Development and Application of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Antigen-Specific DAS-ELISA Detection Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements
2.2. Cells and Viruses
2.3. Preparation of IHNV N Protein Antigen
2.4. Generation of mAbs
2.5. Specificity Identification of the Antibodies
2.6. Optimization of the DAS-ELISA
2.7. Preparation of Tissue Samples
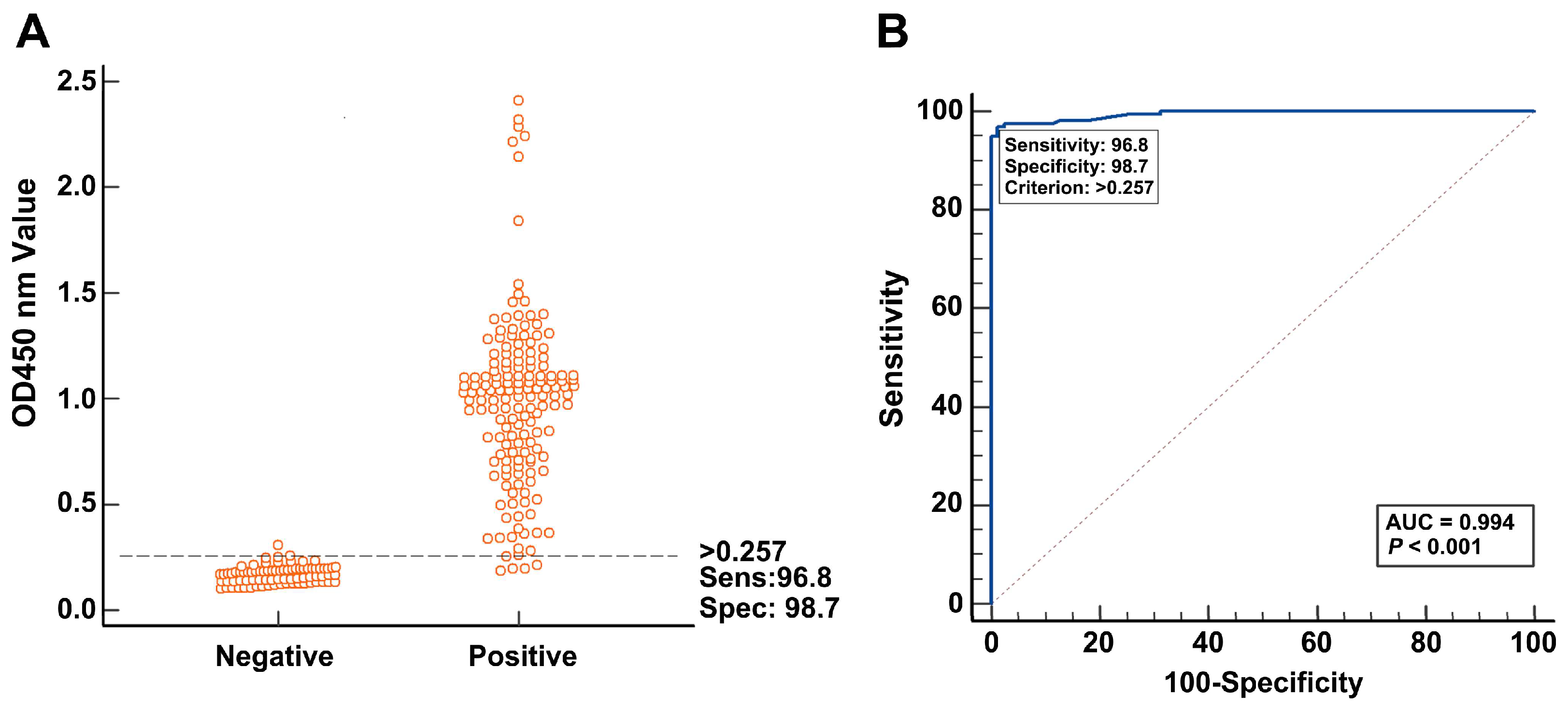
2.8. Determination of the Cut-Off Value
2.9. Determination of the Specificity, Broad-Spectrum Sensitivity, and Repeatability of DAS-ELISA
2.10. Clinical Validation of DAS-ELISA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antigen Epitope Analysis of IHNV N Protein
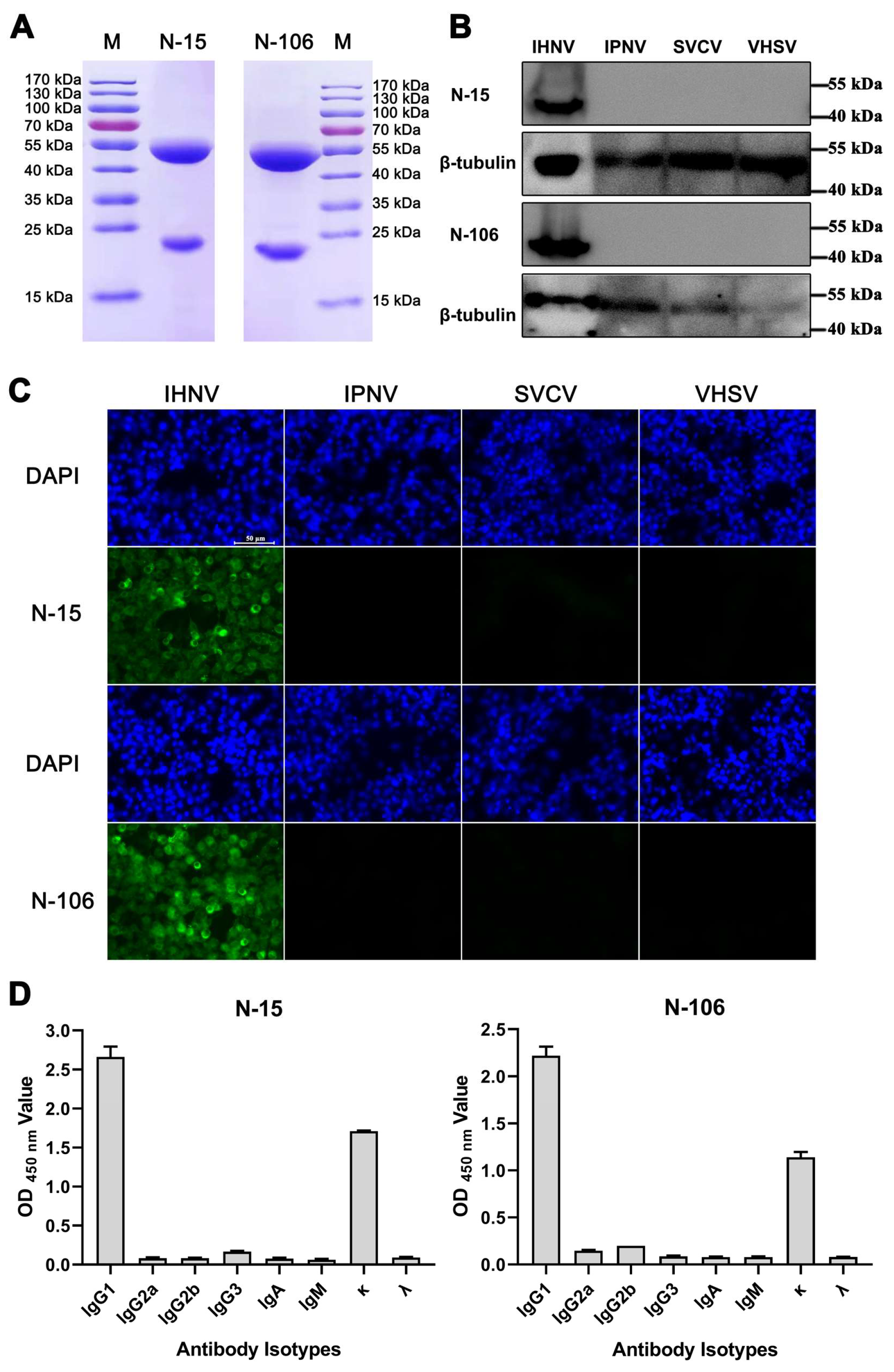
3.2. Production and Characterization of mAbs Against the N Protein
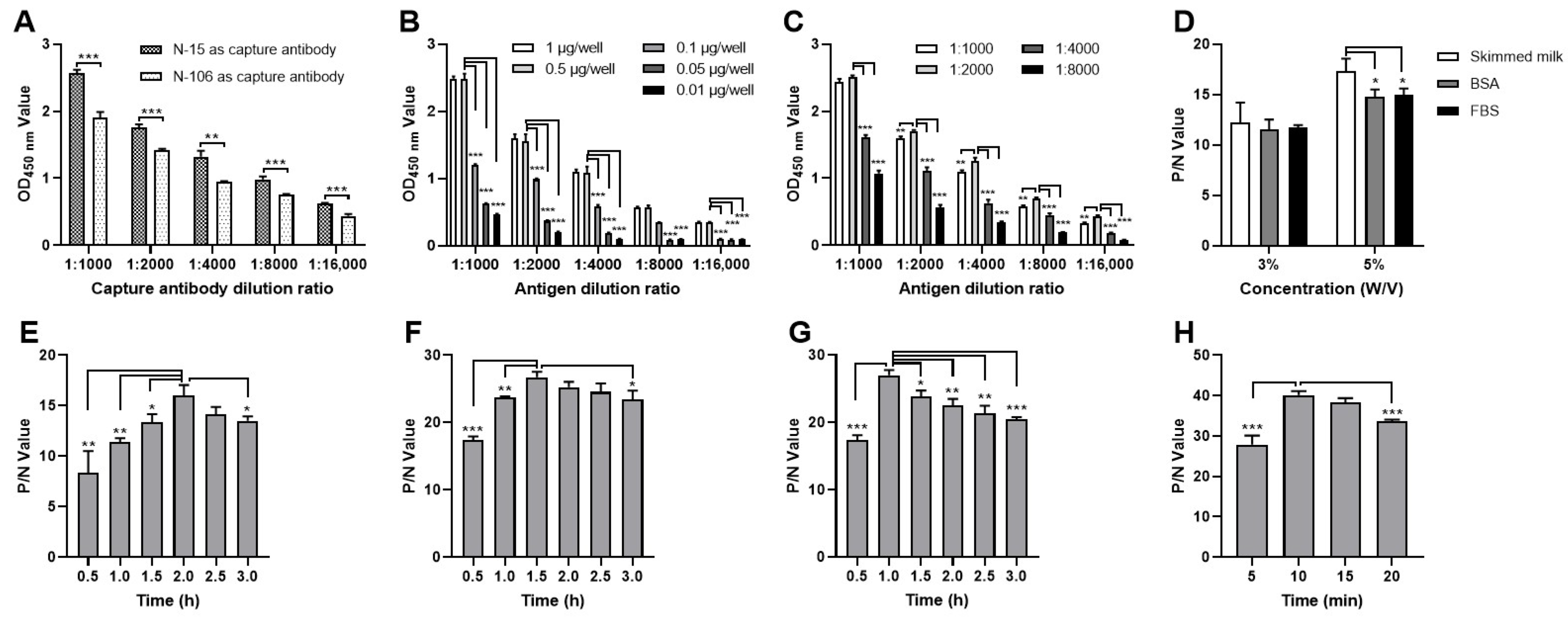
3.3. Development and Optimization of the DAS-ELISA
3.4. Determination of the DAS-ELISA Cut-Off Value
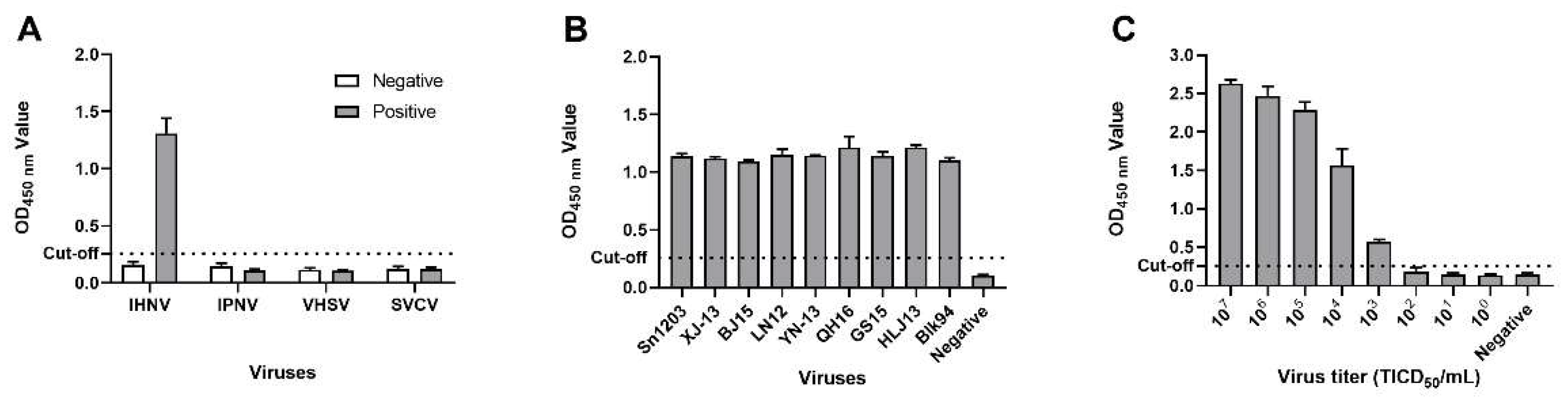
3.5. Specificity and Broad-Spectrum Detection Capability of DAS-ELISA
3.6. Sensitivity and Repeatability of the DAS-ELISA
3.7. Validation of the DAS-ELISA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballesteros, N.A.; Alonso, M.; Saint-Jean, S.R.; Perez-Prieto, S.I. An oral DNA vaccine against infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) encapsulated in alginate microspheres Induces dose-dependent immune responses and significant protection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M.; Schütze, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Fish rhabdoviruses: Molecular epidemiology and evolution. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 292, 81–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zheng, X.-C.; Shi, X.-J.; Kan, S.-F.; Wang, J.-J.; He, J.-Q.; Zheng, W.; Yu, L.; Lan, W.-S.; Hua, Q.-Y.; et al. Determination of the complete genome sequence of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) Ch20101008 and viral molecular evolution in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shan, L.-P.; Xue, M.-Y.; Lu, J.-F.; Hu, Y.; Liu, G.-L.; Chen, J. Potential application of antiviral coumarin in aquaculture against IHNV infection by reducing viral adhesion to the epithelial cell surface. Antivir. Res. 2021, 195, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPatra, S.E.; Corbeil, S.; Jones, G.R.; Shewmaker, W.D.; Lorenzen, N.; Anderson, E.D.; Kurath, G. Protection of rainbow trout against infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus four days after specific or semi-specific DNA vaccination. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, M.; Kurath, G.; Breyta, R.B.; Ren, G.; Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Lu, T. Phylogeography and evolution of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus in China. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 131, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, N.; Shi, W.; et al. Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) nucleoprotein amino acid residues affect viral virulence and immunogenicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbadi, M.; Fusaro, A.; Ceolin, C.; Casarotto, C.; Quartesan, R.; Pozza, M.D.; Cattoli, G.; Toffan, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Panzarin, V. Molecular evolution and phylogeography of co-circulating IHNV and VHSV in Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Ma, Z.; Li, F.; Xu, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xing, W.; Xu, G.; Luo, L.; et al. First isolation and pathogenicity analysis of a genogroup U strain of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus from rainbow trout in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Purcell, M.K.; Pan, G.; Wang, J.; Kan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shi, X.; He, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Analytical validation of a reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) for quantitative detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 245, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapatra, S.E.; Roberti, K.A.; Rohovec, J.S.; Fryer, J.L. Fluorescent antibody test for the rapid diagnosis of infectious hematopoietic necrosis. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1989, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Baek, E.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, J.M.; Kwon, M.G.; Il Kim, K. Development and validation of reverse-transcription cross-priming amplification-based lateral flow assay for the detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2024, 329, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, F.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Xing, J.; Sheng, X.; Chi, H.; Zhan, W. The development of RT-RPA and CRISPR-Cas12a based assay for sensitive detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV). J. Virol. Methods 2024, 326, 114892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P.; Paley, R.; Alegria-Moran, R.; Oidtmann, B. Epidemiological characteristics of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV): A Review. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.; et al. The need for transparency and good practices in the qPCR literature. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.L.; Bizzaro, N.; Cavazzana, I.; Borghi, M.O.; Tincani, A. Automated tests of ANA immunofluorescence as throughput autoantibody detection technology: Strengths and limitations. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrapetyan, H.; Tran, T.; Tellez-Corrales, E.; Madiraju, C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: Types and applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2612, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-Z.; Liu, M.; Xu, L.-M.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Cao, Y.-S.; Shao, Y.-Z.; Yin, J.-S.; Liu, H.-B.; Lu, T.-Y. A chimeric recombinant infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus induces protective immune responses against infectious hematopoietic necrosis and infectious pancreatic necrosis in rainbow trout. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 116, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-Z.; Li, L.-F.; Xu, L.-M.; Shao, Y.-Z.; Ren, G.-M.; Liu, Q.; Lu, T.-Y. Traditional Chinese medicine bufalin inhibits infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus genogroups I and V infection in vitro and in vivo. Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health OIE. Chapter 2.3.4.—Infectious Haematopoietic Necrosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals; OIE: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Ding, N.Z.; He, C.Q. Novirhabdoviruses versus fish innate immunity: A review. Virus Res. 2021, 304, 198525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, M.; Thompson, R.; Garver, K.; Hawley, L.; Batts, W.; Sprague, L.; Sampson, C.; Winton, J. Universal reverse-transcriptase real-time PCR for infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 106, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, A.K.; Bowers, R.M.; Licon, K.S.; LaPatra, S.E. Detection and quantification of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) by SYBR green real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 147, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, M.K.; Hart, S.A.; Kurath, G.; Winton, J.R. Strand-specific, real-time RT-PCR assays for quantification of genomic and positive-sense RNAs of the fish rhabdovirus, infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 132, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.Y.; Yeap, S.K.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, W.S. Advances in the study of nodavirus. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, M.; Kurath, G.; Ren, G.; Lapatra, S.E.; Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, J.; Lu, T. A effective DNA vaccine against diverse genotype J infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus strains prevalent in China. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einer-Jensen, K.; Harmache, A.; Biacchesi, S.; Bremont, M.; Stegmann, A.; Lorenzen, N. High virulence differences among phylogenetically distinct isolates of the fish rhabdovirus viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus are not explained by variability of the surface glycoprotein G or the non-virion protein Nv. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, Z. A brief review of monoclonal antibody technology and its representative applications in immunoassays. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2018, 39, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Shan, F.; Hou, J.; Guo, D.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wei, Z. Establishment and application of PDCoV antigen-specific DAS-ELISA detection method. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Wang, S.-H.; Ding, C.-Z.; Wang, J.-F. Development and application of an indirect ELISA for the serological detection of bovine viral diarrhea virus infection based on the protein E2 antigen. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 4707–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Amino Acid Site | Sequence | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6–28 | RETFTGLRDIKGGVLEDAETEYR | 23 |
| 2 | 41–45 | ADFEL | 5 |
| 3 | 54–60 | HVGGEGT | 7 |
| 4 | 75–82 | TVPSGTGT | 8 |
| 5 | 95–121 | ESLDTGAPLDATFADPNNKLAETIGKE | 27 |
| 6 | 143–144 | DK | 5 |
| 7 | 151–173 | NKLERLATSQGIDELVNFNSNRG | 23 |
| 8 | 186–187 | QK | 2 |
| 9 | 203–207 | PATAA | 5 |
| 10 | 234–238 | NLGAL | 5 |
| 11 | 285–295 | EGYFKSYGINE | 11 |
| 12 | 308–325 | DRYDEGTSGGLAGMKVSE | 18 |
| 13 | 343–351 | DGDGSTGEG | 9 |
| 14 | 360–388 | ETASRRPDPDEEEEEEEEDDDPSEPEDSD | 29 |
| Samples | Intra-Batch | Inter-Batch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X ± SD | CV (%) | X ± SD | CV (%) | |
| Positive 1 | 2.191 ± 0.054 | 2.445 | 2.133 ± 0.017 | 0.787 |
| Positive 2 | 2.178 ± 0.040 | 1.819 | 2.115 ± 0.043 | 2.010 |
| Positive 3 | 1.520 ± 0.052 | 3.402 | 1.487 ± 0.031 | 2.052 |
| Positive 4 | 1.045 ± 0.009 | 0.906 | 1.043 ± 0.022 | 2.131 |
| Positive 5 | 2.101 ± 0.051 | 2.436 | 2.137 ± 0.048 | 2.261 |
| Negative 1 | 0.102 ± 0.006 | 6.028 | 0.090 ± 0.003 | 3.653 |
| Negative 2 | 0.110 ± 0.005 | 4.133 | 0.109 ± 0.022 | 2.247 |
| Negative 3 | 0.112 ± 0.004 | 3.341 | 0.109 ± 0.019 | 1.891 |
| DAS-ELISA | WOAH-Recommended Method | Concordance | Kappa Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | |||
| Positive | 142 | 9 | 151 | 94.04% | |
| Negative | 12 | 130 | 142 | 91.55% | |
| Total | 154 | 139 | 293 | 92.83% | 0.856 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.-Z.; Wu, M.; Xu, L.-M.; Shao, Y.-Z.; Liu, W.-T.; Lu, T.-Y. Development and Application of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Antigen-Specific DAS-ELISA Detection Method. Fishes 2025, 10, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100533
Zhao J-Z, Wu M, Xu L-M, Shao Y-Z, Liu W-T, Lu T-Y. Development and Application of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Antigen-Specific DAS-ELISA Detection Method. Fishes. 2025; 10(10):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100533
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jing-Zhuang, Min Wu, Li-Ming Xu, Yi-Zhi Shao, Wei-Tong Liu, and Tong-Yan Lu. 2025. "Development and Application of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Antigen-Specific DAS-ELISA Detection Method" Fishes 10, no. 10: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100533
APA StyleZhao, J.-Z., Wu, M., Xu, L.-M., Shao, Y.-Z., Liu, W.-T., & Lu, T.-Y. (2025). Development and Application of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Antigen-Specific DAS-ELISA Detection Method. Fishes, 10(10), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100533






