Abstract
The Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) is an important aquatic species in southern China that is threatened by many serious diseases. Edwardsiella tarda is one of the highly pathogenic bacteria that cause the white abdominal shell disease. Yet, little is known about the immune and metabolic responses of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle against E. tarda infection. In the paper, gene expression profiles in the turtle liver were obtained to study the immune responses and metabolic regulations induced by E. tarda infection using RNA sequencing. A total of 3908 differentially expressed unigenes between the experimental group and the control group were obtained by transcriptome analysis, among them, were the significantly upregulated unigenes and downregulated unigenes 2065 and 1922, respectively. Further annotation and analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, and steroid hormone biosynthesis pathways, indicating that they were mainly associated with defense mechanisms in the turtle liver against E. tarda four days post infection. For the first time, we reported on the gene profile of anti-E. tarda response in the soft-shelled turtle, and our research might provide valuable data to support further study on anti-E. tarda defense mechanisms in turtles.
1. Introduction
The Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) is an important freshwater aquaculture species in southern China and many other Asian countries. With its high nutritional and medicinal value, it contributes a considerable portion of animal protein sources to people [1,2]. In the long development terms of the soft-shelled turtle cultivation industry, diseases have brought severe economic losses to it, commonly reported as white abdominal shell disease, putrid skin disease, and red neck disease, etc. [3,4,5]. Aeromonas spp., Edwardsiella tarda, and Citrobacter freudii are common bacterial pathogens detected in diseased turtles [5,6,7,8,9], and Edwardsiella tarda is widely regarded as one of the pathogens that causes the white abdominal shell disease [10,11]. The turtle is named by the clinical signs, and the abdominal shell of diseased turtles appears pale and is accompanied by visible hepatic pathological changes and intestinal hemorrhaging when dissected [11,12]. Our laboratory also separated a strain of highly pathogenic E. tarda previously from the turtles with the syndrome of white abdominal shell disease, whose pathogenicity was verified by the artificially infection trials [12].
E. tarda is a Gram-negative and intracellular bacterium, a deadly pathogen to many aquatic species. Fish, such as largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides), Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica), and tilapia (Tilapia nilotica), are all reported as its sensitive hosts [13]; moreover, studies have shown that the bacteria could even cause human gastroenteritis, bacteremia, cephalomeningitis, and malignancy [14,15]. To prevent and control diseases caused by E. tarda, several studies on host defense responses against E. tarda have been reported in teleosts [16,17,18,19], but detailed data are still lacking for the turtle. So far, several crucial immune and metabolic molecules of the turtle, e.g., immuneglobulins, receptor proteins, cytokines, and hormone genes have already been cloned and validated [20,21,22,23], yet more information that clarifies how turtle immune systems defend against pathogens still needs to be collected.
RNA-seq is a rapid and effective technology that can draw a whole profile of gene transcription and reveal specific biological processes [24,25], and it has now been widely adopted to identify crucial genes and pathways involved in responses to environmental or pathogenic stressors of many aquatic animals, including fish, shrimp, molluscs, and some reptiles [26,27,28,29], which could thus help determine the underlying physiological and immune mechanisms. Transcriptome sequencing was formerly applied in studying intestinal molecular immune responses to lipopolysaccharide stimulation [30], differential gene expression of immunity and growth in hybrids compared with parental varieties [31], and physiological and immune responses to acute cold stress at the transcriptional level [32] in P. sinensis. A recent study firstly reported the turtle lung tissue immune responses against Trionyx sinensis hemorrhagic syndrome virus (TSHSV) using RNA-seq and found differentially expressed genes closely associated with virus recognition, immune initiation, endocytosis, and steroid metabolism, which helped deepen the understanding of molecular mechanisms in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle against TSHSV [33]. However, data are still lacking about turtle immune and metabolic responses against bacterial infection through a whole gene expression profile.
Therefore, based on statistical analysis of transcriptome sequencing, in the present study, differential gene expression profiles of healthy soft-shelled turtles and ones infected with E. tarda were captured and compared to find crucial defense genes and pathways possibly involved in the antibacterial responses. Our research might provide valuable data to support intensive study on immune defense mechanisms against E. tarda infection in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle, which might go a step further to help understand antibacterial responses and regulations in aquatic reptiles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statements, Bacterial Challenge, and Sample Collection
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province for Zhejiang Fisheries Test and Aquatic Disease Prevention Center [SYXK(Zhe)2020-0009, 26 May 2020].
Two hundred healthy Chinese soft-shelled turtles with an average weight of 30 ± 5 g were bred in the national turtle breeding center (Deqing, Huzhou, China). Before the challenge test, turtles were maintained in the breeding tanks at 25 ± 1 °C, then averagely divided into two teams as the control group and experimental group. The pathogenic E. tarda separated from the animals suffering from the white abdominal shell disease and verified by our laboratory was used in the experiment [12]. After 18 h culture, E. tarda was suspended with a sterile normal saline solution (NS), and each turtle in the experimental group was intraperitoneally injected with 107 CFU of the bacteria (100 μL per turtle), while in the control group, turtles each were injected with equivalent NS. During the experiment, fifty turtles of each group were used to calculate the mortality. After 4 days post injection (dp.i.), five turtles from each group were randomly selected, and their livers were respectively pooled and stored in liquid nitrogen for a later experiment soon after being euthanized.
The artificial infection was guaranteed through nutrient agar separation, then physiological and biochemical identification using the automatic microbe identification instrument (VITEK 2, Bio Mérieux, Lyons, France), which was performed as described by Zhu et al. [12].
2.2. RNA Isolation and Illumina Sequencing
Total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) following the manufacturer’s procedure. The total RNA quantity and purity were analyzed using Bioanalyzer 2100 and RNA 1000 Nano LabChip Kit (Agilent, Follsom, CA, USA) with RIN number > 7.0. Poly(A). RNA was purified from total RNA (5 μg) using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads using two rounds of purification. Following purification, the mRNA was fragmented into small pieces using divalent cations under elevated temperature. Then the cleaved RNA fragments were reverse transcribed to create the final cDNA library in accordance with the protocol for the mRNASeq sample preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The average insert size for the paired-end libraries was 300 bp (±50 bp). Finally, we performed the paired-end sequencing on an IlluminaHiseq4000 at the (LC Sciences, Houston, TX, USA) following the vendor’s recommended protocol.
2.3. De Novo Assembly, Unigene Annotation and Functional Classification
Firstly, Cutadapt [34] and perl scripts in house were used to remove the reads that contained adaptor contamination, low quality bases, and undetermined bases. Then sequence quality was verified using FastQC (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/, accessed on 16 January 2019), including the Q20, Q30, and GC content of the clean data. All downstream analyses were based on clean data of high quality. De novo assembly of the transcriptome was performed with Trinity 2.4.0 [35]. Trinity groups transcripts into clusters based on shared sequence content. Such a transcript cluster is very loosely referred to as a ‘gene’. The longest transcript in the cluster was chosen as the ‘gene’ sequence (also known as unigene). All assembled unigenes were aligned against the nonredundant (Nr.) protein database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 16 January 2019), Gene ontology (GO) (http://www.geneontology.org, accessed on 16 January 2019), SwissProt (http://www.expasy.ch/sprot/, accessed on 16 January 2019), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/, accessed on 16 January 2019), and eggNOG (http://eggnogdb.embl.de/, accessed on 16 January 2019) databases using DIAMOND [36] with a threshold of E value < 0.00001.
2.4. Differentially Expressed Unigene and GO/KEGG Enrichment Analysis
Salmon [37] was used to perform expression level for unigenes by calculating TPM [38]. The differentially expressed unigenes were selected with log2 (fold change) > 1 or log2 (fold change) < −1 and with statistical significance (p value < 0.05) by R package edgeR [39]. Next, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were again performed on the differentially expressed unigenes by perl scripts in house.
2.5. Gene Expression Validation by Real-Time Quantitative PCR
To confirm the DEGs from the RNA-seq data, ten of DEGs involved in the three key pathways were selected for validation by qRT-PCR analysis, performed as described in the assay by Tang et al. [40]. Total RNA was extracted from each liver sample using a trizol reagent, and its quality and quantity were examined by a Nanodrop 8000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Single-strand cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg total RNA by the PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, Kusatsu, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Thereafter, the real-time quantitative PCR was performed adopting SYBR Green I Master mix (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) in a LightCycler®480 II Real Time PCR System (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Each optimized reaction system contained 10 μL of SYBR Green I Master mix, 0.6 μL each of forward and reverse primers (10 mM), with 100 ng of cDNA added and RNase-free water up to a volume of 20 μL. The real-time quantitative PCR assay here was performed in triplicate with β-actin gene as the reference gene. The Procedures are described as follows: 1 cycle at 95 °C for 5 min and 40 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s and annealing at specific temperature (shown in Table 1) for 20 s and at 78 °C for 1 s. The melting curve was calculated to confirm that only one product was amplified and detected at the end of each reaction. Results were analyzed relative to the β-actin gene [33] by the 2−ΔΔCt method.

Table 1.
Primers used in gene expression validation.
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Challenge and Accumulative Mortality
After the artificial infection, the turtles in the experimental group began to die as of 1 dp.i. and displayed an increase in mortality from 1 to 4 dp.i., and then it showed a stable death ratio after 4 dp.i. (black line). During the whole process, all of the turtles in the control group (injected with NS, red line) showed no death (shown in Figure 1).
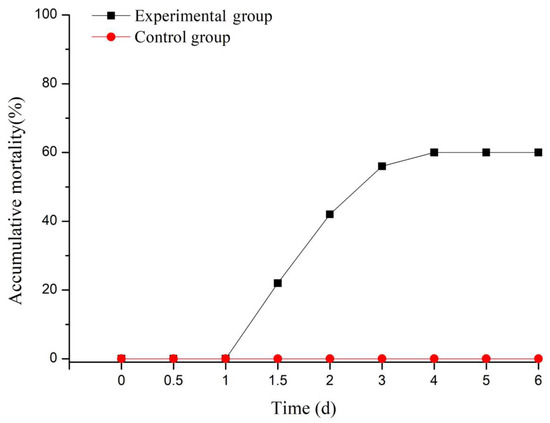
Figure 1.
Accumulative mortality of the Chinese soft-shelled turtles after bacterial challenge.
3.2. Sequencing Identify and Functional Annotation of the Unigenes
It was notably found that the death ratio of turtles in the experimental group began to remain stable as of 4 dp.i., which we took as the key time point for the turtle to battle the bacteria. Therefore, the livers of both groups at the time point were taken out for transcriptome sequencing by using the IlluminaHiseq4000 platform. In total, 38,691 high-quality unigenes with a N50 length of 1343 bp were obtained by transcriptome profiling; the sequencing quality is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Sequencing quality.
3.3. Identification and Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
A total of 3987 unigenes showed differentially expressed levels between the experimental group and the control group, among them, the significantly upregulated unigenes and downregulated unigenes were 2065 and 1922, respectively. The differentially expressed gene volcano plots is shown in Figure 2.
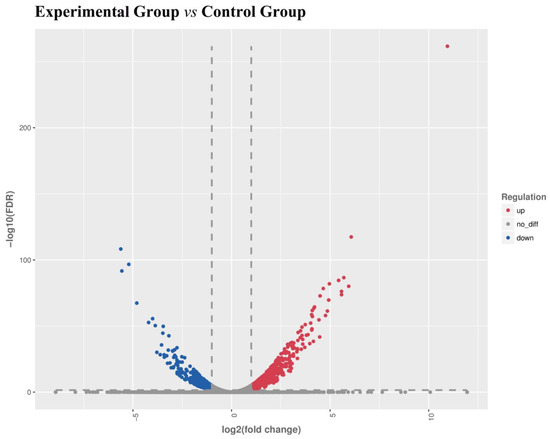
Figure 2.
Volcano plots of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). X-axis: log2(FC), the differential expression of multiple changes of genes in different samples, Y-axis: −log10(FDR), the statistical significance of changes in gene expression levels. Red scatters represent significantly upregulated differentially expressed genes, blue scatters represent significantly downregulated differentially expressed genes, and no represents nonsignificantly differentially expressed genes.
3.4. Gene Ontology Classification and Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
By a GO classification analysis, the DEGs between the experimental group and the control group were classified into three major categories (biological process, BP; cellular component, CC; and molecular function, MF). Figure 3 shows that the DEGs were mostly enriched in the oxidation reduction process, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, and signal transduction in the BP category; integral component of membrane, cytoplasm, and extracellular exosome in the CC category; and ATP binding, protein binding, zinc ion binding in the MF category, respectively.
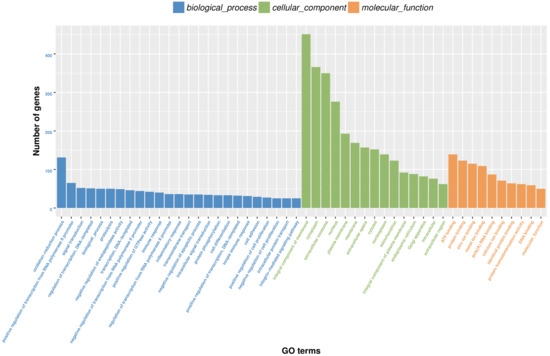
Figure 3.
Gene ontology classifications of the DEGs.
3.5. KEGG Pathway Classification and Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
By a KEGG pathway enrichment analysis (shown in Figure 4), the DEGs of the experimental and control groups were enriched in a total of 43 pathways (p value < 0.05); they were mainly enriched in 20 pathways, especially in complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, and steroid hormone biosynthesis. Among them, important immune response related pathways included complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, toll-like receptor signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, and ABC transporters, etc., while vital metabolic regulation related pathways included steroid hormone biosynthesis, vitamin digestion and absorption, tryptophan metabolism, retinol metabolism, and N-Glycan biosynthesis, etc.
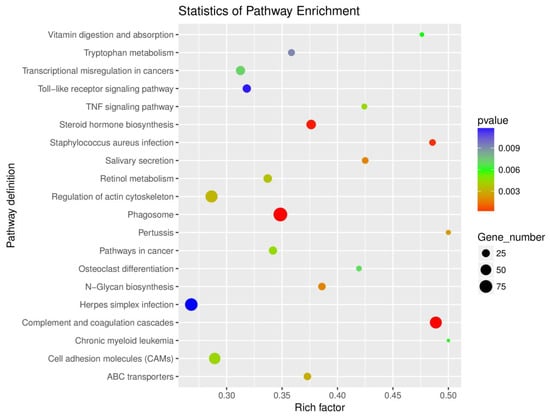
Figure 4.
Scatterplot of enriched KEGG pathways for DEGs.
The typical DEGs involved in three key pathways (p value = 0.000) are presented in Table 3. It was suggested that these genes might be crucial in immune responses and metabolic regulations in the liver of P. sinensis against E. tarda.

Table 3.
The representative differentially expression genes involved in the key pathways.
3.6. Results of Gene Expression Validation
The ten DEGs involved in the three key pathways were randomly chosen, and their expressions were validated by real-time quantitative PCR (shown in Figure 5). The qPCR results were mainly consistent with the results of RNA-seq except for slight differences in expression levels.
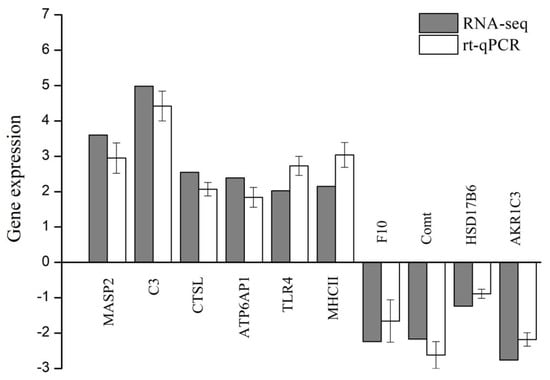
Figure 5.
Validation of ten DEGs by real-time quantitative PCR. X-axis: gene name, Y-axis: the relative expression level is expressed as log2 (fold change) in gene expression. The relative expression of ten random genes was determined by real-time qPCR (white column) and compared with the results of RNA-seq (grey column). Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3).
4. Discussion
Recently, determining the optimized dietaries and molecular mechanisms of growth and metabolism [31,41,42,43,44,45,46] and clarifying the turtle’s defense mechanisms against external stresses especially pathogen infection [20,21,22,30,32,33] are two major research hotspots of the soft-shelled turtle. Several crucial immune and metabolic molecules of the turtle have already been cloned and validated, yet more detailed studies are still lacking on host defense responses against pathogens in turtles. In the paper, we focused on the changes of gene expression in immune responses and metabolic regulations of Pelodiscus sinensis post Edwardsiella tarda infection using RNA-seq technology.
In the artificial infection trial, we were intrigued to find that the death ratio of turtles in the experimental group began to remain stable as of 4 dp.i., which we took as the key time point for the turtle to battle the bacteria, and our previous studies found livers of moribund turtles after E. tarda infection seemed to contain the maximal bacterial loads (unpublished), while the liver is also considered as the immune and metabolic center so that we chose the turtle liver as our research objective. By transcriptome analysis, the three pathways complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, and steroid hormone biosynthesis were found to be closely associated with defense mechanisms, and the key involved genes were discussed as follows.
Complement and coagulation cascades. The complement system is one of the major effector mechanisms of the innate immune system and is also important in the instruction of the adaptive immune response [47,48]. Three distinct pathways are responsible for target recognition and formation of the protease complex, including the classical pathway, alternative pathway, and lectin pathway (though mammal-like biological function not yet confirmed in reptiles), and the complement C3 is the core component for activation of the system. Latest reports have indicated the complement and coagulation cascades pathway plays an important part in responses against bacteria or other pathogens in aquatic species, such as large yellow croakers, sturgeons, fat greenlings, and giant salamanders [29,49,50,51]. Similarly, we found that the complement cascades pathway was greatly induced to defend against E. tarda. Our results show that a series of key genes including C1q in the classic pathway, MASP2 in the lectin pathway, and complement C3 attack complex members e.g., C6, C7, C8, and C9 were significantly upregulated. As for the alternative pathway, it was found that the complement factor CFB and CFD were both significantly upregulated except for the inhibitor factor CFH, which was highly expressed. Besides, our results found that some of the downstream molecules that led to the activation of phagocytosis and the B cell receptor signaling pathway were significantly upregulated, including CRIg, CR1, and CR2, which might indicate that the adaptive immune system was enhanced against the bacteria at the time point [52,53]. However, in the coagulation cascades pathway, though anticoagulant gene antithrombin showed downregulated, many other coagulant factors, except for fibrinogen, including coagulation factors X, XII, and VII were significantly downregulated, which might suggest that the coagulation cascades pathway was inhibited as the bacterial infection progressed. In addition, it corresponded with what we evidenced in that the turtle liver and even some other tissue, e.g., intestine, showed hemorrhaging at the time point, which might be one of the pathological damages caused by the E. tarda infection.
Phagosome. Phagocytosis plays an important role in killing bacteria and presenting antigens that bridges the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system, and phagosome is the key component in this biological process [54,55]. Transcriptome analyses on pathogen-challenged sea urchins, shrimps, and fish [56,57,58] have suggested the importance of the phagosome pathway in a host defending against the pathogens, and it was also found that phagocytosis plays a significant role in turtle antibacterial responses [59,60]. Our results found that the ER-mediated phagocytosis was the major way, and the key genes, e.g., V-type proton ATPase and cathepsins (CTSL, CTSS) were significantly upregulated. V-type proton ATPase could hydrolyze ATP and establish a transmembrane proton electrochemical gradient to acidify the intracellular and extracellular environments, which would help activate the protein hydrolysis function of cathepsin [61]. Meanwhile, NADPH oxidase system was also greatly activated to accelerate the whole process [62]. Moreover, several phagocytosis-promoting genes, e.g., iC3b(complement), TLR2, TLR4, and CD14 (toll-like receptors) were also found upregulated, which indicated that the phagosomes ought to be continuously processed and maturated for manipulating with the bacterial particles in the turtle liver at the time. Furthermore, the connection phagocytosis links between innate and adaptive immunity is the antigen processing and presentation [51,63] where the phagocytosed pathogens are degraded as antigen peptides and then combined to MHCI and MHCII and presented to the adaptive immune system to trigger the cellular and humoral immunity. In our study, the transport protein genes TAP (antigen peptide transporters) and SEC (protein transport proteins, e.g., sec22 and sec61) were highly expressed, and a significant upregulation of both MHCI and MHCII genes might indicate that antigen processing and presentation was strongly activated to enhance the adaptive immune responses [64].
Steroid hormone biosynthesis. Steroid hormones are believed to be major determinants of both physiological and pathological processes, and alterations of steroid hormone biosynthesis and metabolism seem to be involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases [65]. In the steroid hormone family, stress hormones (cortisol and cortisone) might contact with the immune system through interaction with some inflammatory cytokines, e.g., IL-1β, TNFα, IL-6, and INFγ, etc. [66,67]. Corticosteroids are the key factors in stress responses; corticosterone is especially key in reptiles [68], and when turtles suffered from E. tarda infection stress, several related enzyme genes became significantly regulated, which was evidenced in our study that two dehydrogenase genes including HSD11B1 (corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1, involved in the dehydrogenization of corticosterone) and AKR1D1 (3-oxo-5-beta-steroid 4-dehydrogenase, involved in the transformation of cortisol and cortisone, respectively, into the precursor of cortol and cortolone) were significantly upregulated. To our knowledge, excessive doses of stress hormones might inhibit the immune responses, while efficient catabolic effects of the hormone level could lower the inhibition effects [68], and it can be inferred that many corticosteroid catabolic enzyme genes were still upregulated so as to maintain suitable hormone levels to help enhance the immune responses against the bacteria. And several enzyme genes involved in the biosynthesis and transformation of testosterone, e.g., HSD17B6 (17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 6), AKR1C3 (aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3), and those involved in estrone-related pathway were all significantly down-regulated, including HSD17B6 (17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 6), AKR1C3 (aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3), CYP3A24 (cytochrome P450 3A24), and Comt (catechol O-methyltransferase), which might indicate that sex hormone biosynthesis pathway was affected by E. tarda infection.
In summary, our research found that three main pathways were closely related to the soft-shelled turtle immune and metabolic responses in turtle livers against E. tarda infection, which might help initially understand the turtle defense against E. tarda infection, yet more information on the molecular characteristics and biological functions of vital genes involved in the pathways needs to be confirmed to deepen our understanding of the turtle’s antibacterial defense mechanisms, the pathogenesis of E. tarda, and the host–bacteria interaction, which would be useful for finding the accurate drug targets and establishing new therapies of the bacterial infection for the soft-shelled turtles.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, and steroid hormone biosynthesis pathways might be closely associated with the anti-E. tarda defense mechanisms in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle. Complement C3, C1q, V-type proton ATPase, cathepsins, MHCI, MHCII, HSD11B1, and AKR1D1 were the main genes significantly regulated in immune and metabolic responses against E. tarda infection of the turtle.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.L. and T.Z.; methodology, N.Z.; software, X.Z. and X.D.; validation, R.H., H.X. (Hongsen Xu), F.C. and H.X. (Huili Xue); formal analysis, Q.L. and N.Z.; investigation, Q.L., N.Z. and T.Z.; resources, X.D.; data curation, Q.L. and F.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.L.; writing—review and editing, N.Z. and T.Z.; visualization, R.H., H.X. (Hongsen Xu), F.C., H.X. (Huili Xue) and F.Z.; supervision, X.D. and T.Z.; project administration, Q.L., N.Z. and T.Z.; funding acquisition, X.D. and T.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by key agricultural projects of major science and technology programs of the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province [grant no. 2015C02028]; key scientific and technological grant of Zhejiang for breeding new agricultural varieties [grant no. 2021C02069-8]; key research and development project on special agricultural new variety breeding of major science and technology program of the Zhejiang Province [grant no. 2016C02055-4].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province for Zhejiang Fisheries Test and Aquatic Disease Prevention Center [SYXK(Zhe)2020-0009, 26 May 2020].
Data Availability Statement
Data can be accessed from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the field staff of Zhejiang Fishery Extension Center who put in countless hours feeding and collecting project-associated data, especially Xiaoming Chen and Gaohua Yao.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Haitao, S.; Parham, J.F.; Zhiyong, F.; Meiling, H.; Feng, Y. Evidence for the massive scale of turtle farming in China. Oryx 2008, 42, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Y. High-Efficiency Culture Models Strategy for Soft-Shelled Turtle; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Yin, W.; Qian, D.; Cao, Z.; Shen, Z. Studies on the immunization of bacterin against bacterial diseases of cultivated soft-shelled turtle. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci. Version) 2000, 26, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Rosskopf, W.J.; Shindo, M.K. Syndromes and conditions of commonly kept tortoise and turtle species. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet. Med. 2003, 12, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, X.; Zhu, N.; Kong, L.; He, Z. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas species from diseased Chinese soft-shelled turtles (Trionyx sinensis). Aquacult. Res. 2013, 46, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Hao, G.; Yao, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J.; Yin, W. Identification and pathogenic facts studying for Edwardsiella tarda from Edwardsiellosis of Trionyx sinensis. Freshw. Fish. 2010, 40, 40–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Xie, N. Isolation, determination and antimicrobial susceptibility test of the Citrobacter freundii septicemia from soft-shelled turtle Trionyx sinensis. Fish. Sci. 2008, 27, 42–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Trotta, A.; Marinaro, M.; Sposato, A.; Galgano, M.; Ciccarelli, S.; Paci, S.; Corrente, M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta): A Comparison between Clinical and Commensal Bacterial Isolates. Animals 2021, 11, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, A.; Margie, C.; Mariarosaria, M.; Sunčica, B.; Georgia, D.; Stefano, C.; Serena, P.; Domenico, B.; Marialaura, C. Detection of multi-drug resistance and AmpC β-lactamase/extended-spectrum β-lactamase genes in bacterial isolates of loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta) from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Yue, Y.; Song, J. Pathogenic bacteria and drug therapy for white floor and ulcerate disease of Trionyx sinensis. Freshw. Fish. Sin. 2001, 31, 46–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Pan, X.; Yu, X.; Yin, W.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y. Pathogen in white abdominal shell disease of soft-shelled turtle (Trionyx sinensis) J. Fish. Sci. Chin. 2007, 14, 815–822, (Abstract in English). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Cao, F.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, T. Identification of Edwardsiella tarda from diseased Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) and analysis on antimicrobial resistance. Chin. Fish. Qual. Stan. 2018, 8, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, X.-H. Edwardsiella tarda: An intriguing problem in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.; Abbott, S. Infections associated with the genus Edwardsiella: The role of Edwardsiella tarda in human disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1993, 17, 742–748. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, K.Y.; Siame, B.A.; Tenkink, B.J.; Noort, R.J.; Mok, Y.-K. Edwardsiella tarda—Virulence mechanisms of an emerging gastroenteritis pathogen. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Wu, H.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Role of intestinal inflammation in predisposition of Edwardsiella tarda infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Tang, X.; Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. Antigen uptake and expression of antigen presentation-related immune genes in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) after vaccination with an inactivated Edwardsiella tarda immersion vaccine, following hyperosmotic treatment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, S.; Anand, D.; Sharma, R.; Tripathi, G.; Makesh, M.; Rajendran, K.; Bedekar, M.K. Tissue specific expression profile of some immune related genes in Labeo rohita to Edwardsiella tarda infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.A.N.; Mohapatra, S.; Shimizu, S.; Kitamura, S.-I.; Harakawa, S.; Kawakami, H.; Nakayama, K.; Sawayama, E.; Matsubara, T.; Ohta, K.; et al. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of complement components in red sea bream (Pagrus major) after Edwardsiella tarda and red sea bream Iridovirus (RSIV) challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, G.; Nie, P. Ig M, Ig D and Ig Y and their expression pattern in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, W.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Fang, W.; Li, X. Characterization and functional analysis of toll-like receptor 4 in Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 63, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, Q.; Dai, H. Molecular characterization and expression profiles in response to bacterial infection of Chinese soft-shelled turtle interleukin-8 (IL-8), the first reptilian chemokine gene. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, J.-T.; Chowdhury, I.; Lin, Y.-S.; Liao, C.-F.; Shen, S.-T.; Yu, J.Y.-L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding pituitary thyroid stimulating hormone β-subunit of the Chinese soft-shell turtle Pelodiscus sinensis and regulation of its gene expression. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 146, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdlickova, R.; Toloue, M.; Tian, B. RNA -Seq methods for transcriptome analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 8, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutz, K.-O.; Heilkenbrinker, A.; Lönne, M.; Walter, J.-G.; Stahl, F. Transcriptome analysis using next-generation sequencing. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain and spleen infected with spring viremia of carp virus (SVCV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Transcriptome Analysis on Chinese Shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis during WSSV Acute Infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, H. Transcriptome analysis and discovery of genes involved in immune pathways in Solen strictus (Gould, 1861) under Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhou, J.; Holland, J.W.; Gao, Q. Transcriptome analysis of the endangered Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus): Immune modulation in response to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Veter-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 169, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; Lu, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, H. Evaluation of differentially expressed immune-related genes in intestine of Pelodiscus sinensis after intragastric challenge with lipopolysaccharide based on transcriptome analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; He, Z.; Zheng, T.; Shao, J. De novo transcriptome analysis reveals insights into different mechanisms of growth and immunity in a Chinese soft-shelled turtle hybrid and the parental varieties. Gene 2017, 605, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Y.; Niu, C.-J.; Chen, B.-J.; Storey, K.B. Digital Gene Expression Profiling reveals transcriptional responses to acute cold stress in Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis juveniles. Cryobiology 2018, 81, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, H.; Hang, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Y. Transcriptome profiling analysis of lung tissue of Chinese soft-shell turtle infected by Trionyx sinensis Hemorrhagic Syndrome Virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-seq. Nat. Met. 2008, 5, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cui, C.; Liang, Q.; Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. Apoptosis of hemocytes is associated with the infection process of white spot syndrome virus in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 94, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Cai, W.; Qian, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Xu, W. Growth performance, digestion and metabolism to fish meal replacement by rice protein concentrate in Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-H.; Pan, Y.-X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.-L.; Huang, X.-Q.; Zhong, Y.-W.; Tang, T.; Zhang, J.-S.; Chu, W.-Y.; Shen, Y.-D. Effects of high-fat diet on muscle textural properties, antioxidant status and autophagy of Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Chu, J.-H. Dietary lipid level influences fatty acid profiles, tissue composition, and lipid peroxidation of soft-shelled turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 142, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Ding, X.-Y.; Feng, H.; Xu, Y.-B.; Xue, H.-L.; Zhang, J.-R.; Ng, W.-K. The dietary protein requirement of a new Japanese strain of juvenile Chinese soft shell turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis. Aquaculture 2013, 412–413, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumasu, S.; Uzawa, M.; Iwasawa, A.; Yoshizaki, N. Hatching mechanism of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 155, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.-Y.; Ge, C.-T.; Lei, L.; Gao, Y.-L.; Qian, G.-Y. De-novo characterization of the soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis transcriptome using Illumina RNA-Seq technology. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2013, 14, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouw, L.A.; Daha, M.R. Role of complement in innate immunity and host defense. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 138, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, L.M.; Vogel, L.A.; Bowden, R.M. Understanding the vertebrate immune system: Insights from the reptilian perspective. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Gao, Q.; Tang, B.; Sun, P.; Han, K.; Huang, W. Transcriptome and analysis on the complement and coagulation cascades pathway of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) to ciliate ectoparasite Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Lu, T. Trancriptome profiles of Amur sturgeon spleen in response to Yersinia ruckeri infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, F.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Gai, C.; Yu, X.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Ye, H. Transcriptome analysis of immune response in fat greenling (Hexagrammos otakii) against Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Schlitzer, A.; Placek, K.; Joosten, L.A.; Schultze, J.L. Innate and Adaptive Immune Memory: An Evolutionary Continuum in the Host’s Response to Pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calame, D.G.; Mueller-Ortiz, S.L.; Wetsel, R.A. Innate and adaptive immunologic functions of complement in the host response to Listeria monocytogenes infection. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oss, C.J. Phagocytosis: An overview. Methods Enzymol. 1986, 132, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stuart, L.M.; Ezekowitz, R.A.B. Phagocytosis: Elegant Complexity. Immunity 2005, 22, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Chang, Y. Transcriptome profiling reveals key roles of phagosome and NOD-like receptor pathway in spotting diseased Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ge, H.; Zhai, Q. Transcriptome analysis of the hepatopancreas in Exopalaemon carinicauda infected with an AHPND-causing strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Lü, A.; Liu, R.; Sun, J.; Sung, Y.Y.; Song, Y. Transcriptome analysis in the skin of Carassius auratus challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasmans, F.; Herdt, P.; Nerom, A.; Haesebrouck, F. Induction of the respiratory burst in turtle peritoneal macrophages by Salmonella muenchen. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 25, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Levin, M.; Gebhard, E.; Higgins, B.M.; DeGuise, S.; Godard-Codding, C. Evaluation of immune functions in captive immature loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta). Veter-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 156, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. A structural model of the vacuolar ATPase from transmission electron microscopy. Micron 2005, 36, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.R.; Bortolussi, R.; Issekutz, T.B.; Issekutz, A.C. Increased chemoattractant induced neutrophil oxidative burst, accelerated apoptosis, and dysregulated tyrosine phosphorylation associated with lifelong bacterial infections. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 117, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciraci, C.; Janczy, J.R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Cassel, S.L. Control of innate and adaptive immunity by the inflammasome. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, K.; Reits, E.; Neefjes, J. Present Yourself! By MHC Class I and MHC Class II Molecules. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auchus, R.; Miller, W. The Principles, Enzymes, and Pathways of Human Steroidogenesis. In Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 1784–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, I.P.B.; Brüne, M.; Bradley, A.J. The evolution of the molecular response to stress and its relevance to trauma and stressor-related disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kemenade, B.L.V.-V.; Cohen, N.; Chadzinska, M. Neuroendocrine-immune interaction: Evolutionarily conserved mechanisms that maintain allostasis in an ever-changing environment. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 66, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, A.M. How to Assess Stress in Reptiles. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2014, 23, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).