Groundwater Quality of Some Parts of Coastal Bhola District, Bangladesh: Exceptional Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Description of the Study Area
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Water Sample Collection and Preservation
3.4. Sample Grounding for Investigation
3.5. Determination of Physico-Chemical Parameters
3.6. Determination of Heavy Metals and Metalloids
3.7. Methods Used to Evaluate the Irrigation Water Quality
3.8. Data and Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Nonmetallic Ion Concentrations
4.3. Metallic Ion Concentrations
4.4. Arsenic Concentration
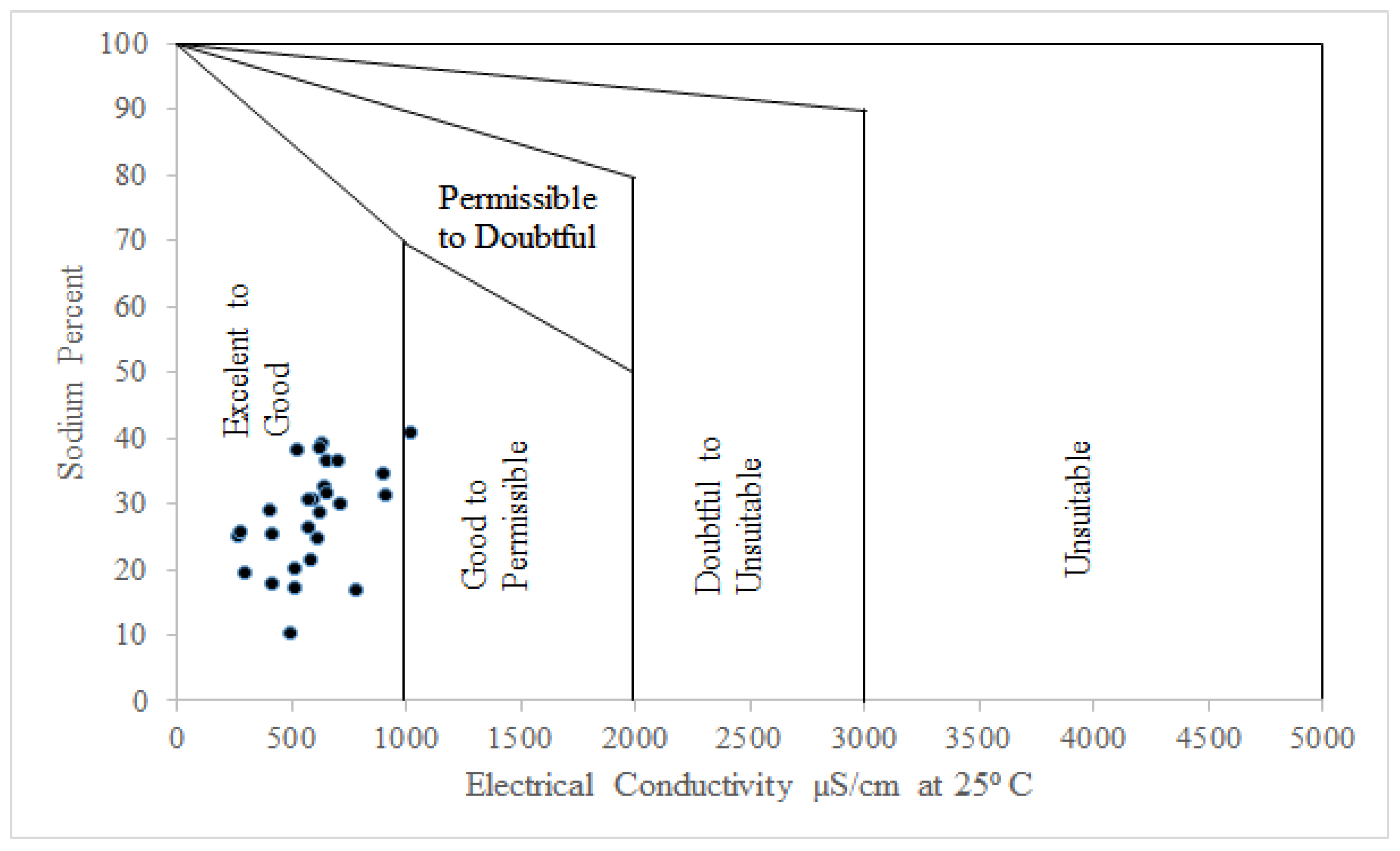
4.5. Parameters Related to the Irrigation Water Quality
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Shaibur, M.R.; Khan, M.H.; Rashid, M.S. Climate change may cause natural disasters in Shyamnagar, Satkhira: The southwestern parts of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 32, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmmed, I.; Shaibur, M.R.; Sarwar, S. Adaptation strategies with changing climatic conditions: A case study of coastal Bhola district, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2020, 2, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, N.; Shaibur, M.R.; Hossain, M.I.; Hossain, M.S.; Karim, R. Effects of natural hazards, its management and adaptation strategies in the Islamkati Union (Tala), Satkhira, Bangladesh. J. Jessore Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Hassain, M.Z.; Hasan, M.A.; Molla, S.R.; Asif, A.A. Disaster (SIDR) causes salinity intrusion in the south-western parts of Bangladesh. Asian-Aust. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Shamim, A.H.M.; Khan, M.H.; Tanzia, F.K.S. Exploration of soil quality in agricultural perspective at Gabura and Buri Goalini union: Shyamnagar, Satkhira, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 32, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Hoque, M.A.; Ansari, M.S.B.; Mallik, M.R. Impact of salinity on cropping pattern in selected areas of Barguna district. J. Patuakhali Sci. Technol. Univ. 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Rizvi, M.M.; Islam, S. Salinity causes ecosystem disruption and biodiversity losses in Beel Khuksia: Keshabpur, Jashore, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Shamim, A.H.M.; Khan, M.H. Water quality of different sources at Buri Goalini and Gabura unions of Shyamnagar upazila, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2019, 1, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Shamim, A.H.M.; Rizvi, M.M.; Amara, S.U.; Sarwar, S. Local adaptation strategies with waterlogging condition in beel Kapalia region, Jashore, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2019, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Masum, S. Working Together for Responsible & Eco-Friendly Shrimp Farming in Bangladesh; Coastal Development Partnership: Khulna, Bangladesh, 2011; Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/1533374/working-together-for-responsible-eco-friendly-shrimp-farming-in-bangladesh/2223185/ (accessed on 23 June 2023)CID: 20.500.12592/22rk25.
- Jabed, M.A.; Paul, A.; Nath, T.K. Peoples’ perception of the water salinity impacts on human health: A case study in south-eastern coastal region of Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Parvin, S.; Ahmmed, I.; Rahaman, M.H.; Das, T.K.; Sarwar, S. Gradients of salinity in water sources of Batiaghata, Dacope and Koyra upazila of coastal Khulna District, Bangladesh. Environ. Chall 2021, 4, 10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Nakagawa, K.; Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Berndtsson, R. Is road-side fishpond water in Bangladesh safe for human use? An assessment using water quality indices. Environ. Chall 2022, 6, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahin, K.T.K.; Basak, R.; Alam, R. Groundwater vulnerability assessment with DRASTIC index method in the salinity-affected southwest coastal region of Bangladesh: A case study in Bagerhat sadar, Fakirhat and Rampal. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 83–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H. Probable Impacts of Climate Change and Plantation on Embankment and Social Environment in Shyamnagar: Satkhira, Bangladesh. Bachelor’s Thesis, Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Jessore University of Science and Technology, Jessore, Bangladesh, September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- APCAEM. Asian and Public Center for Agricultural Engineering and Machinery: Adaptation to Climate Change for Sustainable Development of Bangladesh Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 3rd Session of Technical Committee of Asian and Pacific Center for Agricultural Engineering and Machinery (APCAEM), Beijing, China, 20–22 November 2007; Bangladesh Country Paper. pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- SRDI. Soil Resource Development Institute, Annual Report of 2012–2013; Ministry of Agriculture, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Farmgate, Dhaka, 2014; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.D.; Sarker, P.; Rahaman, M.; Ahmed, F.F.; Shaibur, M.R.; Uddin, M.K. Biological treatment of textile wastewater by total aerobic mixed bacteria and comparison with chemical fenton process. Pollution 2022, 8, 1418–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Pujari, M.; Demeke, G.; Worku, A.; Komarabathina, S. Potentiality of tannery buffing chromium-containing solid waste in making concrete blocks. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 80, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Jacks, G.; Ahmed, K.M.; Routh, J.; Khan, A.A. Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal Delta Plain aquifers in Bangladesh. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 69, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.E.; Ireson, A.; Kovats, S.; Mojumder, S.K.; Khusru, A.; Rahman, A.; Vineis, P.; Labrese, E.J. Drinking water salinity and maternal health in coastal Bangladesh: Implications of climate change. Environ. Health Pers. 2011, 119, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PDOICZMP. Program Development Office for Integrated Coastal Zone Management Plan: Where Land Meets the Sea: A Profile of the Coastal Zone of Bangladesh; University Press: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, A.; Sraboni, H.J.; Hasan, M.M.; Sorker, R. Eco-environmental assessment of the Turag river in the megacity of Bangladesh. Environ. Chall 2022, 6, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Shaibur, M.R.; Mamun, M.A. Hydro-geochemistry and quality assessment of deep groundwater in Shymnagor upazila, south-western Bangladesh. Int. J. Exp. Agric. 2019, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shammi, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Zahid, A.; Akter, Y.; Quaiyum, S.; Kurasaki, M. Spatio-temporal assessment and trend analysis of surface water salinity in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14273–14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.; Shekari, F.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Juhos, K.; Végvári, G.; Biró, B. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria enhanced salinity tolerance of salt-tolerant alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars at high salinity. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Shamim, A.H.M.; Kawai, S. Growth response of hydroponic rice seedlings at elevated concentrations of potassium chloride. J. Agric. Rural. Dev. 2008, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Rani, K.; Mamun, A.M.; Howlader, M.; Shaibur, M.R. Determination and distribution of groundwater composition in deep aquifer of Satkhira Municipality, Bangladesh. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4485–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.M.D.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Rume, T.; Azam, G. Hydrogeochemical investigation of groundwater in shallow coastal aquifer of Khulna district, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4219–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Shaibur, M.R.; Rahman, M.M. Groundwater chemistry at deep aquifer in coastal Koyra upazila under Khulna district of Bangladesh. Curr. World Environ. 2021, 16, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, P.; McArthur, J.M.; Hoque, M.A. Stable groundwater quality in deep aquifers of Southern Bangladesh: The case against sustainable abstraction. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R. Distribution of arsenic and heavy metals and correlation among them in groundwater of South Fukra, Kashiani, Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2019, 1, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Howlader, M. Groundwater composition at some unions in Kashiani and Kotalipara upazila of south-central coastal Gopalganj District, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2020, 2, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Anzum, H.M.N.; Rana, M.S.; Khan, M.A.S. Assessment of supplied water quality at Jashore Municipality (Pourashava), Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Environ. Res. 2012, 10, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Ahmmed, I.; Rumpa, S.S.; Parvin, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Sarwar, S. Physico-chemical parameters of groundwater at Jashore University of Science and Technology campus and its surrounding villages. J. Jessore Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Hossain, M.S.; Sony, S.J. Drinking water quality of hand tube well water at sub-urban areas of Jashore municipality, Bangladesh. J. Jessore Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, G.C.; Khan, M.J.H.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Zaman, S.; Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Tanaka, H. Human health risk assessment of elevated and variable iron and manganese intake with arsenic-safe groundwater in Jashore, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, S.; Ahmmed, I.; Mustari, S.; Shaibur, M.R. Uses of weighted arithmetic water quality index (WAWQI) to determine the suitability of groundwater of Chaugachcha and Manirampur upazila, Bangladesh. Environ. Biol. Res. 2020, 2, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Hossain, M.S.; Khatun, S.; Tanzia, F.K.S. Assessment of drinking water contamination in food stalls of Jashore Municipality, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Nakagawa, K.; Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Khan, A.S.; Goni, M.A.; Berndtsson, R. Spatial distribution and source identification of water quality parameters of an industrial seaport riverbank area in Bangladesh. Water 2022, 14, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Zahid, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.J.; Akter, Y.; Shammi, M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Roy, B. Investigation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the south-central part of the coastal region in Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DPHE/DANIDA. Hydrogeology Summary Report Five Districts Water Supply and Sanitation Group (5DWSG), DPHE-DANIDA Water Supply and Sanitation Components, Bangladesh; Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE) and Danish International Development Assistance (DANIDA): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2001; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- BBS. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Statistics and Informatics Division (SID), District Statistics of Bhola: Preliminary Results, Ministry of Planning; Government People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Das, T.K. Quantification of potentially toxic element contamination in groundwater using the novel particle-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) technique and human health impacts. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A.; Hossain, A.A.; Ali, M.H.; Islam, K.; Abbassi, S.U. Monitoring the coastal groundwater of Bangladesh. In Groundwater of South Asia; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, P.; McArthur, J.M. Mechanism of regional scale enrichment of groundwater by boron: The examples of Bangladesh and Michigan, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BWDB-UNDP. Groundwater Survey: The Hydrogeological Conditions of Bangladesh; UNDP Technical Report DP/UN/BGD-74-009/1; Bangladesh Water Development Board—United Nations Development Programme: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1982; 113p. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Basu, A.R.; Kulkarni, K.M.; Froehlich, K.; Tarafdar, S.A.; Ali, M.; Ahmed, N.; Hussain, A.; Rahman, M.; Ahmed, S.R. A Report on Isotope Hydrology of Groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications for Characterization and Mitigation of Arsenic in Groundwater; Isotope Hydrology of Groundwater in Bangladesh (IAEA-TC Project: BGD/8/016); International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Tushar, M.A.N.; Zahid, A.; Ahmed, K.M.U.; Siddique, M.A.M.; Mustafa, M.G. Spatiotemporal distribution of boron in the groundwater and human health risk assessment from the coastal region of Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21964–21977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A.; Rahman, M.; Hassan, M.R.; Ali, M.H. Determining sources of groundwater salinity in the multi-layered aquifer system of the Bengal Delta, Bangladesh. BRAC Univ. J. XI 2016, 2, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Bhattacharya, P.; Hasan, M.A.; Akhter, S.H.; Alam, S.M.; Bhuyian, M.H.; Imam, M.B.; Khan, A.A.; Sracek, O. Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, P. Overview of the hydrogeology of Bangladesh. In Groundwater Resources Development in Bangladesh: Background to the Arsenic Crisis, Agricultural Potential, and the Environment; Atiq Rahman, A., Ravenscroft, P., Eds.; The University Press Limited: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2003; pp. 43–86. [Google Scholar]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Rice, E.W.; Greenberg, A.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 2nd ed.; Centennial Edition: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huq, S.M.I.; Alam, M.D. A Handbook on Analyses of Soil, Plant and Water: Bangladesh Australia Center for Environmental Research; University of Dhaka: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.M.; Fujii, R. Selenium and arsenic. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3-Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series 5; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2001; pp. 793–831. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.M.L. Groundwater Hydrology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 535. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. In US Department of Agricultural Handbook; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 60, p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29, Rev. 1; UN Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, H.M. Groundwater; Wiley Eastern Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1987; pp. 344–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci. 1963, 95, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Water; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- SAS. SAS/STAT User’s Guide, No. 1, ANOVA, Version 6, 4th ed.; Statistical Analysis System Institute: Cary, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- BNDWQS. Bangladesh National Drinking Water Quality Survey of 2009; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Planning Division, Ministry of Planning, Govt. of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guideline for Drinking Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- DoE (Department of Environment). The Environment Conservation Rules 1997; Bangladesh gazette no. DA-1; Ministry of Environment and Forest: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Water Quality for Agriculture: Rome, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibur, M.R. Salinity Levels in Pond, Deep Tube Well and Pond Sand Filter Water in Two Unions of Southwestern Coastal District Satkhira, Bangladesh. In Water-Energy-Nexus in the Ecological Transition; Naddeo, V., Choo, K.H., Ksibi, M., Eds.; Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation (ASTI); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mahmud, A.; Md, M.A.; Haque, T.; Hossain, M.S.; Hasan, M.Y.; Shaibur, M.R.; Hossain, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Bai, L. Drinking water quality assessment based on index values incorporating WHO and Bangladesh standards. Phys. Chem. Earth 2023, 129, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Parvin, S.; Ahmmed, I.; Rahaman, M.H.; Sarwar, S. Climate Change and Salinity Intrusion in the Water Sources of Coastal Khulna District, Bangladesh. In Water-Energy-Nexus in the Ecological Transition; Naddeo, V., Choo, K.H., Ksibi, M., Eds.; Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation (ASTI); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 123–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.S.G.; Haque, A.; Hall, J.W. Have coastal embankments reduced flooding in Bangladesh? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, S.; Wang, X.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Hasan, R.; Harun, S.B.; Shamsuddin, S. Spatial assessment of groundwater over-exploitation in Northwestern Districts of Bangladesh. J. Geol. Soc. India 2015, 85, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. Elements of the Nature and Properties of Soils; Pearson Education International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zakir, H.M.; Sharmin, S.; Akter, A.; Rahman, M.S. Assessment of health risk of heavy metals and water quality indices for irrigation and drinking suitability of waters: A case study of Jamalpur Sadar area, Bangladesh. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, R.; Gazi, S.R.; Al-Mamun, A.A.; Khan, M.H.; Muliadi, M.; Mamun, S.A. Assessment of water quality in surface water of shipbreaking sites at Kumira Ghat, Sitakunda, Bangladesh. Techno J. Penelit. 2021, 10, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, S.A.; Roy, S.; Rahaman, M.S.; Jahan, M.; Islam, M.S. Status of fisheries resources and water quality of Tanguar Haor. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2013, 6, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Islam, A.; Majumder, A. Seawater intrusion into groundwater and its impact on irrigation and agriculture: Evidence from the coastal region of West Bengal, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Maifadi, S.; Mamba, B.B.; Verliefde, A.R.; Mhlanga, S.D. Spectroscopic determination of water salinity in brackish surface water in Nandoni Dam, at Vhembe District, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water 2018, 10, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Shen, S.; Haque, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Maw, K.W.; Habib, M.A. Assessing groundwater quality and its sustainability in Joypurhat district of Bangladesh using GIS and multivariate statistical approaches. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 1935–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.R. Groundwater; Frentce-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, N.; Lanon, M.A.H.; Sah, B.; Shaibur, M.R. Assessment of physico-chemical properties of water of Gorai river at Kushtia town in 2014: A case study. J. Sci. Technol. Environ. Inform. 2016, 2, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.G.; Uddin, S.M.H.; Haque, A.B.M.H. Assessment of hydro-geochemistry and groundwater quality of Rajshahi city in Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesmin, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Molla, S.R. The effect of drinking water sources due to Cyclone Aila at Shyamnagar, Satkhira district, Bangladesh. J. Trop. Resour. Sustain. Sci. 2022, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, M.; Rahman, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Karmakar, B.; Uddin, M.K. Assessment of salinity hazard in existing water resources for irrigation and potentiality of conjunctive uses: A case report from Gopalganj district, Bangladesh. Sustain. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, C.B.; Hoque, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Dewan, A. Groundwater constituents and trace elements in the basement aquifers of Africa and sedimentary aquifers of Asia: Medical hydrogeology of drinking water minerals and toxicants. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, E.M. Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthavigar, M.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vijayaravan, K.; Rajiv-Ganthi, R.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Manivannan, R.; Vasudevan, S. Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacmaz, H.; Nakoman, M.E. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater aquifer containing Uranyl phosphateminerals in the Koprubasi (Manisa) area, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, G.N.; McCarthy, D.L. Chemistry of Sanitary Engineers, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967; p. 518. [Google Scholar]




| Sample ID | Sampling Site | GPS Coordination | Depth | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Union | Location | Latitude | Longitude | (ft) | (m) | ||
| S1 | 01 BSU | Bhola Sadar | * | 22°41′4.82″ | 90°38′50.49″ | 950 | 290 |
| S2 | 02 BSU | Illisha | Nabokumar | 22°44′32.22″ | 90°37′1.98″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S3 | 03 BSU | Kachia | Porangonj | 22°43′41.83″ | 90°38′3.81″ | 950 | 290 |
| S4 | 04 BSU | Bapta | Hazirhat | 22°42′27.88″ | 90°38′25.8″ | 1200 | 366 |
| S5 | 05 BSU | Dhonia | * | 22°43′33.32″ | 90°39′19.99″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S6 | 06 BSU | Alinagor | Madrashabazar | 22°41′24.80″ | 90°37′13.47″ | 1400 | 427 |
| S7 | 07 BSU | Samaiya | * | 22°39′43.69″ | 90°35′33.66″ | 850 | 260 |
| S8 | 08 BSU | Veduria | Pulgora | 22°39′54.44″ | 90°33′4.76″ | 850 | 260 |
| S9 | 09 BSU | South Dighaldi | * | 22°35′38.97″ | 90°38′58.41″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S10 | 10 BSU | North Dighaldi | * | 22°36′55.93″ | 90°38′50.42″ | 950 | 290 |
| S11 | 11 BSU | Veduria | Launchghat | 22°42′4.51″ | 90°33′55.24″ | 1350 | 411 |
| S12 | 12 CFU | CMS | CM School | 22°9′47.64″ | 90°47′24.48″ | 1300 | 396 |
| S13 | 13 CFU | CMN | CMGS | 22°9′31.76″ | 90°46′9.87″ | 1250 | 381 |
| S14 | 14 CFU | Char Hazarigonj | Hazarigonj | 22°8′ 24.62″ | 90°45′45.81″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S15 | 15 CFU | Zahanpur | Zahanpur | 22°3′11.92″ | 90°26′44.56″ | 1350 | 411 |
| S16 | 16 CFU | Ewazpur | Minabazar | 22°0′50.84″ | 90°37′41.24″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S17 | 17 CFU | Aichabazar North | Aichabazar | 22°4′1.57″ | 90°37′8.91″ | 850 | 260 |
| S18 | 18 CFU | Rosulpur | * | 22°2′32.36″ | 90°40′56.36″ | * | * |
| S19 | 19 CFU | Jinnahghar | Kashemgonj | 22°5′42.08″ | 90°41′42.48″ | * | * |
| S20 | 20 CFU | Aslampur | Vuyerhat | 22°13′55.19″ | 90°45′40.74″ | 950 | 290 |
| S21 | 21 CFU | Janotabazar | * | 22°14′12.04″ | 90°46′1.55″ | * | * |
| S22 | 22 CFU | Osmangonj | Janotabazar North | 22°12′22.44″ | 90°47′2.88″ | 1250 | 381 |
| S23 | 23 CFU | Aminabazar | Rodrerhat | * | * | 1250 | 381 |
| S24 | 24 CFU | Aminabazar North | Majirhaat | 22°10′11.76″ | 90°43′30.99″ | 1050 | 320 |
| S25 | 25 CFU | Nilkamal | Dulahat | 22°11′38.59″ | 90°38′38.76″ | * | * |
| S26 | 26 CFU | Nurabad | Hajirhat | 22°10′16.23″ | 90°40′23.62″ | 1400 | 430 |
| S27 | 27 CFU | Char Kolmi | Anjurhat | 22°6′30.64″ | 90°38′24.61″ | 1400 | 430 |
| S28 | 28 CFU | CMMC | CMGS | 22°12′39.75″ | 90°45′11.28″ | * | * |
| Sample ID | Turbidity | EC | pH | TDS | NO3− | NH4+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTU | µS cm−1 | -------------------mg L−1---------------- | |||||
| ---------------------------------------------------Drinking Water Quality----------------------------------------------- | |||||||
| BNDWQS 2011 | 10.0 | 300–1500 | 6.5–8.5 | 1000.0 | 10.0 | 0.5 | |
| WHO 1984 | 5.0 | 750 | 6.5–8.5 | 1000.0 | 50.0 | 1.50 | |
| S1 | 01 BSU | 0.47 | 570.0 | 7.97 | 270.0 | 7.00 | 0.42 |
| S2 | 02 BSU | 0.50 | 650.0 | 8.03 | 330.0 | 7.00 | 0.46 |
| S3 | 03 BSU | 1.47 | 620.0 | 7.21 | 300.0 | 7.00 | 0.35 |
| S4 | 04 BSU | 0.78 | 510.0 | 7.80 | 250.0 | 6.00 | 0.32 |
| S5 | 05 BSU | 1.04 | 590.0 | 8.06 | 290.0 | 5.00 | 0.17 |
| S6 | 06 BSU | 0.64 | 630.0 | 7.81 | 350.0 | 6.00 | 0.55 |
| S7 | 07 BSU | 0.44 | 510.0 | 7.73 | 250.0 | 4.00 | 0.68 |
| S8 | 08 BSU | 1.32 | 700.0 | 7.70 | 360.0 | 7.00 | 0.42 |
| S9 | 09 BSU | 0.45 | 640.0 | 7.71 | 310.0 | 4.00 | 0.36 |
| S10 | 10 BSU | 0.85 | 910.0 | 7.83 | 430.0 | 7.00 | 1.46 |
| S11 | 11 BSU | 1.49 | 900.0 | 7.64 | 450.0 | 5.00 | 1.12 |
| S12 | 12 CFU | 2.52 | 270.0 | 8.12 | 130.0 | 6.00 | 0.78 |
| S13 | 13 CFU | 1.77 | 490.0 | 7.85 | 250.0 | 4.00 | 0.77 |
| S14 | 14 CFU | 0.38 | 300.0 | 7.36 | 130.0 | 5.00 | 1.06 |
| S15 | 15 CFU | 3.49 | 1020.0 | 7.60 | 510.0 | 4.00 | 1.42 |
| S16 | 16 CFU | 0.71 | 780.0 | 7.45 | 360.0 | 7.00 | 0.87 |
| S17 | 17 CFU | 0.77 | 280.0 | 8.00 | 170.0 | 3.00 | 1.59 |
| S18 | 18 CFU | 0.88 | 520.0 | 7.90 | 260.0 | 4.00 | 1.26 |
| S19 | 19 CFU | 0.30 | 410.0 | 7.55 | 200.0 | 5.00 | 1.46 |
| S20 | 20 CFU | 2.57 | 420.0 | 7.77 | 210.0 | 6.00 | 0.71 |
| S21 | 21 CFU | 1.29 | 570.0 | 7.72 | 280.0 | 6.00 | 0.96 |
| S22 | 22 CFU | 0.76 | 710.0 | 7.46 | 360.0 | 4.00 | 1.36 |
| S23 | 23 CFU | 1.18 | 420.0 | 8.02 | 210.0 | 5.00 | 0.76 |
| S24 | 24 CFU | 1.10 | 610.0 | 8.14 | 300.0 | 6.00 | 1.05 |
| S25 | 25 CFU | 0.60 | 580.0 | 7.83 | 280.0 | 4.00 | 1.00 |
| S26 | 26 CFU | 0.40 | 620.0 | 7.79 | 300.0 | 7.00 | 2.17 |
| S27 | 27 CFU | 1.40 | 650.0 | 7.95 | 330.0 | 4.00 | 1.75 |
| S28 | 28 CFU | 28.6 | 310.0 | 7.89 | 150.0 | 6.00 | 0.22 |
| --------------------------------------------------Descriptive Statistics---------------------------------------------- | |||||||
| Maximum | 3.49 | 1020 | 8.14 | 510.0 | 7.00 | 2.17 | |
| Minimum | 0.30 | 270 | 7.21 | 130.0 | 3.00 | 0.17 | |
| Mean | 1.11 | 588.15 | 7.78 | 291.48 | 5.40 | 0.94 | |
| Median | 0.85 | 590 | 7.80 | 290 | 5.00 | 0.87 | |
| SD | 0.76 | 181.96 | 0.23 | 89.56 | 1.30 | 0.50 | |
| ---------------------------------------------------Irrigation Water Quality------------------------------------------- | |||||||
| DoE 1997 | ** | 2250 | 6.5–8.5 | 2100 | ** | ** | |
| FAO 1976 | ** | 700–3000 | 6.5–8.5 | 0–2000 | ** | ** | |
| MRV * | ** | 1500 | 6.5–8.4 | 1000 | 50.0 | 1.50 | |
| Sample ID | Na | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Cu | Zn | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -----------------------------------------mg L−1------------------------------------------------- | ||||||||||
| BNDWQS 2011 | 200.0 | 12.0 | 75.0 | 30–35 | 0.3–1.0 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 0.05 | |
| WHO 1984 | 200.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 | 150.0 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 0.01 | |
| S1 | 01 BSU | 65.0 | 5.0 | 80.16 | 46.06 | 0.16 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S2 | 02 BSU | 65.0 | 10.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.20 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S3 | 03 BSU | 60.0 | 10.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.68 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S4 | 04 BSU | 55.0 | 5.0 | 96.19 | 55.27 | 0.20 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S5 | 05 BSU | 65.0 | 5.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.09 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S6 | 06 BSU | 75.0 | 15.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.90 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S7 | 07 BSU | 45.0 | 5.0 | 96.19 | 55.27 | 0.18 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S8 | 08 BSU | 65.0 | 10.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.36 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S9 | 09 BSU | 55.0 | 10.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.06 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S10 | 10 BSU | 85.0 | 10.0 | 80.16 | 46.06 | 1.07 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S11 | 11 BSU | 80.0 | 15.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.03 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S12 | 12 CFU | 50.0 | 10.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.07 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S13 | 13 CFU | 25.0 | 5.0 | 96.19 | 55.85 | 0.01 | 0.50 | BDL | BDL | 0.002 |
| S14 | 14 CFU | 45.0 | 10.0 | 80.16 | 46.06 | 0.03 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S15 | 15 CFU | 80.0 | 15.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.17 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S16 | 16 CFU | 45.0 | 10.0 | 96.19 | 55.27 | 0.55 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S17 | 17 CFU | 75.0 | 5.0 | 96.19 | 55.27 | 1.02 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S18 | 18 CFU | 70.0 | 10.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.13 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S19 | 19 CFU | 60.0 | 5.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.04 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S20 | 20 CFU | 40.0 | 5.0 | 80.16 | 46.06 | 0.32 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 0.003 |
| S21 | 21 CFU | 50.0 | 10.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.03 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S22 | 22 CFU | 65.0 | 15.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.12 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S23 | 23 CFU | 50.0 | 5.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.02 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S24 | 24 CFU | 60.0 | 5.0 | 80.16 | 46.06 | 0.07 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S25 | 25 CFU | 40.0 | 5.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.56 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S26 | 26 CFU | 75.0 | 20.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 1.05 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S27 | 27 CFU | 70.0 | 15.0 | 64.13 | 36.85 | 0.78 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S28 | 28 CFU | 55.0 | 15.0 | 128.26 | 73.70 | 0.22 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| ------------------------------------------Descriptive Statistics------------------------------------------- | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 85.0 | 20.0 | 96.19 | 55.85 | 1.07 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Minimum | 25.0 | 5.0 | 48.09 | 27.66 | 0.01 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Mean | 59.81 | 9.26 | 68.28 | 39.27 | 0.33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Median | 60.00 | 10.00 | 64.13 | 36..85 | 0.17 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| SD | 14.51 | 4.32 | 17.56 | 10.12 | 0.36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| ---------------------------------------------------Irrigation Water Quality-------------------------------------------- | ||||||||||
| DoE | 200 | 12.0 | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | 0.05 | |
| FAO | 0–40 | 0–20 | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| MRV * | 230.0 | 20.0 | ** | ** | 5.0 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 2.0 | 0.10 | |
| Category | Grade | n = 27 | % | Category | Grade | n = 27 | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (µS cm−1; Wilcox 1955) | SSP (Wilcox 1955) | ||||||
| Excellent | <250 | 0 | 0.0 | Excellent | 0–20 | 5 | 18.0 |
| Good | 250–750 | 23 | 85.0 | Good | 20–40 | 21 | 78.0 |
| Permissible | 750–2250 | 4 | 15.0 | Permissible | 40–60 | 1 | 4.0 |
| Doubtful | 2250–3000 | 0 | 0.0 | Doubtful | 60–80 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Unsuitable | >5000 | 0 | 0.0 | Unsuitable | >80 | 0 | 0.0 |
| EC (µS cm−1; WHO 2004) | SSP (Eaton 1950) | ||||||
| Low salinity | 0–250 | 0 | 0.0 | Safe | <60 | 27 | 100.0 |
| Medium salinity | 251–750 | 23 | 85.0 | Unsafe | >60 | 0 | 0.0 |
| High salinity | 751–2250 | 4 | 15.0 | SAR (Vasanthavigar et al., 2010) | |||
| Very high salinity | 2251–6000 | 0 | 0.0 | Suitable | <2 | 10 | 37.0 |
| Extensively high salinity | 6001–10,000 | 0 | 0.0 | Unsuitable | >2 | 17 | 63.0 |
| Brine | >10,000 | 0 | 0.0 | ||||
| TDS (mg L−1; WHO 2004) | MAR (Kacmaz and Nakoman 2010) | ||||||
| Excellent | <300 | 17 | 63.0 | S uitable | <50 | 27 | 100.0 |
| Good | 300–600 | 10 | 37.0 | Unsuitable | >50 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Fair | 600–900 | 0 | 0.0 | KR (Kelley 1963) | |||
| Poor | 900–1200 | 0 | 0.0 | Suitable | <1 | 27 | 100.0 |
| Unacceptable | >1200 | 0 | 0.0 | Unsuitable | >1 | 0 | 0.0 |
| TH (mg L−1; Sawyer and McCarthy 1967) | |||||||
| Soft | 27 | 100.0 | |||||
| Moderately hard | 75–150 | 0 | 0.0 | ||||
| Hard | 150–300 | 0 | 0.0 | ||||
| Very hard | >300 | 0 | 0.0 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaibur, M.R.; Ahmmed, I.; Sarwar, S.; Karim, R.; Hossain, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Shah, M.S.; Khan, A.S.; Akhtar, F.; Uddin, M.G.; et al. Groundwater Quality of Some Parts of Coastal Bhola District, Bangladesh: Exceptional Evidence. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030071
Shaibur MR, Ahmmed I, Sarwar S, Karim R, Hossain MM, Islam MS, Shah MS, Khan AS, Akhtar F, Uddin MG, et al. Groundwater Quality of Some Parts of Coastal Bhola District, Bangladesh: Exceptional Evidence. Urban Science. 2023; 7(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaibur, Molla Rahman, Ishtiaque Ahmmed, Sabiha Sarwar, Rezaul Karim, Md. Musharraf Hossain, M. Shahidul Islam, Md. Shaheen Shah, Abu Shamim Khan, Farhana Akhtar, Md. Galal Uddin, and et al. 2023. "Groundwater Quality of Some Parts of Coastal Bhola District, Bangladesh: Exceptional Evidence" Urban Science 7, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030071
APA StyleShaibur, M. R., Ahmmed, I., Sarwar, S., Karim, R., Hossain, M. M., Islam, M. S., Shah, M. S., Khan, A. S., Akhtar, F., Uddin, M. G., Rahman, M. M., Salam, M. A., & Ambade, B. (2023). Groundwater Quality of Some Parts of Coastal Bhola District, Bangladesh: Exceptional Evidence. Urban Science, 7(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030071







