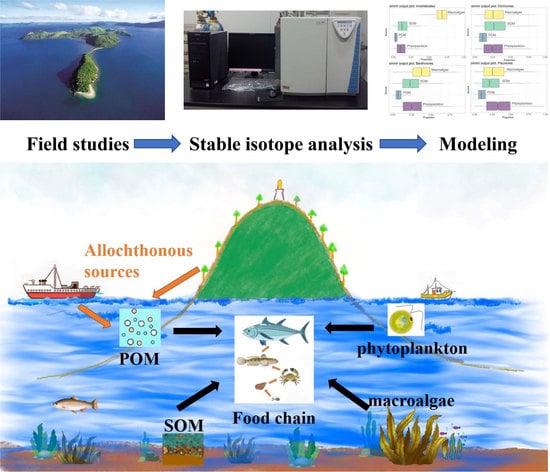
Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
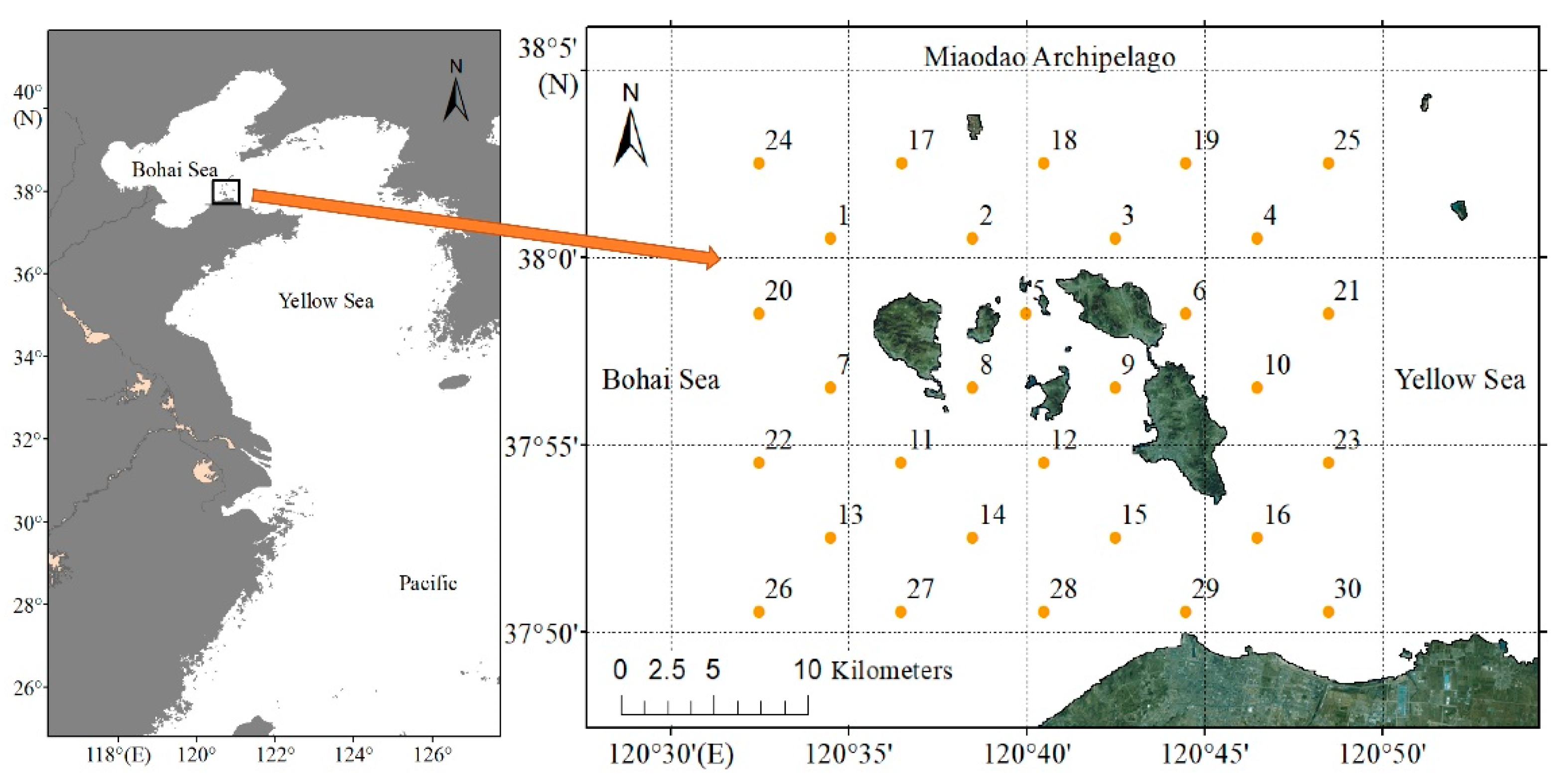
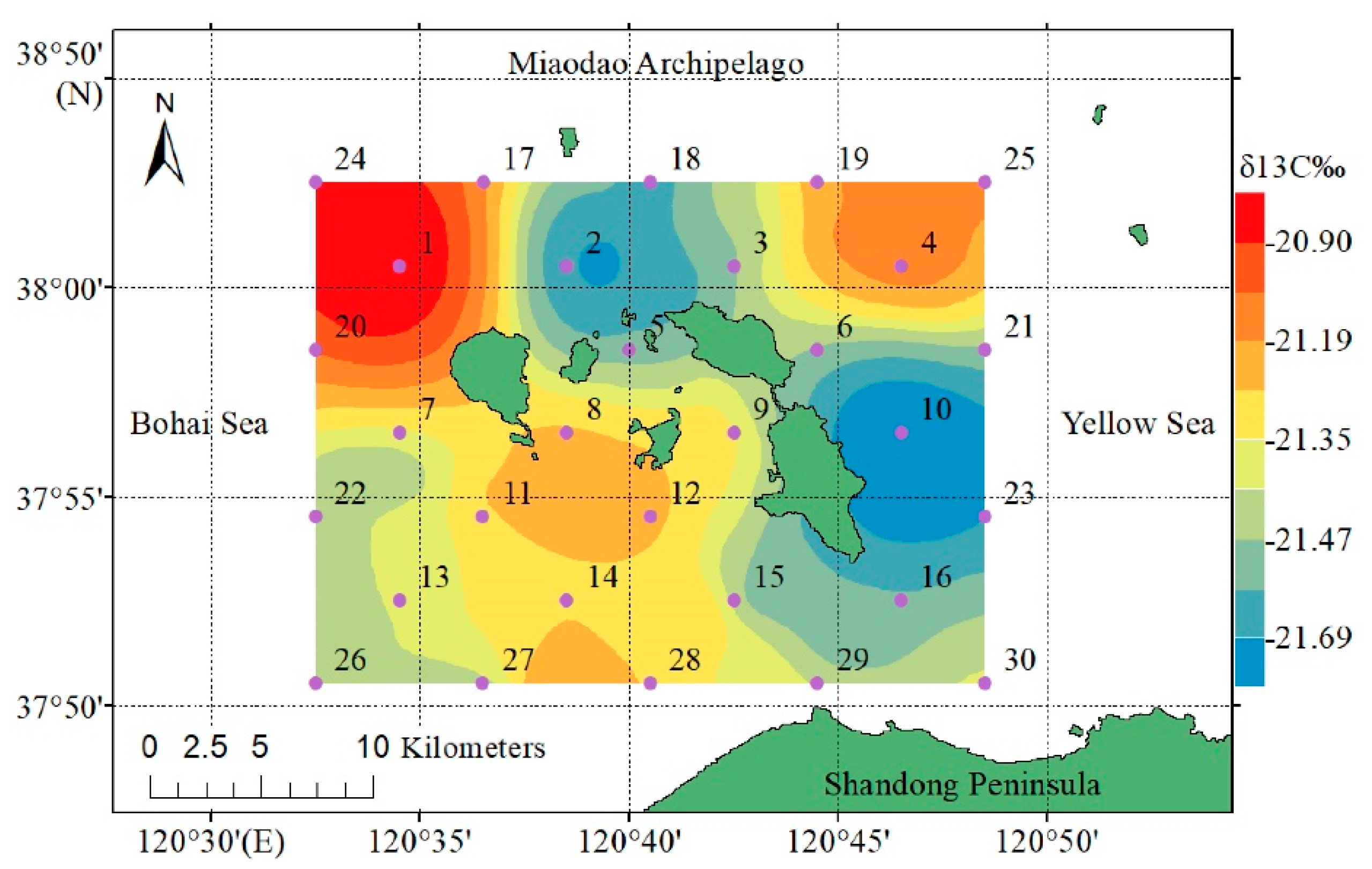
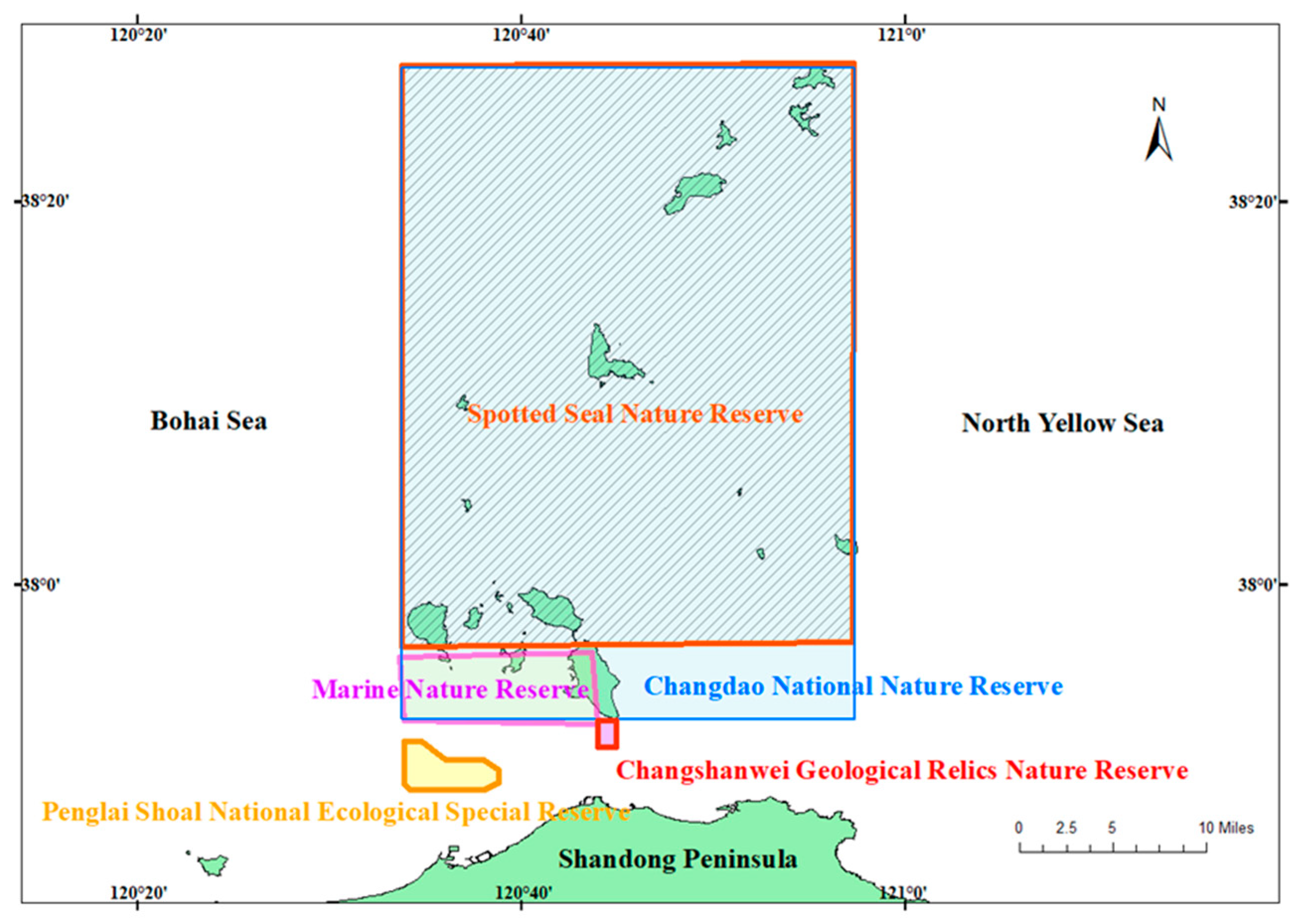
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
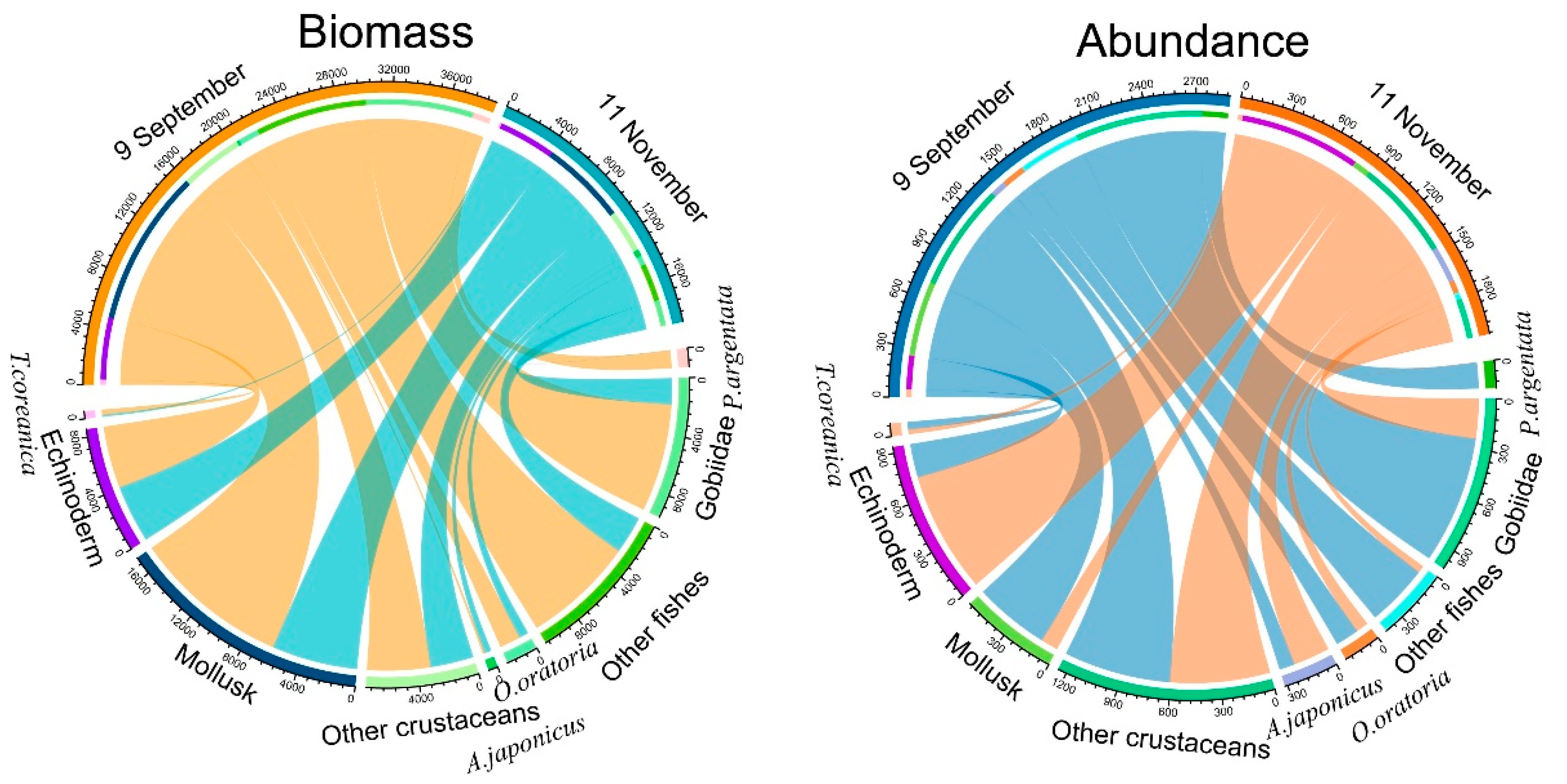
3.1. Fishery Resources
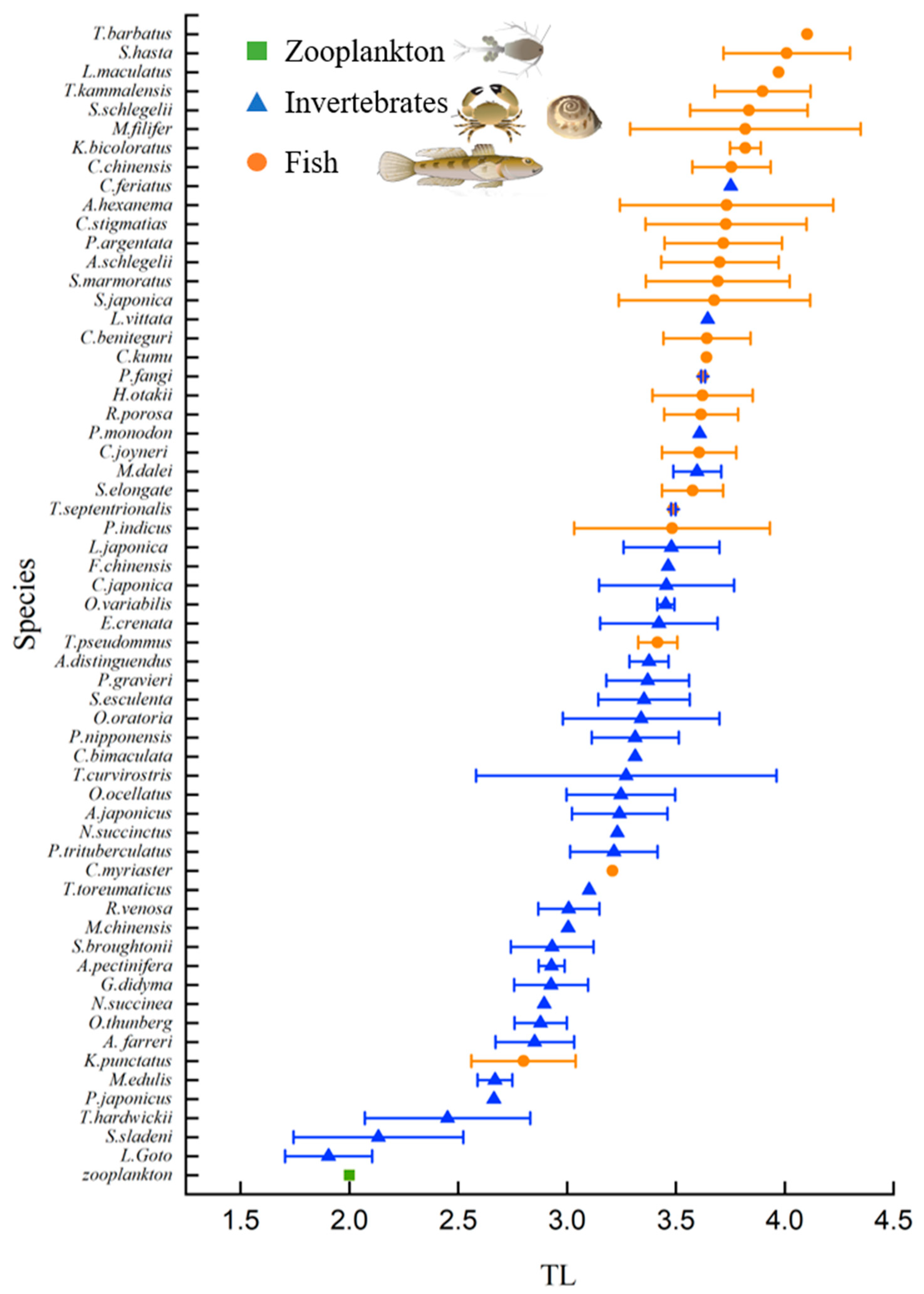
3.2. Trophic Level
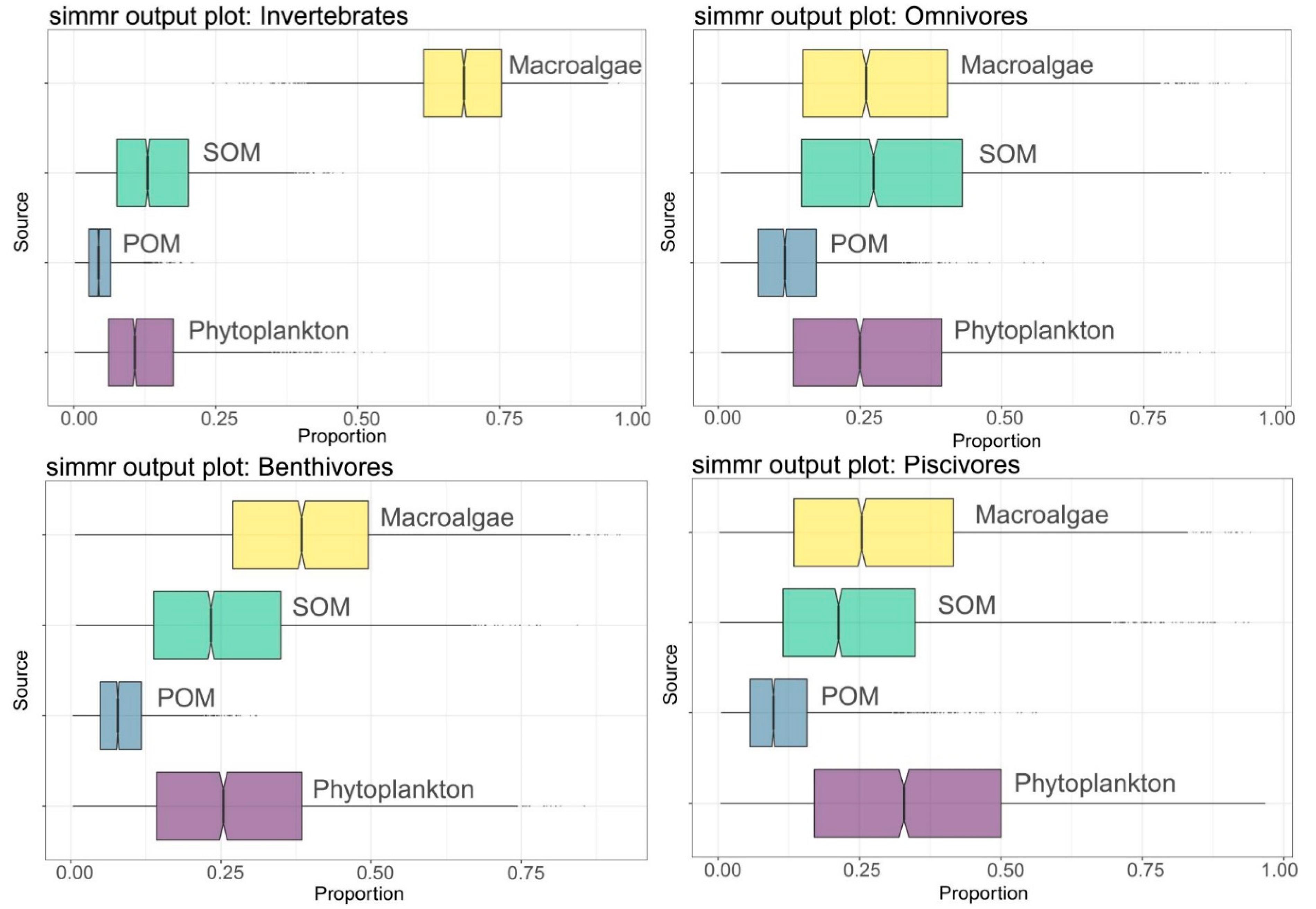
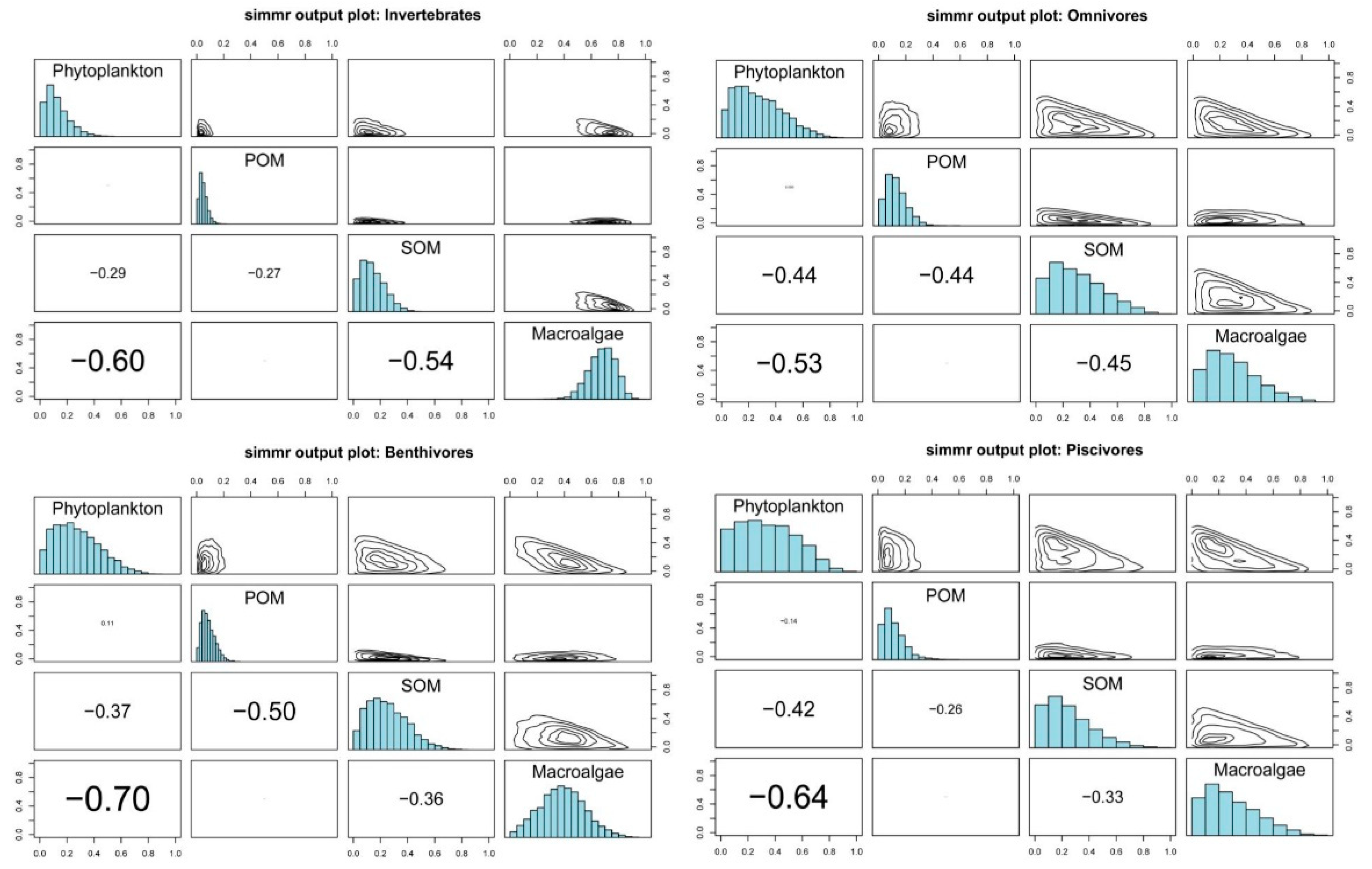
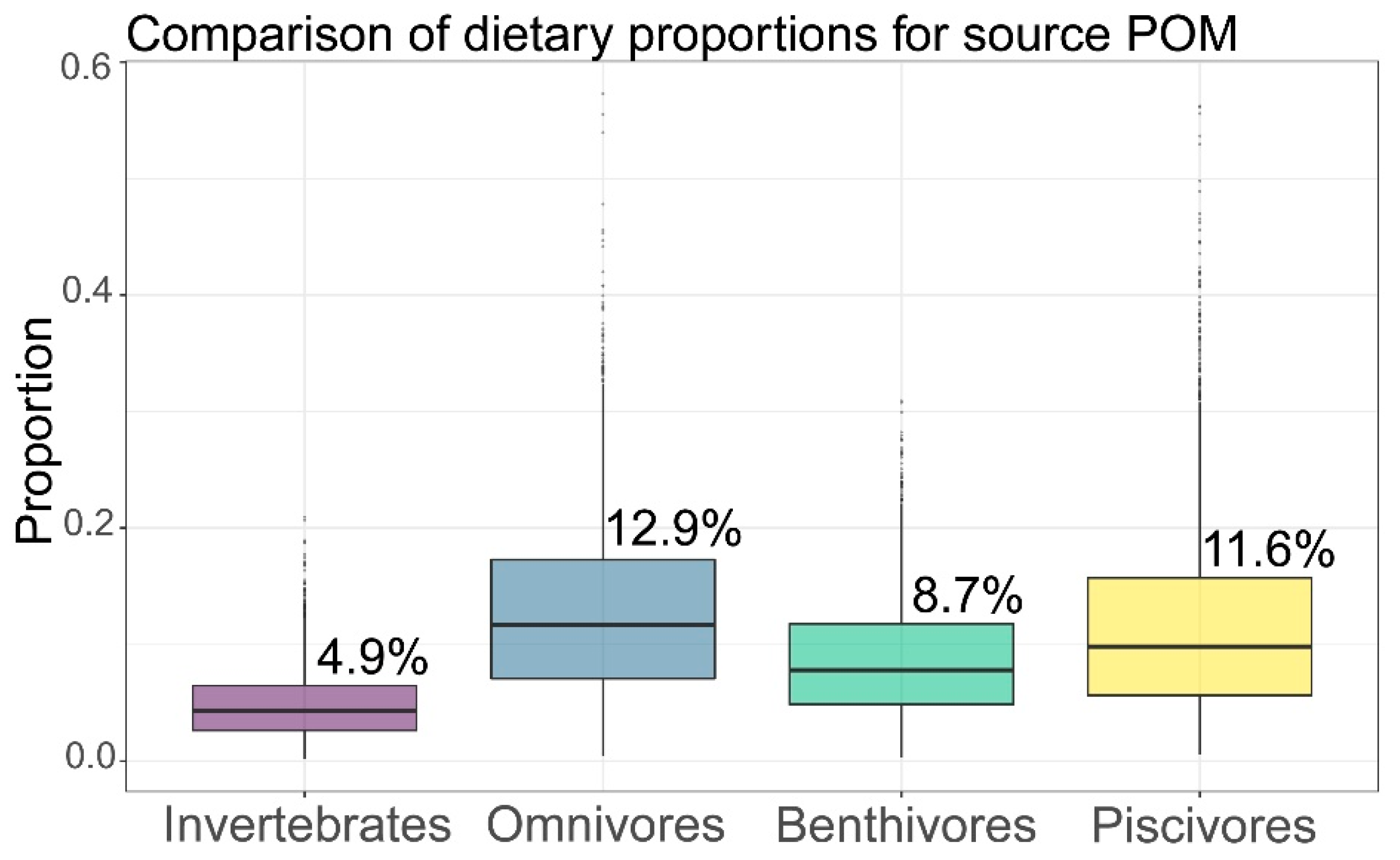
3.3. Basic Carbon Source Contribution
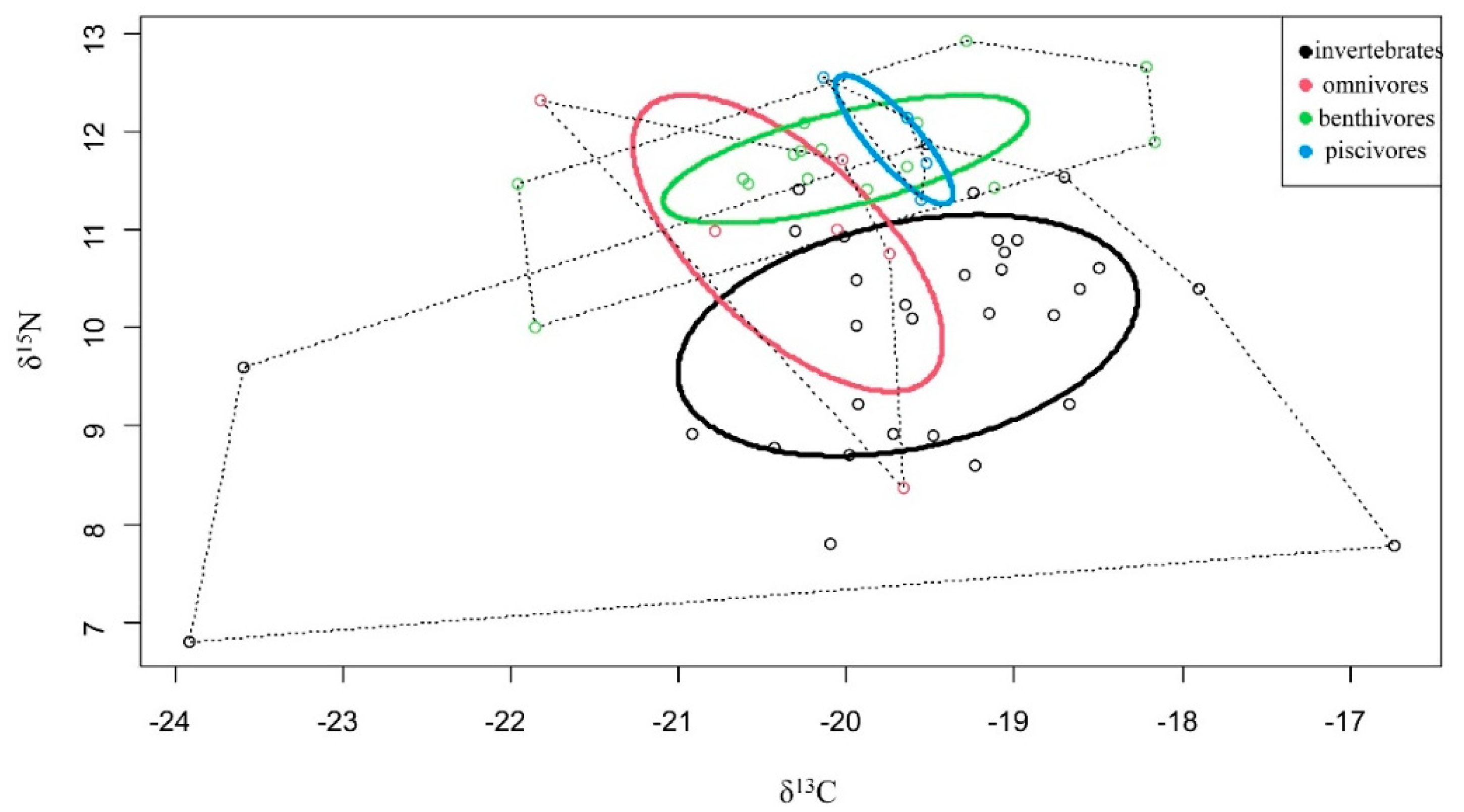
3.4. Isotopic Niche Width
4. Discussion
4.1. Division of Basic Carbon Sources and Consumers
4.2. Analysis of Potential Carbon Sources in Food Web
4.3. Marine Consumers’ Resource Utilization of Different Primary Producers’ Carbon Sources
4.4. Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metz, B.; Davidson, O.; Swart, R. Climate Change 2001: Mitigation, Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment [TAR] Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; ISBN 0521807697. [Google Scholar]
- Melillo, J.M.; Callaghan, T.V.; Woodward, F.I. Climate change: The IPCC scientific assessment. In Effects on Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; pp. 283–310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhang, F.; Jiao, N.Z. Deciphering the mechanisms of carbon sink through a holistic view of interactions between land and ocean. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3399–3405. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.D.L.; Cabral, R.B.; Cantor, M.; Hatton, I.; Kortsch, S.; Patrício, J.; Yamamichi, M. Linking structure and function in food webs: Maximization of different ecological functions generates distinct food web structures. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelkerken, I.; Goldenberg, S.U.; Ferreira, C.M.; Ullah, H.; Connell, S.D. Trophic pyramids reorganize when food web architecture fails to adjust to ocean change. Science 2020, 369, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovinszky, T.; van Veen, F.J.F.; Jongema, Y.; Dicke, M. Direct and indirect effects of resource quality on food web structure. Science 2008, 319, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J. Stable isotopes dissect aquatic food webs from the top to the bottom. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoint, G.; Nyssen, F.; Gobert, S.; Dauby, P.; Bouquegneau, J.M. Relative impact of a seagrass bed and its adjacent epilithic algal community in consumer diets. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Ríos, C.; Gerdes, D.; Brey, T. Trophic structure of shallow-water benthic communities in the sub-Antarctic Strait of Magellan. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillikin, D.P.; Lorrain, A.; Bouillon, S.; Willenz, P.; Dehairs, F. Stable carbon isotopic composition of Mytilus edulis shells: Relation to metabolism, salinity, δ13CDIC and phytoplankton. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, M.J.; Irl, S.D.H.; Beierkuhnlein, C. Elevation-driven ecological isolation promotes diversification on Mediterranean islands. Acta Oecologica 2013, 47, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Shi, H.; Zheng, W.; Ding, D. Spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem health and its sensitivity to pressure in the waters of nearshore archipelago. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Qin, X.; Zheng, W.; Peng, S. Impact factors identification of spatial heterogeneity of herbaceous plant diversity on five southern islands of Miaodao Archipelago in North China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, E. Evaluation on island ecological vulnerability and its spatial heterogeneity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.Z.; Peng, G.G.; Tao, Y.C.; Huang, J.J.; Lin, X.Q.; Huang, L.F. Trophic gauntlet effects on fisheries recovery: A case study in Sansha Bay, China. Ecosyst. Heal. Sustain. 2021, 7, 1965035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlbach, D.; Graeve, M.; ALange, B.; David, C.; Peeken, I.; Flores, H. The importance of ice algae-produced carbon in the central Arctic Ocean ecosystem: Food web relationships revealed by lipid and stable isotope analyses: Ice algal carbon in Arctic food web. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2027–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Li, C.H.; Chen, Z.Z.; Huang, H.H. Stable isotopes of nitrogen in zooplankton in the southern South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2015, 2, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollff, C. Seasonal variation in δ13C and δ15N of size-fractionated plankton at a coastal station in the northern Baltic proper. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 203, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, P.B.; Flecker, A.S. Rapid turnover of tissue nitrogen of primary consumers in tropical freshwaters. Oecologia 2006, 148, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, K.; Zeng, Q.F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H. Collection, treatment and preservation of biologically stable isotopes in aquatic ecology. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2020, 44, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.M.; Jardine, T.D.; Miller, T.J.; Bunn, S.E.; Cunjak, R.A.; Lutcavage, M.E. Lipid corrections in carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analyses: Comparison of chemical extraction and modelling methods. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; MacNeil, M.A.; McMeans, B.C.; Olin, J.; Dudley, S.F.; Cliff, G.; Wintner, S.P.; Fennessy, S.T.; Fisk, A.T. Rescaling the trophic structure of marine foodwebs. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reum, J.C.P.; Jennings, S.; Hunsicker, M.E. Implications of scaled δ15N fractionation for community predator-prey body mass ratio estimates in size-structured food webs. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Phillips, D.L.; Bearhop, S.; Semmens, B.X.; Ward, E.J.; Moore, J.W.; Jackson, A.L.; Grey, J.; Kelly, D.J.; Inger, R. Bayesian stable isotope mixing models. Environmetrics 2013, 24, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.; Moore, J.W.; Parnell, A.; Semmens, B.X.; Ward, E.J. Best practices for use of stable isotope mixing models in food-web studies. Can. J. Zool. 2014, 92, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER-Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R: Bayesian isotopic niche metrics. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Food relationship of fish in the Bohai Sea. Adv. Fish. Sci. 2018, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Han, D.Y.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xue, Y.; Ji, Y.P. Analysis of feeding habits of blenny fong in Jiaozhou Bay using stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Fish. Sci. China 2014, 21, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.F.; Liu, S.D.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of feeding habits of small-eyed greenfin in haizhou bay in autumn. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 17, 6433–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaude, A.M. Fish ecology and terrestrial carbon use in coastal areas: Implications for marine fish production. J. Anim. Ecol. 2005, 74, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Stable isotope analysis of food sources sustaining the subtidal food web of the Yellow River Estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Araujo, M.S.; Boucek, R.; Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Harrison, E.; Jud, Z.R.; Matich, P.; Rosenblatt, A.; Vaudo, J.J.; Yeager, L. Applying stable isotopes to examine food-web structure: An overview of analytical tools. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, C.; Ke, Z.; Li, D.; Gao, Y. Effects of resource availability and hydrological regime on autochthonous and allochthonous carbon in the food web of a large cross-border river (China). Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 612, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Gong, Y. Food web structure of the East Lake Taihu by analysis of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Chin. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.L.; Meng, F.; Han, Y.B. Studies on 13C/12C ratios ai a tracer for food web in a marine ecosystem–the trophic relations in pelagic food webs in Laoshan Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1999, 6, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Li, Y.K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Food web foundation and seasonal variation of trophic structure based on the stable isotopic technique in the marine ranching of Haizhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2292–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.K.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S. The potential carbon source and trophic level analysis of main organisms in coastal water of Lüsi fishing ground, based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis. Haiyang Xuebao 2021, 43, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.J.; Zhu, X.M.; JI, Y.N.; JIANG, Y.Z.; LIN, N.; WANG, Y. Study on the food web structure and their trophic levels of marine ranching area in Xiangshan Harbor. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Collins, S.; Hamilton, S.K.; Tank, J.L.; Johnson, S.; Webster, J.R.; Simon, K.S.; Whiles, M.R.; Rantala, H.M.; McDowell, W.; et al. You are not always what we think you eat: Selective assimilation across multiple whole-stream isotopic tracer studies. Ecology 2014, 95, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miyatake, T.; Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.C.W.; Stal, L.J.; Boschker, H.T.S. Tracingcarbon flow from microphytobenthos to major bacterial groups in an intertidal marine sediment by using an in situ 13C pulse-chase method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Wu, H.L.; Yu, K.F.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.H. Research progress on the effects of macroalgae on carbon sink. J. Fish. Sci. China 2015, 22, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Currin, C.A.; Newell, S.Y.; Pearl, H.W. The role of standing dead Spartina alterniflora and benthic microalgae in saltmarsh food webs: Considerations based on multiple stable isotope analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 121, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A. Seasonal variations in the stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (13C/12C and 15N/14N) of primary producers and consumers in a western Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, P.; Rajagopal, S.; van der Velde, G.; Fenzi, G.; Kassenberg, J.; Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A.; Giordani, G. Sediment features, macrozoobenthic assemblages and trophic relationships (δ13C and δ15N analysis) following a dystrophic event with anoxia and sulphide development in the Santa Giusta lagoon (western Sardinia, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.A.E.; Fox, M.D. Characterizing energy flow in kelp forest food webs: A geochemical review and call for additional research. Ecography 2021, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorke, C.E.; Page, H.M.; Miller, R.J. Sea urchins mediate the availability of kelp detritus to benthic consumers. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2019, 286, 20190846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabara, S.S. Trophic structure and potential carbon and nitrogen flow of a rhodolith bed at Santa Catalina Island inferred from stable isotopes. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, S.M.; Wing, S.R. Importance of local production versus pelagic subsidies in the diet of an isolated population of bottlenose dolphins Tursiops sp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 321, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lesage, V.; Hammill, M.; Kovacs, K. Marine mammals and the community structure of the Estuary and Gulf of St Lawrence, Canada: Evidence from stable isotope analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 210, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B. How to heal an ocean. Nature 2017, 543, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernansky, R. The biodiversity revolution. Nature 2017, 546, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.H.; Meng, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, Q.F.; Yu, K.F.; Cai, C.E.; He, P.M. Studies on photosynthesis carbon fixation and ocean acidification prevention in Ulva prolifera. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 34, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, C.T. Preliminary analysis of carbon sink mechanism and potential of artificial reef ecosystem. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2013, 34, 65–69. [Google Scholar]

| Fish | Diet | Fish | Diet | Fish | Diet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. argentata | Benthivores | C. chinensis | Benthivores | R. porosa | Benthivores |
| A. schlegelii | Omnivores | T. barbatus | Benthivores | T. septentrionalis | Omnivores |
| S. schlegelii | Piscivores | H. otakii | Benthivores | S. japonica | Benthivores |
| C. stigmatias | Benthivores | C. joyneri | Benthivores | K. bicoloratus | Benthivores |
| A. hexanema | Benthivores | P. fangi | Benthivores | P. indicus | Omnivores |
| S. hasta | Benthivores | C. beniteguri | Benthivores | S. elongate | Piscivores |
| M. filifer | Benthivores | T. pseudommus | Omnivores | K. punctatus | Omnivores |
| T. kammalensis | Omnivores | L. maculatus | Piscivores | C. kumu | Benthivores |
| S. marmoratus | Piscivores | C. myriaster | Benthivores |
| Category | Number | δ13C ± SD (‰) | δ13C Range (‰) | δ15N ± SD (‰) | δ15N Range (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phytoplankton | 12 | −19.44 ± 0.80 | −21.85~−18.52 | 4.39 ± 1.99 | 0.38~7.54 |
| POM | 11 | −25.14 ± 1.24 | −26.54~−22.29 | 3.23 ± 1.73 | 1.38~7.59 |
| SOM | 11 | −21.38 ± 0.28 | −21.85~−20.69 | 4.7 ± 2.11 | 0.85~8.96 |
| macroalgae | 6 | −19.65 ± 2.31 | −22.05~−16.92 | 6.10 ± 1.81 | 3.64~8.58 |
| invertebrates | 272 | −19.27 ± 2.05 | −25.43~−16.74 | 9.61 ± 1.74 | 2.84~13.06 |
| fish | 208 | −20.04 ± 0.92 | −22.26~−15.10 | 11.55 ± 0.89 | 7.35~14.54 |
| Consumers | Invertebrates | Omnivores | Benthivores | Piscivores | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources | Mean% | SD% | Mean% | SD% | Mean% | SD% | Mean% | SD% |
| Phytoplankton | 12.7 | 8.6 | 27.6 | 17.4 | 27.5 | 16.4 | 34.4 | 20.6 |
| POM | 4.9 | 2.9 | 12.9 | 7.6 | 8.7 | 5 | 11.6 | 7.9 |
| SOM | 14.4 | 8.7 | 30.3 | 19 | 25.2 | 14.5 | 24.9 | 17.1 |
| Macroalgae | 68.1 | 10 | 29.2 | 18 | 38.6 | 16.5 | 29 | 19.1 |
| Invertebrates | Omnivores | Benthivores | Piscivores | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 23.02 | 3.21 | 5.42 | 0.22 |
| SEA | 4.88 | 5.63 | 1.56 | 0.21 |
| SEAc | 5.04 | 3.29 | 1.68 | 0.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.; Shan, X.; Jin, X.; Teng, G.; Wei, C. Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China). Fishes 2022, 7, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010032
Zhao Y, Yang T, Shan X, Jin X, Teng G, Wei C. Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China). Fishes. 2022; 7(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yongsong, Tao Yang, Xiujuan Shan, Xianshi Jin, Guangliang Teng, and Chao Wei. 2022. "Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China)" Fishes 7, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010032
APA StyleZhao, Y., Yang, T., Shan, X., Jin, X., Teng, G., & Wei, C. (2022). Stable Isotope Analysis of Food Web Structure and the Contribution of Carbon Sources in the Sea Adjacent to the Miaodao Archipelago (China). Fishes, 7(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010032