Environmental DNA Metabarcoding as a Tool for Fast Fish Assessment in Post-Cleanup Activities: Example from Two Urban Lakes in Zagreb, Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Lab Analysis
2.2.1. eDNA Filtration
2.2.2. eDNA Isolation
2.2.3. eDNA Amplification
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Llumina Sequencing Handling
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatics and Data-Set Cleanup
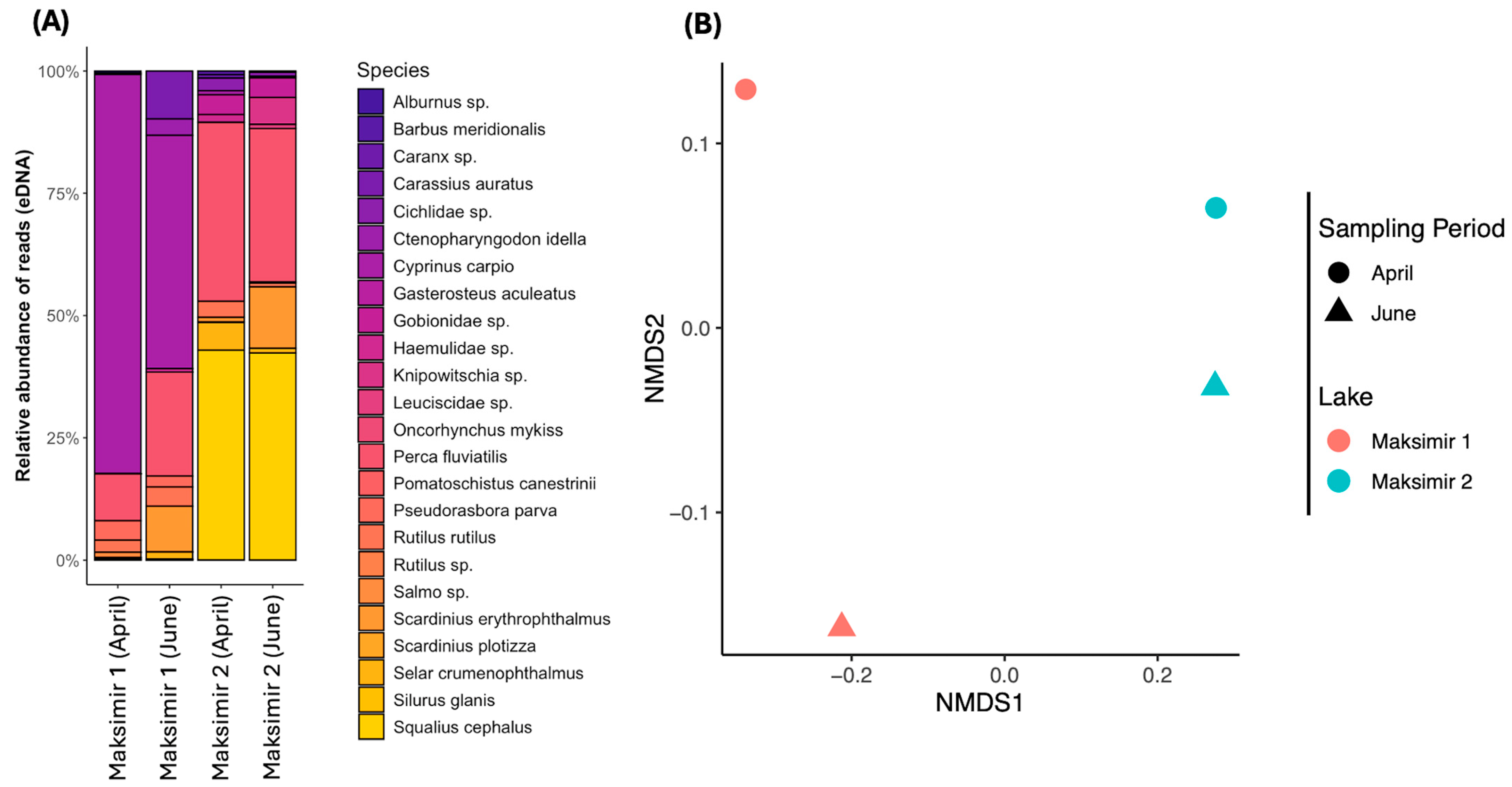
3.2. Post Cleanup Results and Biodiversity Assessment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Sullivan, C.A. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status, and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisseuil, C.; Cornu, J.F.; Beauchard, O.; Brosse, S.; Darwall, W.; Holland, R.; Oberdorff, T. Global diversity patterns and cross-taxa convergence in freshwater systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Hermoso, V.; Levin, N.; Kark, S. Biodiversity research: Geographical linkages between threats and imperilment in freshwater fish in the Mediterranean Basin. Divers. Distrib. 2010, 16, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, C.A.; Fernando, E.; Jimenez, R.R.; Macfarlane, N.B.; Rapacciuolo, G.; Böhm, M.; Darwall, W.R. One-quarter of freshwater fauna threatened with extinction. Nature 2025, 638, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, F.; Bertolino, S.; Bodon, M.; Casellato, S.; Cianfanelli, S.; Ferraguti, M.; Tricarico, E. Animal xenodiversity in Italian inland waters: Distribution, modes of arrival, and pathways. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, A.L.; Beisner, B.E.; Arnott, S.E.; Paterson, A.M.; Winter, J.G.; Johannsson, O.E.; Yan, N.D. Direct and indirect effects of an invasive planktonic predator on pelagic food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.L.; Tricarico, E.; Panov, V.E.; Cardoso, A.C.; Katsanevakis, S. Pathways and gateways of freshwater invasions in Europe. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barreras, R.; Zapata-Arroyo, C.; Falcón, L.W.; Olmeda, M.D.L. An island invaded by exotics: A review of freshwater fish in Puerto Rico. Neotrop. Biodivers. 2020, 6, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, R.N.; Diagne, C.; Hudgins, E.J.; Turbelin, A.J.; Ahmed, D.A.; Albert, C.; Bodey, T.W.; Briski, E.; Essl, F.; Haubrock, P.J.; et al. Biological invasion costs reveal insufficient proactive management worldwide. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Essl, F.; Dawson, W.; Fuentes, N.; Moser, D.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Weber, E.; Winter, M.; et al. Global rise in emerging alien species results from increased accessibility of previously inaccessible regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018097118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, R.E.; Britton, J.R.; Cowx, I.; Copp, G.H. Current knowledge on non-native freshwater fish introductions. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 751–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The Impact of COVID-19 on Fisheries and Aquaculture—A Global Assessment from the Perspective of Regional Fishery Bodies; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucherousset, J.; Olden, J.D. Ecological impacts of nonnative freshwater fishes. Fish. 2011, 36, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihinjač, T.; Sučić, I.; Špelić, I.; Vucić, M.; Ješovnik, A. Strane Vrste Slatkovodnih Riba u Hrvatskoj; Croatian Ministry for Nature Protection: Zagreb, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baudry, T.; Smith-Ravin, J.; Arqué, A.; Goût, J.P.; Cucherousset, J.; Paillisson, J.M.; Grandjean, F. Trophic niche of the invasive Cherax quadricarinatus and extent of competition with native shrimps in insular freshwater food webs. Biol. Invasions 2024, 26, 3227–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, C.; Leroy, B.; Vaissière, A.C.; Gozlan, R.E.; Roiz, D.; Jarić, I.; Salles, J.M.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Courchamp, F. High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature 2021, 592, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBES. Thematic Assessment Report on Invasive Alien Species and Their Control; Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES): Bonn, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ventura, L.; Konecny, L.; Zangl, L.; Thomsen, P.F.; Traugott, M. eDNA as a tool for freshwater biodiversity monitoring: Current use and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-González, A.; Pearce, L.; Willmott, A.; Dudgeon, D.; Canning-Clode, J.; Franklin, T.; Bodey, T.W. Integrating eDNA and spatial analysis (GIS) for early detection of aquatic invasive species in complex landscapes. Divers. Distrib. 2023, 29, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbelin, A.J.; Malamud, B.D.; Francis, R.A. Mapping the global state of invasive alien species: Patterns of invasion and policy responses. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Capinha, C.; Dawson, W.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Kühn, I.; et al. Projecting the continental accumulation of alien species through to 2050. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4401–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, C.; Meinard, Y.; Courchamp, F. Over-invasion: The saturation of a continent with non-native species. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, T.; Baudry, T.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Arqué, A.; Courty, C.; Delaunay, C.; Grandjean, F. The development of early monitoring tools to detect aquatic invasive species: eDNA assay development and the case of the armored catfish Hypostomus robinii. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćaleta, M.; Marčić, Z.; Buj, I.; Zanella, D.; Mustafić, P.; Duplić, A.; Horvatić, S. A review of extant Croatian freshwater fish and lampreys: Annotated list and distribution. Croat. J. Fish. 2019, 77, 137–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Furlan, E.M.; Pearce, L.; Daly, T.; Gleeson, D.M. Improving the containment of a freshwater invader using environmental DNA (eDNA) based monitoring. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.C.; Fraser, D.J.; Derry, A.M. Meta-analysis supports further refinement of eDNA for monitoring aquatic species-specific abundance in nature. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.M.; Oakleaf, J.R.; Baruch-Mordo, S.; Theobald, D.M.; Kiesecker, J. Finding middle ground: Extending conservation beyond wilderness areas. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukk, L.; Kanefsky, J.; Heathman, A.L.; Weise, E.M.; Nathan, L.R.; Herbst, S.J.; Sard, N.M.; Scribner, K.T.; Robinson, J.D. eDNA metabarcoding in lakes to quantify influences of landscape features and human activity on aquatic invasive species prevalence and fish community diversity. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 2016–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, T.; Vasselon, V.; Delaunay, C.; Sweet, M.; Grandjean, F. When methodological innovation changes the game: A 10-year review of environmental DNA (eDNA) applied to crayfish. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2024, 34, e4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creer, S.; Deiner, K.; Frey, S.; Porazinska, D.; Taberlet, P.; Thomas, W.K.; Bik, H.M. The ecologist’s field guide to sequence-based identification of biodiversity. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinger, J.; Britton, J.R.; Carlson, S.M.; Magurran, A.E. Effective monitoring of freshwater fish. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetz, C.R.I.I.I.; Uzarski, D.G.; Krueger, D.M.; Rutherford, E.S. Sampling a littoral fish assemblage: Comparison of small-mesh fyke netting and boat electrofishing. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag 2007, 27, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänfling, B.; Handley, L.L.; Read, D.S.; Hahn, C.; Li, J.; Nichols, P.; Blackman, R.C.; Oliver, A.; Winfield, I.J. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of lake fish communities reflects long-term data from established survey methods. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfrin, C.; Souty-Grosset, C.; Anastácio, P.M.; Reynolds, J.; Giulianini, P.G. Detection and control of invasive freshwater crayfish: From traditional to innovative methods. Divers 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.M.; Scheele, B.C.; Legge, S.; Southwell, D.M.; Carter, O.; Lintermans, M.; Radford, J.Q.; Skroblin, A.; Dickman, C.R.; Koleck, J.; et al. How to ensure threatened species monitoring leads to conservation. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2018, 19, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, C.C.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Geist, J. Taxonomic and geographical representation of freshwater environmental DNA research in aquatic conservation. Aquat. Conserv. 2019, 29, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, T.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Gout, J.P.; Arqué, A.; Delaunay, C.; Smith-Ravin, J.; Sweet, M.; Grandjean, F. Mapping a super-invader in a biodiversity hotspot, an eDNA-based success story. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucić, M.; Jelić, D.; Klobučar, G.; Pavlinec, Ž.; Ghrib, F.L.; Jarak, M.; Galov, A. First application of environmental eDNA for detecting the presence of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla, Linnaeus 1758) in the Adriatic, as a basis for conservation remarks. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2023, 24, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Institution Maksimir. Available online: http://www.park-maksimir.hr (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Njegovan, V.; Orešković, M.; Hudina, S.; Maguire, I. Crayfish fauna of the Maksimir lakes in the urban area of Zagreb. Freshw. Crayfish 2017, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, F.A.; Richards, E.; Flück, B.; Valentini, A.; Altermatt, F.; Brosse, S.; Walser, J.-C.; Eme, D.; Marques, V.; Manel, S.; et al. Comparing the performance of 12S mitochondrial primers for fish environmental DNA across ecosystems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, T.H.; Schütz, R.; Yildiz, A.; Beermann, A.; Leese, F. Evaluating five primer pairs for environmental DNA metabarcoding of Central European fish species based on mock communities. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2023, 7, e108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerovec, M.; Meštrov, M.; Stilinović, B.; Mrakovčić, M.; Plenković-Moraj, A.; Hršak, V.; Ternjej, I.; Mihaljević, Z.; Gottstein-Matočec, S.; Popijač, A.; et al. Detaljni Istražni Radovi u Svezi Ispitivanja Kakvoće Voda u Maksimirskim Jezerima; Biološki odsjek, Prirodoslovno-matematički fakultet Sveučilišta u Zagrebu: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Priroda Grada Zagreba. Radovi na Prvom i Drugom jezeru u parku Maksimir. Available online: https://park-maksimir.hr/radovi-na-prvom-i-drugom-jezeru-u-parku-maksimir/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Shu, L.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z. Environmental DNA metabarcoding primers for freshwater fish detection and quantification: In silico and in tanks. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8281–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anmarkrud, J.A.; dos Anjos Santa Rosa, F.; Thorbek, L.; Schrøder-Nielsen, A.; Sviggum, S.M.; Ready, J.S.; de Boer, H.J.; Mauvisseau, Q. eDNA Replicates, Polymerase and Amplicon Size Impact Inference of Richness Across Habitats. Environ. DNA 2025, 7, e70095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Knowlton, N.; Machida, R.J. MIDORI2: A collection of quality controlled, preformatted, and regularly updated reference databases for taxonomic assignment of eukaryotic mitochondrial sequences. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R package version 2.6-4. The Comprehensive R Archive Network. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Cambray, J. Impact on indigenous species biodiversity caused by the globalisation of alien recreational freshwater fisheries. Hydrobiologia 2003, 500, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprieur, F.; Beauchard, O.; Blanchet, S.; Oberdorff, T.; Brosse, S. Fish invasions in the world’s river systems: When natural processes are blurred by human activities. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Pagad, S.; Starfinger, U.; ten Brink, P.; Shine, C. Technical Support to EU Strategy on Invasive Alien Species (IAS); Institute for European Environmental Policy (IEEP): Brussels, Belgium, 2009; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.G.; Nunes, A.L.; Aegerter, J.; Baker, S.E.; Di Silvestre, I.; Ferreira, C.C.; Griffith, M.; Lane, J.; Muir, A.; Binding, S.; et al. A Manual for the Management of Vertebrate Invasive Alien Species of Union Concern, Incorporating Animal Welfare; Technical report prepared for the European Commission; contract no. 07.027746/2019/812504/SER/ENV.D.2. Indian National Biology Olympiad (INBO): Bruxelles, Belgium, 2022. Available online: https://pureportal.inbo.be/en/publications/a-manual-for-the-management-of-vertebrate-invasive-alien-species- (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Clusa, L.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Fernández, S.; Meyer, A.; Machado-Schiaffino, G. Nuisance species in Lake Constance revealed through eDNA. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojžišová, M.; Weiperth, A.; Gebauer, R.; Laffitte, M.; Patoka, J.; Grandjean, F.; Petrusek, A. Diversity and distribution of Aphanomyces astaci in a European hotspot of ornamental crayfish introductions. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 202, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piria, M.; Matulić, D.; Šprem, N.; Reljanović, M.; Novosel, H.; Buničić, S.; Režić, J. Ihtiofauna donjeg toka potoka Blizneca. Croat. J. Fish. 2009, 67, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) FishBase. 2024. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Cowx, I.G.; Funge-Smith, S.J.; Lynch, A.J. Stocking fish in inland waters: Opportunities and risks for sustainable food systems. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2023, 30, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowx, I.G.; Gerdeaux, D. The effects of fisheries management practices on freshwater ecosystems. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2004, 11, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, W.; Stauffer, J. The introduced fish problem and the aquarium fish industry. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1990, 21, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zięba, G.; Copp, G.; Davies, G.; Stebbing, P.; Wesley, K.; Britton, J. Recent releases and dispersal of non-native fishes in England and Wales, with emphasis on sunbleak Leucaspius delineatus (Heckel, 1843). Aquatic Invasions 2010, 5, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassey, P.; Hogg, C.J. Escaping captivity: The biological invasion risk from vertebrate species in zoos. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 181, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.P.; Port, J.A.; Yamahara, K.M.; Crowder, L.B. Using environmental DNA to census marine fishes in a large mesocosm. PLoS ONE 2014, 159, e86175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, F.; Couton, M.; Altermatt, F. Navigating the seven challenges of taxonomic reference databases in metabarcoding analyses. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, K.C.; Myler, E.; Hanner, R.; Tetreault, G. Taxonomic Blind Spots: A Limitation of Environmental DNA Metabarcoding-Based Detection for Canadian Freshwater Fishes. Environ. DNA 2024, 6, e70054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nynatten, A.; Castañeda, R.A.; Chakona, A.; Lovejoy, N.R.; Weyl, O.L.; Mandrak, N.E. Environmental DNA metabarcoding in the Cape Fold aquatic ecoregion: Opportunities and challenges for eDNA uptake in an endemism hotspot. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 69, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.P.; Cote, M.; Rezvanifar, A.; Albu, A.B.; Ersahin, K.; Mudge, T.; Gauthier, S. Instance segmentation-based identification of pelagic species in acoustic backscatter data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4378–4387. [Google Scholar]
- Ćaleta, M.; Karlović, R.; Janev Hutinec, B.; Jelić, L. Usporedba ihtiofaune maksimirskih jezera—kakve su promjene u 18 godina. In Gradski prozori u prirodu, Gradski prozori u prirodu Conference, Zagreb, Croatia, 9–10 of September 2021; Dolenc, N., Janev Hutinec, B., Šaško, P., Banić, S., Jelić, L., Ambrožić, J., Maljković, D., Eds.; Javna ustanova Priroda grada Zagreba: Zagreb, Croatia, 2021; Volume 13, pp. 39–41. [Google Scholar]
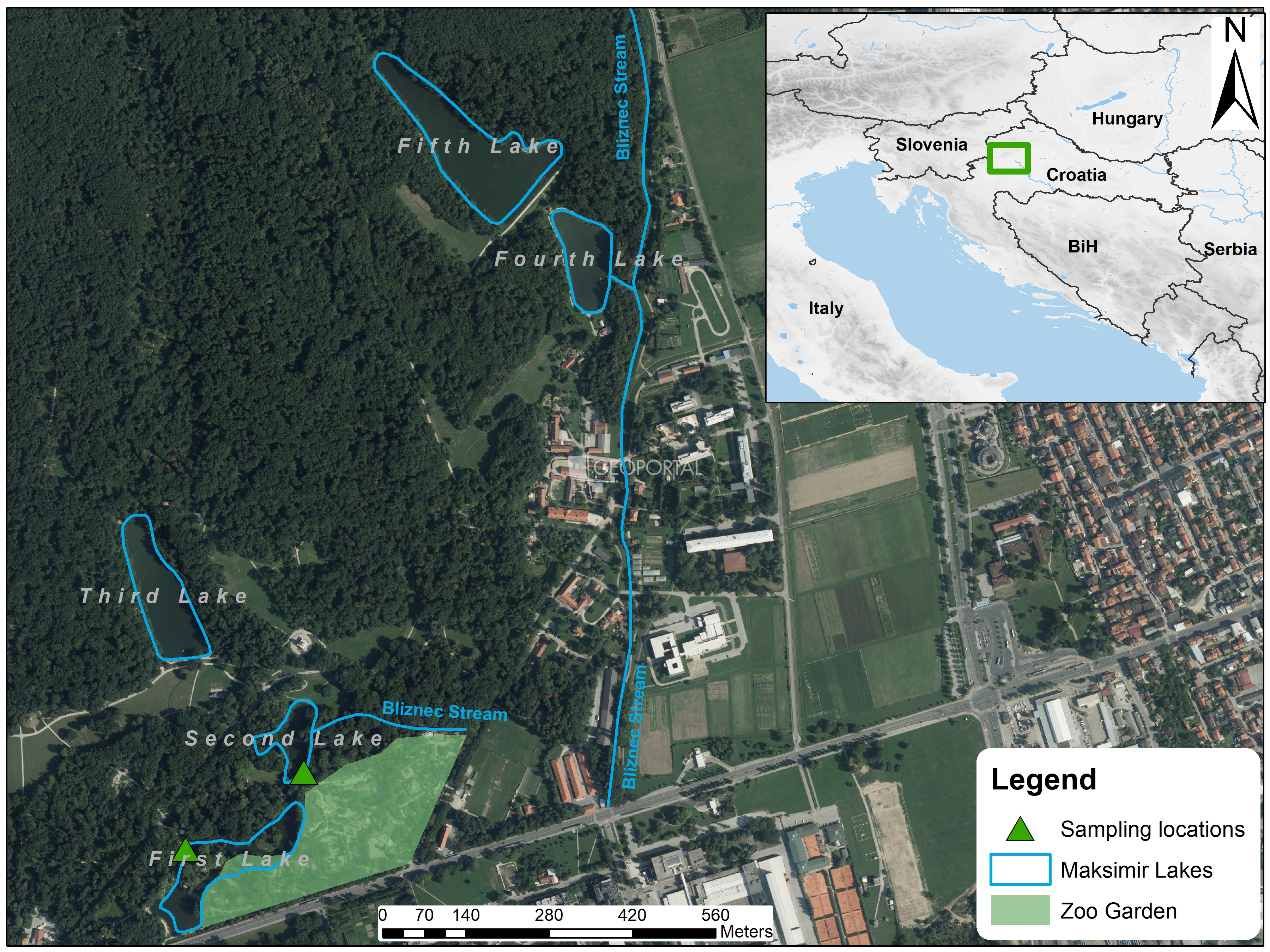
| Name | Surface Area (km2) | Depth | X | Y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Lake | Maksimir 1 | 0.017 | 1.4 m | 16.02126 | 45.8226 |
| Second Lake | Maksimir 2 | 0.0057 | 1.5 m | 16.01867 | 45.8211 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vucić, M.; Baudry, T.; Jelić, D.; Galov, A.; Pavlinec, Ž.; Jelić, L.; Hutinec, B.J.; Klobučar, G.; Slivšek, G.; Grandjean, F. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding as a Tool for Fast Fish Assessment in Post-Cleanup Activities: Example from Two Urban Lakes in Zagreb, Croatia. Fishes 2025, 10, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080375
Vucić M, Baudry T, Jelić D, Galov A, Pavlinec Ž, Jelić L, Hutinec BJ, Klobučar G, Slivšek G, Grandjean F. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding as a Tool for Fast Fish Assessment in Post-Cleanup Activities: Example from Two Urban Lakes in Zagreb, Croatia. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080375
Chicago/Turabian StyleVucić, Matej, Thomas Baudry, Dušan Jelić, Ana Galov, Željko Pavlinec, Lana Jelić, Biljana Janev Hutinec, Göran Klobučar, Goran Slivšek, and Frédéric Grandjean. 2025. "Environmental DNA Metabarcoding as a Tool for Fast Fish Assessment in Post-Cleanup Activities: Example from Two Urban Lakes in Zagreb, Croatia" Fishes 10, no. 8: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080375
APA StyleVucić, M., Baudry, T., Jelić, D., Galov, A., Pavlinec, Ž., Jelić, L., Hutinec, B. J., Klobučar, G., Slivšek, G., & Grandjean, F. (2025). Environmental DNA Metabarcoding as a Tool for Fast Fish Assessment in Post-Cleanup Activities: Example from Two Urban Lakes in Zagreb, Croatia. Fishes, 10(8), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080375











