Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Samples Collection and Preparation
2.3. Samples Analyses
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Metal Pollution and Intestinal Helminth Parasites of Fishes in the Two Bays
3.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters in Uncontaminated–Uninfected Fishes (Reference Group)
3.3. Serum Biochemical Parameters in Contaminated-Uninfected Fishes
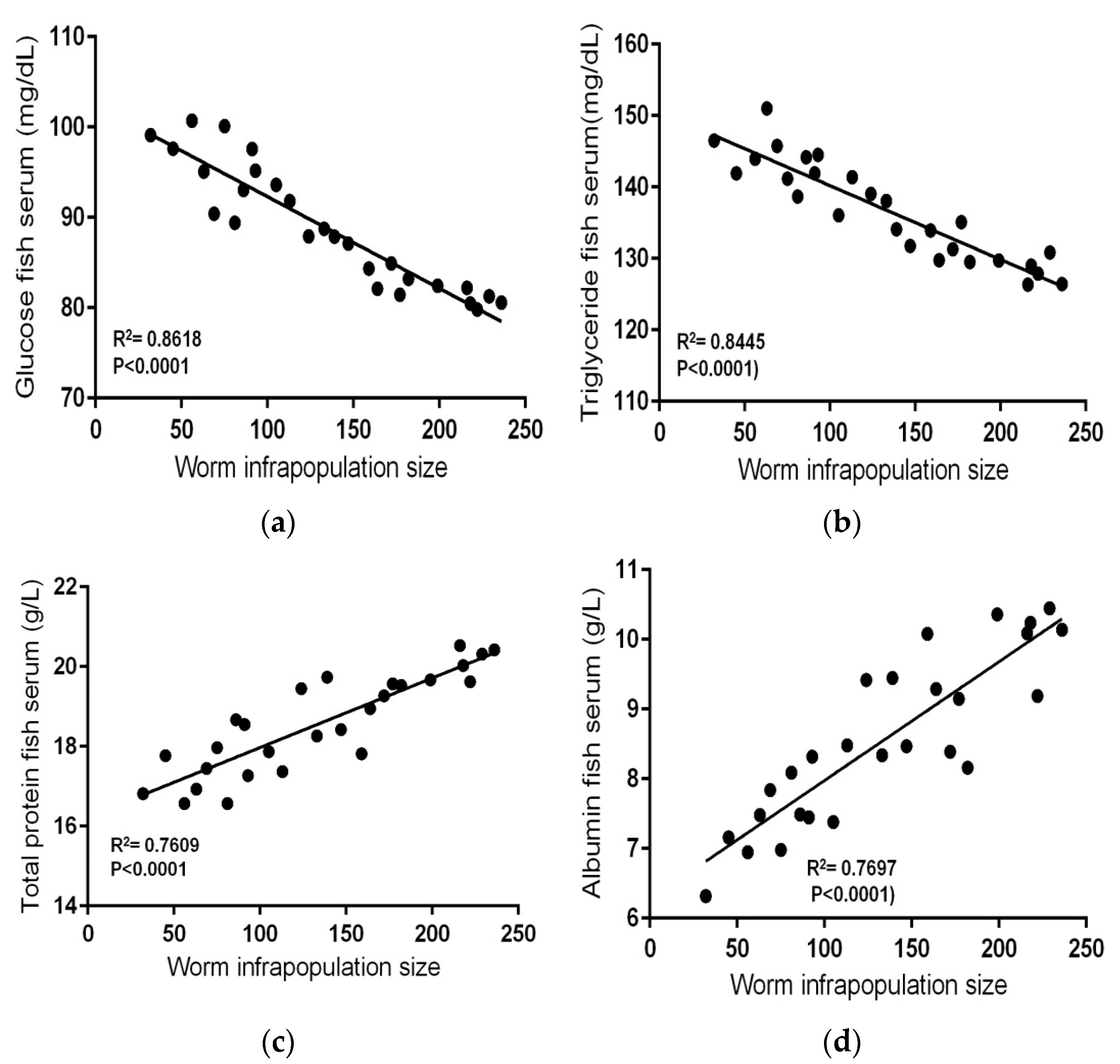
3.4. Serum Biochemical Parameters in Contaminated-Infected Fishes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jezierska, B.; Witeska, M. The metal uptake and accumulation in fish living in polluted waters. In Soil and Water Pollution Monitoring, Protection and Remediation, 1st ed.; Twardowska, I., Allen, H.E., Häggblom, M.M., Stefaniak, S., Eds.; NATO Science Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2006; Volume 69, pp. 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F.; Piccione, G.; Tribulato, K.; Ferrantelli, V.; Giangrosso, G.; Arfuso, F.; Faggio, C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Busaidi, M.; Yesudhason, P.; Al-Mughairi, S.; Al-Rahbi, W.A.K.; Al-Harthy, K.S.; Al-Mazrooei, N.A.; Al-Habsi, S.H. Toxic metals in commercial marine fish in Oman with reference to national and international standards. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Molla, A.H.; Saha, N.; Rahman, A. Study on heavy metals levels and its risk assessment in some edible fishes from Bangshi River Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food. Chem. 2012, 134, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, M.Z.; El-Sayed, E.M. Impact of water pollution with heavy metals on fish health: Overview and updates. Glob. Vet. 2014, 12, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. An overview of the adverse effects of heavy metal contamination on fish health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 89, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Kagi, J.H.R. Metallothionein. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1978, 3, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.T.; Roch, M.; McCarter, J.A.; Rendell, C.A.; Matheson, A.T. Chronic exposure of Coho salmon to sublethal concentration of copper. Effect on growth, on accumulation out distribution of copper and on copper tolerance. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1992, 72C, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, A.G. Water Pollution and Fish Physiology, 2nd ed.; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group): London, UK, 1995; pp. 1–384. [Google Scholar]
- Dural, M.; LugalGöksu, M.Z.; Özak, A.A.; Derici, B. Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in different tissues of Dicentrarchus labrax L, 1758, Sparus aurata L, 1758 and Mugil cephalus L, 1758 from the ÇamlIk lagoon of the eastern cost of Mediterranean (Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 118, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousafzai, A.M.; Khan, A.R.; Shakoori, A.R. Trace metal accumulation in the liver of an endangered South Asian fresh water fish dwelling in sublethal pollution. Pak. J. Zool. 2009, 41, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Kelle, H.I.; Ngbede, E.O.; Oguezi, V.U.; Ibekwe, F.C. Determination of heavy metals in fish (Clarias gariepinus) organs from Asaba Major Markets, Delta State, Nigeria. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 2015, 5, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanine, R.M.; Al-Hasawi, Z.M.; Hariri, M.S.; Touliabah, H.E.-S. Sclerocollum saudii Al-Jahdali, 2010 (Acanthocephala: Cavisomidae) as a sentinel for heavy-metal pollution in the Red Sea. J. Helminthol. 2019, 93, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Casanova, J.C. Acanthocephalans. In Micro Mammals and Macroparasites: From Evolutionary Ecology to Management, 1st ed.; Morand, S., Krasnov, B., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Taraschewski, H. Host-parasite interactions in Acanthocephala: A morphological approach. Adv. Parasitol. 2000, 46, 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Simoni, E.; Bosi, G.; Manera, M.A. Histopathology, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of the intestine of Leuciscus cephalus (L.) naturally infected with Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala). J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Pironi, F.; Giari, L.; Domeneghini, C.; Bosi, G. Effect of Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) on putative neuromodulators in the intestine of naturally infected Salmo trutta. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 51, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.; Kim, C.; Park, M.A.; Park, J.J. Fine structure of Longicollum pagrosomi (Acanthocephala: Pomphorhynchidae) and intestinal histopathology of the red sea bream, Pagrus major, infected with acanthocephalans. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah Eldeen, Y.M.H.; Omer, F.I.; Murwan, K.S.; Mohamed, I.A. Histopathological alterations in small intestine of rabbit fish (Siganus rivulatus) infected by helminth parasite (Sclerocollum sp.), Red Sea coast, Sudan. Int. J. Environ. 2014, 3, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Matos, L.V.; de Oliveira, M.I.B.; Gomes, A.L.S.; da Silva, G.S. Morphological and histochemical changes associated with massive infection by Neoechinorhynchus buttnerae (Acanthocephala: Neoechinorhynchidae) in the farmed freshwater fish Colossomam acropomum Cuvier, 1818 from the Amazon State, Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, O.M.; Heckmann, R.A.; Bannai, M.A. Cavisoma magnum (Cavisomidae), a unique Pacific acanthocephalan redescribed from an unusual host, Mugil cephalus (Mugilidae), in the Arabian Gulf, with notes on histopathology and metal analysis. Parasite 2018, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, L.S.; de Oliveira, M.I.B.; de Matos, L.V.; Gomes, A.L.S.; da Costa, J.I.; da Silva, G.S. Distribution of the acanthocephalan Neoechinorhynchus buttnerae and semiquantitative analysis of histopathological damage in the intestine of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B.; Siddall, R. Pomphorhynchus laevis: The intestinal acanthocephalan as a lead sink for its fish host, chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Exp. Parasitol. 1999, 93, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B. Accumulation of heavy metals by intestinal helminths in fish: An overview and perspective. Parasitology 2003, 126, S53–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B. Environmental parasitology: Relevancy of parasites in monitoring environmental pollution. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Buron, I.; James, E.; Riggs-Gelasco, P.; Ringwood, A.H.; Rolando, E.; Richardson, D. Overviewof the status of heavy metal accumulation by helminthes with a note on the use of in vitro culture of adult acanthocephalans to study the mechanisms of bioaccumulation. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2009, 3, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nachev, M.; Schertzinger, G.; Sures, B. Comparison of the metal accumulation capacity between the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis and larval nematodes of the genus Eustrongylides sp. infecting barbel (Barbus barbus). Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hasawi, Z.M. Environmental Parasitology: Intestinal helminth parasites of the siganid fish Siganus rivulatus as bioindicators for trace metal pollution in the Red Sea. Parasite 2019, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duarte, G.S.C.; Lehun, A.L.; Lucas, R.L.A.; Consolin-Filho, N.; Bellay, S.; Takemoto, R.M. Acanthocephalans parasites of two Characiformes fishes as bioindicators of cadmium contamination in two neotropical rivers in Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Dezfuli, B.S.; Krug, H.F. The intestinal parasite Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) interferes with the uptake and accumulation of lead (210Pb) in its fish host chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehana, E.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elblehi, S.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, A.A. Biomonitoring of heavy metal pollution using acanthocephalans parasite in ecosystem: An updated overview. Animals 2020, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázová, T.; Hanzelová, V.; Miklisová, D.; Šalamún, P.; Vidal-Martínez, V.M. Host–parasite relationships as determinants of heavy metal concentrations in perch (Perca fluviatilis) and its intestinal parasite infection. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachev, M.; Sures, B. Environmental parasitology: Parasites as accumulation bioindicators in the marine environment. J. Sea Res. 2016, 113, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, V.G.V.; Resurreccion, D.J.B.; de la Cruz, C.P.P.; Bandal, M.Z. Acanthocephalan parasites (Acanthogyrus sp.) of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) as biosink of lead (Pb) contamination in a Philippine freshwater lake. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Nachev, M.; Selbach, C.; David, J.; Marcogliese, D.J. Parasite responses to pollution: What we know and where we go in ‘Environmental Parasitology’. ParasitesVectors 2017, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, R.K.; Granner, D.K.; Mayes, P.A.; Rodwell, V.W. Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry, 26th ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 1–693. [Google Scholar]
- Coz-Rakovac, R.; Smuc, T.; Topic Popovic, N.; Strunjak-Perovic, I.; Hacmanjek, M.; Jadan, M. Novel methods for assessing fish blood biochemical data. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlie, R.C.; Foster, J.D.; Lange, A.J. Regulation of glucose production by the liver. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 1999, 19, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandre, L.C.G.; Buzollo, H.; Neira, L.M.; Nascimento, T.M.T.; Jomori, R.K.; Carneiro, D.J. Growth and energy metabolism of Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) fed diets with different levels of carbohydrates and lipids. Fish. Aquacul. J. 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Schaperclaus, W.; Kulow, H.; Schreckenbach, K. Fish Disease, 5th ed.; A.A. Balkema Press: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 1–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.L.; Chen, H.C. Serum metabolic enzyme activities and hepatocyte ultrastructure of common carp after gallium exposure. Zool. Stud. 2003, 42, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R.K.D.K.; Rranne, P.A.M.; Rodwell, V.W. Harper’s Biochemistry Publisher, 22nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Medical: Norwalk, CT, USA; Los Altos, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 1–720. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, V.; Parvathy, S.; Balasubramanian, R.S. Effect of heavy metals on the blood protein biochemistry of the fish Cyprinus carpio and its use as a bio-indicator of pollution stress. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 1997, 48, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.; Akhtar, T. Assessment of chromium toxicity in Cyprinus carpio through hematological and biochemical blood markers. Turk. J. Zool. 2012, 36, 682–690. [Google Scholar]
- Abalaka, S.E. Evaluation of the haematology and biochemistry of Clarias gariepinus as biomakers of environmental pollution in Tiga dam Nigeria. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Seify, M.A.; Zaki, M.S.; Desouky, A.R.Y.; Abbas, H.H.; Abdel Hady, O.K.; Abou Zaid, A.A. Study on clinopathological and biochemical changes in some freshwater fishes infected with external parasites and subjected to heavy metals pollution in Egypt. Life Sci. 2011, 8, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ogechi, U.N.; Ejikeme, O.G.; Didiugwu, N.C.; Ncha, O.S.; Onahs, S.P.; Amarachi, A.C. Effect of parasites on the biochemical and haematological indices of some clariid (Siluriformes) catfishes from Anambra River, Nigeria. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 3, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Hamed, H.A.; El-Shaer, W.A. Study on clinicopathological and biochemical changes in some marine water fishes infested with internal parasites in Red Sea. Egypt. J. Chem. Environ. Health 2015, 1, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Rastiannasab, A.; Afsharmanesh, S.; Rahimi, R.; Sharifian, I. Alternations in the liver enzymatic activity of Common carp, Cyprinus carpio in response to parasites, Dactylogyrus spp. and Gyrodactylus spp. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omeji, S.; Alo, J.A.; Garba, A.A. Impact of parasites on the haematological and biochemical parameters of selected bagrid species from lower river Benue Nigeria. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2018, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Soengas, J.L.; Agra-Lago, M.J.; Carballo, B.; Andres, M.D.; Veira, J.A.R. Effect of an acute exposure to sublethal concentration of cadmium on liver carbohydrate metabolism of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 57, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.D.; Paperna, I. Sclerocollum rubrimaris gen. et sp. n. (Rhadinorhynchidae: Gorgorhynchinae), and other Acanthocephala of marine fishes from Israel. J. Parasitol. 1978, 64, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, A. Ecology of the acanthocephalan Sclerocollum rubrimaris Schmidt and Paperna, 1978 (Rhadinorhynchidae: Gorgorhynchinae) from wild populations of rabbitfish (genus Siganus) in the northern Red Sea. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 34, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanine, R.M. Acanthocephalans from Red Sea fishes. Family Cavisomidae Meyer, 1932: The seasonal cycle of Diplosentisnudus (Harada, 1938) Pichelin et Cribb, 2001 in a definitive fish host, and a comment on Sclerocollum Schmidt et Paperna, 1978. Acta Parasitol. 2006, 51, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Menzel, C.; Berner, Z.; Eckhardt, J.D.; Stüben, D.; Alt, F.; Messerschmidt, J.; Taraschewski, H.; Sures, B. Trace analysis of platinum in biological samples: A comparison between high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HR-ICP-MS) following microwave digestion and adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry (ACSV) after high pressure ashing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 439 (Suppl. 2), 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachev, M. Bioindication Capacity of Fish Parasites for the Assessment of Water Quality in the Danube River. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, L.; Esch, G.W.; Holmes, J.C.; Kuris, A.M.; Shad, G.A. The use of ecological terms in parasitology (report of an ad hoc committee of the American Society of Parasitologists). J. Parasitol. 1982, 68, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and Multiple F-test. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merian, E.; Anke, M.; Ihnat, M.; Stoeppler, M. Elements and Their Compounds in the Environment. Occurrence, Analysis and Biological Relevance, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Grahl, K. Erkennung von Schadstoffeinflussen auf die Gesundheit von Fischenmittels Gallendiagnostik. In Fischkrankheiten, 1st ed.; Huskamp, B., Deegen, E., Eds.; Tagung der Fachgruppe Fischkrankheiten: Schmiedefeld, Germany, 1990; pp. 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, R.; Lackner, R. Fischtoxikologie–Theorie und Praxis, 2nd ed.; Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1995; pp. 1–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sures, B. Competition for minerals between Acanthocephalus lucii and its definitive host perch (Perca fluviatilis). Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Siddall, R.; Taraschewski, H. Parasites as accumulation indicators of heavy metal pollution. Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eira, C.; Torres, J.; Miquel, J.; Vaqueiro, J.; Soares, A.M.; Vingada, J. Trace element concentrations in Proteocephalus macrocephalus (Cestoda) and Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda) in comparison to their fish host, Anguilla anguilla in Ria de Aveiro, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Eira, C.; Miquel, J.; Ferrer-Maza, D.; Delgado, E.; Casadevall, M. Effect of intestinal tapeworm Clestobothrium crassiceps on concentrations of toxic elements and selenium in European hake Merluccius merluccius from the Gulf of Lion (northwestern Mediterranean Sea). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9349–9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R. Evolutionary Ecology of Parasites, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–360. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jahdali, M.O.; Hassanine, R.M. El-S. Infrapopulations of Sclerocollum saudii Al-Jahdali, 2010 (Acanthocephala: Cavisomidae) in the rabbitfish Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei, Siganidae) from the Saudi coast of the Red Sea. J. Helminthol. 2012, 86, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.W.; Hoffmann, W.E. Clinical Enzymology. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 1–315. [Google Scholar]
- De La Torre, F.R.; Salibian, A.; Ferrari, L. Biomarkers assessment in juvenile Cyprinus carpio exposed to waterborne cadmium. Environ. Pollut. J. 2000, 109, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, H.M.; Moon, T.W.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Hontela, A. Seasonal variation in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) chronically exposed to metals in the field. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, W.T.; Wales, J.H. Microscopic Anatomy of Salmonids: An Atlas; United States Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Resource Publication 50: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Ballantyne, J.S. Amino acid metabolism. In Fish physiology; Wright, P.A., Anderson, P.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 77–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zikic, R.V.; Stajn, S.; Pavlovic, Z.; Ognjanovic, B.I.; Saicic, Z.S. Activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase in erytrocyte and plasma transaminases of goldfish (Carassius auratus gibelio Bloch.) exposed to cadmium. Physiol. Res. 2001, 50, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, U.U.; George, A.D.I. Plasma enzymes in Clarias gariepinus exposed to chronic levels of round up. Environ. Ecol. 2005, 23, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yousafzai, M.A.; Shakoori, R.A. Hepatic response of a fresh water fish against aquatic pollution. Pak. J. Zool. 2011, 43, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, Z.T.B.; Banaee, M.; Yousefi, J.A.; Nematdoost, H.B.; Seyed, H.M.H. Effects of selenium (Sel-Plex) supplement on blood biochemical parameters of juvenile Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2018, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ugbomeh, A.P.; Bob-manuel, K.N.O.; Green, A.; Taylorharry, O. Biochemical toxicity of Corexit 9500 dispersant on the gills, liver and kidney of juvenile Clarias gariepinus. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2019, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soleimany, V.; Banaee, M.; Mohiseni, M.; Nematdoost, H.B.; Mousavi, D.L. Evaluation of pre-clinical safety and toxicology of Althaea officinalis extracts as naturopathic medicine for common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 613–629. [Google Scholar]
- Sallie, R.; Tredger, R.S.; Williams, F. Drugs and the liver. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1991, 12, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, D.P. Clinical Chemistry in Diagnosis and Treatment, 6th ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 1–480. [Google Scholar]
- Palanivelu, V.; Vijayavel, K.; Ezhilarasil, B.S.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Influence of insecticidal derivatives (Cartap Hydrochloride) from the marine polychaete on certain enzyme systems of the freshwater fish Orechromis mossambicus. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Asgah, N.A.; Abdel-Wahab, A.A.-W.; El-Sayed, M.Y.; Hassan, Y.A. Haematological and biochemical parameters and tissue accumulations of cadmium in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to various concentrations of cadmium chloride. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silbergeld, K.E. Blood glucose: A sensitive indicator of environmental stress in fish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1974, 11, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, G.K. Stress in Fish. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 851, 1–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, A.; Jumarie, C.; Hontela, A. Effects of Cu on plasma cortisol and cortisol secretion by adrenocortical cells of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.C.; Daniel, C.; Anderson, P.; Hontela, A. Effects of subchronic exposure to cadmium chloride on endocrine and metabolic functions in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1998, 34, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, K.; Pankhurst, N.W. Endocrine and metabolic responses to stress in a laboratory population of the tropical damselfish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeshwarlu, R.; Sunitha Devi, G. Effect of Sublethal copper exposure on glycogen, glucose and total lipid levels in (muscle and liver) fish, Oreochromis mossambicus (peters). Int. J. Zool. Stud. 2018, 3, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.A.; Novelli, E.L.B.; Dal-Pa, I.S.; Alves-Junior, R. Environmental cadmium exposure and metabolic responses of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.J.S.; Jerônimo, G.T.; Costa, O.T.F.D.; Malta, J.C.O.; Martins, M.L.; Maciel, P.O.; Chagas, E.C. Changes in hematological and biochemical parameters of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum ) parasitized by metazoan species. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2018, 27, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, A.; Ozabo, L.L.; Ophem, K.E. Clinicalchemistry: Interpretation and Techniques, 3rd ed.; LeaandFebiger: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1988; pp. 1–400. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, A.A.; Shokr, A.E.; Alwan, S.F. Effects of Aluminum on the Biochemical parameters of Freshwater fish, Tilapia zillii. J. Sci. A 2009, 3, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.K.; Prakash, S. Effect of Sublethal Concentration of Zinc Sulphate on the Serum Biochemical Parameters of Freshwater Cat Fish, Clarias batrachus (Linn). Ind. J. Biol. 2018, 5, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.S.; ElDesoky, M.A.; Nahed, S.G. The Changes in triglyceride and total cholesterol concentrations in the liver and muscle of two fish species from Qarun Lake. Egypt. Oceanogr. Fish. J. 2019, 9, 555770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Gisladottir, B.; Audunsdottir, S.S.; Bragason, B.T. Humeral response in early stages of infection of cod (Cadusmorhua) with a typical furunculosis. Icel. Agric. Sci. 2010, 23, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Wooster, G.A.; Bowser, P.R. Comparative blood chemistry and histopathology of tilapia infected with Vibrio vulnificus or Streptococcus iniae or exposed to carbon tetrachloride, gentamicin, or copper sulphate. Aquaculture 2004, 239, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.J.S.; Yang, X.; Patel, V.; Madabushi, R.; Strauss, D.G. Liver Microphysiological Systems for Predicting and Evaluating Drug Effects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 106, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoskopf, M.K. Fish Medicine, 1st ed.; WB Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA; London, UK, 1993; pp. 1–902. [Google Scholar]
- Alkaladi, A.; NasrEl-Deen, N.A.M.; Afifi, M.; AbuZinadah, O.A. Hematological and biochemical investigations on the effect of vitamin E and C on Oreochromis niloticus exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randall, D.J.; Wright, P.A. Ammonia distribution and excretion in fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

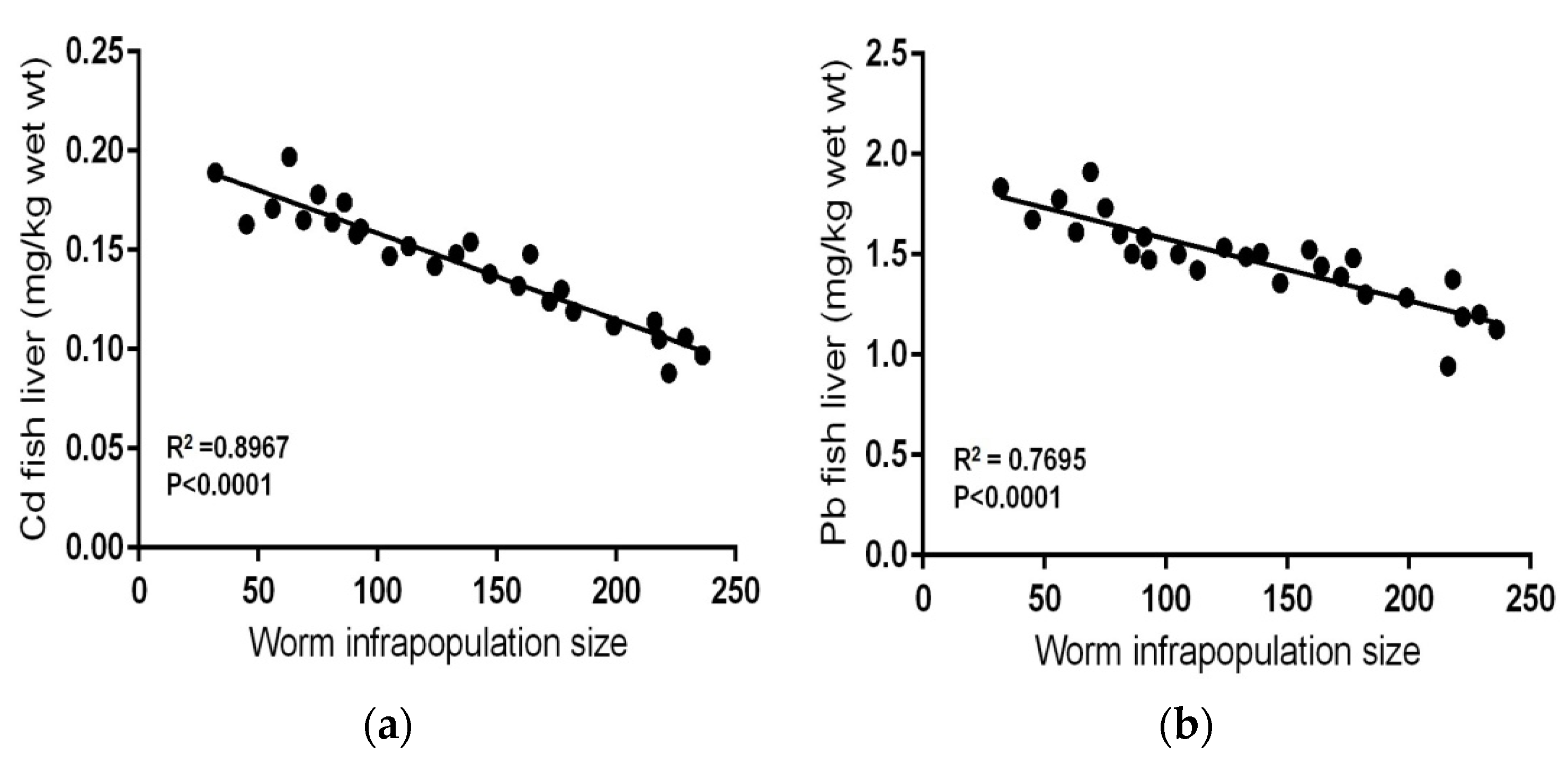
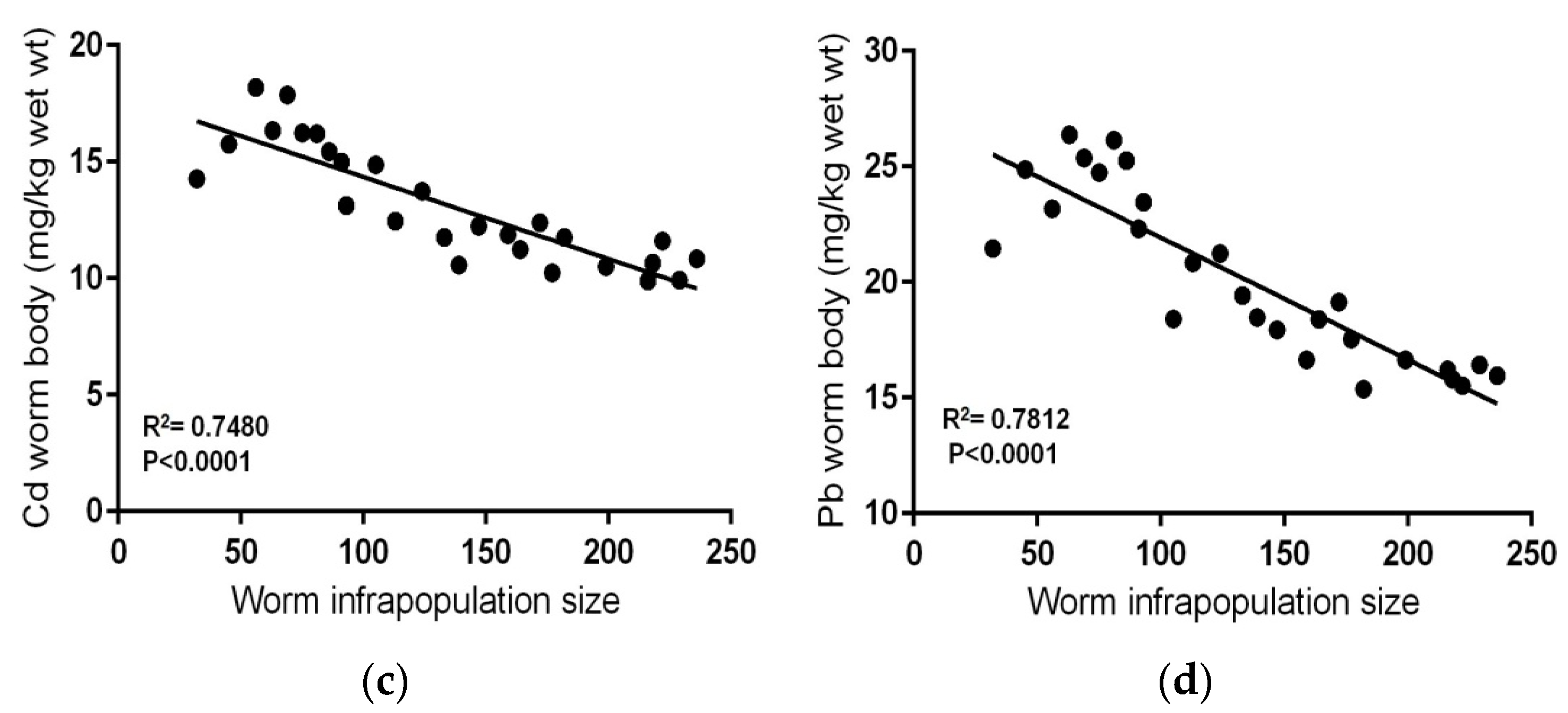
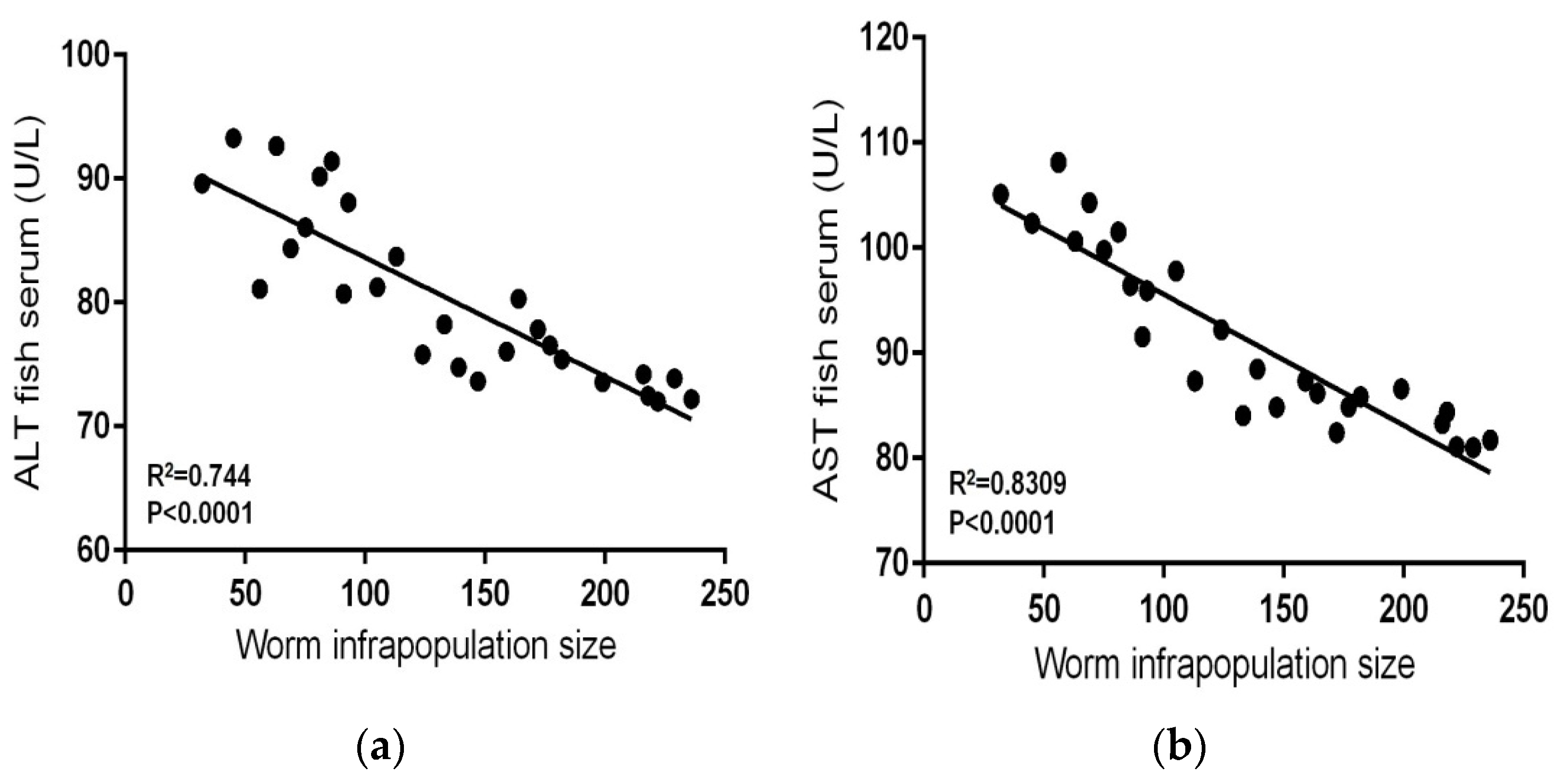
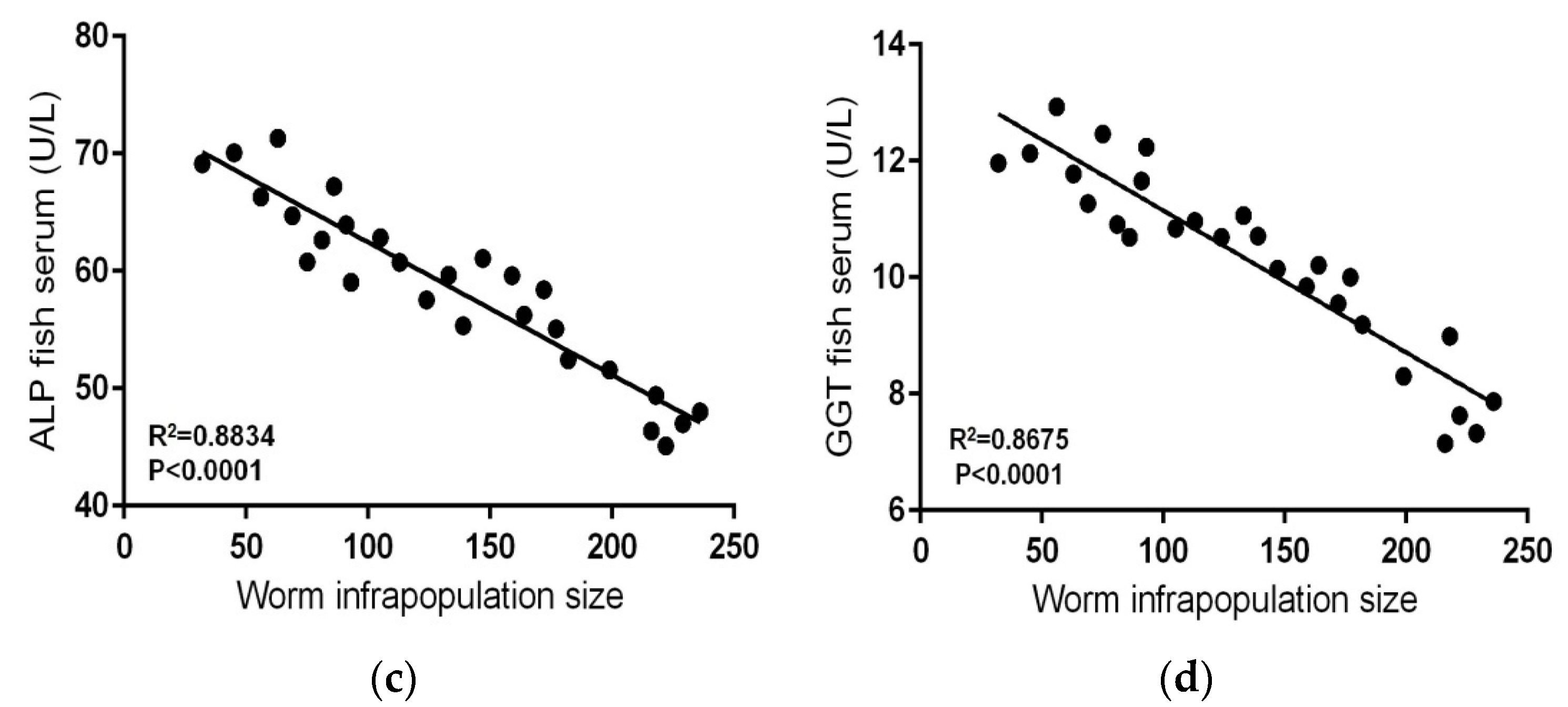

| Metal | Standard Reference Materials | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRM–NIST 1640-Trace Elements in Natural Water | Dogfish Liver DOLT-5 | |||||||
| Certified Value (mg L−1) | Recovered Value (mg L−1) | Accuracy (%) | Detection Limit (mg L−1) | Certified Value (mg/km) | Recovered Value (mg/km) | Accuracy (%) | Detection Limit (mg/km) | |
| Cd | 3.961 ± 0.072 | 3.904 ± 0.016 | 98.56 | 0.007 | 14.5 ± 0.400 | 14.26 ± 0.019 | 98.34 | 0.004 |
| Pb | 12.005 ± 0.040 | 11.550 ± 0.014 | 96.20 | 0.008 | 0.16 ± 0.036 | 0.154 ± 0.022 | 96.25 | 0.006 |
| Fish | No. Worms in Fish Intestine (Infrapopulation Size) | Metal in Fish Liver (mg kg−1 Wet Weight) | Fish Serum Parameter (Enzymes) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | ALT(U/L) | AST(U/L) | ALP(U/L) | GGT (U/L) | |||
| Reference group (n = 22) | - | Range | Not detectable | Not detectable | 55.28–65.64 | 71.25–84.76 | 38.78–46.83 | 6.30–10.70 |
| Mean ± SD | - | - | 60.65 ± 3.26 | 77.76 ± 4.02 | 43.02 ± 2.88 | 8.46 ± 1.26 | ||
| Contaminated–uninfected (n = 20) | - | Range | 0.196–0.367 | 1.588–3.168 | 81.82–110.08 | 98.45–126.45 | 53.24–86.92 | 10.03–16.86 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.267 ± 0.046 | 2.278 ± 0.46 | 96.02 ± 7.47 | 115.04 ± 7.43 | 67.54 ± 10.90 | 13.64 ± 2.17 | ||
| Contaminated–infected (n = 27) | 32–236 | Range | 0.088–0.197 | 0.943–1.912 | 72.01–93.28 | 81.02–108.16 | 45.11–71.32 | 7.15–12.93 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.143 ± 0.02 | 1.47 ± 0.21 | 80.35 ± 6.88 | 91.31 ± 8.46 | 58.58 ± 7.43 | 10.31 ± 1.62 | ||
| Fish | No. Worms in Fish Intestine (Infrapopulation Size) | Metal in Fish Liver (mg kg−1 Wet Weight) | Fish Serum Parameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Glucose (mg/dL) | Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Total Protein (g/L) | Albumin (g/L) | Urea (mg/dL) | |||
| Reference group (n = 22) | - | Range | Not detectable | Not detectable | 62.72–70.73 | 109.23–117.83 | 17.65–26.52 | 7.97–13.77 | 26.21–31.25 |
| Mean ± SD | - | - | 66.09 ± 2.80 | 114.29 ± 3.20 | 22.32 ± 2.76 | 10.46 ± 01.76 | 28.45 ± 1.66 | ||
| Contaminated–uninfected (n = 20) | - | Range | 0.196–0.367 | 1.588–3.168 | 102.67–125.48 | 148.49–172.53 | 12.15–16.53 | 4.08–7.20 | 42.34–55.27 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.267 ± 0.046 | 2.278 ± 0.46 | 112.15 ± 6.87 | 161.66 ± 7.95 | 14.44 ± 1.28 | 6.97 ± 0.90 | 49.31 ± 3.70 | ||
| Contaminated–infected (n = 27) | 32–236 | Range | 0.088–0.197 | 0.943–1.912 | 79.80–100.71 | 126.35–151.03 | 16.57–20.53 | 6.32–10.45 | 33.06–45.48 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 1.47 ± 0.21 | 88.82 ± 6.77 | 136.66 ± 6.97 | 18.57 ± 1.23 | 8.56 ± 1.20 | 38.09 ± 3.71 | ||
| No. Fish | No. Worms in Fish Intestine (Infrapopulation Size) | Cd (mg kg−1 Wet Weight) | Pb (mg kg−1 Wet Weight) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish Liver | Worm | Fish Liver | Worm | ||
| 1 | 32 | 0.189 | 14.268 | 1.834 | 21.453 |
| 2 | 45 | 0.163 | 15.762 | 1.673 | 24.876 |
| 3 | 56 | 0.171 | 18.193 | 1.776 | 23.172 |
| 4 | 63 | 0.197 | 16.342 | 1.611 | 26.382 |
| 5 | 69 | 0.165 | 17.872 | 1.912 | 25.371 |
| 6 | 75 | 0.178 | 16.237 | 1.732 | 24.746 |
| 7 | 81 | 0.164 | 16.214 | 1.602 | 26.136 |
| 8 | 86 | 0.174 | 15.438 | 1.504 | 25.258 |
| 9 | 91 | 0.158 | 14.984 | 1.588 | 22.313 |
| 10 | 93 | 0.161 | 13.123 | 1.474 | 23.459 |
| 11 | 105 | 0.147 | 14.872 | 1.501 | 18.402 |
| 12 | 113 | 0.152 | 12.457 | 1.421 | 20.836 |
| 13 | 124 | 0.142 | 13.741 | 1.534 | 21.238 |
| 14 | 133 | 0.148 | 11.763 | 1.488 | 19.418 |
| 15 | 139 | 0.154 | 10.571 | 1.507 | 18.472 |
| 16 | 147 | 0.138 | 12.234 | 1.358 | 17.943 |
| 17 | 159 | 0.132 | 11.873 | 1.523 | 16.634 |
| 18 | 164 | 0.148 | 11.243 | 1.440 | 18.391 |
| 19 | 172 | 0.124 | 12.384 | 1.389 | 19.146 |
| 20 | 177 | 0.130 | 10.236 | 1.483 | 17.541 |
| 21 | 182 | 0.119 | 11.763 | 1.301 | 15.382 |
| 22 | 199 | 0.112 | 10.505 | 1.285 | 16.637 |
| 23 | 218 | 0.105 | 10.652 | 1.375 | 15.812 |
| 24 | 216 | 0.114 | 9.894 | 0.943 | 16.211 |
| 25 | 222 | 0.088 | 11.611 | 1.189 | 15.533 |
| 26 | 229 | 0.106 | 9.921 | 1.201 | 16.432 |
| 27 | 236 | 0.097 | 10.841 | 1.126 | 15.961 |
| Range | 0.088–0.197 | 9.894–18.193 | 0.943–1.912 | 15.382–26.382 | |
| Mean ± SD | 0.143 ± 0.02 | 13.147 ± 2.51 | 1.47 ± 0.21 | 20.12 ± 3.70 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassanine, R.; Al-Hasawi, Z. Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts. Fishes 2021, 6, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040049
Hassanine R, Al-Hasawi Z. Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts. Fishes. 2021; 6(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassanine, Reda, and Zaki Al-Hasawi. 2021. "Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts" Fishes 6, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040049
APA StyleHassanine, R., & Al-Hasawi, Z. (2021). Acanthocephalan Worms Mitigate the Harmful Impacts of Heavy Metal Pollution on Their Fish Hosts. Fishes, 6(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040049







