Nondestructive Monitoring of Soft Bottom Fish and Habitats Using a Standardized, Remote and Unbaited 360° Video Sampling Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
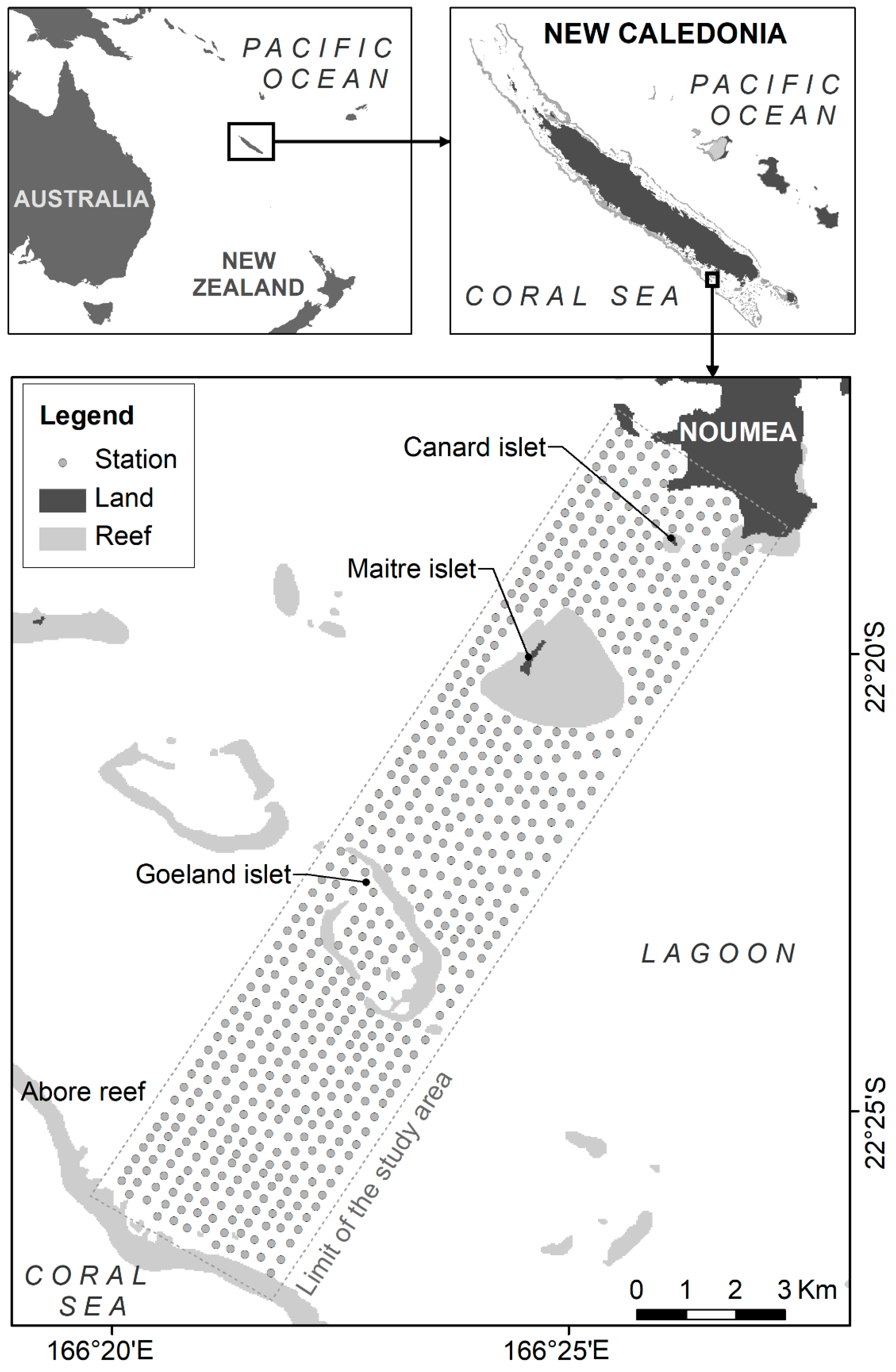
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Sampling Technique and Images Analysis
2.3. Sampling Cost
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Typology of the Habitat and Fish Assemblages
2.4.2. Influence of Soak Time and Number of Stations Sampled on Fish Assemblages
3. Results
3.1. Sampling Cost
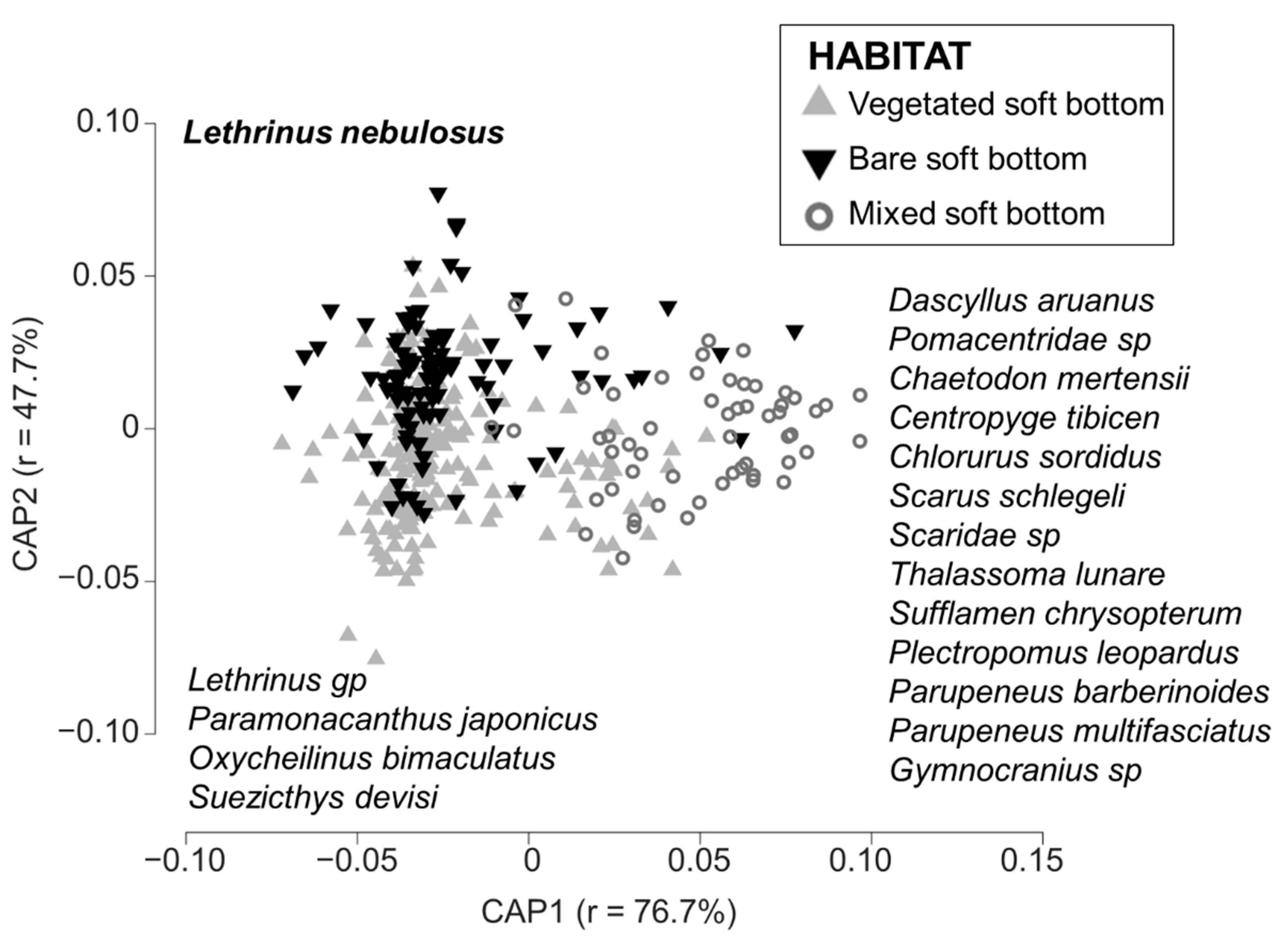
3.2. Typology of the Habitat
3.3. Fish Assemblages
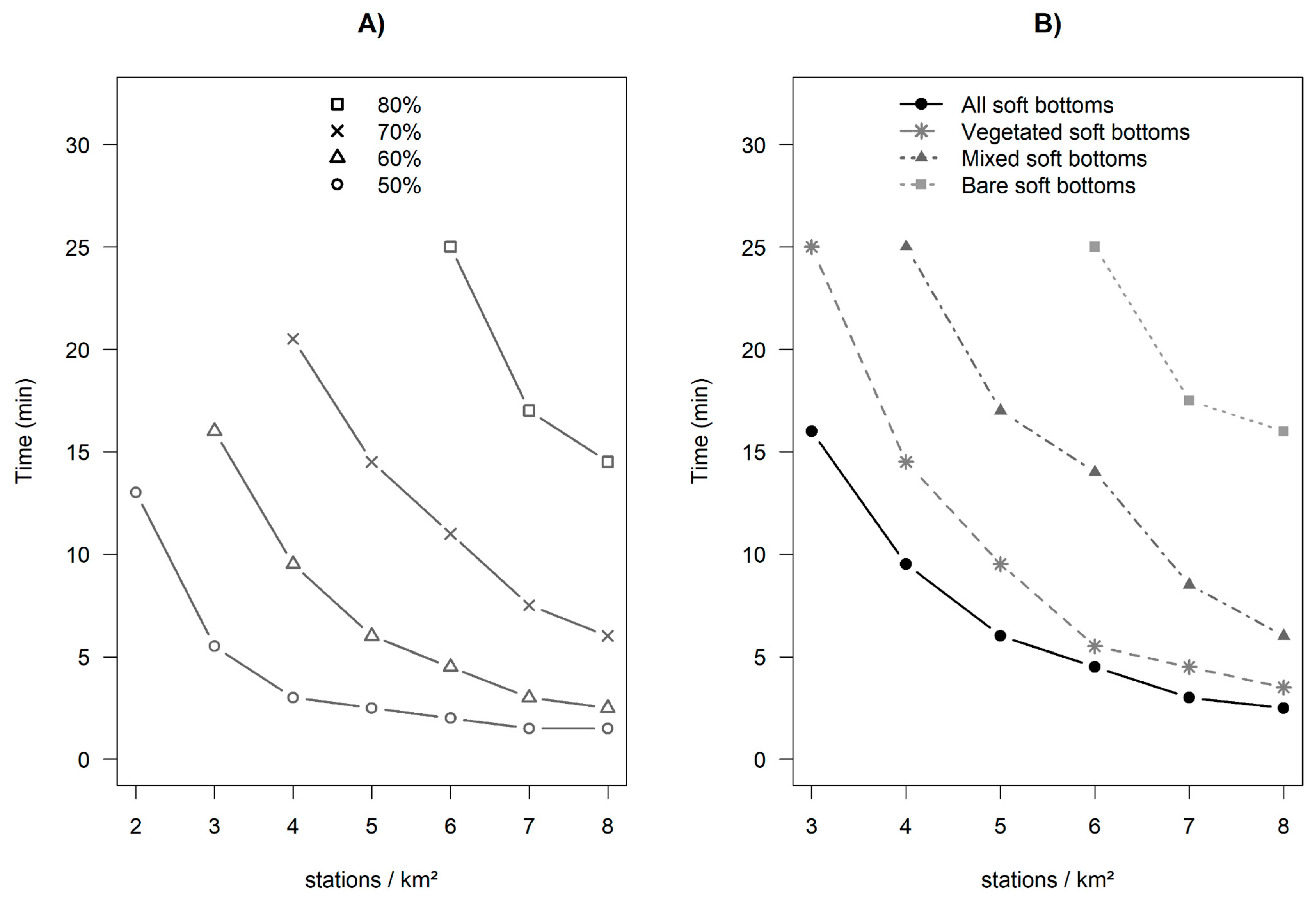
3.4. Influence of Soak Time and Number of Stations Sampled on Fish Assemblages
4. Discussion
4.1. Fieldwork Implementation and Costs
4.2. Biodiversity Sampled
4.3. Optimization of the Sampling Design Using RUV360
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulbicki, M.; Vigliola, L.; Wantiez, L. La biodiversité des poissons côtiers. In Bonvallot Jacques (coord.).Gay Jean-Christophe (coord.). Habert Elisabeth (coord.). Atlas de la Nouvelle Calédonie; Congrès de la Nouvelle-Calédonie: Marseille, France, 2012; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Giakoumi, S.; Kokkoris, G.D. Effects of habitat and substrate complexity on shallow sublittoral fish assemblages in the Cyclades Archipelago. North-eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.J. Connectivity of reef fish between mangroves and coral reefs: Algorithms for the design of marine reserves at seascape scales. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 128, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaffar, Z.; Pearman, J.K.; Cúrdia, J.; Ellis, J.; Calleja, M.L.I.; Ruiz-Compean, P.; Roth, F.; Villalobos, R.; Jones, B.H.; Moran, X.A.G.; et al. The role of seagrass vegetation and local environmental conditions in shaping benthic bacterial and macroinvertebrate communities in a tropical coastal lagoon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.J.; Abesamis, R.A.; Berkstom, C.; Depczynski, M.; Graham, N.A.J.; Holmes, T.H.; Kulbicki, M.; Noble, M.M.; Radford, B.T.; Tinkler, P.; et al. Form and function of tropical macroalgal reefs in the Anthropocene. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.J.; Berkstrom, C.; Wilson, S.K.; Abesamis, R.A.; Bradley, M.; Akerlund, C.; Barrett, L.T.; Bucol, A.A.; Chacin, D.H.; Chong-Seng, K.M.; et al. Macroalgal meadow habitats support fish and fisheries in diverse tropical seascapes. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priester, C.R.; Martinez-Ramirez, L.; Erzini, K.; Abecasis, D. The impact of trammel nets as an MPA soft bottom monitoring method. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripp-Valdez, A.; Arreguin-Sanchez, F.; Zetina-Rejon, M.J. The use of stable isotopes and mixing models to determine the feeding habits of soft bottom fishes in the southern Gulf of California. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, I.; Goncalves, J.M.S.; Claudet, J.; Coelho, R.; Goncalves, E.J.; Erzini, K. Soft-bottom fishes and spatial protection: Findings from a temperate marine protected area. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Castillo, J.; Barjau-González, E.; López-Vivas, J.M.; Armenta-Quintana, J.Á. Taxonomic diversity of the fish community associated with soft bottoms in a coastal lagoon of the west coast of Baja California Sur. México. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 9, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wantiez, L. Trophic networks of the soft bottom fish community in the lagoon of New Caledonia. C. R. Acad. Sci. III 1994, 317, 847–856. [Google Scholar]
- Richer de Forges, B.; Bargibant, G. Le lagon nord de la Nouvelle Calédonie et les atolls de Huon et Surprise. Rapp. Sci. Tech. Cent. Nouméa (Océanogr) 1985, 37, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Richer de Forges, B.; Bargibant, G.; Menou, J.L.; Garrigue, C. Le lagon sud-ouest de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Observations préalables à la cartographie bionomique des fonds meubles. Rapp. Sci. Tech. Sci. Mer. Biol. Mar. 1987, 45, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Clavier, J.; Laboute, P. Connaissance et mise en valeur du lagon nord de la Nouvelle Calédonie: Premiers résultats concernant le bivalve pectinidé Amusium japonicum balloti (étude bibliographique, estimation de stock et données annexes). Rapp. Sci. Tech. Sci. Mer. Biol. Mar. 1987, 48, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Kulbicki, M.; Bargibant, G.; Menou, J.L.; Mou-Tham, G.; Thollot, P.; Wantiez, L.; Williams, J. Evaluations des ressources en poissons du lagon d'Ouvéa: 3ème partie: Les poissons. Rapp. Conv. Sci. Mer. Biol. Mar. 1994, 11, 448. [Google Scholar]
- Kulbicki, M.; Labrosse, P.; Letourneur, Y. Fish stock assessment of the northern New Caledonian lagoons: 2—Stocks of lagoon bottom and reef-associated fishes. Aquat. Living Resour. 2000, 13, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronen, M.; Sauni, S.; Magron, F.; Fay-Sauni, L. Status of reef and lagoon resources in the South Pacific—The influence of socioeconomic factors. In Proceedings of the 10th International Coral Reef Symposium, Okinawa, Japan, 28 June–2 July 2004; Secretariat of the Pacific Community: Noumea, New Caledonia, 2006; pp. 1185–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Labrosse, P.; Ferraris, J.; Letourneur, Y. Assessing the sustainability of subsistence fisheries in the Pacific: The use of data on fish consumption. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2006, 49, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, N.; Léopold, M.; Cuif, M.; Chabanet, P. Characterization and management of informal fisheries confronted with socio-economic changes in New Caledonia (South Pacific). Fish. Res. 2009, 98, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, A.W.J.; Godley, B.J.; Sheehan, E.V.; Votier, S.C.; Witt, M.J. Camera technology for monitoring marine biodiversity and human impact. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, D.; Pelletier, D. Underwater video techniques for observing coastal marine biodiversity: A review of sixty years of publications (1952–2012). Fish. Res. 2014, 154, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalley, K.L.; Gregory, R.S.; Morris, C.J.; Cote, D. Seabed habitat determines fish and macroinvertebrate community associations in a subarctic marine coastal nursery. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2017, 146, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiggins, R.S.; Knott, N.A.; Davis, A.R. Miniature baited remote underwater video (mini-BRUV) reveals the response of cryptic fishes to seagrass cover. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2018, 101, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiggins, R.S.; Knott, N.A.; New, T.; Davis, A.R. Fish assemblages in protected seagrass habitats: Assessing fish abundance and diversity in no-take marine reserves and fished areas. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 5, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Perello, S.; Enríquez, S. Remote underwater video reveals higher fish diversity and abundance in seagrass meadows, and habitat differences in trophic interactions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, D.; Leleu, K.; Mallet, D.; Mou-Tham, G.; Hervé, G.; Boureau, M.; Guilpart, N. Remote High-Definition Rotating Video Enables Fast Spatial Survey of Marine Underwater Macrofauna and Habitats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mallet, D. Des systèmes vidéo rotatifs pour étudier l’ichtyofaune: Applications à l’analyse des variations spatiales et temporelles dans le lagon de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Ingénierie de l’environnement; Université de la Nouvelle-Calédonie: Noumea, New Caledonia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Letessier, T.B.; Juhel, J.B.; Vigliola, L.; Meewig, J.J. Low-cost small action cameras in stereo generates accurate underwater measurements of fish. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 466, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhel, J.B.; Vigliola, L.; Mouillot, D.; Kulbicki, M.; Letessier, T.B.; Meeuwig, J.J.; Wantiez, L. Reef accessibility impairs the protection of sharks. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juhel, J.B.; Vigliola, L.; Wantiez, L.; Letessier, T.B.; Meewing, J.J.; Mouillot, D. Isolation and no-entry marine reserves mitigate anthropogenic impacts on grey reef shark behavior. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladstone, W.; Lindfield, S.; Coleman, M.; Kelaher, B. Optimisation of baited remote underwater video sampling designs for estuarine fish assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 429, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, K.; Reis-Filho, J.A.; Harvey, E.; Giarrizzo, T. Baited remote underwater video as a promising nondestructive tool to assess fish assemblages in Clearwater Amazonian rivers: Testing the effect of bait and habitat type. Hydrobiologia 2017, 784, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmarsh, S.K.; Fairweather, P.G.; Huveneers, C. What is Big BRUVver up to? Methods and uses of baited underwater video. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2017, 27, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréfouët, S.; Cabioch, G.; Flamand, B.; Pelletier, B. A reap-praisal of the diversity of geomorphological and genetic processes of New Caledonian coral reefs: A synthesis from optical remote sensing, coring and acoustic multibeam observations. Coral Reefs 2009, 28, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, D.; Vigliola, L.; Wantiez, L.; Pelletier, D. Diurnal temporal patterns of the diversity and the abundance of reef fishes in a branching coral patch in New Caledonia. Austral Ecol. 2016, 41, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clua, E.; Legendre, P.; Vigliola, L.; Magron, F.; Kulbicki, M.; Sarramegna, S.; Labrosse, P.; Galzin, R. Medium scale approach (MSA) for improved assessment of coral reef fish habitat. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 333, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappo, M.; Harvey, E.; Malcolm, H.; Speare, P. Potential of video techniques to monitor diversity, abundance and size of fish in studies of Marine Protected Areas. Aquatic Protected Areas—What Works Best and How Do We Know? In Proceedings of the World Congress on Aquatic Protected Areas, Cairns, Australia, 17 August 2002; pp. 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Lebart, L.; Morineau, A.; Piron, M. Statistique Exploratoire Multidimensionnelle, 2nd ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 1997; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 3rd ed.; Plymouth Primer-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2014; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K.; Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Mao, C.X.; Chazdon, R.L.; Longino, J.T. Models and estimators linking individual-based and sample-based rarefaction, extrapolation and comparison of assemblages. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiarucci, A.; Bacaro, G.; Rocchini, D. Discovering and rediscovering the sample-based rarefaction formula in the ecological literature. Community Ecol. 2008, 9, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, I.; Jonez, E.G.; Davie, S.L.; Neat, F.C.; Wigham, B.D.; Priede, I.G. Variability in behaviour of four fish species attracted to baited underwater cameras in the North Sea. Hydrobiologia 2011, 670, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, K.M.; Marian Scott, E.; Parsons, D.; Bailey, D.M. Do agonistic behaviours bias baited remote underwater video surveys of fish? Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.L.; Huntington, B.E. Assessing the performance of a cost-effective video lander for estimating relative abundance and diversity of nearshore fish assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 483, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Garcon, J.; Newman, S.J.; Harvey, E.S. Development and validation of a mid-water baited stereo-video technique for investigating pelagic fish assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 452, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, T.; Goetze, J.; Bond, T.; Monk, J.; Abesamis, R.A.; Asher, J.; Barrett, N.; Bernard, A.T.F.; Bouchet, P.J.; Birt, M.J.; et al. A field video annotation guide for baited remote underwater stereo-video surveys of demersal fish assemblages. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratwicke, B.; Speight, M.R. Effects of habitat complexity on Caribbean marine fish assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 292, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréon, P.; Cury, P.; Shannon, L.; Roy, C. Sustainable exploitation of small pelagic fish stocks challenged by environmental and ecosystem changes: A review. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2005, 76, 385–462. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, D.; Wantiez, L.; Lemouellic, S.; Vigliola, L.; Pelletier, D. Complementarity of rotating video and underwater visual census for assessing species richness, frequency and density of reef fish on coral reef slopes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, R.; Kulbicki, M.; Wantiez, L. Cheklist of the fishes of New Caledonia, and their distribution in the Southwest Pacific Ocean (Pisces). Stuttg. Beitr. Nat. Kd. A 2011, 4, 341–463. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, T.J. Visual census methods underestimate density and diversity of cryptic reef fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantiez, L. Comparison of the fish assemblages as determined by a shrimp trawl net and a fish trawl net, in St. Vincent Bay, New Caledonia. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK 1996, 76, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbicki, M.; Wantiez, L. Comparison Between Fish by catch from Shrimp Trawl net and Visual Censuses in St. Vincent Bay, New Caledonia. Fish. Bull. 1990, 88, 667–675. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, N.L.; Mapstone, B.D. Sampling and the description of spatial pattern in marine ecology. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1987, 25, 39–90. [Google Scholar]




| Time Required (Min) | Fieldwork | Analysis of One Video | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Preparation of Boat and Material + Trips to the Sampling Area | Sampling a Set of 4 Stations | ||
| Min | 19 | 40 | 24 |
| Max | 113 | 92 | 78 |
| Mean ± SE | 46 ± 3 | 40 ± 3 | 49 ± 3 |
| Total | 1123 | 7839 | 25,494 |
| Trophic Group | Families | Genera | Species | MaxN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carnivores | 22 | 58 | 99 | 4184 |
| Herbivores-detritus | 7 | 14 | 29 | 1507 |
| Piscivores | 7 | 18 | 26 | 450 |
| Plankton feeders | 7 | 12 | 18 | 3866 |
| Species Richness per Station | Abundance per Station (MaxN) | |
|---|---|---|
| Total ichthyofauna | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 19.0 ± 1.4 |
| Commercial species | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 6.3 ± 0.6 |
| Lethrinidae | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 1.86 ± 0.20 |
| Scaridae | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 1.44 ± 0.24 |
| Carangidae | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.95 ± 0.34 |
| Acanthuridae | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.15 |
| Proportion of the Theoretical SR-Time (%) | Deployment Duration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Soft Bottoms | Bare Soft Bottoms | Vegetated Soft Bottoms | Mixed Soft Bottoms | |
| 50 | 1 min 06 | 3 min 15 | 1 min 15 | 1 min 18 |
| 80 | 5 min 00 | 11 min 00 | 5 min 00 | 4 min 30 |
| 85 | 7 min 00 | 14 min 00 | 9 min 00 | 7 min 30 |
| 90 | 10 min 00 | 15 min 30 | 11 min 30 | 10 min 30 |
| 95 | 14 min 00 | 17 min 00 | 14 min 30 | 15 min 30 |
| Proportion of the Theoretical SR-Station. (%) | Number of Stations per km2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Soft Bottoms | Bare Soft Bottoms | Vegetated Soft Bottoms | Mixed Soft Bottoms | |
| 50 | 1.6 | 4.3 | 2 | 2.7 |
| 80 | 6.2 | 18 | 7.5 | 11.1 |
| 85 | 7.8 | 24.4 | 11.5 | 15.9 |
| 90 | 14.1 | 38.8 | 18.2 | 24.6 |
| 95 | 29.5 | 83.7 | 38.4 | 55.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallet, D.; Olivry, M.; Ighiouer, S.; Kulbicki, M.; Wantiez, L. Nondestructive Monitoring of Soft Bottom Fish and Habitats Using a Standardized, Remote and Unbaited 360° Video Sampling Method. Fishes 2021, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040050
Mallet D, Olivry M, Ighiouer S, Kulbicki M, Wantiez L. Nondestructive Monitoring of Soft Bottom Fish and Habitats Using a Standardized, Remote and Unbaited 360° Video Sampling Method. Fishes. 2021; 6(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallet, Delphine, Marion Olivry, Sophia Ighiouer, Michel Kulbicki, and Laurent Wantiez. 2021. "Nondestructive Monitoring of Soft Bottom Fish and Habitats Using a Standardized, Remote and Unbaited 360° Video Sampling Method" Fishes 6, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040050
APA StyleMallet, D., Olivry, M., Ighiouer, S., Kulbicki, M., & Wantiez, L. (2021). Nondestructive Monitoring of Soft Bottom Fish and Habitats Using a Standardized, Remote and Unbaited 360° Video Sampling Method. Fishes, 6(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040050








