Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cocaine
3. European Eel
4. The Effects of Cocaine on the European Eel
4.1. Accumulation of Cocaine in Eel Tissues
4.2. Neuroendocrine Effects of Cocaine in the Eels
4.2.1. Nervous Tissue
4.2.2. Endocrine System
- HPA axis
- HPT axis
- Prolactin
- Gonadotropins
4.3. Histopathological Changes Induced by Cocaine
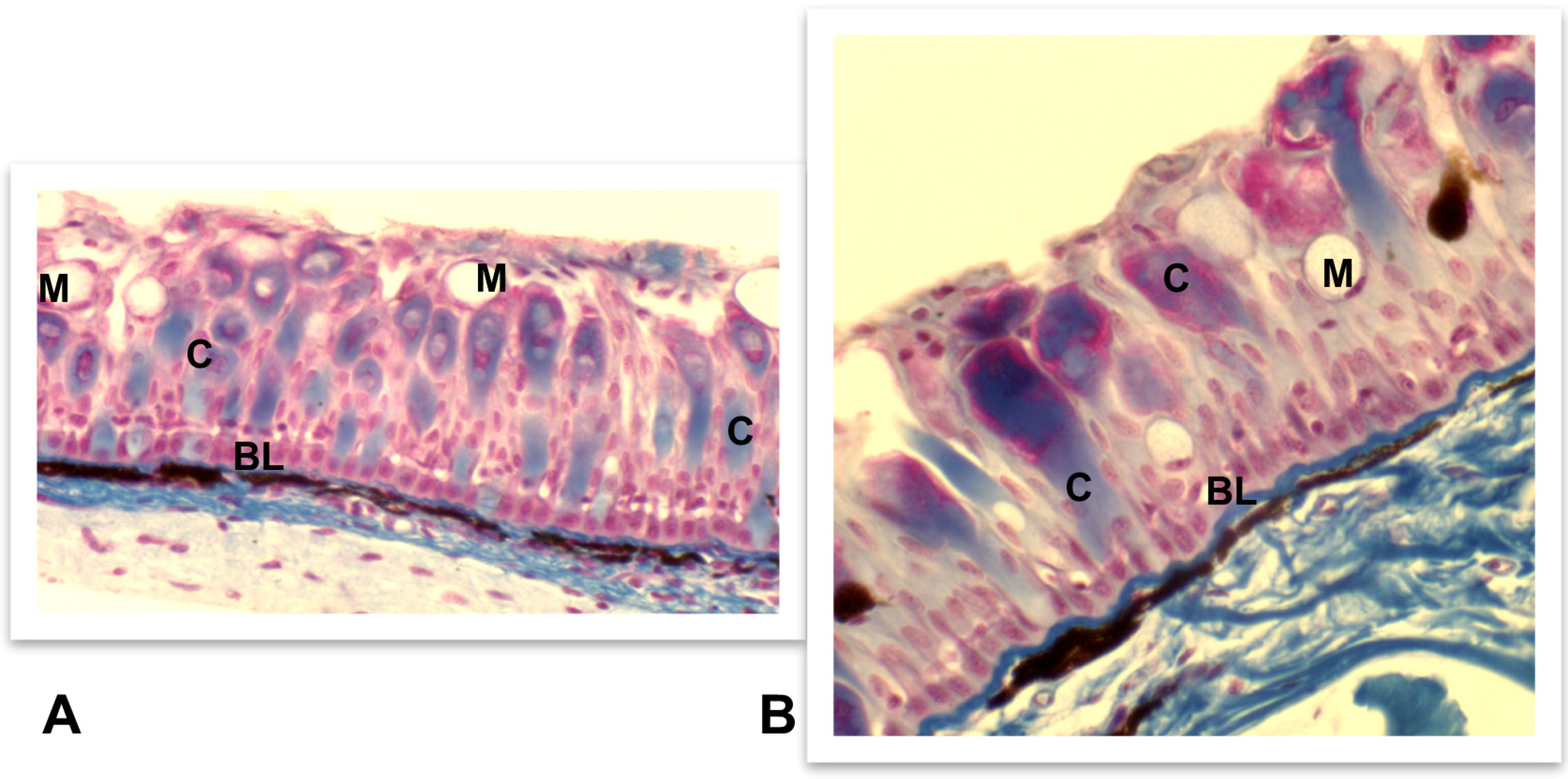
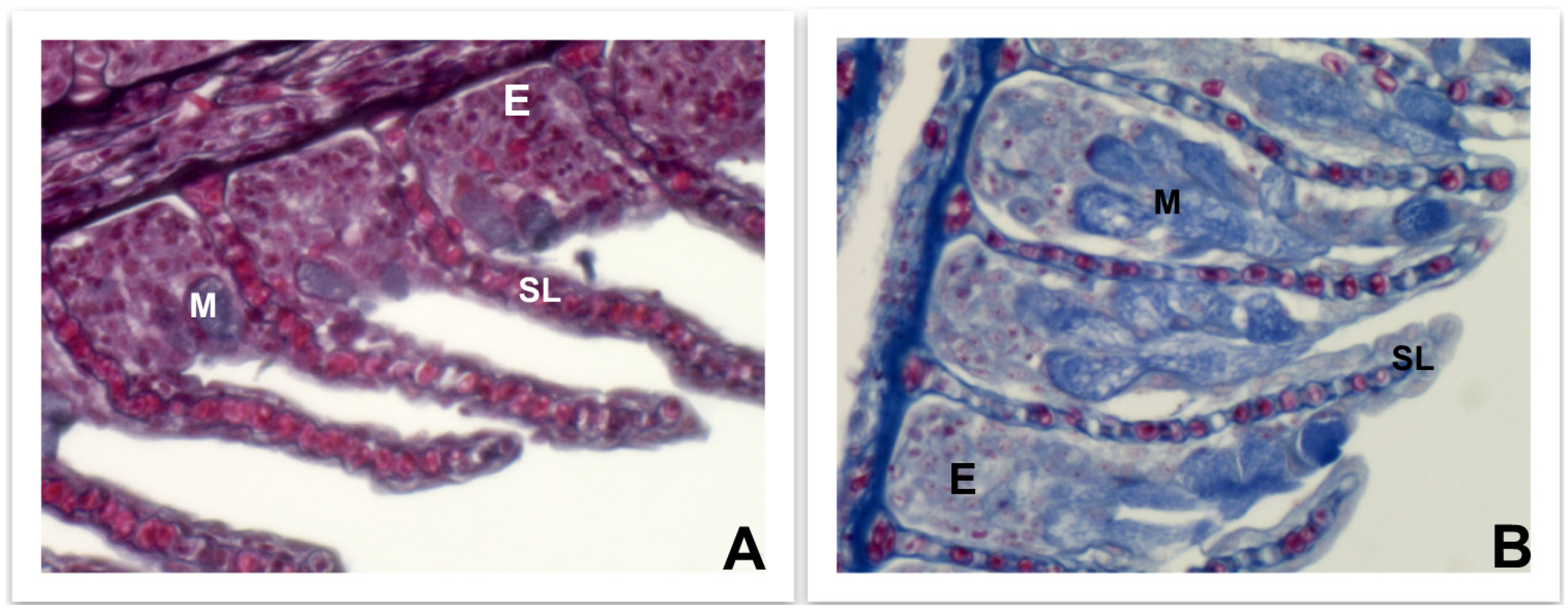
4.3.1. Skin, Intestine, and Gills
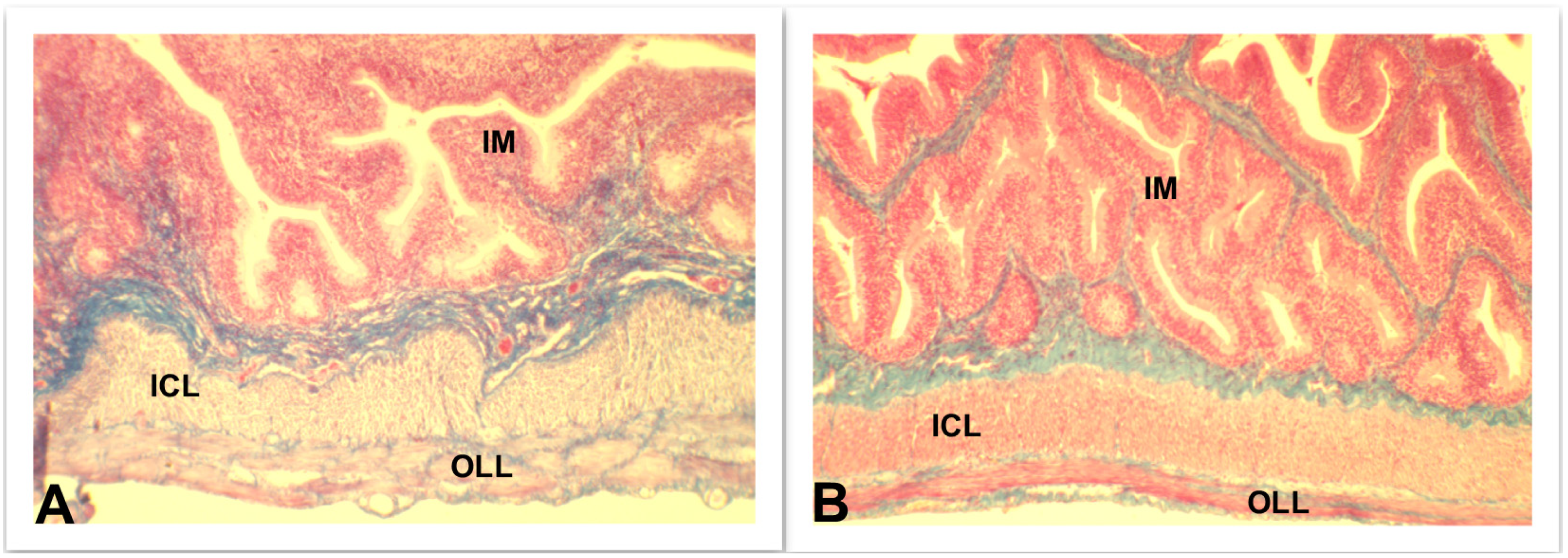
4.3.2. Skeletal Muscle
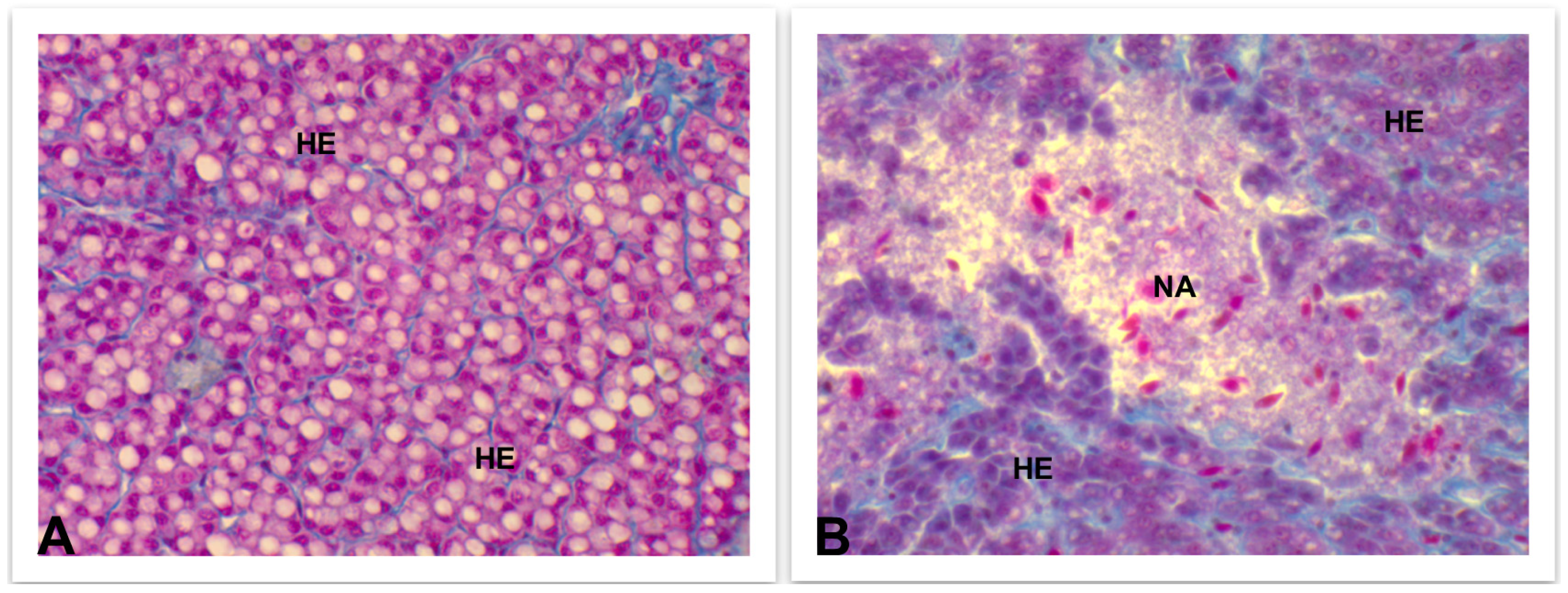
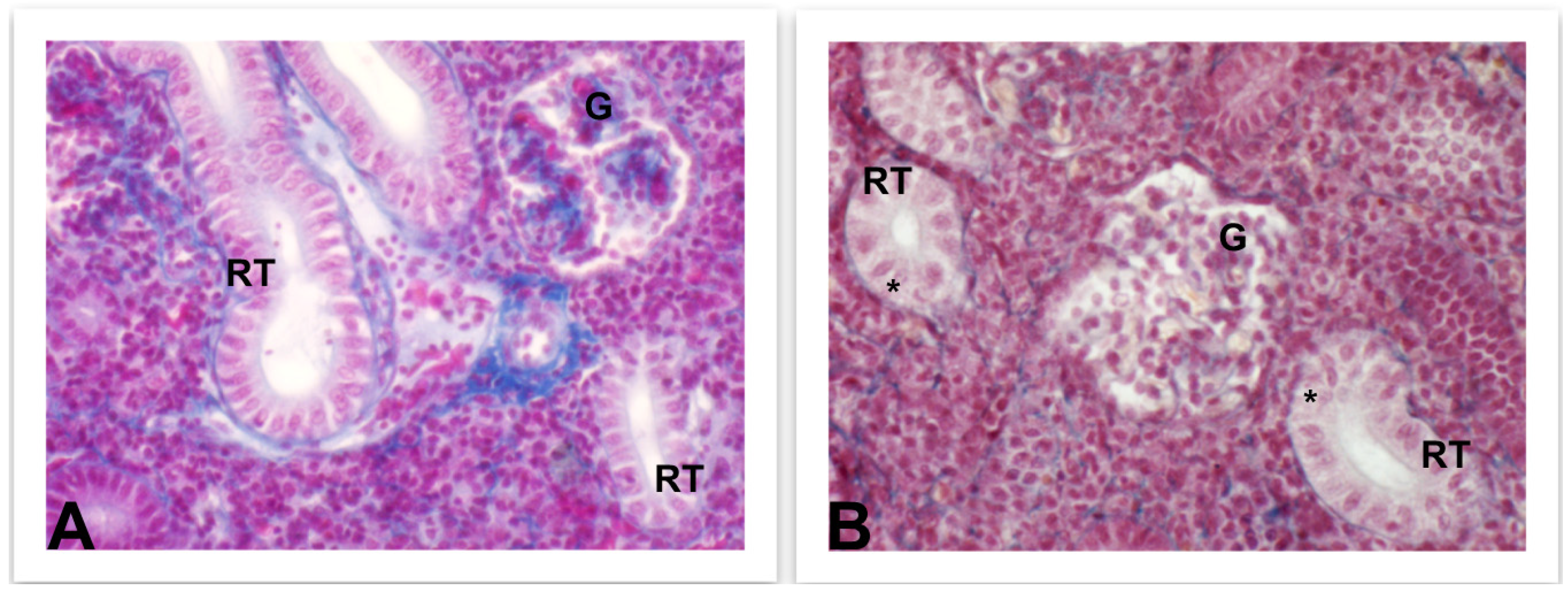
4.3.3. Liver and Kidney
4.3.4. Ovaries
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNODC. Book 2: Drug use and health consequences. In World Drug Report; (United Nations Publication, sales, No. E.22.XI.8); UNODC: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- UNODC. Book 5: Drug and the environment. In World Drug Report; (United Nations Publication, sales, No. E.22.XI.8); UNODC: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R.; Megharaj, M.; Kirkbride, K.P.; Naidu, R. Illicit drugs and the environment—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.K.; Maranho, L.; Pereira, C.D.S. Review on the occurrence and biological effects of illicit drugs in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30998–31034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.K.; Dourado, P.L.R.; de Campos, B.G.; Maranho, L.A.; de Almeida, E.A.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; Pereira, C.D.S. Environmentally realistic concentrations of cocaine in seawater disturbed neuroendocrine parameters and energy status in the marine mussel Perna perna. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2022, 251, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J. Occurrence, bioaccumulation and toxicological effect of drugs of abuse in aquatic ecosystem: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedhu Krishnan, R.; Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Biruntha, M.; Balachandar, R.; Karmegam, N. Origin, transport and ecological risk assessment of illicit drugs in the environment A review. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilly, M.G.; Salamone, J.D. Drugs, Brain and Behavior, 6th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 132–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra-Pereira, C.D.; Maranho, L.A.; Cortez, F.S.; Pusceddu, F.H.; Santos, A.R.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Cesar, A.; Guimarães, L.L. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and cocaine in a Brazilian coastal zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoli, E.; Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S. Illicit drugs in drinking water. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 7, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Xu, J. Occurrence and removal of illicit drugs in different wastewater treatment plants with different treatment techniques. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, C.J.E.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Pratorius, A.; ter Laak, T.L.; van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence, hazard, and risk of psychopharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in European surface waters. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetta, A.M.; Roveri, V.; Lopes Guimarães, L.; de Oliveira, T.M.N.; Correia, A.T. First report on the occurrence of pharmaceuticals and cocaine in the coastal waters of Santa Catarina, Brazil, and its related ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63099–63111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, K.; Palmer, R.; Zahniser, N.R. Mechanisms of acute cocaine toxicity. Open Pharmacol. J. 2008, 2, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkov, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Fischman, M.W.; Foltin, R.; Fowler, J.S.; Franceschi, D.; Franceschi, M.; Logan, J.; Gatley, S.J.; Wong, C.; et al. Effects of route administration on cocaine induced dopamine transporter blockade in the human brain. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, E.J.; Tsadik, A.; Oyler, J.; Darwin, W.D. Cocaine metabolism and urinary excretion after different routes of administration. Ther. Drug Monit. 1998, 20, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Hua, Z.; Hou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Xu, J. Drugs of abuse and their metabolites in the urban rivers of Beijing, China: Occurrence, distribution, and potential environmental risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Chiabrando, C.; Grassi, P.; Fanelli, R. Illicit drugs, a novel group of environmental contaminants. Water Res. 2008, 42, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.V.; Silva, F.M.A.; Langford, K.H.; Souza, A.D.F.; Nizzeto, L.; Waichman, A.V. Screening for selected human pharmaceuticals and cocaine in the urban streams of Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterhaus, S.L.; Grace, R.; Hamilton, M.C.; Yee, D. Method validation and reconnaissance of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and alkylphenols in surface water, sediments, and mussels in an urban estuary. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevacqua, D.; Melià, P.; Gatto, M.; De Leo, G. A global viability assessment of the European eel. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3323–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, S.W. The Eel, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Science, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Belpaire, C.; Goemans, G. The European eel Anguilla anguilla, a rapporteur of the chemical status for the water framework directive? Vie et Milieu/Life Environ. 2007, 57, 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginneken, V.; Palstra, A.; Leonards, P.; Nieveen, M.; van den Berg, H.; Flik, G.; Spanings, T.; Niemantsverdriet, P.; van der Thillart, G.; Murk, A. PCBs and the energy cost of migration in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinetti, R.; Galassi, S.; Quadroni, S.; Volta, P.; Capoccioni, F.; Ciccotti, E.; De Leo, G.A. Use of Anguilla anguilla for biomonitoring persisten organic pollutants (POPs) in brackish and riverine waters in central and southern Italy. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Lepretti, M.; Paolella, G.; Martucciello, S.; Lionetti, L.; Caputo, I.; Laforgia, V. Effects of environmental cocaine concentrations on the skeletal muscle of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poklis, A.; Maginn, D.; Barr, J.L. Tissue disposition of cocaine in man: A report of five fatal poisonings. Forensic Sci. Int. 1987, 33, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.K.; Misra, A.L.; Mulè, S.J. Physiological disposition and biotransformation of (3H) cocaine in acutely and chronically treated rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 196, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.K.; de Campos, B.G.; Cortez, F.S.; Pusceddu, F.H.; Nobre, C.R.; Moreno, B.B.; Lebre, D.T.; Maranho, L.A.; Pereira, C.D.S. Mussels get higher: A study on the occurrence of cocaine and benzoylecgonine in seawater, sediment and mussels from a subtropical ecosystem (Santos Bay, Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklaus, S.; Kirla, K.T.; Kraemer, T.; Groh, K.; Schirmer, K.; Neuhauss, S. Cocaine accumulation in zebrafish eyes leads to augmented amplitudes in the electroretinogram. Matters 2017, 3, e201703000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.H.; Ng, K.T.; Bury, S.T.; Bury, S.E.; Bury, N.R.; Barron, L.P. Biomonitoring of pesticides, pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in a freshwater invertebrate to estimate toxic or effect pressure. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondarza, P.M.; Haddad, S.P.; Avigliano, E.; Miglioranza, K.S.B.; Brooks, B.W. Pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs and their metabolites in fish from Argentina: Implications for protected areas influenced by urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Maddaloni, M.; Valiante, S.; De Falco, M.; Lenzi, M.; Laforgia, V. Presence of cocaine in the tissues of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla, exposed to environmental cocaine concentrations. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, C.; Deng, Y.; Jin, X.; Teng, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, F. Tissue-specific accumulation, elimination, and toxicokinetics of illicit drugs in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnok, P.; Singh, R.R.; Burakham, R.; Pérez-Fuentetaja, A.; Aga, D.S. Selective uptake and bioaccumulation of antidepressants in fish from effluent-impacted Niagara River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10652–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Werner, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L.; Barber, L.B.; Blazer, V.S.; Norris, D.O.; Vajda, A.M. Antidepressant pharmaceuticals in two U.S. effluent-impacted streams: Occurrence and fate in water and sediment, and selective uptake in fish neural tissue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Painter, M.M.; Bartell, S.E.; Logue, A.; Furlong, E.T.; Wemer, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L. Selective uptake and biological consequences of environmentally relevant antidepressant pharmaceutical exposures on male fathead minnows. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 104, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyz-Lukasisk, R.; Chalabis-Mazurek, A.; Gondek, M. Basic and functional nutrients in the muscle of fish: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.; Smith, A.S.T.; Vo, N.T.K.; Muster, J.; Weston, W.; Bertero, A.; Maves, L.; Mack, D.L.; Rostain, A. A more open approach is needed to develop cell-based fish technology: It starts with zebrafish. One Earth 2020, 3, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sébert, M.E.; Weltzien, F.A.; Moisan, C.; Pasqualini, C.; Dufour, S. Dopaminergic systems in the European eel: Characterization, brain distribution, and potential role in migration and reproduction. Hydrobiologia 2008, 602, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.; Sebert, M.E.; Weltzien, F.A.; Rousseau, K.; Pasqualini, C. Neuroendocrine control by dopamine of teleost reproduction. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Maddaloni, M.; Valiante, S.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Endocrine disruption in the European eel, Anguilla anguilla, exposed to an environmental cocaine concentration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lòpez-Patiño, M.A.; Yu, L.; Cabral, H.; Zhdanova, I.V. Anxiogenic effects of cocaine withdrawal in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 93, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofuoglu, M.; Nelson, D.; Babb, D.A.; Hatsukami, D.K. Intravenous cocaine increases plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine in humans. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 68, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.F.; Capaldo, A. The autonomic nervous system and chromaffin tissue: Neuroendocrine regulation of catecholamine secretion in non-mammalian vertebrates. Auton. Neurosci. 2011, 165, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Grässel, S. Role of proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides and their receptors in the osteoarticular system: From basic to translational research. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 623–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, D.O. Vertebrate Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, L.; Rossignoli, M.T.; Delfino-Pereira, P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; de Lima Umeoka, E.H. A comprehensive overview on stress neurobiology: Basic concepts and clinical implications. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Mizusawa, N.; Okubo, K.; Amiya, N.; Mizusawa, K.; Chiba, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, A. Cloning of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) precursor cDNA and immunohistochemical detection of CRH peptide in the brain of the Japanese eel, paying special attention to gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 356, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugars, G.; Mauvois, X.; Martin, P.; Aroua, S.; Rousseau, K.; Dufour, S. New insights into the evolution of corticotropin-releasing hormone family with a special focus on teleosts. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 937218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K. Hormones, nicotine and cocaine: Clinical studies. Horm. Behav. 2010, 58, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, L.; Cavagnini, F.; Martino, E.; Ambrogio, A. Effects of cocaine on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelar Bonga, S.E. The stress response in fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.; Burzawa-Gérard, E.; Le Belle, N.; Sbaihi, M.; Vidal, B. Reproductive endocrinology of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. In Eel Biology; Aida, K., Tsukamoto, K., Yamauchi, K., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2003; pp. 373–383. [Google Scholar]
- Robinet, T.; Feunteun, E. Sublethal effects of exposure to chemical compounds: A cause for the decline in Atlantic eels? Ecotoxicology 2002, 11, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, G.; Dosoretz, C. The effect of 3,3′,5–triiodo–L–thyronine and 17–a–methyltestosterone on growth and body composition of the glass stage of the eel (Anguilla anguilla L). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1986, 1, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, C.K.; Volkoff, H. The role of the thyroid axis in fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 596585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.C.S. The role of thyroid hormones in stress response of fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseau, K.; Le Belle, N.; Sbaihi, M.; Marchelidon, J.; Schmitz, M.; Dufour, S. Evidence for negative feedback in the control of eel growth hormone by thyroid hormones. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 175, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budziszewska, B.; Jaworska-Feil, L.; Lasoń, W. The effect of repeated amphetamine and cocaine administration on adrenal, gonadal and thyroid hormone levels in the rat plasma. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. 1996, 104, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhopesh, V.P.; Burke, W.M.; Maany, I.; Ravi, N.V. Effect of cocaine on thyroid functions. Am. J. Drug Alcohol. Abuse 1991, 17, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, M.E.; Utzschneider, K.M. Cocaine intoxication and thyroid storm: Similarity in presentation and implications for treatment. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2014, 2, 2324709614554836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, J.M.; De Luze, A.; Leloup-Hatey, J.; Leloup, J. Suppression of plasma thyroid hormone concentrations by cortisol in the European eel Anguilla anguilla. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1986, 83, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, M.M.; Flett, P.A.; Leatherland, J.F. Effects of cortisol on the in vitro hepatic conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in brook charr (Salvelinus fontinalis Mitchill). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1988, 70, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Martin, H.; Coates, P. Prolactin biology and laboratory measurement: An update on physiology and current analytical issues. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2018, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Breves, J.P.; McCormick, S.D.; Karlstrom, R.O. Prolactin and teleost ionocytes: New insights into cellular and molecular targets of prolactin in vertebrate epithelia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 203C, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; McCormick, S.D. Prolactin and growth hormone in fish osmoregulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 147, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, F.; Ferrandino, I.; Monaco, A.; Cerulo, M.; Capasso, G.; Capaldo, A. Histological and hormonal changes in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) after exposure to environmental cocaine concentration. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Mendelson, J.H.; Drieze, J.M.; Teoh, S.K.; Kelly, M.L.; Sholar, J.W. Effects of dopamine on prolactin: Interactions with cocaine self-administration by female rhesus monkeys. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 270, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olivereau, M. Dopamine, prolactin control, and osmoregulation in eels. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1975, 26, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, R.; Royan, M.R.; von Krog, K.; Weltzien, F.A.; Baker, D.M. Direct and indirect effect of sex steroids on gonadotrope cell plasticity in the teleost fish pituitary. Front Endocrinol 2020, 11, 605068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenegu, S.; Pranoty, A.; Mamta, S.K.; Senthilkumaran, B. Development and organization of gonadal steroidogenesis in bony fishes. A review. Aquac. Fish 2021, 6, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.K.; Rosati, L.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Maranho, L.A.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Aquatic pollution and risks to biodiversity: The example of cocaine effects on the ovaries of Anguilla anguilla. Animals 2022, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesch, C.M.; Negus, B.H.; Bost, J.E.; Kaffer, J.H.; Snyder, N.W.; Eichhorn, E.J. Effects of cocaine on anterior pituitary and gonadal hormones. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 278, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, N.K.; Mendelson, J.H.; Negus, S.S.; Kelly, M.; Knudson, I.; Roth, M.E. The effects of cocaine on gonadal steroid hormones and LH in male and female rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeraerts, C.; Belpaire, C. The effects of contaminants in European eel: A review. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 239–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghattas, S.M.; Yanai, T. Light microscopical study on the skin of European eel (Anguilla anguilla). World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bragadeswaran, S.; Thangaraj, S. Hemolytic and antibacterial studies on skin mucus of eel fish, Anguilla anguilla Linnaeus, 1758. Asian J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 4, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Laforgia, V. Changes in the gills of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) after chronic exposure to environmental cocaine concentration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in fish: Proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.D.; Meyes, A.; Bostwick, J.M.; Hamacher, K.L.; Pittelkow, M.R. Cocaine abuse: Dermatologic manifestations and therapeutic approaches. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 59, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, B.; Aslanian, H.R. Gastric perforations associated with the use of crack cocaine. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 6, 733–735. [Google Scholar]
- De Felice, B.; Parolini, M. Effects of single and combined exposure to cocaine and benzoylecgonine on the oxidative status of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Barbosa Ortega, A.; Maranho, L.A.; Nobre, C.R.; Moreno, B.B.; Guimarães, R.S.; Temponi Lebre, D.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Pereira, C.D.S. Detoxification, oxidative stress, and cytogenotoxicity of crack cocaine in the brown mussel Perna perna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27569–27578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauro, N.D.; Zorn, M.E. Prolactin induces proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. J. Cell Physiol. 1991, 148, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaccio, P.; Lippi, G.; Maffulli, N. Biochemical markers of muscular damage. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazeau, G.A.; McArdle, A.; Jackson, M.J. Effects of cocaine on leakage of creatine kinase from skeletal muscle: In vitro and in vivo studies in mice. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Paolella, G.; Di Gregorio, I.; Martucciello, S.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Rosati, L.; Laforgia, V. Effects of environmental cocaine concentrations on COX and caspase-3 activity, GRP-78, ALT, CRP and blood glucose levels in the liver and kidney of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinc, E.; Bozcaarmutlu, A. Catalyzation of cocaine N-demethylation by cytochromes P4502B, P4503A, and P4502D in fish liver. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2003, 17, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.J.; Henrique, R.; Vilas-Boas, V.; Silva, R.; de lourdes Bastos, M.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Cocaine-induced kidney toxicity: An in vitro study using primary cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttemann, M.; Helling, S.; Sanderson, T.H.; Sinkler, C.; Samavati, L.; Mahapatra, G.; Varughese, A.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Ramzan, R.; et al. Regulation of mitochondrial respiration and apoptosis through cell signaling: Cytochrome c oxidase and cytochrome c in ischemia/reperfusion injury and thermoregulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1817, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, C.R.; Sumpter, J.P. Oocyte growth and development in teleosts. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 1996, 6, 287–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, J.; Naftolin, F. Aromatase: Contributions to physiology and disease in women and men. Physiology 2016, 31, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, T.S.; Stojknov, N.J.; Bjelic, M.M.; Mihajlovic, A.I.; Janjic, M.M.; Andric, S.A. Pharmacological doses of testosterone upregulated androgen receptor and 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta-5-delta-4 isomerase and impaired Leydig cells steroidogenesis in adult rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 121, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranyakanout, C.; Ijiri, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Adachi, S. 17 β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 12 is responsible for maturation inducing steroid synthesis during oocyte maturation in Nile tilapia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 290, 113399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, R.A.; Savoy-Moore, R.; Sacco, A.G.; Subramanian, M.G. The effect of cocaine on oocyte development and the follicular microenvironment in the rabbit. Fertil. Steril. 1990, 54, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, D.A.; Moreno, A.; Luther, M.F.; Eddy, C.A.; Siler-Khodr, T.M.; King, T.S.; Schenken, R.S. Effects of follicular-phase cocaine administration on menstrual and ovarian cyclicity in rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Obstet. Ginecol. 1998, 178, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, S.S.; Koss, C.M.; Cronmiller, C. Chronic cocaine exposure in Drosophila: Life, cell death and oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2006, 296, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosati, L.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Fontes, M.K.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Capaldo, A. Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine. Fishes 2023, 8, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030166
Rosati L, Caputo I, Lionetti L, Fontes MK, Pereira CDS, Capaldo A. Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine. Fishes. 2023; 8(3):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030166
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosati, Luigi, Ivana Caputo, Lillà Lionetti, Mayana Karoline Fontes, Camilo Dias Seabra Pereira, and Anna Capaldo. 2023. "Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine" Fishes 8, no. 3: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030166
APA StyleRosati, L., Caputo, I., Lionetti, L., Fontes, M. K., Pereira, C. D. S., & Capaldo, A. (2023). Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine. Fishes, 8(3), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030166







