Spatiotemporal Variations and Convergence Characteristics of Green Technological Progress in China’s Mariculture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method for Measuring GTP in Mariculture
2.2. Dagum Gini Coefficient
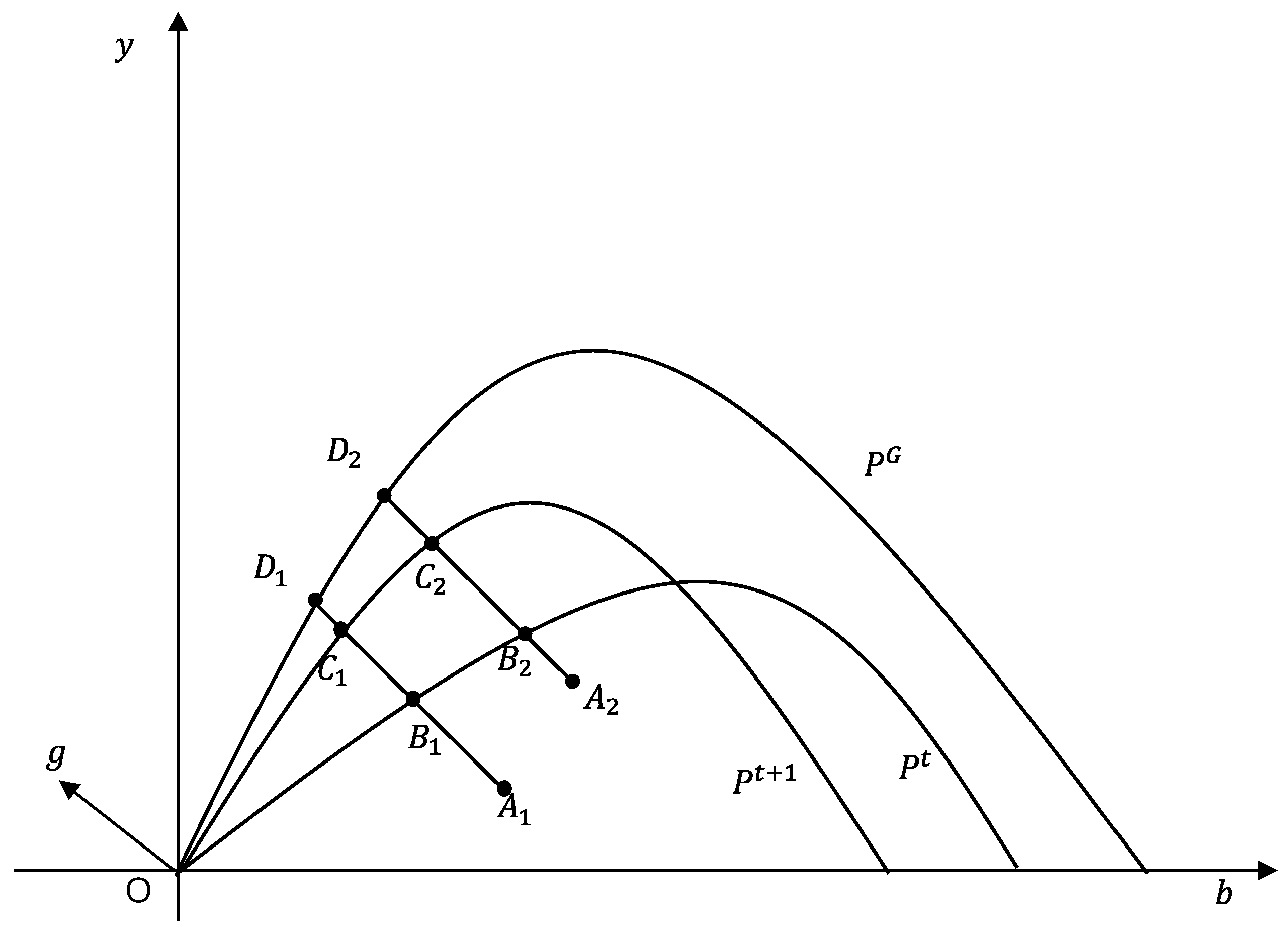
2.3. Test of Convergence
2.3.1. σ Convergence
2.3.2. Absolute β Convergence
2.3.3. Conditional β Convergence
3. Results and Discussion
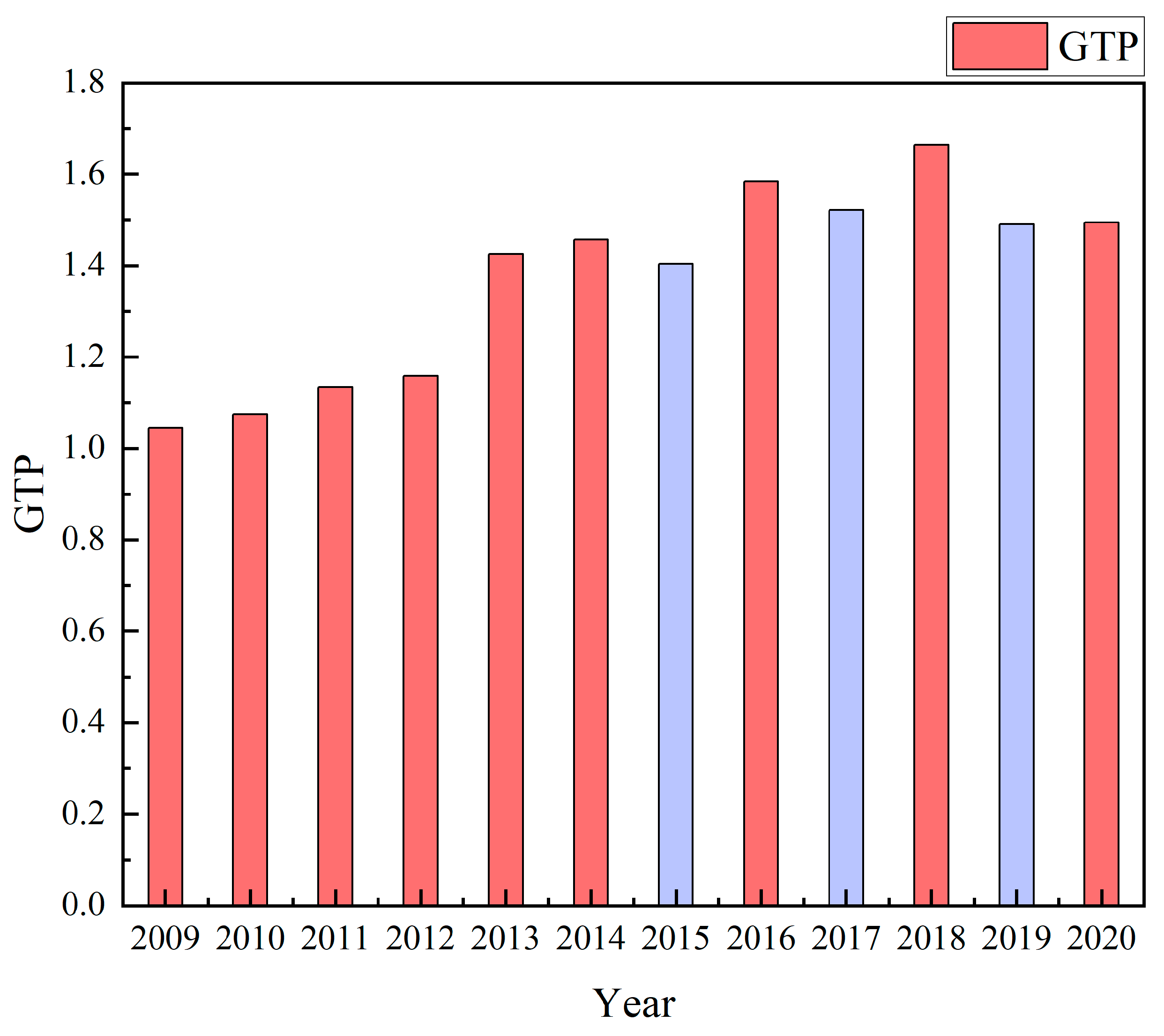
3.1. Temporal Variation of GTP in Mariculture
3.2. Spatial Variation of GTP in Mariculture
3.2.1. Overall Differences and Sources of GTP in Mariculture
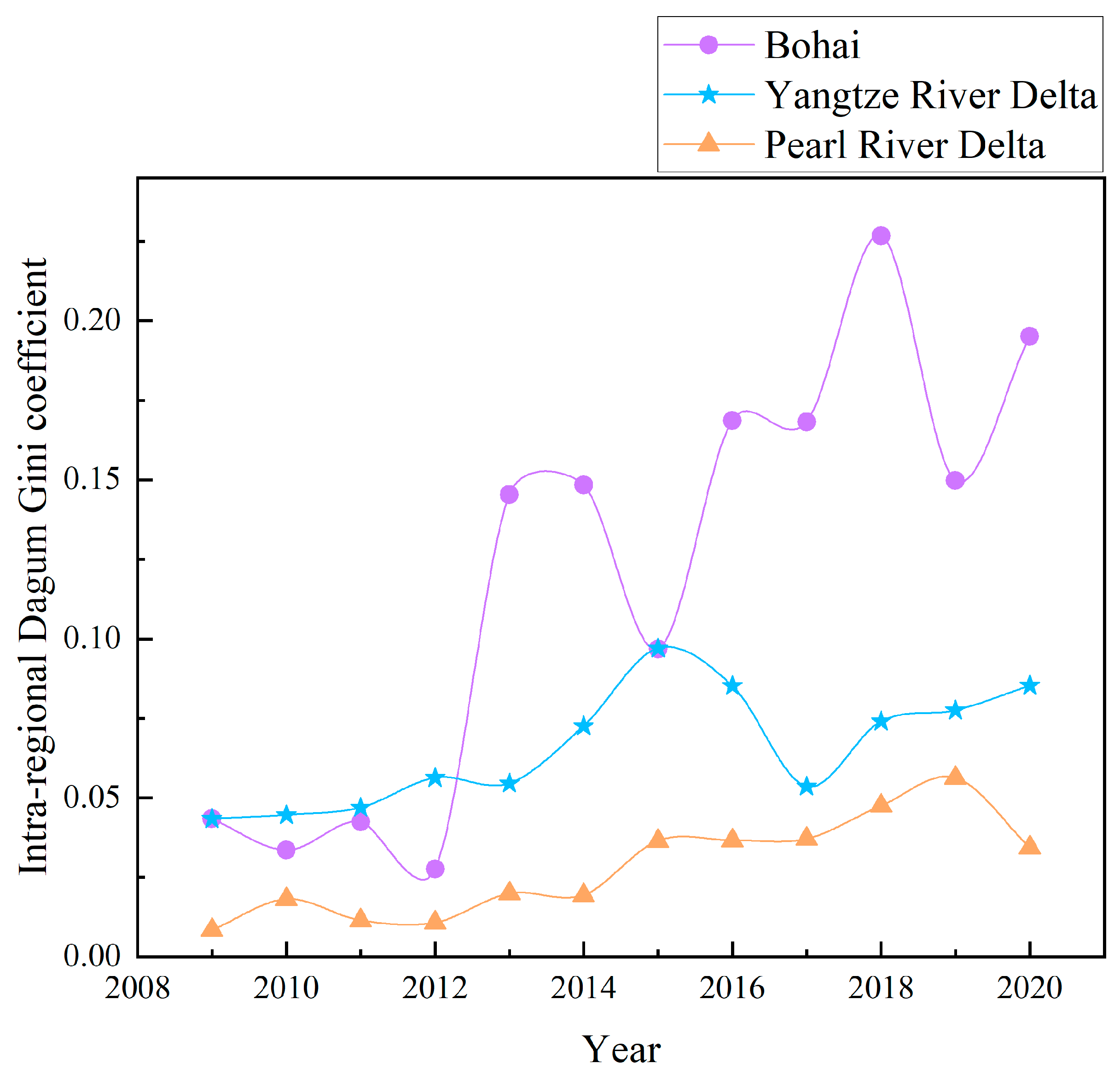
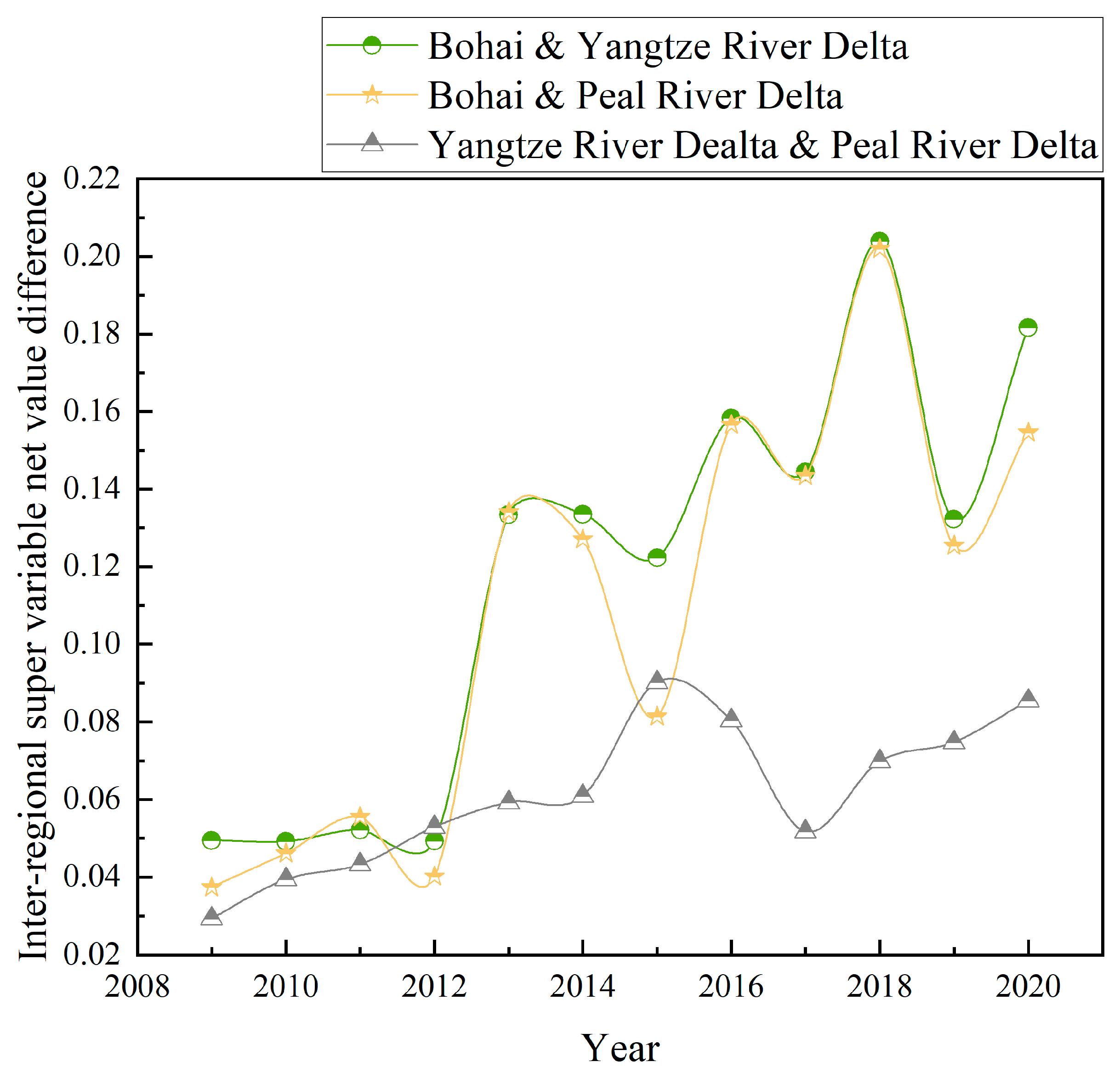
3.2.2. Intra-Regional and Inter-Regional Variation in Mariculture GTP
3.3. Convergence Results
3.3.1. σ Convergence Results
3.3.2. Absolute Convergence Results
3.3.3. Conditional Convergence Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mc Carthy, U.; Uysal, I.; Badia-Melis, R.; Mercier, S.; O’Donnell, C.; Ktenioudaki, A. Global food security—Issues, challenges and technological solutions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jin, X.; Han, B.; Sun, R.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; He, J.; Li, J. China’s food security situation and key questions in the new era: A perspective of farmland protection. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Han, Q. Food security of mariculture in China: Evolution, future potential and policy. Mar. Policy 2020, 115, 103892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Feagin, R.A. Mariculture is a double-edged sword in China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 222, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yue, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, H. The Impact of Pollution on China Marine Fishery Culture: An Econometric Analysis of Heterogeneous Growth. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 760539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P. Aquaculture environment interactions: Past, present and likely future trends. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, D.; Xu, N. Special aquatic products supply chain coordination considering bilateral green input in the context of high-quality development. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 2022, 33, 819–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, T. Research on the efficiency of marine aquaculture production in Guangdong province based on the Malmquist index. Ocean. Dev. Manag. 2018, 35, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Dong, S.; Qian, J.; Lyu, K. Measuring the Green Total Factor Productivity in Chinese Aquaculture: A Zofio Index Decomposition. Fishes 2022, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zeng, Q. A study on the total factor productivity of China’s Mariculture—Considered undesirable outputs based on global Malmquist-Luenberger index. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc. Sci.) 2017, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Ji, J. Measurement and analysis of technological progress bias in China’s mariculture industry. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2022, 53, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Sun, Y.; Yin, X. Study on green output bias of China’s mariculture technological progress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 60558–60571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, L.; Beusen, A.; Glibert, P.M.; Overbeek, C.; Pawlowski, M.; Herrera, J.; Mulsow, S.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Mariculture: Significant and expanding cause of coastal nutrient enrichment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Han, L.; Yin, W. Research on the ecologicalization efficiency of mariculture industry in China and its influencing factors. Mar. Policy 2022, 137, 104935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, H.; Shutes, B.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, X. Historical evolution of mariculture in China during past 40 years and its impacts on eco-environment. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Environmental effects of mariculture in China: An overall study of nitrogen and phosphorus loads. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ji, J. Research on China’s mariculture efficiency evaluation and influencing factors with undesirable outputs—An empirical analysis of China’s ten coastal regions. Aquacult. Int. 2017, 25, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Wu, N.; Zhang, J. Experimental Study of the Environmental Effects of Summertime Cocultures of Seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) and Japanese Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis in Sanggou Bay, China. Fishes 2022, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Li, Y. Research on green technology progress measurement and influencing factors in marine aquaculture industry in China. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc. Sci.) 2019, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Zeng, Q. Is the green technological progress bias of mariculture suitable for its factor endowment?—Empirical results from 10 coastal provinces and cities in China. Mar. Policy 2021, 124, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA—A third pole of technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Du, J. The impact of urban land misallocation on inclusive green growth efficiency: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.H. A global Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J. Prod. Anal. 2010, 34, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassdal, T.; Sørensen Holst, H.M. Technical progress and regress in Norwegian salmon farming: A Malmquist index approach. Mar. Resour. Econ. 2011, 26, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, N. Spatio-Temporal disparities of mariculture area production efficiency considering undesirable output: A case study of China’s east coast. Water 2022, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, G.; Zhao, W.; Chen, J. Estimating pollutant loadings from mariculture in China. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, X.; Robinson, S. Structural change and economic growth in China. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2003, 7, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagum, C. A new approach to the decomposition of the Gini income inequality ratio. Empir. Econ. 1997, 22, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, D. Regional differences, dynamic evolution, and driving factors of tourism development in Chinese coastal cities. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 226, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, R.I.; Yitzhaki, S. Improving the accuracy of estimates of Gini Coefficients. J. Econ. 1989, 42, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wenxin, L.; Khan, S.U.; Yu, C.; Jun, Z.; Yue, D.; Zhao, M. Regional Differential Decomposition and Convergence of Rural Green Development Efficiency: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22364–22379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Ram, R. Cross-country convergence in energy and electricity consumption, 1971–2007. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.C.; Chen, X. The green total factor productivity and convergence in China. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 2794–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shi, R.; Mi, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, G. Spatial Distribution and Convergence of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, R.J.; Sala-i-Martin, X. Convergence. J. Political Econ. 1992, 100, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Green productivity growth and convergence in Chinese agriculture. J. Environ. Plann. Manag. 2023, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Gu, X. Research on meta-frontier total-factor energy efficiency and its spatial convergence in Chinese provinces. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Folmer, H.; Ji, M.; Zhou, P. Revisiting cross-province energy intensity convergence in China: A spatial panel analysis. Energy Policy 2018, 121, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, W. Measurement of the contributions of science and technology to the marine fisheries industry in the coastal regions of China. Mar. Policy 2019, 108, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Hanson, A.; Huang, B.; Leadbitter, D.; Little, D.C.; Pikitch, E.K.; Qiu, Y.S.; de Mitcheson, Y.S.; et al. Opportunity for marine fisheries reform in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, R.; Lin, Z. “Crisis” or “opportunity”? COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on environmentally sound invention efficiency in China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Provinces | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin | 1.003 | 0.999 | 1.059 | 1.019 | 1.133 | 1.007 | 1.048 | 1.023 | 0.913 | 1.020 | 0.967 | 0.930 |
| Hebe | 1.213 | 0.955 | 1.050 | 1.002 | 1.920 | 1.036 | 0.838 | 1.387 | 0.920 | 1.325 | 0.697 | 1.185 |
| Liaoning | 0.977 | 1.002 | 0.998 | 1.086 | 1.514 | 0.975 | 0.868 | 1.303 | 0.943 | 1.127 | 0.742 | 1.012 |
| Jiangsu | 0.918 | 1.031 | 1.064 | 1.035 | 1.338 | 0.916 | 0.867 | 1.310 | 0.970 | 1.023 | 0.914 | 0.900 |
| Zhejiang | 1.087 | 1.029 | 1.019 | 1.005 | 1.018 | 1.035 | 1.002 | 1.001 | 1.034 | 0.995 | 0.990 | 0.972 |
| Fujian | 1.048 | 1.110 | 1.071 | 1.075 | 1.117 | 1.107 | 1.021 | 1.050 | 0.897 | 1.089 | 0.996 | 0.989 |
| Shandong | 1.028 | 0.999 | 1.055 | 1.018 | 1.115 | 1.040 | 1.003 | 1.058 | 0.946 | 1.045 | 0.948 | 1.073 |
| Guangdong | 1.039 | 1.059 | 1.062 | 0.996 | 1.026 | 1.061 | 1.004 | 1.032 | 1.033 | 1.024 | 1.004 | 0.991 |
| Guangxi | 1.079 | 1.004 | 1.136 | 0.982 | 1.083 | 1.056 | 1.082 | 1.019 | 1.012 | 1.056 | 1.027 | 0.886 |
| Hainan | 1.048 | 1.120 | 1.031 | 1.010 | 1.050 | 0.992 | 1.013 | 1.005 | 1.009 | 1.008 | 0.987 | 0.974 |
| Provinces | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin | 1.000 | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.061 | 1.081 | 1.225 | 1.233 | 1.292 | 1.321 | 1.206 | 1.230 | 1.188 | 1.106 |
| Hebei | 1.000 | 1.213 | 1.158 | 1.216 | 1.218 | 2.340 | 2.424 | 2.032 | 2.818 | 2.593 | 3.435 | 2.396 | 2.840 |
| Liaoning | 1.000 | 0.977 | 0.980 | 0.978 | 1.061 | 1.607 | 1.567 | 1.360 | 1.772 | 1.671 | 1.883 | 1.397 | 1.413 |
| Jiangsu | 1.000 | 0.918 | 0.947 | 1.008 | 1.043 | 1.395 | 1.279 | 1.108 | 1.452 | 1.408 | 1.441 | 1.317 | 1.185 |
| Zhejiang | 1.000 | 1.087 | 1.118 | 1.139 | 1.145 | 1.165 | 1.206 | 1.208 | 1.209 | 1.251 | 1.244 | 1.231 | 1.197 |
| Fujian | 1.000 | 1.048 | 1.163 | 1.247 | 1.341 | 1.497 | 1.657 | 1.691 | 1.776 | 1.593 | 1.735 | 1.728 | 1.708 |
| Shandong | 1.000 | 1.028 | 1.027 | 1.084 | 1.103 | 1.230 | 1.280 | 1.284 | 1.358 | 1.285 | 1.343 | 1.273 | 1.366 |
| Guangdong | 1.000 | 1.039 | 1.101 | 1.168 | 1.164 | 1.195 | 1.267 | 1.273 | 1.314 | 1.356 | 1.389 | 1.395 | 1.383 |
| Guangxi | 1.000 | 1.079 | 1.083 | 1.230 | 1.208 | 1.308 | 1.381 | 1.495 | 1.524 | 1.542 | 1.628 | 1.671 | 1.480 |
| Hainan | 1.000 | 1.048 | 1.174 | 1.210 | 1.222 | 1.284 | 1.274 | 1.291 | 1.297 | 1.308 | 1.319 | 1.302 | 1.267 |
| Regional | Coefficient | t-Statistic | p-Value | Convergence Rate | Convergence or Divergence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | −0.3304 | −4.44 | 0.000 | 0.0334 | convergence |
| Bohai | −0.3750 | −3.02 | 0.003 | 0.0392 | convergence |
| Yangtze River Delta | −0.4221 | −3.03 | 0.002 | 0.0457 | convergence |
| Pearl River Delta | −0.4254 | −2.39 | 0.017 | 0.0462 | convergence |
| Regional | Coefficient | t-Statistic | p-Value | Convergence Rate | Convergence or Divergence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | −0.6805 | −10.22 | 0.000 | 0.0951 | convergence |
| Bohai | −0.6721 | −6.28 | 0.008 | 0.0929 | convergence |
| Yangtze River Delta | −0.7003 | −12.70 | 0.006 | 0.1004 | convergence |
| Pearl River Delta | −0.6742 | −14.05 | 0.005 | 0.0935 | convergence |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal Variations and Convergence Characteristics of Green Technological Progress in China’s Mariculture. Fishes 2023, 8, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070338
Ji J, Zhao N, Zhou J, Wang C, Zhang X. Spatiotemporal Variations and Convergence Characteristics of Green Technological Progress in China’s Mariculture. Fishes. 2023; 8(7):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070338
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jianyue, Nana Zhao, Jinglin Zhou, Chengjia Wang, and Xia Zhang. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Variations and Convergence Characteristics of Green Technological Progress in China’s Mariculture" Fishes 8, no. 7: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070338
APA StyleJi, J., Zhao, N., Zhou, J., Wang, C., & Zhang, X. (2023). Spatiotemporal Variations and Convergence Characteristics of Green Technological Progress in China’s Mariculture. Fishes, 8(7), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070338




