Diagnostic Techniques of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Impact on Control Measures
Abstract
1. Global Burden of Disease and Importance in Epidemiology
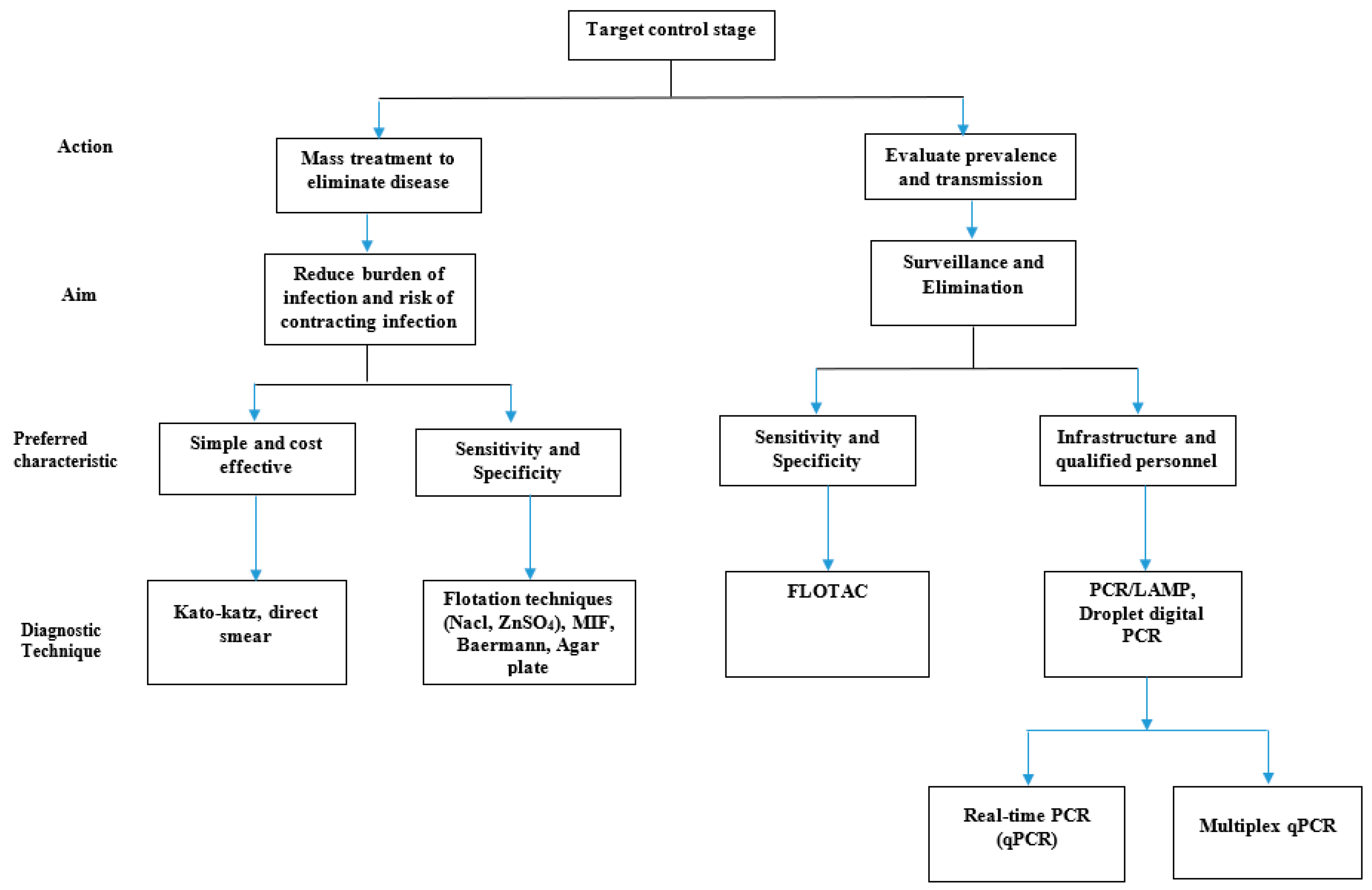
2. Choice of Diagnostic Technique
3. Methodology
4. Diagnostic Techniques
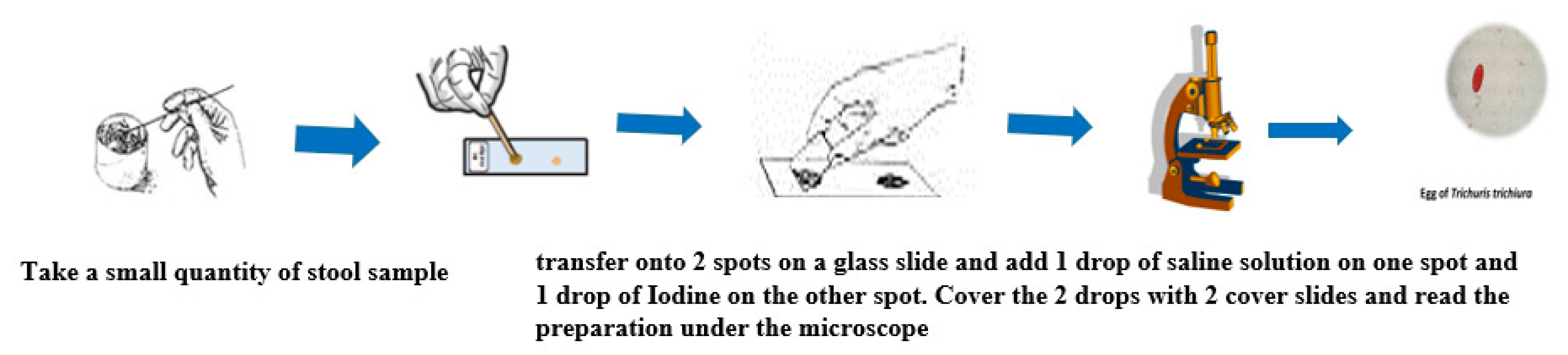
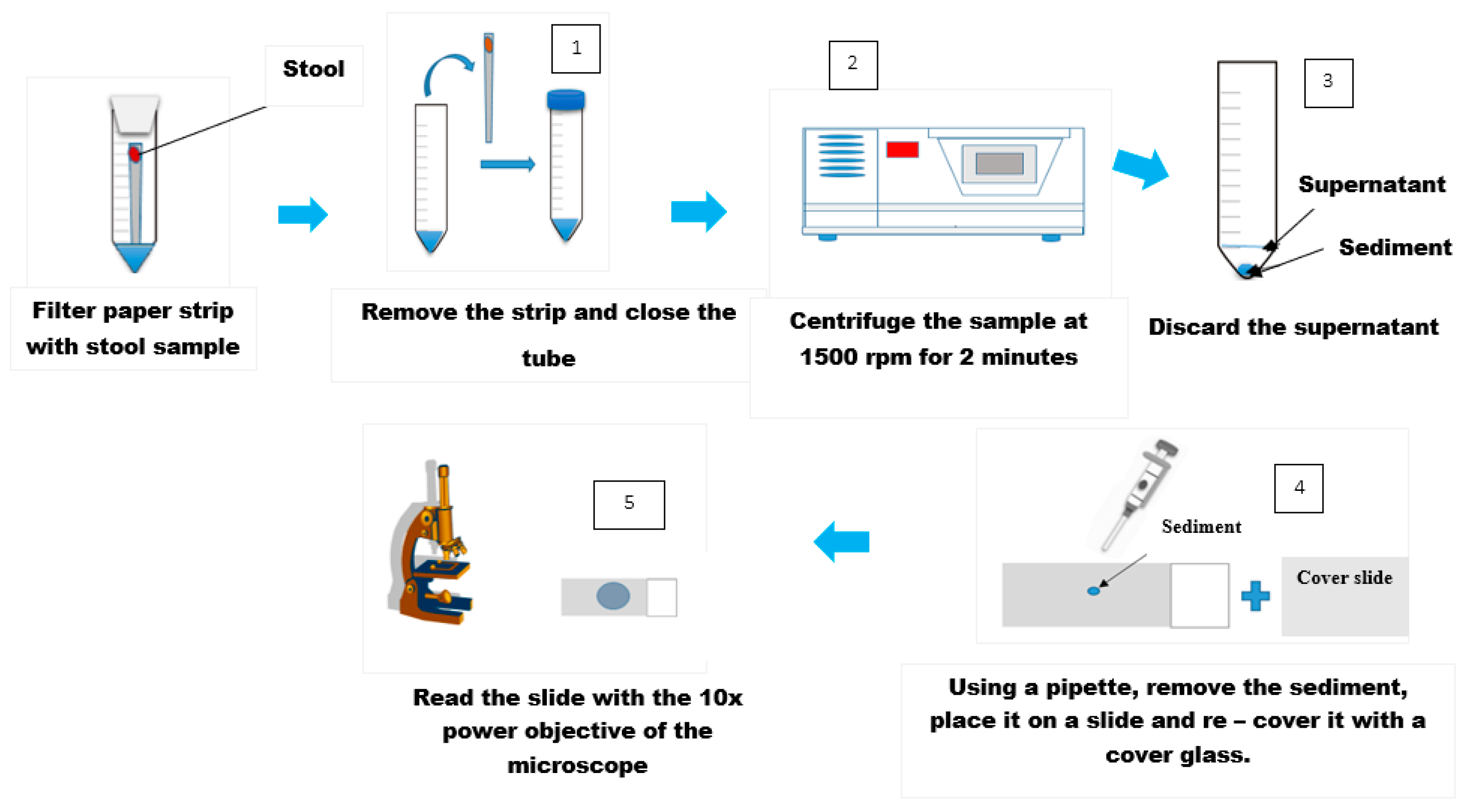
4.1. Direct Examination
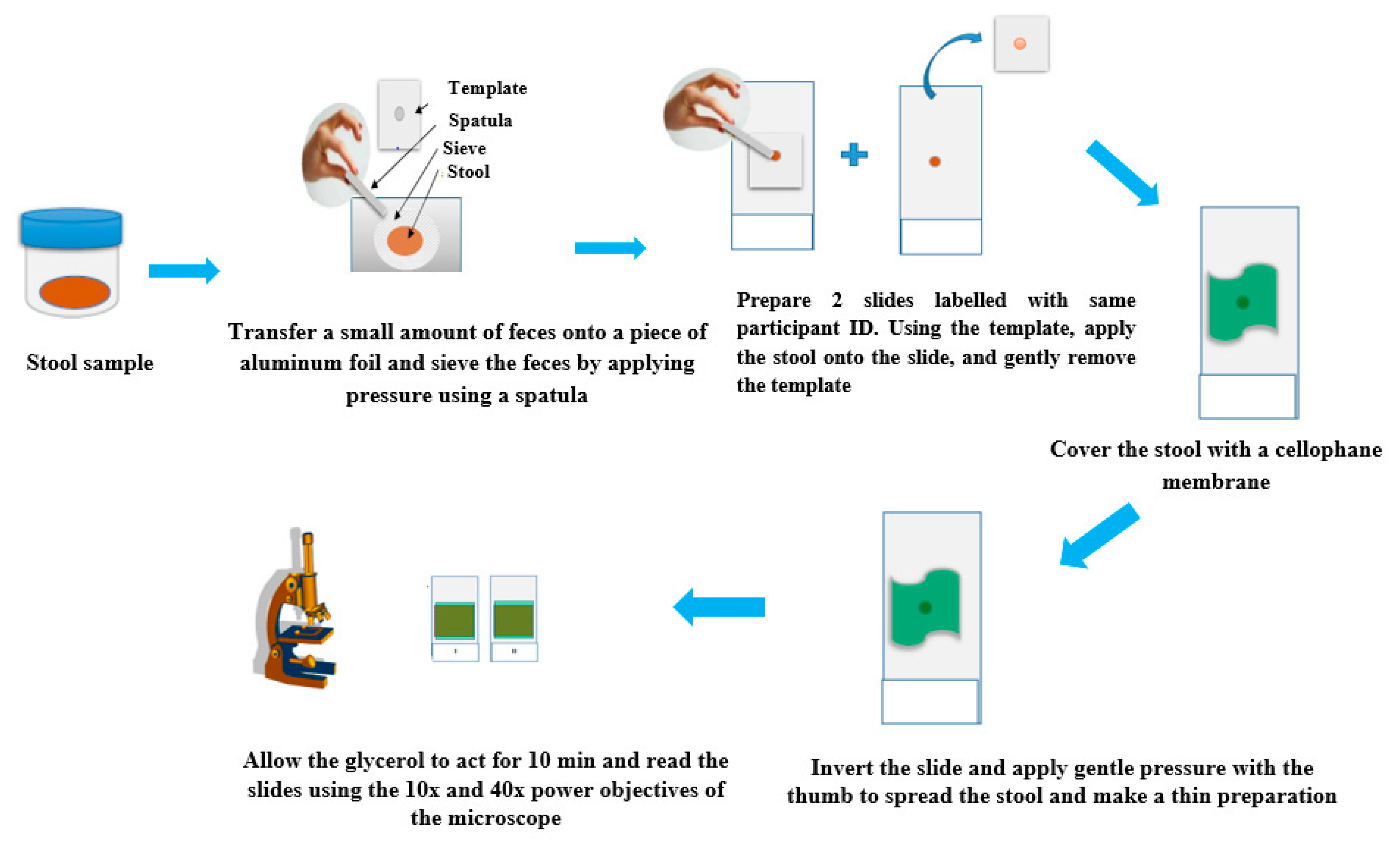
4.2. Kato-Katz Technique
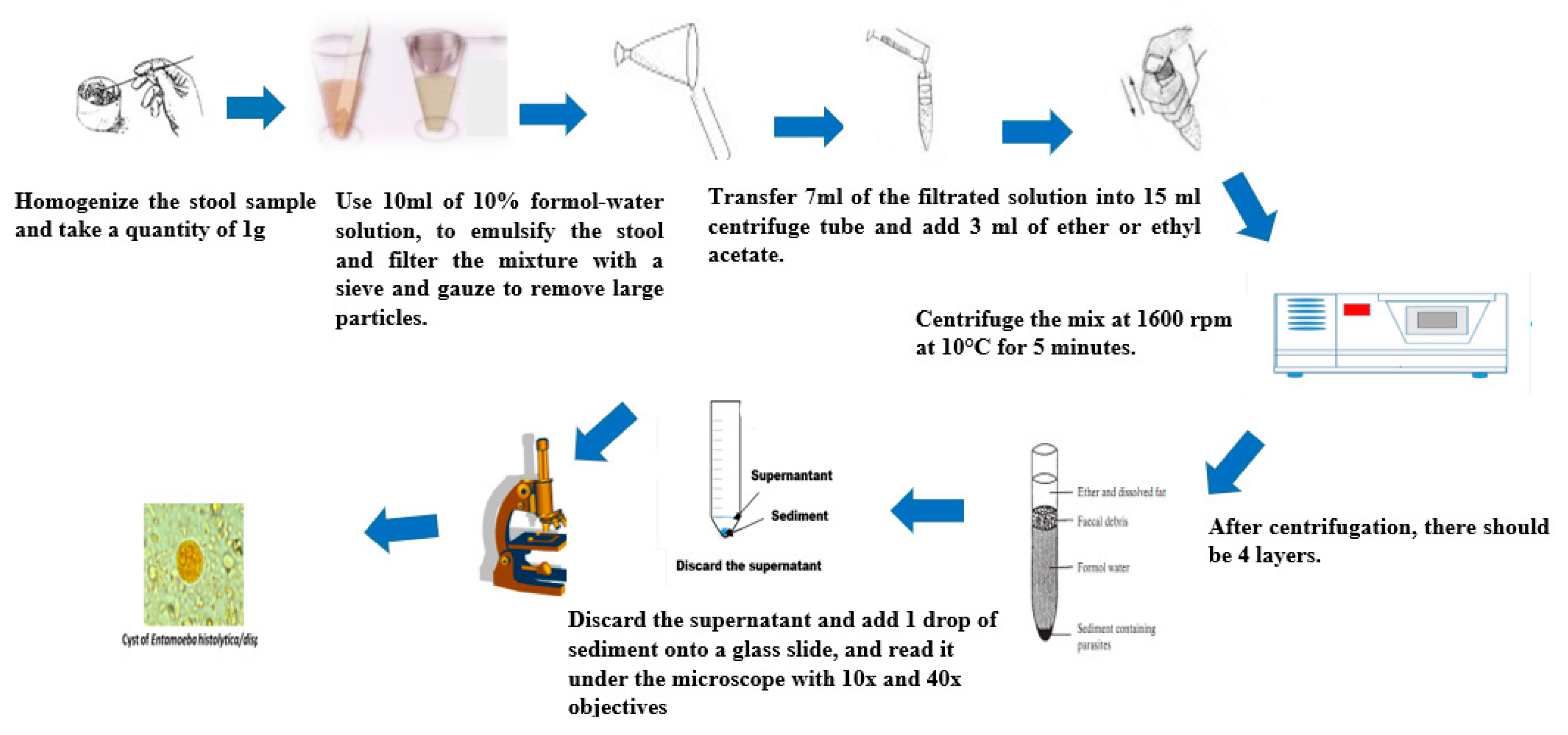
4.3. Formol-Ether Concentration Technique
4.4. Agar Plate Culture Technique
4.5. Baermann Technique
4.6. Water Emergence Technique for Detecting Strongyloides Larvae in Feces
4.7. Harada-Mori Technique
4.8. Merthiolate-Iodine-Formaldehyde-Concentration Technique (MIFC)
4.9. Flotation Techniques
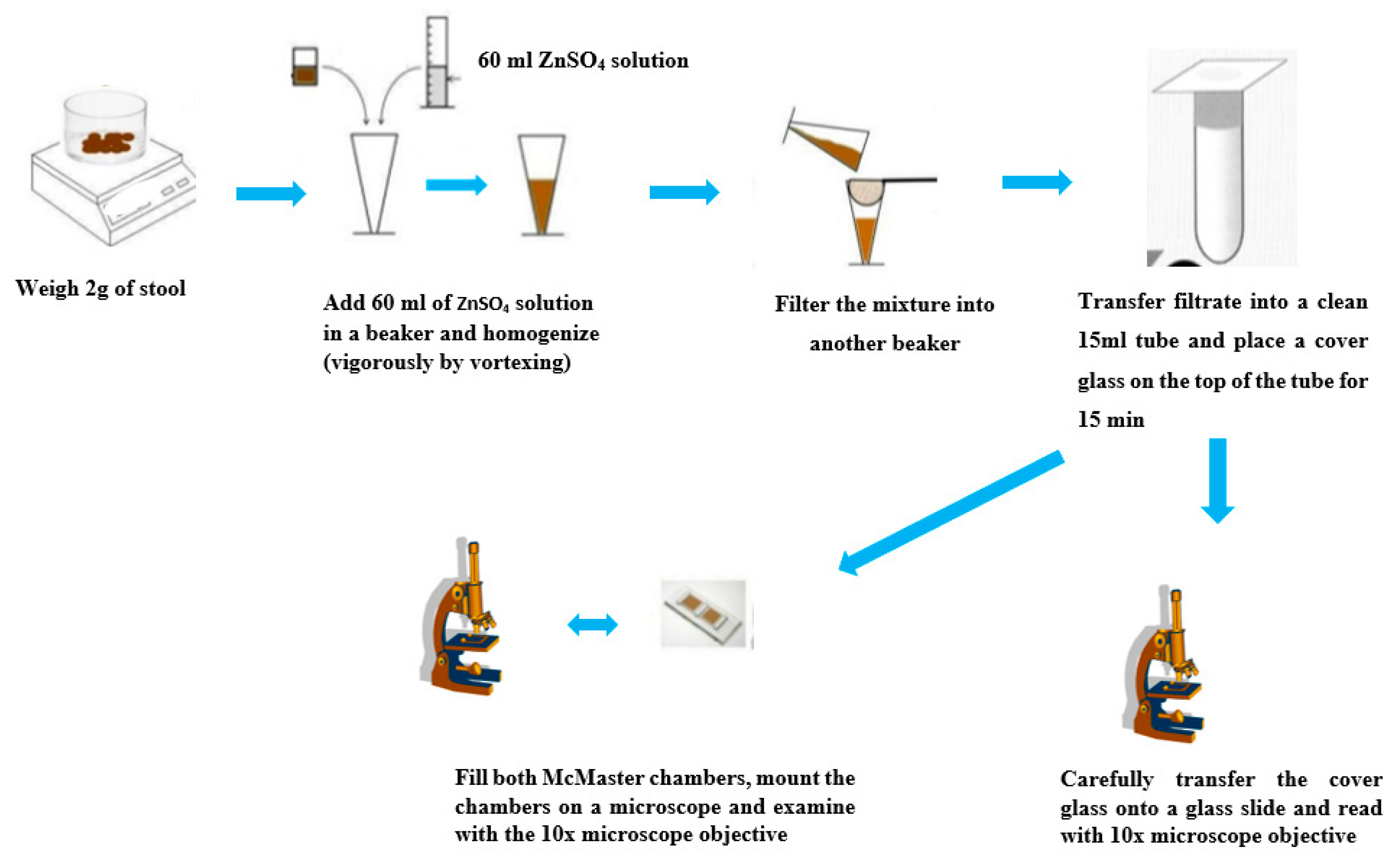
4.10. Zinc Sulfate Flotation Technique
4.11. Saturated Sodium Chloride Flotation Technique
4.12. FLOTAC Techniques for Detecting Helminths Eggs
4.13. Stoll’s Dilution Egg-Counting Technique
4.14. McMaster Method for Quantitative Fecal Examination
4.15. Antigen Detection
4.16. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Technique
5. How to Choose a Diagnostic Technique
5.1. Operational Cost and Infrastructure
5.2. Sensitivity and Specificity
5.3. Safety Issues and Personnel Qualification
6. The Way Forward
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Prevention and Control of Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis; WHO-UNICEF joint statement;World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- WHO World Health Organization. Investing to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: Third WHO Report on Neglected Diseases; World Health Organisation Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Sakti, H.; Nokes, C.; Subagio Hertanto, W.; Hendratno, S.; Hall, A.; Bundy, D.A.; Satoto, P. Evidence for an association between hookworm infection and cognitive function in Indonesian school children. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1999, 4, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullan, R.L.; Smith, J.L.; Jasrasaria, R.; Brooker, S.J. Global numbers of infection and disease burden of soil transmitted helminth infections in 2010. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkins, M.H.D.; Anderson, R.M. The influence of individual, social group and household factors on the distribution of Ascaris lumbricoides within a community and implications for control strategies. Parasitology 1989, 98, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, H.M. Selective Primary Health Care: Strategies for Control of Disease in the Developing World. XVII. Hookworm Infection and Anemia. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1985, 7, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethony, J.; Brooker, S.; Albonico, M.; Geiger, S.M.; Loukas, A.; Diemert, D.; Hotez, P.J. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: Ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet 2006, 367, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, D.; Haji, H.J.; Bickle, Q.D.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Tielsch, J.M.; Ramsan, M.; Savioli, L.; Albonico, M. A comparison of methods for detecting the eggs of ascaris, trichuris, and hookworm in infant stool, and the epidemiology of infection in zanzibari infants. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegnika, A.A.; Agnandji, S.T.; Chai, S.K.; Ramharter, M.; Breitling, L.; Kendjo, E.; Issifou, S.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Kombila, M.; Kremsner, P.G. Increased prevalence of intestinal helminth infection during pregnancy in a Sub-Saharan African community. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2007, 119, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammie, P.J.; Fenwick, A.; Utzinger, J. A blueprint for success: Integration of neglected tropical disease control programmes. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Prevention and Control of Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Report of a WHO Expert Committee; Geneva Technical Report Series; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, M.A.; Hooper, P.J.; Ottesen, E.A. Projected benefits from integrating NTD programs in sub-Saharan Africa. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, S.; Clements, A.C.A.; Bundy, D.A.P. Global epidemiology, ecology and control of soil-transmitted helminth infections. Adv. Parasitol. 2006, 62, 221–261. [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick, A. New initiatives against Africa’s worms. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, D.H.; Hotez, P.J.; Fenwick, A. “Rapid-Impact Interventions”: How a Policy of Integrated Control for Africa’s Neglected Tropical Diseases Could Benefit the Poor. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Guideline: Preventive Chemotherapy to Control Soil-Transmitted Helminths Infections in at Risk Population Groups; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. Efficacy of Current Drugs Against Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2008, 299, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegnika, A.A.; Lötsch, F.; Maurin, R.; Mba, O.; Ramharter, M. Update on Treatment and Resistance of Human Trichuriasis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2015, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Booth, M.; Vounatsou, P.; N’Goran, E.; Tanner, M.; Utzinger, J. The influence of sampling effort and the performance of the Kato-Katz Technique in diagnosing Schistosoma mansoni and Hookworm co-infections in rural Côte D’ivoire. Parasitology. Parasitology 2003, 127, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoo, S.; Bell, D.; Bossuyt, P.; Herring, A.; Mabey, D.; Poole, F.; Smith, P.G.; Sriram, N.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Linke, R.; et al. Evaluation of diagnostic tests for infectious diseases: General principles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, S21–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Smith, P.G.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. A guide for diagnostic evaluations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, A.V.; Oliveira, R.G.; Walker, M.; O’Connell, E.M.; Njenga, S.M.; Mwandawiro, C.S.; Webster, J.P.; Nutman, T.B.; Anderson, R.M. Sources of variability in the measurement of Ascaris lumbricoides infection intensity by Kato-Katz and qPCR. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.M.; Schad, G.A. Hookworm burdens and faecal egg counts: An analysis of the biological basis of variation. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 79, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesbrough, M. Parasitilogical Test and Concentration techniques in District laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Tropical Health technologies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; Volume 306, pp. 178–306. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Bench Aids for the Diagnosis of Intestinal Parasites; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, N.; Chavas, A.; Pellegrino, J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smears technique in Schistosoma mansosni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1972, 14, 379–400. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, H.; Escher, E. SAF-an alternative fixative solution for the parasitological stool specimens. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1990, 120, 1473–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.J.; Gross, J.; Smith, M.C.; Ichardson, D.E.J.R.; Ross, J.E.G. Comparison of Kato-Katz Direct Smear and Sodium Nitrate Flotation for Detection of Geohelminth Infections. Comp. Parasitol. 2008, 75, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, P.; Utzinger, J.; Du, Z.-W.; Zhou, X.-N. Chapter 2—Multiparasitism: A Neglected Reality on Global, Regional and Local Scale. In Important Helminth Infections in Southeast Asia: Diversity and Potential for Control and Elimination, Part B; Zhou, X.-N., Bergquist, R., Olveda, R., Utzinger, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 73, pp. 21–50. ISBN 0065-308X. [Google Scholar]
- Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Maurelli, M.P.; Utzinger, J. FLOTAC: New multivalent techniques for qualitative and quantitative copromicroscopic diagnosis of parasites in animals and humans. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.H.; Bullock, S.L.; Melvin, D.M.; Spruill, C.L. Ethyl acetate as a substitute for diethyl ether in the formalin-ether sedimentation technique. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 10, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, R.G. Diagnostics take centre stage. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 6, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, L.L., Jr.; Baker, C.B.; Gam, A.A.; Nutman, T.B.; Neva, F.A. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Treatment of Chronic Strongyloidiasis in Ex-Prisoners of War. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, K.; Kasuya, S.; Khamboonruang, C.; Sukhavat, K.; Ieda, M.; Takatsuka, N.; Kita, K.; Ohtomo, H. A Modified Agar Plate Method for Detection of Strongyloides Stercoralis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 45, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Bruckner, D. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology; American Society for Microbiology Press: Sterling, VA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–791. [Google Scholar]
- Arakaki, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Asato, R.; Ikeshiro, T.; Kinjo, F.; Saito, A.; Iwanaga, M.; December, R.; January, A. A new method to detect Strongyloides stercoralis from human stool. Jpn. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, S.A.; Gutierrez, C.; Berk, S.L. Value of the agar plate method for the diagnosis of intestinal strongyloidiasis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 23, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.G.; Lima, P.J. Diagnosis of Strongyloidiasis: Importance of Baermann’s Method. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1961, 6, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, Y.; Mori, O. A new method for culturing hookworm. Yonago Acta Med. 1955, 1, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.C. A Test-Tube Filter-Paper Method for the Diagnosis of Ancylostoma Duodenale, Necator Americanus and Strongyloides Stercoralis; WHO Technical. Report Series 255; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1962; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sasa, M.; Hayashi, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shirasaka, R. Application of test-tube cultivation method on the survey of hookworm and related human nematode infection. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1958, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sapero, J.J.; Lawless, D.K. The “MIF” Stain-Preservation Technic for the Identification of Intestinal Protozoa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1953, 2, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagg, W.; Schloegel, E.L.; Mansour, N.S.; Khalaf, G.I. A New Concentration Technic for the Demonstration of Protozoa and Helminth Eggs in Feces1. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1955, 4, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, E.; Sawitz, W.; Tobie, J.; Odom, V.; Peres, C.; Lincicome, D.R. Comparative efficiency of various techniques for the diagnosis of protozoa in feces. J. Parasitol. 1939, 25, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzinger, J.; Rinaldi, L.; Lohourignon, L.K.; Rohner, F.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Tschannen, A.B.; N’Goran, E.K.; Cringoli, G. FLOTAC: A new sensitive technique for the diagnosis of hookworm infections in humans. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, S.; Rinaldi, L.; Khamis, I.S.; Stothard, J.R.; Rollinson, D.; Maurelli, M.P.; Steinmann, P.; Marti, H.; Cringoli, G.; Utzinger, J. A single FLOTAC is more sensitive than triplicate Kato-Katz for the diagnosis of low-intensity soil-transmitted helminth infections. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, S.; Glinz, D.; Rinaldi, L.; Mohammed, K.A.; N’Goran, E.K.; Stothard, J.R.; Marti, H.; Cringoli, G.; Rollinson, D.; Utzinger, J. FLOTAC: A promising technique for detecting helminth eggs in human faeces☆. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinz, D.; Silué, K.D.; Knopp, S.; Lohourignon, L.K.; Yao, K.P.; Steinmann, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J. Comparing diagnostic accuracy of Kato-Katz, Koga agar plate, ether-concentration, and FLOTAC for Schistosoma mansoni and soil-transmitted helminths. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levecke, B.; Behnke, J.M.; Ajjampur, S.S.R.; Albonico, M.; Ame, S.M.; Charlier, J.; Geiger, S.M.; Hoa, N.T.V.; Kamwa Ngassam, R.I.; Kotze, A.C.; et al. A comparison of the sensitivity and fecal egg counts of the McMaster egg counting and Kato-Katz thick smear methods for soil-transmitted helminths. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levecke, B.; De Wilde, N.; Vandenhoute, E.; Vercruysse, J. Field validity and feasibility of four techniques for the detection of Trichuris in simians: A model for monitoring drug efficacy in public health? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungiro, R.D.; Cappello, M. Detection of excretory/secretory coproantigens in experimental hookworm infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, A.M.; McCarthy, J.S. A coproantigen diagnostic test for Strongyloides infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hove, R.J.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Vervoort, T.; Van den Ende, J.; Van Lieshout, L.; Verweij, J.J. Molecular diagnostics of intestinal parasites in returning travellers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniuchi, M.; Verweij, J.J.; Noor, Z.; Sobuz, S.U.; Van Lieshout, L.; Petri, W.A., Jr.; Haque, R.; Houpt, E.R. High throughput multiplex PCR and probe-based detection with Luminex beads for seven intestinal parasites. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lieshout, L.; Roestenberg, M. Clinical consequences of new diagnostic tools for intestinal parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, M.B.; John-Stewart, G.; Richardson, B.A.; Singa, B.; Van Lieshout, L.; Verweij, J.J.; Sangaré, L.R.; Mbogo, L.W.; Naulikha, J.M.; Walson, J.L. Impact of helminth diagnostic test performance on estimation of risk factors and outcomes in HIV-positive adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Blangé, R.A.; Templeton, K.; Schinkel, J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Van Rooyen, M.A.A.; Van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Simultaneous detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium parvum in fecal samples by using multiplex real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Ziem, J.; Yelifari, L.; Polderman, A.M. Simultaneous Detection and Quantification of Ancylostoma duodenale, Necator americanus, and Oesophagostomum bifurcum in Fecal Samples Using Multiplex. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: The polymerase chain reaction. 1986. Biotechnology 1992, 24, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, T.C. Polymerase chain reaction: Basic protocol plus troubleshooting and optimization strategies. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckeand, J.B. Molecular diagnosis of parasitic nematodes. Parasitology 1998, 117, S87–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Recent progress in research and development. J. Infect. Chemother. 2013, 19, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashwan, N.; Diawara, A.; Scott, M.E.; Prichard, R.K. Isothermal diagnostic assays for the detection of soil-transmitted helminths based on the SmartAmp2 method. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duewer, D.L.; Kline, M.C.; Romsos, E.L.; Toman, B. Evaluating droplet digital PCR for the quantification of human genomic DNA: Converting copies per nanoliter to nanograms nuclear DNA per microliter. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta Soto, L.; Santísima-Trinidad, A.B.; Bornay-Llinares, F.J.; Martín González, M.; Pascual Valero, J.A.; Ros Muñoz, M. Quantitative PCR and Digital PCR for Detection of Ascaris lumbricoides Eggs in Reclaimed Water. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7515409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia, R.; Vicuña, Y.; Broncano, N.; Sandoval, C.; Vaca, M.; Chico, M.; Cooper, P.J.; Nutman, T.B. A novel, multi-parallel, real-time polymerase chain reaction approach for eight gastrointestinal parasites provides improved diagnostic capabilities to resource-limited at-risk populations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, K.; Clarke, N.; Awburn, C.V.; Vaz Nery, S.; Khieu, V.; Traub, R.J.; Jex, A.R. Development and validation of a multiplexed-tandem qPCR tool for diagnostics of human soil-transmitted helminth infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.J.; Stothard, J.R.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.; Armoo, S.; Verweij, J.J.; Adams, E.R. Developing a real-time PCR assay based on multiplex high-resolution melt-curve analysis: A pilot study in detection and discrimination of soil-transmitted helminth and schistosome species. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, R.; Johansen, M.V.; Utzinger, J. Diagnostic dilemmas in helminthology: What tools to use and when? Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidance on Control Materials for Antigen Detecting Malaria RDTs Tools for Preparation and Validation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agbana, T.E.; Diehl, J.-C.; Van Pul, F.; Khan, S.M.; Patlan, V.; Verhaegen, M.; Vdovin, G. Imaging & identification of malaria parasites using cellphone microscope with a ball lens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205020. [Google Scholar]
- Mudanyali, O.; Dimitrov, S.; Sikora, U.; Padmanabhan, S.; Navruz, I.; Ozcan, A. Integrated rapid-diagnostic-test reader platform on a cellphone. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enk, M.J.; Carolina, A.; Lima, L.; Massara, C.L.; Marcos, P.; Coelho, Z. A Combined Strategy to Improve the Control of Schistosoma mansoni in Areas of Low Prevalence in Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Assefa, L.M.; Crellen, T.; Kepha, S.; Kihara, J.H.; Njenga, S.M.; Pullan, R.L.; Brooker, S.J. Diagnostic accuracy and cost-effectiveness of alternative methods for detection of soil-transmitted helminths in a post-treatment setting in western Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parasite | Formol-Ether | Kato-Katz | MIFC | McMaster | FLOTAC | Sat. NaCl | ZnSO4 | Agar Plate/Baermann |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eggs | ||||||||
| A. lumbricoides | ++ | ++ | - | + | + | + | - | - |
| T. trichiura | ++ | ++ | - | + | + | - | + | - |
| Hookworm | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Larvae | ||||||||
| Strongyloides | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | ++ |
| Hookworm | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | ++ |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Kato-Katz |
|
|
| Ether-based concentration techniques |
|
|
| Flotation techniques: (ZnSO4 and saturated NaCl) |
|
|
| Harada-Mori |
|
|
| McMaster techniques |
|
|
| FLOTAC |
|
|
| Serology (antibody detection) |
|
|
| Antigen detection |
|
|
| PCR |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mbong Ngwese, M.; Prince Manouana, G.; Nguema Moure, P.A.; Ramharter, M.; Esen, M.; Adégnika, A.A. Diagnostic Techniques of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Impact on Control Measures. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020093
Mbong Ngwese M, Prince Manouana G, Nguema Moure PA, Ramharter M, Esen M, Adégnika AA. Diagnostic Techniques of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Impact on Control Measures. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(2):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020093
Chicago/Turabian StyleMbong Ngwese, Mirabeau, Gédéon Prince Manouana, Paul Alvyn Nguema Moure, Michael Ramharter, Meral Esen, and Ayola Akim Adégnika. 2020. "Diagnostic Techniques of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Impact on Control Measures" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 2: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020093
APA StyleMbong Ngwese, M., Prince Manouana, G., Nguema Moure, P. A., Ramharter, M., Esen, M., & Adégnika, A. A. (2020). Diagnostic Techniques of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: Impact on Control Measures. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(2), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020093







