Light-Based Reaction Speed Does Not Predict Field-Based Reactive Agility in Soccer Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Physical Performance Tests
2.3.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.2. The 40 m Speed Test
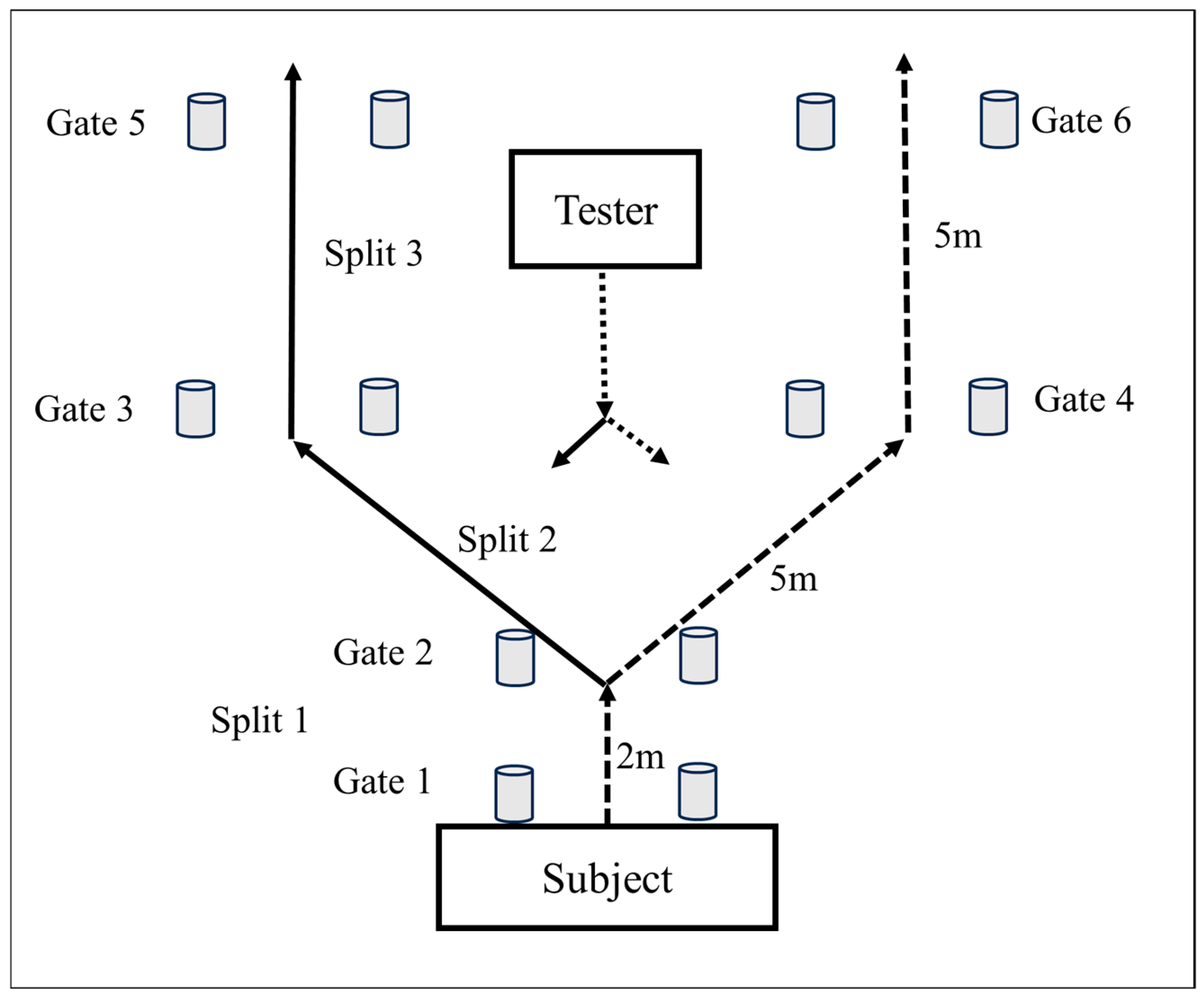
2.3.3. Reactive Agility Test (RAT)
- Step forward to the player’s dominant side, with the player evading towards his non-dominant side.
- Step forward to the player’s non-dominant side, with the player evading towards his dominant side.
2.3.4. Sports Vision Test (SVT)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | Reactive Agility |
| RAT | Reactive Agility Test |
| SVT | Sports Vision Test |
| COD | Change of Direction |
| NWU | North-West University |
References
- Faude, O.; Koch, T.; Meyer, T. Straight Sprinting Is the Most Frequent Action in Goal Situations in Professional Football. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldbeck, P.; Dos’Santos, T. How Do Soccer Players Sprint from a Tactical Context? Observations of an English Premier League Soccer Team. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 40, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfen, H.E.; Memmert, D. The Relationship between Cognitive Functions and Sport-Specific Motor Skills in Elite Youth Soccer Players. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ade, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Bradley, P.S. High-Intensity Efforts in Elite Soccer Matches and Associated Movement Patterns, Technical Skills and Tactical Actions. Information for Position-Specific Training Drills. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.J.; Drust, B.; Ade, J.D.; Robinson, M.A. Change of Direction Frequency off the Ball: New Perspectives in Elite Youth Soccer. Sci. Med. Footb. 2022, 6, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.; Rayner, R.; Talpey, S. It’s Time to Change Direction on Agility Research: A Call to Action. Sports Med. Open 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Oliveira, J.; Williams, M.; Garganta, J. Expertise and Perceptual-Cognitive Performance in Soccer: A Review. Rev. Port. Cienc. Desporto 2009, 9, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Klatt, S.; Smeeton, N.J. Processing Visual Information in Elite Junior Soccer Players: Effects of Chronological Age and Training Experience on Visual Perception, Attention, and Decision Making. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.B.; Dawson, B.; Henry, G.J. Agility and Change-of-Direction Speed Are Independent Skills: Implications for Training for Agility in Invasion Sports. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2015, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos’santos, T.; Mcburnie, A.; Thomas, C.; Comfort, P.; Jones, P. Biomechanical Comparison of Cutting Techniques: A Review and Practical Applications. Strength Cond. J. 2019, 4, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horníková, H.; Jeleň, M.; Zemková, E. Determinants of Reactive Agility in Tests with Different Demands on Sensory and Motor Components in Handball Players. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horníková, H.; Skala, F.; Zemková, E. Sport-Specific Differences in Key Performance Factors among Handball, Basketball and Table Tennis Players. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Sport 2023, 22, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, M.M.; Feliu, G.M.; Bishop, C.; Gonzalo-Skok, O. Assessing the Reliability and Validity of Agility Testing in Team Sports: A Systematic Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajković, N.; Sporiš, G.; Krističević, T.; Madić, D.M.; Bogataj, Š. The Importance of Reactive Agility Tests in Differentiating Adolescent Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrašić, S.; Gušić, M.; Stanković, M.; Mačak, D.; Bradić, A.; Sporiš, G.; Trajković, N. Speed, Change of Direction Speed and Reactive Agility in Adolescent Soccer Players: Age Related Differences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, O.; Eroglu, H. Correlation between Reaction Time and Speed in Elite Soccer Players. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2006, 4, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ricotti, L.; Rigosa, J.; Niosi, A.; Menciassi, A. Analysis of Balance, Rapidity, Force and Reaction Times of Soccer Players at Different Levels of Competition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, N. Prediction of Talent in Youth Soccer Players: Prospective Study over 4-6 Years. Footb. Sci. 2011, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kida, N.; Oda, S.; Matsumura, M. Intensive Baseball Practice Improves the Go/Nogo Reaction Time, but Not the Simple Reaction Time. Cogn. Brain Res. 2005, 22, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, G.B. Visual Performance Evaluation. In Sports Vision: Vision Care for the Enhancement of Sports Performance; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 45–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, P.H.; Sparks, S.A.; Murphy, P.N.; Carnegie, E.; Marchant, D.C. Determining Eye-Hand Coordination Using the Sport Vision Trainer: An Evaluation of Test-Retest Reliability. Res. Sports Med. 2014, 22, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemková, E. Differential Contribution of Reaction Time and Movement Velocity to the Agility Performance Reflects Sport-Specific Demands. Hum. Hum. Mov. 2016, 17, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöllner, A.; Memmert, D.; von Lehe, M.; Jungilligens, J.; Scharfen, H.E. Specific Relations of Visual Skills and Executive Functions in Elite Soccer Players. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 960092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coh, M.; Vodičar, J.; Zvan, M.; Šimenko, J.; Stodolka, J.; Rauter, S.; Maćkala, K. Are Change-of-Direction Speed and Reactive Agility Independent Skills Even When Using the Same Movement Pattern? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, S.; Ringhof, S.; Neumann, R.; Woll, A.; Rumpf, M.C. Validity and Reliability of Speed Tests Used in Soccer: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, J.; Pearce, A.; Carlson, J.; John, S. Reliability and Validity of a Reactive Agility Test for Australian Football. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; L. Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sawilowsky, S.S. New Effect Size Rules of Thumb. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2009, 8, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.M. Applied Statistics: From Bivariate Through Multivariate Techniques, 2nd ed.; Sage: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, F.; Gray, R.; Wachsmuth, S.; Höner, O. Perceptual-Motor and Perceptual-Cognitive Skill Acquisition in Soccer: A Systematic Review on the Influence of Practice Design and Coaching Behavior. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 772201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfen, H.E.; Memmert, D. Cognitive Training in Elite Soccer Players: Evidence of Narrow, but Not Broad Transfer to Visual and Executive Function. Ger. J. Exerc. Sport Res. 2021, 51, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, L.G.; Erickson, G. Sports Vision Training: A Review of the State-of-the-Art in Digital Training Techniques. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2018, 11, 160–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.F.; Ellis, J.K.; Bench, J.; Khoury, J.; Graman, P. High-Performance Vision Training Improves Batting Statistics for University of Cincinnati Baseball Players. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.T.Y.; Williams, A.M.; Ward, P.; Janelle, C.M. Perceptual-Cognitive Expertise in Sport: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2007, 29, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, M.W.; Kramer, A.F.; Basak, C.; Prakash, R.S.; Roberts, B. Are Expert Athletes “expert” in the Cognitive Laboratory? A Meta-Analytic Review of Cognition and Sport Expertise. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2010, 24, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemková, E.; Hamar, D. Association of Speed of Decision Making and Change of Direction Speed with the Agility Performance. Funct. Neurol. Rehabil. Ergon. 2017, 7, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Buscemi, A.; Mondelli, F.; Biagini, I.; Gueli, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Coco, M. Role of Sport Vision in Performance: Systematic Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presta, V.; Vitale, C.; Ambrosini, L.; Gobbi, G. Stereopsis in Sports: Visual Skills and Visuomotor Integration Models in Professional and Non-Professional Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Young, W.B.; Doyle, T.L.A.; Sheppard, T.A.; Newton, R.U. An Evaluation of a New Test of Reactive Agility and Its Relationship to Sprint Speed and Change of Direction Speed. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2006, 9, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmoni, A.W.; Schmidt, R.A.; Walter, C.B. Knowledge of Results and Motor Learning: A Review and Critical Reappraisal. Psychol. Bull. 1984, 3, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlák, J.; Fridvalszki, M.; Korodi, V.; Szamosszegi, G.; Pólyán, E.; Kovács, B.; Kolozs, B.; Langmar, G.; Rácz, L. Relationship between Cognitive Functions and Agility Performance in Elite Young Male Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 38, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stølen, T.; Chamari, K.; Castagna, C.; Wisløff, U. Physiology of Soccer an Update. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Garganta, J.; Oliveira, J.; Casanova, F. The Contribution of Perceptual and Cognitive Skills in Anticipation Performance of Elite and Non-Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 4, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.; Sitthiworachart, J.; Morris, J. Application of Simulation Technology in Football Training: A Systematic Review of Empirical Studies. Open Sports Sci. J. 2024, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physical Test | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Speed: 5 m (s) | 1.5 ± 0.05 |
| Speed: 10 m (s) | 1.79 ± 0.06 |
| Speed 20 m (s) | 3.08 ± 0.1 |
| Speed: 40 m (s) | 5.51 ± 0.2 |
| RAT: DL: Total (s) | 2.42 ± 0.11 |
| RAT: DL: Split 2 (s) | 1.01 ± 0.07 |
| RAT: DL: Split 3 (s) | 0.89 ± 0.21 |
| RAT: NDL: Total (s) | 2.45 ± 0.13 |
| RAT: NDL: Split 2 (s) | 1.02 ± 0.08 |
| RAT: NDL: Split 3 (s) | 0.92 ± 0.2 |
| SVT: minimum (ms−1) | 0.28 ± 0.1 |
| SVT: maximum (ms−1) | 0.52 ± 0.2 |
| SVT: average (ms−1) | 0.36 ± 0.12 |
| SVT: total (ms−1) | 7.11 ± 2.38 |
| Defenders n = 16 | Forwards n = 14 | Midfielders n = 10 | Goalkeepers n = 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed: 5 m (s) | 1.05 ± 0.04 | 1.04 ± 0.04 | 1.07 ± 0.07 | 1.04 ± 0.05 |
| Speed: 10 m (s) | 1.78 ± 0.06 | 1.77 ± 0.05 | 1.81 ± 0.08 | 1.79 ± 0.08 |
| Speed 20 m (s) | 3.09 ± 0.1 | 3.06 ± 0.09 | 3.11 ± 0.1 | 3.09 ± 0.17 |
| Speed: 40 m (s) | 5.54 ± 0.19 | 5.42 ± 0.19 | 5.56 ± 0.19 | 5.55 ± 0.32 |
| RAT: DL: Total (s) | 2.43 ± 0.12 | 2.42 ± 0.12 | 2.40 ± 0.10 | 2.39 ± 0.15 |
| RAT: DL: Split 2 (s) | 1.02 ± 0.08 | 1.00 ± 0.07 | 1.00 ± 0.08 | 0.99 ± 0.07 |
| RAT: DL: Split 3 (s) | 0.90 ± 0.21 | 0.88 ± 0.23 | 0.91 ± 0.24 | 0.85 ± 0.05 |
| RAT: NDL: Total (s) | 2.48 ± 0.15 | 2.42 ± 0.09 | 2.44 ± 0.12 | 2.51 ± 0.15 |
| RAT: NDL: Split 2 (s) | 1.03 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.06 | 1.01 ± 0.07 | 1.07 ± 0.08 |
| RAT: NDL: Split 3 (s) | 0.92 ± 0.21 | 0.91 ± 0.19 | 0.94 ± 0.24 | 0.90 ± 0.06 |
| SVT: minimum (ms−1) | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.04 * | 0.28 ± 0.14 * | 0.31 ± 0.05 |
| SVT: maximum (ms−1) | 0.58 ± 0.10 | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.59 ± 0.15 | 0.56 ± 0.07 |
| SVT: average (ms−1) | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
| SVT: total (ms−1) | 7.81 ± 0.56 | 7.90 ± 0.83 | 7.79 ± 1.04 | 7.67 ± 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broodryk, A.; Skala, F.; Broodryk, R. Light-Based Reaction Speed Does Not Predict Field-Based Reactive Agility in Soccer Players. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030239
Broodryk A, Skala F, Broodryk R. Light-Based Reaction Speed Does Not Predict Field-Based Reactive Agility in Soccer Players. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(3):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030239
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroodryk, Adele, Filip Skala, and Retief Broodryk. 2025. "Light-Based Reaction Speed Does Not Predict Field-Based Reactive Agility in Soccer Players" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 3: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030239
APA StyleBroodryk, A., Skala, F., & Broodryk, R. (2025). Light-Based Reaction Speed Does Not Predict Field-Based Reactive Agility in Soccer Players. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(3), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030239






