Abstract
White feces syndrome (WFS), a gastrointestinal disorder of cultivated penaeid shrimp, causes severe economic and production losses worldwide. Shrimp with WFS usually show a reduced feed consumption and growth rate, hepatopancreatic discoloration, and loose shells. Recently, WFS has been said to be related to an infection with Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), a microsporidian parasite, and other opportunistic bacteria, such as the Vibrio species. Vibrio spp. may play an important role in WFS occurrence; nevertheless, Vibrio sp., as a single pathogen, cannot reproduce this syndrome under laboratory conditions. To date, no novel treatment has been found for WFS; therefore, preventive measures, such as strict biosecurity systems to eliminate or inactivate EHP spores and limit the total Vibrio number, have been suggested. This review summarizes the information regarding the association between WFS and water parameters, gut microbiomes, EHP and Vibrio, and disease control strategies.
1. Introduction
White feces syndrome (WFS) is a gastrointestinal disorder affecting cultivated penaeid shrimp worldwide. The syndrome is characterized by the presence of white fecal strings floating on the water surface of grown-out ponds. Infected shrimp usually exhibit whitish to yellowish midguts, retarded growth, high size variation, reduced average daily growth, elevated feed conversion ratios, loose exoskeletons, and sometimes mortality [1,2]. The histopathology of the intestine has revealed a thin intestinal wall combined with the detachment of intestinal epithelial cells and the reduction in or disappearance of microvilli [3]. WFS usually occurs during 50–60 days of stocking. It weakens shrimp, resulting in persistent mortalities, which can reduce the production yield by up to 60% [3,4].
The histopathology of WFS-affected shrimp also reveals remarkable lesions in the hepatopancreas. Wang et al. [5] described histological lesions of naturally occurring WFS in the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, which can be divided into three phases. During Phase I, the pulpiness and succulent appearance of the hepatopancreas were visible, which may have been caused by the expansion of the hepatopancreatic tubules, while the B-, R-, and F-cells were still intact. Then, the thickness of the tubular epithelium was reduced in size, and the lumen was relatively enlarged, as the disease progressed in Phase II, accompanied by severe hemocyte infiltration at the proximal part of the sinus. In addition, a reduction in F-cells and R-cells was observed during Phase II. In Phase III, the B-, F- and R-cell cells disappeared, and most of the tubules collapsed, displaying a thinned epithelium and large lumen. The detached microvilli layer aggregated in the lumen of some tubules. The sloughing hepatopancreatic tubular epithelium then aggregated to form a vermiform body and was once misunderstood as the gregarine parasite of shrimp but was later recognized as aggregated and transformed microvilli (ATM) [2,6]. When the ATM accumulates in a very high amount combined with varied compositions, such as lipids and mixed bacterial components, they result in white fecal strings [2,7]. Recently, observations of the ATM under light microscopy of squash mounts (Figure 1) or stained smears from fresh HP tissue have been used as indicators for WFS monitoring in shrimp ponds [8]. In addition, clusters of microsporidia Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), an intracellular parasite causing slow growth syndrome in shrimp, attached to white fecal strings have been reported [9,10].
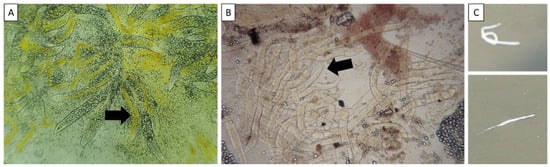
Figure 1.
Squash mounts of the hepatopancreas (A) and intestinal tissue (B) of the WFS-affected shrimp observed under a light microscope, showing an accumulation of aggregated, transformed microvilli (arrow). White fecal strings floating on the water surface of the affected pond (C).
To date, the etiology of WFS has been proposed as the combination of EHP with opportunistic marine pathogens, including Vibrio spp. and Propionigenium sp. [1,11], but the experimental challenge using the individual pathogen cannot fulfill Koch’s postulate. Moreover, the concept of gut dysbiosis (the imbalance of intestinal microflora) has been introduced; however, it is difficult to discern whether the dysbiosis occurred before or after the occurrence of WFS. Gut dysbiosis may be influenced by several noninfectious causes, such as the alteration of a diet’s nutrition and the water quality [3], but in order to induce white feces formation, we cannot neglect the involvement of particular pathogens notably EHP [1]. Many researchers have discussed the involvement of EHP in WFS. Taken together, WFS is hypothesized as a multifactorial disease, and the concept of “pathobiome” has been introduced. This review summarizes the overall and updated information on WFS, the investigation of bacterial and EHP involvement, the microbiome of WSF-affected shrimp, and the treatment or control strategies that have been proposed.
2. Water Parameters and WFS
There are few reports on the water quality related to the occurrence of WFS. WFS cases were reported in both low (<5 ppt) and high saline (>30 ppt) environments [5,12]. The mortality following WFS incidence in the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon was observed when low dissolved oxygen (>3 mg/L) and low alkalinity (<80 ppm) levels were reported in Thailand [13]. A study in Indonesia reported that WFS-affected ponds showed a lower water pH (7.71–7.84) and dissolved oxygen (5.57–5.98 mg mL−1), compared to a water pH > 8 and dissolved oxygen at >6 mg mL−1 in the healthy ponds [14]. Lower water pH and increased organic matter waste promotes the growth of heterotrophic bacteria, while deteriorating water quality also affects shrimp intestinal microbiota [14]. In general, water quality may not have a direct impact on WFS occurrence but rather a collateral effect on shrimp health and pond microbial populations.
3. Etiology of WFS
3.1. Bacterial Pathogens Associated with WFS
Bacterial infections causing whitish or yellowish gastrointestinal exudates have been reported not only for WFS in shrimp. The formation of white intestinal excretion in other aquatic species was also found in Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baerii and barramundi Lates calcarifer infected with low lethal doses of Streptococcus iniae [15,16]. The white gastrointestinal matters were caused by exudative inflammation and excessive mucin production induced by the bacteria. These reports show evidence of bacterial involvement in the gastrointestinal pathology of aquatic species. For shrimp WFS, Vibrio, a marine opportunistic pathogen, was a point of attention during the initial investigation of WFS. Vibrio spp. are Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacteria of the Vibrionaceae family, ubiquitously found worldwide, of which some of the Vibrio spp., such as V. parahaemolyticus and V. harveyi, are the primary pathogens in shellfish [17]. Vibrio spp. seem to play an important role in WFS occurrence, as a significantly higher load of Vibrio spp. in pond water, intestine, and hemolymph has been found in WFS-affected shrimp than in the healthy population [18,19]. Bacterial isolation and 16s rRNA sequencing from the intestine of WFS-affected shrimp cultured in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, revealed five dominant groups of Vibrio, including V. parahaemolyticus, V. haveryi, V. vulnificus, V. cholerae, and V. alginolyticus [20]. A similar finding was reported in India, where V. parahaemolyticus and V. alginolyticus were the dominant Vibrio species isolated from diseased shrimp [21]. A study of P. monodon grow-out ponds in Sri Lanka showed a strong correlation between the percentage occurrence of WFS and the total Vibrio count in the gut, hepatopancreas, and hemolymph, where the dominant Vibrio species were V. alginolyticus and V. fluvialis [22]. A strain of V. cholerae containing virulence genes (ompU, hlyA, and toxR) was isolated from freshwater-reared L. vannamei exhibiting WFS from China, and white fecal string formation was also reproduced by immersion challenge using this strain [12]. However, this procedure has never been repeated by other researchers even though WFS remains problematic worldwide. It is possible that the reported V. cholerae was a different Vibrio species, since the phylogenetic tree of Vibrio species based on the 16S rRNA sequence is less reliable [1]. The induction of WFS under laboratory conditions using an individual bacterium has never been successful. A theory of WFS etiology as a complex relationship between more than one pathogen related to shrimp gut dysbiosis was then proposed.
3.2. Microbiome Analysis of WFS-Affected Shrimp
Microbiome analysis provides intensive detail on the species and quantity of microbes residing in a certain condition. This technique helps us to understand the changes in the gut microbiome that are likely to have an impact on shrimp health. A differential abundance of particular microbial taxa or the reduction in bacterial diversity within the gut may be linked to the onset of pathogenesis since the gut microbiota and the host immune system are connected [23]. Intestinal microbiota dysbiosis or imbalance of the microbial community in the GI tract has been suggested to be strongly associated with the occurrence of WFS. Transplantation of gut microbiota via reverse gavage from WFS-affected donors induced white fecal sting formation in 36.7% of healthy recipient shrimp [3]. Although a 100% replication rate was not achieved, this study provided some evidence that gut dysbiosis was connected to WFS. Several studies have found that the intestinal microbiome of shrimp suffering from WFS has low α-diversity and is less homogeneous [24]. In addition, opportunistic pathogens, such as Vibrio, Candidatus Bacilloplasma, Phascolarctobacterium, Photobacterium, and Aeromonas, were overrepresented in WFS-affected shrimp, while the beneficial bacteria of shrimp, including Shewanella, Chitinibacter, Rhodobacter, Paracoccus, and Lactococcus were more abundant in healthy shrimp [3,4,24]. Comparable findings were reported in a case of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND), showing an increase in Candidatus bacilloplasma abundance along with several Vibrio clusters [25]. Nevertheless, the relative abundance of Candidatus Bacilloplasma may have contributed to the reduction in other taxa in the shrimp gut, as it is a commensal bacterium commonly found in several aquatic invertebrates, and this genus is well adapted to the gut environment [23,26]. Metagenomic analysis was conducted on WFS-affected L. vannamei reared in greenhouse ponds in China. V. tubiashii and V. harveyi were identified from the analysis of the operational taxonomic unit, and the expression of innate immune pathways related to bacterial infection (Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs)) were found, suggesting bacterial involvement during disease progression [27,28]. Furthermore, the authors also investigated gut predator–prey interactions and summarized that the population of gut phagotrophs and Bdellovibrio and similar organisms (BALOs; shrimp gut commensals that predate on Gram-negative bacteria, especially Vibrio spp.) were significantly reduced in WFS-affected shrimp [27].
In Indonesia, the association between the bacterial communities in shrimp (or ponds) affected by WFS and deteriorating water quality (decreased pH, dissolved oxygen, and increased organic matter) was evaluated. In WFS-affected farms, microbiome analysis showed similarities in the bacterial communities of white fecal strings and water fractions of the affected ponds [14]. In the WFS pondwater, Alteromonas, Marinomonas, Photobacterium, Pseudoalteromonas, and Vibrio were the dominant populations. In contrast, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas were dominant in healthy shrimp, and bacteria related to the nitrification process, including Exiguobacterium, Halomonas, Psychrobacter, Salegentibacter, and Sulfitobacte, dominated the bacterial communities in the pondwater of healthy individuals [14].
In addition to the bacterial microbiome, communities of gut eukaryotes have been studied in shrimp farms in China. The diversity of the gut eukaryotes also decreased, whereas the number of pathogenic eukaryotes increased. Gut parasite taxa, including Pseudoperkinsidae, parasitic Prostapa, Malassezia sp., and Acineta sp., are positively associated with disease exacerbation [29]. Another study on WFS-affected L. vannamei showed that the opportunistic pathogens Basidiomycota and Ascomycota (affiliated with fungi) were overrepresented, while Desmodesmus, the common commensals in healthy individuals, were underrepresented in WFS-affected shrimp. The authors suggested that shrimp with weaker WFS may have less ability to exclude these external invaders. Alternatively, the abundance of these opportunistic pathogens may be due to the higher eutrophic water found in the WFS-affected ponds [30]. These studies suggest that WFS inspection is possible by observing changes in the gut eukaryotic population.
In essence, several microbiome studies have indicated that the reduction in bacterial diversity and the dominance of opportunistic pathogens in the gut or culture water are significant characteristics of WFS. Metagenome and metabolome analyses suggest that alterations in the microbial communities affect the functional pathways and metabolic profiles, which may contribute to disease [3]. However, the increase in particular gut microbes, such as Candidatus Bacilloplasma or Bdellovibrio due to the imbalanced condition of the gut environment may only reflect the unhealthy status of the gut health rather than a specific indication of WFS. Although the hypothesis of intestinal dysbiosis has been proposed, it is difficult to differentiate between the cause and effect of an outbreak because followup studies involving gut supplementation and/or gnotobiotic organisms are lacking [23]. Furthermore, EHP, an important pathogen associated with WFS, was not tested in these studies.
3.3. Association between EHP and Vibriosis in WFS Occurrence
When EHP was first investigated in cultured shrimp, EHP microsporidium was suggested as a sole cause of WFS. Soon after, this hypothesis was not fully accepted because a high prevalence of EHP was also detected by PCR and in situ hybridization in shrimp samples not exhibiting WFS [31]. In addition, an experimental challenge with a high dose of EHP failed to produce the clinical signs representing WFS [32]. However, more evidence supports the association between WFS and EHP. From Indonesian farms, L. vannamei exhibiting WFS presented with packed EHP spores in their fecal string, midgut, and rod-shaped bacteria, presumably Vibrio accompanied by septic hepatopancreatic necrosis (SHPN), which were histologically observed in HP tubules [10]. In Vietnamese farms, P. monodon exhibited WFS that manifested with EHP [33]. Additionally, all the gut samples of the WFS-affected shrimp collected in India and Vietnam were EHP-positive, and spores were detected in and around the transformed microvilli, while approximately 90% of the normal gut shrimp from WFS-affected farms were EHP-positive [34]. Caro et al. [35] found that all WFS-affected shrimp from two different geographical locations (Indonesia and Venezuela) were EHP-positive by real-time PCR and histology and that the EHP loads were significantly higher in the affected ponds than in the non-WFS ponds. This implies that WFS is associated with a synergetic effect between EHP infection and other pathogens. It is possible that EHP weakens the shrimp from the disruption of the infected hepatopancreatic cells. The sloughed cells and the exposed basement membrane are favorable to subsequent infection of opportunistic pathogens, especially Vibrio bacteria already present in GI tract [36]. Therefore, the concept of “pathobiome” was introduced. Bass et al. [37] suggested that the pathogenesis of a disease may not be solely linked to the relative abundance of a particular taxon but rather to the change in interactions between multiple taxa, host-associated symbionts, and/or the host itself. The complexity of the prokaryotic–eukaryotic pathobiome has been suggested as a cause of WFS in a study of L. vannamei cultured in Thailand. EHP-infected populations present or absent from the WFS were investigated. The quantity of EHP was much higher in the WFS group, and microbiome analysis revealed that bacteria from the genera Vibrio and Propionigenium were predominant in the intestinal tract of EHP–WFS-affected shrimp, while the non-WFS group had higher bacterial diversity [2].
WFS cannot be reproduced in the laboratory using a single pathogen, such as EHP, but may be associated with multiple pathogens, including Vibrio species. A challenging study with specific strains of V. sinaloensis or V. parahaemolyticus in L. vannamei by reverse gavage produced histopathological lesions of the hepatopancreas comparable to naturally occurring WFS but failed to induce white fecal strings [4]. However, white fecal strings were induced by feeding shrimp with HP from diseased shrimp [34] or by gut microbiome transplantation from WFS donors [3]. In addition, the synergetic effects of EHP and vibriosis were proposed by Caro et al. [1], which induced white feces formation in laboratory-produced EHP-infected shrimp challenged with a specific strain of V. parahaemolyticus isolated from WFS-affected shrimp.
4. Control Strategies
To date, specific drugs or treatments for WFS are not available. The management mainly focuses on implementing good aquaculture practices to reduce the risk of WFS occurrence, which are the use of unhealthy seed, poor water quality, gut dysbiosis, EHP infection, and a high Vibrio load in shrimp gastrointestinal tracts and the environment [2,38]. In terms of pathogen exclusion, preventive measures for WFS aim to eliminate EHP spores and limit the number of total Vibrio in the culture system. The combination of physical, chemical, and biological control is recommended for WFS management.
4.1. Physical Control
Physical methods involve manipulating physiological conditions to eliminate or inactivate the disease agent and using physical barriers to prevent contact between the disease agent and the host. Standard practices, such as pond drying prior to stocking and manually removing pond sediment during culture are recommended to improve the water quality and minimize pathogen growth. Strict biosecurity measures are needed for EHP since no effective therapeutic drug is available, and prevention may be the only option [39]. EHP PCR-negative post larvae (PL) should be confirmed before shrimp stocking. Fresh or live feed, for example, polychaetes from WFS-affected ponds, have also been reported to be EHP-positive by PCR [40]. Fresh feed was frozen at −20 °C for at least 48 h or at 70 °C for 15 min [39]. Munkongwongsiri et al. [41] stated that EHP spores are highly sensitive to heat inactivation at 75 °C for one minute.
4.2. Chemical and Biological Control
The general objective of chemical and biological approaches to prevent WFS is to limit the number of pathogens, especially EHP and Vibrio bacteria in the culture system. The use of inorganic and organic substances to reduce the numbers of EHP spores and the Vibrio population in ponds or shrimp has been widely implemented. Adding quick lime (CaO) to increase the environmental pH to 9, to induce EHP spore germination, and applying chlorine or potassium permanganate (KMnO4) to inactivate the spores before shrimp stock is also recommended [42]. Once EHP is excluded from the system, Supono et al. [19] suggested that total Vibrio count in culture water should not exceed 104 CFU mL−1 to reduce the risk of WFS occurrence. Several studies have shown promising results in controlling Vibrio spp. isolated from WFS-affected shrimp. Shrimp that suffered from WFS recovered without recurrence until harvest, after receiving extracted lysozyme derived from egg white for five days. This enzyme inhibits the growth of Vibrio spp. both in vitro and in vivo and helps stimulate the immune response of shrimp [43]. Passive immunization by feeding immunoglobulin Y (IgY) derived from egg yolk can significantly reduce the numbers of V. harveyi and V. parahaemolyticus in shrimp [44]. Subsequently, Keetanon et al. [45] demonstrated the implementation of egg yolk IgY to inhibit V. parahaemolyticus isolated from WFS-affected shrimp. The severity of hepatopancreas sloughing after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge was inversely related to the dosage of IgY administration [45]. The use of Bacillus subtilis probiotics to reduce the risk of WFS is also suggested [38]. A study in India revealed that feeding with commercial probiotics containing lactic acid-producing Bacillus, digestive enzymes, and organic acids (Gut Probiotics, V Sthiraa Bioscience, India) at 5 g kg−1 helped shrimp recover from WFS [46]. Several plant extracts have also shown inhibitory effects against Vibrio spp. isolated from WFS-affected shrimp. L. vannamei fed galangal extract Alpinia galanga Linn. showed lower total Vibrio count and incidence of EHP found in the intestinal tracts, which might help reduce the incidence of WFS under culture conditions [47]. Leaf flower Phyllanthus urinaria L. shows antibacterial activity against V. harveyi and V. alginolyticus isolated from WFS-affected shrimp [20]. Palanikumar, et al. [48] assessed the possibility of herbal medicines, including lemon Citrus limon, garlic Allium sativum, ginger Zingiber officinale, doub palm Borassus flabellifer, and black gram Vigna mungo in reducing EHP infestation in culture shrimp and may eventually treat WFS. The active compounds, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, pigments, phenolics, terpenoids, tannins, and glycosides found in these plants have been reported to have a hepatoprotective effect, promote growth, have antioxidant ability, and have the capability of eliminating the parasite by interfering with its metabolism. However, these herbal medicines have not been specifically evaluated under experimental conditions for WFS treatment.
In Thailand, the strategy of combating WFS is usually initiated by stopping feeding for a few days and changing the type of feed to a higher quality protein source. Organic acids may be applied, followed by supplementation with herbal extracts, such as galangal or curcumin extracts to reduce the number of EHP and Vibrio. Subsequently, probiotics, such as Bacillus or Lactobacillus are administered to colonize and compete with bacterial pathogens residing in the gut. Some farmers also apply chemical treatments to reduce the total number of bacteria in the water column [49]. However, there is no fixed formula for this multifactorial disorder in shrimp cultures. Only strict biosecurity and good aquaculture, such as providing good quality feed, good feeding management, and maintaining good water quality during culture, may reduce the risk of WFS occurrence. Routinely checking for the presence of ATM in the shrimp intestinal tract may help in early diagnosis, leading to prompt management. Other supplements, such as enzymes, probiotics, or herbal medicines, are choices that have not been completely guaranteed to cure WFS.
5. Conclusions
WFS is a gastrointestinal disorder of shrimp, associated with Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) and other bacteria, such as Vibrio and Propionigenium species. The pathogenesis is suggested to be that EHP induces disruption of the hepatopancreatic tubules, and sloughing cells that move through the gastrointestinal tract aid opportunistic bacteria growth. The change in the microbial community may result in gut dysbiosis, metabolic disorder, and eventually white fecal formation. Consequently, infected shrimp show reduced feed consumption and growth rate, along with hepatopancreatic discoloration. Although the disease leads to severe economic and production losses in several shrimp farming countries, ideal treatments and control methods have not been found for WFS. Therefore, strict biosecurity systems to eliminate EHP spores and manage the total Vibrio number have been suggested for WFS prevention.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, P.P.; writing—review and editing, J.E.H.; visualization, P.P. and J.E.H.; supervision, J.E.H.; project administration, P.P. and J.E.H.; funding acquisition, J.E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF2019R1C1C1006212) and the Ministry of Education (NRF-2022R1I1A3066435).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aranguren Caro, L.F.; Mai, H.N.; Cruz-Florez, R.; Marcos, F.L.A.; Alenton, R.R.R.; Dhar, A.K. Experimental reproduction of White Feces Syndrome in whiteleg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prachumwat, A.; Munkongwongsiri, N.; Eamsaard, W.; Lertsiri, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Stentiford, G.D.; Sritunyalucksana, K. A potential prokaryotic and microsporidian pathobiome that may cause shrimp white feces syndrome (WFS). bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiong, J.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H. Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durai, V.; Gunalan, B.; Johnson, P.M.; Maheswaran, M.; Pravinkumar, M. Effect on white gut and white feces disease in semi-intensive Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp culture system in south Indian state of Tamilnadu. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wan, X.; Xie, G.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Insights into the histopathology and microbiome of Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, suffering from white feces syndrome. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriurairatana, S.; Boonyawiwat, V.; Gangnonngiw, W.; Laosutthipong, C.; Hiranchan, J.; Flegel, T.W. White feces syndrome of shrimp arises from transformation, sloughing and aggregation of hepatopancreatic microvilli into vermiform bodies superficially resembling gregarines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitamadee, S.; Prachumwat, A.; Srisala, J.; Jaroenlak, P.; Salachan, P.V.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Itsathitphaisarn, O. Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, B.; Haq, M.B.; Prathap, T.; Meetei, K.; Baharlooeian, M.; Sureandiran, B.; Tiwary, C. Surveillance of White feces syndrome (WFS) in penaeid shrimps captured from the Tuticorin group of islands near an area of semi-intensive aquaculture activity. JICR 2020, 12, 2051–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.F.; Pantoja, C.R.; Redman, R.M.; Han, J.E.; Tran, L.H.; Lightner, D.V. Development of in situ hybridization and PCR assays for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), a microsporidian parasite infecting penaeid shrimp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 130, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.; Han, J.E.; Aranguren, L.F.; White-Noble, B.; Schmidt, M.M.; Piamsomboon, P.; Risdiana, E.; Hanggono, B. Dense populations of the microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) in feces of Penaeus vannamei exhibiting white feces syndrome and pathways of their transmission to healthy shrimp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 140, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkongwongsiri, N.; Prachumwat, A.; Eamsaard, W.; Lertsiri, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Stentiford, G.D.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Propionigenium and Vibrio species identified as possible component causes of shrimp white feces syndrome (WFS) associated with the microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 192, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wen, L.; He, S.; Lu, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, B. Vibrio cholerae: A causal agent for white feces syndrome in freshwater cultured whiteleg shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Isr. J. Aquac. 2015, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Limsuwan, C. White Feces Disease in Thailand. Buletines Nicovita Magazine, Lima, April–June 2012; 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alfiansah, Y.R.; Peters, S.; Harder, J.; Hassenrück, C.; Gärdes, A. Structure and co-occurrence patterns of bacterial communities associated with white faeces disease outbreaks in Pacific white-leg shrimp Penaeus vannamei aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Peng, S.; Chen, D.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, K. Low lethal doses of Streptococcus iniae caused enteritis in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piamsomboon, P.; Tanpichai, P.; Wongtavatchai, J. Enteritis associated with subclinical infection of Streptococcus iniae in juvenile Asian seabass Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790). J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Avunje, S.; Tandel, R.S.; Sandeep, K.P.; Panigrahi, A. Biocontrol of luminous vibriosis in shrimp aquaculture: A review of current approaches and future perspectives. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 25, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboon, M.; Purivirojkul, W.; Limsuwan, C.; Chuchird, N. Effect of Vibrio spp. in white feces infected shrimp in Chanthaburi, Thailand. J. Fish. Environ. 2012, 36, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Supono, S.; Wardiyanto, W.; Harpeni, E. Identification of Vibrio sp. as a cause of white feces diseases in white shrimp Penaeus vannamei and handling with herbal ingredients in East Lampung Regency, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux 2019, 12, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, M.U.; Dao, T.T.U.; Tu, T.D. Antimicrobial activity of herbal extracts against Vibrio spp. bacteria isolated from white feces syndrome on white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in some provinces in the mekong delta. CTUJS 2021, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastan, S. Incidences of white feces syndrome (WFS) in farm-reared shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, Andhra Pradesh. IAJPS 2015, 5, 3044–3047. [Google Scholar]
- Kumara, K.; Hettiarachchi, M. White faeces syndrome caused by Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio fluvialis in shrimp, Penaeus monodon (Fabricius 1798)-multimodal strategy to control the syndrome in Sri Lankan grow-out ponds. Asian Fish Sci. 2017, 30, 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, C.C.; Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; van der Giezen, M. Understanding the role of the shrimp gut microbiome in health and disease. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Weng, S.; Yan, Q.; He, J. Intestinal bacterial signatures of white feces syndrome in shrimp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Ng, T.H.; Wu, J.-H.; Chen, J.-W.; Wang, H.-C. Microbiome dynamics in a shrimp grow-out pond with possible outbreak of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostanjsek, R.; Strus, J.; Avgustin, G. “Candidatus Bacilloplasma,” a novel lineage of Mollicutes associated with the hindgut wall of the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber (Crustacea: Isopoda). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5566–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, X.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Gut interkingdom predator-prey interactions are key determinants of shrimp health. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yu, W.; Xuan, L.; Tao, Z.; Xiong, J. Integrating molecular and ecological approaches to identify potential polymicrobial pathogens over a shrimp disease progression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Yu, W.; Dai, W.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Ou, C. Quantitative prediction of shrimp disease incidence via the profiles of gut eukaryotic microbiota. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Gut eukaryotic disease-discriminatory taxa are indicative of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) white feces syndrome. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangprasittipap, A.; Srisala, J.; Chouwdee, S.; Somboon, M.; Chuchird, N.; Limsuwan, C.; Srisuvan, T.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. The microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei is not the cause of white feces syndrome in whiteleg shrimp Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritunyalucksana, K. Research update on emergent shrimp pathogens in Thailand. Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Promotion of Sustainable Aquaculture, Aquatic Animal Health, and Resource Enhancement in Southeast Asia, Iloilo City, Philippines, 25–27 June 2019; Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center Aquaculture Department: Tigbauan, Philippines, 2021; p. 217. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, N.; Ha, D.; Thuy, N.; Lien, V. Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei Parasitizing on tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) infected by white feces culture in Vietnam, has been detected. Agric. Rural Dev. Sci. Technol. 2010, 12, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Makesh, M.; Alavandi, S.; Vijayan, K. Clinical manifestations of White feces syndrome (WFS), and its association with Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in Penaeus vannamei grow-out farms: A pathobiological investigation. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, L.F.A.; Mai, H.N.; Pichardo, O.; Cruz-Flores, R.; Hanggono, B.; Dhar, A.K. Evidences supporting Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei association with white feces syndrome in farmed Penaeus vannamei in Venezuela and Indonesia. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2020, 141, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranguren, L.F.; Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F. Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) is a risk factor for acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) and septic hepatopancreatic necrosis (SHPN) in the Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2017, 471, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; Wang, H.-C.; Koskella, B.; Tyler, C.R. The pathobiome in animal and plant diseases. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniasih, R.A.; Suwiryono, J.; Penataseputro, T. White feces syndrome. Volume II. Crustacean and Mollusks Diseases. In Aquaculture Pathophysiology; Kibenge, F.S.B., Baldisserotto, B., Chong, R.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 235–242. ISBN 978-0-323-95434-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chaijarasphong, T.; Munkongwongsiri, N.; Stentiford, G.D.; Aldama-Cano, D.J.; Thansa, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Itsathitphaisarn, O. The shrimp microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP): Biology, pathology, diagnostics and control. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrina, D.; Prayitno, S.B.; Haditomo, A.H.C.; Latritiani, R.; Sarjito, S. Detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) DNA in the polychaetes from shrimp ponds suffering white feces syndrome outbreaks. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkongwongsiri, N.; Aldama-Cano, D.J.; Suebsing, R.; Thaiue, D.; Prasartset, T.; Itsathitphaisarn, O.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) spores are inactivated in 1 min at 75 °C. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldama-Cano, D.J.; Sanguanrut, P.; Munkongwongsiri, N.; Ibarra-Gámez, J.C.; Itsathitphaisarn, O.; Vanichviriyakit, R.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Thitamadee, S. Bioassay for spore polar tube extrusion of shrimp Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP). Aquaculture 2018, 490, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraprayote, W.; Pumpuang, L.; Tepaamorndech, S.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Phromson, M.; Jangsutthivorawat, W.; Jeamsripong, S.; Visessanguan, W. Suppression of white feces syndrome in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, using hen egg white lysozyme. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, D.; Sun, J.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Passive immune-protection of Litopenaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections with anti-Vibrio egg yolk (IgY)-encapsulated feed. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keetanon, A.; Chuchird, N. Effects of Antibody IgY on Growth, Survival, Immune Responses and Prevention to Vibrio parahaemolyticus Causing White Feces Syndrome and White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection in Pacific White Shrimp in Laboratory Conditions; Kasetsart University: Bangkok, Thailand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pravinkumar, M.; Ponraj, J.G.; Ravi, A.V. Efficacy of Evaluation of Gut Probiotics against White Gut and White Feces Disease in Litopenaeus vannamei Shrimp Aquaculture Systems in Two Different Geographical Regions of Andhra Pradesh. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chaweepack, T.; Muenthaisong, B.; Chaweepack, S.; Kamei, K. The potential of galangal (Alpinia galanga Linn.) extract against the pathogens that cause white feces syndrome and acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Int. J. Biol. 2015, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, P.; Wahjuningrum, D.; Abinaya, P.; Babu, M.M.; Citarasu, T. Usage of plant natural products for prevention and control of white feces syndrome (WFS) in Pacific whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei farming in India. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaweepack, T. The Use of Galangal Extract in Combination with Organic Acid Effectively Reduce the Number of Vibrio and the Presence of ATM in Cultured Shrimp; The Research report of the Agricultural Research Development Agency (Public Organization); Agricultural Research Development Agency: Bangkok, Thailand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).