Organochlorine Pesticide Residues and Microbiological Quality Assessment of Dried Barb, Puntius sophore, from the Northeastern Part of Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pesticide Analysis
2.2. Microbiological Analysis
2.2.1. Total Plate Count
2.2.2. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
2.2.3. Fungal Counts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
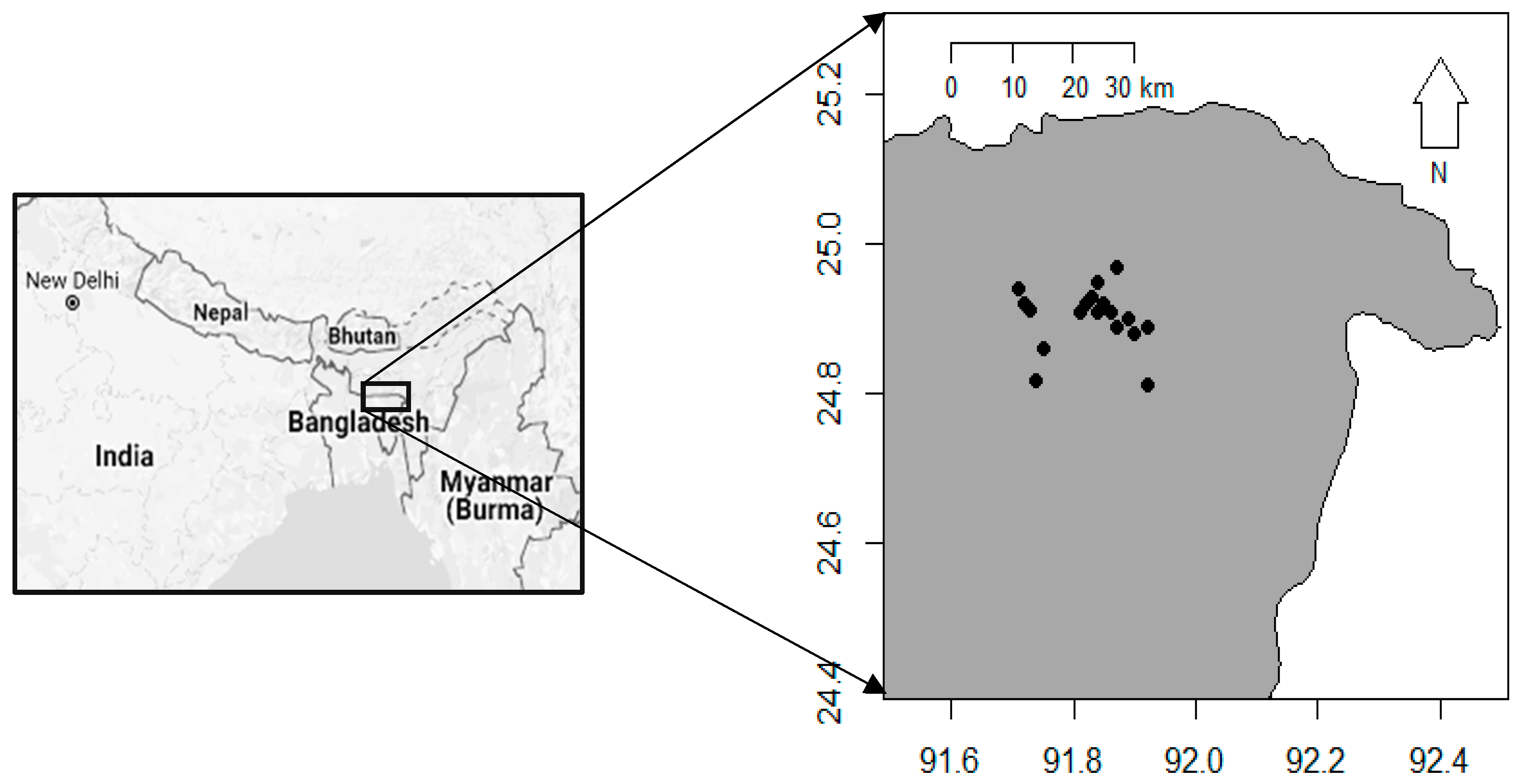
4.1. Study Area and Sampling
4.2. Organochlorine Pesticide Residue Analysis
4.2.1. Sample Preparation, Extraction, and Cleanup
4.2.2. GC Analysis
4.2.3. Analytical Quality Control
4.2.4. Quantification of Detected Pesticide
4.3. Microbiological Quality Analysis
4.3.1. Total Plate Count (TPC)
4.3.2. Fungal Count
4.3.3. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DoF. Yearbook of Fisheries Statistics of Bangladesh 2016–17; Fisheries Resources Survey System (FRSS), Department of Fisheries: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017.
- Khan, M.A.A.; Khan, Y.S.A. Insect Infestation and Preventive Measures in Dry Fish Storage of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2001, 1, 963–965. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, K.; Bashar, M.M.; Ali, M.Y.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.M. Comparative Study of Organoleptic, Microbiological and Biochemical Qualities of Four Selected Dried Fish in Summer and Winter. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 6, 2030–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, R.; Howard, J.J.; Bindu, J. The Seasonal Abundance of Blowflies Infesting Drying Fish in South-West India. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowra, F.A.; Tumpa, A.S.; Islam, M.T. Study on the Insect Infestation of Dry Fishes at Singra. J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh Sci. 2014, 39, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Wood, C.D. Non-Insecticidal Methods of Reducing Losses Caused by Infestation of Blow-Flies (Diptera) during Fish Curing Procedures; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Aktar, M. Detection of Health Hazard Insecticide Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) in Some Common Marine Dry Fish Samples from Bangladesh. Health 2012, 4, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.N.; Islam, H.M.R.; Ahmed, K.K.U.; Mahmud, Y.; Siddiqee, S. Screening and Quantification of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and Dichlorovos in Selected Dry Fish Species of Bangladesh by GC-ECD Detector. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. 2013, 1, 352–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.N.; Islam, H.M.R.; Akter, R.; Mahmud, Y.; Ahmed, K.K.U.; Siddiquee, S. Determination of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane Residues Levels in Commercial Marine Dry Fish from Different Regions of Bangladesh. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2014, 4, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, N.H.; Bhuiyan, H.; Ahmed, K.; Dawlatana, M.; Haque, K.M.F.; Rahim, M.; Bhuiyan, N.I. Organochlorine Insecticides (DDT and Heptachlor) in Dry Fish: Traditional Washing and Cooking Effect on Dietary Intake. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graikoski, J.T. Microbiology of Cured and Fermented Fish. In Microbial Safety of Fisheries Products; Chichester, C.O., Graham, H.D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.J.; Sayeed, M.A.; Akhtar, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Liza, A.A. Consumers Profile Analysis Towards Chicken, Beef, Mutton, Fish and Egg Consumption in Bangladesh. Br. Food. J. 2018, 120, 2818–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.L. The Protection of Smoke-Dried Freshwater Fish from Insect Damage during Storage in Zambia. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1972, 8, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immaculate, K.; Sinduja, P.; Velammal, A.; Patterson, J. Quality and Shelf Life Status of Salted and Sun Dried Fishes of Tuticorin Fishing Villages in Different Seasons. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar]
- Pawsey, R.; Davies, R. Safety of Intermediate Moisture Foods with Respect to Staphylococcus aureus. Intermed. Moisture Foods 1976, 68, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food & Agriculture Organization). Perspective on Mycotoxins: Selected Documents of the Joint FAO/WHO/UNEP Conference on Mycotoxins Held in Nairobi, 19-27 September 1977. In Perspective on Mycotoxins: Selected Documents of the Joint FAO/WHO/UNEP Conference on Mycotoxins held in Nairobi; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Mugula, J.K.; Lyimo, M.H. Microbiological Quality of Traditional Market Cured Fish in Tanzania. J. Food Saf. 1992, 13, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritha, K.; Immaculate, K.; Aiyamperumal, V.; Patterson, J. Microbial and Biochemical Qualities of Salted and Sun Dried Sea Foods of Cuddalore, Southeast Coast of India. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 3, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, S.; Jeyasanta, I.; Patterson, J. Microbial Quality of Salted and Sun Dried Sea Foods of Tuticorin Dry Fish Market, Southeast Coast of India. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 2, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lilabati, H.; Vishwanath, W. Changes in Bacterial and Fungal Quality During Storage of Smoked, Esomus danricus of Manipur. Fish. Technol. 1999, 36, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority. Agricultural and Veterinary Chemicals Code Instrument No. 4 (MRL Standard) 2012; Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority: Symonston, Australia, 2014; pp. 1–264.
- FDA. Compliance Policy Guides—CPG Sec. 575.100 Pesticide Residues in Food and Feed—Enforcement Criteria; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008.
- Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Amin-ud-Din, M.; Malek, M.A.; Zaman, M.A. DDT Residue and Its Metabolites in Dried Fishes of Dhaka City Markets. Soil Environ. 2010, 29, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, N.H.; Bhuiyan, H.R.; Rahim, M. Screening of Organochlorine Insecticides (DDT and Heptachlor) in Dry Fish Available in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabber, S.M.A.; Khan, Y.S.A.; Rahman, M.S. Levels of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Some Organs of the Ganges Perch, Lates calcarifer, from the Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna Estuary, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Khan, Y.S.A.; Das, P.; Shaheen, S. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Catfish, Tachysurus thalassinus (Ruppell, 1835), from the South Patches of the Bay of Bengal. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Das, P. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediment, and Muscle of River Shad, Hilsa ilisha (Hamilton 1822) from the South Patches of the Bay of Bengal. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 72, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESDO. Country Situation Report on Persistent Organic Pollutants in Bangladesh Environment and Social Development Organization. In International POPs Elimination Project; Environment and Social Development Organization—ESDO: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2005; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Persistent Organic Pollutants: A Global Issue, A Global Response. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/international-cooperation/persistent-organic-pollutants-global-issue-global-response (accessed on 8 June 2017).
- World Health Organization. The Who Recommended Classification of Pesticides By Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2009; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.; Spoo, J.W.; Kedderis, L.B. Toxicological Profile for Endrin; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GE, USA, 1996.
- Patterson, J.; Ranjitha, G. Qualities of Commercially and Experimentally Sun Dried Fin Fish, Scomberoides tol. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2009, 3, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Logesh, A.R.; Pravinkuma, M.; Raffi, S.M.; Kalaiselva, M. An Investigation on Microbial Screening on Salt Dried Marine Fishes. J. Food Resour. Sci. 2012, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Ahmed, S.; Sultana, M.A.; Tumpa, A.S.; Flowra, F.A. Nutritional and Food Quality Assessment of Dried Fishes in Singra Upazila under Natore District of Bangladesh. Trends Fish. Res. 2013, 2, 2319–4758. [Google Scholar]
- Mrityunjoy, A.; Kaniz, F.; Fahmida, J.; Shanzida, J.S.; Aftab, U.; Rashed, N. Prevalence of Vibrio cholerae in Different Food Samples in the City of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, N.; Siddique, M.P.; Farhana, Z.; Dina, M.A.; Uddin, M.I. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria From Dried Fishes Collected. Int. J. Biores. 2010, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Iyer, T.S.; Shrivastava, K.P. Incidence and Low Temperature Survival of Salmonella in Fishery Products. Fish. Technol. 1989, 26, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.A. Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents and Microbiological Quality among Escherichia coli Isolated from Dry Fishes in Southeast Coast of India. Sci. York 2008, 13, 3984–3989. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, M. Isolation of Mycotoxin-Producing Fungi from Fishes Growing in Aquacultures. Res. J. Microbiol. 2011, 6, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Code of Practice for Fish and Fishery Products; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miwa, K.; Low, S.J. Aerobic Plate Count. In Laboratory Manual on Analytical Methods and Procedures for Fish and Fish Products; Marine Fisheries Research Development Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center/JICA: Singapore, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, A.H.; Uddin, N. Bacterial Diversity of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Cultured in Brackish Water in Saudi Arabia. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.G.; Krieg, N.R.; Sneath, P.H.A.; Staley, J.T. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Assaad, H.I.; Zhou, L.; Carroll, R.J.; Wu, G. Rapid Publication-Ready MS-Word Tables for One-Way ANOVA. Springerplus 2014, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhujel, R.C. Statistics for Aquaculture; John Wiley & Sons: Ames, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
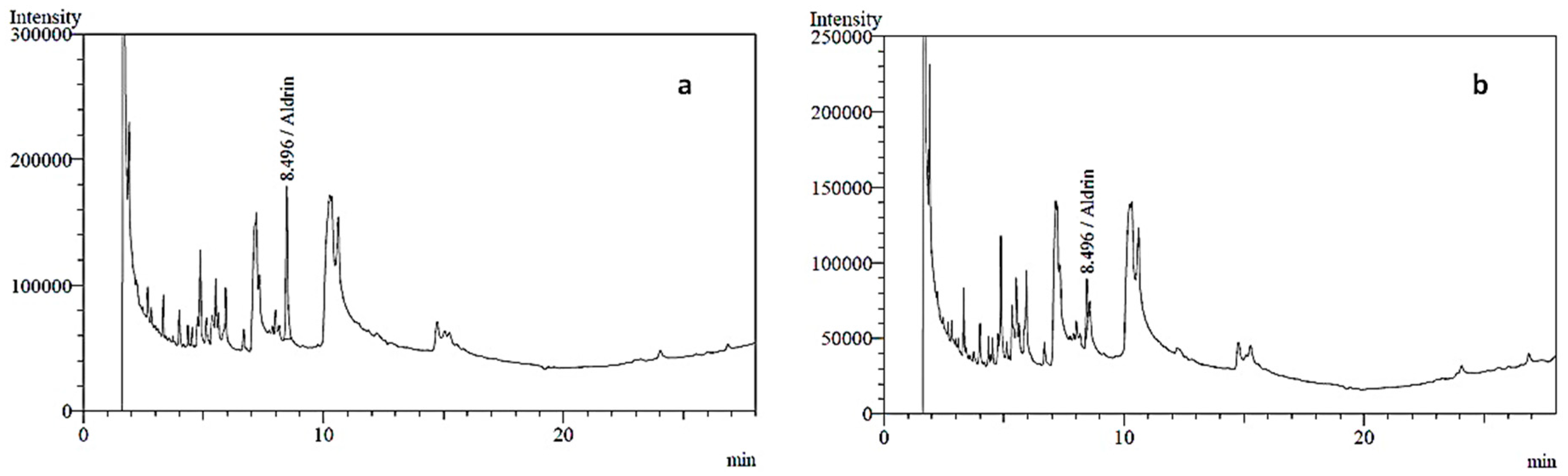
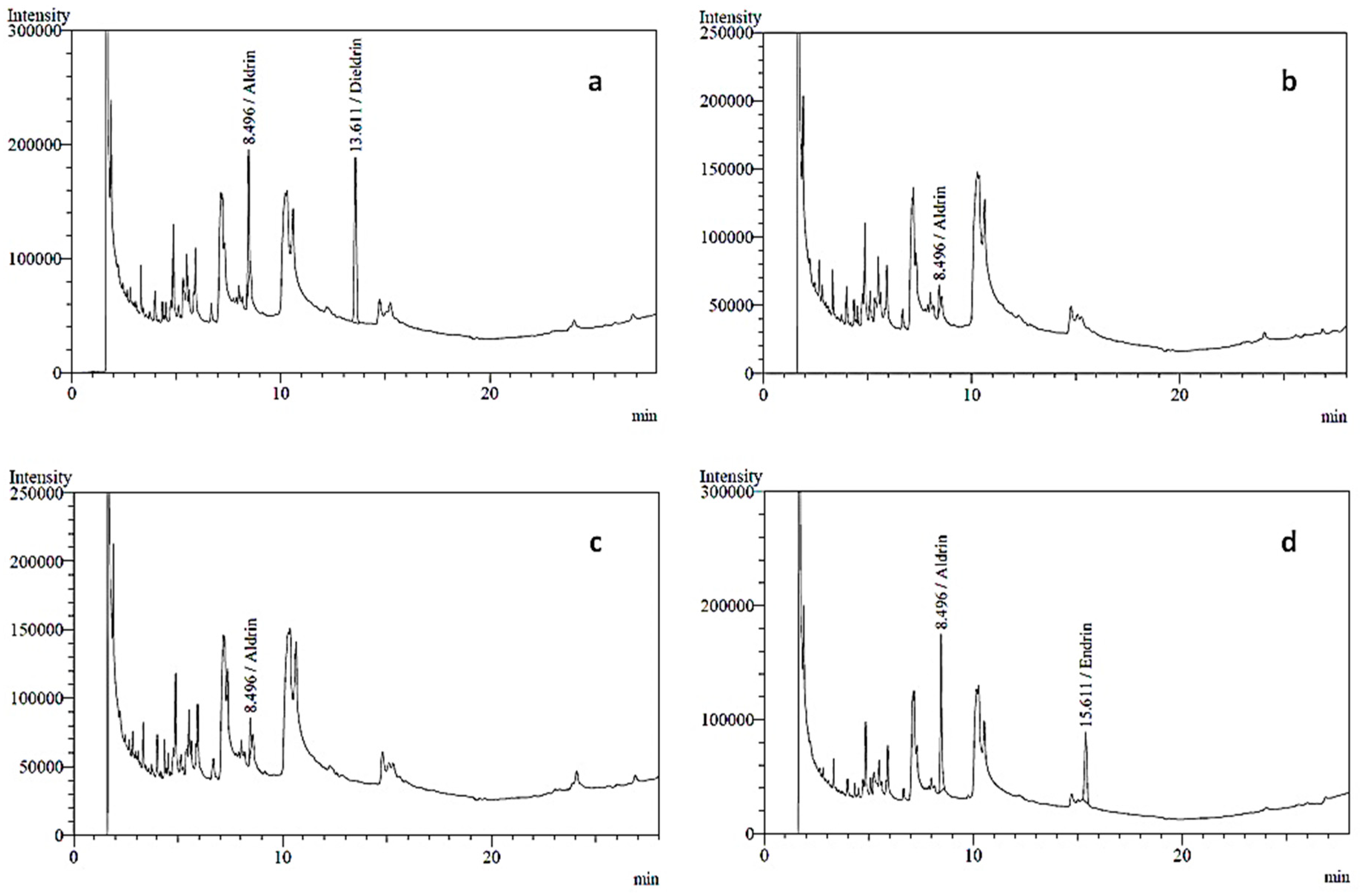
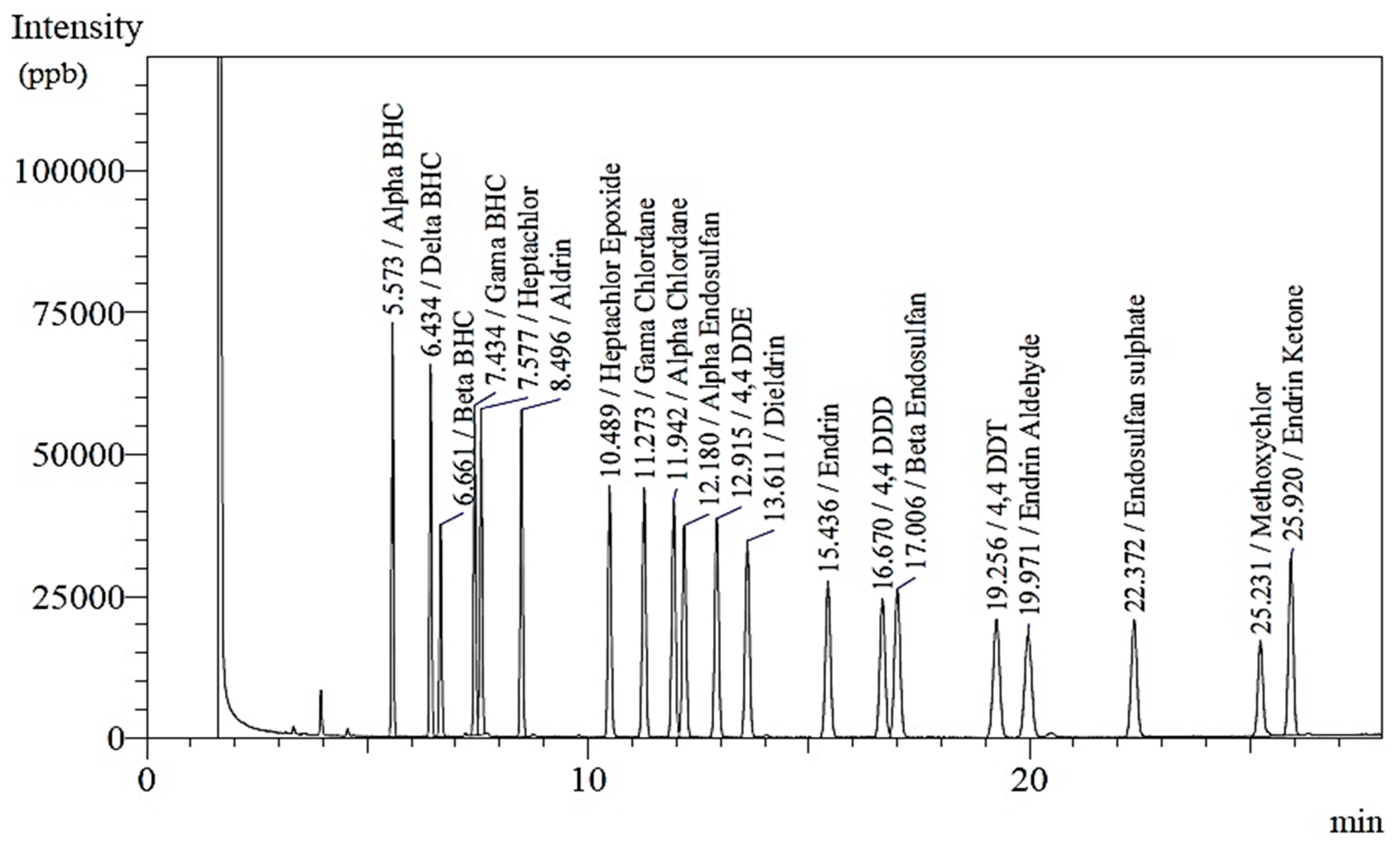
| Sample Source | No. of Analyzed Samples | Adulterated Samples | Detected Pesticide | Residue Level (ppm) | MRL (ppm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Single Pesticide | Multiple Pesticides | |||||
| Producer | 9 | 2 | 1 | – | Aldrin | 0.617 | 0.1 |
| 1 | Aldrin | 0.812 | |||||
| Retailer | 9 | 4 | 1 | – | Aldrin | 0.332 | |
| 1 | Aldrin | 0.479 | |||||
| – | 1 | Aldrin | 0.818 | ||||
| Dieldrin | 0.762 | ||||||
| – | 1 | Aldrin | 0.967 | ||||
| Endrin | 0.828 | ||||||
| Control | 9 | – | – | – | Not detected | – | – |
| Month | TPC (log value) cfu g−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Retailer | Producer | |
| December 2016 | 5.1 ± 0.03 c | 6.3 ± 0.03 a | 5.4 ± 0.03 b |
| January 2017 | 5.0 ± 0.03 c | 6.2 ± 0.02 a | 5.3 ± 0.03 b |
| February 2017 | 5.1 ± 0.05 c | 6.3 ± 0.06 a | 5.3 ± 0.02 b |
| March 2017 | 5.2 ± 0.04 c | 6.4 ± 0.01 a | 5.4 ± 0.02 b |
| April 2017 | 5.2 ± 0.01 c | 6.4 ± 0.02 a | 5.4 ± 0.01 b |
| Bacteria | No. of Samples Analyzed | Positive Percentage (%) | χ2 Value | df | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer | Retailer | Control | Producer | Retailer | Control | ||||
| E. coli | 15 | 15 | 15 | 100 (15) | 100 (15) | 33.3 (5) | 25.71 | 2 | 0.000 |
| Salmonella sp. | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13.3 (2) | 20 (3) | 0 (0) | 3.15 | 2 | 0.100 |
| Vibrio sp. | 15 | 15 | 15 | 0 (0) | 13.3 (2) | 0 (0) | 4.186 | 2 | 0.101 |
| Month | Fungal Count (log cfu g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Retailer | Producer | |
| December 2016 | 2.4 ± 0.04 b | 3.5 ± 0.04 a | 3.4 ± 0.04 a |
| January 2017 | 2.2 ± 0.05 b | 3.4 ± 0.04 a | 3.2 ± 0.04 a |
| February 2017 | 2.3 ± 0.05 b | 3.5 ± 0.02 a | 3.3 ± 0.02 a |
| March 2017 | 2.4 ± 0.05 b | 3.6 ± 0.02 a | 3.5 ± 0.02 a |
| April 2017 | 2.5 ± 0.03 b | 3.6 ± 0.03 a | 3.5 ± 0.04 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.A.; Kabir, M.L.; Sayeed, M.A.; Mahbub-E-Elahi, A.T.M.; Ahmed, M.S.; Islam, M.J. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues and Microbiological Quality Assessment of Dried Barb, Puntius sophore, from the Northeastern Part of Bangladesh. Fishes 2018, 3, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3040044
Hussain MA, Kabir ML, Sayeed MA, Mahbub-E-Elahi ATM, Ahmed MS, Islam MJ. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues and Microbiological Quality Assessment of Dried Barb, Puntius sophore, from the Northeastern Part of Bangladesh. Fishes. 2018; 3(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Md. Ashraf, Md. Lutful Kabir, Md. Abu Sayeed, A.T.M. Mahbub-E-Elahi, Md. Sultan Ahmed, and Md Jakiul Islam. 2018. "Organochlorine Pesticide Residues and Microbiological Quality Assessment of Dried Barb, Puntius sophore, from the Northeastern Part of Bangladesh" Fishes 3, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3040044
APA StyleHussain, M. A., Kabir, M. L., Sayeed, M. A., Mahbub-E-Elahi, A. T. M., Ahmed, M. S., & Islam, M. J. (2018). Organochlorine Pesticide Residues and Microbiological Quality Assessment of Dried Barb, Puntius sophore, from the Northeastern Part of Bangladesh. Fishes, 3(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3040044





