Abstract
In this paper, a piecewise-defined function is proposed to estimate traffic noise in urban areas. The proposed approach allows the use of the model even in the case of very low or zero flows for which the classical logarithmic form is not suitable. A model based on the proposed approach is calibrated for a real case and compared with the results obtained with a model based only on the logarithmic form. The results obtained show how the proposed piecewise-defined function, linear for low traffic flows and logarithmic for medium-high volumes, is able to better represent real noise pollution levels in all conditions. The proposed approach is particularly useful when comparing two plan scenarios from the point of view of noise effects.
1. Introduction
In urban areas, road traffic contributes significantly to environmental noise and is its main source. As is evident to anyone living in congested cities, noise causes annoyance, sleep disturbance and damage to human health, reducing the quality of life.
The World Health Organisation [1] has estimated that at least one million years of life are lost every year due to road traffic noise in Western Europe. Impacts on human health have been widely studied. Muzet [2] and Pirrera et al. [3] studied the effects of environmental noise on sleep and, consequently, on health. Some studies [4,5,6,7,8] focused on cardiovascular problems related to noise. Sakhvidi et al. [9] studied the association between noise exposure and diabetes. Jafari et al. [10] evaluated if noise exposure can accelerate cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Noise and annoyance were studied in [11,12,13,14,15]. Other general studies can be found in [16,17,18], while the effects of noise on property prices were studied in [19,20,21].
There is extensive literature on models for estimating noise pollution. Some reviews can be found in [22,23,24]. Most of the proposed models relate road traffic noise to vehicle flows; some also consider other variables such as average speed or certain characteristics of the road infrastructure (slope, type of pavement, distance and height of buildings, etc.); here, we just mention [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43].
The analysis of the literature allows us to identify two main types of models:
- general, i.e., applicable to different situations and case studies;
- specific, calibrated in correspondence with a specific case study and applicable only in the reference context or in very similar contexts.
General models relate noise to vehicle flow and/or average speed, but also take into account other context-specific characteristics (traffic type, gradient, road surface, barrier geometry, mean wind speed, traffic composition, local topography, etc.). Some examples are the models FHWA [44], CoRTN [45], RLS (see [46,47]), ASJ RTN [48], Harmonoise [49,50], Son Road [51], Nord 2000 [52], NMPB-2008 [53] and CNOSSOS-EU [43]. A comparison of these models and more details can be found in [23].
On the other hand, specific models are calibrated for specific situations, such as urban roads with similar characteristics, or sometimes for single infrastructures. These models estimate the noise emissions, for that specific case study, as a function of the traffic flow and sometimes the average speed of that traffic. Most models are based only on traffic flows; the simplest functional form is the following:
where:
Leq (f) = β0 + β1 · log10 f
- Leq is the equivalent noise level at a specific distance from the centre of the road, in dB(A);
- β0 and β1 are the coefficients of the model to be calibrated;
- f is the homogenised traffic flow (veh/h).
Other models include the distance of the receiver from the source within the formula, or other features such as the percentage of heavy vehicles or the average flow speed, trying to extend the use of the model to other contexts as much as possible. In almost all formulations, the term log10 f, or its functional transformation, is present and plays the main role in the calculation. Some papers that use the approach (1) or similar are [26,27,46,54,55,56,57,58,59].
Model (1) surely cannot be easily generalised but it is very easy to calibrate in specific contexts. A specific model, once calibrated in correspondence of some roads of a city, can be used to estimate noise pollution levels also in other roads of the same city, in order to estimate the exposed population, identify the most critical areas to intervene on and assess the overall effects of interventions on traffic circulation [60].
In this paper, the calibration of a specific model based on a piecewise-defined function is proposed, to avoid the use of the logarithmic form that can create problems for zero or very low flow, which can occur in simulation models of a whole road network.
2. The Proposed Approach
Model (1) and most models based on the logarithm of traffic flows work very well when traffic flows are not extremely low or zero. It is well known that power and sound pressure levels vary with a logarithmic law. Indeed, the intensity of auditory sensations is in first approximation proportional to the logarithm of the stimulus and not to its absolute value.
For example, if we use the model calibrated in [59], below:
we can see that it is not applicable in case of null flow (the second term would tend to less infinite) and would give a value equal to 17.594 dB(a) in case of 1 veh/h and 34.971 in case of 10 veh/h. As also written in [59], the model is valid only if the flow is greater than about 50 veh/h, at which the equivalent noise level is equal to 47.1 dB(A).
Leq (f) = 17.594 + 17.377 · log10 f
In most cases, this underestimation of equivalent noise levels for very low flows is not a problem, because roads with low traffic, or periods with low traffic, do not receive attention in noise analysis. The problem arises when we want to analyse the overall noise level of a city, perhaps by comparing pre- and post-intervention scenarios. For example, in Urban Traffic Plans, it is useful to check with simulation whether changes in traffic patterns may or may not have a positive impact on noise pollution. The approximations included in the simulation models, such for example the discretisation of the study area into traffic zones (zoning), may lead to estimate zero or very low traffic flows on some links of the network and any comparative analysis would be compromised in these cases.
To avoid this problem, in this paper we propose the use of a piecewise-defined function, in order to calibrate specific models, which has a first linear part (for low traffic values) and a second logarithmic part (for high traffic values). In any case, the function must be continuous and derivable; therefore, we propose to extend linearly model (1), with an inclination equal to the first derivative of the model, for flows lower than a minimum value, fmin. This way, we can formulate a model that is valid for all traffic conditions. Under these assumptions, the model can be formulated as follows:
Leq (f) = [β0 + β1 · log10 fmin − fmin · (1/(fmin · ln(10))) · β1] + [(1/(fmin · ln(10))) · β1] · f if f < fmin
Leq (f) = β0 + β1 · log10 f if f ≥ fmin
The calibration of models (3)–(4) requires the calculation of three values, in contrast to model (1) for which it was sufficient to calibrate two coefficients (β0 and β1); indeed, in addition to the β0 and β1 coefficients, it is necessary to calibrate the value of fmin.
3. Model Calibration
The calibration of the model is performed using the same data collected in the testing campaign reported in [59] in the city of Benevento. These data refer to four road sections (see Figure 1) representative of the prevailing type of roads in the urban network; the pavement was bituminous in all cases.
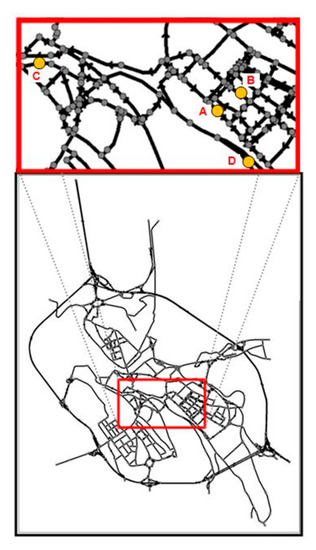
Figure 1.
Survey locations.
The phonometric surveys were conducted by a specialised technician using a Svantek 949 sound level meter, with the periodic certification, equipped with a preamplifier Svantek SV 12L and a pre-polarised microphone Svantek SV22. Before and after the measurements, the tuning of the system was verified with a precision calibrator DELTA OHM. A microclimatic station for measuring temperature and wind speed and direction was used; indeed, the phonometric measures must be recorded in absence of rain, snow or fog and the maximum wind speed must be lower than 5 m/s. The phonometer is disposed to 1.5 m in height from the road level and on the side of the road. The traffic surveys were obtained with a manual procedure, counting cars, light-duty vehicles (LDV) and heavy-duty vehicles (HDV) every 15 min (motorcycle flows are negligible in Benevento), and assuming the following equivalence coefficients: LDV = 2 cars; HDV = 8 cars. Overall, 32 measures were conducted; in Table 1 the main data are summarised.

Table 1.
Survey measures.
The phonometric measures have to be corrected for the locations A and B according to the distance from the centre of the road; indeed, as reported in Figure 2, the distances are different in these locations since there are parking lots (the measures were, anyway, performed where no cars were parked). Assuming a linear noise source, the sound in locations A and B arrives to the receptor attenuated by the following factor:
ΔLeq = 10 · log10 (6.18/3.81) = 2.1 dB(A)
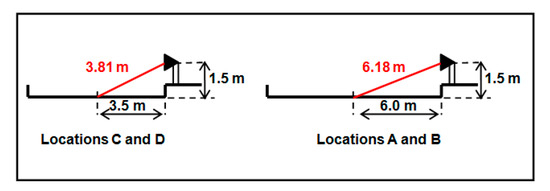
Figure 2.
Distances of phonometer from the centre of the road.
Therefore, the measures on locations A and B are incremented of 2.1 dB(A); these corrected values, Leqc, are reported in the third column of Table 1.
The model was calibrated using the generalized least squares method and the following values were obtained: β0 = 4.427; β1 = 22.109; fmin = 287 veh/h. With these values, models (3)–(4) become:
Leq (f) = 49.160 + 0.0335 · f if f < 287
Leq (f) = 4.427 + 22.109 · log10 f if f ≥ 287
The value of the coefficient of determination, R2, is significantly high (0.878); Figure 3 reports the comparison between measured and estimated data and the comparison between the model curve and the experimental data. This model improves model (2) for which R2 was equal to 0.847. The RMSE value also improved, decreasing from 2.48 to 2.22.
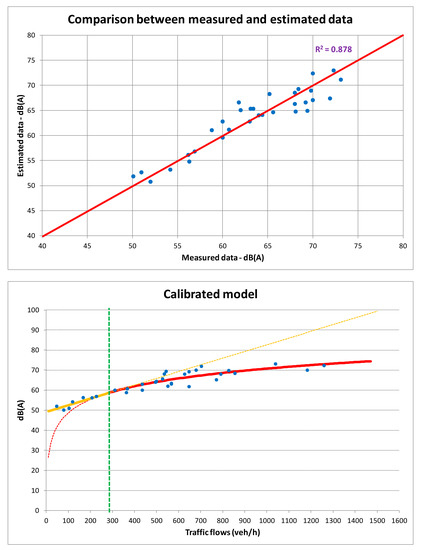
Figure 3.
Comparison between measured and estimated data.
It is interesting to compare the results obtained between the two models for low traffic flow values. It is noted that the proposed model can provide plausible results in all flow ranges, while the logarithmic model provides acceptable values only for sufficiently high flow values (see Table 2 and Figure 4).

Table 2.
Comparison of models.
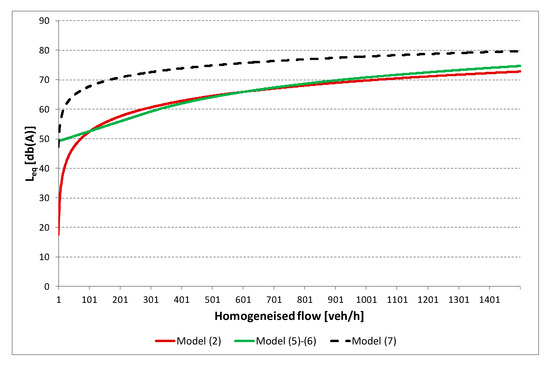
Figure 4.
Comparison of models.
Moreover, the proposed model was also compared with the model proposed in [54], which has been widely used:
where:
Leq (f) = 55.5 + 10.2 · log10 f + 0.3 P − 19.3 log10 d
- P is the percentage of heavy vehicles;
- d is the distance from the source.
For the comparison, we assume a percentage of heavy vehicles of 10% and a distance from the source equal to 3.81 m.
It should be noted that model (7) was not calibrated for the case study, so it is possible to compare only the trend of the function, which is similar to that of model (2); model (7) overestimates the noise levels for the case study examined, but, from the trend of the function, it presents the same problems as model (2).
4. Conclusions
Noise pollution is one of the main external impacts of the road transport system. Numerous models have been proposed in the literature, some more general, others more specific, for its estimation. In almost all models, equivalent noise levels are assumed to be a function of the logarithm of traffic flows; this theoretically correct hypothesis does not, however, allow the use of such models for very low or zero flows.
On the other hand, in practice, in particular for urban roads, there is always background noise to which the noise emitted by vehicular traffic is added. The approach proposed in this paper, based on the use of a piecewise-defined function to be calibrated for the specific context, makes it possible to use the calibrated model even on roads with very low or no traffic.
Comparison with a logarithmic model calibrated with the same data shows the robustness of the proposed approach.
In the literature, the need to estimate noise emissions at low traffic values has always been considered unimportant, because noise pollution is usually a real problem in case of high traffic flows. Often, models have been calibrated and used only on high traffic roads and at peak times.
The need to have a model that is also valid for low (or no) traffic flows occurs when we want to examine, in simulation, the situation of an overall city network, also before and after interventions on traffic schemes. In these cases, it may occur that on some road sections, the level of traffic is very low or zero, even for the approximations of the model. The proposed approach makes it possible to use a unique model to estimate all traffic conditions and, consequently, to compare the intervention scenarios.
The proposed approach can be used to calibrate specific models in other contexts; the calibrated models (5)–(6), on the other hand, have uses limited to the case study or very similar situations.
The research prospects can be directed to test the proposed approach on other urban contexts and to generalise the model based on this type of function so that it can also be used in contexts other than the one in which it has been calibrated.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author is very grateful to Giuseppe Mazza (Artea Srl) and Orazio Mascolino for having supported the survey activities.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muzet, A. Environmental noise, sleep and health. Sleep Med. Rev. 2007, 11, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrera, S.; De Valck, E.; Cluydts, R. Nocturnal road traffic noise: A review on its assessment and consequences on sleep and health. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhri, A.; Aasvang, G.M. Noise, sleep and poor health: Modeling the relationship between road traffic noise and cardiovascular problems. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4935–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunovic, K.; Stansfeld, S.; Clark, C.; Belojevic, G. Epidemiological studies on noise and blood pressure in children: Observations and suggestions. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio, A.; Linares, C.; Banegas, J.R.; Diaz, J. Road traffic noise effects on cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic health: An integrative model of biological mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munzel, T.; Schmidt, F.P.; Steven, S.; Herzog, J.; Daibner, A.; Sorensen, M. Environmental Noise and the Cardiovascular System. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravipour, M.; Khanlari, P. The association between road traffic noise and myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhvidi, M.J.Z.; Sakhvidi, F.Z.; Mehrparvar, A.H.; Foraster, M.; Dadvand, P. Association between noise exposure and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, Z.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Noise exposure accelerates the risk of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: Adulthood, gestational, and prenatal mechanistic evidence from animal studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. R. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen-Guzejev, M.; Vuorinen, H.S.; Kaprio, J.; Heikkilag, K.; Mussalo-Rauhamaa, H. Self Report of Transportation noise exposure, annoyance and noise sensitivity in relation to noise map information. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 234, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouis, D. Annoyance from Road Traffic Noise: A Review. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klæboe, R.; Amundsen, A.H.; Fyhri, A.; Solberg, S. Road traffic noise–the relationship between noise exposure and noise annoyance in Norway. Appl. Acoust. 2004, 65, 893–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klæboe, R.; Kolbenstvedt, M.; Clench-Aas, J.; Bartonova, A. Oslo traffic study part 1: An integrated approach to assess the combined effects of noise and air pollution on annoyance. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4727–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, Y.; He, L. The relationship between urban combined traffic noise and annoyance: An investigation in Dalian, north of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohrstrom, E. Effects of low levels of road traffic noise during the night a laboratory study on number of events maximum noise levels and noise sensitivity. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 179, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Garraín, D.; Vidal, R. Methodological proposals for improved assessments of the impact of traffic noise upon human health. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekaviciute, J.; Kephalopoulos, S.; Stanfeld, S.; Clark, C. ENNAH-European Network on Noise and Health; EU Project no. 226442; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013.
- Theebe, M.A.J. Planes, Trains, and Automobiles: The impact of traffic noise on houses prices. J. Real Estate Financ. 2004, 28, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Park, S.J.; Kweon, Y.J. Highway traffic noise effects on land price in an urban area. Transport. Res. D 2007, 12, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.S.; Kim, D.-J. Hedonic estimates of rail noise in Seoul. Transport. Res. D 2013, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C. A critical review of some traffic noise prediction models. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Maji, S. A critical review of principal traffic noise models: Strategies and implications. Environ. Impact Asses. 2014, 46, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Ketzel, M.; Kakosimos, K.; Sorensen, M.; Jensen, S.S. Road traffic air and noise pollution exposure assessment–A review of tools and techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamanikabud, P.; Vivitjinda, P. Noise prediction for highways in Thailand. Transport. Res. D 2002, 7, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, A.; Diniz, F.B.; Zannin, P.H.T. The statistical modeling of road traffic noise in an urban setting. Cities 2003, 20, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Plutino, D.; Cannistraro, G. Evaluation and analysis of the environmental noise of Messina, Italy. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansatcha, M.; Pamanikabud, P.; Brown, A.L.; Affum, J.K. Motorway noise modelling based on perpendicular propagation analysis of traffic noise. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, O.; Gokdagb, M.; Yuksel, F. A traffic noise prediction method based on vehicle composition using genetic algorithms. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Leclercq, L.; Lelong, J. Dynamic estimation of urban traffic noise: Influence of traffic and noise source representations. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Mun, S. Development of a highway traffic noise prediction model that considers various road surface types. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamanikabud, P.; Tansatcha, M.; Brown, A.L. Development of a highway noise prediction model using an Leq20 s measure of basic vehicular noise. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 316, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumara, H.N.; Gowda, R.M.M. Road Traffic Noise Prediction Model under Interrupted Traffic Flow Condition. Environ. Model. Assess. 2009, 14, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, J.F.; Besnard, F.; Doisy, S.; Lelong, J.; le Duc, E. New vehicle noise emission for French traffic noise prediction. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedepo, O.S.; Abdullahi, A.S. Evaluation and analysis of noise levels in Ilorin metropolis, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamanikabud, P.; Tansatcha, M. 3D analysis and investigation of traffic noise impact from a new motorway on building and surrounding area. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.Y.T.; Yano, T.; Sato, T.; Nishimura, T. Characteristics of road traffic noise in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Swami, B.L. Comprehensive approach for the development of traffic noise prediction model for Jaipur city. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 172, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, R.; Gałuszka, M. Road traffic noise prediction based on speed-flow diagram. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Kamali, M.J. Modeling of road-traffic noise with the use of genetic algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.C.; Park, T.H.; Ko, J.H.; Chang, S.I.; Kim, M.; Holt, J.B.; Mehdi, M.R. Modeling of road traffic noise and estimated human exposure in Fulton County, Georgia, USA. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirianni, F.; Leonardi, G. Environmental modeling for traffic noise in urban area. Am. J. Environm. Sci. 2012, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kephalopoulos, S.; Paviotti, M.; Anfosso-Lédée, F. Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU); EUR 25379 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2012.
- Barry, T.M.; Reagan, J.A. FHWA Highway Traffic Noise Prediction Model., FHWA-RD-77-108; US Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Office of Research, Office of Environmental Policy, US Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Office of Research, Office of Environmental Policy: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Department of Transport. Calculation of Road Traffic Noise; Department of Transport Welsh office: Cardiff, UK; HMSO: Richmond, UK, 1998.
- Quartieri, J.; Mastorakis, N.E.; Iannone, G.; Guarnaccia, C.; Ambrosio, S.D.; Troisi, A.; Lenza, T.L.L. A review of traffic noise predictive models. In Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS International Conference on “Applied and Theoretical Mechanics” (MECHANICS’09), Puerto De La Cruz, Canary Islands, Spain, 14–16 December 2009; pp. 72–80, ISBN 978-960-474-140-3, ISSN 1790-2769. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, P.; Ahmad, K.; Afsar, S.S.; Akhtar, N. Validation of the Road Traffic Noise Prediction Model RLS-90 in an Urban Area. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Engineering: Machine Learning and Internet of Things (ICETCE-2020), Jaipur, India, 7–8 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K. Road traffic noise prediction model “ASJ RTN-Model 2008”: Report of research committee on road traffic noise. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Watts, G. Harmonoise Prediction Model for Road Traffic Noise, PPR 034; TRL Limited: Wokingham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson, H.G. Acoustical source modeling of road vehicles. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2007, 93, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Heutschi, K. Son Road: New Swiss road traffic noise model. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2007, 90, 548–554. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh, J.; Svein, Å.; Jonasson, H.G. Nordic Environmental Noise Prediction Methods; Nord 2000, Summary Report; DELTAAcoustics & Vibration: Kogens Lyngby, Denmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dutilleux, G.; Defrance, J.; Ecotière, D.; Gauvreau, B.; Bèrengier, M.; Besnard, F.; Duc, E.L. NMPB-Routes 2008: The revision of the French method for road traffic noise prediction. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2010, 96, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.A. Noise prediction for urban traffic conditions-related to measurements in the Sydney Metropolitan Area. Appl. Acoust. 1977, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelli, G.B.; Gluck, K.; Santoboni, S.A. A mathematical model for evaluation and prediction of mean energy level of traffic noise in Italian towns. Acustica 1983, 53, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- García, A.; Bernal, D. The prediction of traffic noise levels in urban areas. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Noise Control Engineering, (NCE’ 85), Munich, Germany, 18–24 September 1985; pp. 843–846. [Google Scholar]
- Fagotti, C.; Poggi, A. Traffic Noise Abatement Strategies. The Analysis of Real Case not Really Effective. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress for Noise Abatement, Bologna, Italy, 10–12 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, W.K.H.; Tam, M.L. Reliability analysis of traffic estimates in Hong Kong. Transport. Res. D 1998, 3, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Mascolino, O.; Mazza, G. A model for estimating road traffic noise in urban areas. In Proceedings of the IEEE EEEIC 2016–16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, M.; De Luca, G. A methodology for evaluating urban traffic plan scenarios from the point of view of traffic noise. Wseas Trans. Circuits Syst. 2016, 15, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).