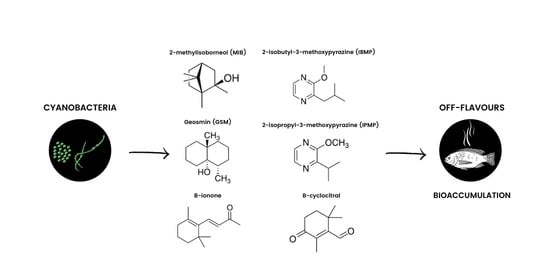
Off-Flavors in Aquacultured Fish: Origins and Implications for Consumers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Off-Flavor Compounds in the Environment: An Overview
3. Off-Flavor Detection Methods
| Target Gene | Primer | Sequence 5′-3′ | Product Length | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| geoA | geo78F | GCATTCCAAAGCCTGGGCTTA | 912 pb | [20] |
| geo971R | CCCTYGTTCATGTARCGGC | |||
| geo982R | ATCGCATGTGCCACTCGTGAC | 905 pb | ||
| MIB synthase | MIB3313F | CTCTACTGCCCCATTACCGAGCGA | 913 pb | [60] |
| MIB4226R | GCCATTCAAACCCGCCGCCCATCCA | |||
| MIB3324F | CATTACCGAGCGATTCAACGAGC | 726 pb | ||
| MIB4050R | CCGCAATCTGTAGCACCATGTTGA | |||
| 16S rRNA | 27F | AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG | 850 pb | [61] |
| 1492R | TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
4. Transfer of Off-Flavor Compounds, Bioaccumulation in Fish, and Toxicity
5. Depuration of Off-Flavors in Fish
6. Effects of Off-Flavors and Consequences for Producer and Consumer
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/state-of-fisheries-aquaculture (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Carriço, J.M.M.; Nakanish, L.I.T.; Chammas, M.A. Manual Do Piscicultor, 1st ed.; SEBRAE, Ed.; SEBRAE: Sergipe, Brazil, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Funge-Smith, S.; Philips, M.J. Aquaculture Systems and Species. In Aquaculture in the Third Millennium, Proceedings of the Conference on Aquaculture in the Third Millennium, Bangkok, Thailand, 20–25 February 2000; NACA: Bangkok, Thailand; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn, J. The Potential for Integrated Biological Treatment Systems in Recirculating Fish Culture—A Review. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Wing, M.T.; Malone, R.F. Biological Filters in Aquaculture: Trends and Research Directions for Freshwater and Marine Applications. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, L.; van Rijn, J. Identification of Conditions Underlying Production of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in a Recirculating System. Aquaculture 2008, 279, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.F.; Hammond, A.; Jauncey, K.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Lawton, L.A. An Investigation into the Occurrence of Geosmin Responsible for Earthy–Musty Taints in UK Farmed Rainbow Trout, Onchorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2006, 259, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, K.K.; Blevins, W.T. Effects of Carbon Source, Phosphorus Concentration, and Several Micronutrients on Biomass and Geosmin Production by Streptomyces halstedii. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 26, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podduturi, R.; Petersen, M.A.; Vestergaard, M.; Jørgensen, N.O.G. Geosmin Fluctuations and Potential Hotspots for Elevated Levels in Recirculated Aquaculture System (RAS): A Case Study from Pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca) Production in Denmark. Aquaculture 2020, 514, 734501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejón, R.M.; Ubeda, C.; Ríos-Reina, R.; Morales, M.L.; Troncoso, A.M. Recent Developments in the Analysis of Musty Odour Compounds in Water and Wine: A Review. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargesheimer, E.E.; Watson, S.B. Drinking Water Treatment Options for Taste and Odor Control. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.S.; Pereira, R.G.; Rodrigues, L.A.; de Matos Casaca, J.; Valenti, W.C.; Fabregat, T.E.H.P. Economic Analysis of Family Trout Farming in Southern Brazil. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; Barros, H.P.; Moraes-Valenti, P.; Bueno, G.W.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil: Past, Present and Future. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Park, Y.G. Geosmin and 2-MIB Removal by Full-Scale Drinking water Treatment Processes in the Republic of Korea. Water 2021, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The Rise of Harmful Cyanobacteria Blooms: The Potential Roles of Eutrophication and Climate Change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.M.; Wang, X.X.; Zhong, Q.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B. Increasing Outbreak of Cyanobacterial Blooms in Large Lakes and Reservoirs under Pressures from Climate Change and Anthropogenic Interferences in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Rai, P.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E. The Role of Algae and Cyanobacteria in the Production and Release of Odorants in Water. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahtera, E.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Kuosa, H.; Pitkänen, H.; Savchuk, O.P.; Tamminen, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Voss, M.; Wasmund, N.; et al. Internal Ecosystem Feedbacks Enhance Nitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria Blooms and Complicate Management in the Baltic Sea. AMBIO 2007, 36, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.G.; DeSellas, A.M.; Fletcher, R.; Heintsch, L.; Morley, A.; Nakamoto, L.; Utsumi, K. Algal Blooms in Ontario, Canada: Increases in Reports since 1994. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, S.; Jiang, J.; Saint, C.P.; Cane, D.; Monis, P.T. Isolation and Characterization of the Gene Associated with Geosmin Production in Cyanobacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8027–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, N.O.G.; Podduturi, R.; Burford, M.A. Relations between Abundance of Potential Geosmin- and 2-MIB-Producing Organisms and Concentrations of These Compounds in Water from Three Australian Reservoirs. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.-AQUA 2016, 65, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hobson, P.; An, W.; Burch, M.D.; House, J.; Yang, M. Earthy Odor Compounds Production and Loss in Three Cyanobacterial Cultures. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5165–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, M.B.; de Jonge, N.; Bjerregaard, S.M.; Podduturi, R.; Jørgensen, N.O.G.; Petersen, M.A.; David, G.S.; da Silva, R.J.; Nielsen, J.L. Microbial Production of the Off-Flavor Geosmin in Tilapia Production in Brazilian Water Reservoirs: Importance of Bacteria in the Intestine and Other Fish-Associated Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Ridal, J.; Boyer, G.L. Taste and Odour and Cyanobacterial Toxins: Impairment, Prediction, and Management in the Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.S. Off-Flavor Problems in Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2000, 8, 45–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Kuzuyama, T.; Komatsu, M.; Shin-Ya, K.; Omura, S.; Cane, D.E.; Ikeda, H. Terpene Synthases Are Widely Distributed in Bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, B.K.; Chislock, M.F.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication Mediates a Common Off-Flavor Compound, 2-Methylisoborneol, in a Drinking Water Reservoir. Water Res. 2016, 92, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Ohta, A.; Iwata, C.; Horikawa, A.; Tsuji, K.; Ito, E.; Ikai, Y.; Harada, K. Lysis of Cyanobacteria with Volatile Organic Compounds. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Mao, M.; Li, L.; Liao, W. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Formation of Earthy and Musty Odor Compounds: Chloroanisoles during Water Chlorination. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houle, S.; Schrader, K.K.; Le Franccois, N.R.; Comeau, Y.; Kharoune, M.; Summerfelt, S.T.; Savoie, A.; Vandenberg, G.W. Geosmin Causes Off-Flavour in Arctic Charr in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Monis, P.; Baker, P.; Giglio, S. Biochemistry and Genetics of Taste- and Odor-Producing Cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, N.N.; Lechevalier, H.A. Geosmin, an Earthy-Smelling Substance Isolated from Actinomycetes. Appl. Microbiol. 1965, 13, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medsker, L.L.; Jenkins, D.; Thomas, J.F.; Field, R.; Richmond, C.; Koch, C. Odorous Compounds in Natural Waters 2-Exo-Hydroxy-2-Methylbornane, the Major Odorous Compound Produced by Several Actinomycetes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1969, 3, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-S.; Lee, C.S.; Srivastava, A.; Oh, H.-M. Effects of Environmental Factors on Cyanobacterial Production of Odorous Compounds: Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, C.; Abril, M.; Guasch, H.; Pou, N.; Proia, L.; Ricart, M.; Ordeix, M.; Llenas, L. Water Flow and Light Availability Influence on Intracellular Geosmin Production in River Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.W. Observations on the African Lung-Fish, Protopterus aethiopicus, and on Evolution from Water to Land Environments. Ecology 1931, 12, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.A.; Mashini, C.I.; Safferman, R.S. Recent Developments in the Chemistry of Odour in Water: The Cause of Earthy/Musty Odour. Water Treat. Exam. 1970, 19, 106–119. [Google Scholar]
- Piet, G.J.; Zoeteman, B.C.J.; Kraayeveld, A.J.A. Earthy Smelling Substances in Surface Waters of the Netherlands. Water Treat. Exam. 1972, 19, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yagi, M.; Kajino, M.; Matsuo, U.; Ashitani, K.; Kita, T.; Nakamura, T. Odor Problems in Lake Biwa. Water Sci. Technol. 1983, 15, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.H.; Corado, A.; Chou, D.; McGuire, M.J.; Butterworth, S. AWWA Taste and Odor Survey. J.-Am. Water Works Assoc. 1996, 88, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömür-Özbek, P. Global Taste and Odor Survey of Water Utilities: Final Report to the American Water Works Association from the Taste and Odor Committee; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, P.-E. Off-Flavours in Aquatic Ecosystems—An Introduction. Water Sci. Technol. 1983, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangchai, N.; Wigraiboon, S.; Shimizu, K.; Iwami, N.; Itayama, T. Off-Flavor in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Reared in Cages and Earthen Ponds in Northern Thailand. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 44, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.-M.; Roxborough, M.; Mazumder, A. Origins and Implications of Drinking Water Odours in Lakes and Reservoirs of British Columbia, Canada. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.S. Harmful algal blooms: Musty Warnings of Toxicity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, A473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.; Watson, S.B. Biochemical and Ecological Control of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Source Waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitlin, B.; Watson, S.B. Actinomycetes in Relation to Taste and Odour in Drinking Water: Myths, Tenets and Truths. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcombe, G.; Ho, L.; Baker, P. Management Strategies for Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae): A Guide for Water Utilities; Research Report 74; Water Quality Research Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Hu, N.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L. Aquaculture Feeds Can Be Outlaws for Eutrophication When Hidden in Rice Fields? A Case Study in Qianjiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A.M. USEPA Secondary Maximum Contaminant Limits: A Strategy for Drinking Water Quality and Consumer Acceptability Iron and Dairy View Project Heavy Metals Mobility in Soil View Project. 2015. Available online: https://www.waterrf.org/resource/epa-secondary-maximum-contaminant-levels-strategy-drinking-water-quality-and-consumer-0 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Viana, L.; English, M. The Application of Chromatography in the Study of Off-Flavour Compounds in Pulses and Pulse by-Products. LWT 2021, 150, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Feng, X.; Wilkin, J.D.; Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Abrahams, A.M.; Tugizimana, F. Application of Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)-Based Metabolomics for the Study of Fermented Cereal and Legume Foods: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1514–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, N.; Sasamoto, K.; Takino, M.; Yamashita, S.; Daishima, S.; Heiden, A.; Hoffman, A. Determination of Trace Amounts of Off-Flavor Compounds in Drinking Water by Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction and Thermal Desorption GC-MS. Analyst 2001, 126, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltussen, E.; Sandra, P.; David, F.; Cramers, C. Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction SBSE, a Novel Extraction Technique for Aqueous Samples: Theory and Principles. J. Microcolumn Sep. 1999, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Lord, H.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Applications of Solid-Phase Microextraction in Food Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 880, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, R.; Gundlach, M.; Su, C.-P. Novel Concepts and Challenges of Flavor Microencapsulation and Taste Modification. In Microencapsulation in the Food Industry; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Chapter 33; pp. 421–442. ISBN 978-0-12-404568-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; He, X.; Cane, D.E. Biosynthesis of the Earthy Odorant Geosmin by a Bifunctional Streptomyces coelicolor Enzyme. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Tsuda, M.; Omura, S.; Oikawa, H.; Ikeda, H. Identification and Functional Analysis of Genes Controlling Biosynthesis of 2-Methylisoborneol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7422–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, R. Genes Associated with 2-Methylisoborneol Biosynthesis in Cyanobacteria: Isolation, Characterization, and Expression in Response to Light. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurnäkki, S.; Gomez-Saez, G.V.; Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Sivonen, K. Identification of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Cyanobacteria and Molecular Detection Methods for the Producers of These Compounds. Water Res. 2015, 68, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, A.G.; Dees, P.M.; Sayler, G.S. Growth of a Bacterial Consortium on Triclosan. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 36, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Laventer, C.; Chorin-Kirsch, I. Off-flavor in Carp from Fishponds in the Coastal Plain and the Galil. Bamidgeh 1967, 19, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, R.; Whangchai, N.; Sompong, U.; Prarom, W.; Iwami, N.; Itayama, T.; Nomura, N.; Sugiura, N. Off-Flavour in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Cultured in an Integrated Pond-Cage Culture System. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, Z.G.; Kerepeczki, É.; Pekár, F.; Gál, D. Natural Origins of Off-Flavours in Fish Related to Feeding Habits. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P.; Koskela, J.; Kaseva, J.; Vielma, J. Accumulation of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in European Whitefish Coregonus lavaretus and Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in RAS. Fishes 2020, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffret, M.; Yergeau, É.; Pilote, A.; Proulx, É.; Proulx, D.; Greer, C.W.; Vandenberg, G.; Villemur, R. Impact of Water Quality on the Bacterial Populations and Off-Flavours in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.A.; Hyldig, G.; Strobel, B.W.; Henriksen, N.H.; Jørgensen, N.O.G. Chemical and Sensory Quantification of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) from Recirculated Aquacultures in Relation to Concentrations in Basin Water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12561–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howgate, P. Tainting of Farmed Fish by Geosmin and 2-Methyl-Iso-Borneol: A Review of Sensory Aspects and of Uptake/Depuration. Aquaculture 2004, 234, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, G.S.; Wolters, W.R.; Schrader, K.K.; Summerfelt, S.T. Impact of Depuration of Earthy-Musty off-Flavors on Fillet Quality of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo salar, Cultured in a Recirculating Aquaculture System. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 50, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, L.; Lehmann, M.; Simon, D.; de Andrade, H.H.R.; de Abreu, B.R.R.; Nabinger, D.D.; Grivicich, I.; Juliano, V.B.; Dihl, R.R. Agents of Earthy-Musty Taste and Odor in Water: Evaluation of Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Toxicogenomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.; Scolding, J. Direct Application of Ozone in Aquaculture Systems. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurangwa, E.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Microorganisms in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems and Their Management. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 7, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyantha Indrajith, H.; Davey, K. A Predictive Model for Taste Taint Accumulation in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) Farmed-Fish–Demonstrated with Geosmin (GSM) and 2-Methylisoborneol (MIB). Ecol. Model. 2014, 291, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Z.; Sourinejad, I.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. Application of Zeolites in Aquaculture Industry: A Review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam-Koong, H.; Schroeder, J.P.; Petrick, G.; Schulz, C. Removal of the Off-Flavor Compounds Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol from Recirculating Aquaculture System Water by Ultrasonically Induced Cavitation. Aquac. Eng. 2016, 70, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiou, T.; Triantis, T.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A. Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Based Catalysts for the Degradation and Mineralization of Cyanobacterial Toxins and Water Off-Odor Compounds under UV-A, Solar and Visible Light. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 261, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Motoo, U.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Photocatalytic Degradation of Geosmin by Pd Nanoparticle Modified WO3 Catalyst under Simulated Solar Light. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Evgenidou, E.; Lambropoulou, D.; Konstantinou, I. A Review on Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Taste and Odor Compounds from Aqueous Media. Water Res. 2014, 53, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, L.; Pettit, S.L.; Zhao, W.; Michaels, J.T.; Kuhn, J.N.; Alcantar, N.A.; Ergas, S.J. Oxidation of off Flavor Compounds in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems Using UV-TiO2 Photocatalysis. Aquaculture 2019, 502, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaria, S.; van Rijn, J. Off-Flavor Compounds in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS): Production and Removal Processes. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 83, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Grimm, C.; Summerfelt, S.; Fischer, G.; Good, C. Depuration System Flushing Rate Affects Geosmin Removal from Market-Size Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 90, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.A. Food Safety Knowledge and Practices of Consumers in the USA. J. Consum. Stud. Home Econ. 1995, 19, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.F.; Bennett, L.W.; Graham, W.H. Off-Flavor in the Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Due to 2-Methylisoborneol and Its Dehydration Products. Water Sci. Technol. 1988, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, P.B.; Lloyd, S.W. Influence of Fat Content on Uptake and Depuration of the Off-Flavor 2-Methylisoborneol by Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 2406–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q. Accumulation and Depuration of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Japanese Seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus) Fed Diets Containing Different Dietary Protein and Lipid Levels in a Recirculating Aquaculture System; Norwegian University of Life Sciences: Ås, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schram, E.; Schrama, J.W.; van Kooten, T.; Kwadijk, C.J.A.F.; Kampen, H.; van de Heul, J.W.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Murk, A.J. Experimental Validation of Geosmin Uptake in Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Waldbaum) Suggests Biotransformation. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, S.M.G.; Mathies, V.D.; Fioravanzo, R.F. Off-Flavor Por Geosmina e 2-Metilisoborneol Na Aquicultura. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2012, 33, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johnsen, P.; Lloyd, S.; Vinyard, B.; Dionigi, C. Effects of Temperature on the Uptake and Depuration of 2-Methylisoborneol (MIB) in Channel Catfish Ictalurus punctatus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 27, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Schrader, K.; Ruan, E.; Swift, B.; Aalhus, J.; Juarez, M.; Wolters, W.; Burr, G.; Good, C.; Summerfelt, S.T. Evaluation of Depuration Procedures to Mitigate the Off-Flavor Compounds Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol from Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar Raised to Market-Size in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 61, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.F.; Plakas, S.M.; Holley, J.H.; Kitzman, J.V.; Guarino, A.M. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Disposition of the Off-Flavor Compound 2-Methylisoborneol in the Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd-Bredbenner, C.; Maurer, J.; Wheatley, V.; Cottone, E.; Clancy, M. Observed Food Safety Behaviors of Young Adults. Br. Food J. 2007, 109, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costell, E.; Tárrega, A.; Bayarri, S. Food Acceptance: The Role of Consumer Perception and Attitudes. Chemosens. Percept. 2010, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklinder, I.; Lindblad, M.; Eriksson, L.; Finnson, A.; Lindqvist, R. Home Storage Temperatures and Consumer Handling of Refrigerated Foods in Sweden. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammarco, M.; Ripabelli, G.; Grasso, G. Consumer Attitude and Awareness towards Food-Related Hygienic Hazards. J. Food Saf. 2007, 17, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, K.S. Health Benefits and Potential Risks Related to Consumption of Fish or Fish Oil. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 38, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calanche, J.B.; Beltrán, J.A.; Hernández Arias, A.J. Aquaculture and Sensometrics: The Need to Evaluate Sensory Attributes and the Consumers’ Preferences. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Peña, E.; Manthey, F.A. Ingredient Composition and Pasta:Water Cooking Ratio Affect Cooking Properties of Nontraditional Spaghetti. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Brennan, M.A.; Brennan, C.S. The Effect of Semolina Replacement with Protein Powder from Fish (Pseudophycis bachus) on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Pasta. LWT 2018, 89, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P.; Vielma, J.; Pakkanen, H.; Alén, R. Depuration of Geosmin- and 2-Methylisoborneol-Induced off-Flavors in Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) Farmed European Whitefish Coregonus lavaretus. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höckelmann, C.; Jüttner, F. Off-Flavours in Water: Hydroxyketones and β-Ionone Derivatives as New Odour Compounds of Freshwater Cyanobacteria. Flavour Fragr. J. 2005, 20, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, T. Economic Impact of Off-Flavor to the U.S. Catfish Industry. In Off-Flavors in Aquaculture; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 13–29. ISBN 0-8412-3821-9. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | Chemical Structure | Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight | CAS Number | Water Half-Life | Log Kow | Water Solubility (mg·cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIB | 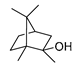 | C11H20O | 168.3 | 2371-42-8 | 19.5 days | 3.13 | 0.45 |
| GEO | 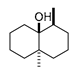 | C12H22O | 182.3 | 16423-19-1 | 24.5 days | 3.7 | 0.0512 |
| IPMP | 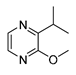 | C8H12N2O | 152.2 | 25773-40-4 | n.a. | 2.41 | 61.4 |
| IBMP |  | C9H14N2O | 166.2 | 24683-00-9 | n.a. | 2.72 | 20.9 |
| β-Ionone | 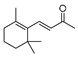 | C13H20O | 192.2 | 14901-07-6 | n.a. | 2.9 | 0.104 |
| β-Cyclocitral | 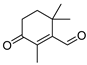 | C10H16O | 152.2 | 432-25-7 | n.a. | 2.4 | Insoluble |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moretto, J.A.; Freitas, P.N.N.; Souza, J.P.; Oliveira, T.M.; Brites, I.; Pinto, E. Off-Flavors in Aquacultured Fish: Origins and Implications for Consumers. Fishes 2022, 7, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010034
Moretto JA, Freitas PNN, Souza JP, Oliveira TM, Brites I, Pinto E. Off-Flavors in Aquacultured Fish: Origins and Implications for Consumers. Fishes. 2022; 7(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoretto, Jéssica A., Paloma N. N. Freitas, Juliana P. Souza, Thalita M. Oliveira, Isabella Brites, and Ernani Pinto. 2022. "Off-Flavors in Aquacultured Fish: Origins and Implications for Consumers" Fishes 7, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010034
APA StyleMoretto, J. A., Freitas, P. N. N., Souza, J. P., Oliveira, T. M., Brites, I., & Pinto, E. (2022). Off-Flavors in Aquacultured Fish: Origins and Implications for Consumers. Fishes, 7(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010034