Diagnostic Accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect™ ELISA for the Detection of IgM Antibodies in Chittagong, Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Reference Testing
2.3. Scrub Typhus Detect™ IgM ELISA
2.4. Analysis and Practical Assessment of Diagnostic Utility
3. Results
3.1. Reference Assay Results
3.1.1. Patient Results
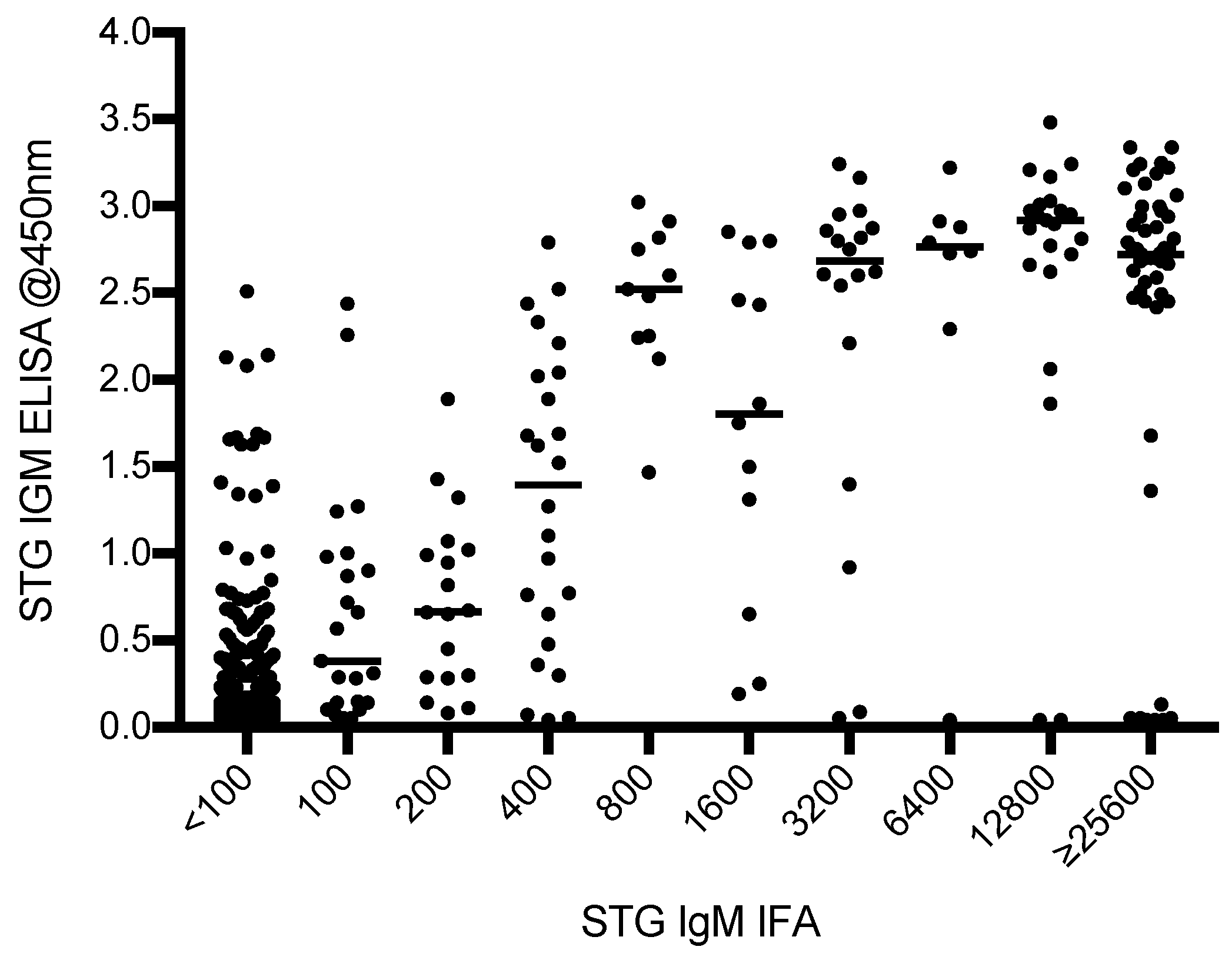
3.1.2. Characteristics of ELISA vs. IFA Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| 95% CI | 95% confidence interval |
| CMCH | Chittagong Medical College Hospital |
| STG | Scrub typhus group |
| TG | Typhus group |
| SFG | Spotted fever group |
| AUROCC | Area under receiver operator characteristic curve |
| mSTIC | Modified scrub typhus infection criteria |
| OxTREC | Oxford Tropical Research Ethics Committee |
| EDTA | Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid |
References
- Weitzel, T.; Dittrich, S.; López, J.; Phuklia, W.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Velásquez, K.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Abarca, K. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Nguyen, C.; Jiang, J.; Fenwick, S.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.H.; Blacksell, S.D.; Nawtaisong, P.; Jenjaroen, K.; Teeraratkul, A.; Chierakul, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Kantipong, P.; Day, N.P.J. Diagnostic accuracy of a loop-mediated isothermal PCR assay for detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi during acute scrub typhus infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.H.; Dumler, J.S. State of the art of diagnosis of rickettsial diseases: The use of blood specimens for diagnosis of scrub typhus, spotted fever group rickettsiosis, and murine typhus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Bryant, N.J.; Paris, D.H.; Doust, J.A.; Sakoda, Y.; Day, N.P.J. Scrub typhus serologic testing with the indirect immunofluorescence method as a diagnostic gold standard: A lack of consensus leads to a lot of confusion. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Paris, D.H.; Blacksell, S.D.; Laongnualpanich, A.; Kandipong, P.; Chierakul, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Day, N.P.J.; Cooper, B.S.; Limmathurotsakul, D. How to determine the accuracy of an alternative diagnostic test when it is actually better than the reference tests: A re-evaluation of diagnostic tests for scrub typhus using Bayesian LCMs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.L.; Blacksell, S.D.; Nawtaisong, P.; Nawtaisong, A.; Smith, D.J.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H. Antigenic relationships among human pathogenic Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates from Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, G.C.; Maude, R.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N.; Blacksell, S.D. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, H.W.; Blacksell, S.D.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Laongnualpanich, A.; Basnyat, B.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H. Comparative accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect IgM rapid test for the detection of IgM antibodies by using conventional serology. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Blacksell, S.D.; Laongnualpanich, A.; Kantipong, P.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H.; Limmathurotsakul, D. Optimal cutoff titers for indirect immunofluorescence assay for diagnosis of scrub typhus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3663–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, H.W.; Hossain, M.; Leopold, S.; Anantatat, T.; Tanganuchitcharncha, A.; Sinha, I.; Plewes, K.; Maude, R.J.; Hassan-Chowdhury, M.A.; Paul, S.; et al. Rickettsial illnesses as important causes of febrile illness in Chittagong, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittrich, S.; Phommasone, K.; Anantatat, T.; Panyanivong, P.; Slesak, G.; Blacksell, S.D.; Dubot-Pérès, A.; Castonguay-Vanier, J.; Stenos, J.; Newton, P.N.; et al. Rickettsia felis infections and comorbid conditions, Laos, 2003–2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1402–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayxay, M.; Castonguay-Vanier, J.; Chansamouth, V.; Dubot-Pérès, A.; Paris, D.H.; Phetsouvanh, R.; Tangkhabuanbutra, J.; Douangdala, P.; Inthalath, S.; Souvannasing, P.; et al. Causes of non-malarial fever in Laos: A prospective study. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e46–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Tanganuchitcharncha, A.; Nawtaisong, P.; Kantipong, P.; Laongnualpanich, A.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H. Diagnostic accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect enzyme-linked immunoassay for the detection of IgM antibodies in Northern Thailand. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 23, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morch, K.; Manoharan, A.; Chandy, S.; Chacko, N.; Alvarez-Uria, G.; Patil, S.; Henry, A.; Nesaraj, J.; Kuriakose, C.; Singh, A.; et al. Acute undifferentiated fever in India: A multicentre study of aetiology and diagnostic accuracy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Chaudhry, R.; Thakur, C.K. Determination of cutoff of ELISA and immunofluorescence assay for scrub typhus. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2016, 8, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koraluru, M.; Bairy, I.; Varma, M.; Vidyasagar, S. Diagnostic validation of selected serological tests for detecting scrub typhus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, R.E.; Sangkasuwan, V.; Suwanabun, N.; Eamsila, C.; Mungviriya, S.; Devine, P.; Richards, A.L.; Rowland, D.; Ching, W.M.; Sattabongkot, J.; et al. Comparative evaluation of selected diagnostic assays for the detection of IgG and IgM antibody to Orientia tsutsugamushi in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Diagnostic Test | Positive n | % Positive Overall |
|---|---|---|
| STG * polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | 48 | 11.7% |
| STG immunoglobulin M (IgM) ≥3200 admission | 54 | 13.1% |
| STG IgM 4-fold rise to ≥3200 | 8 | 1.9% |
| STG IgM ≥3200 or 4-fold rise to ≥3200 | 62 | 15.1% |
| Total STG positives (immunofluorescence assay (IFA) + PCR) | 71 | 17.2% |
| TG ** PCR | 15 | 3.6% |
| SFG *** PCR | 5 | 1.2% |
| Sample Timing | Cut-off OD | % Sensitivity (95% CI *) | % Specificity (95% CI) | AUROCC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission samples | ≥0.00 | 100 | 0 | |
| ≥0.25 | 95.8 (99.1–88.1) | 71.6 (76.3–66.4) | 0.84 (0.87–0.80) | |
| ≥0.50 | 94.4 (98.4–86.2) | 84.2 (87.9–79.8) | 0.89 (0.93–0.86) | |
| ≥0.75 | 91.5 (96.8–82.5) | 88.3 (91.5–84.4) | 0.90 (0.94–0.86) | |
| ≥1.00 | 91.5 (96.8–82.5) | 90.9 (93.7–87.3) | 0.91 (0.95–0.88) | |
| ≥1.25 | 91.5 (96.8–82.5) | 92.4 (95.0–89.0) | 0.92 (0.96–0.88) | |
| ≥1.50 | 88.7 (95.0–79.0) | 93.8 (96.1–90.7) | 0.91 (0.95–0.87) | |
| ≥1.75 | 84.5 (92.0–74.0) | 95.6 (97.5–92.8) | 0.90 (0.94–0.86) | |
| ≥2.00 | 81.7 (89.9–70.9) | 96.2 (98.0–93.6) | 0.89 (0.94–0.84) | |
| ≥2.25 | 78.9 (87.7–67.6) | 97.9 (99.2–95.8) | 0.88 (0.93–0.84) | |
| ≥2.50 | 71.8 (81.9–59.9) | 98.5 (99.5–96.6) | 0.85 (0.91–0.80) | |
| ≥2.75 | 52.1 (64.1–39.9) | 99.1 (99.8–97.5) | 0.76 (0.82–0.70) | |
| ≥3.00 | 22.5 (34.0-13.5) | 99.7 (100–98.4) | 0.61 (0.66–0.56) | |
| Convalescent samples | ≥0.00 | 100 | 0 | |
| ≥0.25 | 71.7 (83.2–57.7) | 75.5 (81.3–68.9) | 0.74 (0.80–0.67) | |
| ≥0.50 | 69.8 (81.7–55.7) | 84.0 (88.8–78.2) | 0.77 (0.84–0.70) | |
| ≥0.75 | 69.8 (81.7–55.7) | 89.5 (93.4–84.4) | 0.80 (0.86–0.73) | |
| ≥1.00 | 66.0 (78.5–51.7) | 92.5 (95.7–87.9) | 0.79 (0.86–0.73) | |
| ≥1.25 | 66.0 (78.5–51.7) | 93.6 (96.5–89.1) | 0.80 (0.86–0.73) | |
| ≥1.50 | 66.0 (78.5–51.7) | 96.0 (98.3–92.3) | 0.81 (0.88–0.74) | |
| ≥1.75 | 64.2 (76.9–49.8) | 97.0 (98.9–93.6) | 0.81 (0.87–0.74) | |
| ≥2.00 | 62.3 (75.2–47.9) | 97.0 (98.9–93.6) | 0.80 (0.86–0.73) | |
| ≥2.25 | 60.4 (73.5–46.0) | 97.5 (99.2–94.3) | 0.80 (0.86–0.73) | |
| ≥2.50 | 50.9 (64.9–36.8) | 99.0 (99.9–96.4) | 0.75 (0.82–0.68) | |
| ≥2.75 | 35.0 (50.2–23.1) | 99.0 (99.9–96.4) | 0.67 (0.74–0.61) | |
| ≥3.00 | 9.4 (20.7–3.1) | 100 (100–98.2) | 0.55 (0.59–0.51) | |
| All samples | ≥0.00 | 100 | 0 | |
| ≥0.25 | 85.5 (91.2–78.0) | 73.4 (77.1–69.4) | 0.79 (0.83–0.76) | |
| ≥0.50 | 83.9 (89.9–76.2) | 84.1 (87.1–80.7) | 0.84 (0.88–0.80) | |
| ≥0.75 | 82.3 (88.5–74.4) | 88.9 (91.4–86.0) | 0.86 (0.89–0.82) | |
| ≥1.00 | 80.6 (87.2–72.6) | 91.5 (93.7–88.8) | 0.86 (0.90–0.82) | |
| ≥1.25 | 80.6 (87.2–72.6) | 92.8 (94.8–90.3) | 0.87 (0.90–0.83) | |
| ≥1.50 | 79.0 (85.8–70.8) | 94.6 (96.4–92.4) | 0.87 (0.91–0.83) | |
| ≥1.75 | 75.0 (82.3–66.4) | 96.1 (97.6–94.1) | 0.86 (0.90–0.82) | |
| ≥2.00 | 73.4 (80.9–64.7) | 96.5 (97.9–94.6) | 0.85 (0.89–0.81) | |
| ≥2.25 | 71.0 (78.8–62.1) | 97.8 (98.8–96.2) | 0.84 (0.88–0.80) | |
| ≥2.50 | 63.7 (72.2–54.6) | 98.7 (99.5–97.4) | 0.81 (0.86–0.77) | |
| ≥2.75 | 43.5 (52.7–34.7) | 99.3 (99.8–98.1) | 0.71 (0.76–0.67) | |
| ≥3.00 | 14.5 (22.0–8.8) | 99.9 (100–99.0) | 0.57 (0.54–0.60) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blacksell, S.D.; Kingston, H.W.F.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Phanichkrivalkosil, M.; Hossain, M.; Hossain, A.; Ghose, A.; Leopold, S.J.; Dondorp, A.M.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect™ ELISA for the Detection of IgM Antibodies in Chittagong, Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030095
Blacksell SD, Kingston HWF, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, Phanichkrivalkosil M, Hossain M, Hossain A, Ghose A, Leopold SJ, Dondorp AM, Day NPJ, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect™ ELISA for the Detection of IgM Antibodies in Chittagong, Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2018; 3(3):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030095
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlacksell, Stuart D., Hugh W. F. Kingston, Ampai Tanganuchitcharnchai, Meghna Phanichkrivalkosil, Mosharraf Hossain, Amir Hossain, Aniruddha Ghose, Stije J. Leopold, Arjen M. Dondorp, Nicholas P. J. Day, and et al. 2018. "Diagnostic Accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect™ ELISA for the Detection of IgM Antibodies in Chittagong, Bangladesh" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 3, no. 3: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030095
APA StyleBlacksell, S. D., Kingston, H. W. F., Tanganuchitcharnchai, A., Phanichkrivalkosil, M., Hossain, M., Hossain, A., Ghose, A., Leopold, S. J., Dondorp, A. M., Day, N. P. J., & Paris, D. H. (2018). Diagnostic Accuracy of the InBios Scrub Typhus Detect™ ELISA for the Detection of IgM Antibodies in Chittagong, Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 3(3), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030095








