Abstract
The Pseudomonas putida strain was primarily identified and tested in vitro against antibiotic sensitivity for several antibiotics using the disc diffusion method. This isolate was also tested against sensitivity to carvacrol oil (c) and formic acid (f). The genotyping of Pseudomonas spp. and virulotyping for P. putida isolate was carried out and verified by 16S rDNA-PCR amplification. Furthermore, we assessed the efficacy of carvacrol oil and formic acid in vivo for treatment of P. Putida infection. For the in vivo challenge, 180 fish (Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus) were divided into six groups: (G1: control (unchallenged), G2: carvacrol prophylaxis (3 g/kg), G3: formic acid prophylaxis (5 mL/kg), G4: control positive (challenged), G5: carvacrol treatment (3 g/kg), and G6: formic acid treatment (5 mL/kg); 30 fish per group) with three replicates. Following the challenge, nitric oxide and lysozyme activity were measured as essential indicators for fish immunity. The antioxidant parameters including SOD and catalase were computed to reflect the antioxidant status. Furthermore, relative percent survival (RPS) and mortality percent were evaluated to indicate functional immunity. The findings of the antibiotic sensitivity test showed that ciprofloxacin exhibited the largest inhibition zone. Additionally, formic acid (f) displayed the greatest inhibition zone compared to carvacrol oil (c) and was more effective in stimulating the immune-antioxidant response compared to carvacrol oil. The tested exotoxin A (tox A), exoenzyme S (exo S), and the nan1 associated-virulence genes were identified in the P. putida isolate. Overall, the current study verified the virulence of P. putida and highlighted the promising role of dietary addition of formic acid for enhancing the immune-antioxidant indicators and for mitigating P. putida infection. Future studies could be devoted to this field.
1. Introduction
Aquaculture plays a crucial role in offering highly nutritious food rich in minerals and vitamins (FAO 2020). Oreochromis niloticus is the most essential commonly cultivated species in Egypt. It is characterized by a high consumption rate and a fast growth rate, and it is a rich source of protein with economic value. It is affected by various infections acquired from its aquatic ecosystem [1,2,3]. With progress in aquaculture industry, many stressful conditions arise, particularly the spread of many bacterial infections [4].
Among bacterial diseases, Pseudomonas spp. is considered one of the most pathogenic fish pathogens, and is responsible for ulcer-type diseases including ulcerative syndrome [5]. Pseudomonas spp. has been described as one of the most common bacterial infectious agents of cultured fish and has been reported to cause stress-related diseases in freshwater fish, especially under farming conditions [6]. Several studies have reported almost 100% mortality due to infection with Pseudomonas spp. in rainbow trout, sea bream, sea bass and ayu in farm settings [7]. Pseudomonas spp. infection is characterized by petechial hemorrhage, darkness of the skin, detached scales, abdominal ascites, and exophthalmia in rainbow trout, African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [8,9,10] (Ilhan et al., 2006; Hanna et al., 2014; Omar et al., 2017). Among pseudomonas spp, P. putida is a pathogenic bacterium that invades O. niloticus and causes exophthalmia, ascites, and ulceration on the fish body [11]. It is also known as a major pathogen in rainbow trout fisheries [8,12]. P. putida is an opportunistic Gram-negative pathogen that normally occurs in aquatic environments and as a part of the normal gut flora of healthy fish. It belongs to the family pseudomonaceae, genus pseudomonas [13].
Traditionally, antibiotics are applied to combat bacterial diseases, but they are useless in this case due to an emerging drug resistance [14]. However, FAO/WHO reports recommend the importance of minimizing the usage of chemotherapeutic agents for therapy in aquaculture because of their hazardous influence on the health of fish and their consumers. Currently, researchers have detected the antibacterial activity of many neutracuticals and their essential oils for their safety, availability, and efficiency [15,16]. Carvacrol oil has been reported to modulate the immune-antioxidant response in O. niloticus and strengthen the fish’s resistance to microbial infection [17]. Among organic acids, formic acid has traditionally been utilized as a storage preservative in feed ingredients to prevent product deterioration caused by microbes [18]. Dietary inclusion of formic acid boosts growth performance and the bioavailability of minerals, including phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, and iron in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer), Caspian Sea brown trout (Salmo trutta caspius), and sea bream (Pagrus major) [19,20]. It has also been utilized as a dietary supplement in shrimp feed for controlling Vibrio outbreaks in shrimp aquaculture systems [21].
Few articles address the application of formic acid and carvacrol oil as natural antibacterial agents in fish. Therefore, the current perspective was designed to (1) assess the in vitro antibacterial activity of carvacrol oil and formic acid towards P. putida to compare the best one in inhibiting the bacterium, (2) identify the bacterium virulence genes, and (3) investigate the influence of a formic acid-enriched diet on the immune-antioxidant response and disease resistance in O. niloticus challenged with P. putida.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolate
2.1.1. Biochemical Identification of P. putida
This study was performed on P. putida which was previously isolated from moribund O. niloticus at the Department of Aquatic Animal Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University. It was identified by conventional biochemical tests and the VITEK 2-C15 automated system for bacterial identification (BioMérieux, Craponne France) according to the manufacturer’s instructions as described by [22,23] at the Microbiology and Immunology Department, National Research Centre (NRC), Dokki, Giza, Egypt.
2.1.2. Antibiotic Resistance Test for P. putida
The Pseudomonas putida strain was tested against antibiotic sensitivity for several antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, Ciprofloxacin, Enrofloxacin, Erythromycin, Gentamicin Norfloxacin, Oxalinic acid, and Oxytetracycline) using the disc diffusion method. The interpretations of the zones of inhibition were estimated according to the table of standards given by (Oxiod Manual) to determine if the tested bacterial species was resistant or sensitive to the antibiotics used.
Antimicrobial resistance of the P. putidia was determined using the Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion method on Mueller Hinton Agar (Oxoid, UK). Ten antibiotic disks (Oxoid, UK) were used in this study including amoxicillin (Ax) (25 μg), ampicillin (AM) (10 μg), Chloramphenicol (C) (30 μg), Ciprofloxacin (CIB) (5 μg), Enrofloxacin (ENR) (10 μg), Erythromycin (E) (15 μg), Gentamicin (GN) (10 μg), Norfloxacin (NOR) (10 μg), Oxalinic acid (OA) (2 μg), and Oxytetracycline (OT) (30 μg). The zone of inhibition was measured and compared to the world standards (CLSI, 2010) and was reported as Resistant (R), Intermediate (I), and Sensitive (S). Isolates were considered multiple drug-resistant (MDR) if the isolate was resistant to three or more separate antimicrobial classes [24].
2.1.3. Sensitivity of P. putida to Carvacrol Oil (c) and Formic Acid (f) Using Disc Diffusion Method
The carvacrol oil was dissolved in 10% aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). An inoculum containing 1.5 × 108 bacterial cells/mL of P. putida was spread on nutrient agar plates. Then, sterile filter papers (6 mm diameter) containing the tested samples (20 µg/disc) of carvacrol and formic acid were laid down on the surface of inoculated agar plates together with a negative control. The plates were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C and the zone of bacterial growth inhibition was measured as millimeter diameter [25].
2.1.4. Molecular Characterization
- A. 16S rDNA amplification
The suspected pseudomonus species were molecularly confirmed using PCR with specific 16S rDNA primers. Then, according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, bacterial DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN GmbH, Hilden, Germany). Strain was cultured in brain heart infusion broth (Oxid, Baasigngstoke, UK, Code: CM1135) and incubated under aerobic conditions, then, 200 μL of AL buffer was added to 200 μL of the sample and 20 μL QIAGEN protease into the bottom of a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. The tube was incubated at 56 °C for 10 min. A 200 μL of ethanol (96%) was added to the sample, and mixed again by pulse vortexing for 15 s. The sample was then washed and centrifuged according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Nucleic acid was eluted with the 100 μL of elution buffer provided in the kit to measure the quantity and purity.
- 2.
- B. Virulotyping
Specific primers targeting the enterotoxin gene (tox A, exo S, and nan1), genes were screened in the confirmed P. putida isolates [26]. Positive controls for P. putida were run alongside the tested isolates and were generously supplied by the Biotechnology Unit, Reference Laboratory for Veterinary Quality Control on Poultry Production, Animal Health Research Institute (Dokki, Giza, Egypt). The cycling conditions which were used in this study are listed in Table 1 and the oligonucleotide primers are listed in Table 2, and the cycling conditions which were used in this study are listed in Table 1. All PCR reactions were performed on a total volume of 50 μL reaction containing 13 μL of DNA template, 25 μL of Emerald Amp GT PCR mastermix, 1 μL of each primer (20 pmol concentration), and 6 μL of PCR grade water. PCR amplification was carried out in a T3 Thermal cycler (Biometra). The amplified product was electrophoresed on 1.5% agarose gel in 100 mL TBE buffer at room temperature, stained with 0.5 μg/mL ethedium bromide. A 100 bp plus DNA ladder (QIAGEN (USA) was used to determine the fragment size (Table 2). The gel was photographed by a GelDoc UVgel documentation system.

Table 1.
Cycling conditions of the different primers during PCR.

Table 2.
Oligonucleotide primers sequences.
2.2. Fish and Experimental Conditions
This study was conducted at the Department of Aquatic Animal Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt. All animal procedures were conducted following Egyptian laws of animal experimentation and with approval from Egypt’s Veterinary Organization, Ethical Committee for Animal Experiments, and maximum efforts were made to minimize suffering. Healthy O. niloticus fingerlings (n = 225), average initial weight 32 ± 0.05 g/fish, were purchased from Fish Research Unit, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Sharkia Province, Egypt. Fish were accustomed to the experimental diet in a lead-in period of 14 days to adapt to the laboratory conditions during which they were fed the control diet with a twice-daily feeding till satiety by hand at 9 am and 4 pm. The fish health status was checked before the experiment, according to CCoA (2005). Fish were stocked in fifteen monitored static water glass aquaria (80 cm × 40 cm × 30 cm) with a daily water exchange of approximately 25%. Water parameters were kept within recommended ranges during the observation period (pH = 7.2 ± 0.5; ammonia = 0.02 ± 0.001 mg/L; nitrite = 0.017 ± 0.001 mg/L; water temperature = 24 ± 2 °C; photoperiod 12:12 light: dark) according to APHA (1998). Ammonia and nitrite were computed using ammonia and nitrite assay kits (abcam company, Fremont, CA, USA, code: ab83360). Fish were observed daily for signs of disease or mortality and whole water changes were given to the aquaria twice weekly.
2.3. Experimental Challenge Test
Primarily, the isolate of P. putida was confirmed to be pathogenic for O. niloticus via the I/P route of inoculation, where the LD 50 value was estimated to be 1 × 105 CFU/fish. A total of 180 apparently healthy O. niloticus with an average body weight (32 ± 5 g) were allocated into six groups: G1, control fish fed basal diet devoid of any supplementations; G2 (carvacrol prophylaxis), O. niloticus that received a diet enriched with carvacrol oil (CO 3 g kg−1); G3 (formic acid prophylaxis), and fish that received a diet enriched with formic acid (FA 5 mL kg−1). The other three groups, G4 (control positive), G5 (carvacrol treatment), and G6 (formic acid treatment) were I/P challenged with a pathogenic isolate of P. putida and received the same diets, respectively, as the previously mentioned first three groups. The challenged groups (G4, G5 and G6) were intraperitoneally inoculated with a sub-lethal dose of P. putida at a dose of 0.1 mL cell suspension containing 1 × 105 cells/mL by using McFarland standard tubes. Each group was represented with 30 fish in three replicates (10 fish/replicate). Fish mortalities, behavioral alterations, and clinical signs were observed for two weeks according to [27].
2.4. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis
Blood samples were collected at the end of the feeding trial experimental challenge. Blood samples were collected without anticoagulants and allowed to clot at room temperature or in the refrigerator for an hour. The serum was separated by centrifuging at 3000× g for 15 min. The serum was transferred into dry, sterile, labeled, stoppered vials and used for determination of the immune-antioxidant parameters.
2.5. Measurement of Immune Parameters
Lysozyme activity was spectrophotometrically computed according to [28]. Meanwhile, nitric oxide level was estimated according to the protocol of [29], using MyBiosource Co. ELISA kits (Cat.MBS005953 and Nos. MBS282651) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6. Measurement of Antioxidant Parameters
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) concentration was computed as recorded by [30] using Velkova-Jordanoska et al.’s (2008) method. Catalase (CAT) activity was estimated following the method of [31] Hadwan (2018).
3. Results
3.1. Results of Antibiotic Resistance Test
The antimicrobial resistance of P. putida isolates to the 10 antibiotics is shown in Table 3. All isolates exhibited resistance to AM and AX, and susceptibility to CIP and CN. According to the results of the antibiotic sensitivity test, ciprofloxacin was the antibiotic of choice for treatment of O. niloticus experimentally infected with P. putida, as it showed the largest inhibition zone.

Table 3.
Results of antibiotic sensitivity test.
3.2. Sensitivity of P. putida to Carvacrol Oil (c) and Formic Acid (f)
The antimicrobial result shows that formic acid exhibited the most inhibition zones against P. putida. The purified compounds exhibited relatively stronger antibacterial activity compared to the carvacrol.
3.3. Genotyping Findings
As shown in Figure 1, P. putida positive isolates (100%) harbor the toxA, nan1, and exoS virulence-associated genes which were demonstrated by the production of a 352, 1316, and 504 bp amplicon respectively.
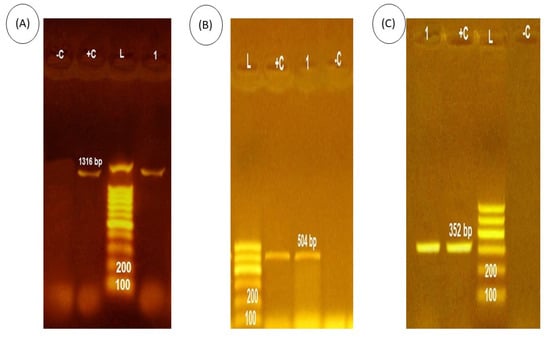
Figure 1.
PCR amplicons of P. putida toxin gene. (A) the expression of nan1, Lane L, 100-bp ladder, Lane +c, positive control. Lane 4 (−c), negative control. Lane 1, P. putida isolates which were positive for gene expression at 1316. (B) the expression of exoS, Lane L, 100-bp ladder, Lane +c, positive control. Lane (−c), negative control. Lane 1, P. putida isolates, which were positive for gene expression at 504 bp. (C) the expression of toxA, Lane L, 100-bp ladder, Lane +c, positive control. Lane 4 (−c), negative control. Lane 1, P. putida isolates, which were positive for gene expression at 352 bp.
3.4. Behavioral Alterations, Clinical Signs, and Mortalities following P. putida Challenge
Fish were exhibiting abnormal signs including being off their food, lethargy, and dullness. Moreover, the fish stayed near the bottom and corners of the aquarium with decreased swimming movement. The response to external stimuli and escape reflex was decreased in the challenged, treated fish while it was completely lost in the challenged, non-treated fish group. Post-mortem inspections showed severe erythema, skin erosions and severe fin rot with hemorrhage at site of inoculation, operculum, pectoral fins, and ventral aspect of the abdomen. Internally, the examined fish were characterized by a congested and enlarged kidney, congested liver, and distended gall bladder. The cumulative mortality is shown in Figure 2.
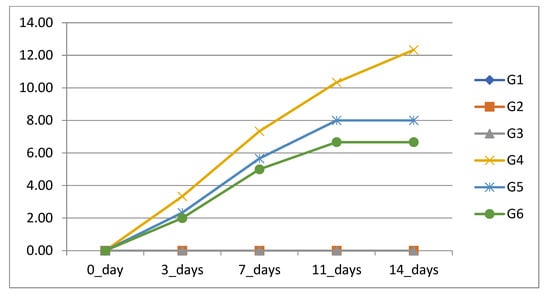
Figure 2.
Cumulative mortality percentage (CM%) of Nile tilapia in response to formic acid and carvacrol supplementation after challenge with P. putida.
3.5. Immunological Parameters Results
As depicted in Figure 3, both the CO-supplemented group (G2) and FA-supplemented group (G3) showed a significant rise in lysozyme activity relative to the control group (G1). Among P. putida- challenged fish, G6 and G5 showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) in the serum levels of lysozymes compared to G4 (Figure 3). Nevertheless, the NO level revealed insignificant elevation (p < 0.05) in comparison to the control. However, the NO level demonstrated a significant (p < 0.05) elevation in the G6 group (FA-treated), followed by G5 (CO-treated), and finally, G4 (control positive) compared to the control.
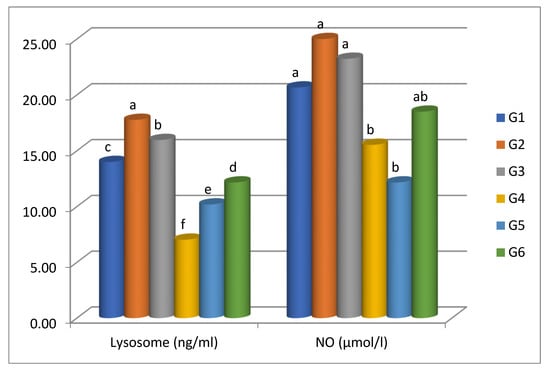
Figure 3.
Lysozyme and serum nitric oxide activities of Nile tilapia fed supplemented diets in formic acid and carvacrol post-challenge with P. putida. Bars represent the arithmetic mean; error bars are SD. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, Tukey’s multiple comparison tests) among groups.
3.6. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers Findings
The activity of the oxidative stress indicators of Nile tilapia are shown in Figure 4. The levels of SOD recorded a significant (p < 0.05) increase in G2 (carvacrol prophylaxis) and a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in G4 (control positive) in comparison to the control (G1). However, G6 (FA-treated) exhibited marked improvement in SOD levels followed by G5 (CO-treated) relative to G4. The CAT activity showed insignificant (p < 0.05) elevation in G2 and G3 compared to the control (G1). In contrast, among the challenged groups, G6 (FA-treated) and G5 (CO-treated) possessed the highest value for serum CAT activity compared to G4 (challenged, non-treated).
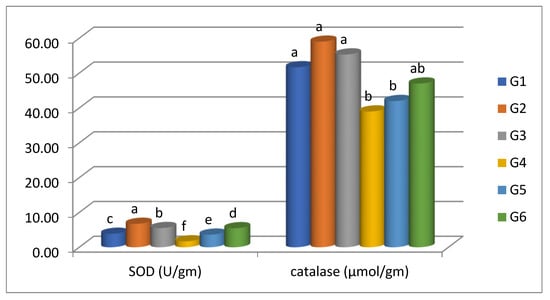
Figure 4.
SOD and CAT activities of Nile tilapia fed supplemented diets in formic acid and carvacrol post-challenge with P. putida. Bars represent the arithmetic mean; error bars are SD. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, Tukey’s multiple comparison tests) among groups.
4. Discussion
Fish are aquatic organisms of prime hazard for the occurrence of disturbance in the immune-antioxidant response induced by many stressors including bacterial infections [32]. P. putida is one of the pathogenic bacteria that affect juvenile O. niloticus and induce signs of dark pigmentation and petechial hemorrhage on various parts of the body surface [33]. Recent studies address and verify the significance of plant extracts for overcoming the alterations induced by bacteria [34,35]. Acidifiers are now widely used in aquaculture as an alternative to antibiotics [36,37]. The acidifiers supplemented in animal feeds are mainly compound acidifiers (CAs) which are generally composed of certain proportions of organic acids or the salts of these organic acids [38]. Organic acids (e.g., formic acid (FA), propionic acid (PA), acetic acid (ACA), butyric acid, citric acid, lactic acid (LA), malic acid, and sorbic acid) and their salts (e.g., sodium, potassium, and calcium) are used to promote growth performance, disease resistance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal health in aquatic animals [39,40]). Herein we focused on testing the antibiotic of choice for treatment of P. putida plus the in vitro antibacterial activity of carvacrol oil and formic acid against P. putida and detecting the bacterium virulence genes. Furthermore, we carried out a bacterial challenge with a trial for treatment of one such bacterial infection.
The current study demonstrated the first report to identify the virulence genes from P. putida that investigated the expression of three significant virulence genes in P. putida. Based on the study outcomes, P. putida was found to harbor the toxA, nan1, and exoS virulence-associated genes. The challenged group with P. Putida exhibited higher mortalities, oxidative stress, and an immuno-impairment. It is opined that the virulence elements detected in P. putida are responsible for the attachment, colonization, termination, and extent through host organs and tissue producing the pathogenic effect of the bacterium. Also, P. Putida owns genes that have the ability to encode algD, rhlI, exoS, exoU, lasR, toxA, aprA, lecA, toxR, lasI, oprI, oprL, rhlR, nan1, and lasB.
In the current study, formic acid was most powerful against P. putida strains in the sensitivity test compared to carvacrol. In line with this study, [40] approved that formic acid was the most potent organic acid against A. veronii strains in sensitivity tests among the various organic acids used (i.e., acetic acid, propionic acid and lactic acid). Similar findings were also obtained by [21] who have proven that formic acid inhibited the growth of five selected Vibrio species with the biggest inhibition zone compared with acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid. This may be because formic acid (FA) inhibits decarboxylases, reducing the carbon supply for Vibrio (C2–C10 monocarboxylic fatty acids) and thus inhibiting Vibrio growth (Adams and Boopathy, 2013).
Lysozymes are the essential defense molecules that reflect the immune status in freshwater fish and are characterized by strong antimicrobial activities [41,42]. The mechanism of action of nitric oxide is to deactivate the specific enzymes linked with macrophage cytotoxic reactions [43]. Herein, we report the occurrence of immunological impairment in the fish challenged with P. putida that was evidenced in a clear reduction in the computed non-specific immune biomarkers (lysozyme activity and nitric oxide) compared to other groups. It is opined that the detected virulence genes in P. putida are responsible for the suppressed immunological response in the challenged bacterial group. On the other hand, a potent immunological response was noted in the group enriched in formic acid, reflected in modulating the measured immune parameters. This could be related to its ability to inhibit the pathogenic bacteria proliferation as reported by [44,45].
The key antioxidant elements including catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzymes have a well-established role in relieving oxidative injury in the body through degenerating free radicals (hydrogen peroxide and superoxide radicals) and inducing potent immune response and antioxidant-protecting activity [46,47]. The current outcomes revealed the occurrence of oxidative damage evidenced by a clear decrease in the antioxidant parameters upon the challenging of fish with P. putida. The findings revealed a marked modulation in CAT and SOD in O. niloticus treated with dietary formic acid. In the same line, [40] reported activated antioxidative response in O. niloticus that received dietary formic acid. The functionality of formic acid in compromising the antioxidative capacity of O. niloticus is linked to its phenolic constituents that enhance immunity and strengthen the resistance against the occurrence of oxidative stress.
Monitoring mortalities and behavioral alterations following dietary supplementations and a bacterium challenge is essential to assessing the antimicrobial activity of the supplements. Herein, the group challenged with P. putida recorded the highest mortality rate. This could be attributed to the presence of virulence genes which are responsible for bacterium pathogenicity, as P. putida has been found to own numerous virulence elements. Many of these elements accelerate the processes of infection which are induced through infectious mediators. Meanwhile, the group supplemented with formic acid and challenged with P. putida exhibited noticeable improvement in fish behavior and a lower mortality rate. This could be attributed to the bacteriostatic or bactericidal effects of formic acid which can be achieved by interfering with nutrient transport by influencing the replication of deoxyribonucleic acid in the bacterial cell wall as reported by [48], or penetrating the cell walls of the bacterium causing its destruction by acidifying the cytoplasm as notified by [49].
5. Conclusions
Based on the study outcomes, ciprofloxacin was the antibiotic of choice for treatment of O. niloticus experimentally infected with P. putida. P. putida is highly pathogenic for O. niloticus and induces higher mortalities because of detecting toxA, nan1, and exoS virulence-associated genes. The dietary intervention of formic acid was more effective in mitigating P. putida infection compared to carvacrol oil, and also for improving the immune-antioxidant status. Further studies are encouraged to investigate the antifungal activity of formic acid and carvacrol and test their antimicrobial activity on various fish species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; methodology, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; software, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; validation, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; formal analysis, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; investigation, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; resources, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; data curation, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E., S.M.S. and M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.M.; writing—review and editing, H.H.M.; visualization, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E. and S.M.S.; supervision, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E. and S.M.S.; project administration, H.H.M., O.M.A., H.S.N., S.A.A.A., A.W.Z., P.E. and S.M.S.; funding acquisition, O.M.A. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding from Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/262).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by ZU-IACUC (approval code ZU-IACUC/2/F/354/2022, approved date is 27 November 2022 to 27 November 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/262), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia for their financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mahboub, H.H.; Shaheen, A. Prevalence, diagnosis and experimental challenge of Dermocystidium sp. infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Shaheen, A.A. Mycological and histopathological identification of potential fish pathogens in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Nada, H.S.; Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Ghanem, R.; Ahmed Ismail, T.; Abdel Rahman, A.N. Detection, diagnosis, Koch’s postulate, hepatorenal and antioxidant indicators for some systemic pathogenic fungi invading the liver and kidneys of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in Egypt with a histopathological approach. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2670–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Rahman, A.N.; Mansour, D.A.; Abd El-Rahman, G.I.; Elseddawy, N.M.; Zaglool, A.W.; Khamis, T.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Mahboub, H.H. Imidacloprid toxicity in Clarias gariepinus: Protective role of dietary Hyphaene thebaica against biochemical and histopathological disruption, oxidative stress, immune genes expressions, and Aeromonas sobria infection. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor oprL and toxA virulence genes and blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and tetA antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.R.; Dieguez, A.L.; Doce, A.; de la Roca, E.; de la Herran, R.; Navas, J.I.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L. Pseudomonas baetica sp. nov., a fish pathogen isolated from wedge sole, Dicologlossa cuneata (Moreau). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, B.; Stobie, M. Recovery of Serratia plymuthica and presumptive Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes from skin lesions in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), otherwise infected with enteric redmouth. J. Fish Dis. 1992, 15, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, A.; Kayis, S.; Capkin, E. Pseudomonas putida infection in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, M.I.; El-Hady, M.A.; Hanaa, A.A.; Elmeadawy, S.A.; Kenwy, A.M. Contribution on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 575–588. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, A.A.; Moustafa, E.M.; Abo-Remela, E.M.; Zayed, M.M. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, Pathogenecity and Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from Oreochromis niloticus. Life Sci. J. 2017, 14, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, S.S.A.; Abd El-Tawab, F.; Gharib, F.A. Parasitic protozoa accompanied with pseudomonas putida infection in cultured Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, M.; Atsuta, S.; Kobayashi, M. Pseudomonas fluorescens Isolated from the Diseased Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Kistato Arch. Exp. Med. 1989, 62, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, W.T.; Kim, J.H.; Jun, J.W.; Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Han, S.J.; Kwon, J.; et al. Genetic Characterization and Pathological Analysis of a Novel Bacterial Pathogen, Pseudomonas tructae, in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microorganisms 2019, 7, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartor, Y.; Taha, M.; Mahboub, H.; El Ghamery, M. Yeast species associated with diseased fish: Occurrence, identification, experimental challenges and antifungal susceptibility testing. Aquaculture 2018, 488, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Elsheshtawy, H.M.; Sheraiba, N.I.; Fahmy, E.M.; Masoud, S.R.; Mohamed, E.A.A.; Abdelnaeim, N.S.; Mohamed, D.I.; Ismail, T.A.; Ahmed, S.A.A. Dietary black cumin (Nigella sativa) improved hemato-biochemical, oxidative stress, gene expression, and immunological response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) infected by Burkholderia cepacia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Faggio, C.; Hendam, B.M.; Algharib, S.A.; Mansour, D.A.; Khamis, T.; Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Ismail, T.A.; Abdel Rahman, A.N. Immune-antioxidant trait, Aeromonas veronii resistance, growth, intestinal architecture, and splenic cytokines expression of Cyprinus carpio fed Apricot kernel-enriched diets. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 124, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Tartor, Y.H. Carvacrol essential oil stimulates growth performance, immune response, and tolerance of Nile tilapia to Cryptococcus uniguttulatus infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2020, 141, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, T.; Momeni, H.; Mesbah, M.; Tabandeh, M.R.; Khosravi, M. Effect of different levels of dietary acidifier ”sodium diformat” on the innate immune system and expression of growth and immunological related genes in Salmo trutta caspius. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 25, 2074–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedi Mostafaloo, A.; Hedayatifard, M.; Keshavarz, M.; Mohammadian, T. Effects of different levels of Sodium diformate and Formic acid salt on growth performance, digestive enzymes, and innate immunological parameters of Beluga (Huso huso) juveniles. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2021, 20, 879–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Boopathy, R. Use of formic acid to control vibriosis in shrimp aquaculture. Biologia 2013, 68, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, E.; Fracalanzza, S.; Teixeira, L.; Cardarelli-Leite, P. RFLP analysis of a PCR-amplified fragment of the 16S rRNA gene as a tool to identify Enterococcus strains. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Song, W.; Shao, Q.; Peng, X.; Xiao, J.; Hua, Y.; Owari, B.N.; Zhang, T.; Ng, W.K. Partial replacement of fish meal by fermented soybean meal in diets for black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii, juveniles. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2011, 42, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.T.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.T.; Giske, C.T.; Olsson-Lijiequist, B. Multidrug resistant, extensively drug resistant and pandrug resistant bacteria:An international expert proposal for interim standered definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majali, I.; Qaralleh, H.; Idid, S.Z.; Saad, S.; Susanti, D.; Althunibat, O. Potential Antimicrobial Activity of Marine Sponge Neopetrosia exigua. J. Basic Appl. Res. 2015, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, M.A.; Nour, M.S.; ElSheshtawy, N.M. Genetic identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes among different isolates. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Lucky, Z. Methods for the Diagnosis of Fish Diseases; Fish and Wildlife Service by Amerind Pub., Co.: New Delhi, India, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, A.E. Lysozyme assays. Tech. Fish Immunol. 1990, 1, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Broderick, M.; Fein, H. Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by using Griess reaction assay. Sensors 2003, 3, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkova-Jordanoska, L.; Kostoski, G.; Jordanoska, B. Antioxidative enzymes in fish as biochemical indicators of aquatic pollution. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 14, 235–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hadwan, H.M. Simple spectrophotometric assay for measuring catalase activity in biological tissues. BMC Biochem. 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, Y.H.; EL-Naenaeey, E.S.Y.; Abdallah, H.M.; Samir, M.; Yassen, M.M.; Abdelwahab, A.M. Virulotyping and genetic diversity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in aquaculture farms in Egypt. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.M.E.; Abou El-Ghiet, E.N.; Shaheen, A.A.; Abbass, A. Characterization of Pseudomonas Species Isolated from Tilapia “Oreochromis niloticus” in Qaroun and Wadi-El-Rayan Lakes, Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2010, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Elshopakey, G.E.; Mahboub, H.H.; Sheraiba, N.I.; Abduljabbar, M.H.; Mahmoud, Y.K.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Ismail, A.K. Ammonia toxicity in Nile tilapia: Potential role of dietary baicalin on biochemical profile, antioxidant status and inflammatory gene expression. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, H.; Faggio, C.; Mahboub, H.H.; Emam, M.A.; Kamel, S.; El Kammar, R.; Abdelnaeim, N.S.; Shaheen, A.; Tresnakova, N.; Matter, A. Mucuna pruriens seeds extract boosts growth, immunity, testicular histology, and expression of immune-related genes of mono-sex Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearlin, B.V.; Muthuvel, S.; Govidasamy, P.; Villavan, M.; Alagawany, M.; Ragab Farag, M.; Dhama, K.; Gopi, M. Role of acidifiers in livestock nutrition and health: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 104, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, X.; Zhai, S. Effect of Dietary Compound Acidifiers Supplementation on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, and Body Composition of Juvenile American Eel (Anguilla rostrata). Fishes 2022, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, S.W. Effects of dietary compound acidifiers supplementation on growth performance and intestinal health of juvenile American eels (Anguilla rostrata) cultured in cement tanks. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2021, 73, 1520998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, P.; Shamna, N.; Sahu, N.P. 2020. Acidifiers in aquafeed as an alternate growth promoter: A short review. Anim. Nutr. Feed. Technol. 2021, 20, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, R.M.; El-Murr, A.; Abd Elhakim, Y. Wessam El-Shahat, W. Aeromonas veronii detection in Egyptian fish farms with summer tilapia mortality outbreaks and the role of formic acid in limiting its spread. Aquac. Res. 2021, 53, 940–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wu, R.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Iden-tification and functional characterization of a c-typelysozyme from Fenneropenaeus penicillatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidian, G.; Lazado, C.C.; Mahboub, H.H.; Mohammadi-Aloucheh, R.; Proki’c, M.D.; Nada, H.S.; Faggio, C. Chemically and green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles alter key immunological molecules in Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) skin mucus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayfer, L.; Kerimoglu, B.; Yaparla, A.; Hodgkinson, J.W.; Xie, J.; Belosevic, M. Mechanisms of fish macrophage antimicrobial immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Naby, A.S.; Khattaby, A.-E.-R.-A.; Samir, F.; Awad, S.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. Stimulatory effect of dietary butyrate on growth, immune response, and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 254, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Khafaga, A.F. Natural co-infection of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus with Aeromonas hydrophila and Gyrodactylus cichlidarum experiencing high mortality during summer. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemouri, L.; Artur, Y.; Herbeth, B.; Jeandel, C.; Cuny, G.; Siest, G. Biological variability of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase in blood. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, Y.; Barouki, R. Repression of gene expression by oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 1999, 342, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derome, N.; Gauthier, J.; Boutin, S.; Llewellyn, M. The rasputin effect: When commensals and symbionts become parasitic. Adv. Environ. Microbiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silliker, J.H. Microbial Ecology of Foods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).