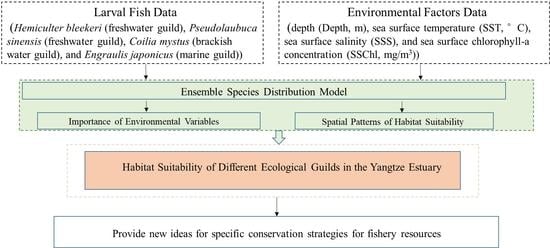
Use of Ensemble Model for Modeling the Larval Fish Habitats of Different Ecological Guilds in the Yangtze Estuary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Ensemble Model Construction
3. Results
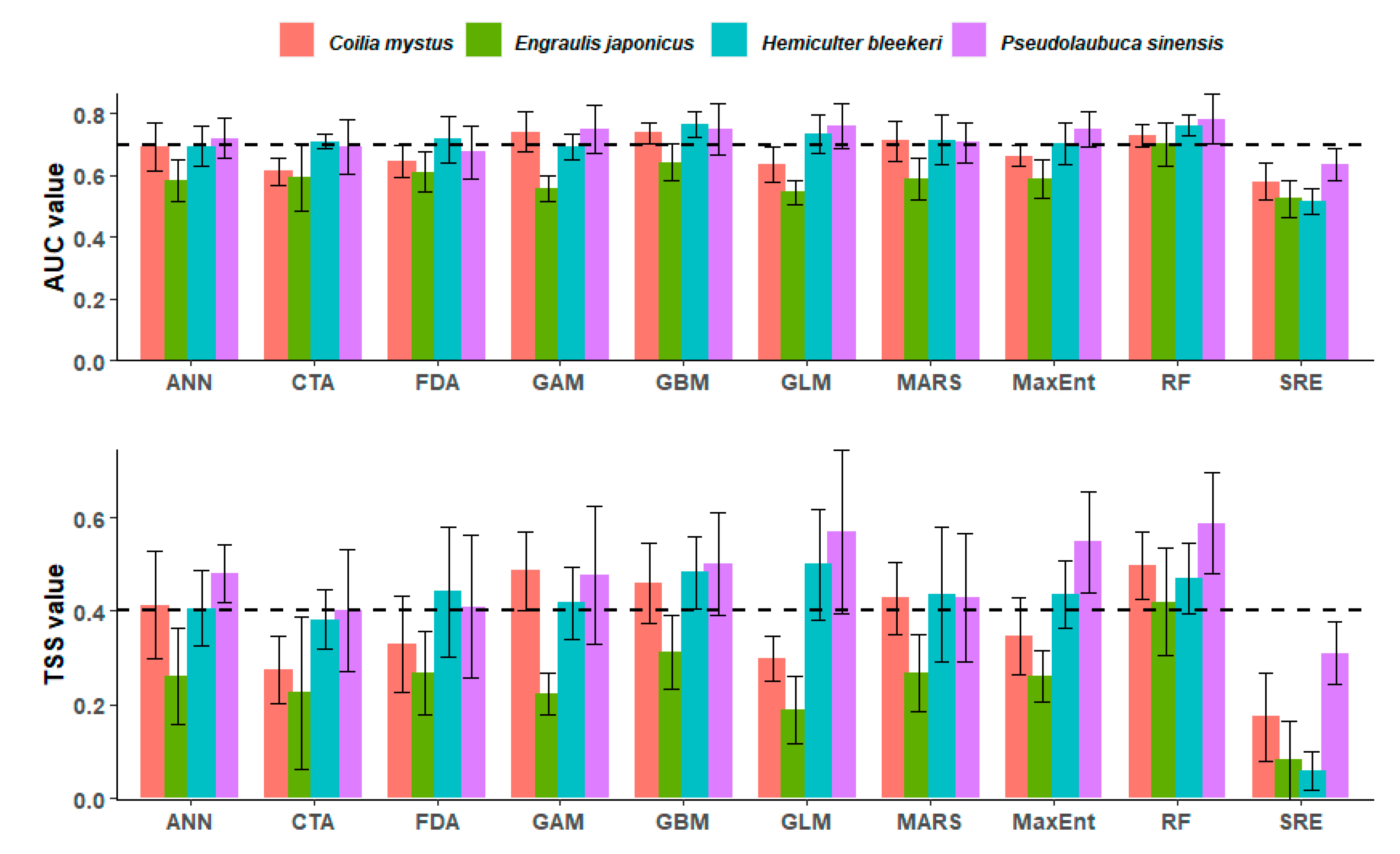
3.1. Model Accuracy Measures
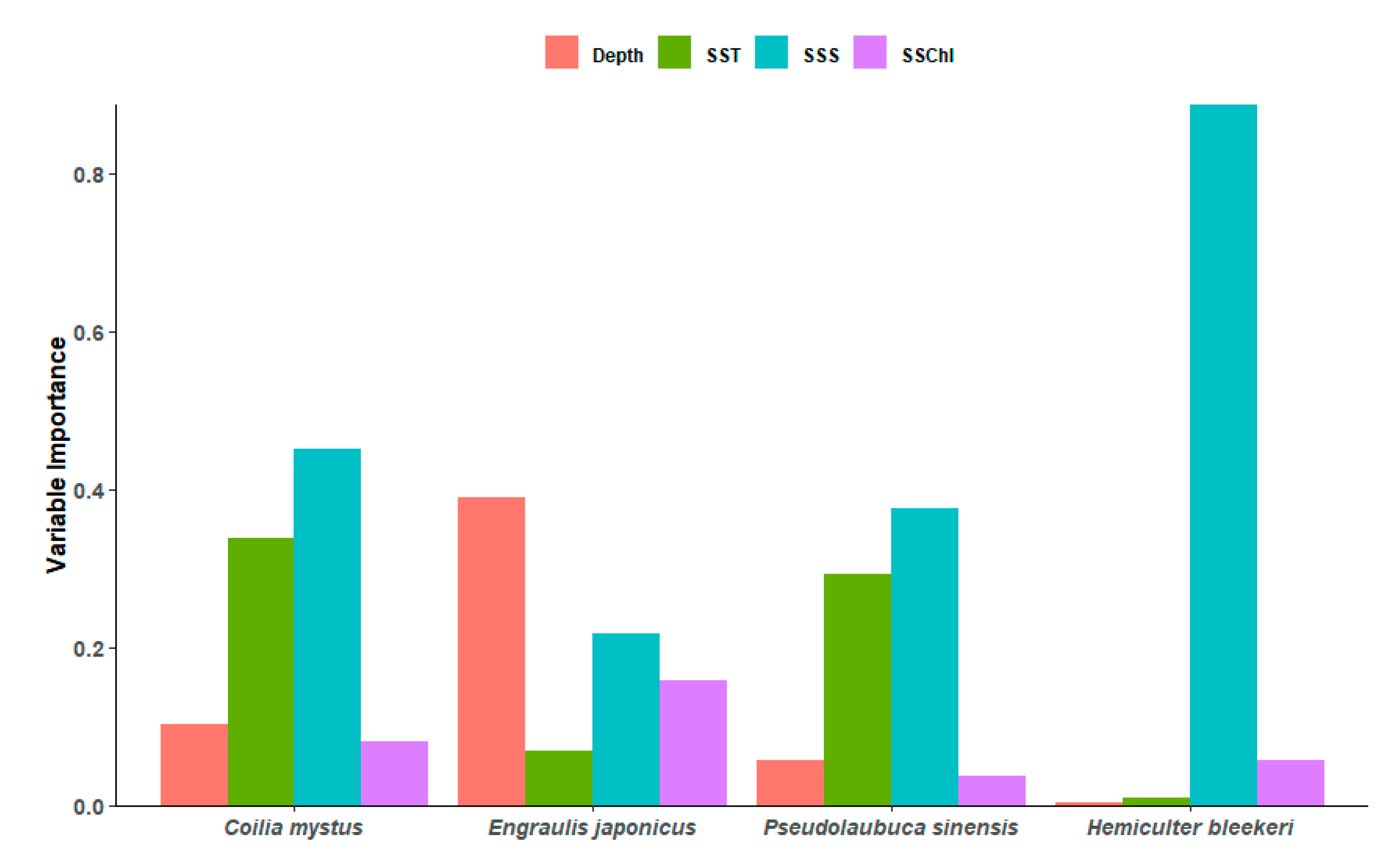
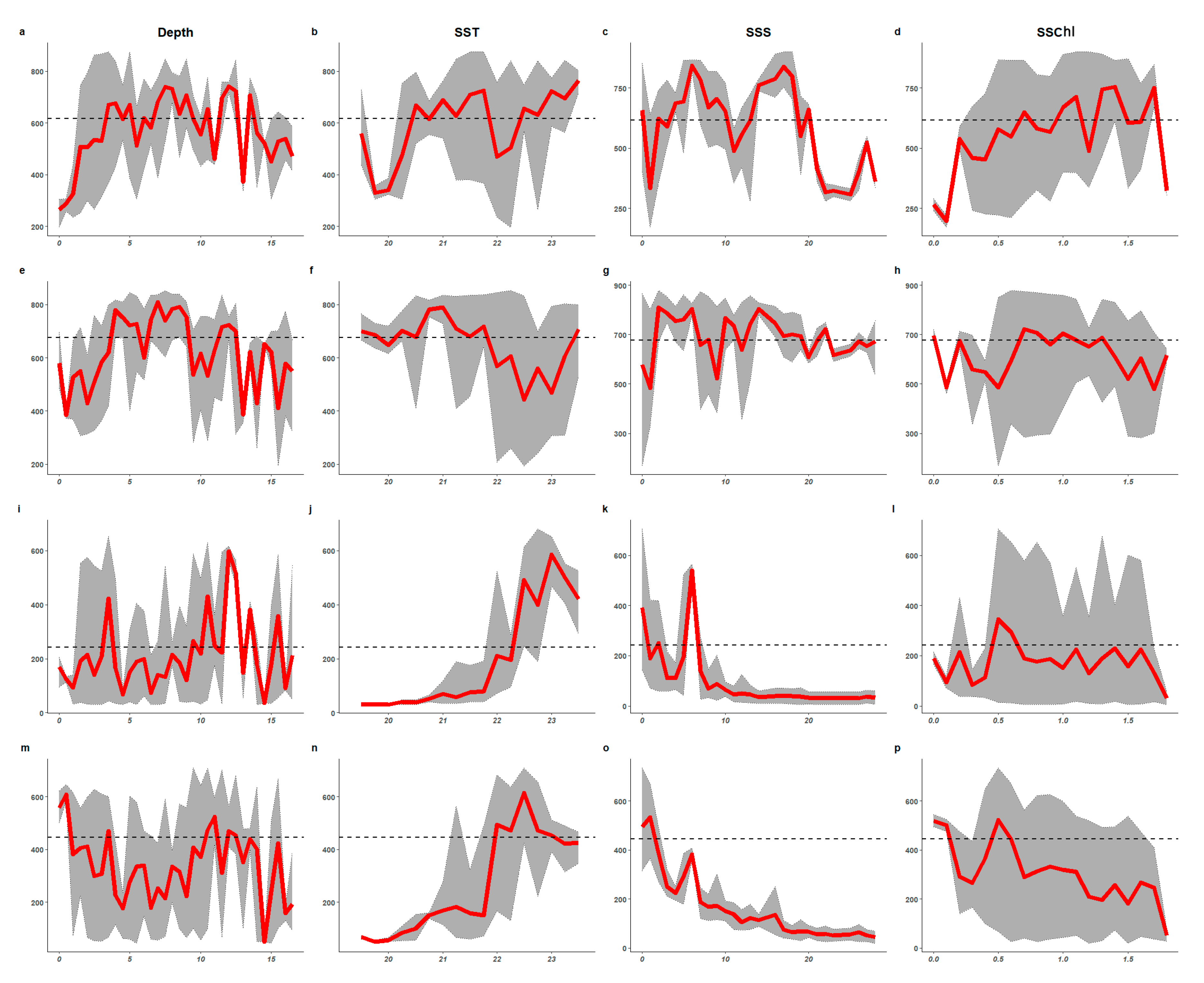
3.2. Importance of Environmental Variables and Response Curves
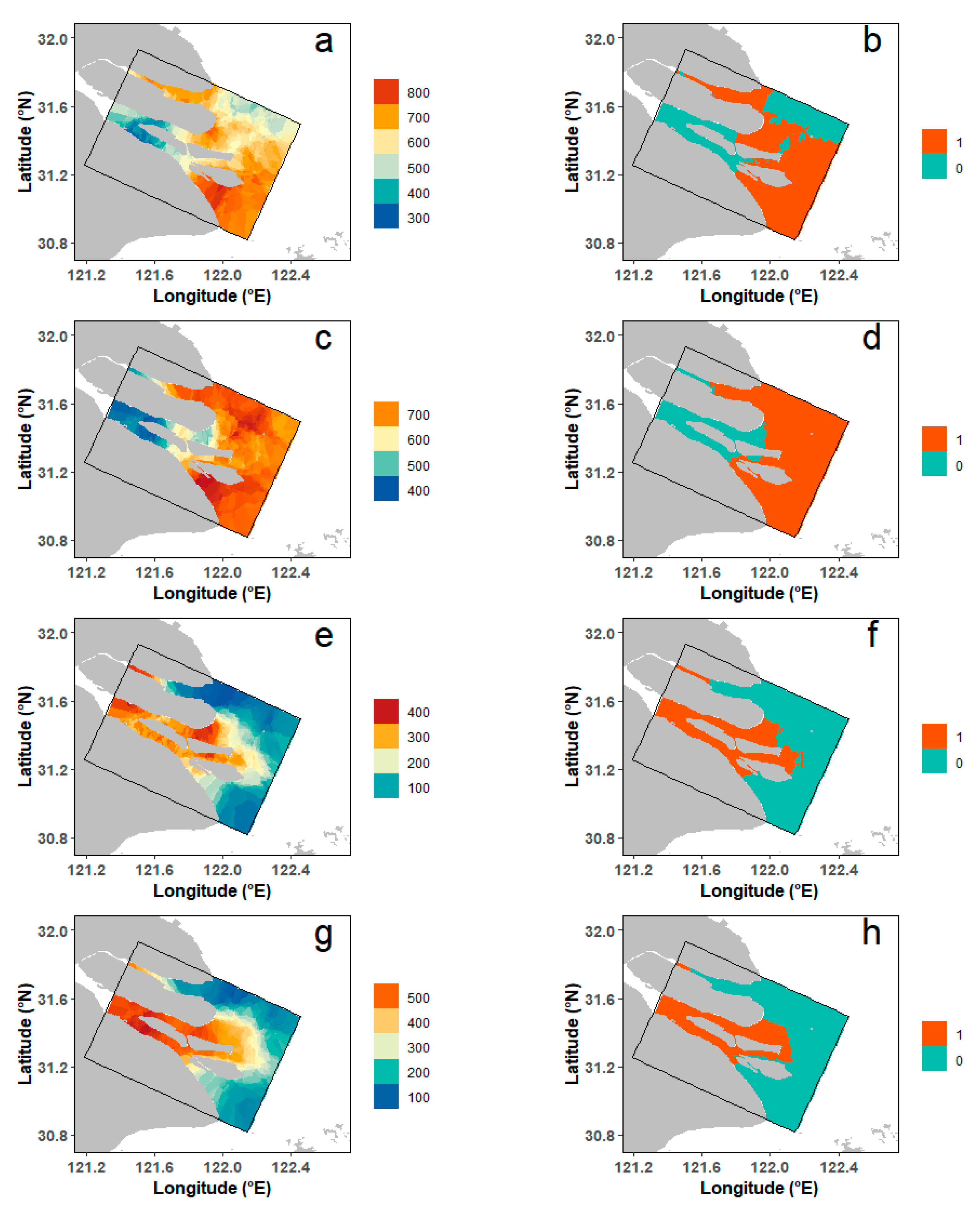
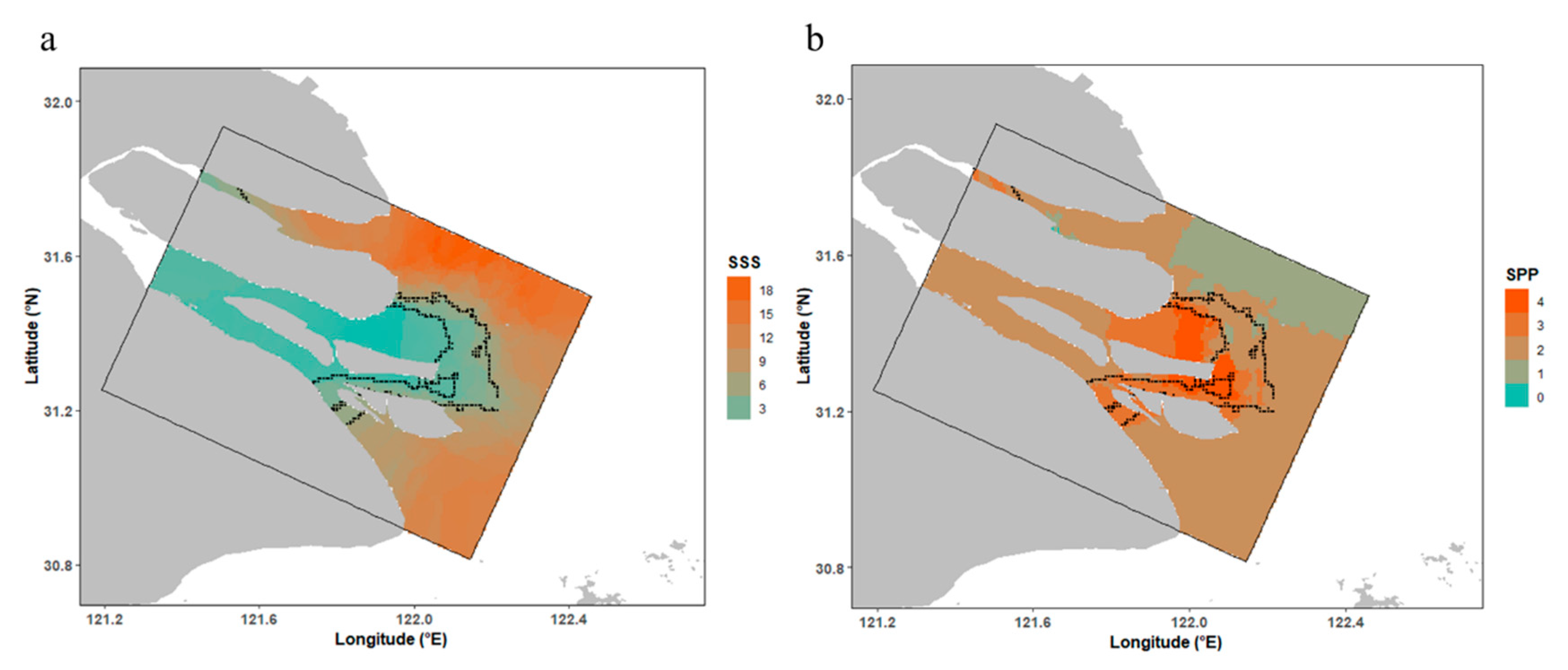
3.3. Spatial Patterns of Habitat Suitability
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performances
4.2. Environmental Variable Predictors
4.3. Potential Habitat Description
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, B.S.; Kendall, A.W. Development of eggs and larvae. In Early Life History of Marine Fishes; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, G. Estuarine vulnerability and ecological impacts. In Estuaries of South Africa; Allanson, B.R., Baird, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; p. 340. [Google Scholar]
- Kennish, M.J. Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.J.; Davenport, J.; Kelly, T.C. A study of the impact of a pipeline construction on estuarine benthic invertebrate communities. Part 2. Recolonization by benthic invertebrates after 1 year and response of estuarine birds. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 47, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, M.; Whitfield, A.K.; Potter, I.C.; Blaber, S.J.M.; Cyrus, D.P.; Nordlie, F.G.; Harrison, T.D. The guild approach to categorizing estuarine fish assemblages: A global review. Fish Fish. 2007, 8, 241–268. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, M.W.; Heck, K.L.; Able, K.W.; Childers, D.L.; Eggleston, D.B.; Gillanders, B.M.; Halpern, B.; Hays, C.G.; Hoshino, K.; Minello, T.J. The identification, conservation, and management of estuarine and marine nurseries for fish and invertebrates. BioScience. 2009, 51, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhatalo, J.; Veneranta, L.; Hudd, R. Species distribution modeling with Gaussian processes: A case study with the youngest stages of sea spawning whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus L. sl) larvae. Ecol. Model. 2012, 228, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.Y.; Wan, R.; Li, Z.G.; Ren, Y.P.; Song, P.B.; Tian, Y.J.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y. Spatio-temporal distribution of Konosirus punctatus spawning and nursing ground in the South Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, I.C.; Tweedley, J.R.; Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K. The ways in which fish use estuaries: A refinement and expansion of the guild approach. Fish Fish. 2015, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Miranda, E.; Palma, A.T.; Ojeda, F.P. Larval fish assemblages in nearshore coastal waters off central Chile: Temporal and spatial patterns. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, E.G.; Grilo, T.F.; Nyitrai, D.; Dolbeth, M.; Pardal, M.A.; Martinho, F. Climate influence on juvenile European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) populations in an estuarine nursery: A decadal overview. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 122, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, M.A.; Martinho, F.; Baptista, J.; Costa, F.; Pardal, M.A.; Primo, A.L. Function of estuaries and coastal areas as nursery grounds for marine fish early life stages. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 170, 105408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Barletta-Bergan, A.; Saint-Paul, U.; Hubold, G. The role of salinity in structuring the fish assemblages in a tropical estuary. J. Fish. Bio. 2005, 66, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, S.; Li, C.; Ni, Y. Fishes of the Yangtze Estuary; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K. Challenging paradigms in estuarine ecology and management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskelä, A.; Hudd, R.; Lehtonen, H.; Huhmarniemi, A.; Sandstrm, O. Habitats of whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus (L.) s.l.) larvae in the Gulf of Bothnia. Aqua. Fennica. 1991, 21, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Pattrick, P.; Strydom, N.A.; Harris, L.; Goschen, W.S. Predicting spawning locations and modelling the spatial extent of post hatch areas for fishes in a shallow coastal habitat in South Africa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 560, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.X.; Hu, H.; Gu, G.W.; Su, C.; Gu, X.J. Salinity front in the Changjiang estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. Supplement. 1995, 26, 23–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, A.K. Estuaries-how challenging are these constantly changing aquatic environments for associated fish species? Environ. Biol. Fish. 2021, 104, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Le Pape, O.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Predicting estuarine use patterns of juvenile fish with generalized linear models. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 120, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, S.Y.; Capinhac, C.; Weteringsd, R.; Gao, T.X. Using Species Distribution Model to Predict the Impact of Climate Change on the Potential Distribution of Japanese Whiting Sillago Japonica. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.H.; Cui, X.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Li, T.T.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.Z.; Fan, B.G. Analysis of the distribution pattern of chinese ziziphus jujuba under climate change based on optimized biomod2 and maxent models. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Murphy, B.R.; Xie, S. Validation of a method of estimating age, modelling growth, and describing the age composition of Coilia mystus from the Yangtze Estuary, China. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.L.; Wu, G.Z.; Sun, J.R. The investigation of pelagic eggs, larvae and juveniles of fishes at the mouth of the Changjiang River and adjacent areas. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1990, 21, 346–354. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xian, W.W.; Liu, S.D. Autumn ichthyoplankton assemblage in the Yangtze Estuary shaped by environmental factors. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xian, W.W.; Liu, S.D. Ichthyoplankton assemblage structure of springs in the Yangtze Estuary revealed by biological and environmental visions. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J.; Shen, J.Z.; Gong, J.; Li, Q.; Li, C.S.; Wang, K.X.; Mei, Z.G. Reproductive biology of Hemiculter bleekeri in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 48, 53–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Song, P.; Li, Z.; Long, X.; Wang, D.; Zhai, L. Larval Fish Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Different Ecological Guilds in Yangtze Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.T.; Xu, S.N.; Li, M.; Dai, J.G.; Li, Z.H.; Zou, K.S.; Liu, L. Microsatellite primers screening and genetic diversity analysis of five geographical populations of Pseudolaubuca sinensis in the pearl river basin. Acta Hydrobio. Sin. 2020, 44, 501–508. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wan, R.; Li, Z.G.; Zhang, J.B.; Long, X.Y.; Song, P.B.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, S. The Non-stationary Environmental Effects on Spawning Habitat of Fish in Estuaries: A Case Study of Coilia mystus in the Yangtze Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 766616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Mammola, S.; Xian, W.W.; Zhang, H. Modelling the potential impacts of climate change on the distribution of ichthyoplankton in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, J.H.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Gao, C.X.; Wang, X.F.; Tian, S.Q. Analysis of spatiotemporal fish density distribution and its influential factors based on generalized additive model (GAM) in the Yangtze River Estuary. Chin. J. Fish. 2020, 44, 936–946. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kindong, R.; Chen, J.H.; Dai, L.B.; Gao, C.X.; Han, D.Y.; Tian, S.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Ma, Q.Y.; Tang, J.Y. The effect of environmental conditions on seasonal and inter-annual abundance of two species in the Yangtze River estuary. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmerman, N.E. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.B.; New, M. Ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R. Species distribution models: Ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J. Mapping Species Distributions: Spatial Inference and Prediction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Ciannelli, L.; Bailey, K.M.; Anderson, J.T. Spatial and temporal patterns of walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) spawning in the eastern Bering Sea inferred from egg and larval distributions. Fish. Oceanogr. 2010, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Wan, R.; Ye, Z.J.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.Q. Use of random forests and support vector machines to improve annual egg production estimation. Fish. Sci. 2017, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, S.; Cabral, H.N. Distribution models of estuarine fish species: The effect of sampling bias, species ecology and threshold selection on models’ accuracy. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 51, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W. BIOMOD–optimizing predictions of species distributions and projecting potential future shifts under global change. Global Change Biol. 2003, 9, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Ye, Z.J.; Wan, R.; Zhang, C. Model selection between traditional and popular methods for standardizing catch rates of target species: A case study of Japanese Spanish mackerel in the gillnet fishery. Fish. Res. 2015, 161, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Georges, D.; Engler, R.; Breiner, F. biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=biomod2 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Zhang, R.Z.; Lu, H.F. Eggs and Larvae in the Offshore of China; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1985. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y. Early Morphogenesis and Species Identification of Fishes in Yangtze River; Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Science: Wuhan, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Arranz, I.; Mehner, T.; Benejam, L.; Argillier, C.; Holmgren, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Volta, P.; Winfield, I.J.; Winfield, S. Density-dependent effects as key drivers of intraspecific size structure of six abundant fish species in lakes across Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.H.; Gillingham, P.K.; Britton, J.R.; Blanchet, S.; Gozlan, R.E. Predicting global invasion risks: A management tool to prevent future introductions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Guéguen, M.; Renaud, J.; Karger, D.N.; Zimmermann, N.E. Uncertainty in ensembles of global biodiversity scenarios. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Xie, B.Y.; Wan, F.H.; Xiao, Q.M.; Dai, L.Y. Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 4, 365–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Hijmans, R.J. Terra: Spatial Data Analysis; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=terra (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Deckmyn, A. Maps: Draw Geographical Maps; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=maps (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Han, X.L.; Han, Z.Q. Effects of Climate Change on the Potential Habitat Distribution of Swimming Crab (Portunus trituberculatus) under the Species Distribution Model. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Han, Z.Q. Predicting the Effects of Climate Change on the Suitable Habitat of Japanese Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Based on the Species Distribution Model. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 927790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Ye, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y. Spawning strategy of Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in the coastal Yellow Sea: Choice and dynamics. Fish. Oceanogr. 2020, 30, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, S.J.; Olden, J.D. Assessing transferability of ecological models: An underappreciated aspect of statistical validation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Elliott, M.; Basset, A.; Blader, S.J.M.; West, R.J. Paradigms in the estuarine ecology: A review of the Remane diagram with a suggested revised model for estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 97, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Shen, X.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, L.F. Species of fish eggs and larvae and distribution in Changjiang Estuary and vicinity waters. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2006, 28, 171–174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Yang, Z.F.; Shen, Z.Y.; Zhao, R. Environmental flows for the Yangtze estuary based on salinity objectives. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2009, 14, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, J.R.; Wu, H. Impacts of wind stress on saltwater intrusion in the Yangtze Estuary. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1178–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.J.; Song, C.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, J.; Liu, R.H.; Zhuang, P. Temporal and spatial distribution of Coilia mystus larvae and juveniles in the Yangtze Estuary during primary breeding season. J. Chin. Fish. Sci. 2021, 28, 1152–1161. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.J.; Huang, D.J.; Zhang, J. Abundance and distribution of eggs and larvae of Engraulis japonicus in the Northern part of East China Sea and the Southern part of Yellow Sea and its relationship with environmental conditions. J. Chin. Fish. 2002, 26, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Olden, J.D.; Neff, B.D. Cross-correlation bias in lag analysis of aquatic time series. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, A.P.; Thurman, H.V. Essentials of Oceanography, 12th ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 403–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Kerr, L.A.; Record, N.R.; Bridger, E.; Tupper, B.; Mills, K.E.; Armstrong, E.M.; Pershing, A.J. Modeling marine pelagic fish species spatiotemporal distributions utilizing a maximum entropy approach. Fish. Oceanogr. 2018, 27, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.Y. Study on Annual Resource Variation of Larvae and Juveniles in the Southern Branch of the Yangtze River Estuary; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.Q. Biological characteristics of Coilia mystus in the Changjiang estuary. J. Fish. Sci. 1999, 6, 69–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Reglero, P.; Ciannelli, L.; Alvarez-Berastegui, D.; Balbín, R.; Alemany, F. Geographically and environmentally driven spawning distributions of tuna species in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 463, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, T.; van Damme, C.J.G.; Samson, M.; Dickey-Collas, M. Quantifying the influence of geography and environment on the northeast Atlantic mackerel spawning distribution. Fish. Oceanogr. 2017, 27, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kang, Y.S.; Oh, H.; Suh, Y.S.; Hwang, J.D. Spatial distribution of early life stages of anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) and hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus) and their relationship with oceanographic features of the East China Sea during the 1997–1998 El Niño Event. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 63, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Yasuma, H.; Masuda, R.; Minami, K.; Matsukura, R.; Morioka, S.; Miyashita, K. Swimming angle and target strength of larval Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus). Fish. Sci. 2011, 77, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, K.; Kiyomoto, Y. Distribution settling of Japanese anchovy (Englaulis japonicus) eggs at the spawning ground off Changjing river in the East China sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 1997, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaKun, A. Fronts and eddies as key structures in the habitat of marine fish larvae: Opportunity, adaptive response and competitive advantage. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.R.; Shi, J.X.; Cai, Y.M.; Liu, C.G. Biological productivity front in the Changjiang Estuary and Hangzhou Bay and its ecological effects. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2004, 26, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Chen, J.F.; Li, H.L.; Jin, H.Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, S.Q.; Lu, Y.; Huang, D.J. The influence of freshwater-saline water mixing on phytoplankton growth in Changjiang Estuary. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 17–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
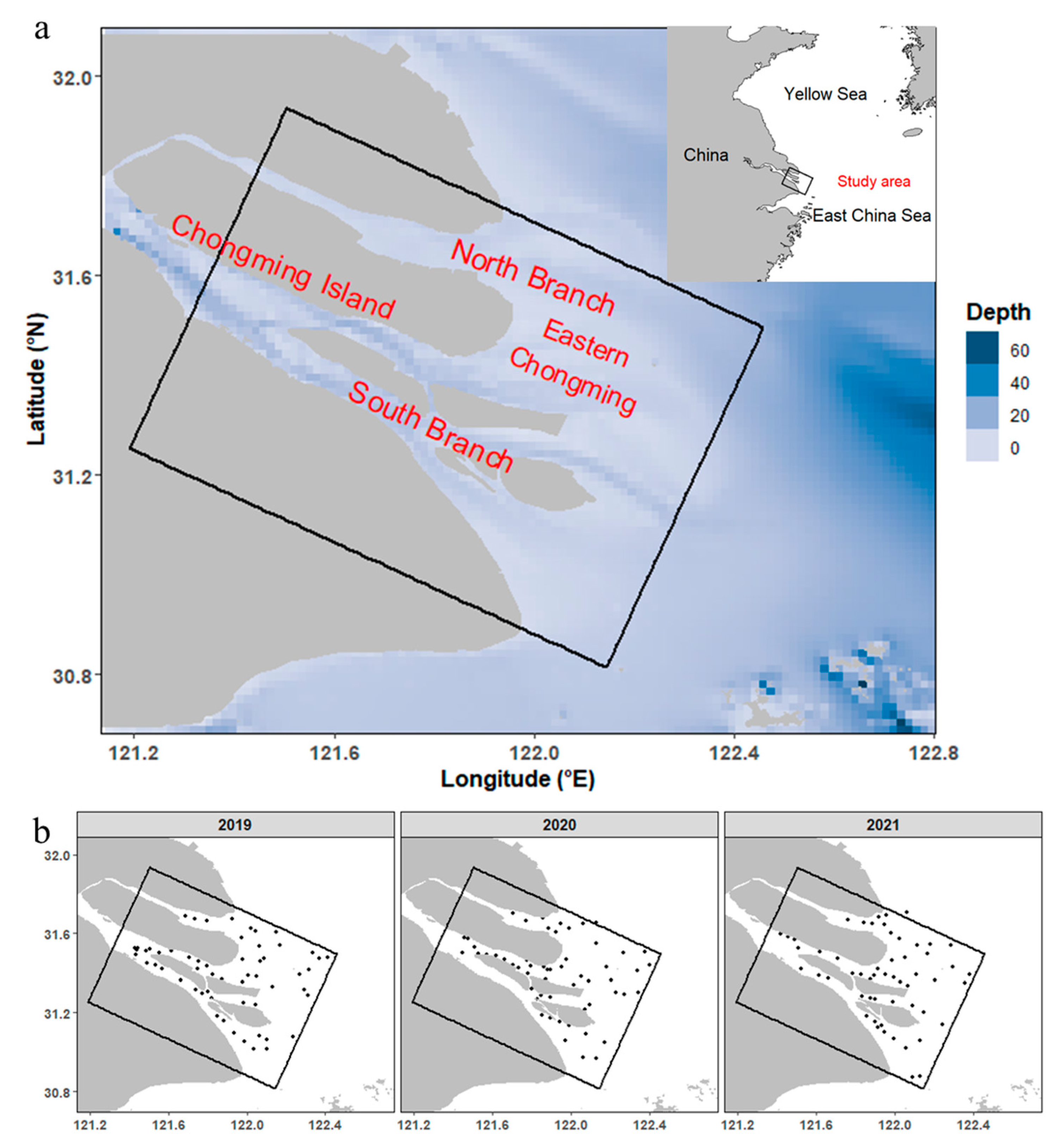
| Cruise Timing | Stations | Number of Stations with Larval Fish Present (Number of Larval Fish) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. mystus | E. japonicus | P. sinensis | H. bleekeri | ||
| May 2019 | 57 | 11 (2627) | 37 (25,406) | 1 (21) | 25 (734) |
| May 2020 | 56 | 43 (40,572) | 30 (6399) | 18 (5509) | 17 (3106) |
| May 2021 | 55 | 48 (25,379) | 42 (32,366) | 12 (26,027) | 13 (19,077) |
| Species | AUC | TSS | Cutoff | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. mystus | 0.938 | 0.766 | 616.0 | 87.255 | 87.897 |
| E. japonicus | 0.945 | 0.740 | 677.0 | 80.734 | 93.220 |
| P. sinensis | 0.928 | 0.749 | 243.0 | 96.774 | 78.102 |
| H. bleekeri | 0.899 | 0.641 | 445.0 | 81.818 | 82.301 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, R.; Song, P.; Li, Z.; Long, X.; Wang, D.; Zhai, L. Use of Ensemble Model for Modeling the Larval Fish Habitats of Different Ecological Guilds in the Yangtze Estuary. Fishes 2023, 8, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040209
Wan R, Song P, Li Z, Long X, Wang D, Zhai L. Use of Ensemble Model for Modeling the Larval Fish Habitats of Different Ecological Guilds in the Yangtze Estuary. Fishes. 2023; 8(4):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040209
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Rong, Pengbo Song, Zengguang Li, Xiangyu Long, Dong Wang, and Lu Zhai. 2023. "Use of Ensemble Model for Modeling the Larval Fish Habitats of Different Ecological Guilds in the Yangtze Estuary" Fishes 8, no. 4: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040209
APA StyleWan, R., Song, P., Li, Z., Long, X., Wang, D., & Zhai, L. (2023). Use of Ensemble Model for Modeling the Larval Fish Habitats of Different Ecological Guilds in the Yangtze Estuary. Fishes, 8(4), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8040209