A Review of the Characteristics of Recycled Aggregates and the Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced by Replacing Natural Coarse Aggregates with Recycled Ones—Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.1.1. Application of the PRISMA Protocol for Data Collection
Identification
Screening
2.2. Bibliographic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis Results
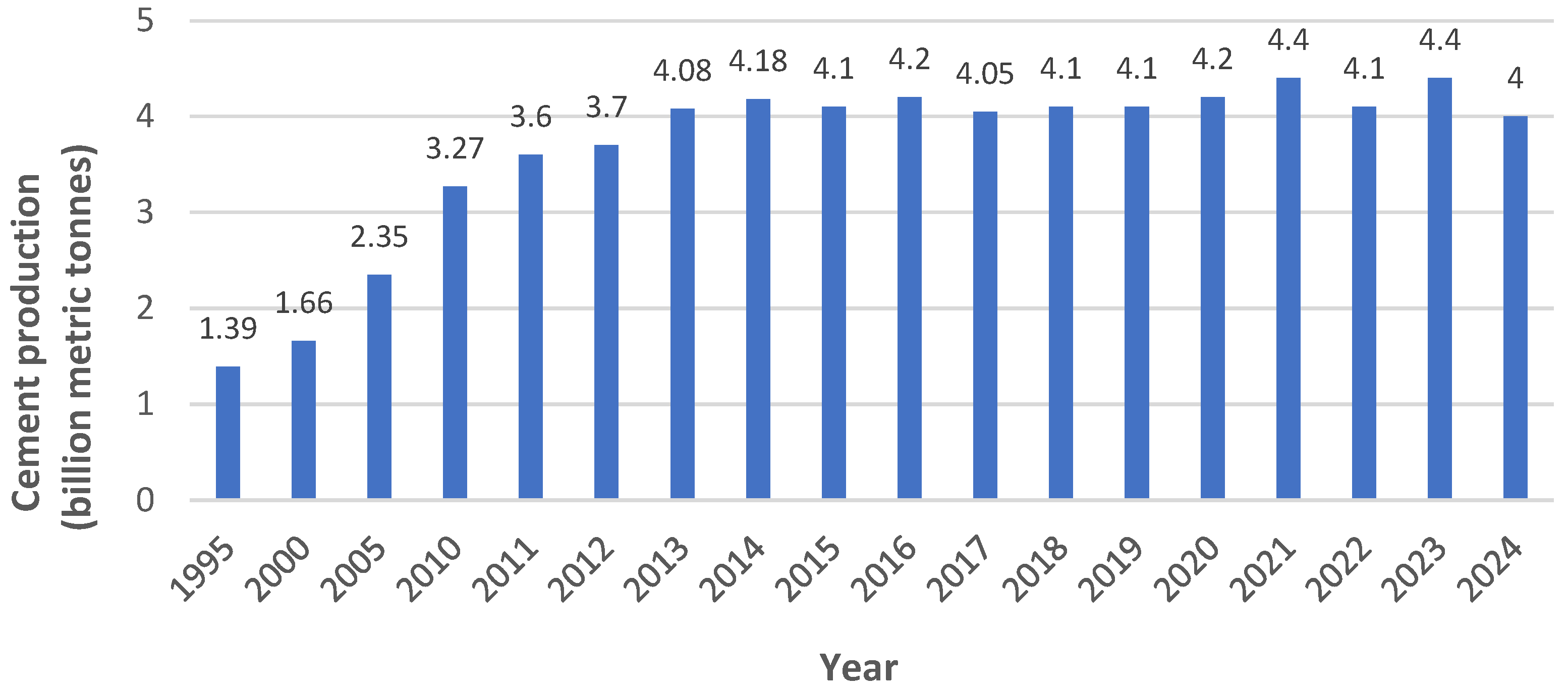
3.1.1. Analysis of Publications by Year
3.1.2. Analysis of the Most Influential Studies
3.1.3. Analysis of the Most Productive Authors
3.1.4. Co-Authorship Mapping
3.1.5. Most Influential Countries
3.1.6. Keyword Analysis
3.2. Bibliographic Analysis Results
3.2.1. Recycled Concrete
3.2.2. Recycling Process
3.2.3. Replacement Rate
3.2.4. Specific Gravity
3.2.5. Residual Mortar
3.2.6. Treatment of Recycled Aggregates
3.2.7. Water Absorption
3.2.8. Abrasion Resistance
3.2.9. Slump Test
3.2.10. Compressive and Tensile Strength
3.2.11. Durability
3.2.12. Modulus of Elasticity
3.2.13. Flexural Strength
4. Conclusions
- The CDW recycling process is typically conducted using horizontal impact crushers or jaw crushers;
- Replacement rates of natural aggregate by recycled material vary, with limits between 20 and 60%. There are also researchers who advocate the possibility of 100% replacement, as long as the matrix concrete has a minimum compressive strength of 60 MPa;
- The specific density of most recycled aggregates varies from 1.91 to 2.70, maintaining an average density of 2.32 g/cm3;
- Most research mentions that the amount of adhered mortar varies from 20% to 56%;
- The treatment of recycled aggregates can be performed through the addition of nanomaterials, carbonation, coating with cementitious materials, immersion in sodium sulfate, autogenous cleaning, heat treatment, ultrasonic cleaning, and treatment with pozzolans;
- The water absorption process of recycled aggregate varies from 2% to 15%;
- The abrasion resistance of most natural coarse aggregates in Los Angeles is greater than that of natural ones;
- The slump test demonstrates that the use of recycled aggregates negatively affects the workability of recycled concrete compared to concrete with natural aggregates, making it difficult to achieve the workability required by the project;
- The use of recycled aggregates results in a compressive strength approximately 2.6% to 43% lower than that of concrete with natural aggregates, depending on the replacement rate. The same behavior was observed in relation to tensile strength. However, there is still considerable discrepancy between the results obtained in the various studies analyzed;
- Studies mention that, as replacement rates of natural aggregates with recycled ones increase, the flexural strength is reduced by up to 15%;
- The durability properties of concrete containing recycled aggregate depend on the porosity and pore distribution of the aggregates, which decrease with increasing replacement of natural aggregate by recycled aggregate;
- The modulus of elasticity of the concrete mix is primarily influenced by its porosity and the modulus of elasticity of the cement paste. As natural aggregate replacement rates increase, the modulus of elasticity decreases by 25%.
- Articles on the topic may have been excluded from the sample obtained by the PRISMA protocol during the screening stage;
- No articles were identified that addressed these indicators under study applied directly to recycled concrete;
- Articles on the topic may have been identified but were not included in the sample because the authors did not have access to their content, as it was closed access.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Rank | Manuscript Title | Authors | TC 1 | CPA 2 | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Experimental investigation on the variability of the main mechanical | Pacheco et al. (2019) [50] | 177 | 16.09 | Construction and Building Materials |
| properties of concrete produced with coarse recycled concrete aggregates | |||||
| 2 | Life cycle assessment of concrete structures | Xia et al. (2020) [352] | 111 | 18.5 | Waste Management |
| with reuse and recycling strategies: A novel framework and case study | |||||
| 3 | Towards Circular Economy through Industrial Symbiosis in the | Yu et al. (2021) [51] | 105 | 26.25 | Journal of Cleaner Production |
| Dutch construction industry: A case of recycled concrete aggregates | |||||
| 4 | Durability properties evaluation of self-compacting | Sasanipour & Aslani (2020) [353] | 105 | 21 | Construction and Building Materials |
| concrete prepared with waste fine and coarse recycled concrete aggregates | |||||
| 5 | Mechanical and durability properties of concrete based | Berredjem et al. (2020) [354] | 100 | 20 | Construction and Building Materials |
| on recycled coarse and fine aggregates produced from demolished concrete | |||||
| 6 | Utilization of waste concrete recycling materials in self-compacting concrete | Sun et al. (2020) [355] | 99 | 19.8 | Conservation and recycling |
| 7 | Multi-criteria optimization of recycled aggregate concrete mixes | Rashid et al. (2020) [356] | 87 | 17.4 | Journal of Cleaner Production |
| 8 | Sustainability evaluation of concretes with mixed recycled aggregate based on holistic approach: Technical, economic and environmental analysis | Martínez-Lage et al. (2020) [357] | 87 | 17.4 | Waste Management |
| 9 | Use of recycled concrete aggregates from precast block for | Zhao et al. (2020) [358] | 84 | 16.8 | Conservation and recycling |
| the production of new building blocks: An industrial scale study | |||||
| 10 | Properties of self-compacting high-strength concrete | Abed et al. (2020) [132] | 84 | 16.8 | Journal of King Saud |
| containing multiple use of recycled aggregate | University—Engineering |
References
- Smitha, J.S.; Thomas, A. Integrated Model and Index for Circular Economy in the Built Environment in the Indian Context. Constr. Econ. Build. 2021, 21, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.S.; Snehal, K.; Das, B.B.; Barbhuiya, S. A comprehensive review towards sustainable approaches on the processing and treatment of construction and demolition waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangcharoenrat, C.; Intrachooto, S.; Peansupap, V.; Sutthinarakorn, W. Factors infuencing construction waste generation in building construction: Thailand’s perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, E.; Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Llatas, C.; Traverso, M. How to obtain accurate environmental impacts at early design stages in BIM when using environmental product declaration. A method to support decision-making. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, G.; Damci, A.; Turkoglu, H.; Gurgun, A.P. Identifcation of root causes of construction and demolition (C&D) waste: The case of Turkey. Procedia Eng. 2017, 196, 948–955. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Shi, C.; Shi, Z.; Lu, B.; Wan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, J.; Zhang, T. Alkali-aggregate reaction in recycled aggregate concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. Materials and the Environment: Eco-Informed Material Choice, 2nd ed.; Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.R.; Sultana, R.; Patwary, M.M.; Khunga, N.; Sharma, P.; Shaker, S.J. Self-healing concrete for sustainable buildings. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Babu, V.S.; Arunachalam, S. Influence of modified two-stage mixing approaches on recycled aggregate treated with a hybrid method of treatment. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 23, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Danish, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Yeon, J.H. Mechanical and durability properties of natural fiber-reinforced geopolymers containing lead smelter slag and waste glass sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 129043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chin, C.S.; Xia, J. Material characterization for sustainable concrete paving blocks. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Bian, W. Mechanical performance of concrete made with recycled aggregates from concrete pavements. Adv. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5035763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Llanes, M.; Romero, M.; Gazquez, M.J.; Bolívar, J.P. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste in the manufacture of urban pavements. Materials 2021, 14, 6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.; Yildirim, H.; Ozyurt, N.; Ozturan, T. Evaluation of mechanical properties and structural behaviour of concrete pavements produced with virgin and recycled aggregates: An experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 5239–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Cement Research Academy. Closing the Loop: What Type of Concrete Re-Use is the Most Sustainable Option? Technical Report A-2015/1860; European Cement Research Academy Gmbh: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cerchione, R.; Colangelo, F.; Farina, I.; Ghisellini, P.; Passaro, R.; Ulgiati, S. Life Cycle Assessment of Concrete Production within a Circular Economy Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góra, J.; Piasta, W. Impact of Mechanical Resistance of Aggregate on Properties of Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00438. [Google Scholar]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Conc. Res. 2016, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Horvath, A.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Impacts of booming concrete production on water resources worldwide. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.J.M.; Miller, S.A.; Horvath, A. Towards sustainable concrete. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbabi, M.; Carrigan, C.; McKenna, S. Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable cement production—Present and future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Global Cement Report 15th Edition. Available online: https://www.cemnet.com/Publications/global-cement-report (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Production Volume of Cement Worldwide from 1995 to 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1087115/global-cement-production-volume (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Danish, A.; Salim, M.U.; Ahmed, T. Trends and developments in green cement “a sustainable approach”. Sustain. Struct. Mater. 2019, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling, J.H.; Vooren, A.V.D. Lock-in of mature innovation systems: The transformation toward clean concrete in the Netherlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, M.; Iversen, L.L.; Best, J.; Franks, D.M.; Hackney, C.R.; Latrubesse, E.M.; Tusting, L.S. Sand, gravel, and UN sustainable development goals: Confict, synergies, and pathways forward. One Earth 2021, 4, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pok, P.; Julnipitawong, P.; Tangtermsirikul, S. Properties of cement fly ash mixtures with substandard fly ash as a partial cement and fine aggregate replacement. ASEAN Eng. J. 2021, 11, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, J.K.; Krausmann, F.; Eisenmenger, N. Global patterns of materials use: A socioeconomic and geophysical analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.L.S.; Anjos, M.A.S.; Nóbrega, A.K.C.; Pereira, J.E.S.; Ledesma, E.F. The role of powder content of the recycled aggregates of CDW in the behaviour of rendering mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Stakeholder-associated factors influencing construction and demolition waste management: A systematic review. Buildings 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Song, Y. How to promote sustainable development of construction and demolition waste recycling systems: Production subsidies or consumption subsidies. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 32, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscati, A.; Johansson, P.; Kebede, R.; Pula, A.; Törngren, A. Information exchange between construction and manufacturing industries to achieve circular economy: A literature review and interviews with Swedish Experts. Buildings 2023, 13, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcan, H.; Sahin, O.; Kul, A.; Ozcelikci, E.; Sahmaran, M. Rheological property and extrudability performance assessment of construction and demolition waste-based geopolymer mortars with varied testing protocols. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 136, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.O.; Othman, A.A.E.; Ebohon, O.J.; Bayyati, A. Overcoming the limitations of the green pyramid rating system in the Egyptian construction industry: A critical analysis. Arch. Eng. Des. Manag. 2020, 18, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Le, K.N.; Hao, J.L.; Wang, J. Life cycle assessment of recycled aggregate concrete on its environmental impacts: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 125950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriletea, M.D. Environmental impacts of sand exploitation: Analysis of sand market. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, L.; Lu, Q. Infuence of recycled coarse aggregate replacement percentage on fatigue performance of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V. Mechanical and elastic behaviour of concretes made of recycled concrete coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1616–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Nayak, D.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V. Effects of recycled fine aggregates on properties of concrete containing natural or recycled coarse aggregates: A comparative study. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Cummings, L.; Tweedie, D. Exploring integrated thinking in integrated reporting—An exploratory study in Australia. J. Intellect. Cap. 2017, 18, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Wang, B.; Yao, Q.; Li, Q.; Jia, X.; Zhang, J. The Impact of Obesity on Thyroid Autoimmunity and Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.; Ho, Y. Bibliometric analysis of tsunami research. Scientometrics 2007, 73, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikowski, P.Z. A bibliometric analysis of born global firms. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 85, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, N. Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis: From the Science Citation Index to Cybermetrics; The Scarecrow Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhl, D.D.; De Oliveira, L. Tecnologias para a economia circular na agropecuária. Iheringia-Série Botânica. 2022, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.; De Brito, J.; Chastre, C.; Evangelista, L. Experimental investigation on the variability of the main mechanical properties of concrete produced with coarse recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yazan, D.M.; Bhochhibhoya, S.; Volker, L. Towards Circular Economy through Industrial Symbiosis in the Dutch construction industry: A case of recycled concrete aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Recycled Concrete; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Tam, V.W.; Li, W. Uniaxial compressive behaviors of fly ash/slag-based geopolymeric concrete with recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.B.; Lima, P.R.L. Experimental and statistical evaluation of the interaction effect of recycled aggregate and water/Cement ratio on concrete compressive strength. Recent Prog. Mater. 2021, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, K.; Kang, T.H.-K. Recycled concrete aggregates: A review. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2013, 7, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Bui, Q. Recycled aggregate concretes—A state-of-the-art from the microstructure to the structural performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ji, Y.; Xing, Z. Mechanical performance of recycled aggregate concrete in green civil engineering: Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnezhad, A.; Ong, K.C.G.; Tam, C.T.; Zhang, M.H. Effects of the parent concrete properties and crushing procedure on the properties of coarse recycled concrete aggregates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Abu Bakar, B.H.; Nemes, R. Two-Year Non-Destructive Evaluation of Eco-Efficient Concrete at Ambient Temperature and after Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.A. Indirect Evaluation of the Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete at Long Ages and after Exposure to Freezing or Elevated Temperatures. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 2021, 57, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.A.B.; Noguchi, T. A conceptual framework for understanding the contribution of building materials in the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamad, M.; Abu-Hamd, M. Life cycle assessment framework for embodied environmental impacts of building construction systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerusha, D. Investigation of the optimal price for recycled aggregate concrete—An experimental approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, Z. Analysis and optimization of mechanical properties of recycled concrete based on aggregate characteristics. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makul, M. Cost-benefit analysis of the production of ready-mixed high-performance concrete made with recycled concrete aggregate: A case study in Thailand. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerusha, D. Barriers to the use of recycled concrete from the perspective of executing companies and possible solution approaches—Case study Germany and Switzerland. Resour. Policy 2021, 73, 102212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Wang, K.; Tam, C.M. Assessing relationships among properties of demolished concrete, recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete using regression analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, P.J. Recycled concrete as an aggregate for concrete—A review. Mater. Struct. 1978, 11, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Poon, C.S.; Zhan, B. New Trends in Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Saikia, N. (Eds.) Methodologies for estimating properties of concrete containing recycled aggregates: Analyses of experimental research. In Recycled Aggregate in Concrete: Use of Industrial, Construction and Demolition Waste; Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2013; Volume 54, pp. 339–378. [Google Scholar]
- De Brito, J.; Saikia, N. (Eds.) Use of construction and demolition waste as aggregate: Properties of concrete. In Recycled Aggregate in Concrete: Use of Industrial, Construction and Demolition Waste; Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2013; Volume 54, pp. 229–337. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, C.S.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Amario, M.; Pepe, M.; De Castro Polisseni, G.; Puente de Andrade, G. Generalized quality control parameter for heterogenous recycled concrete aggregates: A pilot scale case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, J. On statistical characteristics of the compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete. Struct. Concr. 2005, 6, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijer, A.L.; Lasvaux, S.; Citherlet, S.; Viviani, M. Product-specific life cycle assessment of ready mix concrete: Comparison between a recycled and an ordinary concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayasundara, M.; Mendis, P.; Zhang, L.; Sofi, M. Financial assessment of manufacturing recycled aggregate concrete in ready-mix concrete plants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 109, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Wanatowski, D.; Piroozfar, P. An empirical study of perceptions towards construction and demolition waste recycling and reuse in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, I.B.; Sengel, S. Properties of concretes produced with waste concrete aggregate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Dang, F. Potential use of waste tire rubber as aggregate in cement concrete—A comprehensive review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 1183–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Alqedra, M.; Shihada, S.; Hanoona, H. Investigating the effect of sulfate attack on compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2017, 4, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tayeh, B.A.; Al Saffar, D.M.; Alousef, R. The utilization of recycled aggregate in high performance concrete: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8469–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000–2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic, M.; Visser, J.; Šavija, B.; Valcke, S.; Schlangen, E. Use of fine recycled concrete aggregates in concrete: A critical review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete prepared with carbonated recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 84, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Gandomi, A.H.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. New formulations for mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete using gene expression programming. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 122–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Fu, Q.; Kasal, B. A comprehensive review on recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daci, A.; Fenyvesi, O.; Abed, M. An Innovative Approach for Evaluating the Quality of Recycled Concrete Aggregate Mixes. Buildings 2024, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Ebead, U.; Judd, S. Life cycle cost analysis of structural concrete using seawater, recycled concrete aggregate, and GFRP reinforcement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial loading. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinkovic, S.; Radonjanin, V.; Malešev, M.; Ignjatovic, I. Comparative environmental assessment of natural and recycled aggregate concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Juan, M.S.; Gutierrez, P.A. Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.; West, J.S.; Tighe, S.L. Effect of recycled concrete coarse aggregate from multiple sources on the hardened properties of concrete with equivalent compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmini, A.K.; Ramamurthy, K.; Mathews, M.S. Influence of parent concrete on the properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zou, C. Effects of parent concrete and mixing method on the resistance to freezing and thawing of air-entrained recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Han, N.; Singh, A.; Xiao, J. Multi-scale investigation on concrete prepared with recycled aggregates from different parent concrete. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesala, C.R. Properties of recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete: Effect of parent concrete. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesala, C.R.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Barai, S.V. Influence of field recycled coarse aggregate on properties of concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.; Setien, J.; Polanco, J.A.; Alaejos, P.; De Juan, M.S. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Helene, P. Durability of recycled aggregates concrete: A safe way to sustainable development. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, G.; Miren, E. Experimental analysis of properties of high performance recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Z. Experimental study on the failure mechanism of recycled concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Influence of the use of recycled concrete aggregates from different sources on structural concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Influence of quality of recycled aggregates on the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concretes: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Poon, C. Effect of the quality of parent concrete on the properties of high performance recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. Mechanical Behaviour of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, S. Permeability of recycled aggregate concrete containing fly ash and clay brick waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 70, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Grabois, T.M.; Silva, M.A.; Tavares, L.M.; Toledo Filho, R.D. Mechanical behaviour of coarse, lightweight, recycled and natural aggregates for concrete. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Constr. Mater. 2020, 173, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrijo, P.M. Análise da Influência da Massa Específica de Agregados Graúdos Provenientes de Resíduos de Construção e Demolição no Desempenho Mecânico do Concreto. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, W.M.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; Mo, K.H.; Li, L.; Xie, J. Quality improvement techniques for recycled concrete aggregate: A review. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2019, 17, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1992-1-1:2023; Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings, Bridges and Civil Engineering Structures. CEN (Comité Européen de Normalisation): Brussels, Belgium, 2023.
- Deloitte. Study on Resource Efficient Use of Mixed Wastes, Improving Management of Construction and Demolition Waste—Final Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Sun, Z.; Lange, D.A.; Shah, S.P. Properties of interfacial transition zones in recycled aggregate concrete tested by nanoindentation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skocek, J.; Ouzia, A.; Serrano, E.V.; Pato, N. Recycled Sand and Aggregates for Structural Concrete: Toward the Industrial Production of High-Quality Recycled Materials with Low Water Absorption. Sustainability 2024, 16, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C702/C702M-24; Standard Practice for Reducing Samples of Aggregate to Testing Size. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2025.
- EN 933-11:2009/AC:2010; Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates—Part 11: Classification Test for the Constituents of Coarse Recycled Aggregate. Asociacion Española de Normalizacion: Madrid, Espanha, 2009.
- EN 933-1:2014; Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates; Determination of Particle Size Distribution—Sieving Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- NP EN 206:2013+A2:2021; Concrete—Specification, Performance, Production and Conformity. Instituito Português da Qualidade: Caparica, Portugal, 2021.
- BS EN 1097-2:2020-TC; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 2: Methods for the Determination of Resistance to Fragmentation. BSI: London, UK, 2020.
- TS EN 933-3:2012; Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates—Part 3: Determination of Particle Shape-Flakiness Index. BSI: London, UK, 2012.
- Martín-Morales, M.; Zamorano, M.; Ruiz-Moyano, A.; Valverde-Espinosa, I. Characterization of recycled aggregates construction and demolition waste for concrete production following the Spanish Structural Concrete Code EHE-08. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Saikia, N. (Eds.) Concrete with Recycled Aggregates in International Codes. In Recycled Aggregate in Concrete: Use of Industrial, Construction and Demolition Waste; Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 379–429. [Google Scholar]
- RILEM. 121-DRG Guidance for Demolition and Reuse of Concrete and Masonry, Specifications for Concrete with Recycled Aggregates; Materials and Structures: Paris, França, 1994; Volume 27, pp. 557–559. [Google Scholar]
- NBR15116; Agregados Reciclados Para Uso em Argamassas e Concretos de Cimento Portland—Requisitos e Métodos de Ensaio. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas, ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2021.
- DIN 4226-101:2017-08; Recycled Aggregates for Concrete in Accordance with DIN EN 12620—Part 101—Types and Regulated Dangerous Substances. German Institute for Standardisation: Berlim, Germany, 2017.
- WBTC. Specification Facilitating the Use of Concrete Paving Units Made of Recycled Aggregates, Environ; WBTC: Hong Kong, China, 2004; Volume 24, p. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- BS 8500-2:2023; Concreto—Norma Britânica Complementar à BS EN 206—Parte 2: Especificação Para Materiais Constituintes e Concreto. British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 2023.
- LNEC E 471; Guia Para a Utilização de Agregados Reciclados Grossos em Betões de Ligantes Hidráulicos. Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil: Lisboa, Portugal, 2009.
- Fonseca, N.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. The influence of curing conditions on the mechanical performance of concrete made with recycled concrete waste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.B.; Shahria Alam, M. Mechanical and freeze-thaw durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete made with recycled coarse aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbachiya, M.C.; Leelawat, T.; Dhir, R.K. Use of recycled concrete aggregate in high-strength concrete. Mater. Struct. 2000, 33, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.V.; Dang, V.Q.; Lanh, H.S. Evaluating com pressive strength of concrete made with recycled concrete aggre gates using machine learning approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zhu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, B. An evaluation of the recycled aggregate characteristics and the recycled aggregate concrete mechanical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.; Nemes, R.; Tayeh, B.A. Properties of self-compacting high-strength concrete containing multiple use of recycled aggregate. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.C.; Damineli, B.L.; Rebmann, M.S.; Ângulo, S.C. Simple way to model the mechanical properties of concretes with recycled concrete aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 84, 108213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C136/136M-19; Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- BS 812-103.2:1989; Testing Aggregates: Methods for Determination of Particle Size Distribution, Sieve Test. British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 1985.
- BS 812-110: 1990; Methods for Determination of Aggregate Crushing Value (ACV). British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 1990.
- BS 812-112:1990; Testing Aggregates: Method for Determination of Aggregate Impact Value (AIV). British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 1990.
- ASTM C127–24; Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), and Absorption of Coarse Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- BS EN 1097-6:2022; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates. Part 6: Determination of Particle Density and Water Absorption. British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 2022.
- Martín-Morales, M.; Zamorano, M.; Valverde-Palacios, I.; Cuenca-Moyano, G.M.; Sánchez-Roldán, Z. Quality Control of Recycled Aggregates (RAs) from Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW). In Handbook of Recycled Concrete and Demolition Waste; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 270–303. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C138/C138M-24a; Standard Test Method for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM C 33/C33M-24a; Standard Specifications for Concrete Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Verian, K.P.; Ashraf, W.; Cao, Y. Properties of Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Their Influence in New Concrete Production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosic, N.; Torrenti, J.M.; Sedran, T.; Ignjatovic, I. Toward a Codified Design of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Structures: Background for the New Fib Model Code 2020 and Eurocode 2. Struct. Concr. 2021, 22, 2916–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshvir, M.; Barai, S.V. Studies on Recycled Aggregates-Based Concrete. Waste Manag. Res. 2006, 24, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Nemes, R. Los Angeles Index and Water Absorption Capacity of Crushed Aggregates. Pollack Period. 2020, 15, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.M. Properties of Concrete, 5th ed.; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, M.A.; Alrefai, M.; Alali, A.; Nemes, R.; Yehia, S. Effect of Nominal Maximum Aggregate Size on Performance of Recycled Aggregate Self-Consolidating Concrete: Experimental and Numerical Investigation. ACI Mater. J. 2022, 119, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hwang, C.L. Properties of HPC with recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, A.; Mosaberpanah, M.A. A review on recycled con crete aggregates (RCA) characteristics to promote RCA utilization in developing sustainable recycled aggregate concrete (RAC). Eur. J. Env. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 6505–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Lou, C.; Du, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Mechanical properties of recycled concrete with demolished waste concrete aggregate and clay brick aggregate. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTMC70-20; Standard Test Method for Surface Moisture in Fine Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Kwan, W.H.; Ramli, M.; Kam, K.J.; Sulieman, M.Z. Influence of the amount of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete design and durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, H.S.; Pachiappan, T.; Avudaiappan, S.; Maureira-Carsalade, N.; Roco-Videla, A.; Guindos, P.; Parra, P.F. A Comprehensive Review on Recycling of Construction Demolition Waste in Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.R.K.; Yaragal, S.C. A novel approach for optimizing the processing of recycled coarse aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, A. Partial replacement of e-plastic waste as coarse aggregate in concrete. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, S.S.; Fonteboa, B.G.; Abella, F.M.; Taboada, I.G. Time dependent behaviour of structural concrete made with recycled coarse aggregates: Creep and shrinkage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Prediction of the shrinkage behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C128-22:2022; Standard Test Method for Relative Density (Specific Gravity) and Absorption of Fine Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- Shobeiri, V.; Bennett, B.; Xie, T.; Visintin, P. A comprehensive data driven study of mechanical properties of concrete with waste-based aggregates: Plastic, rubber, slag, glass and concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 20, e02815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C29/C29M-23; Standard Test Method for Bulk Density (“Unit Weight”) and Voids in Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- BS EN 1097-3:1998; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 3: Determination of Loose Bulk Density and Voids. British Standards Institution, BSI: London, UK, 1998.
- Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, K.; Kim, J. Quality improvement of recycled aggregates using the acid treatment method and the strength characteristics of the resulting mortar. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, G.; Savva, P.; Petrou, M.F. Enhancing mechanical and durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Poon, C.S.; Xiao, J.; Xuan, D. Effect of carbonated recycled coarse aggregate on the dynamic compressive behavior ofrecycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J. An environmentally friendly method to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, D.; Boyle, S.; Spry, T.; Mjelde, D. Evaluation of Recycled Concrete as Aggregate in New Concrete Pavements; Office of Research and Library Services: Washington, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Movassaghi, R. Durability of Reinforced Concrete Incorporating Recycled Concrete as Aggregate (RCA). Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.T. Recycled Concrete Aggregate—A Viable Aggregate Source for Concrete Pavements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Fathifazl, G.; Isgor, O.B.; Razaqpur, A.G.; Fournier, B.; Foo, S. Proposed method for determining the residual mortar content of recycled concrete aggregates. J. ASTM Int. 2007, 5, JAI101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathifazl, G. Structural Performance of Steel Reinforced Recycled Concrete Members. Ph.D. Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.C.; Narud, H. The strength of recycled concrete made from crushed concrete coarse aggregate. Concr. Int. 1983, 5, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Olofinnade, O.M.; Oyawoye, I.T. Influence of calcined clay on the strength characteristics and microstructure of recycled aggregate concrete for sustainable construction. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2021, 54, 56–70. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chong, L.; Xie, Z. Performance enhancement of recycled concrete aggregate—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinkovic, S.; Carevic, V. Comparative studies of the life cycle analysis between conventional and recycled aggregate concrete: In book: New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete. Trends Eco-Effic. Recycl. Concr. 2019, 257–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.A.; El-dek, S.I.; El–Gamal, S.M.A. Mechanical performance and thermal stability of hardened Portland cement-recycled sludge pastes containing MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Heikal, M.; Abdelwahab, N.R.; Mohamed, O.A. Fabricated CeO2/ZrO2 nanocomposite to improve thermal resistance, mechanical characteristics, microstructure and gamma radiation shielding of OPC composite cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Eessaa, A.K.; Khalil, M.H.; Mohamed, O.A. An initial study on the effect of nano-zirconium on the behavious of alkali-activated slag cement subjected to seawater attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Chung, C.W.; Wang, S.; Lee, M. Accelerated Carbonation of Recycled Aggregates Using the Pressurized Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Sparging Process. Minerals 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verian, K.P.; Whiting, N.M.; Olek, J.; Jain, J.; Snyder, M.B. Using Recycled Concrete as Aggregate in Concrete Pavements to Reduce Materials Cost; Joint Transportation Research Program; Indiana Department of Transportation and Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.I.; Aziz, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Al-Zahrani, M.M.; Shameem, M.; Maslehuddin, M. Improvement of concrete durability using nanocomposite coating prepared by mixing epoxy coating with Submicron/Nano-carbon obtained from heavy fuel oil ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Hou, P.; Ye, Z. Influences of nano-TiO2 on the properties of cement-based materials: Hydration and drying shrinkage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.G. Workability and Compressive Strength Properties of Concrete Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregate. In Sustainable Construction: Use of Recycled Concrete Aggregate, Proceedings of the International Symposium, London, UK, 11–12 November 1998; Thomas Telford Ltd: London, UK, 2018; pp. 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. Quality improvement of recycled concrete aggregate by removal of residual mortar: A comprehensive review of approaches adopted. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 288, 123066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Koenders, E.A.B.; Martinelli, E. Alternative Processing Procedures for Recycled Aggregates in Structural Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 69, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, K.; Touzé, S.; Bourgeois, F.; Lippiatt, N.; Ménard, Y. Assessment of a Microwave-Assisted Recycling Process for the Recovery of High-Quality Aggregates from Concrete Waste. Int. J. Miner. Process 2014, 126, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A. Treatments for the Improvement of Recycled Aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2004, 16, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M.; Le, K.N. Removal of Cement Mortar Remains from Recycled Aggregate Using Pre-Soaking Approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodaini, A.A.; Ridzuan, A.R.M.; Fauzi, M.A.M. Removal of old adhered mortar from crushed concrete waste aggregate (CCWA) with different HCl molarities and its effect on CCWA properties. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 7, 5950–5959. [Google Scholar]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Okoro, U.C. Filler-Ability of highly active metakaolin for improving morphology and strength characteristics of recycled aggregate concrete. Silicon 2018, 11, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muduli, R.; Mukharjee, B.B. Performance assessment of concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregates and metakaolin: A systematic approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Evaluation of high performance concrete with recycled aggregates: Use of densified silica fume as cement replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, K.H.; Alzeebaree, R.; Ismail, A.J.; Khoshnaw, G.J.; Ibrahim, T.K. Performance of recycled coarse aggregate concrete incorporating metakaolin. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 856, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, W.M.; Elbaz, K.; Yang, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Shen, X.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, L. Effect of Pozzolan slurries on recycled aggregate concrete: Mechanical and durability performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaha, M.M.; Badawy, A.A.M.; Hashish, M. Effect of using ground waste tire rubber as fine aggregate on the behaviour of concrete mixes. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2007, 14, 427–435. [Google Scholar]
- Batayneh, M.K.; Marie, I.; Asi, I. Promoting the use of crumb rubber concrete in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaloo, A.R.; Dehestani, M.; Rahmatabadi, P. Mechanical properties of concrete containing a high volume of tire–rubber particles. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM C1585–20; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Rate of Absorption of Water by Hydraulic-Cement Concretes. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Olofinnade, O.; Osoata, O. Performance assessment of mechanical properties of green normal strength concrete produced with metakaolin-cement coated recycled concrete aggregate for sustainable construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C830-00; Standard Test Methods for: Apparent Porosity, Liquid Absorption, Apparent Specific Gravity, and Bulk Density of Refractory Shapes by Vacuum Pressure. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- Gupta, T.; Chaudhary, S.; Sharma, R.K. Assessment of mechanical and durability properties of concrete containing waste rubber tire as fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhana, A.R.; Kartini, K.; Hamidah, M.S. Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Rubber Crumb as Replacement to Fine Aggregate. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1774, 030025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesev, M.; Radonjanin, V.; Marinkovic, S. Recycled concrete as aggregate for structural concrete production. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1204–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Gao, X.F.; Tam, C.M.; Ng, K.M. Physio-chemical reactions in recycle aggregate concrete. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiuddin, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Salam, M.A.; Jumaat, M.Z. Use of recycled concrete aggregate in concrete: A review. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2013, 19, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, T. Research progress on frost resistance of recycled coarse aggregate concrete and its componentes. J. Build. Struct. 2020, 4, 142–157. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. The influence of the use of recycled aggregates on the compressive strength of concrete: A review. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2014, 19, 825–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Larrard, F.; Colina, H. Concrete Recycling—Research and Practice; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Tawana, M.; Huang, X. Review of studies on structural performance of recycled aggregate concrete in China. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, E.; Ambros, W.; Cazacliu, B.; Remond, S. Heterogeneity of recycled concrete aggregates, an intrinsic variability. Construct. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ângulo, S.C. Variabilidade de Agregados Graúdos de Resíduos de Construção e Demolição Reciclados. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Plaza, P.; Del Bosque, I.S.; Frías, M.; De Rojas, M.S.; Medina, C. Use of recycled coarse and fineaggregates instructural eco-concretes. Physical and mechanical properties and CO2 emissions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. Durability and shrinkage performance of concrete made with coarse multi-recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinnezhad, H.; Sürmelioğlu, S.; Çakır, O.A.; Ramyar, K. A novel method for characterization of recycled concrete aggregates: Computerized microtomography. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellah, D.; Barboura, S.; Tilmatine, T.; Benyahi, K.; Kachi, M.S.; Li, J.; Bouafia, Y. Compressive study on recycled concrete: Experiment and numerical homogenization modelling. Frat. Integrità Strutt. 2024, 67, 58–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanish Minister of Public Works. Instruccion de Hormigon Estructural EHE-08 [Spanish Structural Concrete Code]. 2008, Volume 2008. Available online: http://asidac.es/asidac/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/EHE-08.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).[Green Version]
- Pepe, M. A Conceptual Model for Designing Recycled Aggregate Concrete for Structural Applications. In Springer Theses; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Barra, M.; Vazquez, E. The influence of retained moisture in aggregates from recycling on the properties of new hardened concrete. Waste Manag. 1996, 16, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefteh, H.; Kebaïli, O.; Oucief, H.; Berredjem, L.; Arabi, N. Influence of moisture conditioning of recycled aggregates on the properties of fresh and hardened concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.H.; Lam, L.; Fok, H.; Kou, S.C. Influence of moisture states of natural and recycled aggregates on the slump and compressive strength of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortas, R.; Roziere, E.; Staquet, S.; Hamami, A.; Loukili, A.; Delplancke-Ogletree, M.-P. Effect of the water saturation of aggregates on the shrinkage induced cracking risk of concrete at early age. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Saoût, G.L.; Devillers, P.; Garcia-diaz, E. The Effect of Limestone Aggregate Porosity and Saturation Degree on the Interfacial Zone; NUWCEM 2014-2; International Symposium on Cement-based Materials for Nuclear Waste: Avignon, France, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ferreira, L.; De Brito, J.; Barra, M. Influence of the pre-saturation of recycled coarse concrete aggregates on concrete Properties. Mag. Concr. Res. 2011, 63, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Fresh-state performance of recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Construct. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.B.; Figueire do Filho, J.G.L.; Lima, P.R.L. Workability study of concretes made with recycled mortar aggregate. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; She, A.; Yao, W. Investigation of Water Absorption Behavior of Recycled Aggregates and its Effect on Concrete Strength. Materials 2023, 16, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Han, G.; Teng, Y. Influence of recycled coarse aggregate on mechanical properties and carbonization properties of recycled concrete. Concrete 2017, 12, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Maimouni, H.; Remond, S.; Huchet, F.; Richard, P.; Thiery, V.; Descantes, Y. Quantitative assessment of the saturation degree of model fine recycled concrete aggregates immersed in a filler or cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standard of the People´s Republic of China. GB/T 14685-2022; Pebble and Crushed Stone for Construction. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Bentz, D.P.; Snyder, K.A. Protected paste volume in concrete—Extension to internal curing using saturated lightweight fine aggregate. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Keiser, L.; Golias, M.; Weiss, J. Absorption and desorption properties of fine lightweight aggregate for application to internally cured concrete mixtures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Water absorption and chloride diffusivity of concrete under the coupling effect of uniaxial compressive load and freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z. Combined Freeze-Thaw and Chloride Attack Resistance of Concrete Made with Recycled Brick-Concrete Aggregate. Materials 2021, 14, 7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amario, M.; Rangel, C.S.; Pepe, M.; Toledo Filho, R.D. Optimization of normal and high strength recycled aggregate concrete mixtures by using packing model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 84, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrela, F.; Sanchez de Juan, M.; Ayuso, J.; Geraldes, V.L.; Jimenez, J.R. Limiting properties in the characterisation of mixed recycled aggregates for use in the manufacture of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3950–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.P.; Xiao, J.Z.; Zhong, P.H. A method to determine water absorption of recycled fine aggregate in paste for design and quality control of fresh mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, X.-J.; Peng, Z.-G.; Huo, J.-H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H. Characterization of the influence of Nanoparticles on Early Hydration of Oil Cement by Using Low Field NMR. Energ. Source Part. A 2021, 43, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, A.M.; Ma, K.; Liao, G.; Yao, W.; Zuo, J.Q. Investigation of hydration and setting process in nanosilica-cement blended pastes: In situ characterization using low field nuclear magnetic resonance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, C.; Lockington, D.; Dux, P. Unsaturated diffusivity functions for concrete derived from NMR images. Mater. Struct. 2003, 36, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajan, K.C.; Adhikari, R.; Mandal, B.; Gautam, D. Mechanical characterization of recycled concrete under various aggregate replacement scenarios. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C131/C131M-20; Standard Test Method for Resistance to Degradation of Small-Size Coarse Aggregate by Abrasion and Impact in the Los Angeles Machine. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Etxeberria, M.; Vazquez, E.; Marí, A.; Barra, M. Influence of amount of recycled coarse aggregates and production process on properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, H.G.; Taye, S.; Tarekegn, A.G. Disparity in research findings on parent concrete strength effects on recycled aggregate quality as a challenge in aggregate recycling. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagataki, S.; Gokce, A.; Saeki, T.; Hisada, M. Assessment of recycling process induced damage sensitivity of recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasrawi, H. Design of normal concrete mixtures using workability-dispersion-cohesion method. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1035946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI PRC-211.1–91; Recommended Practice for Selecting Proportions for Normal and Heavyweight Concrete (Reapproved 2009). American Concrete Institute, ACI: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2002; pp. 1–38.
- ASTM C192/C192M-24; Standard Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Quan, C.-Q.; Jiao, C.-J.; Chen, W.-Z.; Xue, Z.-C.; Liang, R.; Chen, X.-F. The Impact of Fractal Gradation of Aggregate on the Mechanical and Durable Characteristics of Recycled Concrete. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousfi, S.; Nouri, L.; Saidani, M.; Hadjab, H. The use of the dreux-gorisse method in the preparation of concrete mixes: An automatic approach. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 15, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- González-Taboada, I.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Eiras-López, J.; Rojo-López, G. Tools for the study of self-compacting recycled concrete fresh behaviour: Workability and rheology. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE EN 12350-2:2020; Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 2: Slump Test. European Standards: Plzen, Czech Republic, 2020.
- ASTM C143/C143M-20; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Poon, C.S.; Kou, S.C.; Lam, L. Influence of recycled aggregate on slump and bleeding of fresh concrete. Mater. Struct. 2007, 40, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Salgado, F.; De Andrade Silva, F. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste towards an application on structural concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, J.; Khandel, O.; Sedighardekani, R.; Sahneh, A.R.; Ghahari, S. Enhanced workability, durability, and thermal properties of cement-based composites with aerogel and paraffin coated recycled aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Q. Influence of the moisture states of aggregate recycled from waste concrete on the performance of the prepared recycled aggregate concrete (RAC)—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Alimi, W.; Assaggaf, R.; Salami, B.A.; Oladapo, E.A. An overview of factors influencing the properties of concrete incorporating construction and demolition wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroline, S.R.; Mayara, A.; Marco, P.; Yiming, Y. Tension stiffening approach for interface characterization in recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 82, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Robles, D.; García-González, J.; Juan-Valdés, A.; Morán-del Pozo, J.M.; Guerra-Romero, M.I. Effect of mixed recycled aggregates on mechanical properties of recycled concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, F.; Prayuda, H.; Putri, W.P.A.P.; Saputro, I.; Luthanzah, T.R. Influence of mixed recycled coarse aggregate on the engineering properties of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2023, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Elbeltagi, E.; Diab, A.; Tarsi, G.; Saeed, F.; Sangiorgi, C. Incorporating coarse and fine recycled aggregates into concrete mixes: Mechanical characterization and environmental impact. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boletín Oficial del Estado (BOE). Structural Concrete Code. 2021. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2021/06/29/470 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Vintimilla, C.; Etxeberria, M.; Li, Z. Durable Structural Concrete Produced with Coarse and Fine Recycled Aggregates Using Different Cement Types. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, M.; Mei, J. Compressive stress—Strain curve of recycled concrete under repeated loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 131598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, Z. Mechanical properties of recycled concrete made with different types of coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Kong, Z.; Cai, G.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Su, D.; Liu, J.; Zheng, S. Study of the properties of full component recycled dry-mixed masonry mortar and concrete prepared from construction solid waste. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, Z.; Yue, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q. Study on the effect of recycled coarse aggregate on the shrinkage performance of green recycled concrete. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Chen, J.; Qu, F.; Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Xie, B.; Yuan, M.; Li, W. Degradation prediction of recycled aggregate concrete under sulphate wetting—Drying cycles using BP neural network. Structures 2022, 46, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Xiong, Q.; Zhao, H.; Dong, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, W. Performance of asphalt mortar with recycled concrete powder under different filler-to-asphalt weight ratios. Case. Stud. Constr. Mat. 2023, 18, e01834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Dong, W.; Liang, R.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, K.; Li, W. Fracture behaviours of sustainable multi-recycled aggregate concrete under combined compression-shear loading. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, K.; Li, W. Mechanical properties of multi-recycled aggregate concrete under combined compression-shear loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 143, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, N.; Kumar, A. Split Tensile Behavior of HCFA Based SCC Including CBA and RCA. In Recent Advancements in Civil Engineering; Springer Nature Link: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 659–670. [Google Scholar]
- Dhir, R.K.; De Brito, J.; Silva, R.V.; Lye, C.Q. Sustainable Construction Materials: Recycled Aggregates; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Long, C.; Wu, C.; Duan, W.H.; Shah, S.P. Effects of nanoparticle on the dynamic behaviors of recycled aggregate concrete under impact loading. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoumandi, M.; Steele, A.R.; Volz, J.S. Evaluation of the bond strengths between concrete and reinforcement as a function of recycled concrete aggregate replace ment level. Structures 2018, 16, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Ramli, M. Engineering properties of treated recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) for structural applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C39/C39M-24; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- NF EN 12390-3: 2019; Essais Pour Beton Durci Partie 3: Resistance a la Compression Deseprouvettes. Afnor: Saint-Denis, France, 2019.
- Mahmood, W.; Ayub, T.; Khan, A.U.R. Mechanical prop erties and corrosion resistance of recycled aggregate concrete exposed to accelerated and natural marine environment. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C496/C496M-17; Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Mohammed, D.; Tobeia, S.; Mohammed, F.; Hasan, S. Compressive strength improvement for recycled concrete aggregate. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 162, 02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frondistou-Yannas, S. Waste concrete as aggregate for new concrete. J. Proceed. 1977, 74, 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, A.D. Recycled Concrete as a Source of Aggregate. J. Proc. 1977, 74, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, V.M. Recycled concrete—A new aggregate. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1978, 5, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, K. Mechanical properties of concrete with recycled coarse aggregate. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C. Mechanical properties of 5-year-old concrete prepared with recycled aggregates obtained from three different sources. Mag. Concr. Res. 2008, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F. Concretes with aggregates from demolition waste and silica fume. Materials and mechanical Properties. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhade, A.N.; Choudhari, S.R.; Gajbhiye, A.R. Performance evaluation of recycled aggregate used in concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2012, 2, 1387. [Google Scholar]
- Kebaili, B.; Benzerara, M.; Menadi, S.; Kouider, N.; Belouettar, R. Effect of parent concrete strength on recycled concrete performance. Frat. Integrita Strutt. 2022, 16, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemann, A.; Nygaard, P.; Kaufmann, J.; Loser, R. Relation between carbonation resistance, mix design and exposure of mortar and concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 62, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahami, Y.; Saeidi, A.; Fiset, M.; Ba, K. The Effects of the Type and Quantity of Recycled Materials on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Concrete and Mortar: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabsh, S.W.; Abdelfatah, A.S. Influence of recycled concrete aggregates on strength properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Recycling and reuse of waste concrete in China: Part 1 material behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 53, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damdelen, O. Investigation of 30% recycled coarse aggre gate content in sustainable concrete mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, B.; Cladera, A.; Olmo, T.D.; Pitarch, F. Influence of the amount of mixed recycled aggregates on the properties of con crete for non-structural use. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachim, P.B. Mechanical properties of brick aggregate con crete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Pereira, A.S.; Correira, J.R. Mechanical behaviour of non-structural concrete made with recycled ceramic aggre gates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Yen, T.; Chen, K.H. Use of building rubbles as recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debieb, F.; Kenai, S. The use of coarse and fine crushed bricks as aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukharjee, B.B.; Patra, R.K. Effect of coarse recycled aggregate and rice husk ash on concrete: A factorial design approach. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 4169–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgader, H.S.; Ben-Zeitun, A.E. Tensile strength of two stage concrete measured by double-punch and split tests. Struct. Concr. 2004, 5, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. The effect of superplasticizers on the mechanical performance of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilbas, H.; Şimşek, M.; Çakır, O. An investigation on mechanical and physical properties of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) with and without silica fume. Construct. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasta, W.; Zarzycki, B. The effect of cement paste volume and w/c ratio on shrinkage strain, water absorption and compressive strength of high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.; De Brito, J. Structural concrete with incorporation of coarse recycled concrete and ceramic aggregates: Durability performance. Mater. Struct. 2008, 42, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Thaickavil, N.N.; Wilson, P.M. Strength and durability of concrete containing recycled concrete aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-German, A.M.; Bravo-Gómez, I.D.; Mesa, J.A.; Maury-Ramírez, A. Mechanical Properties of Concrete Using Recycled Aggregates Obtained from Old Paving Stones. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE EN 12390-16:2020; Determination of the Shrinkage of Concrete. Spanish Standard: Madrid, Spain, 2020.
- González-Fonteboa, B.; Seara-Paz, S.; De Brito, J.; González-Taboada, I.; Martínez-Abella, F.; Vasco-Silva, R. Recycled concrete with coarse recycled aggregate. An overview and analysis. Mater. Constr. 2018, 68, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, H. Experimental study and prediction model for autogenous shrinkage of recycled aggregate concrete with recycled coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTMC1202-25; Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–8.
- Zhu, P.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Gu, L. Durability evaluation of recycled aggregate concrete in a complex environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegar, M.; Bašic, A.D.; Bukvic, O.; Serdar, M. Carbonation of Concretes with Different Binder Chemistry—A Comparative Analysis. In International RILEM Conference on Synergising Expertise Towards Sustainability and Robustness of Cement-Based Materials and Concrete Structures (SynerCrete); Jędrzejewska, A., Kanavaris, F., Azenha, M., Benboudjema, F., Schlicke, D., Eds.; RILEM Bookseries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, E.; Barra, M.; Aponte, D.; Jiménez, C.; Valls, S. Improvement of the durability of concrete with recycled aggregates in chloride exposed environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, T.U.; Rahman, M. Effects of cement types on chloride ingress in concrete. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACF Symposium on Assessment and Intervention of Existing Structures, Sapporo, Japan, 10–11 September 2019; The 3rd ACF Symposium: Hokkaido, Japan, 2019; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kopecskó, K.; Balázs, G.L. Concrete with Improved Chloride Binding and Chloride Resistivity by Blended Cements. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7940247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. Durability performance of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Structural concrete with simultaneous incorporation of fine and coarse recycled concrete aggregates: Mechanical, durability and long-term properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Feng, J.; Hu, K. Mechanical Properties and ITZ Microstructure of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using Carbonated Recycled Coarse Aggregate. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, P.N.; Kaura, P.; Singh, B. Studies on mechanical performance of treated and non-treated coarse recycled concrete aggregate and its performance in concrete-an Indian case study. Res. Eng. Struct. Mater. 2024, 10, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariningsih, Y.S.; Nuralinah, D.; Arifi, E. Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Affected by Chloride Diffusion in Submerged Condition. Civ. Eng. Arch. 2023, 11, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cano, D.; Arias-Jaramillo, Y.P.; Bernal-Correa, R.; Tobón, J.I. Effect of enhancement treatments applied to recycled concrete aggregates on concrete durability: A review. Mater. Construcción 2023, 73, e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Ferreira, J.; Pacheco, J.; Soares, D.; Guerreiro, M. Structural, material, mechanical and durability properties and behaviour of recycled aggregates concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez del Bosque, I.F.; Van den Heede, P.; De Belie, N.; Sánchez de Rojas, M.I.; Medina, C. Carbonation of concrete with construction and demolition waste based recycled aggregates and cement with recycled contente. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Use of recycled fine aggregate in concretes with durable requirements. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco Torgal, F.; Miraldo, S.; Labrincha, J.A.; De Brito, J. An overview on concrete carbonation in the context of eco-efficient construction: Evaluation, use of SCMs and/or RAC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xiao, J. Prediction model of carbonation depth for recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 88, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Jha, K.N.; Misra, S. Use of aggregates from nrecycled construction and demolition waste in concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Fathifazl, G.; Isgor, O.B.; Razaqpur, A.G.; Fournier, B.; Foo, S. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete designed with equivalent mortar volume method. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyavaradhan, S.K.; Ling, T.C. Potential of CO2 sequestration through construction and demolition (C&D) waste—An overview. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lovato, P.S.; Possan, E.; Molin, D.C.C.D.; Masuero, Â.B.; Ribeiro, J.L.D. Modeling of mechanical properties and durability of recycled aggregate concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Xiao, J.; Ye, T.; Li, L. Research progress and engineering application of reinforced recycled concrete structures. J. Build. Struct. 2020, 41, 1–16+27. [Google Scholar]
- Iskandar, D.; Sumabrata, R.J.; Prawati, E.; Amran, Y.; Nurkholid, M. Reuse of Construction Waste for Sustainable Development. Civ. Eng. Arch. 2023, 11, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, U.S.; Dinakar, P. Influence of metakaolin and silica fume on the mechanical and durability performance of high-strength concrete made with 100% coarse recycled aggregate. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2022, 26, 04022004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Cai, Z.; Wu, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z. Chloride transport and induced steel corrosion in recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C469/C469M-22; Standard Test Method for Static Modulus of Elastic ity and Poissons Ratio Concrete in Compression. American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Alexander, M.; Mindness, S. Aggregates in Concrete; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, M.; De Brito, J.; Pontes, J.; Evangelista, L. Mechanical performance of concrete made with aggregates from construction and demolition waste recycling plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, B.S.; Dawi, A.H.; Daou, A.; Chehab, G.R. Studies of the effect of recycled aggregates on flexural, shear, and bond splitting beam structural behavior. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 9, e00186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belen, G.F.; Fernando, M.A.; Diego, C.L.; Sindy, S.P. Stress strain relationship in axial compression for concrete using recy cled saturated coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, S.C. Long-term mechanical and durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete prepared with the incorporation of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilbas, H.; Çakır, D.; Atiş, C. Experimental investigation on properties of re cycled aggregate concrete with optimized ball milling method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIS, IS 516 Part 1/Section 1 (2021); Testing of Strength of Hardened Concrete Section 1 Compressive, Flexural and Split Tensile Strength (First Revision). Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2021.
- Zhu, Y.; Jian, W.; Cao, W.; Shao, T. Research on flexural performance of high-strength recycled concrete composite slabs. In Proceedings of the 22nd National Conference on Structural Engineering; 2012; Volume 2, pp. 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W. Flexural performance analysis of profiled steel plate-recycled concrete composite plate. In Proceedings of the 24th National Conference on Structural Engineering, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 28 September–1 October 2015; Volume 1, pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kefyalew, F.; Imjai, T.; Garcia, R.; Kim, B. Structural And Service Performance of Composite Slabs with High Recycled Aggregate Concrete Contents. Eng. Sci. 2024, 27, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouny, A.A.; Issa, U.H.; Miky, Y.; Sharaky, I.A. Evaluating and selecting the best sustainable concrete mixes based on recycled waste materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C. Comparative Analysis of Multi-Criteria Decision Making and Life Cycle Assessment Methods for Sustainable Evaluation of Concrete Mixtures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wu, J.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y. Effect of residual mortar on compressive properties of modeled recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 132511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.H.; Badr, A.H.; Henedy, S.N.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Imran, H. Application of Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS) approach in prediction of compressive strength of eco-friendly concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Ding, T.; Xiao, J. Life cycle assessment of concrete structures with reuse and recycling strategies: A novel framework and case study. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasanipour, H.; Aslani, F. Durability properties evaluation of self-compacting concrete prepared with waste fine and coarse recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berredjem, L.; Arabi, N.; Molez, L. Mechanical and durability properties of concrete based on recycled coarse and fine aggregates produced from demolished concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W. Utilization of waste concrete recycling materials in self-compacting concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.; Rehman, M.U.; De Brito, J.; Ghafoor, H. Multi-criteria optimization of recycled aggregate concrete mixes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lage, I.; Vázquez-Burgo, P.; Velay-Lizancos, M. Sustainability evaluation of concretes with mixed recycled aggregate based on holistic approach: Technical, economic and environmental analysis. Waste Manag. 2020, 104, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Courad, L.; Groslambert, S.; Léonard, A.; Xiao, J. Use of recycled concrete aggregates from precast block for the production of new building blocks: An industrial scale study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
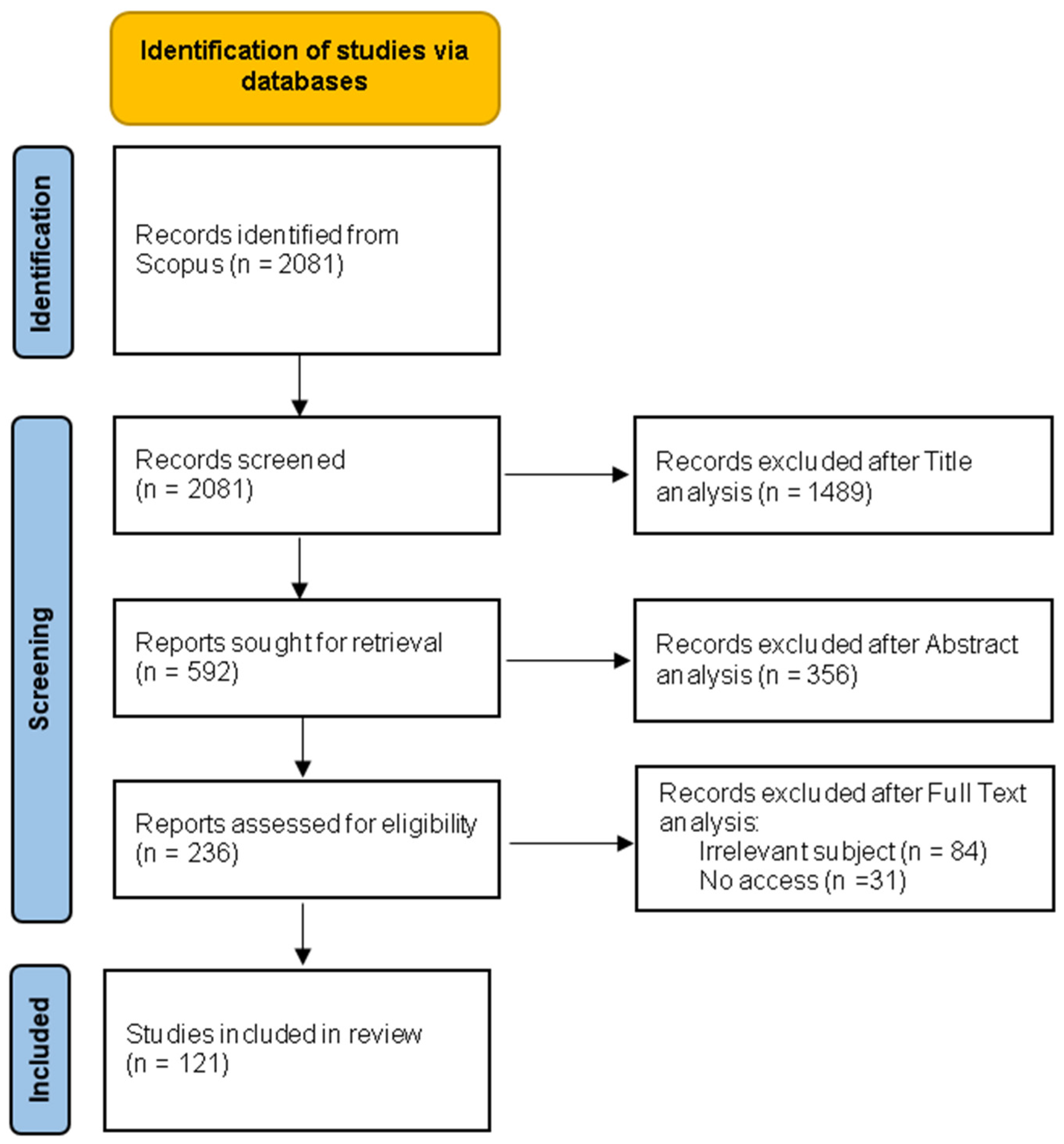

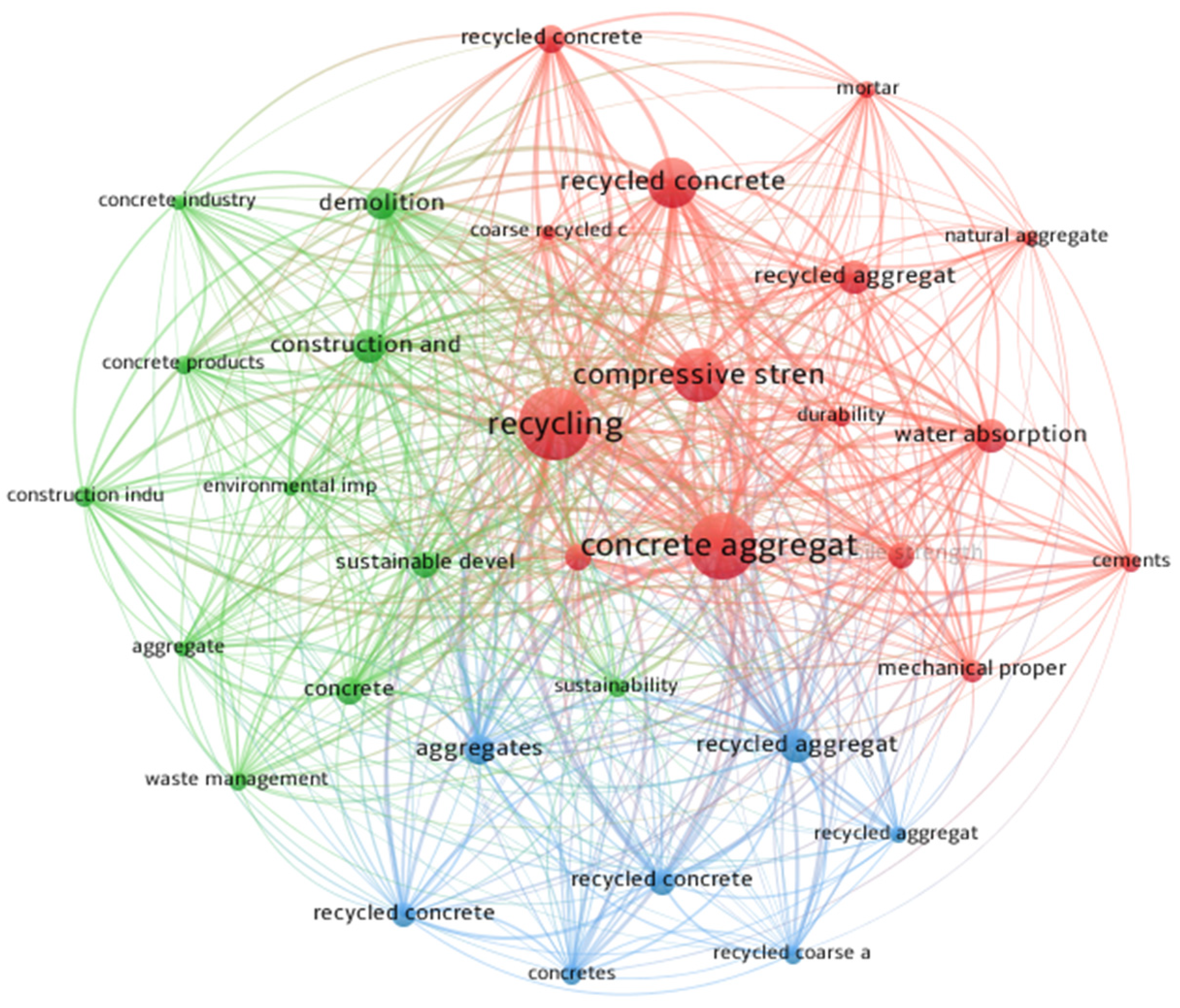

| Parameter | Settings |
|---|---|
| Keyword | “recycled concrete” |
| Year | 2019–2024 |
| Document type | Article |
| Publication Stage | Final |
| Source | Journal |
| Language | English |
| Rank | Author | Documents | Total Citations | Citation per Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | De brito, J. | 4 | 331 | 83 |
| 2 | Xiao, J. | 4 | 329 | 82 |
| 3 | Abed, M. | 3 | 91 | 30 |
| 4 | Li, J. | 3 | 83 | 28 |
| 5 | Nemes, R. | 2 | 91 | 46 |
| 6 | Kumar, R. | 2 | 73 | 37 |
| 7 | Kumar, V. | 2 | 73 | 37 |
| 8 | Singh, R. | 2 | 73 | 37 |
| Rank | Country | Documents | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 22 | 572 |
| 2 | Spain | 12 | 238 |
| 3 | India | 10 | 150 |
| 4 | USA | 9 | 211 |
| 5 | Polonia | 8 | 118 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Junior, G.A.F.; Leite, J.C.T.; Mendez, G.d.P.; Haddad, A.N.; Silva, J.A.F.; da Costa, B.B.F. A Review of the Characteristics of Recycled Aggregates and the Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced by Replacing Natural Coarse Aggregates with Recycled Ones—Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructures. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10080213
Junior GAF, Leite JCT, Mendez GdP, Haddad AN, Silva JAF, da Costa BBF. A Review of the Characteristics of Recycled Aggregates and the Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced by Replacing Natural Coarse Aggregates with Recycled Ones—Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructures. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(8):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10080213
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunior, Gerardo A. F., Juliana C. T. Leite, Gabriel de P. Mendez, Assed N. Haddad, José A. F. Silva, and Bruno B. F. da Costa. 2025. "A Review of the Characteristics of Recycled Aggregates and the Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced by Replacing Natural Coarse Aggregates with Recycled Ones—Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructures" Infrastructures 10, no. 8: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10080213
APA StyleJunior, G. A. F., Leite, J. C. T., Mendez, G. d. P., Haddad, A. N., Silva, J. A. F., & da Costa, B. B. F. (2025). A Review of the Characteristics of Recycled Aggregates and the Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced by Replacing Natural Coarse Aggregates with Recycled Ones—Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructures. Infrastructures, 10(8), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10080213