Behavioral Responses of Migratory Fish to Environmental Cues: Evidence from the Heishui River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Upstream and Downstream Migration Tracking Experiment
2.2.1. Experimental Subjects
2.2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Upstream and Downstream Passage Success Rates in River Sections
3.2. Evaluation of Passage Efficiency in Upstream and Downstream River Sections
3.3. Diel Rhythms of Upstream and Downstream Migration in River Sections
3.4. Influence of Environmental Factor Variations on Upstream and Downstream Passage Efficiency in River Sections
3.5. Identification and Prediction of Key Factors Influencing Upstream and Downstream Migration Behavior of Fish
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Upstream and Downstream Migration Behavior and Ecological Behavioral Explanations
4.2. Mechanisms of Non-Biotic Environmental Factors Influencing Migration Efficiency
4.3. New Findings and Differences
4.4. Relationship Between Fish Passage Facility Attraction Effect and Tributary Habitat
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newbold, L.R.; Shi, X.; Hou, Y.; Han, D.; Kemp, P.S. Swimming performance and behaviour of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis): Application to fish passage and exclusion criteria. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Jorde, K.; Habit, E.; Caamaño, D.; Parra, O. Downstream environmental effects of dam operations: Changes in habitat quality for native fish species. River Res. Appl. 2015, 27, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Bochechas, J.H. Effects of small hydropower plants on fish assemblages in medium-sized streams in central and northern Portugal. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.R.; Gowx, I.G.; Bolland, J.D. Efficiency of a nature-like bypass channel for restoring longitudinal connectivity for a river-resident population of brown trout. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennock, C.A.; Bender, D.; Hofmeier, J.; Mounts, J.A.; Waters, R.; Weaver, V.D.; Gido, K.B. Can fishways mitigate fragmentation effects on Great Plains fish communities? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummers, J.S.; Hudson, S. Evaluating the efficiency of restoring longitudinal connectivity for stream fish communities: Towards a more holistic approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.X.; Liu, D.S.; Ma, H.H.; Chen, Q.W.; Shi, W.Q.; Zhu, H.Y. Effects of fish habitat substitution in tributaries under the cascade hydropower development of Lancang River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 3191–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.N.; Wei, Q.; Ji, Q.F.; Li, K.F.; Liang, R.F.; Wang, Y.M. Determining the position of a fish passage facility entrance based on endemic fish swimming abilities and flow field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 6104–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X. Review of fishway research in China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 115, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, A.K.; Knights, B.C.; Stanton, J.C.; Milde, A.S.; Vallazza, J.M.; Bery, M.K.; Tripp, S.J.; Devine, T.E.; Sleeper, W.; Lamer, J.T.; et al. Lock operations influence upstream passages of invasive and native fishes at a Mississippi River high-head dam. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerig, E.; Castro-Santos, T. Is motivation important to brook trout passage through culverts? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wai, O.W.; Chen, Q. Laboratory study on fish behavioral response to meandering flow and riffle-pool sequence driven by deflectors in straight concrete flood channels. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 125736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Quintella, B.R.; Lança, M.J.; Alexandre, C.M.; Mateus, C.S.; Pedro, S.; Belo, A.F.; Rato, A.S.; Quadrado, M.F.; Telhado, A.; et al. Temporal patterns of the catadromous thinlip grey mullet migration in freshwater. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayse, S.M.; McCormick, S.D.; Castro-Santos, T. How lipid content and temperature affect American shad (Alosa sapidissima) attempt rate and sprint swimming: Implications for overcoming migration barriers. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 76, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicice, F.M.; Pompeu, P.S.; Agostinho, A.A. Fish conservation must go beyond the concrete: A comment on Celestino et al. River Res. Appl. 2020, 36, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, M.L.; Peery, C.A.; High, B. Behavioral thermoregulation and associated mortality trade-offs in migrating adult steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Variability among sympatric populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemasson, B.H.; Haefner, J.W.; Krause, J. Modeling fish navigation and search strategies in complex flow environments. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.; An, R.D.; Cai, L.; Chen, X.J.; Zhao, X.J.; Zou, X. Water flow and substrate preferences of schizothorax wangchiachii (fang, 1936). Ecol. Eng. 2019, 138, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, R.J.; Chapman, J.M.; Souliere, C.M.; Tudorache, C.; Wikelski, M.; Cooke, S.J. Conservation physiology of animal migration. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coz078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Olmeda, J.F.; Madrid, J.A.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Melatonin effects on food intake and activity rhythms in two fish species with different activity patterns: Diurnal (goldfish) and nocturnal (tench). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 144, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vega, A.; Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Fuentes-Pérez, J.F. Seasonal and daily upstream movements of brown troutSalmo truttain an Iberian regulated river. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownscombe, J.W.; Cooke, S.J.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Suski, C.D.; Goldberg, T.L. Ecology of exercise in wild fish: Integrating concepts of individual physiological capacity, behaviour, and fitness through diverse case studies. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, S.D.; Hansen, L.P.; Quinn, T.P.; Saunders, R.L. Movement, migration, and smolting of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55 (Suppl. S1), 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, K.; Baktoft, H.; Thorstad, E.B.; Svendsen, J.C.; Höjesjö, J.; Koed, A. Survival and progression rates of anadromous brown trout kelts Salmo trutta during downstream migration in freshwater and at sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 535, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjarrés-Hernández, A.; Guisande, C.; García-Roselló, E.; Heine, J.; Pelayo-Villamil, P.; Pérez-Costas, E.; González-Vilas, L.; González-Dacosta, J.; Duque, S.R.; Granado-Lorencio, C.; et al. Predicting the effects of climate change on future freshwater fish diversity at global scale. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 43, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Lucas, M.C.; Castro-Santos, T.; Katopodis, C.; Baumgartner, L.J.; Thiem, J.D.; Aarestrup, K.; Pompeu, P.S.; O’Brien, G.C.; Braun, D.C.; et al. The future of fish passage science, engineering, and practice. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeman, J.W.; Hansel, H.C.; Tiffan, K.F.; Perry, R.W.; Smith, C.D. Behavior and dam passage of juvenile Chinook salmon and steelhead during winter flow conditions. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2014, 34, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Denderen, D.; Gislason, H.; Heuvel, J.; Andersen, K.H.; Leprieur, F. Global analysis of fish growth rates shows weaker responses to temperature than metabolic predictions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, L.G.; Siegel, J.E.; Wiesebron, L.E.; Trujillo, E.M.; Burke, B.J.; Sandford, B.P.; Widener, D.L. Snake River sockeye and Chinook salmon in a changing climate: Implications for upstream migration survival during recent extreme and future climates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, D.W.; Hinch, S.G. Effectiveness monitoring of fish passage facilities: Historical trends, geographic patterns and future directions. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Olmeda, J.F.; López-García, I.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Blanco-Vives, B.; Aparicio, R.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Daily rhythms of digestive physiolo.gy, metabolism and behaviour in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, C.M.; Castro-Santos, T.; Haro, A. Performance of fish passage structures at upstream barriers to migration. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C.; Williams, J.G. The development of fish passage research in a historical context. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 48, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Aarestrup, K.; Riis, T.M.O.; Jepsen, N.; Koed, A. Shining a light on the loss of rheophilic fish habitat in lowland rivers as a forgotten consequence of barriers. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; An, R. Effects of hydraulic cues in barrier environments on fish navigation downstream of dams. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, R.; Teichert, N.; Boussarie, G.; Grondin, H.; Valade, P. Upstream migration of amphidromous gobies of La Réunion Island: Implication for management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2015, 22, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; An, R.; Chen, M.; Li, J. Evaluation of Volitional Swimming Behavior of Schizothorax prenanti Using an Open-Channel Flume with Spatially Heterogeneous Turbulent Flow. Animals 2022, 12, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffers, T.; Buijse, A.D.; Geerling, G.W.; Jans, L.H.; Schoor, M.M.; Poos, J.J.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Nagelkerke, L.A.J. Freshwater fish biodiversity restoration in floodplain rivers requires connectivity and habitat heterogeneity at multiple spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
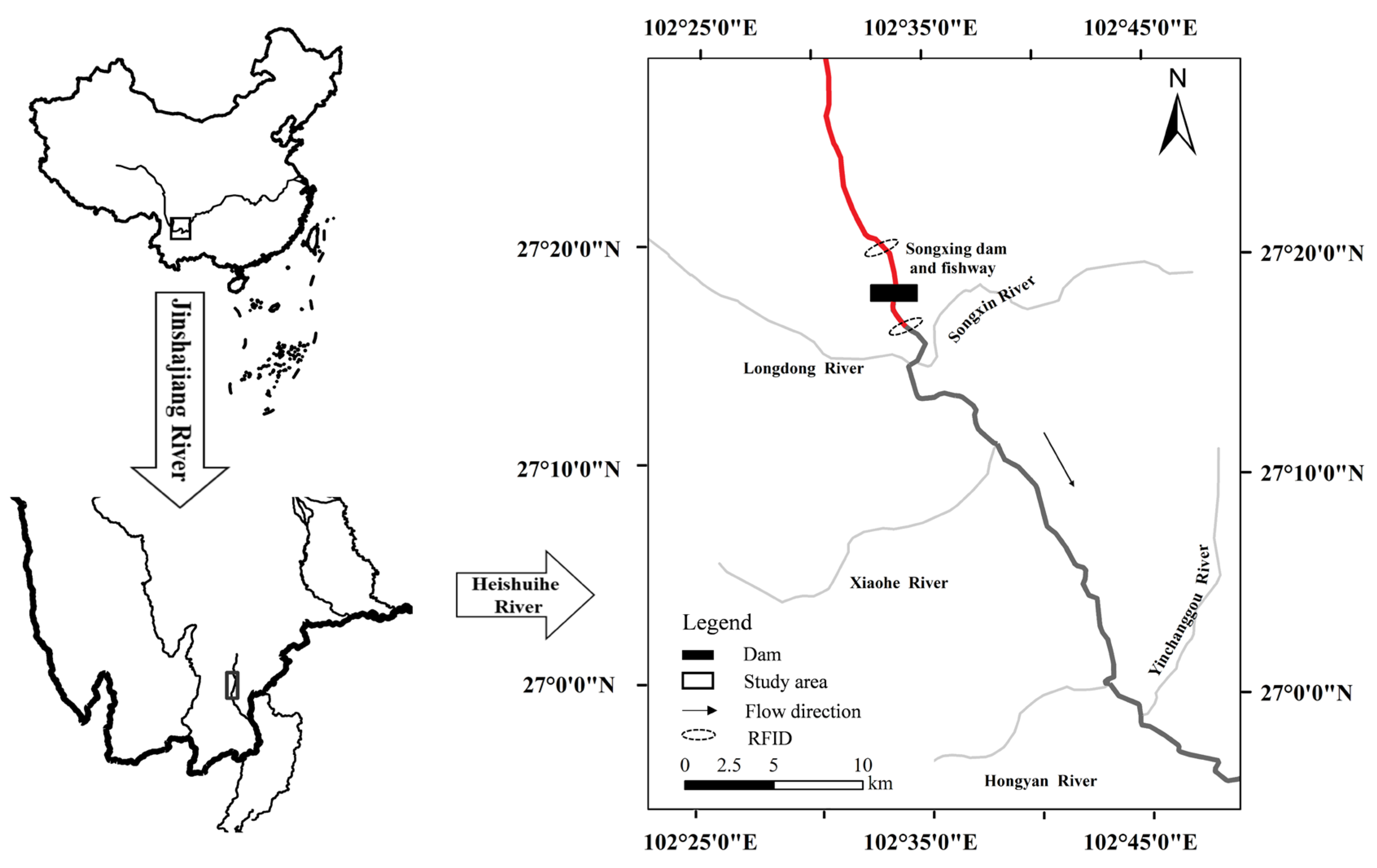


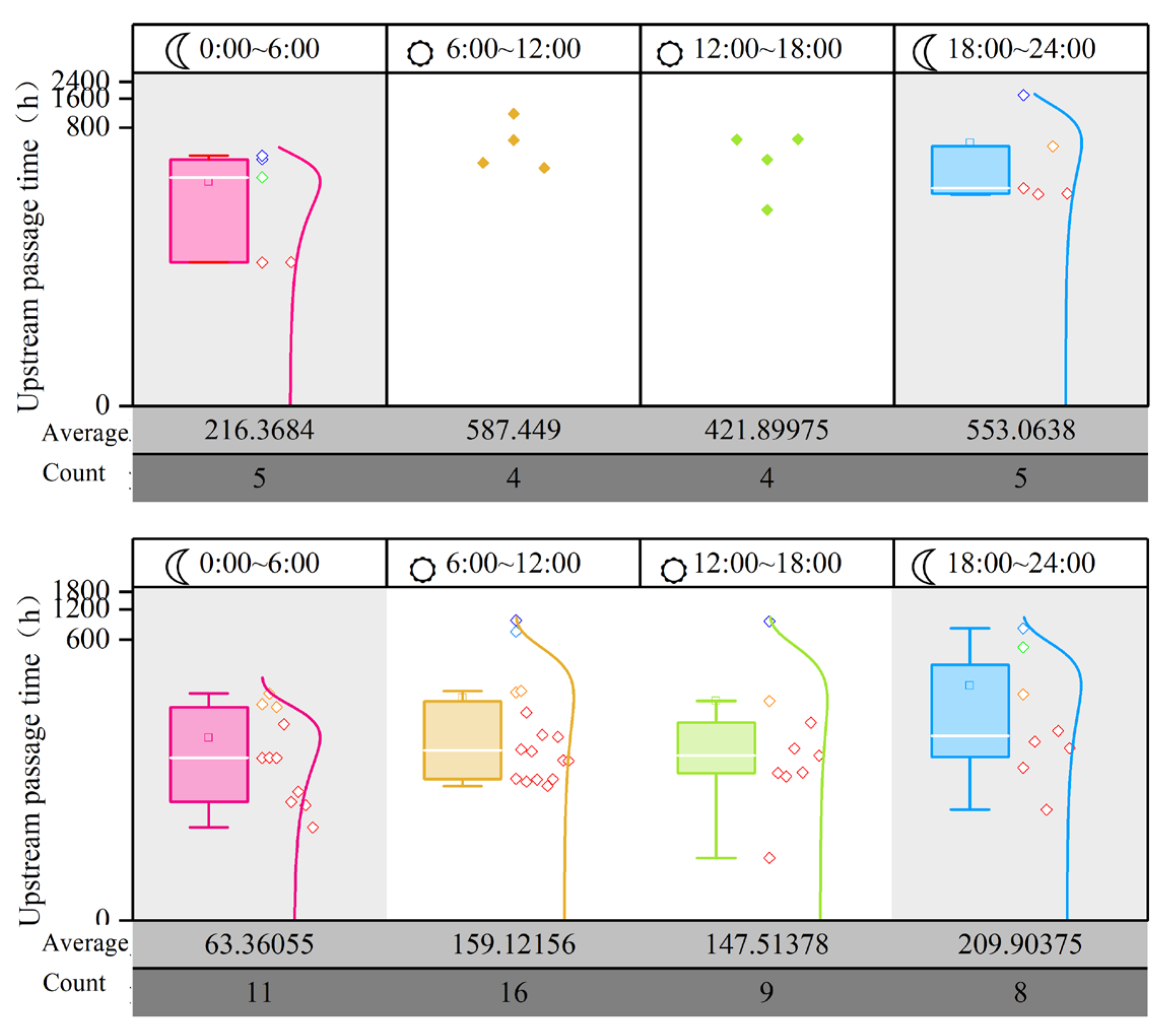
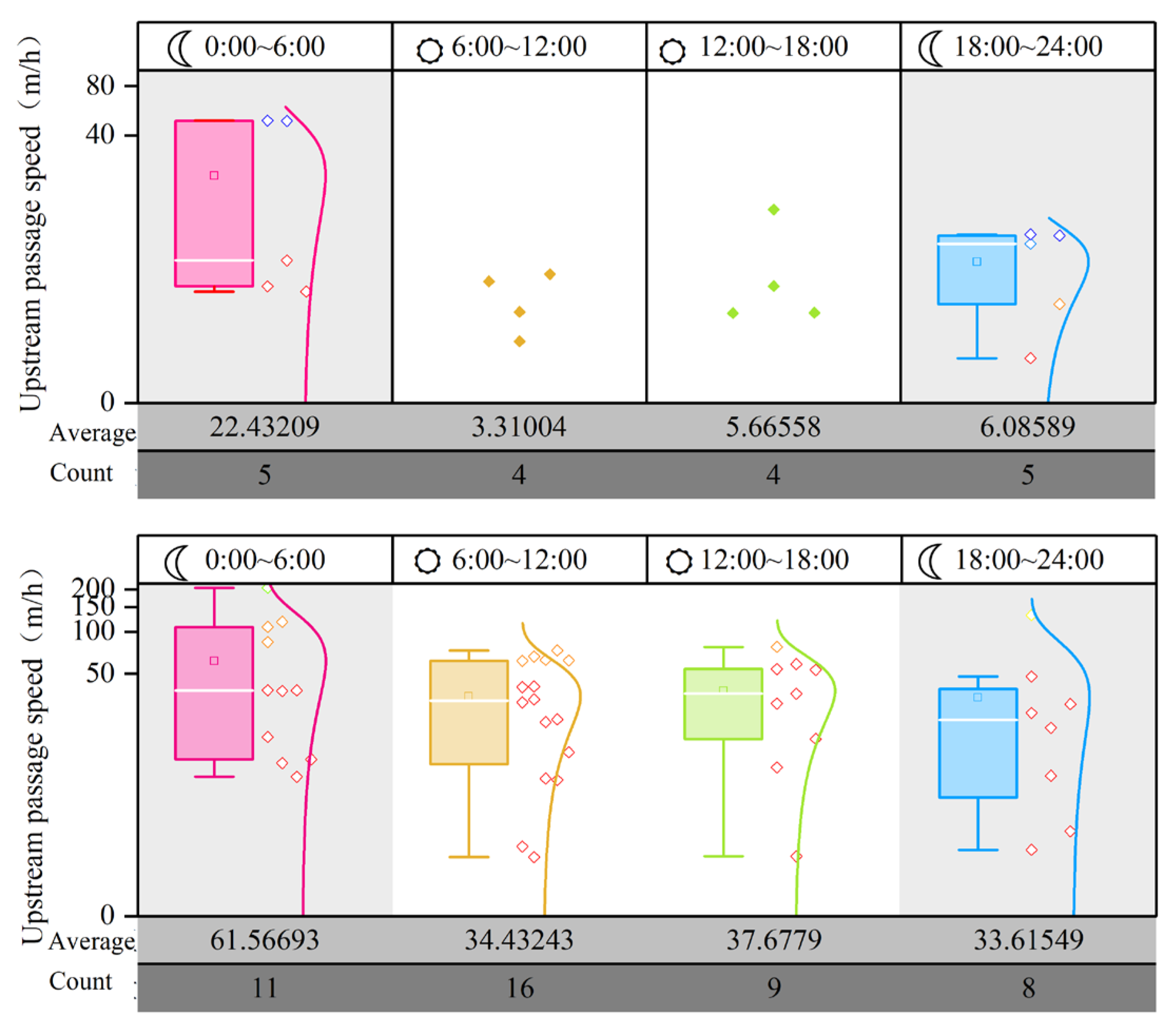
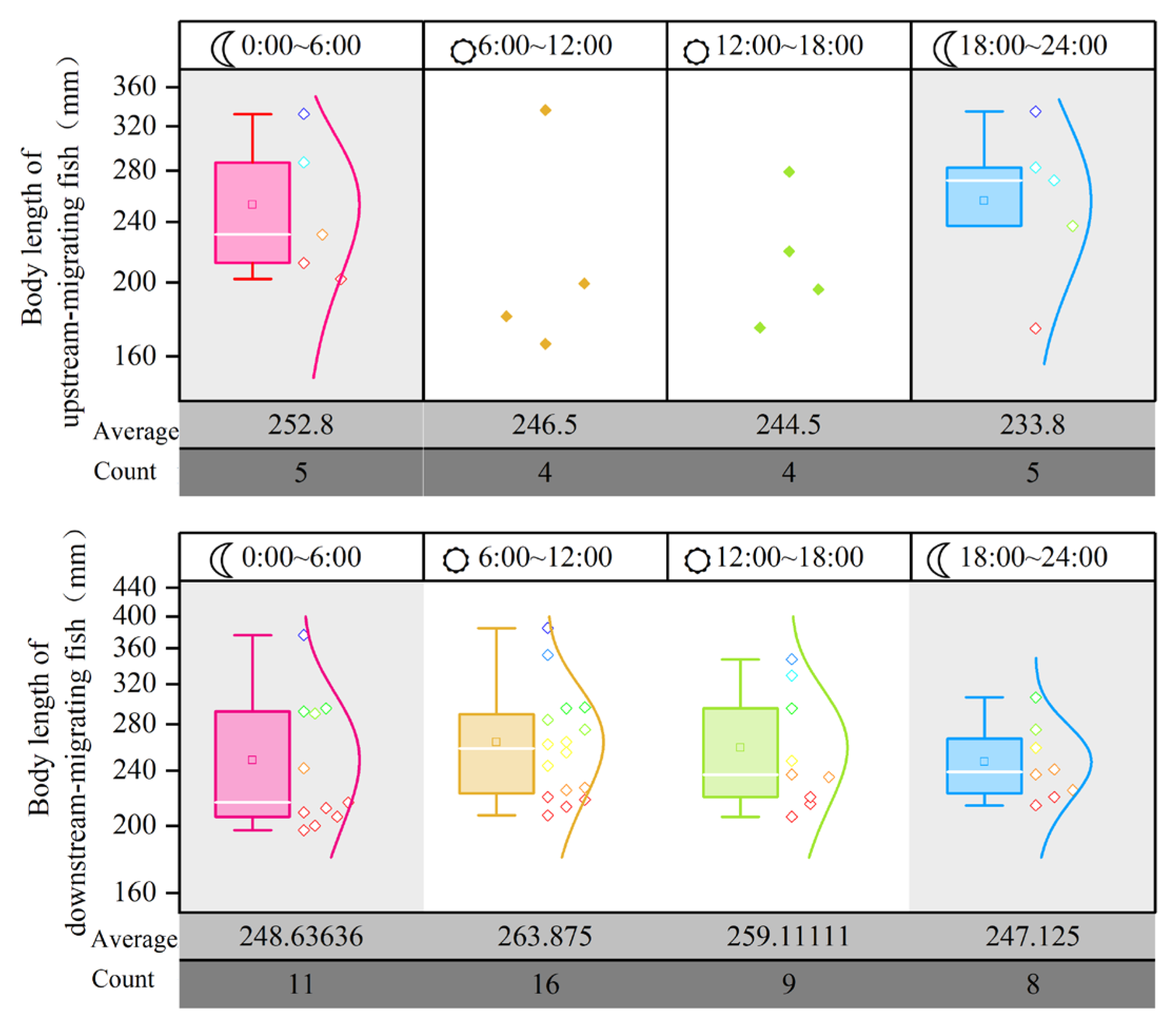


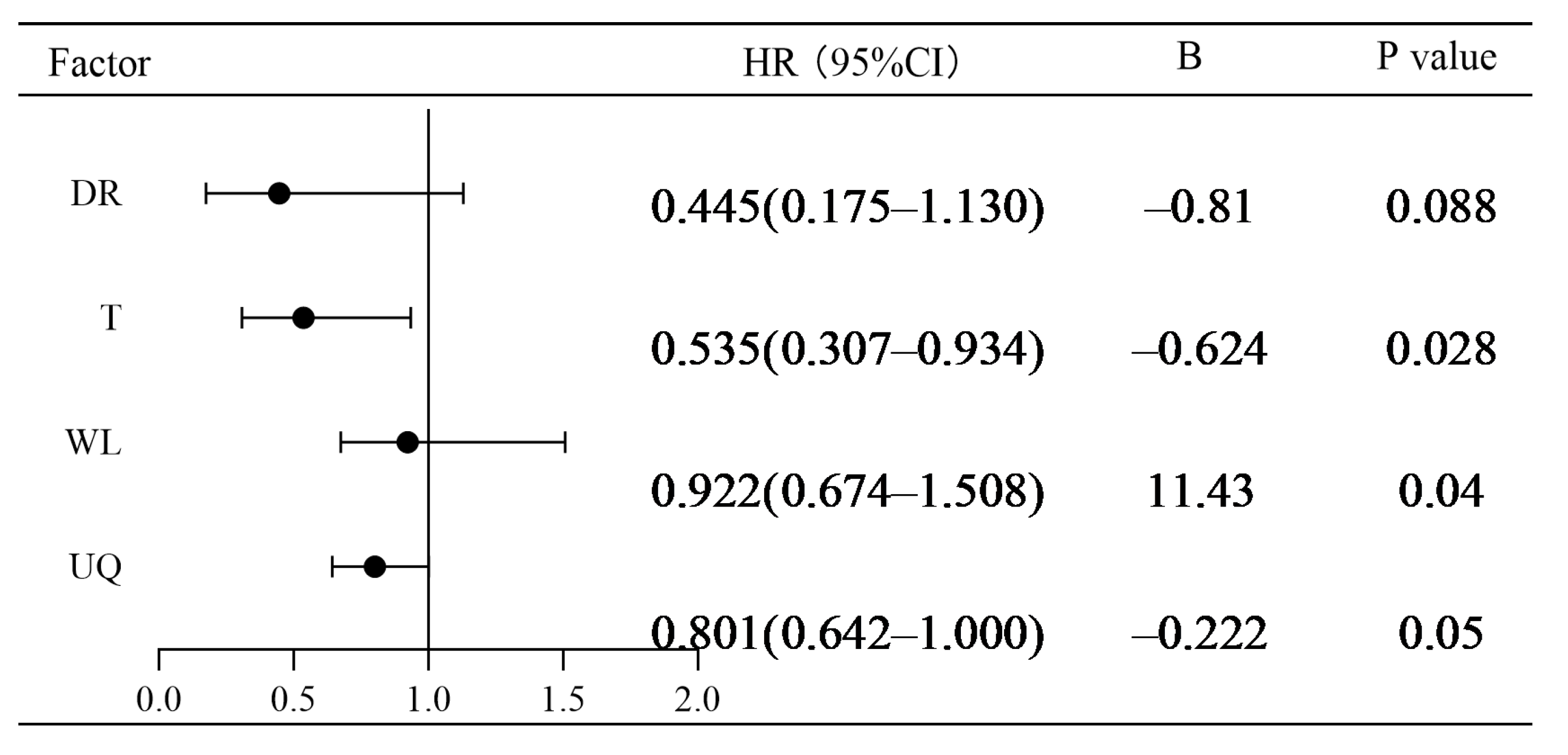
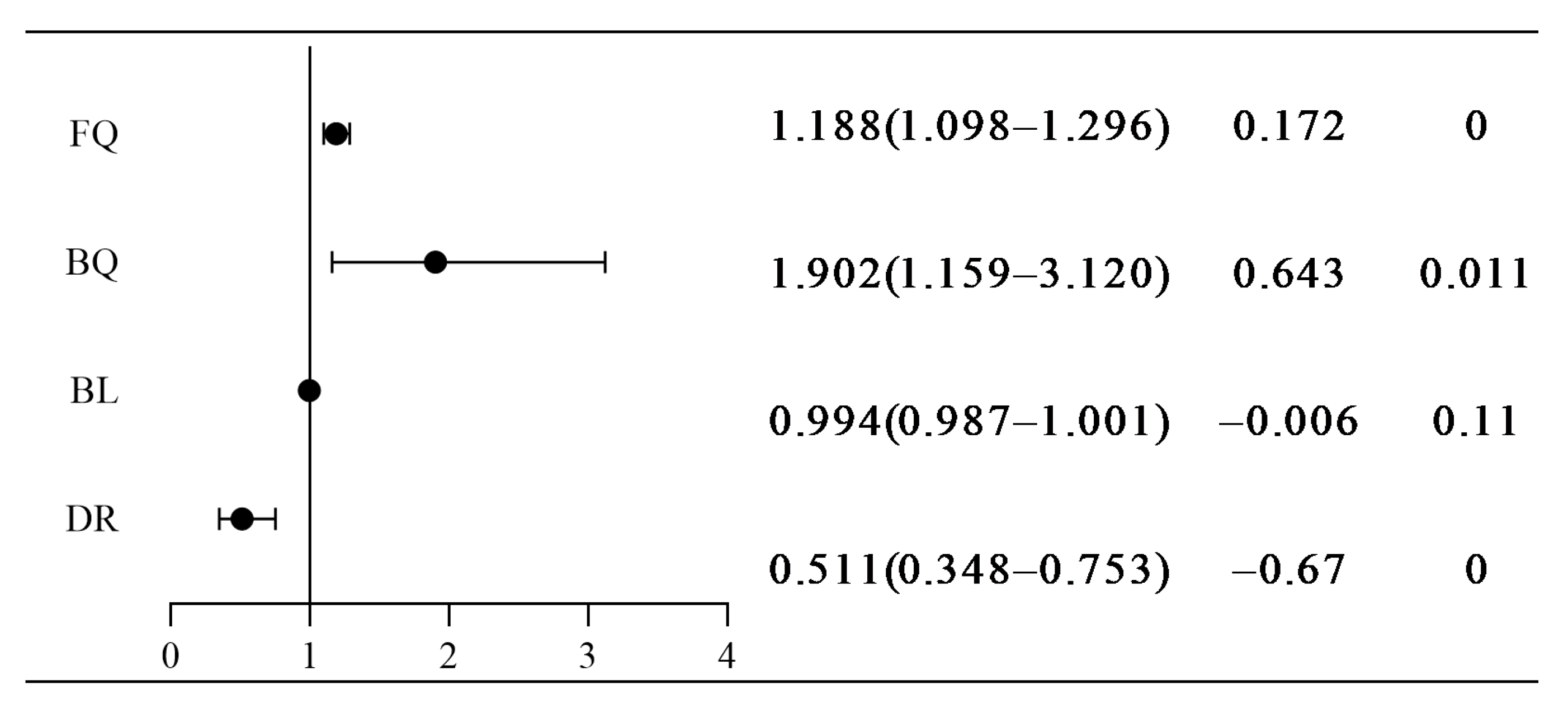

| Release Location | Number Released | Number Arrived | Passage Success Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream Section | 1 m from the fishway exit | 30 | 4 | 13.33% |
| 20 m from the fishway exit | 30 | 5 | 16.67% | |
| 30 m from the fishway exit | 30 | 5 | 16.67% | |
| Downstream Section | 1 m from the fishway entrance | 30 | 18 | 60.00% |
| 20 m from the fishway entrance | 30 | 26 | 86.67% | |
| 30 m from the fishway entrance | 30 | 29 | 96.67% |
| Number | Model | AIC | ΔIAIC | wi | wi/wj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | UQ + WL + T + BL + DR + QC + TC | 71.16 | 2 | 0.156563017 | 2.718281828 |
| 2 | UQ + WL + T + BL + DR + QC | 69.16 | 1.96 | 0.1597258 | 2.664456242 |
| 3 | UQ + WL + T + DR + QC | 67.2 | 1 | 0.258128777 | 1.648721271 |
| 4 | UQ + WL + T + DR | 66.2 | 0 | 0.425582405 |
| Number | Model | AIC | ΔIAIC | wi | wi/wj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FQ + BQ + T + BL + DR + Place | 320.96 | 1.95 | 0.207015322 | 2.651167 |
| 2 | FQ + BQ + BL + DR + Place | 319.01 | 1.62 | 0.244152446 | 2.247908 |
| 3 | FQ + BQ + BL + DR | 317.39 | 0 | 0.548832233 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Soomro, S.-e.-h.; Hu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Lin, C.; Ke, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Behavioral Responses of Migratory Fish to Environmental Cues: Evidence from the Heishui River. Fishes 2025, 10, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070310
Xu J, Jiao Y, Soomro S-e-h, Hu X, Li D, Wang J, Liu B, Lin C, Ke S, Wu Y, et al. Behavioral Responses of Migratory Fish to Environmental Cues: Evidence from the Heishui River. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070310
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiawei, Yilin Jiao, Shan-e-hyder Soomro, Xiaozhang Hu, Dongqing Li, Jianping Wang, Bingjun Liu, Chenyu Lin, Senfan Ke, Yujiao Wu, and et al. 2025. "Behavioral Responses of Migratory Fish to Environmental Cues: Evidence from the Heishui River" Fishes 10, no. 7: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070310
APA StyleXu, J., Jiao, Y., Soomro, S.-e.-h., Hu, X., Li, D., Wang, J., Liu, B., Lin, C., Ke, S., Wu, Y., & Shi, X. (2025). Behavioral Responses of Migratory Fish to Environmental Cues: Evidence from the Heishui River. Fishes, 10(7), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070310







