Appropriateness Evaluation of Releasing Area for Four Marine Organisms in Stock Enhancement: A Fatty Acid Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Fatty Acid Analysis
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fatty Acid Composition of Four Marine Organisms in the Southern Zhejiang Coastal Water
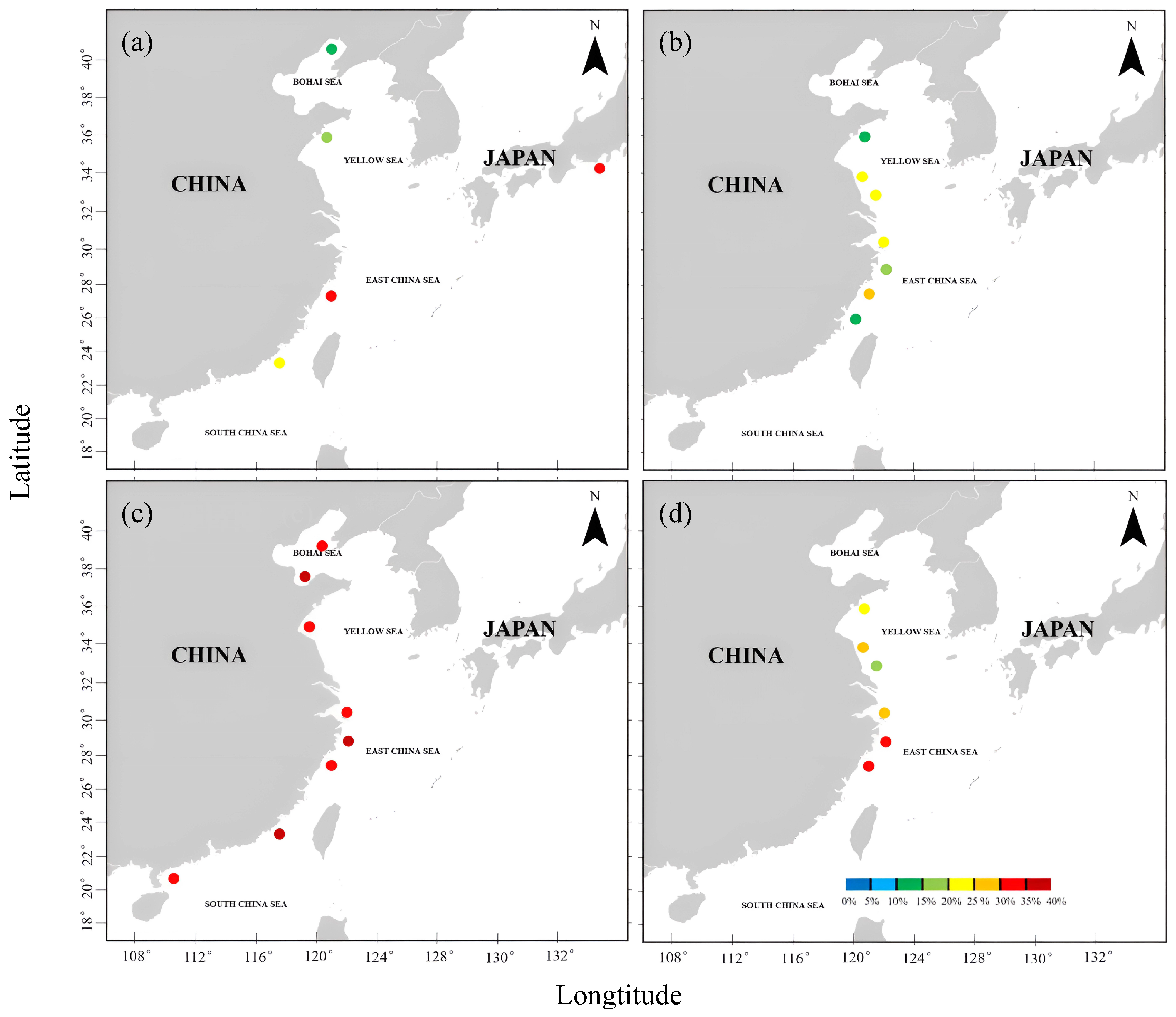
3.2. Analysis of DHA and EPA Levels in Four Marine Organisms from Different Coastal Waters
| Sampling Locations | DHA Content/(%) | EPA Content/(%) | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Little Yellow Croaker | Red Sea Bream | Ridgetail White Prawn | Swimming Crab | Little Yellow Croaker | Red Sea Bream | Ridgetail White Prawn | Swimming Crab | ||
| Southern coastal water of Zhejiang Province | 22.75 ± 1.86 | 31.72 ± 5.47 | 17.24 ± 0.47 | 16.48 ± 1.03 | 5.02 ± 0.21 | 3.59 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.14 | 15.83 ± 50 | This study, [30,31] |
| Southern coastal water of the Shandong Peninsula | 6.84 ± 0.02 | 12.86 | 11.56 | / | 4.07 ± 0.03 | 2.7 | 11.25 | / | [31,32,33] |
| Central coastal water of Zhejiang Province | 11.29 | / | 12.33 | 18.55 ± 0.14 | 5.56 | / | 18.42 | 17.26 ± 0.13 | [30,31,34] |
| Northern coastal water of Zhejiang Province | 17.41 ± 2.47 | / | 11.4 ± 0.2 | 16.16 ± 0.34 | 4.42 ± 1.72 | / | 17.2 ± 0.23 | 17.45 ± 0.28 | [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] |
| Coastal water of Yancheng City | 17.38 ± 0.06 | / | 10.2 ± 1.5 | / | 6.05 | / | 9.2 ± 1.3 | / | [39] |
| Coastal water of Nantong city | 20.2 ± 0.02 | / | 15.61 ± 0.13 | / | 5.67 ± 0.42 | / | 13.13 ± 0.13 | / | [34,40,41] |
| Northern coastal water of Fujian Province | 8.64 | / | / | / | 5.85 | / | / | / | [34] |
| Southern coastal water of Fujian Province | / | 17.1 ± 0.32 | / | 21.69 ± 2.01 | / | 5.2 ± 0.07 | / | 14.75 ± 0.79 | [36,42] |
| Eastern coast of the Kii Peninsula | / | 25.5 | / | / | / | 4.9 | / | / | [43] |
| Northern coastal water of the Bohai Sea | / | 9.14 | / | / | / | 4.55 | / | / | [44] |
| Western coastal water of the Liaodong Peninsula | / | / | / | 17.69 ± 1.71 | / | / | / | 15.2 ± 1.67 | [45] |
| Southern coastal water of the Bohai Sea | / | / | / | 21.96 ± 1.48 | / | / | / | 23.25 ± 1.29 | [36] |
| Coastal water of Lianyungang city | / | / | / | 18.85 ± 3.92 | / | / | / | 19.99 ± 2.82 | [36] |
| Coastal water of Zhanjiang city | 18.55 ± 1.87 | 17.26 ± 1.78 | [36] | ||||||
3.3. Evaluation of the Appropriateness of the Stock Enhancement Area for Four Marine Organisms Based on DE Indicator
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worm, B.; Branch, T.A. The future of fish. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Chick, R.C.; Lorenzen, K.; Agnalt, A.-L.; Leber, K.M.; Blankenship, H.L.; Haegen, G.V.; Loneragan, N.R. Fisheries enhancement and restoration in a changing world. Fish. Res. 2017, 186, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J. Marine ranching construction and management in East China Sea: Programs for sustainable fishery and aquaculture. Water 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.E.; Lenfant, P.; Clarke, L.J.; Fontcuberta, A.; Gudefin, A.; Lecaillon, G.; Le Vay, L.; Radford, A.N.; Simpson, S.D. Examining current best-practices for the use of wild post-larvae capture, culture, and release for fisheries enhancement. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1058497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S. Economic, ecological and genetic impacts of marine stock enhancement and sea ranching: A systematic review. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ren, J.S.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M.; Shan, X.; Gorfine, H. A dynamic energy budget model of Fenneropenaeus chinensis with applications for aquaculture and stock enhancement. Ecol. Model. 2020, 431, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, F.; Ren, J.S.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, W. An ecosystem model for estimating shellfish production carrying capacity in bottom culture systems. Ecol. Model. 2019, 393, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S.; Nakajima, K.; Hamasaki, K.; Shishidou, H.; Waples, R.S.; Kishino, H. Rigorous monitoring of a large-scale marine stock enhancement program demonstrates the need for comprehensive management of fisheries and nursery habitat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Cooper, A.B.; Hilborn, R. A quantitative framework for the analysis of habitat and hatchery practices on Pacific salmon. Ecol. Model. 2005, 183, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, L.; Sousa, M.C.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Dias, J.M. A habitat suitability model for aquaculture site selection: Ria de Aveiro and Rias Baixas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-E.; Dong, S.-L.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Sarà, G.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y.-W. Mapping the potential for offshore aquaculture of salmonids in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsgaard, J.; John, M.S.; Kattner, G.; Müller-Navarra, D.; Hagen, W. Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. In Advances in Marine Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 46, pp. 225–340. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, M.S. Essential fatty acid requirements of cultured marine fish larvae. Aquac. Nutr. 1996, 2, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowasser, G.; McAllen, R.; Pierce, G.J.; Collins, M.A.; Moffat, C.F.; Priede, I.G.; Pond, D.W. Trophic position of deep-sea fish—Assessment through fatty acid and stable isotope analyses. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2009, 56, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabaawi, R.W.; Sastri, A.R.; Dower, J.F.; Mazumder, A. Deciphering the Seasonal Cycle of Copepod Trophic Dynamics in the Strait of Georgia, Canada, Using Stable Isotopes and Fatty Acids. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackman, R.G. Nutritional composition of fats in seafoods. Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 1989, 13, 161–289. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Al-Abdul-Elah, K.; Yaseen, S.B. Seasonal variations in proximate and fatty acid composition of sobaity sea bream (Sparidentex hasta) in Kuwait waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2019, 99, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzikas, Z.; Amvrosiadis, I.; Soultos, N.; Georgakis, S. Seasonal variation in the chemical composition and microbiological condition of Mediterranean horse mackerel (Trachurus mediterraneus) muscle from the North Aegean Sea (Greece). Food Control 2007, 18, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyoung-Chul, S.; Stephen, N. Using the relationship between eye diameter and body length to detect the effects of long-term starvation on Antarctic krill Euphausia superba. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 239, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tufan, B.; Koral, S.; Köse, S. Changes during fishing season in the fat content and fatty acid profile of edible muscle, liver and gonads of anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) caught in the Turkish Black Sea. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, L.; Schmitz, A.; Pelka, J. Rapid preparation of fatty acid esters from lipids for gas chromatographic analysis. Anal. Chem. 1966, 38, 514–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R. Metabolism and Functions of Lipids and Fatty Acids in Teleost Fish. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2003, 11, 107–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitan, K.I.; Rainuzzo, J.R.; Øie, G.; Olsen, Y. A review of the nutritional effects of algae in marine fish larvae. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, X.; He, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, R.-Q.; Wu, Y. Fatty acid composition analyses of commercially important fish species from the Pearl River Estuary, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, A.; Garrido, D.; Monroig, Ó.; Pérez, J.A.; Betancor, M.B.; Acosta, N.G.; Kabeya, N.; Marrero, M.A.; Bolaños, A.; Rodríguez, C. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in three fish species with different trophic level. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.; Shan, X.; Jin, X.; Teng, G.; Wei, C. Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China). Fishes 2022, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou, M.; Berge, G.M.; Baeverfjord, G.; Sigholt, T.; Østbye, T.-K.; Romarheim, O.H.; Hatlen, B.; Leeuwis, R.; Venegas, C.; Ruyter, B. Requirements of n-3 very long-chain PUFA in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): Effects of different dietary levels of EPA and DHA on fish performance and tissue composition and integrity. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y. Releasing capacity of Portunus trituberculatus enhancement in Zhoushan fishing ground and Yangtze river estuary fishing ground and their adjacent waters. South China Fish. Sci. 2019, 15, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Yang, H. Nutritional differences between Natural and Cultured populations of white spiny tail shrimp. J. Hydroecol. 2008, 28, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, X.-G.; Lou, B.; Yang, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y. Comparison of Nutritional Composition of Different Muscle Parts in Portunus triberculatus. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2013, 35, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Fatty acids content of common marine fish from Yellow Sea of China. J. Hyg. Res. 2014, 43, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, Q. Nutritional Characteristics and Umami Assessment of Euphausia superba and Exopalaemon carinicauda. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 149–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-G.; Cornel, A.; Lou, B.; Lu, Q.; Zhan, W.; Chen, R. Nutritional Analysis and Evaluation of Muscle in Small Yellow Croaker Larimichthys polyactis from Four Different Localities. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2018, 40, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chi, C.; Li, H. Analysis of the Nutritional Composition of Pseudosciaena polyacti in Zhoushan. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2013, 35, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Shen, S.; Li, X.; Yan, B.; Sun, X. Fatty acid composition variation and fingerprint of the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus from China Sea based on multivariate analysis method. J. Fish. China 2013, 37, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, S.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Lv, H. Analysis and Comparison of Nutritional Quality between Wild and Cultured Portunus trituberculatus. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 21, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xuan, F.; Shi, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Xu, W. Comparison of nutritional quality of three edible tissues of the wild-caught and pond-reared swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) females. LWT 2017, 75, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S. Study on the Analysis of Fatty Acids characteristics of Several Common Fish Species in Haizhou Bay. In Proceedings of the Abstracts of International Symposium on Modern Marine (Freshwater) Ranching, Chifeng, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 126–127. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Jiang, G.; Shen, H.; Qiao, Y.; Xv, J.; Wan, X. Analysis on Meat Nutritive Composition of Ridgetail White Prawn “Kesuhong No. 1”. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Fatty Acid Composition and Feeding Habits Analysis of the Main Catches from Lüsi Fishing Ground during Spring, Summer and Autumn Prog. Fish. Sci. 2021, 42, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.-M.; Chen, W. Fatty acid composition and nutrition evaluation in muscle of five cultured marine fish. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 20, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Uno, K.; Araki, T.; Takahashi, T. Comparison of the Fatty Acid Compositions in Cultured Red Sea Bream Differing in the Localities and Culture Methods, and Those in Wild Fish. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1989, 55, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Diao, Q.; Hou, D.; Hui, R.; Li, T. Study on Nutritional Evaluation of Fatty Acid in Red Sea Bream. J. Anshan Norm. Univ. 2012, 14, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Li, T.; Oyang, F.; Liu, P. Study of the nutritive compositions of Portunus trituberculatus. Acta Nutr. Sin. 1996, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.C.W.; Murphy, E.W.; McCarty, H.B.; Snyder, B.D.; Schrank, C.S.; McCann, P.J.; Crimmins, B.S. Variation in the essential fatty acids EPA and DHA in fillets of fish from the Great Lakes region. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumolo, P.; Bonanno, A.; Barra, M.; Fanelli, E.; Calabrò, M.; Genovese, S.; Ferreri, R.; Mazzola, S.; Basilone, G. Spatial variations in feeding habits and trophic levels of two small pelagic fish species in the central Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 115, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Hazel, J.R.; Gerking, S.D. Lipid mobilization during starvation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, with attention to fatty acids. J. Fish Biol. 1982, 21, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourente, G.; Tocher, D.R. Effects of weaning onto a pelleted diet on docosahexaenoic acid (22: 6 n-3) levels in brain of developing turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 1992, 105, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Závorka, L.; Blanco, A.; Chaguaceda, F.; Cucherousset, J.; Killen, S.S.; Liénart, C.; Mathieu-Resuge, M.; Němec, P.; Pilecky, M.; Scharnweber, K.; et al. The role of vital dietary biomolecules in eco-evo-devo dynamics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tan, X.-Y.; Wang, W.-M.; Fan, Q.-X. Effects of long-term starvation on body weight and body composition of juvenile channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, with special emphasis on amino acid and fatty acid changes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2009, 25, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bi, Q.; Meng, X.; Duan, M.; Wei, Y.; Liang, M. Response of lipid and fatty acid composition of turbot to starvation under different dietary lipid levels in the previous feeding period. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Ayad, S.M.E.A.; Kestemont, P.; Mélard, C. Dynamics of total lipids and fatty acids during embryogenesis and larval development of Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 23, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Dong, X.; Hu, G. Transcriptome analysis of red sea bream (Pagrus major) head kidney and spleen infected by Vibrio anguillarum. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, H. Demersal fish resources in the east china and yellow seas. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 1993, 22, 195–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Population dynamics modelling with spatial heterogeneity for yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) along the coast of China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, X.; Han, Z. Effects of climate change on the potential habitat distribution of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus under the species distribution model. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, P. Molecular responses of calreticulin gene to Vibrio anguillarum and WSSV challenge in the ridgetail white prawn Exopalaemon carinicauda. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litz, M.N.C.; Brodeur, R.D.; Emmett, R.L.; Heppell, S.S.; Rasmussen, R.S.; O’Higgins, L.; Morris, M.S. Effects of variable oceanographic conditions on forage fish lipid content and fatty acid composition in the northern California Current. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 405, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeman, L.A.; Parrish, C.C. Lipid composition of malpigmented and normally pigmented newly settled yellowtail flounder, Limanda ferruginea (Storer). Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, M.; Nitta, M.; Aomori, S.; Sakamaki, T.; Okano, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Miyata, N. Exploring the use of fish as indicators of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic supply in lake ecosystems. Oecologia 2023, 202, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardenne, F.; Hollanda, S.; Lawrence, S.; Albert-Arrisol, R.; Degroote, M.; Bodin, N. Trophic structures in tropical marine ecosystems: A comparative investigation using three different ecological tracers. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demestre, M.; Muntadas, A.; Sanchez, P.; Garcia-de-Vinuesa, A.; Mas, J.; Franco, I.; Duran, R.; Guillén, J. Bio and Anthropogenic Disturbance of Maërl Communities Settled on Subaqueous Dunes on the Mar Menor Continental Shelf (Western Mediterranean). In Atlas of Bedforms in the Western Mediterranean; Guillén, J., Acosta, J., Chiocci, F.L., Palanques, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- García-de-Vinuesa, A.; Demestre, M.; Lloret, J. Fatty acids as trophic markers and indicators of the quality of benthic habitats: The example of maerl and crinoid beds in the Northwestern Mediterranean. J. Sea Res. 2022, 187, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Importance of Docosahexaenoic Acid in Marine Larval Fish. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1993, 24, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Satoh, N.; Sekiya, S.; Shimizu, T.; Watanabe, T. The effect of dietary EPA and DHA on the molting rate of larval swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1999, 65, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Masuda, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, M. Effects of highly unsaturated fatty acids on escape ability from moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita in red sea bream Pagrus major larvae. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, A.; Pickova, J.; Johansson, L.; Åsgård, T.; Storebakken, T.; Kiessling, K.H. Changes in fatty acid composition in muscle and adipose tissue of farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in relation to ration and age. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Long, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, T.; Cheng, Y. Nutritional quality of different grades of adult male chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.; Gomes-Bispo, A.; Lourenço, H.; Matos, J.; Afonso, C.; Cardoso, C.; Castanheira, I.; Motta, C.; Prates, J.A.M.; Bandarra, N.M. The chemical composition and lipid profile of the chub mackerel (Scomber colias) show a strong seasonal dependence: Contribution to a nutritional evaluation. Biochimie 2020, 178, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo-Andrade, J.; Guzmán-Rivas, F.; Barría, P.; Ortega, J.; Mora, S.; Urzúa, Á. Seasonal dynamics of biochemical composition and fatty acids of swordfish (Xiphias gladius) in the Southeast Pacific Ocean off the coast of Chile. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
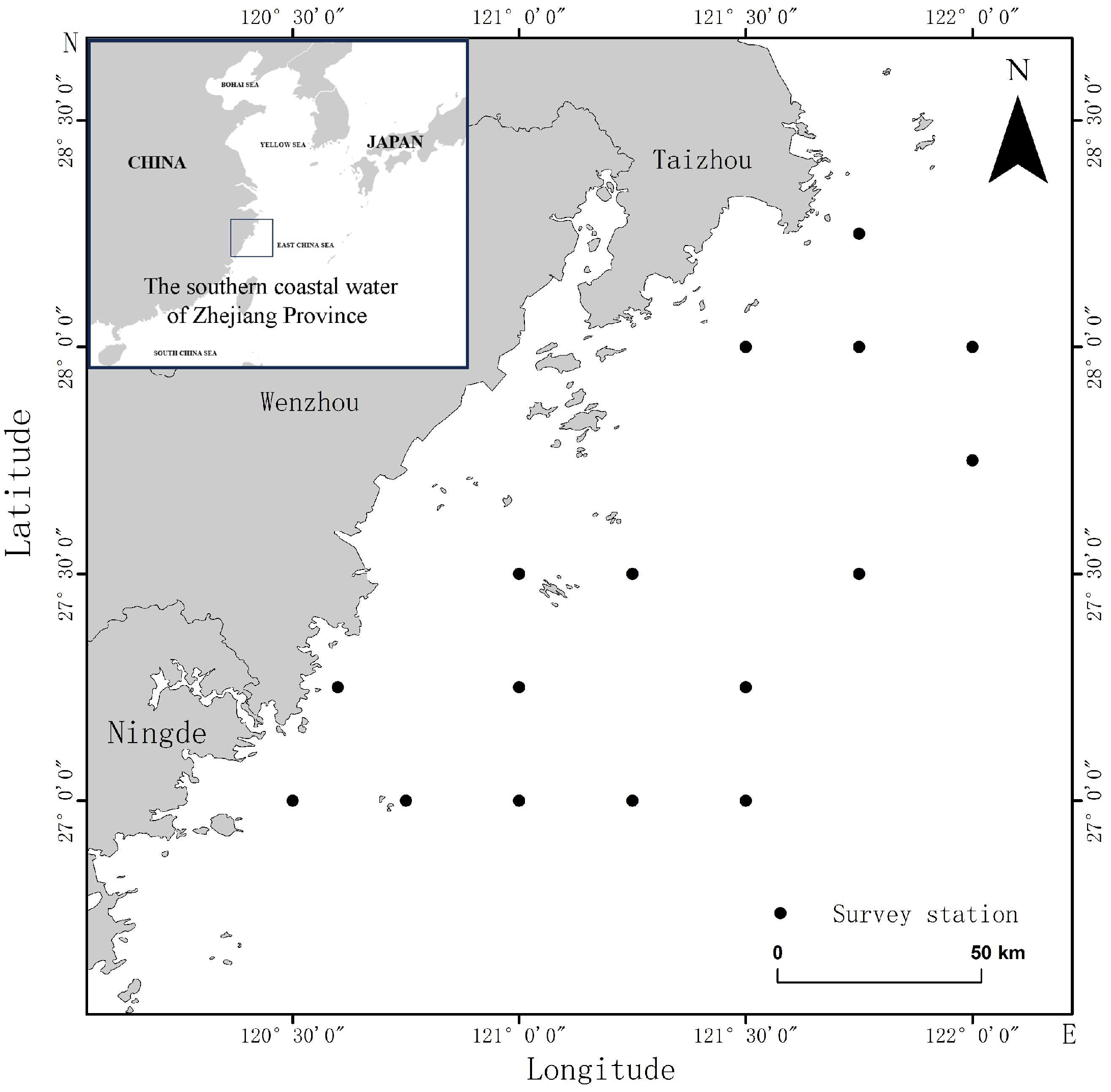
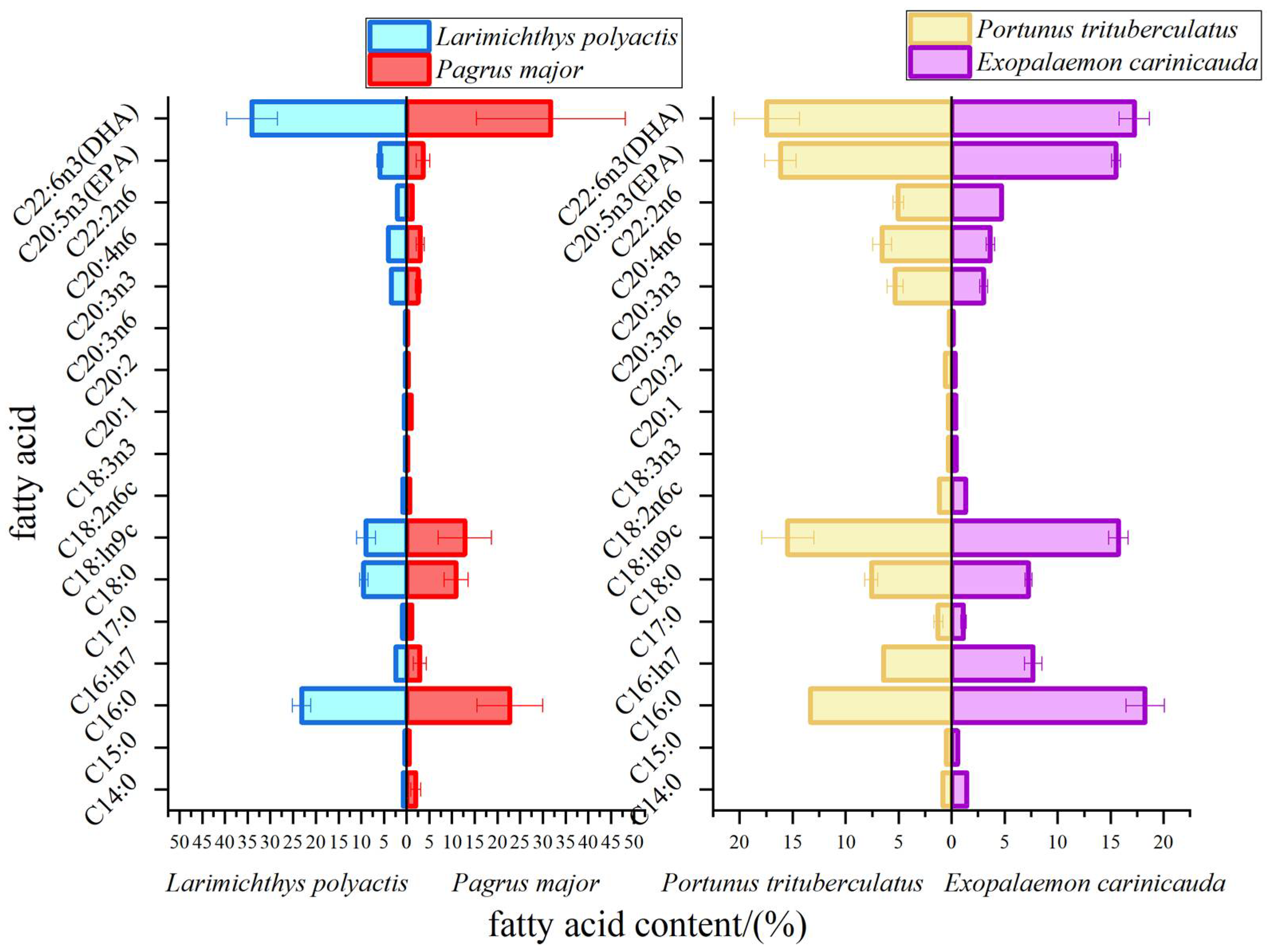
| Common Name | Species | Biological Classification | Feeding Habits | Body Length and Cephalothoracic Length/cm | Weight/g | Sampling Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Little yellow croaker | Larimichthys polyactis | Perciformes, Sciaenidae, and Larimichthys | Benthic feeder, mainly feeding on planktonic crustaceans, but also on decapods and other juvenile fish | 14.43 ± 1.88 | 33.83 ± 5.28 | The white muscle near the first dorsal fin |
| Red sea bream | Pagrus major | Perciformes, Sparidae, and Pagrus | Benthic feeder, mainly feeding on benthic crustaceans, mollusks, prawns, and algae | 11.13 ± 0.52 | 47.89 ± 8.18 | The white muscle near the first dorsal fin |
| Swimming crab | Portunus trituberculatus | Decapoda, Portunidae, and Portunus | Benthic feeders, feeding on benthic algae, shellfish, telopods, etc. | 7.63 ± 0.09 | 57.13 ± 3.64 | The crab claw or abdominal muscles |
| Ridgetail white prawn | Exopalaemon carinicauda | Decapoda, Palaemonidae, and Exopalaemon | Planktonic feeders, feeding on phytoplankton, organic detritus, etc. | 9.92 ± 0.21/5.33 ± 0.33 | 5.76 ± 0.89 | The abdominal muscles |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, J. Appropriateness Evaluation of Releasing Area for Four Marine Organisms in Stock Enhancement: A Fatty Acid Approach. Fishes 2023, 8, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100489
Wang Z, Lv Z, Zhang J. Appropriateness Evaluation of Releasing Area for Four Marine Organisms in Stock Enhancement: A Fatty Acid Approach. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100489
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zichen, Zehua Lv, and Junbo Zhang. 2023. "Appropriateness Evaluation of Releasing Area for Four Marine Organisms in Stock Enhancement: A Fatty Acid Approach" Fishes 8, no. 10: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100489
APA StyleWang, Z., Lv, Z., & Zhang, J. (2023). Appropriateness Evaluation of Releasing Area for Four Marine Organisms in Stock Enhancement: A Fatty Acid Approach. Fishes, 8(10), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100489






