Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegeli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Clinical Signs
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Pathogenic Strains
2.3. Identification of Strains
2.3.1. Biochemical Characteristics
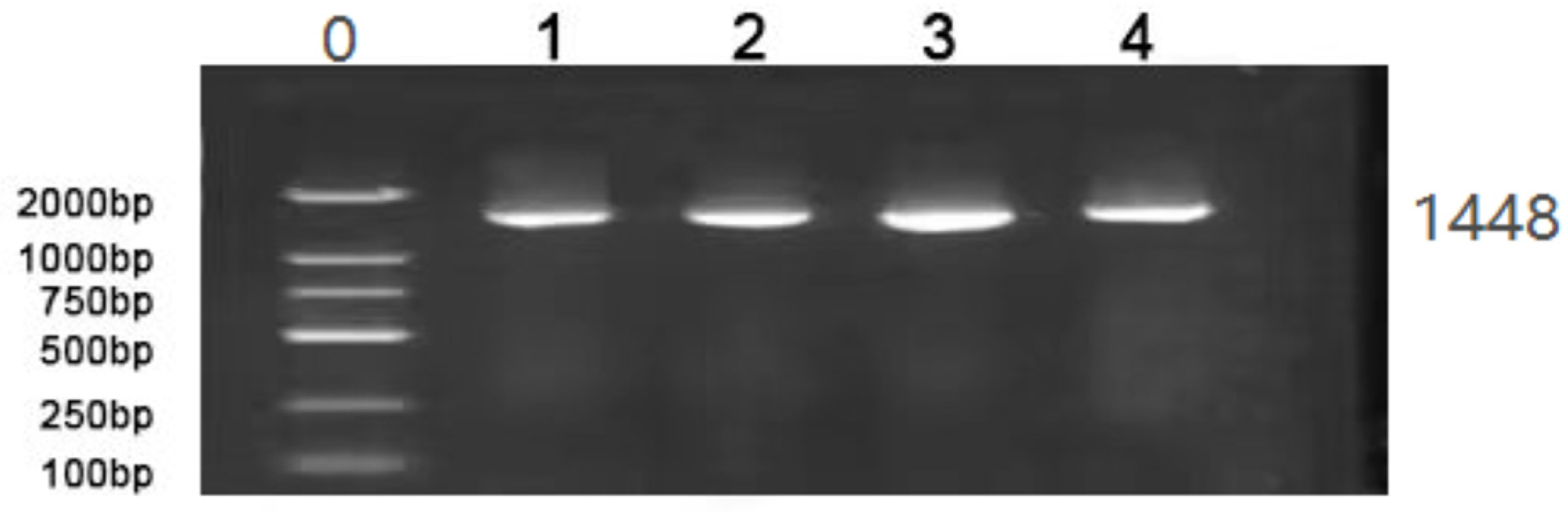
2.3.2. 16S rDNA Amplification of the Isolated Strains
2.4. Determination of Virulence-Related Factors
2.4.1. Determination of Extracellular Enzyme Activity
2.4.2. Detection of Virulence Genes
2.5. Antibiotic Resistance Tests
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Biochemical Identification of Strains
3.2. 16S rDNA Amplification of the Isolated Strains
3.3. Determination of Extracellular Enzyme Activity
3.4. Detection of Virulence Genes
3.5. Antibiotic Resistance Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M.; Rong, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. First report of isolation and complete genome of Vibrio rotiferianus strain SSVR1601 from cage-cultured black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) associated with skin ulcer. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Yu, Y.X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.G.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, M.J.; Rong, X.J. First report of skin ulceration caused by Photobacterium Damselae Subsp. damselae in net-cage cultured black rockfish (Sebastes Schlegeli). Aquaculture 2019, 503, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cao, Y.N.; Liu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, D.J.; Shi, B.; Wang, B. Structural characteristics of intestinal microbiota in black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii during early life stage. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 38, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, K.-D.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, H.S. Effects of diet supplementation with plant juice processing by-products on juvenile black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) growth performance, feed utilization, non-specific immunity, and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madusanka, R.K.; Priyathilaka, T.T.; Janson, N.; Kasthuriarachchi, T.; Jung, S.; Tharuka, M.N.; Lee, J. Molecular, transcriptional and functional delineation of Galectin-8 from black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) and its potential immunological role. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 93, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, Z.; Malanoski, A.; O’Grady, E.A.; Wimpee, C.F.; Vuddhakul, V.; Alves, N., Jr.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Vora, G.J. Comparative genomic analyses identify the Vibrio harveyi genome sequenced strains BAA-1116 and HY01 as Vibrio campbellii. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 2, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhafizah, W.W.I.; Lee, K.L.; Laith A., A.R.; Nadirah, M.; Danish-Daniel, M.; Zainathan, S.C.; Najiah, M. Virulence properties and pathogenicity of multidrug-resistant Vibrio harveyi associated with luminescent vibriosis in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.B.; Zhang, S.S.; Sun, Y.; Ding, Y. Pathogen Identification of bacterial disease in marine cage cultured Sebastes Schlegeli and the study of pathogenicity. Aquaculture 2021, 02, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Adjei, G.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. The extracellular proteases produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunpa, S.; Sermwittayawong, N.; Vuddhakul, V. Extracellular Enzymes Produced by Vibrio alginolyticus Isolated from Environments and Diseased Aquatic Animals. Procedia Chem. 2016, 18, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.-G.; Son, K.-T.; Yu, H.; Lee, T.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Shin, S.; Kwon, J.-Y.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus strains isolated from farmed fish in Korea from 2005 through 2007. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.P.; Liu, M.R. Virulence genes detection and BOX-PCR identification of Vibrio harveyi strains isolated from Takifugu rubripes. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 2, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Erratum to: The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet-Res. 2017, 48, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.H.; Liao, M.J.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.L. Diversity and drug resistance of bacterial pathogens isolated from bacterial ascetic disease in cultured turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2017, 38, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- El-Son, M.A.; Nofal, M.I.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Co-infection of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from diseased farmed striped mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Manzala, Egypt–A case report. Aquaculture 2020, 530, 735738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callinan, R.B.; Keep, J.A. Bacteriology and parasitology of red spot disease in sea mullet, Mugil cephalus L., from eastern Australia. J. Fish Dis. 1989, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrarathna, H.; Nikapitiya, C.; Dananjaya, S.; Wijerathne, C.; Wimalasena, S.; Kwun, H.J.; Heo, G.-J.; Lee, J.; De Zoysa, M. Outcome of co-infection with opportunistic and multidrug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila and A. veronii in zebrafish: Identification, characterization, pathogenicity and immune responses. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 80, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Ren, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Isolation and characterization of nidovirus and bacterial co-infection from cultured turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) in China. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Contreras, A.K.; Quiñones-Ramírez, E.I.; Vázquez-Salinas, C. Prevalence, detection of virulence genes and antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogen Vibrio species isolated from different types of seafood samples at “La Nueva Viga” market in Mexico City. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.P.; Chen, H.; Lin, A.-Q.; Zhong, X.M. Extra-cellular Enzyme-producing Abilities of Vibrios and Heterotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Hybrid Abalone In testiness and the Abalone Culture Waters. Fish. Sci. 2008, 27, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.W.; Ding, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J.H.; Liu, R.Y. Studies on the pustule disease of abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) on the Dalian coast. J. Shellfish Res. 1998, 17, 707–711. Available online: http://ir.qdio.ac.cn/handle/337002/32953 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Yang, Q.; Defoirdt, T. Quorum sensing positively regulates flagellar motility in pathogenic vibrio harveyi. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Salman, A.E.B.; Roess, A.A. Virulence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from seafood from three developing countries and of worldwide environmental, seafood, and clinical isolates from 2000 to 2017. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Tabassum, N.; Anand, R.; Kim, Y.-M. Motility of Vibrio spp.: Regulation and controlling strategies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8187–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwandeepika, H.; Defoirdt, T.; Bhowmick, P.; Shekar, M.; Bossier, P.; Karunasagar, I. Presence of typical and atypical virulence genes in vibrio isolates belonging to the Harveyi clade. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouadja, S.; Suffredini, E.; Baccouche, B.; Croci, L.; Bakhrouf, A. Occurrence of virulence genes among Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains from treated wastewaters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6935–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Lauritz, J.; Jass, J.; Milton, D.L. A ToxR Homolog from Vibrio anguillarum Serotype O1 Regulates Its Own Production, Bile Resistance, and Biofilm Formation. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubensäk, N.; Wagner, G.E.; Schrank, E.; Falsone, F.S.; Berger, T.M.I.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Reidl, J.; Zangger, K.; Wagner-Lichtenegger, G.E. The periplasmic domains of Vibriocholerae ToxR and ToxS are forming a strong heterodimeric complex independent on the redox state of ToxR cysteines. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 115, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Jang, I.-K.; Won, K.M.; Woo, S.H.; Xu, D.-H.; Park, S.I. Pathogenicity comparison of high- and low-virulence strains of Vibrio scophthalmi in olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 2012, 79, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Lee, D.C.; Woo, S.H.; Li, H.; Xu, D.H.; Park, S.I. Microbiological characteristics of Vibrio scophthalmi isolates from diseased olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Li, H.; Xu, D.-H.; Park, S.I. Modified a colony forming unit microbial adherence to hydrocarbons assay and evaluated cell surface hydrophobicity and biofilm production of Vibrio scophthalmi. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2012, 3, 1000130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwandeepika, H.; Jayaweera, T.; Bhowmick, P.P.; Karunasagar, I.; Bossier, P.; Defoirdt, T. Pathogenesis, virulence factors and virulence regulation of vibrios belonging to the harveyi clade. Rev. Aquac. 2012, 4, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanayake, T.; Salleh, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Zamri-Saad, M. Pathology and pathogenesis of Vibrio infection in fish: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Lee, B.-I.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.C. Vibrio scophthalmi infection in Japanese eel Anguilla japonica during seawater adaption. J. Fish Pathol. 2012, 25, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, M. Molecular mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 222, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Alam, M.; Ali, A.; Waldor, M.K.; Qadri, F.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio spp. infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.; Kim, J.; Jin, C.; Lee, J. Identification of Vibrio species isolated from cultured olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) in Jeju Island, South Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, A.; Alio, V.; Sciortino, S.; Oliveri, G.; Cardamone, C.; Butera, G.; Costa, A. Occurrence and Molecular Characterization of Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio spp. in Seafood Collected in Sicily. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, K.; Letchumanan, V.; Law, J.W.; Pusparajah, P.; Goh, B.; Ab Mutalib, N.; He, Y.; Lee, L. Incidence of antibiotic resistance in Vibrio spp. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2590–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, M.; Tang, M.; Rong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genotype Characteristics of Vibrio scophthalmi Isolated from Diseased Mariculture Fish Intestines with Typical Inter-Annual Variability. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 924130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Ullah, R.; Bibi, F.; Khan, S.B.; Al-Sofyani, A.; Stingl, U.; Azhar, E. Draft genome sequence of a multidrug-resistant emerging pathogenic isolate of Vibrio alginolyticus from the Red Sea. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 38, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhakeem, M.A.; Alreshidi, M.; Bardakci, F.; Hamadou, W.S.; De Feo, V.; Noumi, E.; Snoussi, M. Molecular Identification of Bacteria Isolated from Marketed Sparus aurata and Penaeus indicus Sea Products: Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Evaluation of Biofilm Formation. Life 2023, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Wakabayashi, C.; Kim, K.H. Antihelminthic potential of quinacrine and oxyclozanide against gill parasite Microcotyle sebastis in black rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 119, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Corral, Y.; Girons, A.; González-Barreiro, O.; Seoane, R.; Riaza, A.; Santos, Y. Effect of Bivalent Vaccines against Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida Subspecie achromogenes on Health and Survival of Turbot. Vaccines 2021, 9, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Kim, N.; Roh, H.J.; Chun, W.-K.; Ho, D.T.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.-H. Administration of antibiotics can cause dysbiosis in fish gut. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, M.; Sumithra, T.; Anusree, V.; Amala, P.; Reshma, K.; Alex, S.; Sanil, N. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence characteristics of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi from natural disease outbreaks of marine/estuarine fishes. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Chen, C.; Feng, J. What drives changes in the virulence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio harveyi in the South China Sea? J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.; Baek, S.I.; Cho, S.H. Substitution effect of fish meal with meat meal in diet on growth performance, feed consumption, feed utilization, chemical composition, hematology, and innate immune responses of rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 2023, 571, 739467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-W.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.-J.; Hur, S.-W.; Son, M.-H.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, K.-D.; Han, H.-S. A comparative study of effects of dietary mercuric chloride and methylmercury chloride on growth performance, tissue accumulation, stress and immune responses, and plasma measurements in Korean rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quico, C.A.; Astocondor, M.M.; Ortega, R.A. Dietary supplementation with Chlorella peruviana improve the growth and innate immune response of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss fingerlings. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q. A review: Progress in the development of fish Vibrio spp. vaccines. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 226, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Eissa, A.E.; ElBanna, N.I.; Albutti, A. Efficiency of monovalent and polyvalent Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio Parahaemolyticus vaccines on the immune response and protection in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata (L.) against vibriosis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 111, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.; Manchanayake, T.; Danial, A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Azmai, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Nor, N.M.; Salleh, A. Evaluating the Intestinal Immunity of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790) following Field Vaccination Using a Feed-Based Oral Vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquhoun, D.J.; Lillehaug, A. Vaccination against vibriosis. Fish Vaccin. 2014, 15, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Chai, B.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and mucosal igm responses elicited by immersion and injection vaccination with inactivated vibrio anguillarum in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2019, 505, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, G. Development of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. masoucida vaccine in turbot and evaluation of protection efficacy under field conditions. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

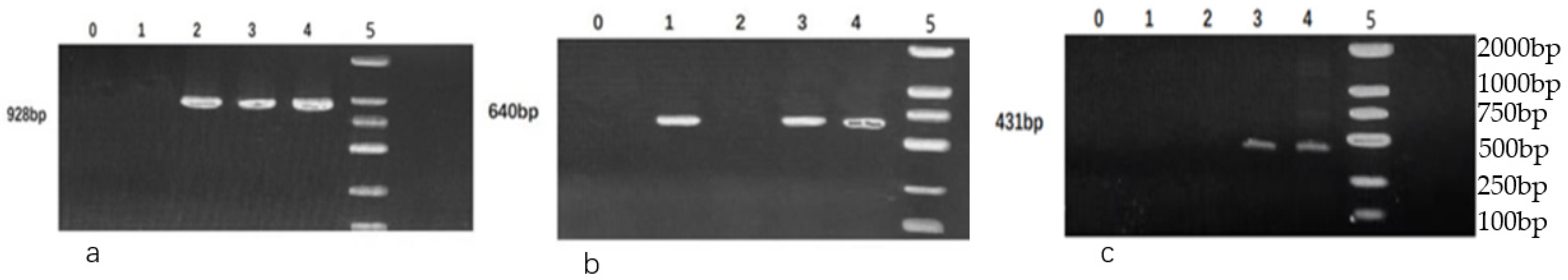
| virulence Gene | Primer Sequence | Primer Sequence (bp) | Product Size (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tdh | GTAAAGGTCTCTGACTTTTGGAC TGGAATAGAACCTTCATCTTCACC | 269 | 60 | [11] |
| Trh | TTGGCTTCGATATTTTCAGTATCT CATAACAAACATATGCCCATTTCCG | 500 | 60 | [11] |
| Tlh | GCTACTTTCTAGCATTTTCTCTGC AAAGCGGATTATGCAGAAGCACTG | 450 | 60 | [11] |
| Zot | CACTGGGCGAGAAAGGAC CGCCCATAGACCACGATA | 737 | 58 | [12] |
| TcpA | ACCGTGGTCTAGGTAATT CAACGCCGAATGGAGCAG | 431 | 58 | [12] |
| ToxS | CCACTGGCGGACAAAATAACC AACAGTACCGTAGAACCGTGA | 640 | 52 | [12] |
| ToxR | GTCTTCTGACGCAATCGTTG ATACGAGTGGTTGCTTCATG | 368 | 52 | [11] |
| FlaB | AACGTATCAGCGATGACC TTGAAACGGTTCTGGAAT | 928 | 50 | [12] |
| Physiological Identification | SF-2 | SF-3 | SF-5 | SF-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram stain | − | − | − | − |
| Oxidase enzyme | + | + | + | + |
| Methyl red | + | + | − | − |
| VP | + | − | + | − |
| H2S | − | + | − | − |
| Citrate | − | + | − | + |
| Glucose gas production | − | − | − | − |
| Salt-free tryptone water | − | − | − | − |
| 6% tryptone water | − | + | + | + |
| 8% tryptone water | − | − | + | + |
| 10% tryptone water | − | − | + | + |
| Enzymes | SF-2 | SF-3 | SF-5 | SF-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caseinase | − | + | + | + |
| Lecithinase | − | + | + | + |
| Lipase | − | + | + | + |
| Gelatinase | − | + | + | + |
| Antibiotic | SF-2 | SF-3 | SF-5 | SF-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gentamicin | R | I | I | I |
| Cotrimoxazole | R | S | R | R |
| Ampicillin | R | R | R | R |
| Penicillin G | R | R | R | R |
| Erythromycin | I | I | I | I |
| Norfloxacin | R | I | R | R |
| Chloramphenicol | R | S | R | R |
| Amikacin | R | R | R | R |
| Ciprofloxacin | R | R | R | R |
| Pioneer V | R | R | R | R |
| Spectinomycin | S | R | S | S |
| Enrofloxacin | I | I | R | R |
| Cefotaxime | I | R | R | I |
| Levofloxacin | R | I | R | R |
| Cefoxitin | R | R | R | R |
| Rifampicin | R | R | R | R |
| Doxycycline | R | R | R | R |
| Imipenem | R | R | R | R |
| Clindamycin | R | R | R | R |
| Metronidazole | R | R | R | R |
| Amoxicillin | R | R | R | R |
| Bacitracin | R | R | R | R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; You, C.; Zeng, Y. Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Fishes 2023, 8, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050235
Liu X, You C, Zeng Y. Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050235
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoling, Cuirong You, and Yong Zeng. 2023. "Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegeli" Fishes 8, no. 5: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050235
APA StyleLiu, X., You, C., & Zeng, Y. (2023). Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Fishes, 8(5), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050235






