Impact of the “BALatrine” Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Central Java, Indonesia: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
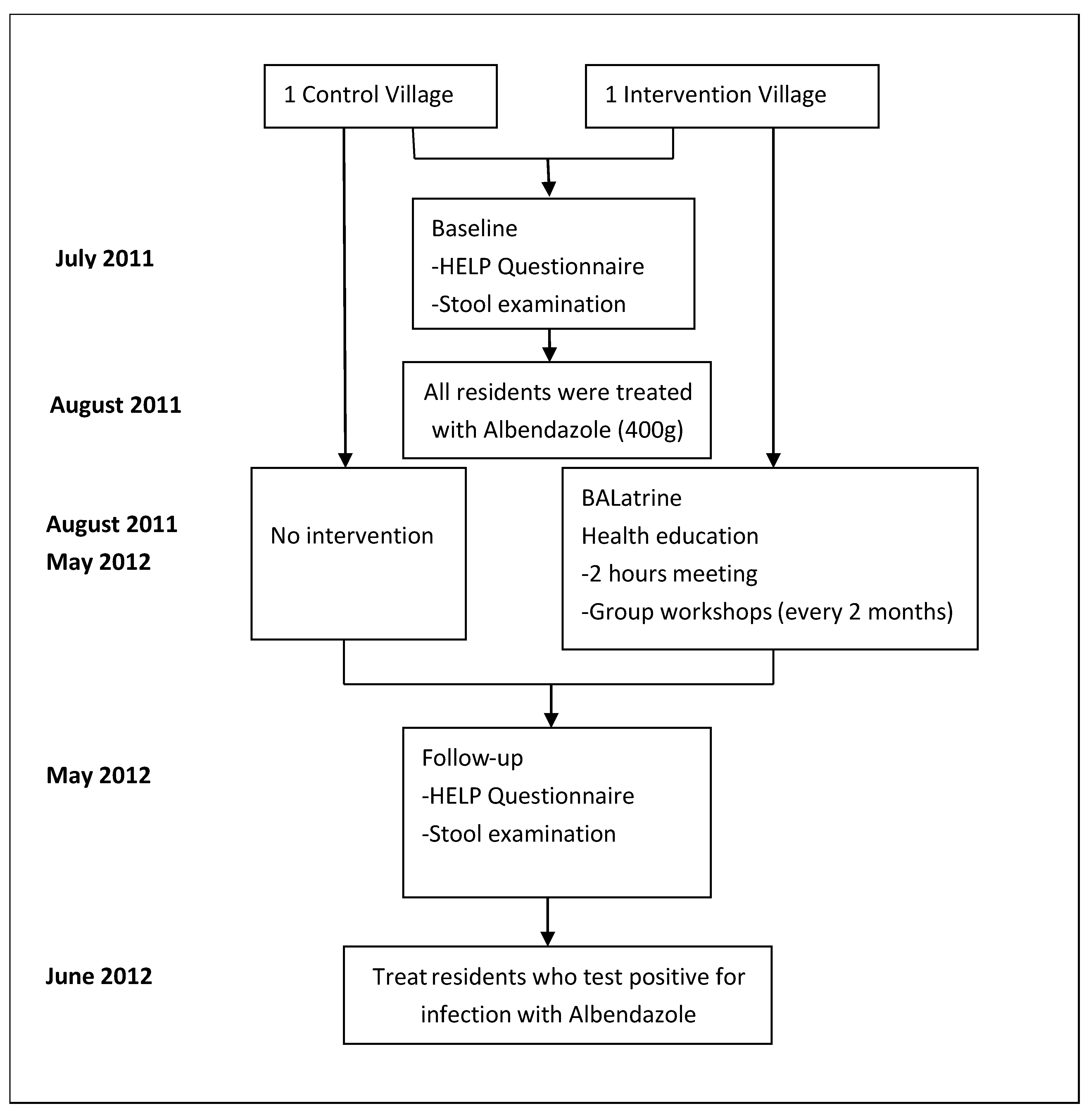
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
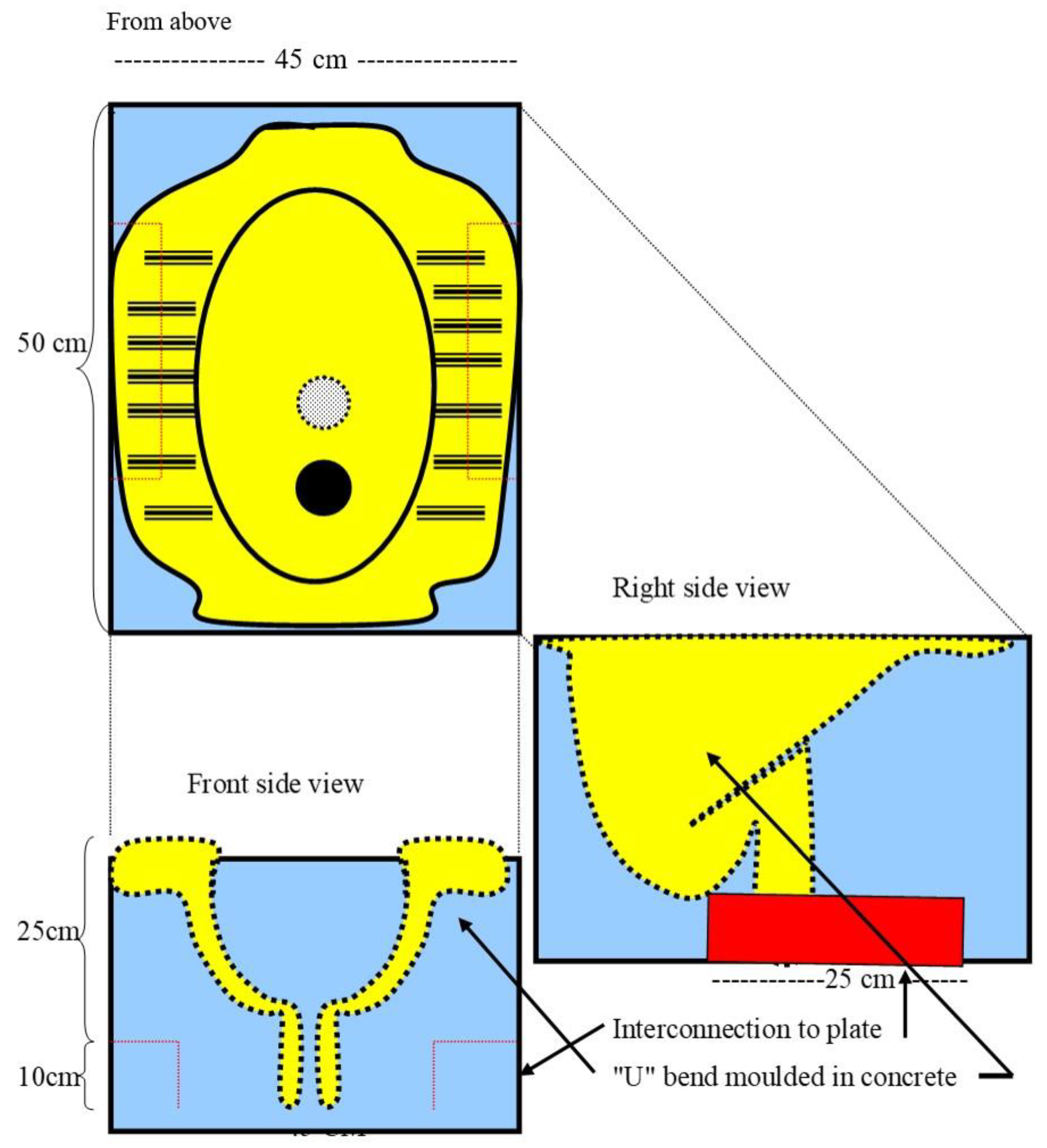
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Measurements and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. STH-Infection Status
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Fact Sheet. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Pullan, R.L.; Smith, J.L.; Jasrasaria, R.; Brooker, S.J. Global numbers of infection and disease burden of soil transmitted helminth infections in 2010. Parasit Vectors 2014, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. The drugs we have and the drugs we need against major helminth infections. Adv. Parasitol. 2010, 73, 197–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bab IV: Pencapaian Program Kesehatan Menuju Jawa Tengah Sehat; Central Java Health Department: Central Java, Indonesia, 2003.
- Laksono, B. The Number of Family Latrines in Kedung Wuni, Pejalongan, Pekalongan and Its Problems; Health Department Pekalongan: Pekalongan, Indonesia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kurscheid, J.; Bendrups, D.; Susilo, J.; Williams, C.; Amaral, S.; Laksono, B.; Stewart, D.; Gray, D. Status of Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Semarang, Central Java, Indonesia (Manuscript in preparation). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chadijah, S.; Sumolang, P.; Veridiana, N. The Association of Knowledge, Practice and Enviromental Sanitation and Soil Transmitted Helminth Prevalence in Elementary School Student in Palu Municipality. Media Litbangkes 2014, 24, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.W.; Melville, S.; Utzinger, J.; King, C.H.; Zhou, X.N. Soil-transmitted helminth reinfection after drug treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clasen, T.F.; Bostoen, K.; Schmidt, W.P.; Boisson, S.; Fung, I.C.; Jenkins, M.W.; Scott, B.; Sugden, S.; Cairncross, S. Interventions to improve disposal of human excreta for preventing diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 6, Cd007180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases. Helminth Control in School-Age Children: A Guide for Managers of Control Programmes; World Health Organization, Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelbauer, K.; Speich, B.; Mäusezahl, D.; Bos, R.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. Effect of Sanitation on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, L.; Shah, M. Scaling up rural sanitation: Findings from the impact evaluation baseline survey in Indonesia (English). In Water and Sanitation Program Technical Paper; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, M.B.; Arianto, I.; Blackett, I.C. Ecological sanitation: Social factors impacting use of EcoSan in rural Indonesia (English). In Water and Sanitation Program Learning Note; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme for Water Supply and Sanitation. Progress on Drinking Water and Sanitation: 2014 Update; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; World Health Organization: Geneva Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme for Water Supply Sanitation. Meeting the MDG Drinking Water and Sanitation Target: The Urban and Rural Challenge of the Decade; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; World Health Organization: Geneva Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF Joint Water Supply Sanitation Monitoring Programme. Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water: 2015 Update and MDG Assessment; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Health Research and Development Agency (Balitbangkes) Indonesian Ministry of Health. Laporan Hasil-Riset Kesehatan Dasar (LHRKD) Indonesia [Report on Basic Health Research-Results Indonesia]; Health Research and Development Agency (Balitbangkes) Indonesian Ministry of Health: Republic of Indonesia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni, Z.; Stewart, D.E. Sanitation in an emergency situation: A case study of the eruption of Mt Merapi, Indonesia, 2010. Int. J. Environ. Prot. 2010, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D.; Laksono, B. Helminth infection, human waste and appropriate technology: An Indonesian case study. Environ. Health 2002, 2, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.J.; Clements, A.C.; Gray, D.J.; Sadler, R.; Laksono, B.; Stewart, D.E. Quantifying accessibility and use of improved sanitation: Towards a comprehensive indicator of the need for sanitation interventions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willis, H.H. A Simple Levitation Method for the Detection of Hookworm Ova. Med. J. Aust. 1921, 2, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Jung, H.S.; Stewart, D.E. Reducing the exposure of children in rural Indonesia to environmental contamination by human waste. Ther. Res. 2018, 39, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.J.; Laksono, B.; Sadler, R.; Clements, A.; Stewart, D.E. Household Latrines to Control Environmental Contamination and Helminthiasis: An Exploratory Study in Indonesia. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2015, 5, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, A.; Sullivan, K.; Soe, M. OpenEpi: Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health, Version. Available online: https://www.openepi.com/Menu/OE_Menu.htm (accessed on 15 June 2015).
- Routray, P.; Schmidt, W.P.; Boisson, S.; Clasen, T.; Jenkins, M.W. Socio-cultural and behavioural factors constraining latrine adoption in rural coastal Odisha: An exploratory qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, D.; Laksono, B.; Park, M.J.; Wang, D.X. An Integrated Approach to the Prevention of Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs): The Way Forward? Athens J. Health 2016, 3, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, M.; Cumming, O.; Peletz, R.; Chan, G.K.; Brown, J.; Baker, K.; Clasen, T. Shared sanitation versus individual household latrines: A systematic review of health outcomes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garn, J.V.; Sclar, G.D.; Freeman, M.C.; Penakalapati, G.; Alexander, K.T.; Brooks, P.; Rehfuess, E.A.; Boisson, S.; Medlicott, K.O.; Clasen, T.F. The impact of sanitation interventions on latrine coverage and latrine use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, C.A.; Kurscheid, J.; Jones, M.K.; Gray, D.J.; McManus, D.P. Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Tropical Australia and Asia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, W.; Schindler, C.; Keiser, J. Efficacy of recommended drugs against soil transmitted helminths: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2017, 358, j4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, A.; Nagel, C.L.; Schmidt, W.P.; Torondel, B.; Boisson, S.; Routray, P.; Clasen, T.F. Assessing patterns and determinants of latrine use in rural settings: A longitudinal study in Odisha, India. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chard, A.N.; Garn, J.V.; Chang, H.H.; Clasen, T.; Freeman, M.C. Impact of a school-based water, sanitation, and hygiene intervention on school absence, diarrhea, respiratory infection, and soil-transmitted helminths: Results from the WASH HELPS cluster-randomized trial. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 020402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, S.V.; McCarthy, J.S.; Traub, R.; Andrews, R.M.; Black, J.; Gray, D.; Weking, E.; Atkinson, J.A.; Campbell, S.; Francis, N.; et al. A cluster-randomised controlled trial integrating a community-based water, sanitation and hygiene programme, with mass distribution of albendazole to reduce intestinal parasites in Timor-Leste: The WASH for WORMS research protocol. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e009293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nery, S.V.; Pickering, A.J.; Abate, E.; Asmare, A.; Barrett, L.; Benjamin-Chung, J.; Bundy, D.A.; Clasen, T.; Clements, A.C.; Colford, J.M.; et al. The role of water, sanitation and hygiene interventions in reducing soil-transmitted helminths: Interpreting the evidence and identifying next steps. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz Nery, S.; Traub, R.J.; McCarthy, J.S.; Clarke, N.E.; Amaral, S.; Llewellyn, S.; Weking, E.; Richardson, A.; Campbell, S.J.; Gray, D.J.; et al. WASH for WORMS: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial of the Impact of a Community Integrated Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene and Deworming Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieri, F.A.; Gray, D.J.; Williams, G.M.; Raso, G.; Li, Y.S.; Yuan, L.; He, Y.; Li, R.S.; Guo, F.Y.; Li, S.M.; et al. Health-education package to prevent worm infections in Chinese schoolchildren. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bieri, F.A.; Yuan, L.P.; Li, Y.S.; He, Y.K.; Bedford, A.; Li, R.S.; Guo, F.Y.; Li, S.M.; Williams, G.M.; McManus, D.P.; et al. Development of an educational cartoon to prevent worm infections in Chinese schoolchildren. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2013, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorkos, T.W.; Maheu-Giroux, M.; Blouin, B.; Casapia, M. Impact of health education on soil-transmitted helminth infections in schoolchildren of the Peruvian Amazon: A cluster-randomized controlled trial. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Village Status | Control | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Village | Cepoko | Palemon |
| Sample Size | 244 | 283 |
| Mean Age (years) | 29.4 | 32.2 |
| Prevalence of STH infection: % (95% CI) | 21.7% (16.5–26.9) | 25.8% (20.7–30.9) |
| Sex Ratio (F/M) | 141/103 | 151/132 |
| Prevalence of STH infection by Sex (F/M) | 22.0%/21.4% | 20.5%/31.8% |
| Variable | Control | Intervention | Odds Ratio | Odds Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p Value | Adjusted * | p Value | |||
| All participants | n = 244 | n = 283 | ||||
| Prevalence of infection at baseline: % (95% CI) | 21.7 (16.5–26.9) | 25.8 (20.7–30.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Cumulative incidence of infection at follow-up: % (95% CI) | 27.5 (21.9–33.1) | 13.4 (9.5–17.4) | 0.41 (0.26–0.64) | <0.001 | 0.38 (0.25–0.60) | <0.001 |
| Children | n = 54 | n = 53 | ||||
| Prevalence of infection at baseline: % (95% CI) | 18.8 (8.2–28.9) | 18.9 (8.3–29.4) | - | - | - | - |
| Cumulative incidence of infection at follow-up: % (95% CI) | 24.1 (12.7–35.5) | 3.8 (0.0–8.9) | 0.12 (0.03–0.58) | 0.01 | 0.12 (0.03–0.56) | 0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gray, D.J.; Kurscheid, J.M.; Park, M.; Laksono, B.; Wang, D.; Clements, A.C.; Hadisaputro, S.; Sadler, R.; Stewart, D.E. Impact of the “BALatrine” Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Central Java, Indonesia: A Pilot Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040141
Gray DJ, Kurscheid JM, Park M, Laksono B, Wang D, Clements AC, Hadisaputro S, Sadler R, Stewart DE. Impact of the “BALatrine” Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Central Java, Indonesia: A Pilot Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGray, Darren J, Johanna M Kurscheid, MJ Park, Budi Laksono, Dongxu Wang, Archie CA Clements, Suharyo Hadisaputro, Ross Sadler, and Donald E Stewart. 2019. "Impact of the “BALatrine” Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Central Java, Indonesia: A Pilot Study" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040141
APA StyleGray, D. J., Kurscheid, J. M., Park, M., Laksono, B., Wang, D., Clements, A. C., Hadisaputro, S., Sadler, R., & Stewart, D. E. (2019). Impact of the “BALatrine” Intervention on Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Central Java, Indonesia: A Pilot Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040141






