A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine
Abstract
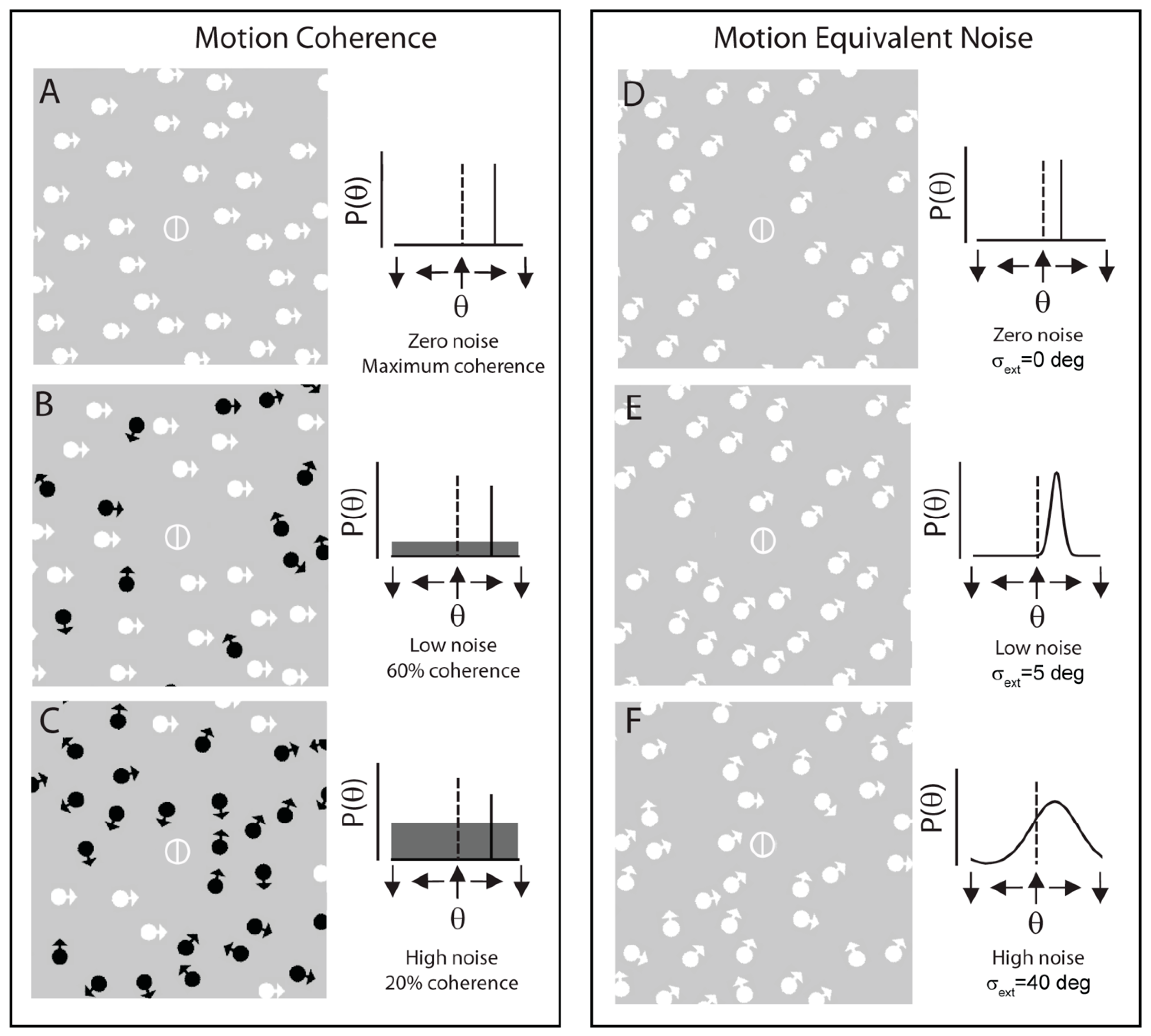
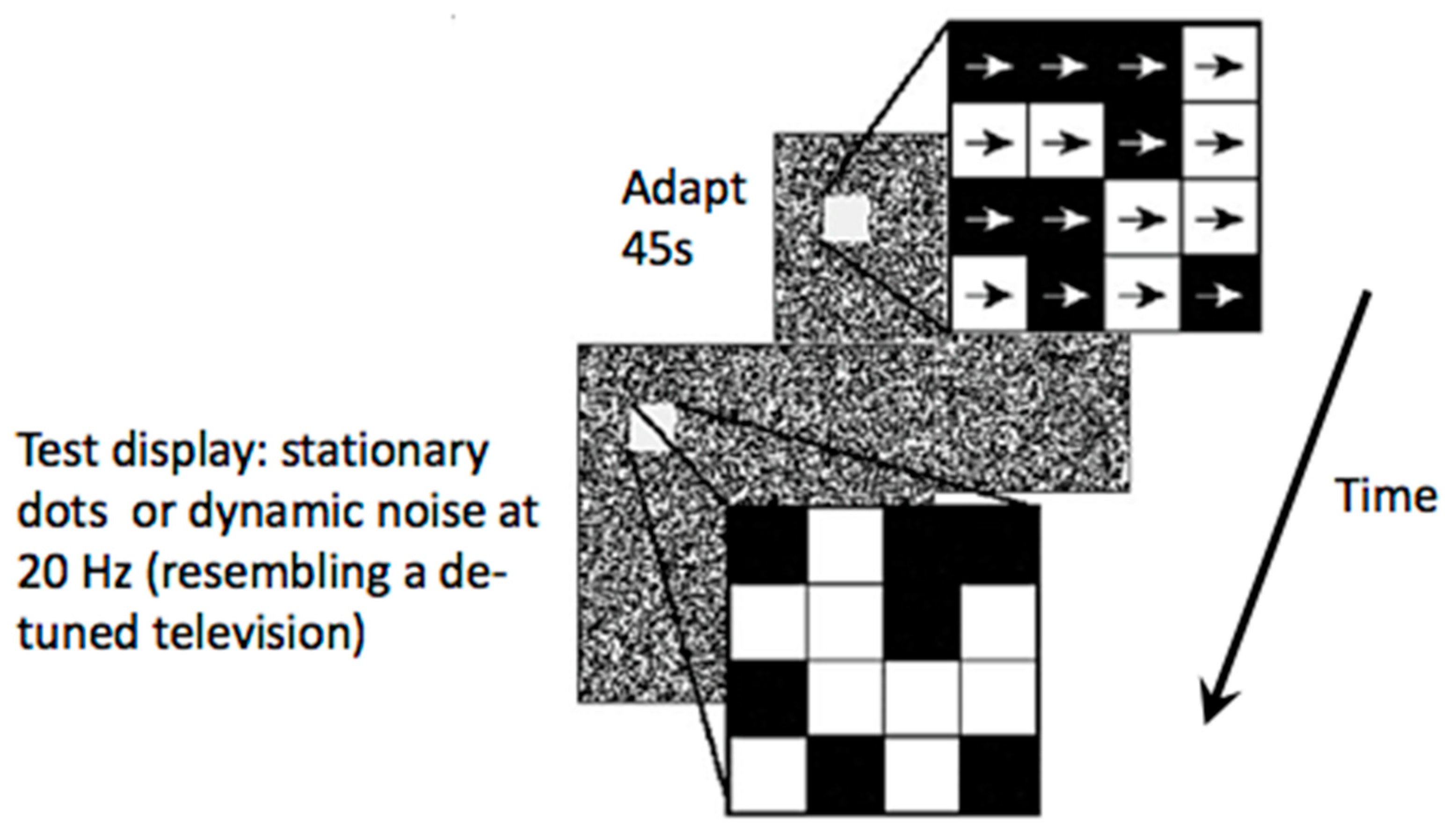
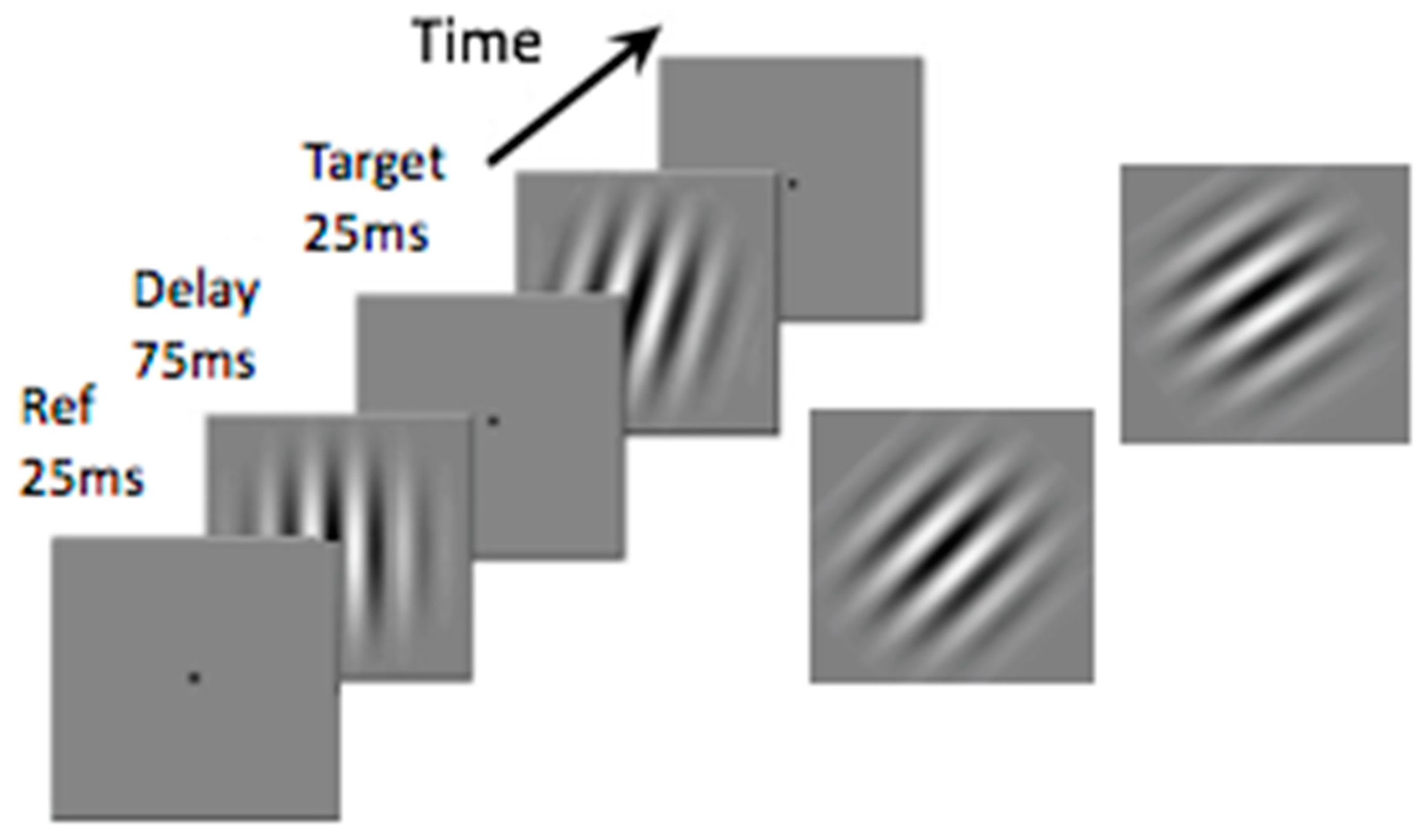
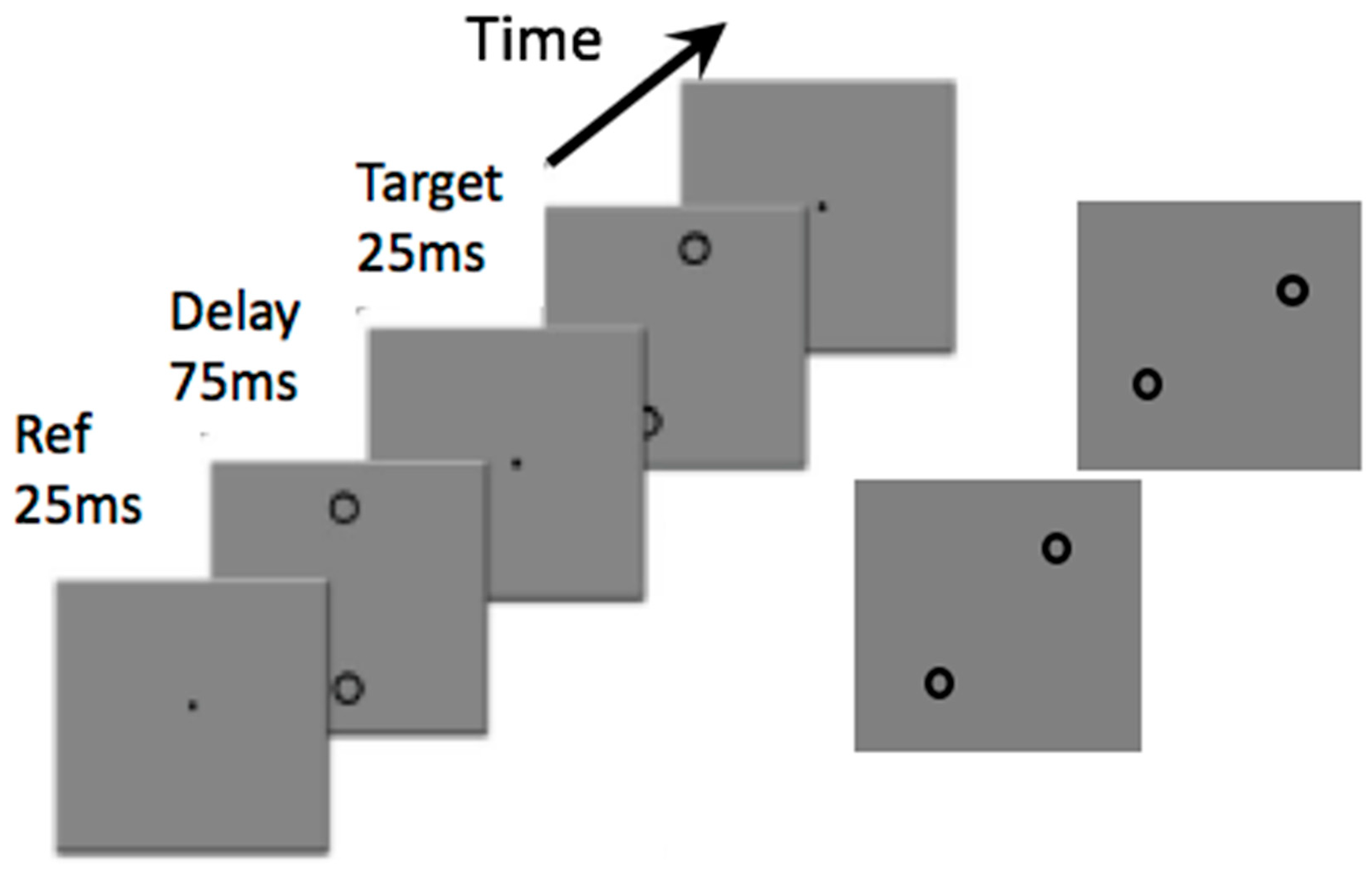
Introduction
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 9859, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation Atlas. Country Resources for Neurological Disorders; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Stovner, L.J.; Hagen, K.; Jensen, R.; Katsarava, Z.; Lipton, R.; Scher, A.; Steiner, T.; Zwart, J.A. The global burden of headache: A documentation of headache prevalence and disability worldwide. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MigraineTrust. Available online: https://www.migrainetrust.org/policy-campaigns/employment/ (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Migraine Action Association. Available online: http://www.migraine.org.uk/information/ (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Shepherd, A.J. Visual stimuli, light and lighting are common triggers of migraine and headache. J. Light Vis. Environ. 2010, 34, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harle, D.E.; Shepherd, A.J.; Evans, B.J.W. Visual stimuli are common triggers of migraine and are associated with pattern glare. Headache 2006, 46, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvaia, J.; Elias, S.; Shepherd, A.J. Symptoms of visual discomfort from automobile lights and their correlation with headache in night-time taxi-drivers. Light. Res. Technol. 2014, 46, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J. Increased visual after-effects following pattern adaptation in migraine: A lack of intracortical excitation? Brain 2001, 124, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J. Local and global motion after-effects are both enhanced in migraine, and the underlying mechanisms differ across cortical areas. Brain 2006, 129, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Beaumont, H.M.; Hine, T.J. Motion processing deficits in migraine are related to contrast sensitivity. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Joly-Mascheroni, R.M. Visual motion processing in migraine: Enhanced motion after-effects are related to display contrast, visual symptoms, visual triggers and attack frequency. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Shepherd, A.J. Enhanced motion aftereffects in migraine are related to contrast sensitivity: Implications for models of differences in precortical/cortical function. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J. Visual contrast processing in migraine. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.M.; Legg, N.J. Pathophysiology of migraine: A study using VEP and contrast sensitivity. In New Advances in Headache Research; Rose, F.C., Ed.; Smith-Gordon: London, UK, 1989; pp. 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.E.; Chronicle, E.P.; Rolan, P.; Mulleners, W.M. Cortical hyperexcitability is cortical under-inhibition: Evidence from a novel functional test of migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Wyatt, G.; Tibber, M.S. Visual metacontrast masking in migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 3, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppen, H.; Palm-Meinders, I.; Kruit, M.; Lim, V.; Nugroho, A.; Westhof, I.; Terwindt, G.; van Buchem, M.; Ferrari, M.; Hommel, B. The impact of a migraine attack and its after-effects on perceptual organization, attention, and working memory. Cephalalgia 2011, 14, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, N.M. Investigations of Visual Function in Migraine Using Visual Evoked Potentials and Visual Psychophysical Tests. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, A.J. Models of cortical function in migraine: Can psychophysical studies distinguish between them? A review of the evidence for interictal cortical hyper- and hypo-excitability. In Migraine Disorders Research Trends; Laura, B., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar]
- Coleston, D.M.; Chronicle, E.; Ruddock, K.; Kennard, C. Pre-cortical dysfunction of spatial and temporal visual processing in migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibber, M.S.; Shepherd, A.J. Transient tritanopia in migraine: Evidence for a large-field retinal abnormality in blue-yellow opponent pathways. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5125–5131. [Google Scholar]
- Tibber, M.S.; Guedes, A.; Shepherd, A.J. Orientation discrimination and contrast detection thresholds in migraine for cardinal and oblique angles. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.; Hibbard, P. Visual processing in migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Hare, L. Temporal integration of motion streaks in migraine. Vision 2018, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Vingrys, A.J.; Badcock, D.R.; Heywood, J.T. Visual dysfunction between migraine events. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Badcock, D.R. Motion processing deficits in migraine. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, A.; Temme, J.; Nitsche, M.A.; Varga, E.T.; Lang, N.; Paulus, W. Altered motion perception in migraineurs: Evidence for interictal cortical hyperexcitability. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchfield, J.A.; McKendrick, A.M.; Badcock, D.R. Processing of global form and motion in migraine. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Badcock, D.R.; Gurgone, M. Vernier acuity is normal in migraine, whereas global form and global motion perception are not. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 7, 3213–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibber, M.S.; Kelly, M.G.; Jansari, A.; Dakin, S.C.; Shepherd, A.J. An inability to exclude visual noise in migraine. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battista, J.; Badcock, D.R.; McKendrick, A.M. Center-surround visual motion processing in migraine. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 11, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar]
- Karanovic, O.; Thabet, M.; Wilson, H.R.; Wilkinson, F. Detection and discrimination of flicker contrast in migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 723–736. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hare, L.; Menchinelli, F.; Durrant, S.J. Resting-state alpha-band oscillations in migraine. Perception 2018, 47, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Granziera, C.; DaSilva, A.F.; Snyder, J.; Tuch, D.S.; Hadjikhani, N. Anatomical alterations of the visual processing network in migraine with and without aura. PLoS Med. 2006, 10, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, R.; Rocca, M.A.; Columbo, B.; Valsasina, P.; Horsfield, M.A.; Copetti, M.; Falini, A.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Cortical abnormalities in patients with migraine: A surface-based analysis. Radiology 2013, 1, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hougaard, A.; Amin, F.M.; Hoffman, M.B.; Rostrup, E.; Larsson, H.B.; Asghar, M.S.; Larsen, V.A.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Interhemispheric differences of fMRI responses to visual stimuli in patients with side-fixed migraine aura. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 6, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunitzer, G.; Rokszin, A.; Kobor, J.; Benedek, G.; Nagy, A.; Kincses, Z.T. Delayed development of visual motion processing in childhood migraine. Cephalalgia 2012, 6, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelli, L.; Black, K.R.; Wray, S.R. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of visual area V5 in migraine. Neurology 2002, 58, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magis, D.; Lisicki, M.; Coppola, G. Highlights in migraine electrophysiology: Are controversies just reflecting disease heterogeneity? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 3, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracking the Migraine Cycle. Available online: http://www.bbk.ac.uk/psychology/e/xp/88/1 (accessed on 8 March 2019).
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shepherd, A.J. A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine. Vision 2019, 3, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision3020012
Shepherd AJ. A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine. Vision. 2019; 3(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision3020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleShepherd, Alex J. 2019. "A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine" Vision 3, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision3020012
APA StyleShepherd, A. J. (2019). A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine. Vision, 3(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision3020012



