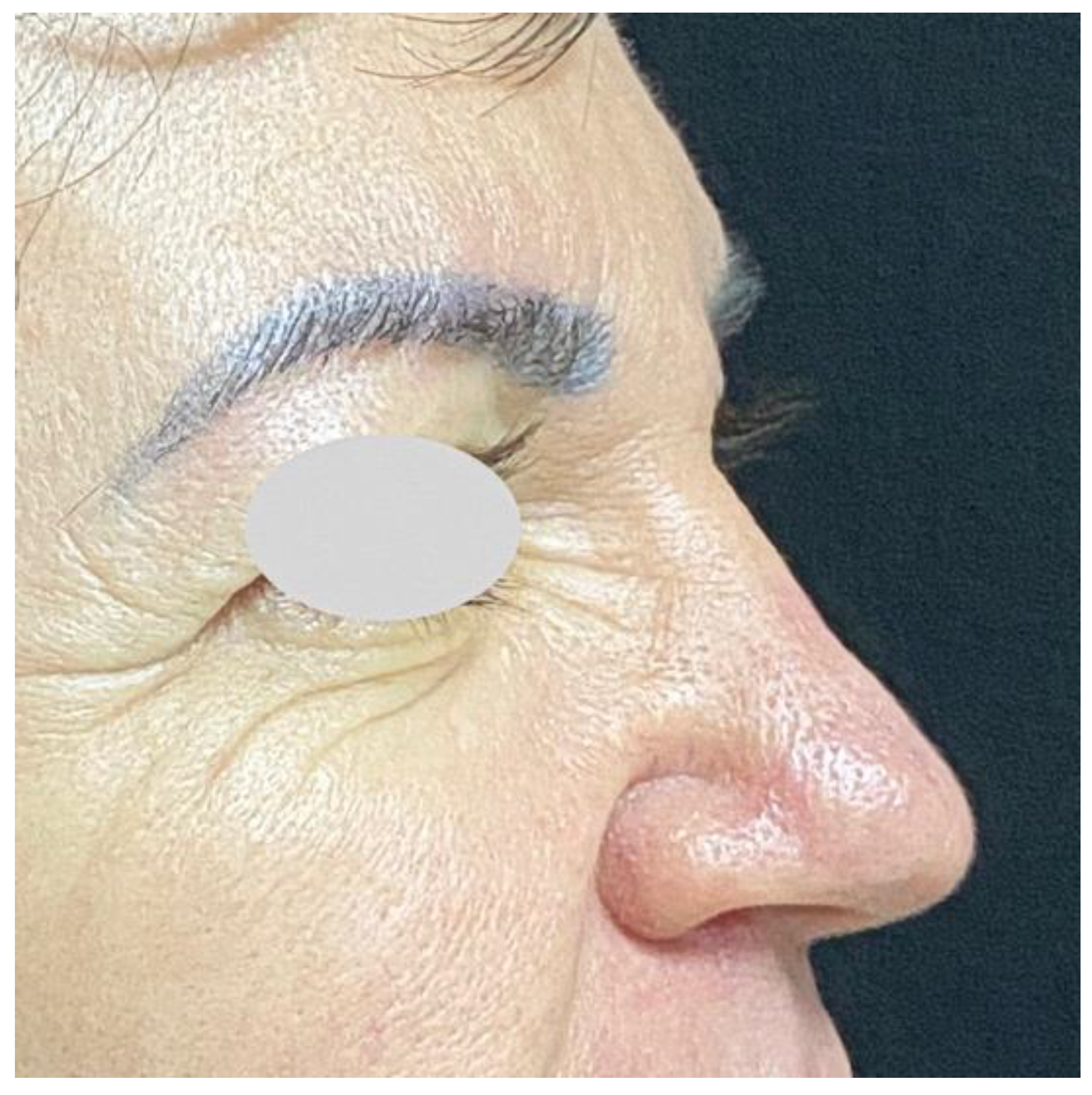
| [42] | 71-y, f | HA, 10 months ago, | 15 mm tumor on the dorsolateral nasal wall | Needle puncture and |
| right in the nasal radix | extrusion | |||
| [54] | 33-y, f | HA, 16 y after injection | Bean-sized mass on the forehead (2×) | Surgery |
| into the nose | ||||
| [67] | 37-y, f | CaH, 3 days after | 6 × 2 cm measuring mass of the left eyebrow and | Surgery |
| injection into the nose | upper eyelid | |||
| Periocular region | ||||
| [50] | 63-y, f | HA, 1 year after | Palpable masses in the right anterior superior orbit, | Surgical excision |
| Injection into forehead | mild lid swelling | |||
| and lateral eyebrow | ||||
| [53] | 54-y, f | Unknown filler, 7 y | Right upper eyelid nodule | Surgery |
| after injection in the | ||||
| lower eyelids | ||||
| [62] | 48–56-y, 3 f | HA, 6 months to 5 y | Bluish nodules with a Tyndall effect on lower | Surgery |
| after correction of tear | eyelids | |||
| trough | ||||
| Cheeks | ||||
| [44] | 41-y, f | HA, 2 weeks ago, on | Subconjunctival nodule on the left eye | Incision and extrusion |
| zygomatic protrusion | ||||
| [47] | 57-y, f | HA, 3 y after injection | Right lower eyelid mass | Surgery |
| In the zygomatic area | ||||
| Nasolabial fold | ||||
| [61] | 48–71-y, 5 f | CaH, 2–12 months | Intraoral nodules (upper lip mucosa and | Unspecified |
| after injection into | vestibulum oris) | |||
| nasolabial folds and | ||||
| perioral region | ||||
| [63] | 86-y, m | Polyalkylimide, | Plaques of the left lower eyelid | Biopsy |
| several months ago | ||||
| into the nasolabial fold | ||||
| 46-y, 48-y, | HA, after 1 and 6 y | Swelling along the lower orbital rim, swelling of | Biopsy | |
| f | after injection into the | the right lower eyelid | ||
| nasolabial fold | ||||
| [65] | 52-y, f | CaH, 1 y after inject- | Inflammatory nodule of vermillion border of the | Biopsy |
| ion into nasolabial | right upper lip | |||
| fold | ||||
| Lips | ||||
| [43] | 34-y, f | HA, 3 months after | 2 cm mobile mass of the right cheek | Surgery |
| lip augmentation | ||||
| [51] | 35-y, f | PDMS, 9 months after | Massive edema of face and neck, inflammation, | Corticosteroids |
| injection into the lip | nodular irregularities | with limited effect, | ||
| surgery | ||||
| [57] | 28–74 y, | Silicone, HA, PMMA, | The number of patients with migration only | Corticosteroids, |
| 26 f | polyalkylimide, | is unknown | antibiotics, | |
| Polyacrylamide | aspiration, | |||
| and others; few months | surgery | |||
| to 8 years after injection | ||||
| into the lips | ||||
| Multiple localizations | ||||
| [45] | 42–67 y, | HA, up to 10 y after | Eyelid swelling, lid mass, nasolacrimal duct | Surgery (6×), |
| 6 f, 1 m | injection into cheeks, | obstruction or neurologic deficit | hyaluronidase (1×) | |
| naso-labial folds or | ||||
| forehead | ||||
| [48] | 52-y, f | HA, 2 y ago, on lips | Buccal “tumor”, multiple granulomas with | Surgical excision |
| and naso-labial folds | inflammation | |||
| [49] | 24–52-y, | Polyalkylimide, 3–7 y | Lower eyelid swelling | Surgical excision, |
| 16 × f | after injection in the | 1 × relapse, 1 × lid | ||
| nasal bridge, temporal | retraction | |||
| region or cheeks | ||||
| [52] | 50-y, f | HA and PDLLA, | Palpable mass from the forehead to the nose | Biopsy, surgery |
| obsessive patient after | suggested | |||
| multiple middle and | ||||
| lower face treatments, | ||||
| 1 y after injections into | ||||
| the cheeks | ||||
| [55] | 44-y, 57y, | HA, 2 × after HA | 2 × eyelid swelling, 1 × non-inflammatory nodule | Hyaluronidase for HA, |
| 77-y; f | injection into the | of the left lateral canthus | surgery offered for HA | |
| nasolabial fold | +acrylamide | |||
| 1.5 and 4 y ago, | ||||
| 1 × HA + acrylamide | ||||
| particles for temporal | ||||
| augmentation 10 y ago | ||||
| [66] | 45-y, 48-y, | Polyalkylimide, 10 to | Irregularities and edema of periorbital area | Aspiration, surgery |
| 51-y, f | 245 months after | |||
| injection into | ||||
| 62-y, m | cheeks, nasolabial folds | |||
| or tear trough | ||||
| [68] | 59-y, f | CaH, 2 weeks after | Nodule of the right vermillion | Biopsy |
| injection into naso- | ||||
| labial folds and | ||||
| marionette lines | ||||
| * | 40-y, 55-y, | PDLLA, PMMA, | Subcutaneous nodules submandibular and on the | Surgery (plus |
| 64-y, f | silicon, injection in | neck, nodules on the nasal radix and dorsum, | intralesional | |
| lower and midface, | nodules in the mentolabial fold | Nd-YAG laser) | ||
| glabella, or mouth | ||||
| commissure between | ||||
| 4 months to 12 y ago | ||||
| 33-y, m | PMMA, injection into | Subcutaneous nodules on nasal radix | Intralesional | |
| glabella, several | Nd-YAG laser | |||
| months ago | ||||
| Unknown specific injection site(s) | ||||
| [56] | 60.8-y | Permanent fillers, | Migration into cervical lymph nodes in 59.6% | Not mentioned |
| (mean), | mean follow-up 16.6 y | |||
| 57 f | ||||
| [58] | 55-y, f | Silicone, after multiple | 6 × 8 cm large pseudocyst of the neck | Surgery, antibiotics |
| facial injections 50 to | ||||
| 60 y ago | ||||
| [59] | 74-y, f | Filler not identified, | Nodule of the left upper eyelid | Biopsy only |
| facial injection 3 y | probably silicone | |||
| ago | ||||
| [60] | 25–76 y, | PMMA, polyacryl- | 5 patients had clinical migration, by MRI 28% | Surgery |
| 16 f, 16 m | amide, polyalkylimide, | (30 of 107) lesions | ||
| facial injection 6–120 | ||||
| months ago | ||||
| [69] | 31–55 y; | Polyalkylimide, | Irregularities and edema in different areas | Surgery |
| 18 f | between 1 month to | |||
| 3 y after facial | ||||
| injection | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wollina, U.; Goldman, A. Filler Migration after Facial Injection—A Narrative Review. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10040115
Wollina U, Goldman A. Filler Migration after Facial Injection—A Narrative Review. Cosmetics. 2023; 10(4):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10040115
Chicago/Turabian StyleWollina, Uwe, and Alberto Goldman. 2023. "Filler Migration after Facial Injection—A Narrative Review" Cosmetics 10, no. 4: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10040115
APA StyleWollina, U., & Goldman, A. (2023). Filler Migration after Facial Injection—A Narrative Review. Cosmetics, 10(4), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10040115






