Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Seafood: Quantitative Literature Research Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
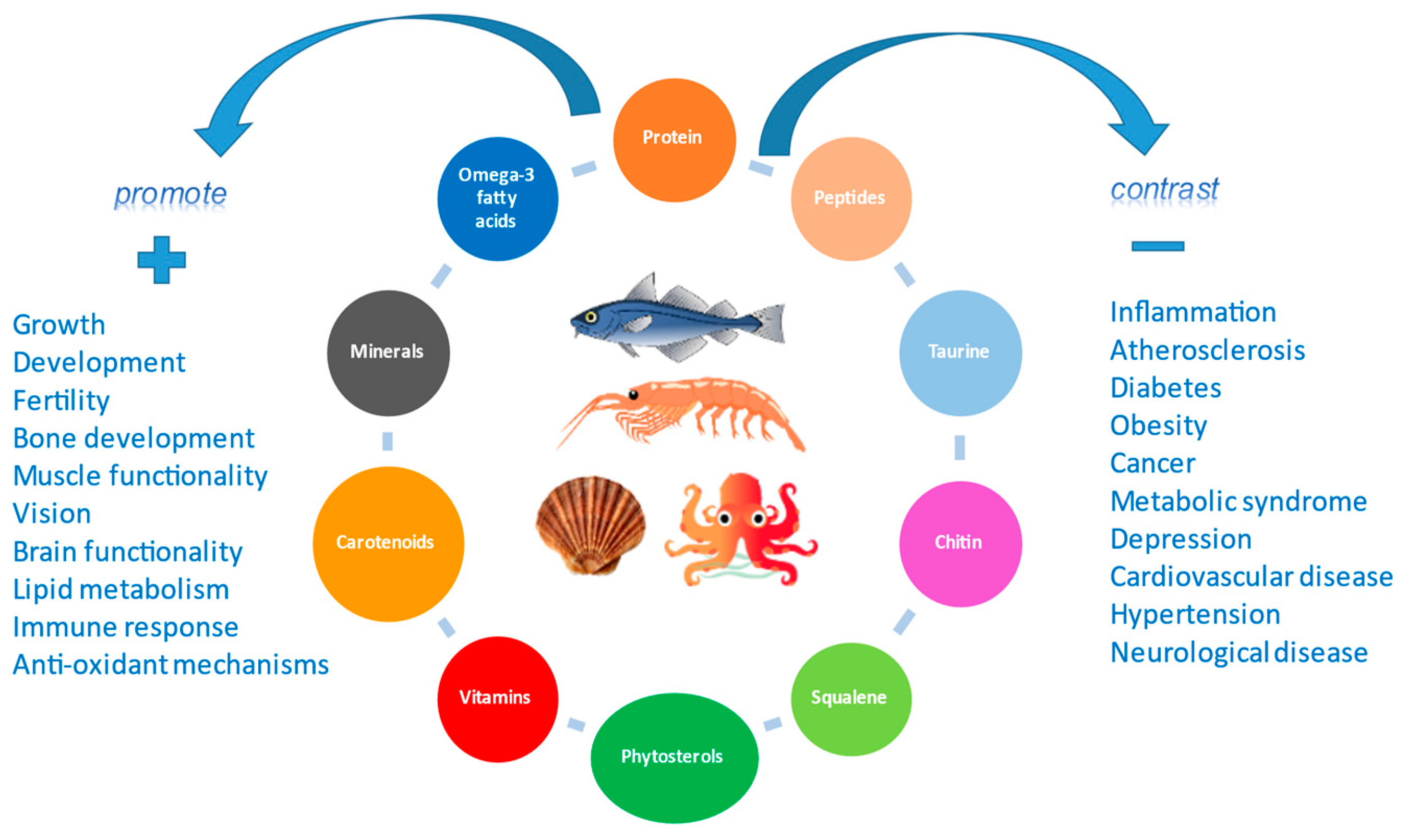
2. Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds
2.1. Proteins, Bioactive Peptides, Amino Acids, Taurine, and Anserine
2.2. Lipids and Omega–3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
2.3. Vitamins, Pro-Vitamins and Carotenoids
2.4. Phytosterols and Squalene
2.5. Minerals and Trace Elements
2.6. Chitin, Chitosan and Chito-Oligosaccharides
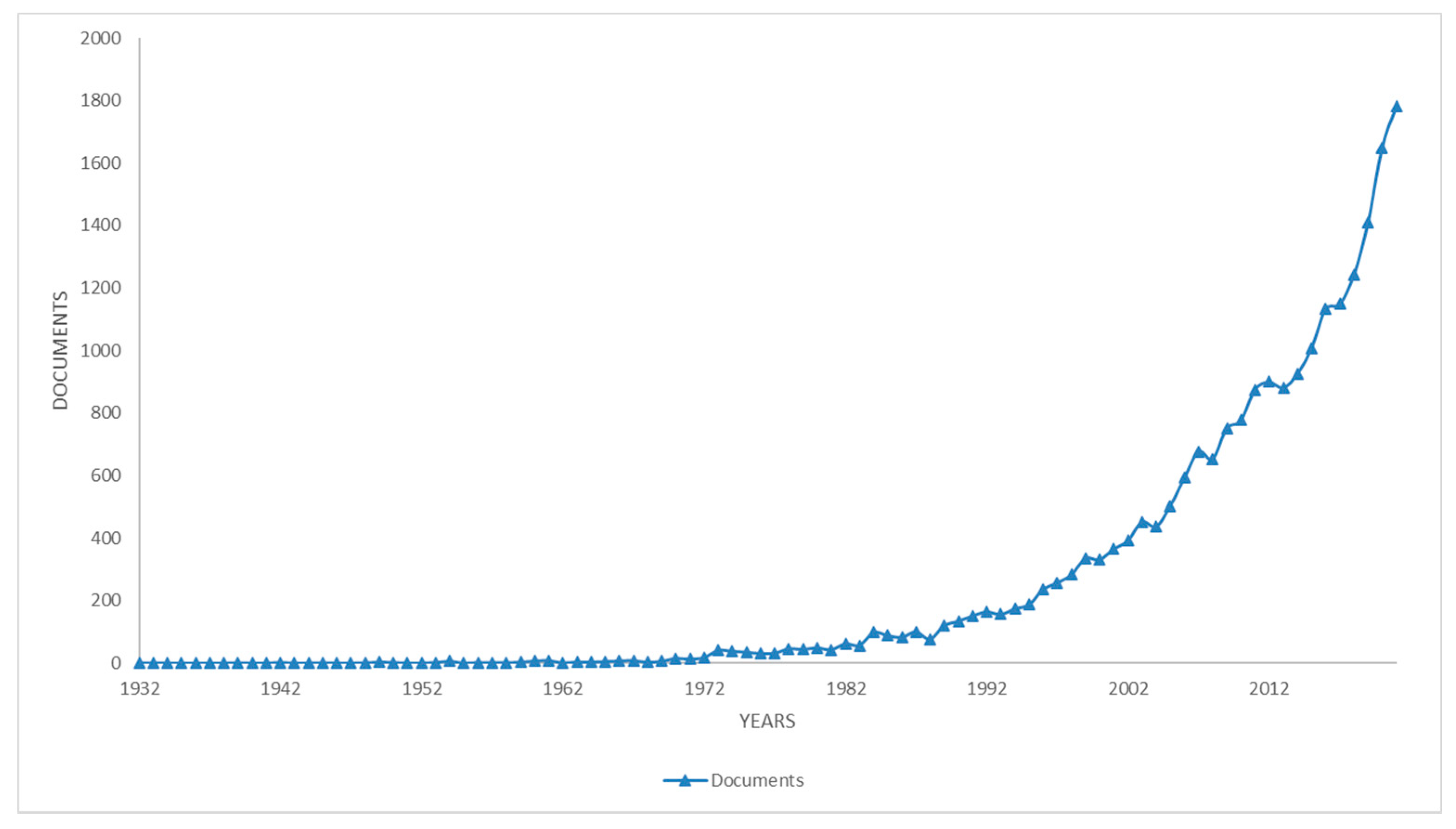
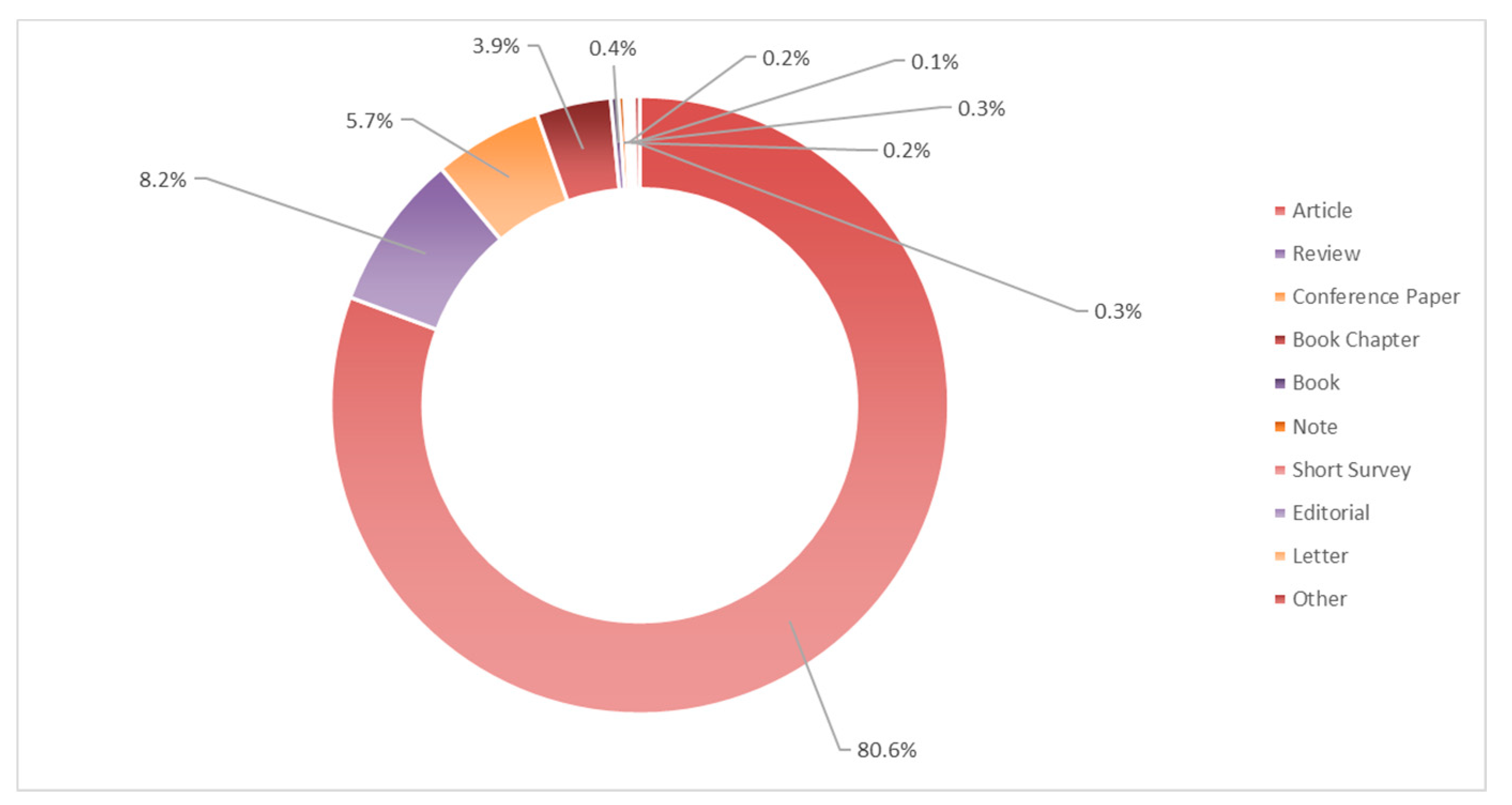
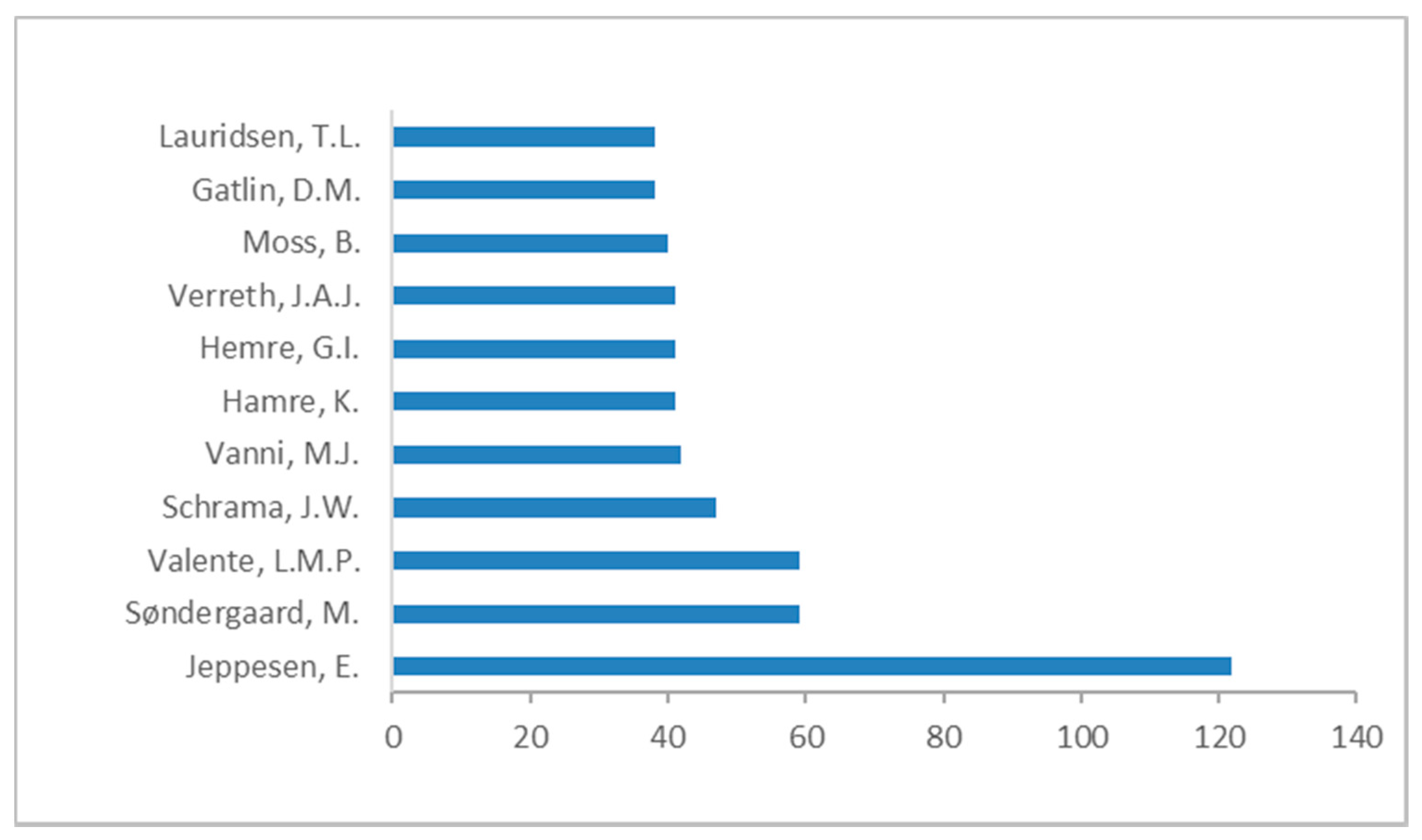
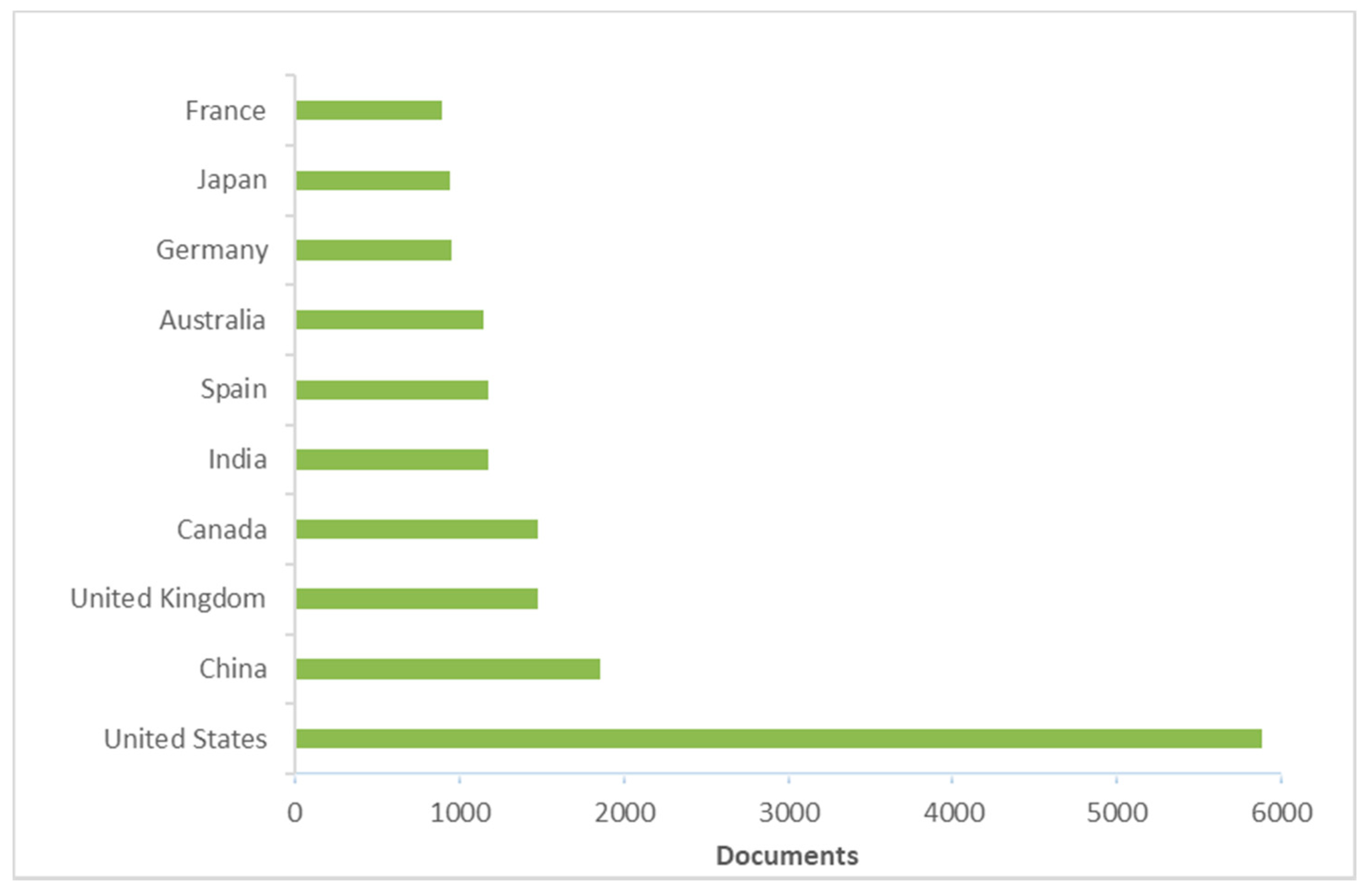
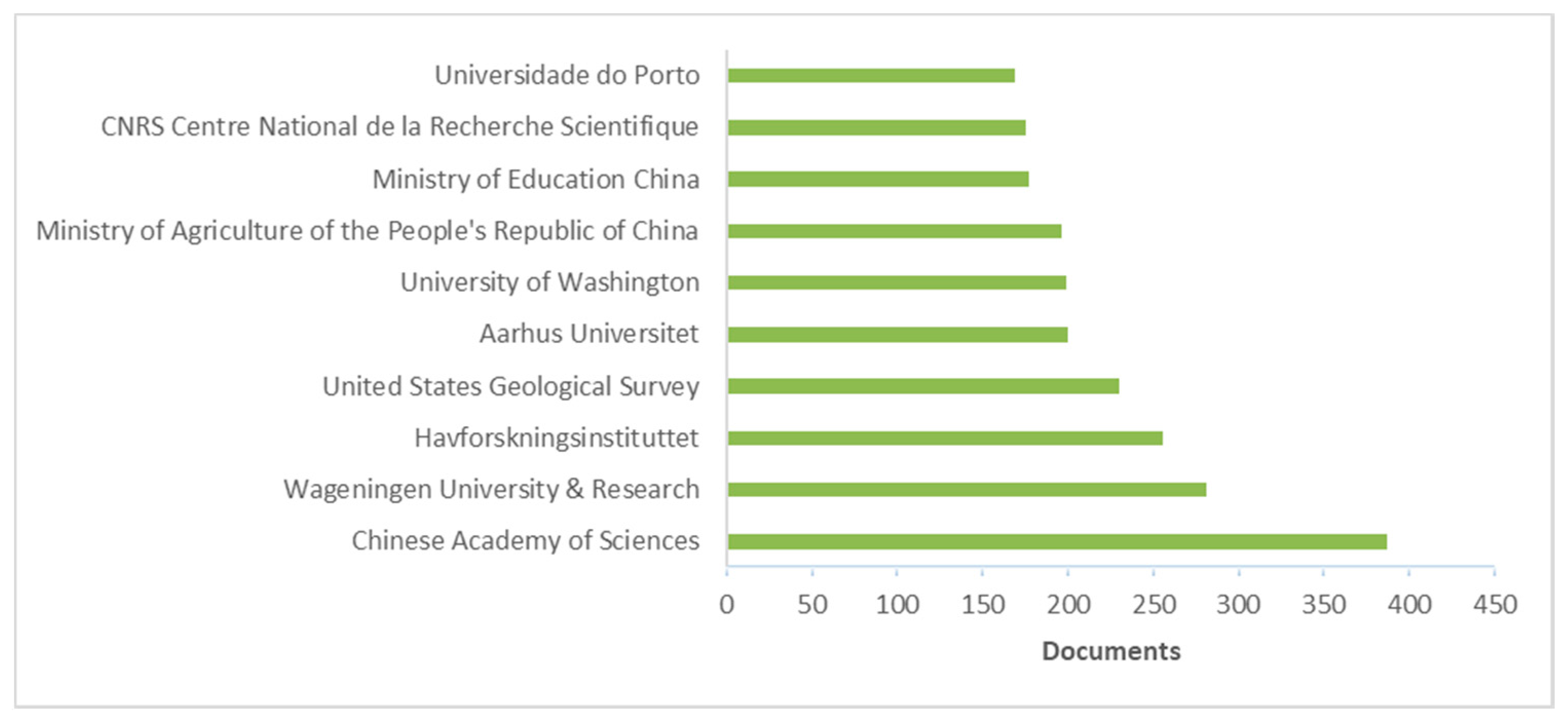
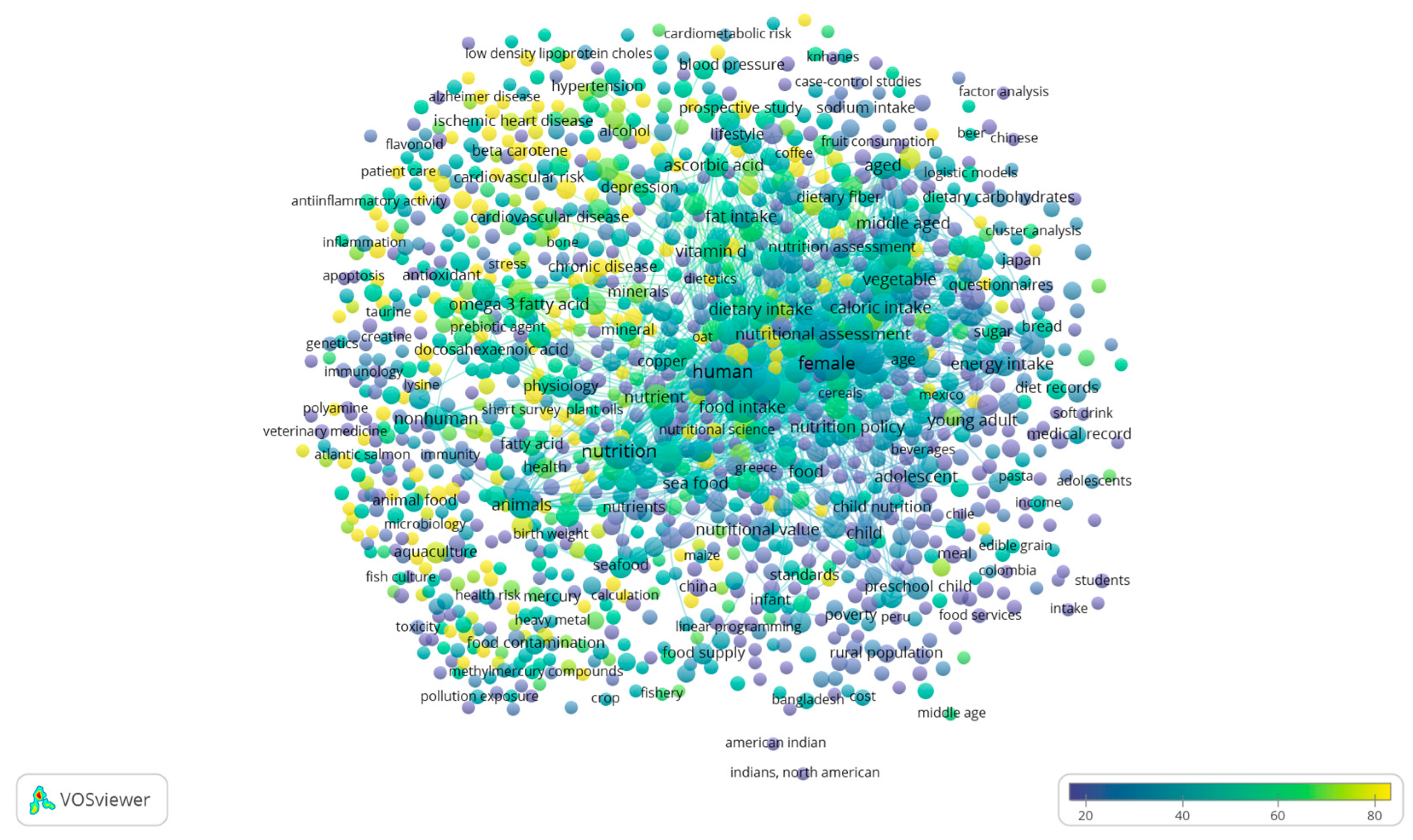
3. Literature Quantitative Research Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelhamid, A.S.; Brown, T.J.; Brainard, J.S.; Biswas, P.; Thorpe, G.C.; Moore, H.J.; Deane, K.H.; AlAbdulghafoor, F.K.; Summerbell, C.D.; Worthington, H.V.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 11, CD003177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, H.; Langkilde, A.M.; Undeland, I.; Lindqvist, H.; Langkilde, A.M.; Undeland, I.; Rådendal, T.; Sandberg, A.S. Herring (Clupea harengus) supplemented diet influences risk factors for CVD in overweight subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringleb, P.A.; Bousser, M.-G.; Ford, G.; Bath, P.; Brainin, M.; Caso, V.; Cervera, Á.; Chamorro, A.; Cordonnier, C.; Csiba, L.; et al. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 25, 457–507. [Google Scholar]
- Calder, P.C.; Ahluwalia, N.; Brouns, F.; Buetler, T.; Clement, K.; Cunningham, K.; Esposito, K.; Jönsson, L.S.; Kolb, H.; Lansink, M.; et al. Dietary factors and low-grade inflammation in relation to overweight and obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, S5–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampelas, A.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Das, U.N.; Chrysohoou, C.; Skoumas, Y.; Stefanadis, C. Fish consumption among healthy adults is associated with decreased levels of inflammatory markers related to cardiovascular disease: The ATTICA study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CREA Centro di Ricerca Alimenti e Nutrizione. Linee Guida Per Una Sana Alimentazione; Centro di Ricerca Alimenti e Nutrizione: Roma, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-88-96597-01-9. Available online: https://www.crea.gov.it/web/alimenti-e-nutrizione/-/linee-guida-per-una-sana-alimentazione-2018 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. In Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, 9th ed.; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, December 2020. Available online: DietaryGuidelines.gov (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A. Nutraceuticals in human health. Foods 2020, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesalski, H.K.; Dragsted, L.O.; Elmadfa, I.; Grossklaus, R.; Müller, M.; Schrenk, D.; Walter, P.; Weber, P. Bioactive compounds: Definition and assessment of activity. Nutrition 2009, 25, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.; Mahanty, A.; Ganguly, S.; Sankar, T.V.; Chakraborty, K.; Rangasamy, A.; Paul, B.; Sarma, D.; Mathew, S.; Asha, K.K.; et al. Amino acid compositions of 27 food fishes and their importance in clinical nutrition. J. Amino Acids 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyz-Łukasik, R.; Chałabis-Mazurek, A.; Gondek, M. Basic and functional nutrients in the muscles of fish: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, V.; Marois, J.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Jacques, H. Dietary cod protein improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant men and women: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2816–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geahchan, S.; Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, M.A. Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomateria l for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.A.; Pintado, M.E. Bioactive peptides derived from marine sources: Biological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 348–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.C.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory, and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnedy-Rothwell, P.A.; McLaughlin, C.M.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Le Gouic, A.V.; Allsopp, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Sharkey, S.; Whooley, J.; McGovern, B.; O’Harte, F.P.; et al. Identification and characterisation of peptides from a boarfish (Capros aper) protein hydrolysate displaying in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and insulinotropic activity. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Tu, M.; Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, B.; Du, M. Identification and inhibitory activity against α-thrombin of a novel anticoagulant peptide derived from oyster (Crassostrea gigas) protein. Food Func. 2018, 9, 6391–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.B.; Cho, Y.S.; Je, J.Y. Purification and anti-inflammatory action of tripeptide from salmon pectoral fin byproduct protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, B.; Romero, A.; Álvarez, L.; Moreira, R.; Pereiro, P.; Costa, M.M.; Dios, S.; Estepa, A.; Parra, F.; Figueras, A. Antiviral activity of myticin C peptide from mussel: An ancient defense against herpesviruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7692–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejpal, C.S.; Vijayagopal, P.; Elavarasan, K.; Prabu, D.L.; Lekshmi, R.G.K.; Asha, K.K.; Anandan, R.; Chatterjee, N.S.; Mathew, S. Antioxidant, functional properties and amino acid composition of pepsin-derived protein hydrolysates from whole tilapia waste as influenced by pre-processing ice storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Functional Amino Acids in Nutrition and Health. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, T.R.; Neumann, T.; Fagan, J.D. Taurine content of raw and processed fish fillets/portions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jia, J.; Lin, Y. Taurine content in chinese food and daily taurine intake of chinese men. In Taurine 3; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 442, pp. 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragnes, B.T.; Larsen, R.; Ernstsen, M.H.; Mæhre, H.; Elvevoll, E.O. Impact of processing on the taurine content in processed seafood and their corresponding unprocessed raw materials. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G. Important roles of dietary taurine, creatine, carnosine, anserine and 4-hydroxyproline in human nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tørris, C.; Småstuen, M.C.; Molin, M. Nutrients in fish and possible associations with cardiovascular disease risk factors in metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2018, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Rizzolo, D.A.; Miro, A.; Gomis, R. Prevention of type 2 diabetes through sardines consumption: An Integrative review. Food Rev. Inter. 2021, 38, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KP, A.D.; Martin, A. Recent insights into the molecular regulators and mechanisms of taurine to modulate lipid metabolism: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Aldini, G.; Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromhout, D.; Bosschieter, E.B.; Coulander de Lezenne, C. The inverse relation between fish consumption and 20-year mortality from coronary hearth disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, B.E.; Rothrock, D.W.; Connor, W.E.; Harris, W.S.; Illingworth, D.R. Reduction of plasma lipids, lipoproteins and apoproteins by dietary fish oils in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, P.M.; Kinsella, J.E. Fish oil consumption and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease: A comparison of findings from animal and human feeding trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 43, 566–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Omega-3 fatty acids in health and disease and in growth and development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 438–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Kumlin, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Wolk, A. Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention of cancer: A review of potential mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. N-3 Fatty acids, inflammation and immunity: New mechanisms to explain old actions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, O.A.; Gaziano, J.M.; Djousse, L. N-3 fatty acids for prevention of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samieri, C.; Morris, M.-C.; Bennett, D.A.; Berr, C.; Amouyel, P.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Tzourio, C.; Chasman, D.I.; Grodstein, F. Fish Intake, Genetic Predisposition to Alzheimer Disease, and Decline in Global Cognition and Memory in 5 Cohorts of Older Persons. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Crivello, F.; Mazoyer, B.; Debette, S.; Tzourio, C.; Samieri, C. Fish intake and mri burden of cerebrovascular disease in older adults. Neurology 2021, 97, E2213–E2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Rampacci, M.; Casini, I.; Caproni, R.; Orban, E. Proximate composition and lipid profile of red mullet (Mullus barbatus) from two sites of the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic seas (Italy): A seasonal differentiation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 45, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F. Total lipid content and fatty acid composition of commercially important fish species from the Mediterranean, Mar Grande Sea. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SINU; 2014 SINU, Società Italiana di Nutrizione Umana. Livelli di Assunzione di Riferimento di Nutrienti ed Energia per la Popolazione Italiana. (IV Revisione); SICS (Società Italiana di Comunicazione Scientifica e Sanitaria): Milano, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 fatty acid ratio increases the risk for obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, P.; Piironen, V.; Uusi-Rauva, E.; Koivistoinen, P. Cholecalciferol and 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol contents in fish and fish products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1995, 8, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.; Bandarra, N.M.; Nunes, L.; Cardoso, C. Tocopherols in Seafood and Aquaculture Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Fujisawa, A.; Hara, A.; Dunlap, W.C. An unusual vitamin E constituent (Alpha-tocomonoenol) provides enhanced antioxidant protection in marine organisms adapted to cold-water environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13144–13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, J.M. Modulation of signal transduction by vitamin E. Mol. Asp. Med. 2007, 28, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriault, A.; Jun-Tzu, C.; Qi, W. Abdul Gapor and Khosrow Adeli. Tocotrienol: A Review of Its Therapeutic Potential. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 32, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K.L.; Khanna, S.L.; Roy, S. Tocotrienols in health and disease: The other half of the natural vitamin E family. Mol. Asp. Med. 2007, 28, 692–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Parinandi, N.L.; Kotha, S.R.; Roy, S.; Rink, C.; Bibus, D.; Sen, C.K. Nanomolar vitamin E α-tocotrienol inhibits glutamate induced activation of phospholipase A2 and causes neuroprotection. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, G.; Liaaen-Jensen, S.; Pfander, H. Carotenoids. Volume 5: Nutrition and Health; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Maoka, T. Carotenoids in marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.M.; Koutsidis, G.; Lodge, J.K.; Ashor, A.; Siervo, M.; Lara, J. Tomato and lycopene supplementation and cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2017, 257, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Murakoshi, M.; Tokuda, H.; Satomi, Y. Cancer prevention by carotenoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.; Eilertsen, K.-E.; Elvevoll, E.O. Health benefits of marine foods and ingredients. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, A.; Plat, J.; Bast, A.; Godschalk, R.W.L.; Basu., S.; Mensink., R.P. Effects of plant sterol and stanol ester consumption on lipid metabolism antioxidant status, and markers of oxidative stress, endothelial function, and low-grade inflammation in paitents on current statin treatment. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talati, R.; Sobieraj, D.M.; Makanji, S.S.; Phung, O.J.; Coleman, C.I. The comparative efficacy of plant sterols and stanols on serum lipids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, L.; Couvreur, P. Squalene: A natural triterpene for use in disease management and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.J.; Franco, F.; Martinho, F.; Carvalho, L.; Pereira, M.E.; Coelho, J.P.; Pardal, M.A. Essential mineral content variations in commercial marine species induced by ecological and taxonomical attributes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cogswell, M.E.; Gillespie, C.; Fang, J.; Loustalot, F.; Dai, S.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Kuklina, E.V.; Hong, Y.; Merritt, R.; et al. Association between usual sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure and hypertension among U.S. adults: NHANES 2005–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lena, G.; Casini, I.; Caproni, R.; Fusari, A.; Orban, E. Total mercury levels in commercial fish species from Italian fishery and aquaculture. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2017, 10, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, M.; Chau, T.C.; Givens, D.I. Iodine Content of Wild and Farmed Seafood and Its Estimated Contribution to UK Dietary Iodine Intake. Nutrients 2022, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Azad, A.K.; Lin, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, H. Biological effects and applications of chitosan and chito-oligosaccharides. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Costa, B.E.; Andrade, C.T. Chitosan as a valuable biomolecule from seafood industry waste in the design of green food packaging. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, H. On the Summer Plankton in the Waters of the Western Aleutian Islands in 1928. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1932, 1, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zulqurnain, S.S.; Sultana, T.; Mahboob, S. Fatty acid profile variations after exposure to textile industry effluents in Indian Major Carps [Variações do perfil de ácidos graxos após exposição a efluentes da indústria têxtil nas principais carpas indianas]. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e254252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Joseph, A.; Nair, B.G. Promising bioactive compounds from the marine environment and their potential effects on various diseases. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintersteen, K.A. The Fishmeal Revolution: The Industrialization of the Humboldt Current Ecosystem; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–225. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading-An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, D.A.; Romero, G.Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Kratina, P.; Alves, D.C.; Antiqueira, P.A.P.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Figueiredo, B.R.S.; Bonecker, C.C.; Pires, A.P.F.; et al. Regime shifts in a shallow lake over 12 years: Consequences for taxonomic and functional diversities, and ecosystem multifunctionality. J. Anim. Ecol. 2022, 91, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepon, A.; Makov, T.; Hamilton, H.A.; Müller, D.B.; Gephart, J.A.; Henriksson, P.J.; Troell, M.; Golden, C.D. Sustainable optimization of global aquatic omega-3 supply chain could substantially narrow the nutrient gap. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, V.F.; Karagas, M.R. Exposure to arsenolipids and inorganic arsenic from marine-sourced dietary supplements. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, C.-H.; Ye, C.; Chen, H.-S.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.-H.; Liu, X.-S.; Li, D. Effects of aquaculture on the shallow lake aquatic ecological environment of Lake Datong, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, L.; Duchatelet, L.; Bird, C.S.; Le Croizier, G.; Michel, L.; Pinte, N.; Lepoint, G.; Schaal, G.; Vieira, R.P.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; et al. Diet consistency but large-scale isotopic variations in a deep-sea shark: The case of the velvet belly lantern shark, Etmopterus spinax, in the northeastern Atlantic region and Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2022, 182, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Text mining and visualization using VOSviewer. ISSI Newsl. 2011, 7, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C. A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J. Inform. 2011, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact: Methods and Practice; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 285–320. [Google Scholar]
- Shalders, T.C.; Champion, C.; Coleman, M.A.; Benkendorff, K. The nutritional and sensory quality of seafood in a changing climate. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jayachandran, M.; Bai, W.; Xu, B. A critical review on the health benefits of fish consumption and its bioactive constituents. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehn, J.Z.; Allison, E.H.; Villeda, K.; Chen, Z.; Nixon, M.; Crigler, E.; Zhao, L.; Chow, M.; Vaitla, B.; Thilsted, S.H.; et al. Fishing for health: Do the world’s national policies for fisheries and aquaculture align with those for nutrition? Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Wang, K.; Xu, G. Metals in Ten Commercial Demersal Fish from the East China Sea: Contribution to Aquatic Products Nutrition and Toxic Risk Assessment. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmance, F.A.; Cohen, P.J.; Huchery, C.; Sutcliffe, S.; Suri, S.K.; Tezzo, X.; Thilsted, S.H.; Oosterveer, P.; McDougall, C.; Ahern, M.; et al. Nudging fisheries and aquaculture research towards food systems. Fish Fish. 2021, 23, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luten, J.B. Marine Functional Food; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-S.; Lim, C.; Gatlin, D.M.; Webster, C.D. Dietary nutrients, additives, and fish health. Diet. Nutr. Addit. Fish Health. 2015, 1–355. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, P. Seaweeds: Biodiversity Environmental Chemistry and Ecological Impacts; Nova Science Pub.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tlusty, M.F.; Tyedmers, P.; Bailey, M.; Ziegler, F.; Henriksson, P.J.; Béné, C.; Bush, S.; Newton, R.; Asche, F.; Little, D.C.; et al. Reframing the sustainable seafood narrative. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 59, 101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Pritam, S.; Mishra, K.; Khan, M.; Upmanyu, N.; Ghosh, D. Nutraceuticals from marine bionetworks. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 15, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, M.; Zuorro, A.; Di Lena, G.; Lavecchia, R.; Durazzo, A.; Benedetti, B.; Lombardi-Boccia, G. Sustainable Management of Secondary Raw Materials from the Marine Food-Chain: A Case-Study Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalipassi, M.; Esposito, R.; Ruocco, N.; Viel, T.; Costantini, M.; Zupo, V. Bioactive Compounds of Nutraceutical Value from Fishery and Aquaculture Discards. Foods 2021, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Meenatchi, R.; Pachillu, K.; Bansal, S.; Brindangnanam, P.; Arockiaraj, J.; Kiran, G.S.; Selvin, J. Identification and characterization of the novel bioactive compounds from microalgae and cyanobacteria for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, P.; Liu, H. Molecular Targets and Related Biologic Activities of Fucoidan: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaa, F.; Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Althobaiti, N.A.; Albalawi, A.E.; Khan, B.A.; Menaa, B. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds: A New Wave of Nanodrugs? Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, V.; Gunasegavan, R.D.; Mustar, S.; Lee, J.C.; Mohd Noh, M.F. Isolation of Industrial Important Bioactive Compounds from Microalgae. Molecules 2021, 26, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; He, N.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, E.P.; Chew, K.W.; Ling, T.C. Application progress of bioactive compounds in microalgae on pharmaceutical and cosmetics. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 2, 132932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Kumar, P.; Bose, D.; Li, X.; Kulshrestha, S. Potential applications of algae in biochemical and bioenergy sector. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durazzo, A.; Di Lena, G.; Gabrielli, P.; Santini, A.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Lucarini, M. Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Seafood: Quantitative Literature Research Analysis. Fishes 2022, 7, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030132
Durazzo A, Di Lena G, Gabrielli P, Santini A, Lombardi-Boccia G, Lucarini M. Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Seafood: Quantitative Literature Research Analysis. Fishes. 2022; 7(3):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030132
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurazzo, Alessandra, Gabriella Di Lena, Paolo Gabrielli, Antonello Santini, Ginevra Lombardi-Boccia, and Massimo Lucarini. 2022. "Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Seafood: Quantitative Literature Research Analysis" Fishes 7, no. 3: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030132
APA StyleDurazzo, A., Di Lena, G., Gabrielli, P., Santini, A., Lombardi-Boccia, G., & Lucarini, M. (2022). Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Seafood: Quantitative Literature Research Analysis. Fishes, 7(3), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030132








