Training Load, Maturity Timing and Future National Team Selection in National Youth Basketball Players
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Anthropometric Data
2.4. Somatic Maturation
2.5. Training Load
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Player’s Demographics
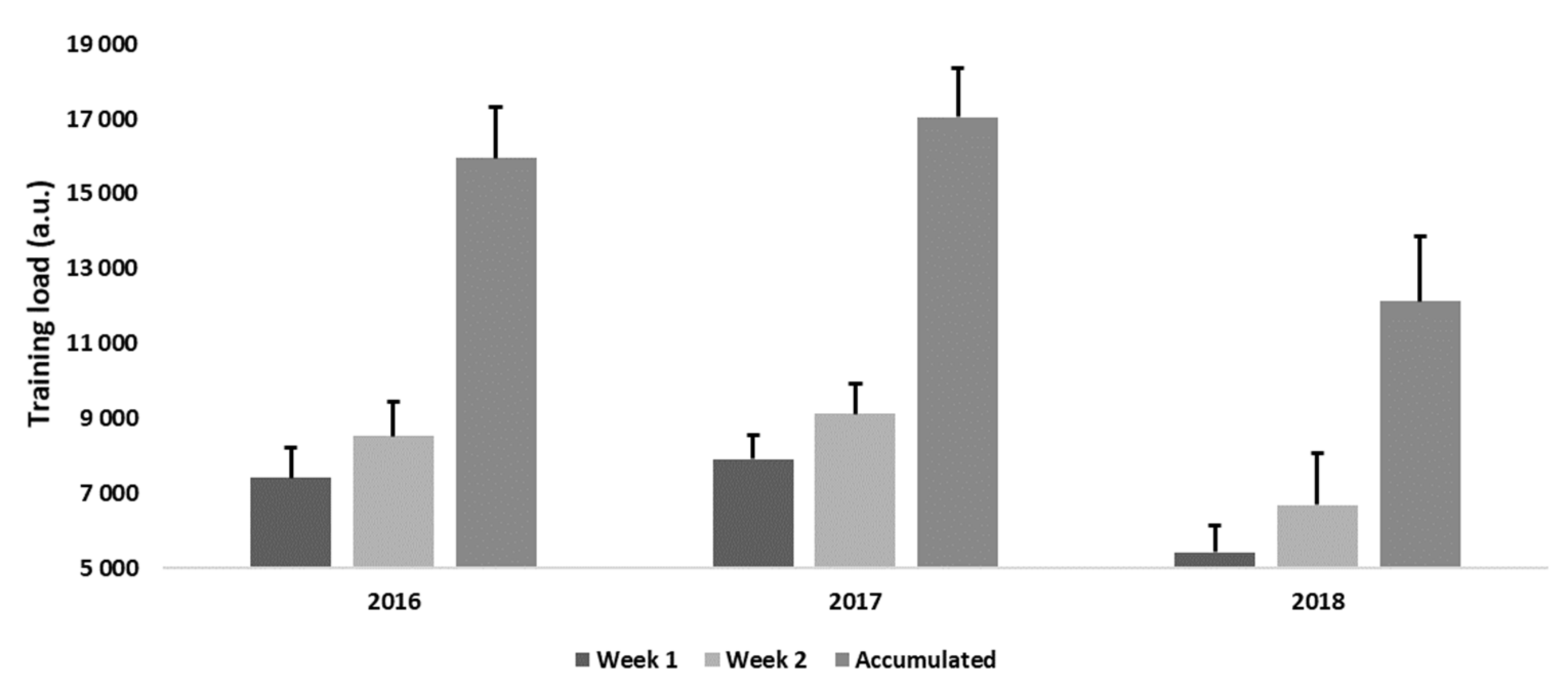
3.2. Training Load Description
3.3. Between-Groups Differences
3.4. Further Selection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arede, J.; Ferreira, A.P.; Esteves, P.; Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Leite, N. Train smarter, play more: Insights about preparation and game participation in youth national team. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2020, 91, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, A.; Jones, M.; Gelis, L.; Duncan, C.; Ehrmann, F.; Dupont, G.; Duffied, R. Monitoring loads and non-contact injury during the transition from club to National team prior to an international football tournament: A case study of the 2014 FIFA World Cup and 2015 Asia Cup. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, A.; Davison, M.; Andersen, T.E.; Beasley, I.; Bizzini, M.; Dupont, G.; Duffiel, R.; Carling, C.; Dvorak, J. Injury prevention strategies at the FIFA 2014 World Cup: Perceptions and practices of the physicians from the 32 participating national teams. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchheit, M.; Dupont, G. Elite clubs and national teams: Sharing the same party? Sci. Med. Footb. 2018, 2, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, N.; Schley, S.; Cumming, S.P.; Myer, G.D.; Saffel, H.; Hartwig, T.; Gabbett, T.J. Developmental training model for the sport specialized youth athlete: A dynamic strategy for individualizing load-response during maturation. Sports Health 2021, 14, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arede, J.; Esteves, P.; Ferreira, A.P.; Sampaio, J.; Leite, N. Jump higher, run faster: Effects of diversified sport participation on talent identification and selection in youth basketball identification and selection in youth basketball. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, C.; Cronin, J.; Oliver, J.; Hughes, M. Review: Talent identification in soccer: The role of maturity status on physical, physiological and technical characteristics. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2010, 5, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Malina, R.M.; Ribeiro, B.; Aroso, J.; Cumming, S.P. Characteristics of youth soccer players aged 13–15 years classified by skill level. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueiredo, A.J.; Gonçalves, C.E.; Coelho ESilva, M.J.; Malina, R.M. Youth soccer players, 11–14 years: Maturity, size, function, skill and goal orientation. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2009, 36, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Unda, J.; Zarrazquin, I.; Gil, J.; Ruiz, F.; Irazusta, A.; Kortajarena, M.; Seco, J.; Irazusta, J. Anthropometric, physiological and maturational characteristics in selected elite and non-elite male adolescent basketball players. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Scott, S.; McGee, D.; Cumming, S.P. Are relative age and biological ages associated with coaches evaluations of match performance in male academy soccer players? Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2020, 16, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Farooq, A.; Whiteley, R. Skeletal maturation status is more strongly associated with academy selection than birth quarter. Sci. Med. Footb. 2017, 1, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arede, J.; Ferreira, A.P.; Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Leite, N. Maturational development as a key aspect in physiological performance and national team selection in elite male basketball players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Unda, J.; Zarrazquin, I.; Gravina, L.; Zubero, J.; Seco, J.; Gil, S.M.; Gil, J.; Irazusta, J. Basketball performance is related to maturity and relative age in elite adolescent players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, J.; Paxton, K.; Jones, B.; Granacher, U.; Sandercock, G.R.; Hope, E.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Variable long-term developmental trajectories of short sprint speed and jumping height in English Premier League academy soccer players: An applied case study. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Castagna, C.; Calleja-González, J.; Jukic, I.; Idrizovic, K.; Stojanovic, M. The biological age of 14-year-old boys and success in adult soccer: Do early maturers predominate in the top-level game? Res. Sports Med. 2014, 22, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, S.; Roe, M.; Doran, D.A.; Gabbett, T.J.; Collins, K.D. Aerobic fitness and playing experience protect against spikes in workload: The role of the acute:chronic workload ratio on injury risk in elite Gaelic football. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arede, J.; Fernandes, J.; Moran, J.; Norris, J.; Leite, N. Maturity timing and performance in a youth national basketball team: Do early-maturing players dominate? Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2020, 16, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.; Lewin, C.; Forsythe, S.; McCall, A. Developing world-class soccer players: An example of the academy physical development program from an English Premier league team. Strength Cond. J. 2017, 30, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBurnie, A.J.; Dos’Santos, T.; Johnson, D.; Leng, E. Training management of the elite adolescent soccer player throughout maturation. Sports 2021, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalén, A.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Lundkvist, E.; Rey, E.; Pérez-Ferreirós, A. Talent selection strategies and relationship with success in european basketball national team programs. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalén, A.; Lundkvist, E.; Ivarsson, A.; Rey, E.; Kalén, A.; Rey, E.; Perez-Ferreiros, A. The influence of initial selection age, relative age effect and country long-term performance on the re-selection process in European basketball youth national teams. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A. Managing the training load in adolescent athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, S242–S249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahr, R. Demise of the fittest: Are we destroying our biggest talents? Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, A.; Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, T.; De Ridder, J. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Lowe Hutt, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mirwald, R.L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Bailey, D.A.; Beunen, G.P. An assessment of maturity from anthropometric measurements. Med. Sci Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Malina, R.M.; Kozieł, S.M. Validation of maturity offset in a longitudinal sample of Polish boys. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherar, L.B.; Mirwald, R.L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Thomis, M. Prediction of adult height using maturity-based cumulative height velocity curves. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borg, G.A.V. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Impellizzeri, F.M.; Rampinini, E.; Coutts, A.J.; Sassi, A.; Marcora, S.M. Use of RPE-based training load in soccer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C. Monitoring training in athletes with reference to overtraining syndrome. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampinini, M.; Rampinini, E.; Riggio, M.; Coutts, A.J.; Pecci, C.; McCall, A. Despite association, the acute: Chronic work load ratio does not predict non-contact injury in elite footballers. Sci. Med. Footb. 2018, 2, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Delecroix, B.; McCall, A.; Dawson, B.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. Workload and non-contact injury incidence in elite football players competing in European leagues. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumming, G. Understanding the New Statistics: Effect Sizes, Confidence Intervals, and Meta-Analysis; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lupo, C.; Tessitore, A.; Gasperi, L.; Gomez, M. Session-RPE for quantifying the load of different youth basketball training sessions. Biol. Sport 2017, 34, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilar, L.; Castellano, J.; Jukic, I.; Casamichana, D. positional differences in elite basketball: Selecting appropriate training-load measures. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, T.; Cormack, S.; Gabbett, T.; Williams, M.; Lorenzen, C. Characteristics impacting on session rating of perceived exertion training load in Australian footballers. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aughey, R.J.; Elias, G.P.; Esmaeili, A.; Lazarus, B.; Stewart, A.M. Does the recent internal load and strain on players affect match outcome in elite Australian football? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokanauskas, O.; Bietkis, T.; Arede, J.; Leite, N. Modelling youth basketball performance profile in European Championships. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2021, 30, 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Paulauskas, H.; Kreivyte, R.; Scanlan, A.T.; Moreira, A.; Siupsinskas, L.; Conte, D. Monitoring workload in elite female basketball players during the in-season phase: Weekly fluctuations and effect of playing time. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Griffiths, P.C.; Mellalieu, S.D. Training load and fatigue marker associations with injury and illness: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 943–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandes, M.; Elvers, S. Elite youth soccer players’ physiological responses, time-motion characteristics, and game performance in 4 vs. 4 small-sided games: The influence of coach feedback. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towlson, C.; Salter, J.; Ade, J.D.; Enright, K.; Harper, L.D.; Page, R.M.; Malone, J.J. Maturity-associated considerations for training load, injury risk, and physical performance in youth soccer: One size does not fit all. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sluis, A.; Elferink-Gemser, M.T.; Brink, M.S.; Visscher, C. Importance of peak height velocity timing in terms of injuries in talented. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, K.R.; Myer, G.D.; Hewett, T.E. Longitudinal effects of maturation on lower extremity joint stiffness in adolescent athletes. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radnor, J.M.; Oliver, J.L.; Waugh, C.M.; Myer, G.D.; Moore, I.S.; Lloyd, R.S. The influence of growth and maturation on stretch-shortening cycle function in youth. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrigley, R.; Drust, B.; Stratton, G.; Scott, M.; Gregson, W. Quantification of the typical weekly in-season training load in elite junior soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulin, B.T.; Gabbett, T.J.; Caputi, P.; Lawson, D.W.; Sampson, J.A. Low chronic workload and the acute:chronic workload ratio are more predictive of injury than between-match recovery time: A two-season prospective cohort study in elite rugby league players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiori, J.P.; Benjamin, H.J.; Brenner, J.S.; Gregory, A.; Jayanthi, N.; Landry, G.L.; Luke, A. Overuse injuries and burnout in youth sports: A position statement from the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malone, S.; Hughes, B.; Doran, D.A.; Collins, K.; Gabbett, T.J. Can the workload–injury relationship be moderated by improved strength, speed and repeated-sprint qualities? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 22, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fransen, J.; Skorski, S.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G. Estimating is not measuring: The use of non-invasive estimations of somatic maturity in youth football. Sci. Med. Footb. 2021, 5, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Massuça, L.; Volossovitch, A.; Ferreira, A.P.; Fragoso, I. Morphological and fitness attributes of young male Portuguese basketball players: Normative values according to chronological age and years from peak height velocity. Front. Sports Act. Living 2021, 3, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Junior, D.B.; Werneck, F.Z.; Oliveira, H.Z.; Panza, P.S.; Ibáñez, S.J.; Vianna, J.M. From talent identification to novo basquete Brasil (NBB): Multifactorial analysis of the career progression in youth brazilian elite basketball. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 617563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Early Maturer (n = 11) | Average Maturer (n = 18) | p | Effect Size (ES) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATURITY | ||||
| CA (years) | 16.04 ± 0.45 | 16.04 ± 0.28 | 0.985 | |
| APHV (years) | 12.63 ± 0.41 | 13.64 ± 0.33 | 0.000 | −2.80 |
| MO (years) | 3.22 ± 0.53 | 2.33 ± 0.41 | 0.000 | 1.93 |
| PAH (cm) | 196.18 ± 5.24 | 189.40 ± 5.44 | 0.003 | 1.26 |
| ANTHROPOMETRICAL | ||||
| Height (cm) | 195.25 ± 5.52 | 187.10 ± 6.12 | 0.001 | 1.38 |
| Sitting height (cm) | 98.84 ± 2.81 | 93.59 ± 1.96 | 0.000 | 2.27 |
| Body mass (kg) | 90.79 ± 9.03 | 76.09 ± 7.52 | 0.000 | 1.81 |
| PLAYING POSITIONS | ||||
| Perimeter players | 23.3% | 66.7% | ||
| Inside players | 72.7% | 33.3% | ||
| YEARS | ||||
| 2016 | 63.6% | 27.8% | ||
| 2017 | 18.2% | 38.9% | ||
| 2018 | 18.2% | 33.3% | ||
| U18 NATIONAL TEAM SELECTION | ||||
| Yes | 54.5% | 77.8% | ||
| No | 45.5% | 22.2% | ||
| TRAINING | ||||
| Training experience (years) | 5.55 ± 2.38 | 8.22 ± 2.10 | 0.004 | −1.21 |
| Week 1—Training load (a.u.) | 7139.82 ± 1248.98 | 6959.68 ± 1274.32 | 0.713 | |
| Week 1—Monotony (a.u.) | 1.59 ± 0.36 | 1.24 ± 0.51 | 0.063 | |
| Week 1—Strain (a.u.) | 11,623.64 ± 4014.43 | 8422.05 ± 3552.59 | 0.033 | 0.86 |
| Week 2—Training load (a.u.) | 8250.64 ± 980.49 | 8184.06 ± 1632.49 | 0.904 | |
| Week 2—Monotony (a.u.) | 1.51 ± 0.30 | 1.75 ± 0.35 | 0.073 | |
| Week 2—Strain (a.u.) | 12,528.11 ± 2922.52 | 14,484.19 ± 4831.89 | 0.237 | |
| Accumulated Training Load (a.u.) | 15,390.46 ± 1885.67 | 15,097.07 ± 2899.33 | 0.768 | |
| Total Monotony (a.u.) | 1.55 ± 0.17 | 1.50 ± 0.17 | 0.404 | |
| Total Strain (a.u.) | 23,950.47 ± 4301.00 | 22,559.76 ± 4663.57 | 0.430 | |
| Week-to-week absolute difference in load (a.u.) | 1110.82 ± 1219.37 | 1177.71 ± 967.67 | 0.871 | |
| Week-to-week workload ratio (a.u.) | 1.18 ± 0.23 | 1.18 ± 0.15 | 0.934 |
| Variable | Standardized Canonical Discriminant Function Coefficients |
|---|---|
| Height | 0.437 |
| Sitting Height | 0.719 |
| Body Mass | 0.574 |
| Training experience | −0.155 |
| Week 1—Strain (a.u.) | 0.090 |
| Eigenvalue | 2.516 |
| Cases correctly classified | 96.6% |
| Function | ^ = 0.284 χ2 (3) = 32.065 (p = 0.000) |
| Entered | Wilks’ Lambda | Exact F | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Step | Entered | Statistic | df 1 | df 2 | df 3 | Statistic | df 1 | df 2 | |
| Under-18 National Team | 1 | Week 2—Training load (a.u.) | 0.818 | 1 | 1 | 27.0 | 6.022 | 1 | 27.0 | 0.021 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arede, J.; Freitas, T.T.; Johnson, D.; Fernandes, J.F.T.; Williams, S.; Moran, J.; Leite, N. Training Load, Maturity Timing and Future National Team Selection in National Youth Basketball Players. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7010021
Arede J, Freitas TT, Johnson D, Fernandes JFT, Williams S, Moran J, Leite N. Training Load, Maturity Timing and Future National Team Selection in National Youth Basketball Players. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2022; 7(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleArede, Jorge, Tomás T. Freitas, David Johnson, John F. T. Fernandes, Sean Williams, Jason Moran, and Nuno Leite. 2022. "Training Load, Maturity Timing and Future National Team Selection in National Youth Basketball Players" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 7, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7010021
APA StyleArede, J., Freitas, T. T., Johnson, D., Fernandes, J. F. T., Williams, S., Moran, J., & Leite, N. (2022). Training Load, Maturity Timing and Future National Team Selection in National Youth Basketball Players. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 7(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7010021









