Diet of the Common Eagle Ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Northern Adriatic Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
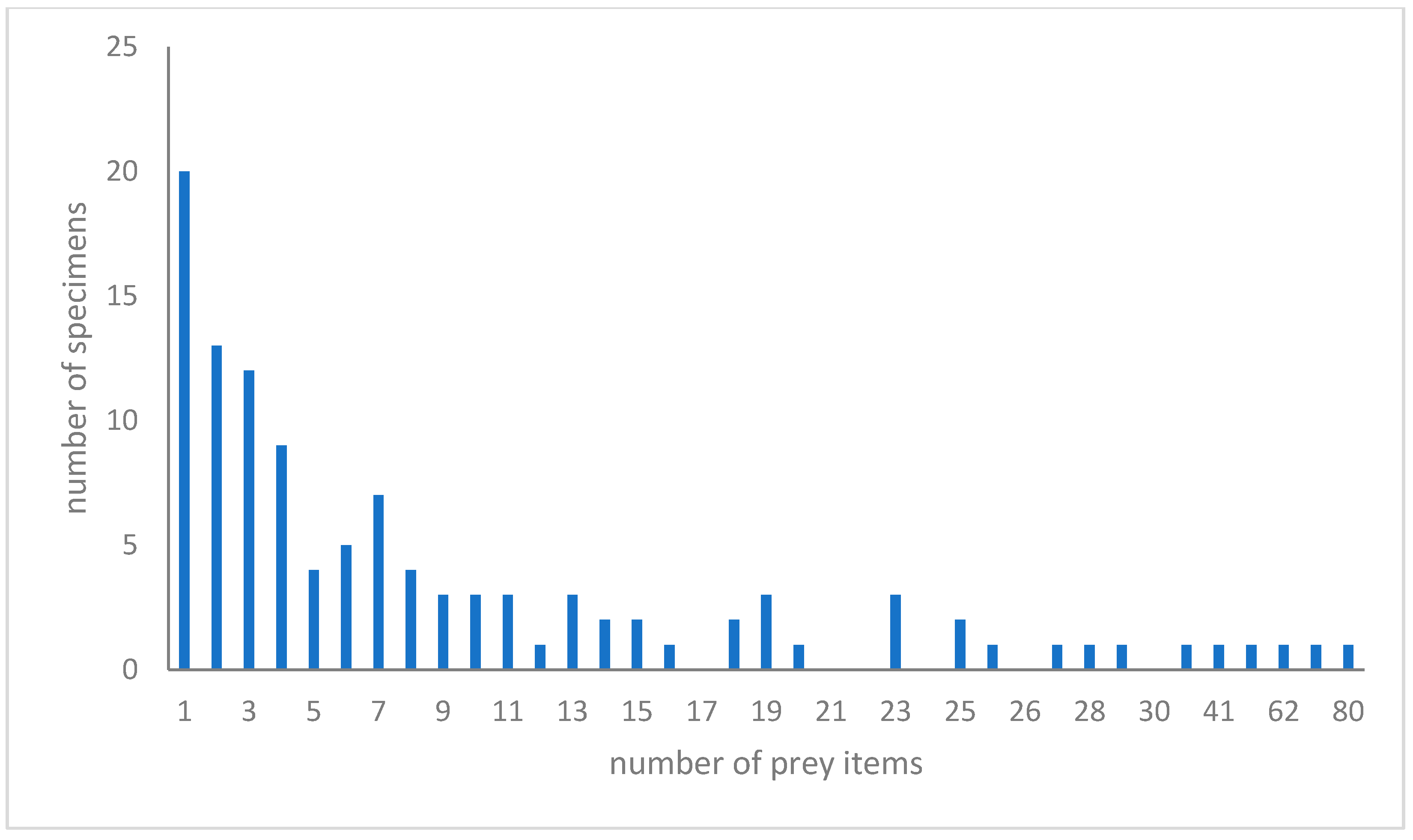
3.1. Biometrical Features
3.2. Overall Diet
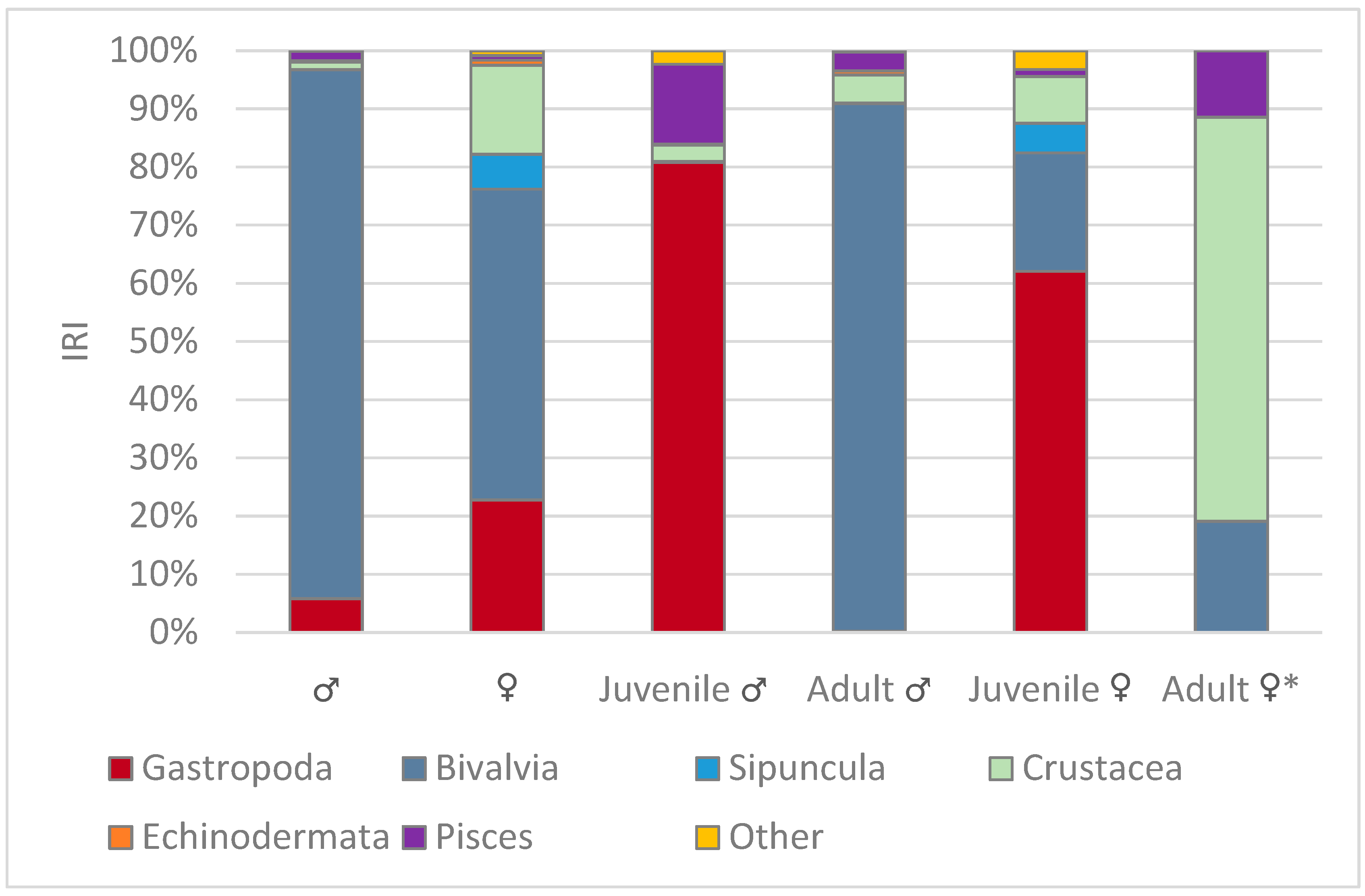
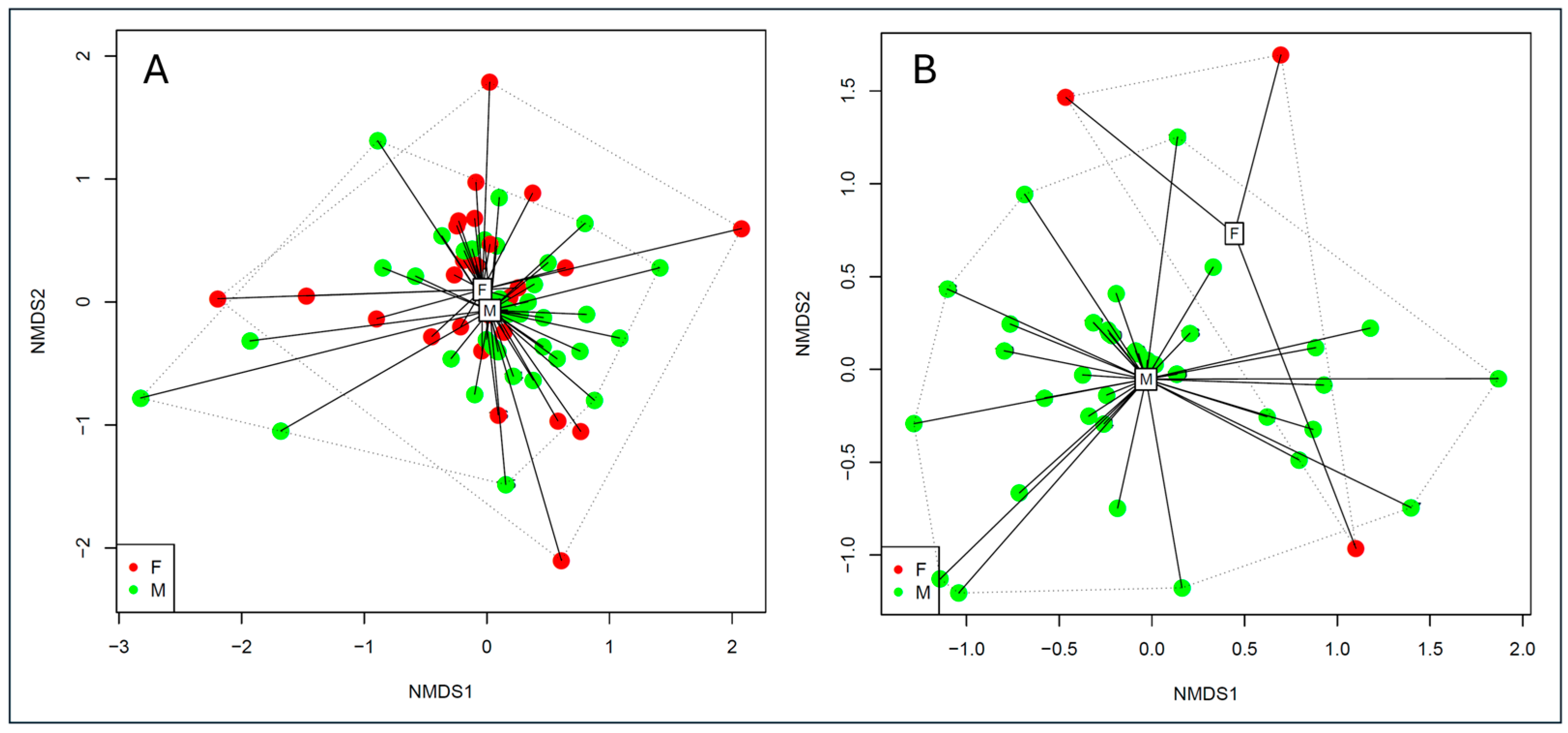
3.3. Diet Related to Sex and Size
4. Discussion
4.1. Feeding Habits
4.2. Ontogenetic Shift in the Diet
4.3. Comparison with Other Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barausse, A.; Duci, A.; Mazzoldi, C.; Artioli, Y.; Palmeri, L. Trophic network model of the Northern Adriatic Sea: Analysis of an exploited and eutrophic ecosystem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortibuoni, T.; Giovanardi, O.; Pranovi, F.; Raicevich, S.; Solidoro, C.; Libralato, S. Analysis of long-term changes in a Mediterranean marine ecosystem based on fishery landings. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barausse, A.; Correale, V.; Čurković, A.; Finotto, L.; Riginella, E.; Visentin, E.; Mazzoldi, C. The role of fisheries and the environment in driving the decline of elasmobranchs in the northern Adriatic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, A.; Lipej, L. An annotated checklist and the conservation status of chondrichthyans in the Adriatic. Fishes 2022, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Bolje, A. Slovenia. In The Global Status of Sharks, Rays, and Chimaeras; Jabado, R.W., Morata, A.Z.A., Bennett, R.H., Finucci, B., Ellis, J.R., Fowler, S., Grant, M.I., Barbosa Martins, A.P., Sinclair, S.L., et al., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, P.J. Prey capture behavior and feeding mechanics of elasmobranchs. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 165–202. [Google Scholar]
- McEachran, J.D.; Capapé, C. Dasyatidae. In Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean; Whitehead, P.J.P., Bauchot, M.L., Hureau, J., Tortonese, E., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1984; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Majoli, F.; Weigel, B.; Chiarabelli, E.; Manfredi, C.; Anibaldi, A.; Isajlović, I.; Vrgoč, N.; Casini, M. Influence of ecological traits on spatio-temporal dynamics of an elasmobranch community in a heavily exploited basin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Bianchi, I. Guida degli Squali e delle Razze del Mediterraneo (Guide to the Sharks and Rays of the Mediterranean Sea); Muzzio Editore: Padova, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, P.; Rodrigues, N.V. Summer aggregations of the common eagle ray, Myliobatis aquila. Arquipélago-Life Mar. Sci. 2015, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Grancagnolo, D.; Arculeo, M. Summer aggregation of common eagle ray, Myliobatis aquila (Chondrichthyes: Myliobatidae), in the Marine Protected Area of the Egadi Islands (southwestern Tyrrhenian Sea). Biogeogr. J. Integr. Biogeogr. 2021, 36, a002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabado, R.; Chartrain, E.; Cliff, G.; da Silva, C.; Derrick, D.V.; Dia, M.; Diop, M.; Doherty, P.; Leurs, G.; Metcalfe, K.; et al. Myliobatis aquila-Common Eagle Ray. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nathan-Pacoureau/publication/383086961_Myliobatis_aquila-Common_Eagle_Ray_The_IUCN_Red_List_of_Threatened_Species_2021/links/66bba6f98f7e1236bc5579dc/Myliobatis-aquila-Common-Eagle-Ray-The-IUCN-Red-List-of-Threatened-Species-2021.pdf?origin=scientificContributions (accessed on 10 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Jardas, I. The Adriatic Ichthyofauna; Školska knjiga, d.d.: Zagreb, Croatia, 1996; 553. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, F.; Osio, G.C.; Jenkins, C.J.; Rosenberg, A.A.; Lotze, H.K. Long-term change in a meso-predator community in response to prolonged and heterogeneous human impact. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, C.M.; Vallinia, C.; Filidei, E., Jr.; Ruffino, M.; Consalvo, I.; Di Muccio, S.; Gion, S.; Scacco, U.; Tarulli, E.; Giovanardi, O.; et al. By-catch of cetaceans and other species of conservation concern during pair trawl fishing operations in the Adriatic Sea (Italy). Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, S.; Pulcinella, J.; Fortuna, C.M.; Moro, F.; Sala, A. Elasmobranch bycatch in the Italian Adriatic pelagic trawl fishery. PLoS ONE 2014, 13, e0191647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, K.I.; Heithaus, M.R.; Papastamatiou, Y.P. Buried in the sand: Uncovering the ecological roles and importance of rays. Fish Fish. 2021, 22, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capapé, C.; Quignard, J.P. Dimorphisme sexuel et observations biologiques sur Myliobatis aquila (L., 1758). Contribution á l’étude systématique du genre Myliobatis, Cuvier, 1817. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Genova 1974, 80, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Capapé, C. Étude du régime alimentaire de l’aigle de mer, Myliobatis aquila (L., 1758) des côtes tunisiennes. J. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer. 1976, 37, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jardas, I.; Šantić, M.; Pallaoro, A. Diet composition of the eagle ray, Myliobatis aquila (Chondrichthyes: Myliobatidae), in the Eastern Adriatic Sea. Cybium 2004, 28, 372–374. [Google Scholar]
- Valls, M.; Quetglas, A.; Ordines, F.; Moranta, J. Feeding ecology of demersal elasmobranchs from the shelf and slope off the Balearic Sea (western Mediterranean). Sci. Mar. 2011, 75, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, G.; Demirel, N. Trophic interactions of uncommon batoid species in the Sea of Marmara. J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2020, 26, 294–309. [Google Scholar]
- Özten, S.; Çiğdem Yiğin, C.; İşmen, A.; Cabbar, K. Biological assessment of common eagle ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) from the Northeastern Mediterranean (Saros Bay), Türkiye. Acta Biol. Turc. 2024, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Paliska, D.; Capapé, C. Feeding habits of the pelagic stingray Pteroplatytrygon violacea (Chondrichthyes: Dasyatidae) in the Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2012, 93, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviben, S.; Trkov, D.; Mavrič, B.; Kružić, P.; Lipej, L. Observations on the diet of the Starry skate, Raja asterias Delaroche, 1809 (Elasmobranchii: Rajidae) in the Adriatic Sea. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capapé, C.; Guélorget, O.; Vergne, Y.; Quignard, J.P. Reproductive biology of the common eagle ray, Myliobatis aquila (Chondrichthyes: Myliobatidae) from the coast of Languedoc (Southern France, northern Mediterranean). Vie Milieu 2007, 57, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Riedel, R. Fauna und Flora der Adria; Verlag Paul Parey: Hamburg und Berlin, Germany, 1963; 630p. [Google Scholar]
- Falciai, L.; Minervini, R. Guida dei Crostacei Decapodi d’Europa; Franco Muzzio Editore: Roma, Italy, 1992; 282p. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis—A review of methods and their application. J. Fish. Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, blue-fin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Fish. Bull. Calif. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, E. A critical review of methods of studying fish feeding based on analysis of stomach contents: Application to elasmobranch fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R Development Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H.; The Vegan Package. Community Ecology Package. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Mayer, D.; Zeileis, A.; Hornik, K.; Garber, F.; Friendly, M. VCD: Visualizing Categorical Data. R Package Version 1. 4–8, 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vcd/vcd.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Krebs, C.J. Ecological Methodology; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.E.; Zaret, M.T. Bias in estimating niche overlap. Ecology 1982, 63, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, H.S. Measurement of “overlap” in comparative ecological studies. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 19–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Trites, A.; Capuli, E.; Christensen, V. Diet composition and trophic levels of marine mammals. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Froese, R.; Sa-a, P.S.; Palomares, M.L.; Christensen, V.; Rius, J. TrophLab Manual; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D.; Palomares, M.L. Approaches for dealing with three sources of bias when studying the fishing down marine food web phenomenon. In Fishing Down the Mediterranean Food Webs? Briand, F., Ed.; CIESM Workshop Series 12: Palermo, Italy, 2000; pp. 61–66. Available online: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/legacy.seaaroundus/doc/Researcher+Publications/dpauly/PDF/2000/Books%26Chapters/ApproachesDealingWithThreeSourcesBias.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Aschliman, N.C. Interrelationships of the durophagous stingrays (Batoidea: Myliobatidae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 97, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, A.P. Stiffening the stingray skeleton—An investigation of durophagy in myliobatid stingrays (Chondrichthyes, Batoidea, Myliobatidae). J. Morphol. 2000, 243, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmann, M.; Crofts, S.; Mason, D.; Summers, A.; Lovejoy, N. Morphology does not predict performance: Jaw curvature and prey crushing in durophagous stingrays. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 3941–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, I.P.; Bennett, M.B. A Comparative Analysis of Feeding and Trophic Level Ecology in Stingrays (Rajiformes; Myliobatoidei) and Electric Rays (Rajiformes: Torpedinoidei). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Vicente, L.M.; Marco-Méndez, C.; Loya-Fernández, A.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Observations on the ecology and reproductive biology of the sipunculan worm Aspidosiphon muelleri in temperate waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2014, 94, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Mai, K.; Tong, T.; Dong, L.; Xu, M. Optimal dietary protein to energy ratio for juvenile peanut Worm Sipunculus nudus Linnaeus. Fish. Sci. 2015, 81, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capapé, C. Diet of the Angular Rough Shark Oxynotus centrina (Chondrichthyes: Oxynotidae) off the Languedocian Coast (Southern France, North-Western Mediterranean). Vie Milieu 2008, 58, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Francour, P. Predation on holothurians: A literature review. Invertebr. Biol. 1997, 116, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, H.; Saïdi, B.; Marouani, S.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouaïn, A. Food habits of the roug ray Raja radula (Chondrichthyes: Rajidae) from the Gulf of Gabès (central Mediterranean Sea). Ital. J. Zool. 2013, 80, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Potter, I.C. Habitat partitioning among four elasmobranch species in nearshore, shallow waters of a subtropical embayment in Western Australia. Mar. Biol. 2004, 145, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, A.F.; Mejía-Falla, P.A.; Giraldo, A. Feeding ecology of elasmobranch fishes in coastal waters of the Colombian Eastern Tropical Pacific. BMC Ecol. 2007, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, H.; Aglama, O.; Kutli, S.; Aydin, I. Diet and feeding strategy of the common stingray Dasyatis pastinaca (Linnaeus, 1758) on the Turkish coast of southeastern Black Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2010, 51, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, I.; Bennett, M. Feeding ecology and dietary comparisons among three sympatric Neotrygon (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae) species. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 80, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianeti, M.D.; Yokota, L.; Texeira Lessa, R.P.; Ferraz Dias, J. Diet of longnose stingray Hypanus guttatus (Myliobatiformes: Dasyatidae) in tropical coastal waters of Brazil. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2019, 99, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D.; FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Version (10/2024). 2024. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Wetherbee, B.M.; Cortes, E. Food consumption and feeding habits. In The Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; Carrier, J., Musick, J., Heihaus, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Szszepanski, D.; Bengtson, A. Quantitative food habits of the bullnose ray, Myliobatis freminvillii, in Delaware Bay. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 97, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.T. Patterns of resource partitioning in sea robins (Pisces: Triglidae). Copeia 1977, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, C.; Whittingham, M.J.; Newton, I. Age-dependent diet choice in an avian top predator. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2006, 273, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponte, D.; Barcelos, L.M.D.; Santos, C.; Medeiros, J.; Barreiros, J.P. Diet of Dasyatis pastinaca and Myliobatis aquila (Myliobatiformes) from the Azores, NE Atlantic. Cybium 2016, 40, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, S.; Obrebski, S. The feeding biology of the bat ray, Myliobatis californica in Tomales Bay, California. In Fish Food Habit Studies; Simenstad, C.A., Lipovski, S.J., Eds.; Washington Sea Grant: Seattle, WA, USA, 1976; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Azouz, A.; Capapé, C. Les relations alimentaires entre les Sélaciens et le zoobenthos des côtes nord de la Tunisie. Bull. Inst. Océanogr. Pêche 2016, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Soldo, A. Status of the sharks in the Adriatic. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Mediterranean Cartilaginous Fish with Emphasis on Southem and Eastern Mediterranean, Ataköy Marina, Istanbul, Turkey, 14–16 October 2006; Turkish Marine Research Foundation: Istanbul, Turkey, 2006; pp. 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lipej, L.; Dulčić, J. The current status of Adriatic fish biodiversity. In Balkan Biodiversity; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Branstetter, S. Early life-history implications of selected carcharinoid and lamnoid sharks of the northwest Atlantic. NOAA Tech. Rep. NMFS 1990, 90, 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Odorico, R.; Koce, U. The diet of the Mediterranean shag Phalacrocorax aristotelis desmarestii roosting along the Slovenian coast. Acrocephalus 2016, 37, 51–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridel, D.; Utmar, P.; Koce, U.; Kralj, J.; Baccetti, N.; Candotto, S.; Ciriaco, S.; de Luca, M.; Pascucci, M.; Sartori, A.; et al. Conservation status of the Mediterranean Shag Gulosus aristotelis desmarestii in the Adriatic Sea during the Non-breeding period: Baseline population, trends, threats. Ardeola 2024, 71, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


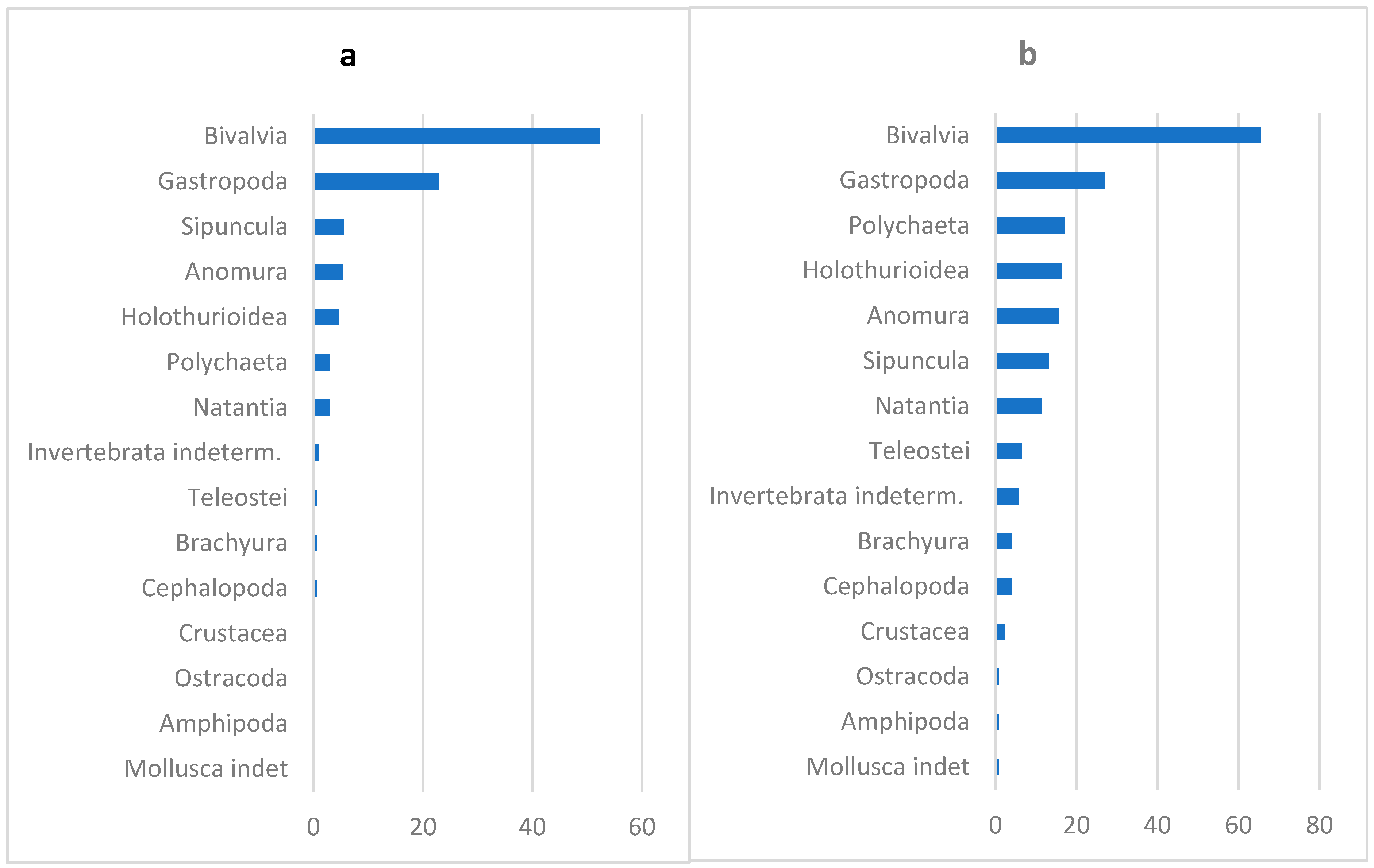

| TAXA | N% | W% | %FO | IRI% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mollusca | |||||
| Bivalvia | |||||
| Corbula gibba | 0.17 | 0.14 | 1.64 | 0.01 | |
| Laevicardium oblongum | 0.17 | 0.70 | 1.64 | 0.02 | |
| Bivalvia indeterminata | 52.00 | 42.22 | 66.39 | 85.85 | |
| Gastropoda | |||||
| Gastropoda indet. | 1.48 | 1.68 | 5.74 | 0.25 | |
| Aporrhais pes pelecani | 0.78 | 0.46 | 5.74 | 0.10 | |
| Cerithium vulgatum | 11.37 | 16.99 | 16.39 | 6.38 | |
| Gibbula sp. | 0.69 | 0.61 | 3.28 | 0.06 | |
| Turritella communis | 8.51 | 3.45 | 6.56 | 1.08 | |
| Cephalopoda | |||||
| Cephalopoda indet. | 0.52 | 0.76 | 4.10 | 0.07 | |
| Mollusca indet. | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 0.00 | |
| Sipunculida | |||||
| Sipunculida indet. | 0.87 | 0.10 | 2.46 | 0.03 | |
| Sipunculus nudus | 0.17 | 1.14 | 1.64 | 0.03 | |
| Aspidosiphon muelleri | 4.51 | 0.51 | 11.48 | 0.79 | |
| Polychaeta | |||||
| Eunicidae | 0.43 | 0.04 | 0.82 | 0.01 | |
| Polychaeta indet. | 2.60 | 1.06 | 16.39 | 0.82 | |
| Crustacea | |||||
| Ostracoda | |||||
| Ostracoda indet. | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.00 | |
| Decapoda | |||||
| Anomura indet. | 1.56 | 3.81 | 7.38 | 0.54 | |
| Diogenes pugilator | 0.17 | 0.03 | 1.64 | 0.00 | |
| Paguristes eremita | 2.08 | 7.78 | 7.38 | 1.00 | |
| Paguridae | 1.48 | 3.12 | 4.10 | 0.26 | |
| Decapoda—Natantia | 1.30 | 0.01 | 9.02 | 0.16 | |
| Processa sp. | 1.65 | 1.03 | 4.92 | 0.18 | |
| Decapoda Brachyura | 0.26 | 0.71 | 2.46 | 0.03 | |
| Thia scutellata | 0.43 | 2.75 | 1.64 | 0.07 | |
| Crustacea indet. | 0.26 | 0.53 | 2.46 | 0.03 | |
| Amphipoda | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.00 | |
| Amphipoda indet. | |||||
| Echinodermata | |||||
| Holothurioidea indet. | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.00 | |
| Labidoplax digitata | 4.60 | 1.49 | 15.57 | 1.30 | |
| Invertebrata indet. | |||||
| Invertebrata indet. | 0.87 | 0.35 | 5.74 | 0.10 | |
| Teleostei | |||||
| Teleostei indet. | 0.69 | 8.46 | 6.56 | 0.82 |
| Overall | Juv | Adults | Males | Females | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| average number of prey | 9.44 | 10.69 | 7.31 | 9.31 | 10.03 |
| average prey weight (g) | 1.22 | 1.18 | 1.37 | 1.14 | 1.46 |
| average meal size (g) | 11.56 | 12.58 | 10.01 | 10.59 | 14.6 |
| Shannon–Wiener index | 1.49 | 1.95 | 1.44 | 1.7 | 1.97 |
| Average Predator weight (kg) | 1.32 | 0.95 | 1.97 | 1.32 | 1.38 |
| prey W/predator weight (%) | 2.59 | 2.83 | 2.16 | 2.28 | 3.51 |
| TROPH index | 3.21 ± 0.40 | 3.23 ± 0.43 | 3.17 ± 0.24 | 3.20 ± 0.39 | 3.25 ± 0.44 |
| Morisita/Horn index | 0.88 | 0.86 | |||
| Area | Sea of Marmara | Azores | Croatian Adriatic | Saros Bay | Tunisian Coasts | Northern Adriatic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | [22] | [60] | [20] | [23] | [19] | this work |
| Anthozoa | 0.51 | |||||
| Nemertina | 1.16 | 0 | ||||
| Bivalvia | 14.43 | 33.00 | 44.42 | 52.34 | ||
| Gastropoda | 85.70 | 30.33 | 65.86 | 17.20 | 22.83 | |
| Scaphopoda | 46.28 | 3.99 | 0.00 | |||
| Cephalopoda | 0.81 | 1.22 | 0.77 | |||
| Mollusca indet. | 13.88 | |||||
| Stomatopoda | 0.00 | 2.82 | ||||
| Decapoda | 3.98 | 14.30 | 9.73 | 9.76 | 11.17 | 8.95 |
| Polychaeta | 14.95 | 4.69 | 6.10 | 6.42 | 3.04 | |
| Sipuncula | 15.76 | 0.77 | 5.56 | |||
| Echinodermata | 0.00 | 1.28 | 4.69 | |||
| Ascidiacea | 0.00 | 1.28 | ||||
| Pisces | 5.66 | 0.60 | 9.76 | 13.86 | 0.69 | |
| other | 7.32 | 1.91 | ||||
| sum | 100.00 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| number of specimens | 15 | 10 | 165 | 85 | 523 | 122 |
| empty stomachs | 6 | 1 | 24 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lipej, L.; Battistella, R.; Mavrič, B.; Ivajnšič, D. Diet of the Common Eagle Ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Fishes 2025, 10, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070311
Lipej L, Battistella R, Mavrič B, Ivajnšič D. Diet of the Common Eagle Ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070311
Chicago/Turabian StyleLipej, Lovrenc, Riccardo Battistella, Borut Mavrič, and Danijel Ivajnšič. 2025. "Diet of the Common Eagle Ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Northern Adriatic Sea" Fishes 10, no. 7: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070311
APA StyleLipej, L., Battistella, R., Mavrič, B., & Ivajnšič, D. (2025). Diet of the Common Eagle Ray, Myliobatis aquila (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Fishes, 10(7), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070311







