Abstract
The intensification of human activities in recent years has led to significant overexploitation of Triplophysa strauchii populations, resulting in a decline in the species’ natural stocks. This underscores the need for research and development initiatives aimed at supporting the recovery and sustainable management of the species. Therefore, this study investigated its biological traits and isozyme characteristics in detail. First, throutigations of fish ecology, the age and growth patterns of T. strauchii were examined. The results revealed that the length of the otoliths was greater than the width and that the intermajor groove was indistinct. The age range of the fish was 0–4 years. A correlation between body length and weight revealed that T. strauchii exhibited isometric growth patterns. In terms of growth parameters, the inflection point in age for T. strauchii was ti = 3.23. Additionally, to analyze the enzymes lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), and esterase (EST) in ten tissues of T. strauchii (liver, muscle, heart, gills, eye, brain, fins, kidneys, gonads, and intestines), vertical plate electrophoresis was performed via polyacrylamide gels. The results of isoenzyme analysis revealed that the LDHA (lactate dehydrogenase A subunit) gene was predominant in all tissues. A maximum of two s-MDH enzyme bands with three m-MDH enzyme bands were detected, with a classic enzyme profile and no gene mutation. The EST enzyme was highly expressed in the liver and kidney and was less polymorphic. In general, T. strauchii exhibited a spindle-like body shape and isometric growth patterns in the Turks River. It exhibited a narrow age range, strong adaptability, and stable genetic traits. This species has high development potential, utilization value and ecological significance.
Key Contribution:
This study revealed, for the first time, the inflection point age for the growth (3.23 years) of Triplophysa strauchii in the Turks River and its unique metabolic adaptation mechanisms (e.g., the LDHA dominated anaerobic metabolic pathway), providing integrated biological and genetic evidence for deciphering growth patterns and guiding genetic diversity conservation in high-altitude loach species.
1. Introduction
Triplophysa strauchii, commonly known as dogfish, is a small cold-water fish belonging to the genus Triplophysa. This species is widely distributed across Central Asia’s mountainous regions, particularly in the Xinjiang Plateau, where it is a vital ecological component, serving as prey for carnivorous fish, and is economically important due to its abundant populations [1]. The Turks River in Xinjiang, located at an average elevation of 3000 m above sea level, contributes approximately 63% of the Ili River’s total discharge, with an estimated annual runoff of 8.0 × 10⁹ m3 [2]. In recent years, intensified anthropogenic activities and unregulated fishing have led to a significant decline in T. strauchii populations, highlighting the need for immediate conservation measures and comprehensive biological studies. The initial research on T. strauchii was conducted by Guo et al. [3,4], who investigated the biology of populations in the Sayram Lake and the Chaiwobo Lake. Subsequently, Kanu [5] expanded on these studies by analyzing the mitochondrial whole genome of the species and assessing its genetic diversity. However, few comprehensive and systematic studies have been conducted on the age, growth, and genetic characteristics of T. strauchii.
Comprehensive investigations into key biological traits of fish species, including growth, reproduction, feeding behavior, and ecological interactions, are essential for providing a robust scientific basis for the rational exploitation and effective management of fishery resources. Moreover, such knowledge plays a critical role in the conservation and sustainable development of aquatic ecosystems [6]. For example, accurately understanding the reproductive cycle and growth rate of fish is helpful for determining the best fishing time and breeding strategy to realize the sustainable utilization of fishery resources [7,8,9].
Isozymes, a class of enzymes that catalyze the same chemical reaction but have different molecular structures in organisms, are widely present in various tissues and cells of fish, with unique application value in fish biology research [10]. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is vital for anaerobic glycolysis, Malate dehydrogenase (MDH) participates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and shuttle processes, and esterase (EST) contributes to lipid metabolism. LDH has two main isoforms, LDHA and LDHB. LDHA is highly expressed in glycolytic tissues, promoting lactate production, while LDHB, abundant in oxidative tissues such as the heart, converts lactate back to pyruvate. MDH exists as supernatant (s-MDH) and mitochondrial (m-MDH) forms, with s-MDH acting in the cytoplasm for reducing equivalent transfer and m-MDH functioning in the citric acid cycle [11]. Studying these isozymes can reveal metabolic adaptations and potential disease biomarkers. This has great practical significance for the protection and utilization of fish germplasm resources and the precise formulation of fishery resource management strategies.
Our research sought to clarify the fundamental characteristics of T. strauchii, including age, growth patterns, and isozyme profiles. The objectives of this study were to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the biological and genetic characteristics of this species and to furnish essential biological and genetic information for the conservation of germplasms and the establishment of germplasm standards, thereby preserving the ecological equilibrium of the Turks River.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
From 2022 to 2023, 496 samples of T. strauchii were collected in four seasons, using tools such as drift gillnets and cages (the cage mesh size was two centimeters) in the Turks River in the Ili River system in Xinjiang (80°96′ E, 42°95′ N; elevation 1746.88 m) (Figure 1). The standard length (SL) and body weight (BW) of these fish were immediately measured to the nearest 0.1 mm and 0.1 g, respectively (Figure 2). One hundred samples were maintained in fresh condition and transported back to the laboratory for isozyme analysis.
Figure 1.
T. strauchii sampling area in the Turks River.
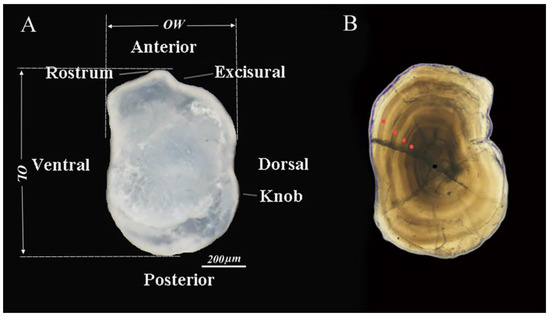
Figure 2.
(A). View of the external surface of the left lapillus otoliths of T. strauchii. OL: Otolith length; OW: Otolith width. (B). Characterization of the otolith chronology of T. strauchii, with age 4 expressed in the figure. The black dots indicate center point, and the red dots indicate annual rings.
The otoliths, vertebrae, and scales were removed and placed in 0.2 mL and 2 mL centrifuge tubes. The liver, muscle, heart, gill, eye, brain, fin, kidney, gonad, and intestine were removed, numbered, placed in plastic bags, and stored at −80 °C. A total of 0.3~0.5 g of frozen tissue sample was collected, the blood was rinsed off with physiological saline, and impurities were removed from the surface. Distilled water was added at a ratio of 1:3 (m/v) and the mixture was homogenized using a sterile homogenizer. The homogenate was centrifuged at 4 °C and 12,000 rpm for 30 min to separate the supernatant, which was subsequently transferred to a new centrifuge tube. The process was repeated 2–3 times until the supernatant was clear. The whole process was carried out at low temperatures.
2.2. Otolith Morphological Characteristics
The outer side of the left lapillus of T. strauchii was photographed, and morphometric indicators were measured via a stereomicroscope (SMZ1270i) and NIS-Element software. To improve image contrast, a uniform black background was chosen for the photographs, and six morphometric indicators were obtained (Figure 2A).
2.3. Age Determination Method
One side of the lapillus was turned upward, fixed on a slide with clear nail polish, and polished with sandpaper in a circular motion (600 to 2000 times) until a clear whorl appeared, i.e., near the central nucleus of the otolith, and then polished with polishing paper. After one side was treated, the otoliths were cleaned with acetone and turned over, and the above steps were repeated on the other side until the central nucleus of the otolith was clear [12]. The identification procedure was carried out on each otolith two to three times, and if all three identifications were different, the identification process was performed again until the results were uniform [13].
2.4. Growth Modeling
The relationship between the SL and BW was evaluated using a power function: W = aLb. Analysis of covariance was used to analyze significance [14]. Fulton’s condition index was calculated using the formula K = W/L3 × 100 [15,16].
The von Bertalanffy growth function (VBGF) was used to fit the growth equation. The formulas were as follows:
where Lt is the SL of individual fish at age t; Wt is the BW of individual fish at age t; L∞ is the asymptotic SL; W∞ is the asymptotic BW; t0 is the age at which SL and BW are theoretically equal to zero; k is the mean curvature of the growth curve; and b is the allometric growth index.
Lt = L∞ (1 − e −k (t − t0))
Wt = W∞ (1 − e −k (t − t0))b,
2.5. Gel Electrophoretic Analysis of Isoenzymes
The isoenzymes were analyzed by polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis (PAGE) [17], which was performed with a 4.0% concentrating gel and a 7.0% separating gel in Tris glycine electrophoresis buffer (pH 8.3). Before the samples were added, constant-current preelectrophoresis was carried out for 30 min with a current of 50 mA to remove impurities from the gel. Then, 20 μL of each prepared sample was added to each well, and electrophoresis was carried out for approximately 10 min at a voltage of 280 V. The sample was carefully extracted from the gel well via a micropipette. Electrophoresis was then performed at a constant voltage of 220 V, with termination occurring when the bromophenol blue tracking dye migrated to within 1 cm of the gel bottom. The whole electrophoresis process was carried out at 4 °C.
2.6. Staining and Decolorization of Gels
After electrophoresis, the film was peeled off from the glass plate and placed in preheated staining solution at 37 °C, and the staining was terminated when all the bands were clear. The staining process used for various isoenzymes was previously described by Zhang [10] and Wei [18]. The stained film was placed in 2.5% glacial acetic acid for decolorization, and the clear film after decolorization was placed in a preservation solution for fixation of the bands. The isoenzyme staining solution composition is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Formula of dyeing solution for isoenzymes.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and the significance of differences was tested via SPSS 18.0. The results are expressed as the means ± standard deviations ( ± SDs). Bandscan 5.0 software was used to identify the enzyme bands in the electrophoresis map, and the pattern for the electrophoresis map was drawn according to the identification results.
3. Results
3.1. Age Composition of T. strauchii
3.1.1. Otolith Morphology
T. strauchii otoliths are small, nearly oval, relatively thick in the middle, and gradually thin toward the edges. The otoliths are longer than they are wide, with a less obvious sulcus acusticus and a well-developed rostrum. Additionally, the edges of the otoliths’ ventral areas are smooth and gently curved, whereas the dorsal areas of the otoliths feature wavy protuberances. (Figure 2A). The otolith length (OL) was greater than the otolith width (OW) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Morphological parameters of otoliths of T. strauchii.
3.1.2. Age Determination
The ages of the T. strauchii specimens ranged from 0 to 4 years (Figure 2B). The mean age was estimated at 1.74 ± 0.77 years, with a predominance of individuals aged 2 years or more. Among them, fish in age group 2+ accounted for 46.8%, those in age group 0+ accounted for 2.4%, those in age group 1+ accounted for 36.6%, those in age group 3+ accounted for 12.6%, and those in age group 4+ accounted for only 1.6% (Figure 3).
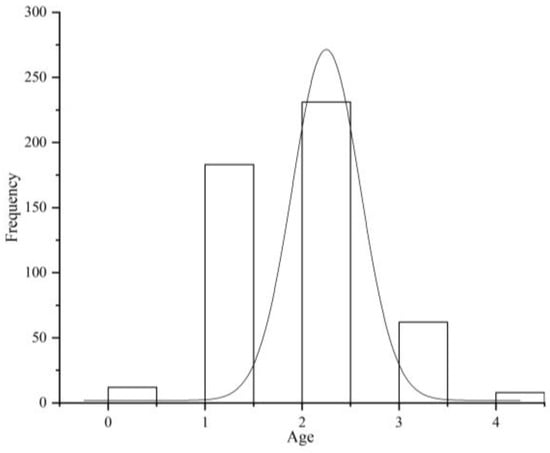
Figure 3.
Age distribution of T. strauchii.
3.2. Growth Characteristics
3.2.1. Distribution of SL (mm) and BW (g)
The SL of T. strauchii in this study varied between 51.63 and 137.09 mm, with an average of 88.69 ± 15.65 mm, aligning with a normal distribution (nonparametric analysis, skewness = 0.39, kurtosis = 0.12) (Figure 4A). The BW ranged from 1.18 to 22.99 g, with an average of 7.69 ± 4.58 g, which did not follow a normal distribution (nonparametric analysis, skewness = 1.39, kurtosis = 2.38) (Figure 4B).
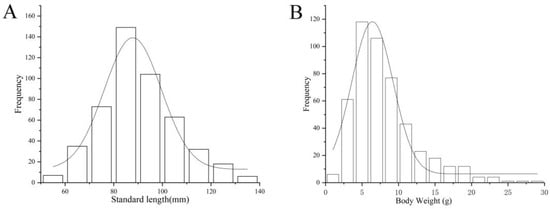
Figure 4.
(A): Standard length distributions of T. strauchii. (B): Body weight distributions of T. strauchii.
3.2.2. Relationship Between SL (mm) and BW (g)
The correlation between the SL and BW of the T. strauchii population was fitted as follows (Figure 5):
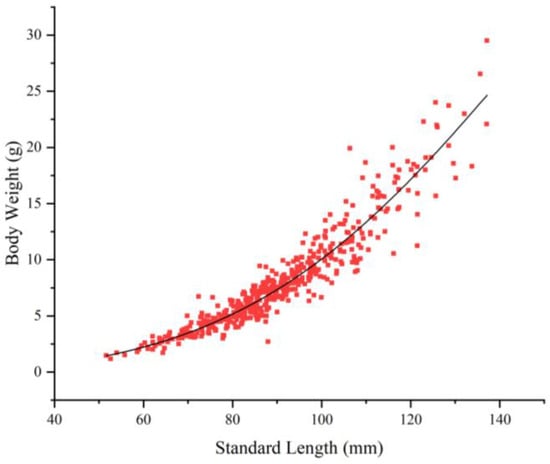
Figure 5.
Length–weight relationships of T. strauchii.
W (g) = 1.148 × 10−5L (mm)2.968 (R2 = 0.917, n = 496).
The b values ranged from 2.5 to 4, which were not significantly different from those of 3 (p > 0.05), indicating that T. strauchii exhibited uniform growth.
3.2.3. Fulton’s Condition Index
Fulton’s condition index assesses fish health patterns on the basis of the relationship between fish length and weight. According to formula K = (W/L3) × 100, the mean index of T. strauchii was 1.21.
3.2.4. Growth Equation
The asymptotic equation for T. strauchii was derived from the following equations:
Lt = 161.13 [1−e−0.32 (t+0.20)] (R2 = 0.9924),
Wt = 40.82 [1−e−0.32(t+0.20)]2.968 (R2 = 0.9651).
First-order derivatives of the growth equation were obtained to determine the growth rate:
dL/dt = 51.08 e−0.32(t+0.20),
dW/dt = 121.15e−0.32 (t+0.20) [1−e−0.32 (t+0.20)]1.968.
Second-order derivatives of the growth equation were obtained to determine the growth acceleration:
dL2/dt2 = −16.19 e−0.32 (t+0.20),
dW2/dt2 = 12.18 e−0.32 (t+0.20)[1−e−0.32 (t+0.20)]0.968 [2.968 e−0.32 (t+0.20)−1].
The growth curves of the SL and BW of T. strauchii showed an increase with age; the growth rate of SL decreased with age, whereas the growth rate of BW increased with age before the age of 3 years and then decreased; the acceleration of SL growth increased with age, whereas that of BW growth decreased with age, and the curves for SL and BW intersected at age 2.5 years. The ti of T. strauchii was 3.23 and the corresponding SL and BW values were 106.89 mm and 12.07 g, respectively. The derivative dW/dt peaked at t = 3.23 years and then started to decrease (Figure 6).
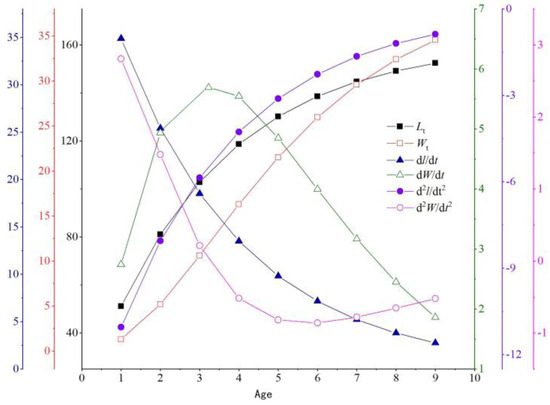
Figure 6.
Growth model of T. strauchii.
3.3. Tissue-Specific Expression of Isozymes in T. strauchii
The content of the Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme is rich in various tissues. LDH1, LDH2, and LDH3 were expressed in only the liver. LDH4 was not expressed in the fin, eye and liver but was expressed in six other tissues. LDH4′ was expressed in the gonad, kidney, heart, and muscle. LDH5 was expressed in all tissues except the liver, with clear bands, and was weakly expressed in the fin and highly expressed in the remaining tissues. LDH5′ was expressed in only the kidney and muscle (Figure 7).
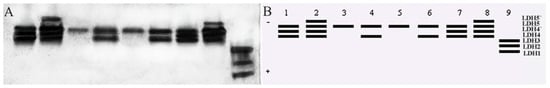
Figure 7.
(A) Electrophoretic profiles of T. strauchii LDH isozymes. (B) Mode chart. Note: 1: gonad; 2: kidney; 3: fin; 4: brain; 5: eye; 6: gill; 7: heart; 8: muscle; 9: liver.
Malate dehydrogenase is a dimeric enzyme that includes the supernatant (s-MDH) and mitochondrial (m-MDH) forms that cannot be interconverted to form heterodimers. The MDH expressed in T. strauchii exhibited up to five enzyme bands. MDH1 and MDH2 were highly expressed in all seven tissues. MDH3, MDH4, and MDH5 were highly expressed in muscle and kidney tissue and weakly expressed in other tissues (Figure 8).
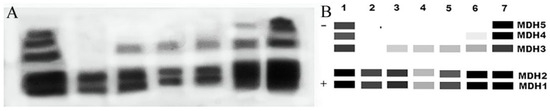
Figure 8.
(A) Electrophoretic profiles of T. strauchii MDH isozymes. (B) Mode chart. Note: 1: muscle; 2: heart; 3: gill; 4: eye; 5: brain; 6: fin; 7: kidney.
In the expressed esterases exhibited two bands in the liver, muscle, heart, gills, eyes, brain, fins, kidneys, gonads, and intestines of T. strauchii. EST1 was weakly expressed in the liver and highly expressed in other tissues. EST2 was highly expressed in muscle, fins, kidneys, and intestines and weakly expressed in other tissues, especially in the liver (Figure 9).
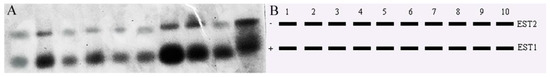
Figure 9.
(A) Electrophoretic profiles of T. strauchii EST isozymes. (B) Mode chart. Note: 1: liver; 2: muscle; 3: heart; 4: gill; 5: eye; 6: brain; 7: fin; 8: kidney; 9: gonad; 10: intestine.
4. Discussion
4.1. Biological Characteristics of T. strauchii in the Turks River
Fish morphology is an important indicator of fish growth and an important basis for fish classification [19,20]. In our study, the T. strauchii specimens were fusiform with a light brown carapace and a grayish brown dorsal side with small irregular black spots. They had a maximum SL of 137.17 mm, a maximum BW of 29.50 g and a maximum age of 4 years. These findings differ from those of other scholars who performed biological studies on T. strauchii, such as Guo et al. [3], who studied the biology of T. strauchii from Sayram Lake and reported SL and BW values greater than those reported in this study. Similarly, Liu [21] and Zhang [10] conducted a comparative study on the morphology of Sebastiscus marmoratus and Gymnodiptychus dybowskii from various geographic populations, revealing that these populations were differentially influenced by distinct habitat conditions. Consequently, distinct habitat environments can induce variations in the morphological characteristics of fish species.
The use of otoliths represents a precise method for age determination in slow-growing and long-living fish species [22]. Liu et al. [13] compared eight specimens of Tibetan double-bearded Ptychobarbus dipogon from different age groups on the basis of age-specific characteristics, and according to their results, lapilluss performed better in age identification for both young and old fish. Cai et al. [23] confirmed that otoliths are the most accurate material for determining the age of Leuciscus waleckii. According to Chen [24] and Zeng [25], otoliths allow the most precise age determination for Triplophysa yarkandensis; therefore, in this study, we chose otoliths for age identification. The otolith of T. strauchii is small and approximately elliptical, being thick in the middle and gradually thinning toward the outer edge, with obvious protrusions in the center of the outer side. Munro et al. [26] noted that the growth of otoliths in fish is closely related to feeding habits and that a high abundance of bait in the aquatic environment and the availability of suitable ecological niches as habitats resulted in faster growth in fish and greater changes in the otoliths of the fish. Additionally, the palatability of bait and spatial ecological niche adaptation significantly influence the deposition of minerals in otoliths.
The growth of fish varies greatly with seasonal changes. In summer and fall, due to high water temperatures, fish exhibit vigorous feeding, fast metabolism, and rapid growth, followed by rapid growth of otoliths, and the opposite is true in winter and spring [27]. In our study, T. strauchii inhabited relatively high altitudes with low habitat temperatures, and the fish had to survive in highly saline and degraded water bodies. Consequently, the slow growth and low mineral deposition rates observed are consistent with previous findings showing that the morphology of otoliths varies due to water temperature, spatial ecological niche adaptations, and other environmental factors [21].
Determining the growth of the SL and BW of fish is extremely important for the basic theoretical study of fish ecology, and evaluating fish growth and related correlation coefficients is highly important in fishery production [28,29,30,31]. In the equation W = a × Lb, the value of a is the condition factor, which can be used to determine the bait base, hydrology and other environmental factors and can indicate the degree of fertilization under certain conditions [32]; the value of b is usually between 2.5 and 4.0, and a value closer to 3 indicates that the fish grow uniformly and that fish growth is satisfactory in terms of SL and BW during the whole growth process [33]. The equation for the relationship between the SL and BW of T. strauchii in this study was W = 1.148 × 10−5 L2.968, with a b value close to 3. Therefore, this fish is a uniformly growing fish. The Fulton’s condition index of T. strauchii in this study was 1.21, which was not significantly different from the results of other studies, e.g., the Fulton’s condition index of T. strauchii in Sayram Lake was 1.26 [3]. These findings indicate that the Turks River is suitable for the survival and reproduction of T. strauchii. The Turks River is recharged by water from glaciers and mountain snow. The basin has high elevation (800–4600 m), low water temperatures, many tributaries and abundant water resources. The water temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, and water chemical properties are suitable for the survival of plateau-dwelling fish [34,35].
The von Bertalanffy growth equation can be used to characterize the growth of populations accurately and is widely used to characterize the growth of fish [36,37,38]. The results of our study revealed that for T. strauchii, L∞ = 161.13 mm, W∞ = 40.82 g, t0 = −0.20, and ti = 3.23., T. yarkandensis [39], another fish belonging to Triplophysa, has a ti value of 1.83, which is significantly lower than that observed for T. strauchii in our study, suggesting that the growth of T. strauchii is slower than that of T. yarkandensis. This is closely related to the altitude, water temperature and bait abundance in the Turks River. The Turks River is located in the southeastern part of the Ili River Valley in Xinjiang, originates from the north side of the Khan Tengri Peak, and has an average elevation of more than 3000 m [2]. It is mainly recharged by glacial snowmelt, with an average annual water temperature of no more than 15 °C, a biomass content of 0.053 mg/L, and large seasonal changes in bait abundance, with large steep elevation gradients [34]. Compared with Triplophysa stewarti [8], which is found in Tibet, the ti value was notably greater at 3.67, significantly exceeding that reported in the present study (p < 0.05). This disparity can be attributed to the average water temperature in Dzhegtso, Tibet, which stands at 4 °C—substantially cooler than that of the Turks River.
4.2. Isoenzymatic Characteristics of T. strauchii in the Turks River
Numerous studies have shown that in terms of isozyme expression in fish, there are obvious differences among tissues, not only in the number of enzyme bands but also in enzyme activity, and these differences are related to the tissue differentiation that occurs when an organism is able to meet the specific physiological needs of each tissue during development [40,41,42]. LDH isozymes are enzymes that catalyze the dehydrogenation of lactate to produce pyruvate, which plays an important role in aerobic oxidation and anaerobic fermentation. LDH isozymes are glycolytic enzymes that exist in almost all tissues. LDH isozymes are tetrameric enzymes in vertebrates that are encoded mostly by two genes, A and B, and exhibit five bands upon electrophoresis (from anode to cathode: B4 (LDH1), AB3 (LDH2), A2B2. (LDH3), A3B (LDH4), and A4 (LDH5) [43]. LDH1 (B4) is involved mainly in anaerobic fermentation and catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate to produce energy in mitochondria. The results of our study revealed that the LDH4 (A3B) and LDH5 (A4) bands were dominant in T. strauchii, i.e., they were rich in A subunits, especially in the muscle and heart. The LDH enzyme profile of T. strauchii is similar to those of T. yarkandensis [18] and Triplophysa xiangxiensis [44], which is a manifestation of the adaptation of highland fish to low-oxygen environments, which is in line with the environment in which T. strauchii survives.
MDH isozymes are enzymes that catalyze the dehydrogenation of malic acid to oxaloacetic acid, which are commonly found in living organisms. They exist in fish as supernatant (s-MDH) and mitochondrial (m-MDH) enzymes that do not form heterodimers with each other, and most of them are dimeric enzymes that are translated from two loci, which are important enzymes that provide energy for organisms when they are under stress [45]. In this study, both types of MDH isozymes were expressed in all tissues and organs of T. strauchii, with obvious differentiation among tissues, and the highest expression was found in muscle and kidney tissues and organs. Compared with that of T. yarkandensis [18], the number of enzyme bands was relatively low, which may be attributed to the different environments in which the two species are found. The Turks River is located at a high altitude, with a mean year-round water temperature of 15 °C, and the mean annual runoff varies greatly with season. It is more challenging for fish to survive in the Turks River than in the Tarim River. Therefore, T. strauchii is highly resistant to stress.
EST isoenzymes, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of esters and play a major role in promoting the proper enzymatic metabolism of organisms and the maintenance of biofilm structures, are mostly present in scleractinian fish as monomers and are mostly polymorphic, organized and differentiated by species [46]. They isoenzymes may be encoded by more than 10 gene sets, as inferred by José et al. [47]. Xu et al. [48] performed correlation analysis on the esterases of Mastacembelus armatus and detected six enzyme bands in different tissues. Zhang [10] performed isozyme analysis on different individuals of Gymnodiptychus dybowskii and reported that EST isozymes presented variability at the individual level, with a maximum of six bands detected. In our study, ESTs expressed two enzyme bands in all the tissues. These genes were most highly expressed in fins, kidney, and intestine and least highly expressed in the liver. These findings suggest that the expression of isoenzymes is related not only to the physiological functions of the fish but also to differences between species.
5. Conclusions
T. strauchii is a major cold-water fish indigenous to the Turks River with an extended, light brown body and gray–brown dorsal side covered with small irregular black spots. T. strauchii grows relatively slowly, its body length and body weight are strongly correlated, it has a relatively low condition factor, it has a long growth cycle, it has a relatively late inflection point age (ti = 3.23 years), and it has been in a state of slow development for years. The isoenzyme analysis revealed LDHA’s dominant expression across tissues and conserved MDH patterns, suggesting metabolic stability crucial for high-altitude adaptation. EST’s tissue-specific high expression in liver and kidney, with low polymorphism, may support detoxification and metabolic homeostasis under hypoxic stress. These findings highlight key enzymatic adaptations that potentially contribute to hypoxia tolerance in high-altitude environments.
The Turks River is located at a high altitude and has a low water temperature. The biomass of T. strauchii changes seasonally, leading to the inflection point occurring at an older age. The growth of T. strauchii is slow, and the maturation of T. strauchii occurs late. T. strauchii is widely distributed in the water in this area, exhibiting a large population, strong adaptability to alpine water systems, stable genetic traits, and high development and utilization value. The results of this study lay a foundation for the collection of classification and biological data for Triplophysa fishes as well as the maintenance of biodiversity and biosafety in the Ili River system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and L.Y.; software, G.S., C.W. and H.W.; formal analysisv, C.W.; alidation, J.L. and Q.H.; investigation, G.S., C.W. and H.X.; data curation, Y.S. and D.R.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S. and L.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Key R&D plan of Xinjiang (2024B02014-1), the Tianshan Talent Training Project of Xinjiang (2023TSYCCX0128). National Key Research and Development Program “Marine Agriculture and Freshwater Fishery Science and Technology Innovation” Key Project (2023YFD2401000).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committees of Tarim University of Technology (Approval code: TDD-KYXF 20200426; Approval date: 26 April 2020) and adhered to animal welfare laws, guidelines, and policies.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Because the project was not finalized, the link to the data was not made public.
Acknowledgments
We thank our Fisheries Department colleagues and Yingcheng Studio.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SL | Standard length |
| BW | Body weight |
| OA | Otolith area |
| Rmin | Minimum radius of otolith |
| Rmax | Maximum radius of otolith |
| OP | Otolith perimeter |
| OL | Otolith length |
| OW | Otolith width |
References
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.M.; Cai, L.G. Xinjiang of Fishery; Xinjiang Science and Technology Press: Urumqi, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.G.; Niu, J.G.; Liu, C.C.; Zou, M.; Xie, P.; Adakbek; Liu, J.; Li, H. Species Diversity and Dominant Fish Species in Different Reaches of the ILI River, XinJiang. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2017, 41, 819–826. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, L.G.; Turxun. Study on the population structure of Triplophysa strauchii in Xinjiang in Sailimu Lake. Chin. J. Fish. 2002, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, L.; ADAKBEK. Biological characteristics of Triplophysa strauchii in Chawaopu Lake. Reserv. Fish. 2008, 3, 49–50+79. [Google Scholar]
- Kanu, U.C. The Complete mtDNA genome, Genetic diversity and population structure of Triplophysa strauchii (Cypriniformes: Cobitidae). Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shervette, V.R.; Rivera Hernández, J.M.; Nunoo, F.K.E. Age and growth of grey triggerfish Balistes capriscus from trans-Atlantic populations. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1120–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Chen, S.A.; Wang, C.X.; Zi, F.Z.; Chang, D.S.; Xu, H.; Li, D.P. Otolith morphology and population discrimination of Triplophysa yarkandensis. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2023, 44, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, N.; Yang, R.B.; Tan, B.Z.; Zeng, X.L.; He, L.Q.; Xu, Z.L.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.P.; Yang, X.F. Age, growth, and reproductive characteristics of Triplophysa stewarti in Lake Chugutso, Tibet. J. Fish. Sci. China 2022, 29, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, S.A.; Liu, M.C.; Xie, C.X. Age and Growth of Triplophysa tenuis in Kaidu River, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2020, 57, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, P.; Sha, W.J.; Wang, R.X.; He, L.; Niu, J.G.; Gan, J.H. Electrophoretic Analysis on 3 Kinds of Isozymes in Gymnodiptychus dybowskii. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2023, 38 (Suppl. S1), 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.A.; Lima, R.C.; Teixeira, A.S. Isoenzyme electrophoretic patterns in discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciatus Pellegrin, 1904 and Symphysodon discus Heckel, 1840) from the Central Amazon. Genet. Mol. Res. 2008, 7, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y. Study on Biology and Population Dynamics of Schizothorax macropogon in the Yarlung Tsangpo River. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, H.P. Values of eight structures as age determination of Ptychobarbus dipogon, Tibet Autonomous Region. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.C. Fish Ecology; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 31–219, ISBN/7-109-03143-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.S. Study on the biology and population dynamics of Schizothorax oconnori. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Ma, Y.W.; Tu, E.X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.M.; Au, B.D.; Au, Z.Z.; Liu, Y. The study on the biology of Triplophysa (Hedinichthys) yarkandensis (Day) in Akesu River. Chin. J. Fish. 2004, 17, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, L.; Gan, J.H.; He, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.G. Preliminary analysis on biochemical genetic characteristics and population genetic structure of Lota lota. Chin. Fish. Qual. Stand. 2022, 12, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Yao, N.; Wang, S.; Xie, C.X.; Adak; Chen, S.A.; Zhou, F.R. Tissues specificity of three isozymes in Triplophysa yarkandensis. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2019, 1, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chizinski, C.J.; Pope, K.L.; Wilde, G.R.; Strauss, R.E. Implications of stunting on morphology of freshwater fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokaç, A.; Herrmann, B.; Gökçe, G.; Krag, L.A.; Nezhad, D.S.; Lök, A.; Kaykaç, H.; Aydın, C.; Ulaş, A. Understanding the size selectivity of red mullet (Mullus barbatus) in Mediterranean trawl codends: A study based on fish morphology. Fish. Res. 2016, 174, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.D.; Gao, T.X. A comparative study of different geographical groups of Sebastiscus marmoratus. J. Hydroecol. 2023, 44, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S.E.; Thorrold, S.R. Otoliths, increments, and elements: Keys to a comprehensive understanding of fish populations? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.L.; Duan, Y.J.; Xu, J.C.; He, Y.; Geng, J.Z.; Liu, X.; Han, M.X.; Liu, Y.H. Comparison of five structure materials in age determination of Amur ide Leuciscus waleckii in Dali Lake. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2020, 35, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.A. Study on Population Ecology of Triplophysa yarkandensis (Day) in Tarim river. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Tang, W.H. Age, Body Growth and Reproductive Characteristics of Triplophysa yarkandensis. Chin. J. Zool. 2010, 45, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, J.L.; Pauly, D. A simple method for comparing the growth of fishes and invertebrates. Fishbyte 2012, 1, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretical Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Nguyen, P.T.; Han, D.W.; Kim, I.C.; Kim, J.H. Length-weight relationships and condition factors of six notothenioid fish species occurring off King George Island and Northern Victoria Land (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2023, 46, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Banik, S. Length-weight relationship and condition factor of the pabo catfish Ompok pabo (Hamilton, 1822) from Tripura, India. Indian J. Fish. 2012, 59, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, G.; Altun, A. Length-Weight Relationship and Condition Factor of Three Endemic and Threatened Freshwater Fishes from Orontes River. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 191, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Lu, H.; Fu, M.; Bai, Y.P.; Su, S.Q.; Yao, W.Z. Age and growth characteristics of Coilia nasus in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, D.J.; Thomson, F.E.; Thuesen, P.A. Age and growth of two newly established invasive populations of Tilapia mariae in northern Australia. Fish Biol. 2013, 82, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yuan, Y.J.; Wei, W.S.; Yu, S.L.; Fan, Z.A.; Zhang, R.B.; Zhang, T.W.; Shang, H.M. Variation and prediction trend of precipitation series for the Turks river basin during the last 236 years. J. Mt. Sci. 2010, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Ren, D.Q.; Chen, S.A.; Cai, L.G.; Niu, J.G.; Xie, C.X. Growth characteristics of Gymnodipty chusdybowskii Kessler in three tributaries of the Ili river in Xinjiang, China. J. Hydroecol. 2015, 36, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, N.P.; Shuter, B.J.; Abrams, P.A. Interpreting the von Bertalanffy model of somatic growth in fishes: The cost of reproduction. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Maravelias, C.D. Modelling fish growth: Multi-model inference as a better alternative to a priori using von Bertalanffy equation. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, M.R.; Barker, R.J.; Taylor, P. Modeling Individual Specific Fish Length from Capture-Recapture Data using the von Bertalanffy Growth Curve. Biometrics 2013, 69, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y. Research on the age, growth, reproduction and population discrimination of Triplophysa yarkandensis. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Champasri, C.; Phetlum, S.; Pornchoo, C. Diverse activities and biochemical properties of amylase and proteases from six freshwater fish species. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcón, H.B.; Forrellat, B.A.; Carrillo, F.O.; Ubieta, H.K. Digestive enzymes of two freshwater fishes (Limia vittata and Gambusia punctata) with different dietary preferences at three developmental stages. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 158, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.T.; Xiong, D.M. Studies on activity, distribution, and zymogram of protease, α-amylase, and lipase in the paddlefish Polyodon spathula. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikova, E.E.; Soldatov, A.A.; Golovina, I.V.; Sysoeva, I.V.; Sysoev, A.A. Effect of acute hypoxia on the brain energy metabolism of the scorpionfish Scorpaena porcus Linnaeus, 1758: The pattern of oxidoreductase activity and adenylate system. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; He, L.; Xu, Y.F.; Wang, X.G.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Z. Isoenzyme analysis of Triplophysa xiangxiensis population. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, P.; Kumar, S.; Sardar, P.; Munilkumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Satheesh, M.; Reena, H.; Mannur, V.; Patel, A. Optimization of weaning strategy in the climbing perch (Anabas testudineus, Bloch 1792) larvae on growth, survival, digestive, metabolic and stress responses. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, G.; Segura, J.A.; Ludemann, V.; Pose, G.N. Surface mycobiota of home-made dry cured sausages from the main producing regions of Argentina and morphological and biochemical characterization of Penicillium nalgiovense populations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 309, 108312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, A.A.; Alvarez, M.C. Genetic identification of sparid species by isozyme markers: Application to interspecific hybrids. Aquaculture 1999, 173, 1–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.D.; Wang, H.H.; Li, Y.H.; Wu, B.; Ma, B.H.; Zeng, Q.X. Investigation on LDH and EST Isozymes in Different Tissues of Mastacembelus armatus. Hunan Arricultural Sci. 2020, 9, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).